Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) consists of the entire spectrum of fatty liver disease in patients without significant alcohol consumption, ranging from nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) to cirrhosis, with NASH recently shown as an important cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). There is a close relationship between insulin resistance (IR) and NAFLD, with a five-fold higher prevalence of NAFLD in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) compared to that in patients without T2DM. IR is involved in the progression of disease conditions such as steatosis and NASH, as well as hepatic fibrosis progression. The mechanisms underlying these processes involve genetic factors, hepatic fat accumulation, alterations in energy metabolism, and inflammatory signals derived from various cell types including immune cells. In NASH-associated fibrosis, the principal cell type responsible for extracellular matrix production is the hepatic stellate cell (HSC). HSC activation by IR involves “direct” and “indirect” pathways. This review will describe the molecular mechanisms of inflammation and hepatic fibrosis in IR, the relationship between T2DM and hepatic fibrosis, and the relationship between T2DM and HCC in patients with NAFLD.
1. Introduction
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a major form of chronic liver disease that affects both adults and children worldwide [1]. It is one of the clinical consequences of obesity and can progress to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is pathologically characterized by the presence of steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis in the liver parenchyma, which ultimately leads to cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and end-stage liver failure [1,2,3]. The prevalence of NAFLD in the world population is estimated to be 25%, whereas the pooled overall NASH prevalence estimated among biopsied NAFLD patients is 59% [4,5]. Recent meta-analysis revealed that over 2146 person-years of follow-up evaluation, 34% had fibrosis progression, 43% had stable fibrosis, and 22% had an improvement in fibrosis stage [6]. The listed diagnosis in the United Network for Organ Sharing database suggests that since 2000, the number of patients with NASH cirrhosis has increased, whereas that of patients with cryptogenic cirrhosis has decreased [7]. Liver-specific mortality and overall mortality among NAFLD and NASH patients were 0.77 and 11.77 per 1000 person-years, and 15.44 and 25.56 per 1000 person-years, respectively [4]. Patients with NAFLD cirrhosis (F4) predominantly develop liver-related events, whereas those with bridging fibrosis (F3) predominantly develop non-hepatic cancers and vascular events [8]. Estimates of NAFLD heritability range from 20% to 70%, with an estimated shared genetic effect or determination between steatosis and fibrosis of 75% [9], depending on ethnicity, study design, environmental factors, and methodology used for NAFLD characterization [10,11].
Recent evidence showed that extra-hepatic organs influence NAFLD progression [12,13,14,15]. Progressive adipose tissue dysfunction and insulin resistance (IR) are key events in NASH development, supporting the existence of an adipose tissue–liver crosstalk [12,13]. Most recently, Vily-Petit et al. reported that increased intestinal gluconeogenesis (IGN) improves glucose control and prevents the onset of hyperglycemia under a high-fat/high-sucrose diet [14]. Conversely, the suppression of IGN promotes lipid accumulation in the liver even under a standard diet. IGN provides metabolic benefits by initiating a gut–brain neural signal, thus triggering brain-dependent regulations of peripheral metabolism [15]. The authors suggested that IGN can specifically modulate the onset of hepatic steatosis and molecular events associated with the development of NAFLD through a gut–brain–liver neural circuit [14].
NAFLD is driven by ectopic fat accumulation in the liver, is an indicator of IR, and signals the possibility of ectopic fat accumulation in inappropriate parts of the body, such as in intramuscular, perivascular, and pericardial regions, and visceral fat deposition [16]. Therefore, NAFLD is often described as the hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome and is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), in which NAFLD is commonly found as a comorbidity [16,17]. Recent meta-analysis showed that the overall prevalence of NAFLD among patients with T2DM is 55.5%, whereas the global prevalence of NASH among patients with T2DM is 37.3% [18]. Compared to western populations, Asians are particularly susceptible to NAFLD partially because of body composition differences in fat and muscle, as well as genetic susceptibility through the predisposition to T2DM, patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 (PNPLA3) SNPs, and polymorphisms in apolipoprotein 3 [3]. T2DM is an important risk factor for NAFLD and seems to accelerate the progression of liver disease in NAFLD patients [1,2,3,4,8,16,17,18]. In this review, we discuss the most updated data characterizing the role of IR and T2DM in the progression of hepatic fibrosis in NAFLD. As described later, improving IR can be one of the potential therapeutic approaches for NASH fibrosis, even in the absence of T2DM. This is an innovative review because we discussed the influence of IR on the progression of hepatic fibrosis in NAFLD, both in basic and clinical aspects, for the first time. Some of the studies reported in this review analyzed data from the Japan Study Group of NAFLD (JSG-NAFLD).
2. Molecular Mechanism of Inflammation in IR
Cell death and inflammation are key drivers of fibrosis in NASH and other forms of chronic liver disease [19,20]. The primary pathophysiological mechanisms of IR induced by inflammatory mediators are probably the result of interference with insulin signaling [17]. Insulin acts in all cells by binding to its specific receptor and activating a cascade of intracellular signaling. Upon insulin binding, the insulin receptor phosphorylates itself and several members of the insulin receptor substrate (IRS) family. IRS1 and IRS2 are the main mediators of insulin signaling in the liver, where they control insulin sensitivity [17,21,22]. The canonical IRS signaling pathways include the IRS1- or IRS2-dependent signaling pathways that use the activities of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase (PDK)-protein kinase B (AKT) and the RAS−extracellular-signal regulated kinase (ERK) [17,21]. The PI3K-PDK-AKT pathway mediates gluconeogenesis and glycogen synthesis. Additionally, the RAS-ERK pathway mediates cell proliferation and survival [21]. IR is defined as the impairment of the appropriate downstream effects of insulin signaling in target tissues, primarily the liver, muscle, and adipose tissue. IR is postulated to begin in muscle tissue, which accounts for up to 70% of glucose disposal, whereas immune-mediated inflammatory change and excess free fatty acids (FFA) cause ectopic lipid deposition [23].
IR in adipose tissue results in increased lipolysis in adipocytes and an increased circulating FFA, which further exacerbates steatosis and IR in muscle tissue. During caloric intake, insulin reduces hepatic glucose production by inhibiting glycogenolysis and limiting the postprandial rise in glucose. In IR, this feedback mechanism is impaired and hepatic glucose production continues to rise even when postprandial glucose increases. Glucotoxicity is associated with elevated glucose levels and further contributes to IR [23].
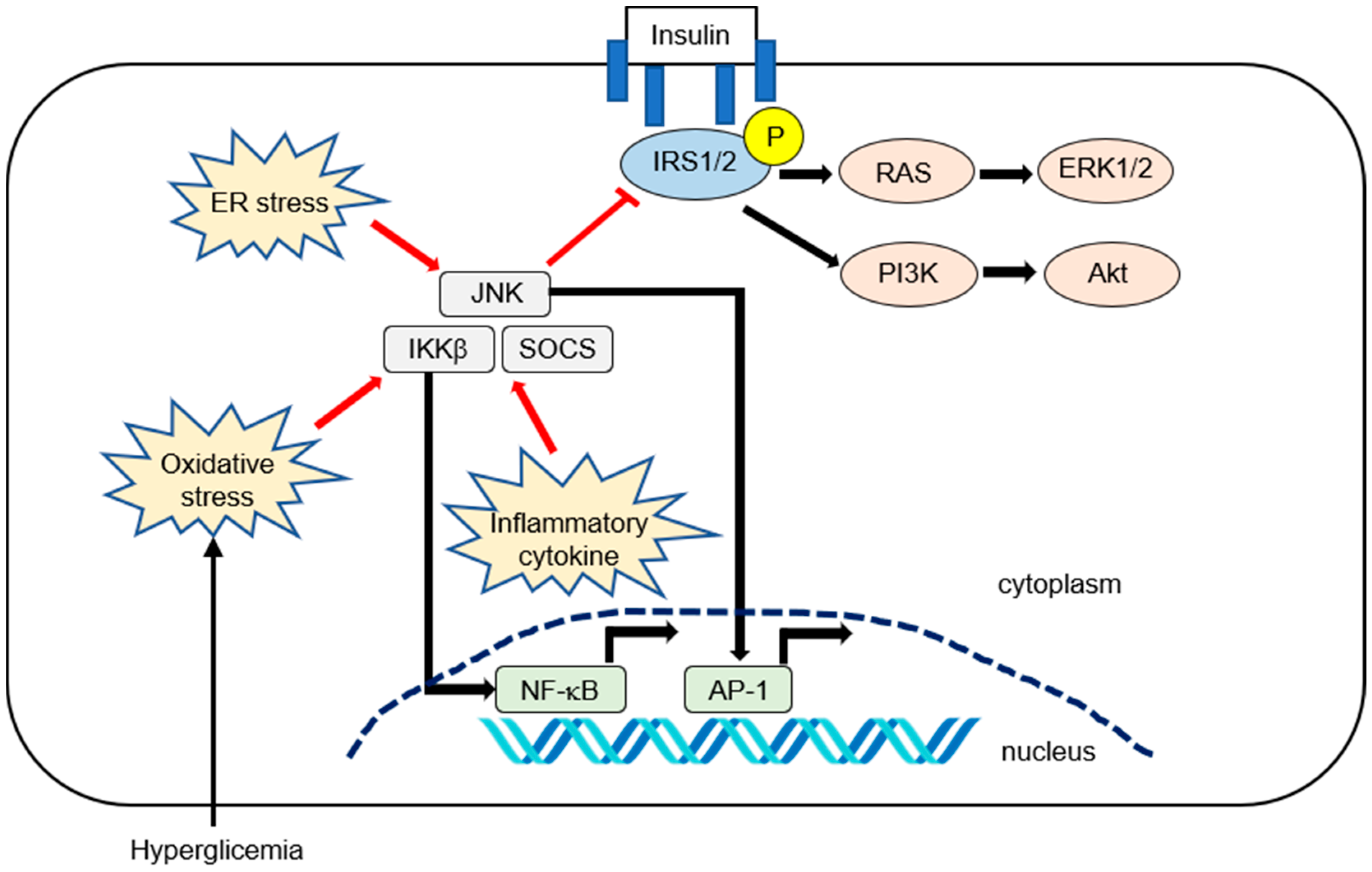
Pro-inflammatory cytokines and transcription factors are highly expressed in various tissues, including adipose tissue or liver in obesity and related disorders. Several inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α or interleukin (IL)-6, can activate the inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB kinase (IKK) complex IKKβ, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), which is also known as mitogen-activated protein kinase. Additionally, suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) can phosphorylate IRS1 and IRS2 to inhibit insulin signaling [17,22]. Hyperglycemia can increase oxidative stress [22], which can inhibit insulin signaling through the activation of inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B (I-κB) kinase subunit beta (IKKβ) and JNK. IKKβ and JNK can activate nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) and cause its translocation to the nucleus. [17]. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress can also activate the JNK pathway [17,24]. The inflammatory pathways that affect IR are summarized in Figure 1.
