Abstract
Chronic inflammation is implicated in the development of various multifactorial diseases, including cancer, diabetes, arthritis, cardiovascular disorders, Alzheimer’s disease, and autoimmune diseases. The enzymes that play a key role in the onset of the inflammation are cyclooxygenases (COXs) and lipoxygenases (LOXs). In recent years, cinnamic acid hybrid molecules, particularly those incorporating a nitric oxide (NO) donor moiety, have attracted considerable attention as potential pharmacological agents for the treatment of multifactorial diseases. In the present study, novel cinnamic acid–nitric oxide (NO) donor hybrids were synthesized as multitarget agents and evaluated for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cytotoxic properties. In particular, hybrids 5a–i, 6a–i, 9a–i, and 11 were synthesized and evaluated as lipid peroxidation and LOX inhibitors, while selected molecules were further tested as COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitors. Hybrids 6a–i, 9a–i, and 11 that contain a NO donor moiety, were additionally tested as albumin denaturation inhibitors and for their ability to release NO. The results indicated that compound 9a is a promising multitarget agent, exhibiting the lowest IC50 for LOX inhibition, significant antioxidant activity, and the highest NO donor potency. Furthermore, compound 9e demonstrated significant inhibitory activity against both COX-2 and LOX, suggesting its potential as a dual COX–LOX inhibitor. Additionally, compound 6i exhibited the strongest cytotoxic activity among the tested compounds, with EC50 values ranging from 36 to 45 μM across multiple cancer cell lines. All synthesized compounds were also evaluated through in silico studies.
Keywords:
chronic inflammation; LOX; COX; cinnamic acid; nitric oxide; NO donor; multitarget agents; hybrid molecules 1. Introduction
Inflammation is the multifactorial defense mechanism of the body to stimuli of various etiologies (microbial, chemical, etc.) that can cause pathophysiological results. There are two main types of inflammation: acute and chronic. Acute inflammation is sudden and temporary, while chronic inflammation is a process of prolonged duration. Chronic inflammation can lead to a variety of multifactorial diseases such as cancer, diabetes, arthritis, cardiovascular, Alzheimer’s, and autoimmune diseases [1,2].
Important enzymes that play a key role in the mechanism of inflammation are cyclooxygenases (COXs) and lipoxygenases (LOXs). Cyclooxygenases metabolize arachidonic acid to produce prostaglandins, prostacyclins, and thromboxane A2, while lipoxygenases lead to leukotrienes [3,4].
Furthermore, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are also significant factors in the progress of inflammatory disorders acting as key signaling molecules. An enhanced ROS generation by polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) at the site of inflammation causes endothelial dysfunction and tissue injury. In addition, oxidative stress is viewed as an imbalance between the production of ROS and their elimination by protective mechanisms, which can lead to chronic inflammation. High levels of ROS can produce changes, e.g., in (OXPHOS), transition metal ions, oxidase activity, protein folding, thymidine, and polyamine catabolism, lipids, proteins, and DNA. It is consistent that rates of ROS production are increased in most diseases [5,6,7].
Nitric oxide (NO) seems to be important in the process of inflammation. It is a neurotransmitter that lowers blood pressure and is an essential reactive oxygen species. It is produced in endothelial cells from nitic oxide synthases (NOSs) by the conversion of L-arginine to L-citrulline and NO. Afterwards, NO enters adjacent cells and stimulates the enzyme soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) that regulates various molecular targets that lead to a range of physiological responses [8]. Into the organism, NO reacts with oxygen to give nitric oxides. In pathological conditions, such as inflammation, there is low bioavailability of NO in the body due to high production of ROS. NO donors are the appropriate therapy in these cases. They can release NO into the body increasing the body’s NO levels in pathological conditions, used to treat cardiovascular disorders. Many well-known NO donors are organic nitrites, oximes, furoxans, NONOates, etc. [9,10].
On the other hand, cinnamic acid is a natural product found in essential oils, resins, and balsams, serving as a precursor to various hydroxy-substituted derivatives with notable biological activities. Synthetic modifications of its structure have led to the development of commercially significant molecules used in producing bioactive compounds and drugs. Substitutions on the cinnamic acid backbone result in derivatives with diverse biological properties, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, and antimicrobial activities [11,12].
Today, there is an increase interest in the combination of two or more pharmacophores on the same scaffold, leadings to hybrid molecules. Hybrid drugs are produced with the goal of creating a chemical entity, more medically effective than its individual components. Furthermore, multifunctional molecules can be beneficial for the treatment of complex and multifactorial diseases instead of a single-target molecule [13]. A variety of multitarget molecules containing the cinnamic acid moiety have been reported.