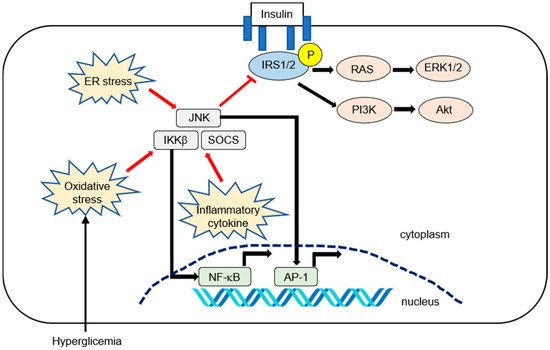
Figure 1.
Summary of inflammatory pathways affecting hepatic insulin resistance (IR) in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Insulin activates its receptor, which results in tyrosine phosphorylation on the insulin receptor substrate (IRS1 and IRS2) and activation of downstream effector pathways, including the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase (PDK)-protein kinase B (AKT) and the RAS−extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathways (i.e., canonical IRS signaling). Numerous pro-inflammatory signaling or reactive oxygen species can activate IKK-β. The activated NF-kB is then translocated into the nucleus and binds to specific DNA response elements. Inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 promote IR by inducing suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) 1 and 3. SOCS1 and SOCS3 impair insulin signaling through ubiquitin-dependent degradation of IRS. The c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK, or mitogen-activated protein kinase) represents another important inhibitory kinase of IRS that is activated in response to a variety of extracellular stimuli and cellular stressors such as oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress.
From a clinical point of view, data on the changes in hepatic expression of IRS1 and IRS2 with the pathological severity of NAFLD in patients are insufficient and do not provide a consensus. Rametta et al. reported that hepatic IRS1 mRNA levels did not differ, but IRS2 mRNA levels progressively increased with the severity of the histology [25]. Conversely, Honma et al. examined mRNA expression in 51 human liver biopsy samples obtained from nondiabetic subjects [26]. The hepatic expression of IRS1 was unchanged in NAFLD conditions, whereas the expression of IRS2 in NASH samples was lower than that in health control samples. Moreover, the severity of lobular inflammation was negatively correlated with hepatic IRS2 mRNA levels (r = −0.35, p < 0.05); by contrast, IRS1 mRNA levels were not significantly correlated with the severity of any of the histological features examined [26]. Enooku et al. examined 146 biopsy-proven NAFLD samples and revealed that IRS1 mRNA levels decreased with increasing degrees of hepatic necroinflammatory activity; however, IRS2 mRNA levels were not significantly correlated with this activity [27]. To date, the effects of changes in hepatic IRS1/IRS2 mRNA levels on hepatic inflammation in NAFLD patients have not been resolved.
3. Genetic Factors Affecting IR and NAFLD
To date, at least five variants in different genes have been found to be strongly associated with the susceptibility to and progression of NAFLD, namely, PNPLA3, transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 (TM6SF2), glucokinase regulator (GCKR), membrane bound O-acyltransferase domain-containing 7 (MBOAT7), and hydroxysteroid 17β-dehydrogenase (HSD17B13) [10]. First, the rs738409 C>G SNP, which results in the I148M protein variant of PNPLA3, has been linked to higher hepatic fat content but with no major effects on IR and adiposity features [10,28]. Second, the rs58542926 C>T SNP, which encodes for the E167K variant TM6SF2, shows higher hepatic and adipose tissue IR and enhanced muscle insulin sensitivity compared to CC homozygotes [29]. Third, the NAFLD risk variant GCKR (P446L) is associated with higher levels of plasma low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides and lower fasting glucose and homeostasis model assessment parameter (HOMA)-IR [30]. Fourth, MBOAT7 suppression by obesity or the MBOAT7 rs641738 variant promotes NAFLD and IR progression [31]. Downregulation of MBOAT7 by hyperinsulinemia contributes to fatty liver independently of genetic background [32]. The rs626283 polymorphism in MBOAT7 is associated with NAFLD and impaired insulin sensitivity in obese children and adolescents [33]. Finally, the rs72613567 variant in HSD17B13 plays a role in regulating retinoic acid metabolism, suggesting that retinol may be involved in NAFLD development [10].
4. Molecular Mechanism of Hepatic IR Affects Hepatic Fibrosis
Fibrosis is the result of excessive production of extracellular matrix (ECM) that is not adequately maintained and, thus, results in net accumulation. In the liver, hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) constitute the main source of ECM-producing fibroblasts in models of toxic and biliary liver disease and NAFLD [19,34]. IR is recognized as an integral component of NAFLD pathogenesis that worsens with disease progression [19,20,21]. Our review suggests that the activation of HSC by IR is largely divided into distinct direct and indirect pathways.
4.1. Indirect Pathway
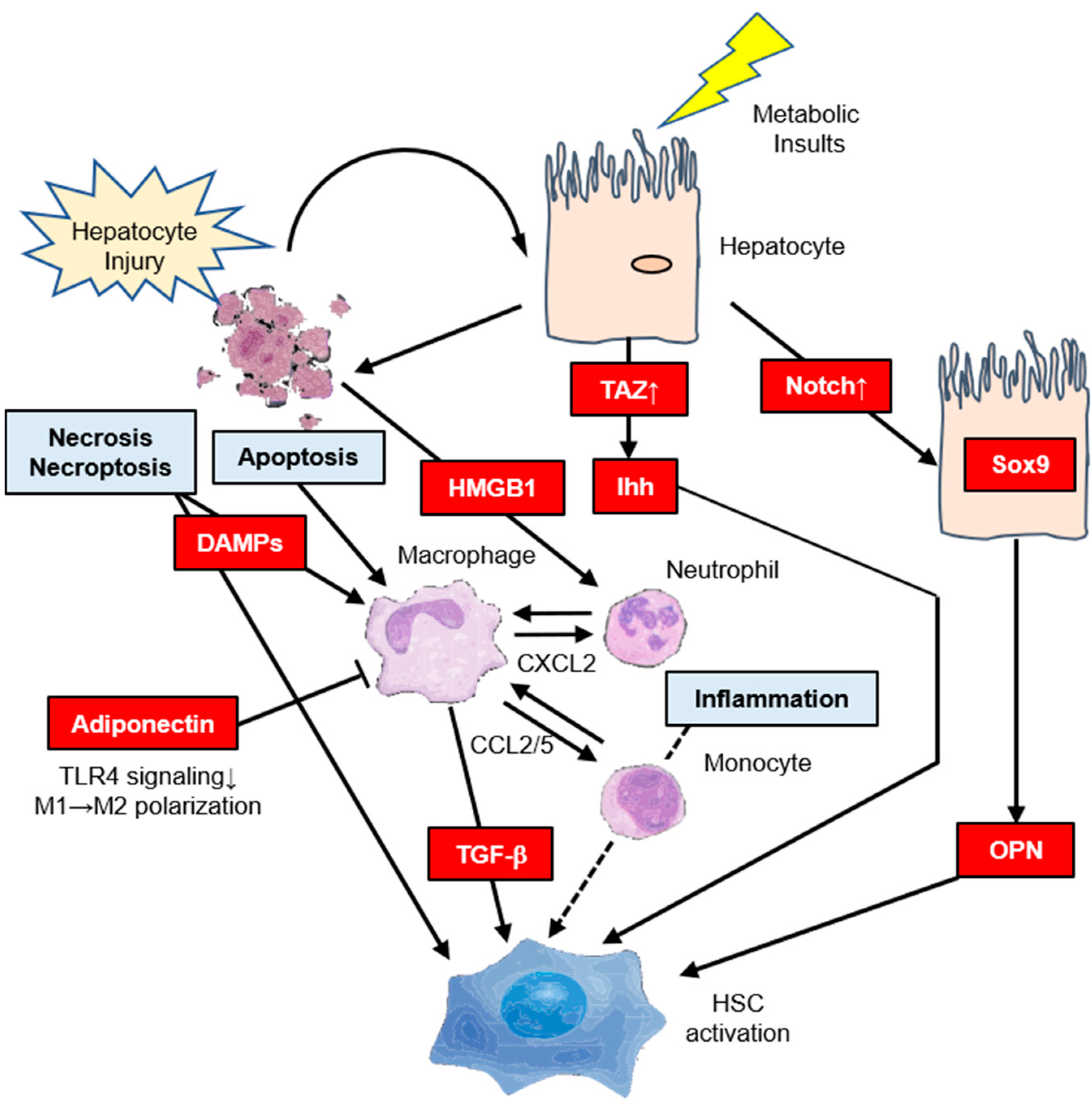
Inflammation can be induced by IR itself. Hepatocyte stress and death also promote inflammation, leading to the recruitment of macrophages and secretion of profibrogenic mediators such as transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), which is the center of the fibrogenic response in NASH [19,20,34,35]. There is also strong evidence for HSC activation through the direct interactions of stressed or dead hepatocytes with HSCs. This may be through the release of profibrogenic damage-associated molecular patterns [36,37] or other profibrogenic mediators such as Hh ligands and osteopontin (OPN) [19], or via apoptotic bodies [38,39] that may directly act on HSCs. High mobility group box 1 released by necrotic hepatocytes also mediates the recruitment of neutrophils in an acetaminophen-induced liver injury model through an interaction with a receptor for advanced glycation end products [40]. C–C chemokine receptors type 2 (CCR2) and 5 (CCR5) and their ligands CCL2 and CCL5 are implicated in the pathogenesis of liver inflammation and fibrosis, especially in NASH [35]. In response to hepatocyte injury, Kupffer cells secrete CCL2, which recruits monocytes to the liver. Inhibition of CCL2/CCR2 or CCL5/CCR5 has been shown to attenuate liver fibrosis in mice [41,42,43], and a recent phase 2b clinical trial showed that treatment with the CCR2/5 antagonist cenicriviroc resulted in an early antifibrotic benefit that was maintained particularly in the subset of NASH patients with advanced fibrosis [44]. Transcriptional coactivator with PDZ binding motif (TAZ) is a paralogue of YAP and key component of the HIPPO-YAP/TAZ-TAZ/TEA domain (TEAD) signaling cascade that is strongly upregulated in hepatocytes in both mouse models and NASH patients [45]. However, TAZ was not upregulated in simple steatosis, suggesting that TAZ could be involved in the transition from simple steatosis to NASH. Hepatocyte TAZ to NASH fibrosis is a TEAD-mediated induction of the secretory factor Indian hedgehog that activates fibrogenic genes in HSCs [45]. The Notch signaling pathway is important for multiple cell differentiation processes during embryonic and adult stages [19]. Notch activity is substantially increased in murine and human NASH [46]. In addition, hepatocyte Notch activation induces Sox9-dependent OPN secretion, which can directly activate HSCs, independent of hepatocellular injury, leading to collagen deposition [46]. Notch activation also increases FoxO1 activation at gluconeogenic promoters, leading to glucose intolerance [47]. The pharmacological blockade of Notch signaling by γ-secretase inhibitors improves glucose tolerance and IR [48]. Dongiovanni et al. reported that IR promotes ECM stabilization by a mechanism encompassing overexpression of lysyl oxidase-like 2 (LOXL2) in response to lipotoxicity [49]. Importantly, hepatic LOXL2 upregulation was specifically detected in NAFLD patients with T2DM progressing to advanced fibrosis [49]. LOXL2 may be a new therapeutic target in chronic liver diseases [50]. Adiponectin, an adipokine that modulates several metabolic processes including glucose metabolism and fatty acid oxidation, acts as an anti-inflammatory cytokine and inhibits the development of IR and NAFLD [51,52]. Adiponectin inhibits the differentiation of myeloid progenitor cells and modulates Kupffer cell function via reduction of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling [52]. Adiponectin inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, monocyte chemotactic protein-1, and IL-6, and suppresses proinflammatory classically activated (M1) macrophage activation [51,52]. In addition, adiponectin upregulates the production of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in macrophage and promotes anti-inflammatory alternatively activated (M2) macrophage proliferation [51,52]. The indirect pathways regulating HSC activation in steatohepatitis are summarized in Figure 2.
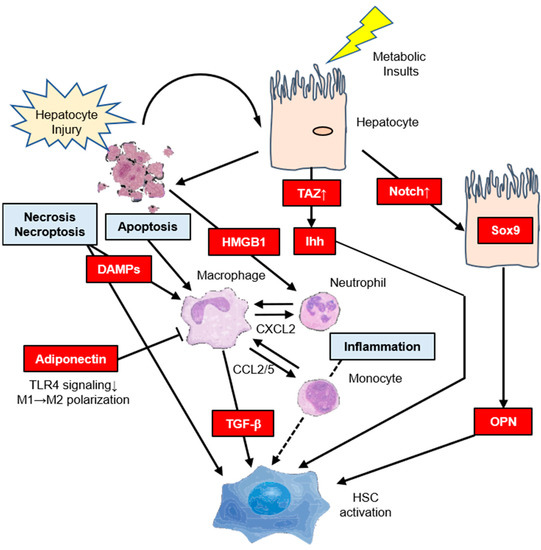
Figure 2.
The indirect pathways regulating hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation in steatohepatitis. Metabolic insults such as hyperinsulinemia/hyperglycemia lead to the activation of transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) in hepatocytes. Increased hepatocyte expression of TAZ in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) but not simple steatosis directly leads to HSC activation through the release of Indian hedgehog (Ihh) and promotes hepatocyte injury and inflammation that may indirectly promote HSC activation. Notch activation by cell-surface ligands on a neighboring cell leads to a Sox9-dependent increase in osteopontin (OPN) secretion to activate HSCs. HSC activation occurs through direct interactions between stressed or dead hepatocytes (i.e., apoptosis, necrosis, or necroptosis) and HSCs. This may be through the release of profibrogenic damage-associated molecular patterns. High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is released by injured hepatocytes to mediate the recruitment of neutrophils. Monocyte infiltration into the liver is primarily controlled by C–C chemokine receptors (CCR2) and its ligand CCL2, which may serve as therapeutic targets in NASH. Adiponectin modulates Kupffer cell function via reduction of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling, and directly stimulates M1→M2 polarization.
4.2. Direct Pathway
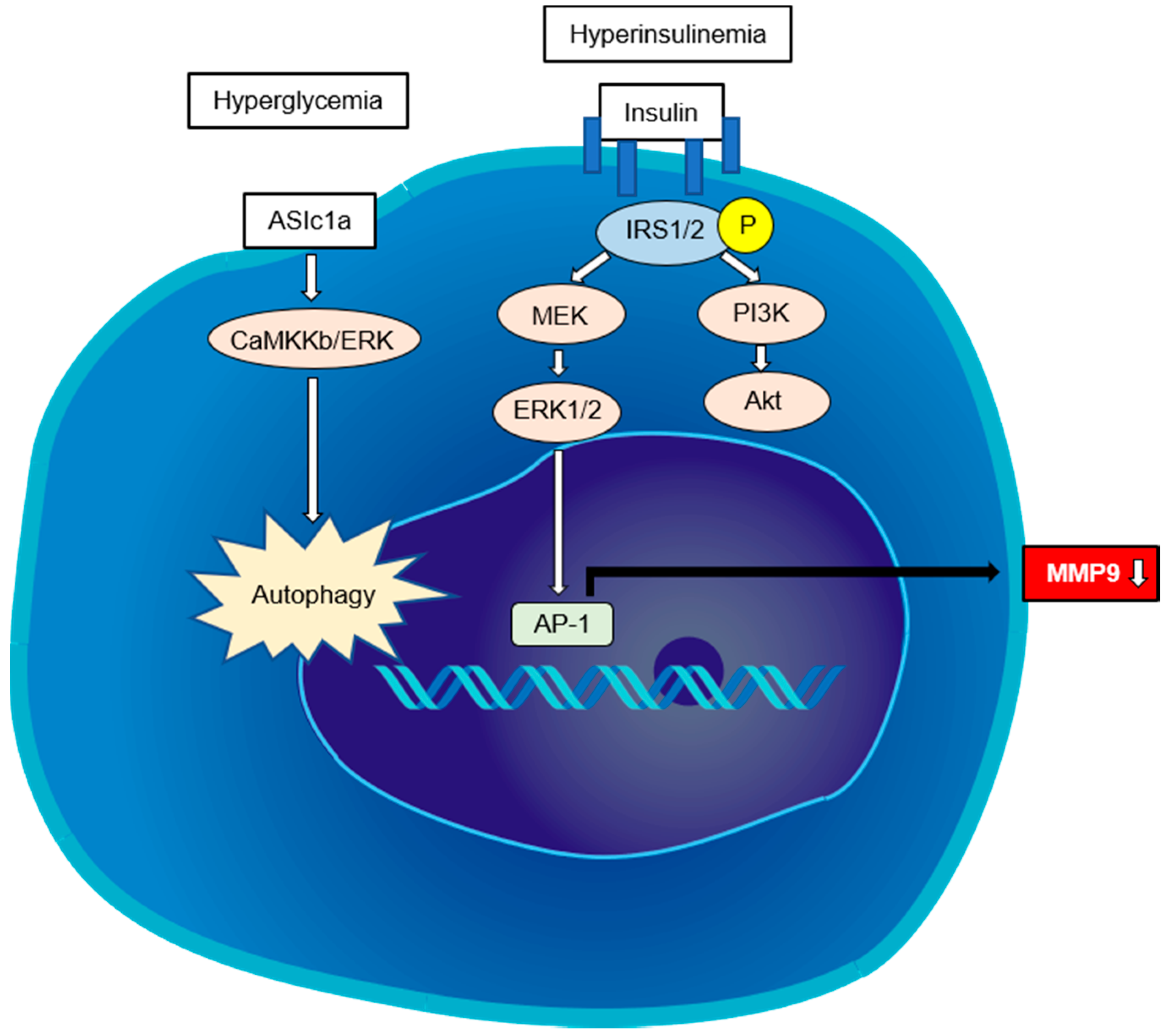
A small number of reports suggest that hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia directly activate HSCs. A study showed that IR-related hyperinsulinemia can directly stimulate HSCs to proliferate and secrete type I collagen by differentially activating PI3K and ERK-dependent pathways [53]. Ota et al. reported that a high-fat diet induced IR and increased the expression of the profibrotic TGF-β1 in obese rats [54]. Recently, another report suggested that insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) binds its receptor (IGF1R) in HSCs to promote IGF1R via IRS2 to trigger ERK1/2 phosphorylation, which leads to the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 9 [55].