Many efforts have been devoted to the synthesis of cinnamic hybrids in order to obtain multifunctional drugs [14]. Notably, hybrids incorporating nitric oxide (NO) donor groups have been synthesized and evaluated. The integration of NO donor groups into existing bioactive molecules has been shown to enhance their biological properties, thereby offering potential for improved therapeutic applications [15].
A considerable number of NO donors have been synthesized as hybrids combined with other pharmacophoric groups. Among them, oximes and furoxanes are of particular interest. Oximes represent one of the most common and widely recognized nitrogen-containing scaffolds, exhibiting diverse biological activities such as antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer effects [16,17,18,19]. In 1998, Koikov et al. [20] reported that oximes, amidoximes, and hydroxamic acids can act as NO donors, releasing NO and the corresponding parent ketones under mild oxidation conditions. Moreover, amidoximes and oximes exert significant physiological effects, including relaxation of both aortic and tracheal rings, as well as reduction of arterial pressure and thrombus formation.
Experimental studies have demonstrated that furoxan derivatives can activate soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) by releasing nitric oxide in the presence of thiol cofactors. Since NO is involved in many bioregulatory processes, the furoxan scaffold represents a valuable structure for the design of hybrid molecules. Such hybrids could serve as novel vasodilators, combining typical NO-dependent effects on both the microvascular and macrovascular systems with additional α1-antagonist activity [21,22].
Thus, we decided to design and synthesize a series of hybrids with cinnamic acid derivatives as advantageous multi-target agents, containing an oxime or a furoxan ring (Figure 1). We made a library of molecules, and we used drug-likeness and modeling studies on our library structures, as tools, in order to design LOX and COX-2 hybrid inhibitors acting as NO donors. The structural modifications are mainly focused on the cinnamic acid (simple) or with condensed rings, heterocyclic rings, and substitution on the double bond.
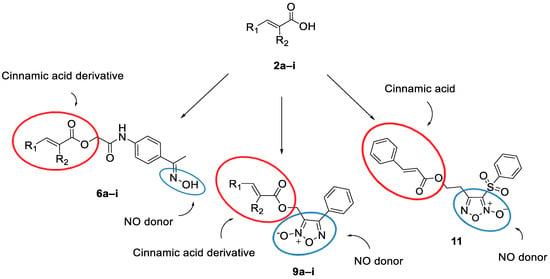
Figure 1.
General structures of the new hybrids with cinnamic acid derivatives containing an oxime or a furoxan ring as NO donor.
The drug-likeness of the hybrids was determined from the theoretical calculation of various molecular properties. The in silico results were performed, and the violations of Lipinski’s rule were considered using several platforms as well as the prediction of Absorbance, Distribution, Metabolism, Elimination, Toxicology (ADMET) properties. The gathered information supported the synthesis of the hybrid compounds in an attempt to define the importance and correlation of lipophilicity, steric, and electronic parameters on the biological activities.
Synthesis of the new hybrids was followed by verification of their structure with NMR, HRMS, and LCMS, while characterization of appearance, melting point, and Rf was performed.
Furthermore, the new synthesized hybrids were evaluated through in vitro studies considering multifunctionality. More specifically they were tested as COX-2/LOX inhibitors, as antioxidants, and also for their ability to release NO. Additionally, in vitro studies were performed in selected hybrids to evaluate their ability as COX-1 inhibitors and as anti-inflammatories by inhibition of denaturation of albumin. Finally, their cytotoxicity was screened in various cancer cell lines.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
The design and synthesis of the new multitarget cinnamic hybrids were based on in silico analysis according to the ADMET results, modeling studies and 2D-QSAR studies supported by our previous publications [23].
To synthesize the new cinnamic acid–NO donor molecules, cinnamic acids 2a–i were used. The acids were synthesized via a Knoevenagel–Doebner condensation of the suitable aldehyde with malonic acid in the presence of pyridine and piperidine [24,25], as shown in Scheme 1. The structures of the known compounds (Table 1) were verified according to literature spectral data or melting points [26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33].
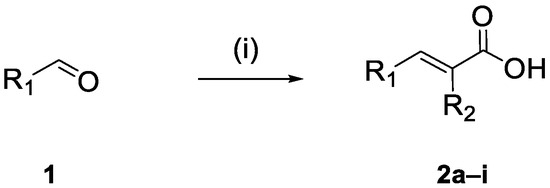
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of cinnamic acids 2a–i. (i) malonic acid, piperidine, pyridine or phenylacetic acid, triethylamine (Et3N), and acetic anhydride (Ac2O).

Table 1.
The chemical structures of compounds 2, 5, 6, and 9.