High serum glucose during hyperglycemia can lead to the activation of the HSCs [56]. Kiss et al. reported that high glucose exposure to LX-2 cells (e.g., an immortalized human HSC cell lineage) resulted in decreased MMP2 activity and deceleration of type I collagen in the ER, with decreased pS6 expression pointing to development of ER stress [57]. Hyperglycemia can also aggravate hepatic fibrosis, which may be associated with HSC autophagy induced by acid-sensing ion channel 1a, which is a subfamily of the degenerin/epithelial Na+ channel family of the non-voltage-gated cation channel that acts through the CaMKKβ/ERK signal pathway [58]. Although it remains unclear whether HSCs are directly activated in prediabetic status, further study will be needed because many NAFLD patients are prediabetes. The direct pathways regulating HSC activation in steatohepatitis are summarized in Figure 3.
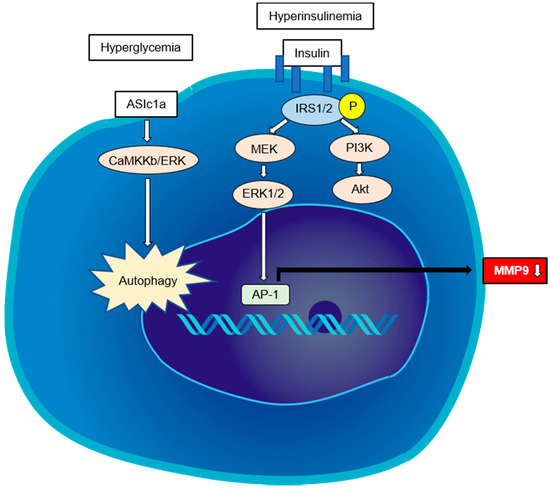
Figure 3.
The direct pathways regulating HSC activation in steatohepatitis. Hyperinsulinemia can directly stimulate HSCs to proliferate and secrete type I collagen by differentially activating PI3K- and ERK-dependent pathways. IGF1R triggers ERK1/2 phosphorylation via IRS2, leading to the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9. Hyperglycemia can aggravate hepatic fibrosis, which may be associated with the HSC autophagy induced by acid-sensing ion channel 1a (ASIC1a).
5. Relationship Between T2DM and Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients with NAFLD
5.1. Liver Biopsy
The gold standard for diagnosing NASH remains a liver biopsy [1]. Many past studies have confirmed that the presence of T2DM is an independent predictor of advanced hepatic fibrosis (F3 or F4) in biopsy-diagnosed patients with NAFLD [1,2,3,4,8,16,17,18]. For example, we previously reported that T2DM was an independent predictor of advanced fibrosis in patients with NAFLD (Odds ratio (OR) 2.9, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.3–6.1, p = 0.007) [59]. An earlier study from JSG-NAFLD showed that in 1365 biopsy-proven Japanese NAFLD patients, 47.3% had T2DM, whereas the multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of T2DM was one of the risk factors for advanced fibrosis (OR 2.39, 95% CI 1.60–3.55, p < 0.001) [60]. A report from Hong Kong showed that in 94 patients with T2DM who underwent liver biopsy, 56% had steatohepatitis and 50% had advanced hepatic fibrosis [61]. A more recent, prospective multicenter study showed that in a cohort of 458 NAFLD patients with advanced fibrosis, 67% had T2DM, suggesting that T2DM is a robust predictor of poor transplantation-free survival (hazard ratio (HR) 3.33) and liver-related outcomes [8]. With the increase in the number of clinical trials, the number of observational studies of biopsy-proven NAFLD has decreased.
5.2. Serum Biomarkers
Several noninvasive biomarkers have been proposed for NASH detection and to avoid redundant liver biopsies. In western countries, serum biomarkers for staging fibrosis include predictive models (e.g., NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS) [62]) and direct measures of fibrosis (e.g., PIIINP [63] or Pro-C3 [64]) to discriminate between patients with advanced fibrosis [65]. Some of these markers were originally designed for hepatitis C using the aspartate transaminase (AST)/alanine transaminase ratio, the aspartate transaminase-to-platelet ratio index [66], and Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) [67]. Yoneda et al. from JSG-NAFLD reported that the platelet (PLT) count is the simplest index for predicting advanced fibrosis in patients with NAFLD [68]. Indeed, PLT levels may be unexpectedly high even when hepatic fibrosis is advanced; for example, patients with stage 3 hepatic fibrosis had a PLT of 189 × 109/L, whereas patients with stage 4 had 153 × 109/L [68].
In Japan, fibrosis markers have also been extensively examined, including hyaluronic acid, type IV collagen 7S, procollagen III peptide, and Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2-binding protein (WFA+-M2BP). WFA+-M2BP is a novel serum fibrosis biomarker for chronic hepatitis C that is clinically validated and covered by the Japanese health insurance system [69]. WFA+-M2BP is also used for assessing liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD [70,71]. Kamada et al. reported that serum levels of Mac-2 binding protein (Mac-2bp) can be used to predict the histologic severity of hepatic fibrosis in patients with NAFLD [72,73]. Furthermore, they tried a head-to-head comparison between WFA+-M2BP and Mac-2bp in which 510 patients with NAFLD from JSG-NAFLD were used. WFA+-M2BP and Mac-2bp were equally useful for NASH diagnosis, although Mac-2bp was superior to WFA+-M2BP for the prediction of the NAFLD fibrosis stage, especially for early stages fibrosis (F1 and F2) [74]. The measurement of autotaxin (ATX) has been covered by the national health insurance in Japan since June 2018 as an auxiliary method of quantifying the degree of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver disease and cirrhosis [75]. Some groups found that the serum ATX concentration significantly correlates with the fibrosis stage in NAFLD patients [75,76,77]. Recently, Okanoue et al. suggested that the combination of type IV collagen 7S and AST (CA index-NASH = 0.994×type IV collagen 7S + 0.0255×AST) is a reliable and simple scoring system to diagnose advanced fibrosis. The area under the receiver operating characteristics (AUROCs) for training/validation data sets are 0.842/0.931 for NASH-related advanced fibrosis [78].
The NFS and FIB-4 have been externally validated in populations of different ethnicities with consistent results. Singh et al. investigated a total of 1319 patients with T2DM who underwent liver biopsy for suspected NAFLD [79]. The diagnostic abilities were FIB-4 > 2.67 and NFS > 0.676 advanced fibrosis, indicating reasonable specificities of 69.9% and 93% but poor sensitivities of 6.7% and 44.1%, respectively. The AUROCs used to detect advanced fibrosis were 0.77 and 0.72, respectively. Another report from Turkey examined 349 patients with biopsy-proven NAFLD (166 with T2DM) and showed that a FIB-4 with a low cutoff value of 1.3 had a specificity of 67% in patients with T2DM and 69% in those without [80]. Conversely, a FIB-4 with a high cutoff value of 2.67 had a sensitivity of 22% in patients with T2DM and 0% in those without [80]. NFS performed similar to FIB-4, suggesting that both FIB-4 and NFS have limited utility in diagnosing advanced fibrosis in NAFLD, especially in patients with T2DM.
5.3. Vibration-Controlled Transient Elastography
There have been some attempts to estimate the prevalence of NASH by noninvasive methods [1]. Vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) is a rapid, safe, and reproducible procedure for liver stiffness measurement (LSM) that can be performed at the bedside with immediate results [81]. VCTE generally provides an accurate per-protocol risk assessment of advanced fibrosis (F3 or F4) in NAFLD (AUROCs ranging from 0.80 to 0.94) [65,82,83]. Several meta-analyses, mostly performed in viral hepatitis patients, reported good (88–89%) and excellent (93–96%) TE accuracy for diagnosing advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis, respectively [65,84]. A recent large prospective diagnostic study from the United Kingdom demonstrated that LSM identified patients with fibrosis from AUROCs of 0.77 (95% CI 0.72–0.82) for ≥ F2, 0.80 (95% CI 0.75–0.84) for ≥ F3, and 0.89 (95% CI 0.84–0.93) for F4. The Youden cutoff values for F2, F3, and F4 were 8.2, 9.7, and 13.6 kPa, respectively [85]. Probe type (M or XL probe) did not affect LSM; Oeda et al. also confirmed that liver fibrosis and steatosis could be equally evaluated with M and XL probes in patients with NAFLD [86]. Roulot et al. examined 705 French diabetic patients and reported that 12.7% (N = 85) had LSM ≥ 8 kPa, which was suggestive of significant fibrosis, whereas 2.1% (N = 14) had LSM ≥ 13 kPa, which indicated cirrhosis [87]. In the Rotterdam study, a population-based study among individuals ≥ 45 y combined the presence of T2DM and hepatic steatosis (OR, 5.20; 95% CI: 3.01–8.98; p < 0.001 for combined presence), which were associated with LSM ≥ 8.0 kPa in multivariable analyses [88]. These studies clearly demonstrated that the presence of T2DM, especially that concurrent with steatosis, resulted in increased probabilities of having clinically relevant fibrosis.
5.4. Magnetic Resonance Elastography
Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is not operator-dependent or affected by obesity or ascites. It is currently the most accurate imaging tool for the detection of liver fibrosis because it is more effective than TE alone or TE with serum biomarkers combined [65,89,90]. For example, Imajo et al. examined 142 patients with biopsy-proven NAFLD in Japan who had an average body mass index (BMI) of 28.1 kg/m2 and underwent VCTE using M-probe, as well as MRE. The authors found that MRE was better than VCTE for detecting fibrosis [89]. Doycheva et al. performed a cross-sectional analysis of 100 patients with T2DM and reported that the prevalence of NAFLD defined as MRI- proton-density fat traction ≥ 5% and advanced fibrosis defined as MRE ≥ 3.6 kPa was 65% and 7.1%, respectively [91]. A recent study using MRE to evaluate fibrosis revealed that the prevalence of F2 (≥ 3.0 kPa) and F3 (≥ 3.6 kPa) in the overall cohort was 5.1% and 1.3%, respectively [92]. Additionally, the prevalence of F2 and F3 in participants with NAFLD plus T2DM was 24.1% and 6.0%, respectively. In a multivariate analysis of this cohort, only age, insulin, T2DM, and fatty liver on MR were independently associated with significant fibrosis [92]. Limitations of MRE include cost and availability, along with patient-dependent factors such as the presence of magnetically susceptible implants, being able to hold their breath, and claustrophobia [81]. Iron overload, high BMI, and significant ascites were also associated with technical failure [81,93]. The benefit of MRE is that it allows for a much larger sampling compared to US techniques and liver biopsy, which may reduce sampling variability secondary to heterogeneity of fibrosis [94]. The utility of MRE in NAFLD patients is promising, but further validation is required [65,95].
6. The Role of IR in Hepatic Fibrosis in NAFLD Patients
In 2014, Jung et al. reported that the value of the HOMA-IR was significantly higher in NASH subjects than in healthy controls (4.4 ± 2.5 vs. 1.7 ± 0.6; p < 0.001), but that this was not the case in patients with T2DM [96]. Unfortunately, their study could not show a significant correlation of HOMA-IR to the severity of either histologic grading or staging, because of the small sample size (41 cases of biopsy-proven NAFLD). Kessoku et al. evaluated 1365 biopsy-proven NAFLD patients registered in the JSG-NAFLD database and showed that HOMA-IR significantly increased depending on the degree of hepatic fibrosis (2.7 ± 1.1 in stage 0, 3.5 ± 1.6 in stage 1, 4.0 ± 1.7 in stage 2, 4.3 ± 1.7 in stage 3, and 4.6 ± 2.1 in stage 4; p < 0.01) [97]. Ballestri et al. in Italy investigated 118 consecutive biopsy-proven NAFLD patients (25% with T2DM) and reported that HOMA-IR independently predicted advanced hepatic fibrosis [98]. In both studies, the subjects included patients with T2DM. In fact, the prevalence of T2DM among patients with NAFLD has been reported to be 22.51% in global studies [4]. Conversely, approximately 80% of NAFLD patients are nondiabetic; therefore, can HOMA-IR also act as an independent predictor of advanced fibrosis even in nondiabetic patients? We recently investigated 361 biopsy-proven Japanese NAFLD patients without T2DM who were registered with JSG-NAFLD. We reported that HOMA-IR ≥ 2.90 was an independent predictor of advanced fibrosis in nondiabetic NAFLD patients, and our data suggest that there may be a pathway for IR to directly activate HSCs [99]. Unfortunately, there are no US Food and Drug Administration-approved medications to treat NAFLD and guidelines for NAFLD management are not well established. In this context, improving IR may be beneficial for anti-fibrotic treatment, even among patients with nondiabetic NAFLD [100,101].
7. Hepatocellular Carcinoma
The exact pathogenesis of HCC in NAFLD has not been fully described; however, both obesity and T2DM seem to play a critical role in hepatocarcinogenesis [102,103]. The global annual incidence of HCC in people with NAFLD is estimated to be 0.44 per 1000 person-years, whereas for those with NASH, the incidence of HCC is higher at 5.29 per 1000 person-years, which most likely results from the inflammatory state in those with NASH that promotes fibrosis and disease progression [4]. Tokushige et al. from JSG-NAFLD examined 532 patients with alcoholic liver disease (ALD)-HCC and 209 patients with NAFLD-HCC and revealed that the prevalence of lifestyle-related diseases including T2DM and hypertension was higher in the NAFLD-HCC group than in the ALD-HCC group [104]. In one study using data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database that covered a six-year period of time from 2004 to 2009, investigators determined that there was a 9% annual increase in the number of HCC cases attributed to NAFLD [105]. In another study using data from four European primary care databases representing the UK, Netherlands, Italy, and Spain, the authors reported that coded NAFLD/NASH patients were more likely to have T2DM, hypertension, and obesity than the matched controls [106]. The HR for HCC in patients compared to those in controls was 3.51 (95% CI 1.72–7.16). The strongest independent predictor of an HCC or cirrhosis diagnosis was baseline diagnosis of T2DM [106]. A recent study demonstrated with a multivariate analysis of 354 patients with NASH cirrhosis that T2DM was associated with an increased risk of developing HCC (HR 4.2; 95% CI 1.2–14.2) [107]. Although the risk of HCC is higher in NASH-related cirrhosis, there is also evidence that HCC can occur in the absence of cirrhosis (26–37%) in both NAFLD and NASH [108,109,110]. Bengtsson et al. examined the mortality rate and concluded that the parameters that independently associate with increased mortality included the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage, number of tumors, lower albumin, and presence of T2DM [110].
A number of genetic factors have also been implicated in the development of NAFLD. PNPLA3 polymorphisms were noted to not only lead to an increased risk of steatohepatitis and fibrosis, but also of a three-fold increased risk of HCC. These risks were independent of age, gender, BMI, T2DM, and presence of fibrosis or cirrhosis [103]. However, whether carrying the transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 (TM6SF2; rs58542926 c.449 C>T, p.E167K) polymorphism is an independent HCC risk factor is still controversial [103,111,112].