2.1.1. Synthesis of the Cinnamic Acid-Arylacetamide Oxime Hybrids 6a–i
The synthesis of the hybrid oxime compounds 6a–i involved the synthesis of the precursor N-(4-acetylphenyl)-2-chloroacetamide (4) [34]. Compound 4 was obtained easily from 4-aminoacetophenone (3) and chloroacetic chloride in the presence of anhydrous potassium carbonate, in dichloromethane DCM (yield: 72%). A coupling reaction between N-(4-acetylphenyl)-2-chloroacetamide (4) and cinnamic acid derivatives 2a–i in the presence of triethylamine and potassium iodide in dimethylformamide DMF resulted in the hybrid cinnamic acid–arylacetamide ketones 5a–i, in yields between 16 and 54%. Nucleophilic addition of hydroxylamine to hybrids 5 in ethanol EtOH and basic conditions, furnished the oxime hybrids 6a–i, as presented in Scheme 2, in yields between 70 and 94%. All the reactions took place in microwaves at 50 W and 50 °C. The synthesis of compound 6a, following a different synthetic route, has already been published [35], however, herein for a first time is presented its synthesis with the aim of microwave irradiation (Scheme 2).
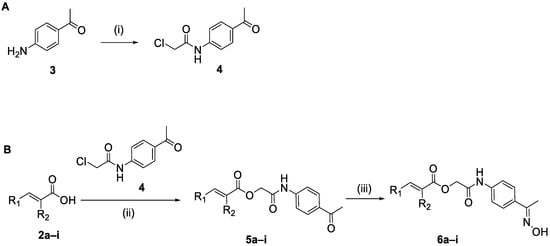
Scheme 2.
(A) Synthesis of N-(4-acetylphenyl)-2-chloroacetamide 4. (i) ClCH2COCl, K2CO3, DCM, rt, 3 h. (B) General synthesis of oxime hybrids 6. (ii) 2a–i, Et3N, KI, DMF, microwave at 50 W, 50 °C, 5 min. (iii) NH2OH·HCl, CH3COONa, EtOH, microwave at 50 W, 50 °C, 5–15 min.
The structural characterization of the new cinnamic acid analogues 5a–i and 6a–i was based on their spectral data and HRMS/LCMS analysis (Supplementary materials). All the compounds are novel with the exception of 5a. Compound 5a is the only known derivative mentioned in the literature for which its physicochemical and spectroscopic data were identical to the reported data [36].
Hybrids 5b–i were analyzed based on their spectroscopic data to confirm their structures. More specifically, in the 1H NMR spectra recorded in DMSO-d6, a characteristic doublet appears around 6 ppm, corresponding to one of the two protons of the molecule’s double bond. The J values (15–17 Hz) are characteristic of a trans (E) configuration of the double bond for the cinnamic hybrids 5a–f. Additionally, the NMR spectra of compounds 5g–i shows the presence of a single isomer, which is likely the E form, as it is generally the more stable configuration. The chemical shift of the second proton of the double bond appears between 7 and 8 ppm also as a doublet, although it may be less distinguishable due to the presence of aromatic protons. Additionally, a distinct signal is observed near 9.5 ppm in all spectra, corresponding to the –NH proton. Subsequent analysis of the 13C NMR spectra in dimethyl sulfoxide DMSO-d6 showed the three carbonyl carbons of the molecules, appearing above 160 ppm, as expected, while the –CH2 and –CH3 group carbons appeared around 60 and 25 ppm, respectively. Finally, the LC–MS results underlined the presence of [M + Na]+ and [M − H]−.
Regarding hybrids 6a–i, in the 1H NMR spectra recorded in DMSO-d6, a characteristic doublet appears approximately at 6 ppm, corresponding to one of the two protons of the molecule’s double bond. This signal shows a slight shift compared to the corresponding shift in the ketonic hybrids 5a–i. Furthermore, the trans-stereochemistry is maintained in 6a–f cinnamic hybrids, as indicated by the J values of 15–17 Hz. Additionally, the NMR spectra of compounds 6g–i shows the presence of a single isomer, which is likely the E form, as it is generally the more stable configuration. The second proton appears in the aromatic region (7–8 ppm) as a doublet, although it may not be clearly distinguishable due to the overlapping of aromatic protons. Additionally, the –NH proton signal is consistently observed near 9.5 ppm in all spectra, and additionally, in these molecules, the proton of the oxime group is also clearly visible as a distinct peak near 10 ppm. In the 13C NMR spectra (DMSO-d6), the two carbonyl carbons appear around 160 ppm, as expected. The third carbonyl carbon that was observed in the ketonic hybrids 5a–i, now is shifted to approximately 150 ppm due to the introduction of the oxime group. The –CH2 carbon appears relatively unchanged compared to cinnamic hybrids 5a–i, around 60 ppm, while the –CH3 carbon is now shifted to approximately 10 ppm, indicating the transformation of the ketone group to an oxime on the adjacent carbon. Finally, HRMS results showed the presence of [M + H]+ and [M − H]−, while LC–MS results revealed the presence of [M + Na]+ and [M − H]− in most cases.