8. Conclusions
In this article, several aspects that potentially contribute to the mechanisms underlying IR and T2DM in the progression of NAFLD are discussed. We also discussed the indirect/direct roles of IR during the progression of hepatic fibrosis. More detailed knowledge of these mechanisms in NAFLD are needed to identify novel therapeutic approaches for this disease. Furthermore, specific biomarkers that can predict the degree of liver damage and NAFLD progression to cirrhosis and cancer should be developed. To achieve these objectives, we need animal models that accurately reflect the metabolic and histological characteristics of human NAFLD. Further investigations using such models can provide additional insight into the underlying mechanism by which extrahepatic organs (e.g., gut, adipose tissue, brain) regulate IR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.F.; original draft preparation, H.F.; review and editing, H.F. and N.K.; supervision: N.K. All authors have read and agreed to the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (grant number 17K09437) to H.F. (2017–2020).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to M. Sato-Matsubara for useful discussions. We acknowledge the scientific contribution and support of the JSG-NAFLD in the Japan Strategic Medical Administration Research Center (J-SMARC). Division of Hepatology and Pancreatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Aichi Medical University (Nagakute, Japan): Yoshio, Sumida, Satoshi Kimoto, and Masashi, Yoneda. Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Yokohama City University Graduate School of Medicine (Yokohama, Japan): Masato, Yoneda, Kento Imajo, Yuji Ogawa, Yasushi Honda, Takaomi Kessoku, and Atsushi Nakajima. Department of General Internal Medicine2, Kawasaki Medical School (Okayama, Japan): Miwa Kawanaka. Liver Center, Saga University Hospital (Saga, Japan): Hirokazu Takahashi. Eguchi Hospital (Saga, Japan): Yuichiro Eguchi. Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Tokyo Women’s Medical University Medical Center East (Tokyo, Japan): Masafumi Ono. Department of Gastroenterology, National Center for Global Health and Medicine (Tokyo, Japan): Yuichi Nozaki. Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Department of Medicine, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine (Osaka, Japan): Masahiro Koseki. Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Suita Municipal Hospital (Osaka, Japan): Yuichi Yoshida. Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, Kurume University School of Medicine (Kurume, Japan): Takumi Kawaguchi. Department of Molecular Biochemistry & Clinical Investigation, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine (Osaka, Japan): Yoshihiro Kamada. Hepatology Center, Saiseikai Suita Hospital (Osaka, Japan): Takeshi Okanoue. Department of Hepatology, Gifu Municipal Hospital (Gifu, Japan): Hideki Hayashi, Yoichi Nishigaki, Takafumi Uchiki, Yusuke Suzuki and Eiichi Tomita. Department of Internal Medicine, Himeji Red Cross Hospital (Himeji, Japan): Toshifumi Tada. Department of Gastroenterology and Metabolism, Graduate School of Biomedical and Health Sciences, Hiroshima University (Hiroshima, Japan): Takashi Nakahara. Department of Internal Medicine II, Shimane University Faculty of Medicine (Izumo, Japan): Hiroshi Tobita and Shuichi Satoh. Department of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology and Hematology/Oncology, Asahikawa Medical University (Asahikawa, Japan): Koji Sawada. Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Kochi Medical School (Kochi, Japan): Kensuke Munekage and Tsunehiro Ochi. Department of Internal Medicine, Institute of Gastroenterology, Tokyo Women’s Medical University (Tokyo, Japan): Tomomi Kogiso, and Katsutoshi Tokushige. Department of Gastroenterology and Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, Kagawa University (Kagawa, Japan): Tomohiro Morishita. Department of Gastroenterology, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine (Fukushima, Japan): Atsushi Takahashi. Second Department of Internal Medicine, Osaka Medical College (Osaka, Japan): Shinya Fukunishi. Department of Hepatology, Hamamatsu University School of Medicine (Hamamatsu, Japan): Kazuhito Kawata. Department of General Internal Medicine, Fukui-ken Saiseikai Hospital (Fukui, Japan): Kazuo Notsumata. Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, National Defense Medical College (Tokorozawa, Japan): Kengo Tomita. Department of Liver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas Diseases, Fujita Health University (Toyoake, Japan): Naoto Kawabe. Department of Gastroenterology, JA Hiroshima General Hospital (Hiroshima, Japan): Michihiro Nonaka, and Hideyuki Hyogo. Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Nippon Medical School Musashi Kosugi Hospital (Kawasaki, Japan): Taeang Arai. Tokyo Medical University Ibaraki Medical Center, Ibaraki, Japan: Tadashi Ikegami. Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Ogaki Municipal Hospital (Ogaki, Japan): Hidenori Toyoda and Takashi Kumada.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| AKT | Protein kinase B |
| ALD | Alcoholic liver disease |
| AST | Aspartate transaminase |
| ATX | Autotaxin |
| AUROC | Area under the receiver operating characteristic |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CCR | C-C chemokine receptors |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| ERK | RAS extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| GCK | Glucokinase regulator |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HOMA | Homeostasis model assessment parameter |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| HSC | Hepatic stellate cell |
| HSD17B13 | Hydroxysteroid 17β-dehydrogenase |
| IGF | Insulin-like growth factor |
| IGN | Intestinal gluconeogenesis |
| IKK | Inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB kinase |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IR | Insulin resistance |
| IRS | Insulin receptor substrate |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| JSG-NAFLD | Japan Study Group of NAFLD |
| LOXL2 | Lysyl oxidase-like 2 |
| LSM | Liver stiffness measurement |
| Mac-2bp | Mac-2 binding protein |
| MBOAT7 | Membrane bound O-acyltransferase domain- containing 7 |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| MRE | Magnetic resonance elastography |
| NAFLD | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NASH | Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-kappa B |
| NFS | NAFLD fibrosis score |
| OPN | Osteopontin |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| PDK | Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PNPLA3 | Patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 |
| SOCS | Suppressor of cytokine signaling |
| TAZ | Transcriptional coactivator with PDZ- binding motif |
| TEAD | TAZ/TEA domain |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-β |
| T2DM | Type2 diabetes mellitus |
| TM6SF2 | Transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| VCTE | Vibration-controlled transient elastography |
| WFA+-M2bp | Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2-binding protein |
References
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.W.; Chan, W.K.; Chitturi, S.; Chawla, Y.; Dan, Y.Y.; Duseja, A.; Fan, J.; Goh, K.L.; Hamaguchi, M.; Hashimoto, E.; et al. Asia-Pacific Working Party on Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease guidelines 2017-Part 1: Definition, risk factors and assessment. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Tacke, F.; Arrese, M.; Chander, S.B.; Mostafa, I.; Bugianesi, E.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Yilmaz, Y.; George, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Allen, A.M.; Wang, Z.; Prokop, L.J.; Murad, M.H.; Loomba, R. Fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver vs. nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of paired-biopsy studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuluvath, P.J.; Kantsevoy, S.; Thuluvath, A.J.; Savva, Y. Is cryptogenic cirrhosis different from NASH cirrhosis? J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Calzadilla-Bertot, L.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Castellanos, M.; Aller-de la Fuente, R.; Metwally, M.; Eslam, M.; Gonzalez-Fabian, L.; Alvarez-Quinones Sanz, M.; Conde-Martin, A.F.; et al. Fibrosis Severity as a Determinant of Cause-Specific Mortality in Patients With Advanced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Multi-National Cohort Study. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Chen, C.H.; Lo, M.T.; Schork, N.; Bettencourt, R.; Gonzalez, M.P.; Bhatt, A.; Hooker, J.; Shaffer, K.; Nelson, K.E.; et al. Shared genetic effects between hepatic steatosis and fibrosis: A prospective twin study. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; George, J. Genetic contributions to NAFLD: Leveraging shared genetics to uncover systems biology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Valenti, L.; Romeo, S. Genetics and epigenetics of NAFLD and NASH: Clinical impact. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overi, D.; Carpino, G.; Franchitto, A.; Onori, P.; Gaudio, E. Hepatocyte injury and hepatic stem cell niche in the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Cells 2020, 9, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Tordjman, J.; Clement, K.; Scherer, P.E. Fibrosis and adipose tissue dysfunction. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vily-Petit, J.; Soty-Roca, M.; Silva, M.; Raffin, M.; Gautier-Stein, A.; Rajas, F.; Mithieux, G. Intestinal gluconeogenesis prevents obesity-linked liver steatosis and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soty, M.; Gautier-Stein, A.; Rajas, F.; Mithieux, G. Gut-Brain Glucose Signaling in Energy Homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, E.J. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes: An epidemiological perspective. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 34, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R.; Roden, M. NAFLD and diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; de Avila, L.; Paik, J.M.; Srishord, M.; Fukui, N.; Qiu, Y.; Burns, L.; Afendy, A.; Nader, F. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Tabas, I.; Pajvani, U.B. Mechanisms of Fibrosis Development in NASH. Gastroenterology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, S.S.; Weigert, C.; Lehmann, R. Divergent Roles of IRS (Insulin Receptor Substrate) 1 and 2 in Liver and Skeletal Muscle. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1827–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.S.; Bril, F.; Cusi, K.; Newsome, P.N. Modulation of Insulin Resistance in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2019, 70, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.M.; Pennings, N. Insulin Resistance; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mota, M.; Banini, B.A.; Cazanave, S.C.; Sanyal, A.J. Molecular mechanisms of lipotoxicity and glucotoxicity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rametta, R.; Mozzi, E.; Dongiovanni, P.; Motta, B.M.; Milano, M.; Roviaro, G.; Fargion, S.; Valenti, L. Increased insulin receptor substrate 2 expression is associated with steatohepatitis and altered lipid metabolism in obese subjects. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, M.; Sawada, S.; Ueno, Y.; Murakami, K.; Yamada, T.; Gao, J.; Kodama, S.; Izumi, T.; Takahashi, K.; Tsukita, S.; et al. Selective insulin resistance with differential expressions of IRS-1 and IRS-2 in human NAFLD livers. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enooku, K.; Kondo, M.; Fujiwara, N.; Sasako, T.; Shibahara, J.; Kado, A.; Okushin, K.; Fujinaga, H.; Tsutsumi, T.; Nakagomi, R. Hepatic IRS1 and ss-catenin expression is associated with histological progression and overt diabetes emergence in NAFLD patients. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 1261–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, S.; Kozlitina, J.; Xing, C.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Cox, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, G.; Cipolla, U.; Cassader, M.; Pinach, S.; Saba, F.; De Michieli, F.; Paschetta, E.; Bongiovanni, D.; Framarin, L.; Leone, N.; et al. TM6SF2 rs58542926 variant affects postprandial lipoprotein metabolism and glucose homeostasis in NAFLD. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speliotes, E.K.; Yerges-Armstrong, L.M.; Wu, J.; Hernaez, R.; Kim, L.J.; Palmer, C.D.; Gudnason, V.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Garcia, M.E.; Launer, L.J.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies variants associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease that have distinct effects on metabolic traits. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsley, R.N.; Varadharajan, V.; Brown, A.L.; Gromovsky, A.D.; Schugar, R.C.; Ramachandiran, I.; Fung, K.; Kabbany, M.N.; Banerjee, R.; Neumann, C.K.; et al. Obesity-linked suppression of membrane-bound O-acyltransferase 7 (MBOAT7) drives non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Elife 2019, 8, e49882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, M.; Dongiovanni, P.; Longo, M.; Carli, F.; Baselli, G.; Rametta, R.; Pelusi, S.; Badiali, S.; Maggioni, M.; Gaggini, M.; et al. Mboat7 down-regulation by hyper-insulinemia induces fat accumulation in hepatocytes. EBioMedicine 2020, 52, 102658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umano, G.R.; Caprio, S.; Di Sessa, A.; Chalasani, N.; Dykas, D.J.; Pierpont, B.; Bale, A.E.; Santoro, N. The rs626283 variant in the MBOAT7 gene is associated with insulin resistance and fatty liver in Caucasian obese youth. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, Y.; Brenner, D.A. Liver inflammation and fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedde, T.; Kaplowitz, N.; Schwabe, R.F. Cell death and cell death responses in liver disease: Mechanisms and clinical relevance. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Luedde, T. Apoptosis and necroptosis in the liver: A matter of life and death. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbay, A.; Taimr, P.; Torok, N.; Higuchi, H.; Friedman, S.; Gores, G.J. Apoptotic body engulfment by a human stellate cell line is profibrogenic. Lab. Investig. 2003, 83, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.S.; Jiang, J.X.; Wu, J.; Halsted, C.; Friedman, S.L.; Zern, M.A.; Torok, N.J. Phagocytosis of apoptotic bodies by hepatic stellate cells induces NADPH oxidase and is associated with liver fibrosis in vivo. Hepatology 2006, 43, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebener, P.; Pradere, J.P.; Hernandez, C.; Gwak, G.Y.; Caviglia, J.M.; Mu, X.; Loike, J.D.; Schwabe, R.F. The HMGB1/RAGE axis triggers neutrophil-mediated injury amplification following necrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Yang, L.; van Rooijen, N.; Ohnishi, H.; Seki, E. Hepatic recruitment of macrophages promotes nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through CCR2. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G1310–G1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, E.; De Minicis, S.; Gwak, G.Y.; Kluwe, J.; Inokuchi, S.; Bursill, C.A.; Llovet, J.M.; Brenner, D.A.; Schwabe, R.F. CCR1 and CCR5 promote hepatic fibrosis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1858–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berres, M.L.; Koenen, R.R.; Rueland, A.; Zaldivar, M.M.; Heinrichs, D.; Sahin, H.; Schmitz, P.; Streetz, K.L.; Berg, T.; Gassler, N.; et al. Antagonism of the chemokine Ccl5 ameliorates experimental liver fibrosis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 4129–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.; Harrison, S.A.; Wong, V.W.; Francque, S.; Goodman, Z.; Aithal, G.P.; Kowdley, K.V.; Seyedkazemi, S.; Fischer, L.; et al. Cenicriviroc Treatment for Adults with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis: Final Analysis of the Phase 2b CENTAUR Study. Hepatology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Caviglia, J.M.; Corey, K.E.; Herfel, T.M.; Cai, B.; Masia, R.; Chung, R.T.; Lefkowitch, J.H.; Schwabe, R.F.; et al. Hepatocyte TAZ/WWTR1 Promotes Inflammation and Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Kim, K.; Wang, X.; Bartolome, A.; Salomao, M.; Dongiovanni, P.; Meroni, M.; Graham, M.J.; Yates, K.P.; Diehl, A.M. Hepatocyte Notch activation induces liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajvani, U.B.; Shawber, C.J.; Samuel, V.T.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Shulman, G.I.; Kitajewski, J.; Accili, D. Inhibition of Notch signaling ameliorates insulin resistance in a FoxO1-dependent manner. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Rametta, R.; Meroni, M.; Valenti, L. The role of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver disease development—A potential therapeutic target? Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 10, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Meroni, M.; Baselli, G.A.; Bassani, G.A.; Rametta, R.; Pietrelli, A.; Maggioni, M.; Facciotti, F.; Trunzo, V.; Badiali, S.; et al. Insulin resistance promotes Lysyl Oxidase Like 2 induction and fibrosis accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, G.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Sahebkar, A. Effects of newer antidiabetic drugs on nonalcoholic fatty liver and steatohepatitis: Think out of the box! Metabolism 2019, 101, 154001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, R.; Xiong, Y.; Du, F.; Zhu, S. A vicious circle between insulin resistance and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Judd, R.L. Adiponectin Regulation and Function. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1031–1063. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Svegliati-Baroni, G.; Ridolfi, F.; Di Sario, A.; Casini, A.; Marucci, L.; Gaggiotti, G.; Orlandoni, P.; Macarri, G.; Perego, L.; Benedetti, A.; et al. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 stimulate proliferation and type I collagen accumulation by human hepatic stellate cells: Differential effects on signal transduction pathways. Hepatology 1999, 29, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, T.; Takamura, T.; Kurita, S.; Matsuzawa, N.; Kita, Y.; Uno, M.; Akahori, H.; Misu, H.; Sakurai, M.; Zen, Y.; et al. Insulin resistance accelerates a dietary rat model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar-Lorenzo, A.; Rada, P.; Rey, E.; Maranon, P.; Arroba, A.I.; Santamaria, B.; Saiz, J.; Ruperez, F.J.; Barbas, C.; Garcia-Monzon, C.; et al. Insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS2) deficiency delays liver fibrosis associated with cholestatic injury. Dis. Models Mech. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, W.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, C.; Cai, L.; Lu, X.; et al. Zinc treatment prevents type 1 diabetes-induced hepatic oxidative damage, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and cell death, and even prevents possible steatohepatitis in the OVE26 mouse model: Important role of metallothionein. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 233, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, K.; Regos, E.; Rada, K.; Firneisz, G.; Baghy, K.; Kovalszky, I. Chronic Hyperglycaemia Induced Alterations of Hepatic Stellate Cells Differ from the Effect of TGFB1, and Point toward Metabolic Stress. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zuo, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y. ASIC1a promotes high glucose and PDGF-induced hepatic stellate cell activation by inducing autophagy through CaMKKbeta/ERK signaling pathway. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 300, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Enomoto, M.; Fukushima, W.; Tamori, A.; Sakaguchi, H.; Kawada, N. Applicability of BARD score to Japanese patients with NAFLD. Gut 2009, 58, 1566–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, T.; Hyogo, H.; Yoneda, M.; Sumida, Y.; Eguchi, Y.; Fujii, H.; Ono, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Imajo, K.; Aikata, H.; et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with the fibrosis severity in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a large retrospective cohort of Japanese patients. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Choi, K.C.; Wong, G.L.; Zhang, Y.; Chan, H.L.; Luk, A.O.; Shu, S.S.; Chan, A.W.; Yeung, M.W.; Chan, J.C.; et al. Screening diabetic patients for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with controlled attenuation parameter and liver stiffness measurements: A prospective cohort study. Gut 2016, 65, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P.; Hui, J.M.; Marchesini, G.; Bugianesi, E.; George, J.; Farrell, G.C.; Enders, F.; Saksena, S.; Burt, A.D.; Bida, J.P.; et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: A noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology 2007, 45, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, A.; Comparcola, D.; Romito, I.; Mantovani, A.; Nobili, V.; Byrne, C.D.; Alisi, A.; Targher, G. Plasma N-terminal propeptide of type III procollagen accurately predicts liver fibrosis severity in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 2317–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, S.J.; Leeming, D.J.; Eslam, M.; Hashem, A.M.; Nielsen, M.J.; Krag, A.; Karsdal, M.A.; Grove, J.I.; Neil Guha, I.; Kawaguchi, T.; et al. ADAPT: An Algorithm Incorporating PRO-C3 Accurately Identifies Patients With NAFLD and Advanced Fibrosis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castera, L.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Loomba, R. Noninvasive Assessment of Liver Disease in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1264–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wai, C.T.; Greenson, J.K.; Fontana, R.J.; Kalbfleisch, J.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Lok, A.S. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003, 38, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; S Sulkowski, M.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, M.; Fujii, H.; Sumida, Y.; Hyogo, H.; Itoh, Y.; Ono, M.; Eguchi, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Aoki, N.; Kanemasa, K.; et al. Platelet count for predicting fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirab, K.; Bekki, Y.; Gantumur, D.; Araki, K.; Ishii, N.; Kuno, A.; Narimatsu, H.; Mizokami, M. Mac-2 binding protein glycan isomer (M2BPGi) is a new serum biomarker for assessing liver fibrosis: More than a biomarker of liver fibrosis. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Miyake, T.; Kuno, A.; Imai, Y.; Sawai, Y.; Hino, K.; Hara, Y.; Hige, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Yamada, G.; et al. Association between Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2 binding protein and the fibrosis stage of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Iwata, Y.; Kishino, K.; Shimono, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Nakano, C.; Takata, R.; Yoh, K.; Nishimura, T.; et al. Clinical significance of serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin positive Mac-2-binding protein level in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, Y.; Fujii, H.; Fujii, H.; Sawai, Y.; Doi, Y.; Uozumi, N.; Mizutani, K.; Akita, M.; Sato, M.; Kida, S.; et al. Serum Mac-2 binding protein levels as a novel diagnostic biomarker for prediction of disease severity and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2013, 7, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, Y.; Ono, M.; Hyogo, H.; Fujii, H.; Sumida, Y.; Mori, K.; Tanaka, S.; Yamada, M.; Akita, M.; Mizutani, K.; et al. A novel noninvasive diagnostic method for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis using two glycobiomarkers. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, Y.; Ono, M.; Hyogo, H.; Fujii, H.; Sumida, Y.; Yamada, M.; Mori, K.; Tanaka, S.; Maekawa, T.; Ebisutani, Y.; et al. Use of Mac-2 binding protein as a biomarker for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease diagnosis. Hepatol. Commun. 2017, 1, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, Y.; Imajo, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Kessoku, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Tomeno, W.; Yoneda, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Saito, S.; Nakajima, A. Autotaxin is a valuable biomarker for the prediction of liver fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Kumada, H.; Enooku, K.; Koike, K.; Kurano, M.; Sato, M.; Nojiri, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Ohkawa, R.; et al. Performance of autotaxin as a serum marker for liver fibrosis. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 55, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimori, N.; Umemura, T.; Kimura, T.; Tanaka, N.; Sugiura, A.; Yamazaki, T.; Joshita, S.; Komatsu, M.; Usami, Y.; Sano, K.; et al. Serum autotaxin levels are correlated with hepatic fibrosis and ballooning in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okanoue, T.; Ebise, H.; Kai, T.; Mizuno, M.; Shima, T.; Ichihara, J.; Aoki, M. A simple scoring system using type IV collagen 7S and aspartate aminotransferase for diagnosing nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and related fibrosis. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Gosai, F.; Siddiqui, M.T.; Gupta, M.; Lopez, R.; Lawitz, E.; Poordad, F.; Carey, W.; McCullough, A.; Alkhouri, N. Accuracy of Noninvasive Fibrosis Scores to Detect Advanced Fibrosis in Patients With Type-2 Diabetes With Biopsy-proven Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkayyali, T.; Qutranji, L.; Kaya, E.; Bakir, A.; Yilmaz, Y. Clinical utility of noninvasive scores in assessing advanced hepatic fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A study in biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Acta Diabetol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Sebastiani, G. Limitations of non-invasive tests for assessment of liver fibrosis. JHEP Rep. 2020, 2, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R. Role of imaging-based biomarkers in NAFLD: Recent advances in clinical application and future research directions. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapper, E.B.; Loomba, R. Noninvasive imaging biomarker assessment of liver fibrosis by elastography in NAFLD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich-Rust, M.; Poynard, T.; Castera, L. Critical comparison of elastography methods to assess chronic liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddowes, P.J.; Sasso, M.; Allison, M.; Tsochatzis, E.; Anstee, Q.M.; Sheridan, D.; Guha, I.N.; Cobbold, J.F.; Deeks, J.J.; Paradis, V.; et al. Accuracy of FibroScan Controlled Attenuation Parameter and Liver Stiffness Measurement in Assessing Steatosis and Fibrosis in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeda, S.; Takahashi, H.; Imajo, K.; Seko, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Moriguchi, M.; Yoneda, M.; Anzai, K.; Aishima, S.; Kage, M. Accuracy of liver stiffness measurement and controlled attenuation parameter using FibroScan((R)) M/XL probes to diagnose liver fibrosis and steatosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A multicenter prospective study. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roulot, D.; Roudot-Thoraval, F.; NKontchou, G.; Kouacou, N.; Costes, J.L.; Elourimi, G.; Le Clesiau, H.; Ziol, M.; Beaugrand, M. Concomitant screening for liver fibrosis and steatosis in French type 2 diabetic patients using Fibroscan. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, E.M.; Plompen, E.P.; Schouten, J.N.; Hansen, B.E.; Darwish Murad, S.; Taimr, P.; Leebeek, F.W.; Hofman, A.; Stricker, B.H.; Castera, L. Presence of diabetes mellitus and steatosis is associated with liver stiffness in a general population: The Rotterdam study. Hepatology 2016, 63, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imajo, K.; Kessoku, T.; Honda, Y.; Tomeno, W.; Ogawa, Y.; Mawatari, H.; Fujita, K.; Yoneda, M.; Taguri, M.; Hyogo, H.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging More Accurately Classifies Steatosis and Fibrosis in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Than Transient Elastography. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.C.; Nguyen, P.; Hernandez, C.; Bettencourt, R.; Ramirez, K.; Fortney, L.; Hooker, J.; Sy, E.; Savides, M.T.; Alquiraish, M.H.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Elastography vs. Transient Elastography in Detection of Fibrosis and Noninvasive Measurement of Steatosis in Patients With Biopsy-Proven Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doycheva, I.; Cui, J.; Nguyen, P.; Costa, E.A.; Hooker, J.; Hofflich, H.; Bettencourt, R.; Brouha, S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Loomba, R. Non-invasive screening of diabetics in primary care for NAFLD and advanced fibrosis by MRI and MRE. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.A.; Jun, D.W.; Kim, M.S.; Kwon, H.J.; Nguyen, M.H. Prevalence of significant hepatic fibrosis using magnetic resonance elastography in a health check-up clinic population. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.; Corcuera-Solano, I.; Lo, G.; Esses, S.; Liao, J.; Besa, C.; Chen, N.; Abraham, G.; Fung, M.; Babb, J.S.; et al. Technical Failure of MR Elastography Examinations of the Liver: Experience from a Large Single-Center Study. Radiology 2017, 284, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, M.; Imajo, K.; Takahashi, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Eguchi, Y.; Sumida, Y.; Yoneda, M.; Kawanaka, M.; Saito, S.; Tokushige, K.; et al. Clinical strategy of diagnosing and following patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease based on invasive and noninvasive methods. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, M.; Imajo, K.; Nakajima, A. Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1409–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.Y.; Cho, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.B.; Song, I.H. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis associated with metabolic syndrome: Relationship to insulin resistance and liver histology. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessoku, T.; Yoneda, M.; Sumida, Y.; Eguchi, Y.; Fujii, H.; Hyogo, H.; Ono, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Nakajima, A. Japan Study Group of NAFLD. Insulin resistance correlated with the severity of liver histology in Japanese NAFLD patients: A multicenter retrospective study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 49, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballestri, S.; Nascimbeni, F.; Romagnoli, D.; Lonardo, A. The independent predictors of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and its individual histological features: Insulin resistance, serum uric acid, metabolic syndrome, alanine aminotransferase and serum total cholesterol are a clue to pathogenesis and candidate targets for treatment. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, H.; Imajo, K.; Yoneda, M.; Nakahara, T.; Hyogo, H.; Takahashi, H.; Hara, T.; Tanaka, S.; Sumida, Y.; Eguchi, Y.; et al. HOMA-IR: An independent predictor of advanced liver fibrosis in nondiabetic non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhouri, N.; Poordad, F.; Lawitz, E. Management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Lessons learned from type 2 diabetes. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, Y.; Yoneda, M.; Tokushige, K.; Kawanaka, M.; Fujii, H.; Yoneda, M.; Imajo, K.; Takahashi, H.; Eguchi, Y.; Ono, M.; et al. Antidiabetic Therapy in the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golabi, P.; Rhea, L.; Henry, L.; Younossi, Z.M. Hepatocellular carcinoma and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Int. 2019, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Reeves, H.L.; Kotsiliti, E.; Govaere, O.; Heikenwalder, M. From NASH to HCC: Current concepts and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokushige, K.; Hyogo, H.; Nakajima, T.; Ono, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Honda, K.; Eguchi, Y.; Nozaki, Y.; Kawanaka, M.; Tanaka, S. Hepatocellular carcinoma in Japanese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and alcoholic liver disease: Multicenter survey. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Otgonsuren, M.; Henry, L.; Venkatesan, C.; Mishra, A.; Erario, M.; Hunt, S. Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in the United States from 2004 to 2009. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, M.; Loomis, A.K.; van der Lei, J.; Duarte-Salles, T.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Ansell, D.; Pasqua, A.; Lapi, F.; Rijnbeek, P.; Mosseveld, M.; et al. Risks and clinical predictors of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma diagnoses in adults with diagnosed NAFLD: Real-world study of 18 million patients in four European cohorts. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Ahmed, F.; Mara, K.C.; Addissie, B.D.; Allen, A.M.; Gores, G.J.; Roberts, L.R. Diabetes Is Associated With Increased Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Cirrhosis From Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2020, 71, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; El-Serag, H.B.; Sada, Y.H.; Kanwal, F.; Duan, Z.; Temple, S.; May, S.B.; Kramer, J.R.; Richardson, P.A.; Davila, J.A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Absence of Cirrhosis in United States Veterans is Associated With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawrieh, S.; Dakhoul, L.; Miller, E.; Scanga, A.; deLemos, A.; Kettler, C.; Burney, H.; Liu, H.; Abu-Sbeih, H.; Chalasani, N.; et al. Characteristics, aetiologies and trends of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients without cirrhosis: A United States multicentre study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, B.; Stal, P.; Wahlin, S.; Bjorkstrom, N.K.; Hagstrom, H. Characteristics and outcome of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with NAFLD without cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Reeves, H.L.; Burt, A.D.; Tiniakos, D.; McPherson, S.; Leathart, J.B.; Allison, M.E.; Alexander, G.J.; Piguet, A.C.; Anty, R.; et al. TM6SF2 rs58542926 influences hepatic fibrosis progression in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, B.; Dongiovanni, P.; Romeo, S.; Meroni, M.; McCain, M.; Miele, L.; Petta, S.; Maier, S.; Rosso, C.; De Luca, L.; et al. MBOAT7 rs641738 variant and hepatocellular carcinoma in non-cirrhotic individuals. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).