Detailed NMR spectra and the physicochemical properties of the novel derivatives are given in the experimental section (Supplementary materials).
2.1.2. Synthesis of the Cinnamic Acid–Phenyl Furoxan Hybrids 9a–i
The synthesis of the cinnamic acid–phenyl furoxan hybrids 9a–i involved the synthesis of the precursor 3-(hydroxymethyl)-4-phenyl-furoxan (8) [37]. Compound 8 was obtained from cinnamoyl alcohol (7) in the presence of sodium nitrite in acetic acid (yield: 62%). A coupling reaction between furoxan 8 and cinnamic acid derivatives 2a–i in the presence of 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide EDCI hydrochloride and 4-dimethylamino pyridine DMAP in dimethylformamide DMF provided the hybrid compounds 9a–i in yields between 40 and 87%, as shown in Scheme 3.
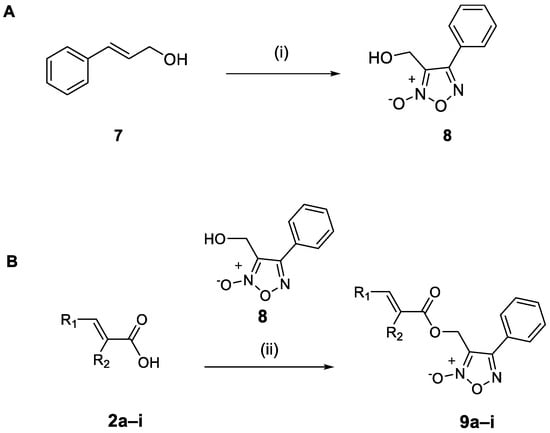
Scheme 3.
(A) Synthesis of 3-(hydroxymethyl)-4-phenyl-furoxan (8). (i) NaNO2, AcOH, rt, 24 h. (B) Synthsis of hybrids 9a–i. (ii) EDCI·HCl, 4-DMAP, DMF, microwave at 50 W, 50 °C, 5–45 min.
The structural characterization of the new cinnamic acid–phenyl furoxan analogues 9a–i was based on their spectral data and HRMS analysis. (Supplementary materials). More specifically, in the 1H NMR spectra in CDCl3, a characteristic doublet appears near 6.5 ppm, which is attributed to one of the two protons of the molecule’s double bond. The J values (15–17 Hz) are characteristic of a trans (E) configuration of the double bond of the cinnamic moiety for compounds 9a–f. Additionally, the NMR spectra of cinnamic hybrids 9g–i support the presence of a single isomer, which is likely the E form, as it is generally the more stable configuration. The second proton of the double bond appears in the aromatic region between 7 and 8 ppm as a doublet, which may not be clearly distinguishable in the spectrum due to the presence of aromatic hydrogens. Additionally, the signal of the –CH2 hydrogen is characteristic in these molecules, appearing around 5.5 ppm in all analogues’ spectra. Subsequently, the analysis of the 13C NMR spectra in CDCl3 showed that the most characteristic signal is the carbonyl carbon near 165 ppm, as expected, and the carbon of the –CH2 group appearing near 60 ppm. Finally, the HRMS results showed the presence of [M + H]+ and [M − H]− ions, while the LC–MS results showed the presence of [M + Na]+ and [M − H]− ions in most cases.
Detailed NMR spectra and the physicochemical properties of the novel derivatives are given in the experimental section (Supplementary materials).
2.1.3. Synthesis of the Cinnamic Acid–Phenylsulfonyl Furoxan Hybrid 11
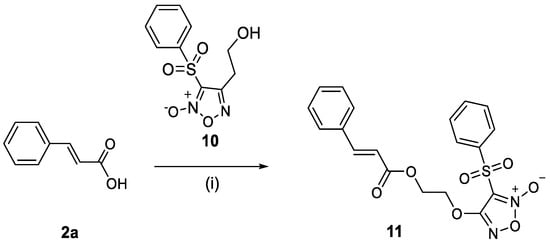
A coupling reaction between phenylsulfonyl furoxan analogue 10 and cinnamic acid 2a in the presence of EDCI hydrochloride and DMAP in DMF provided the cinnamic acid–phenylsulfonyl hybrid compound 11 with 35% yield (Scheme 4). Furoxan 10 was synthesized according to the literature [38].
Scheme 4.
Synthesis of phenylsulfonyl furoxan hybrid molecule 11. (i) EDCI·HCl, 4-DMAP, DMF, microwave at 50 W, 50 °C, 5 min.
Regarding hybrid 11, its structural characterization was based on spectroscopic data, which were compared with literature data [39]. More specifically, in the 1H NMR spectra in CDCl3, a characteristic doublet appears near 6.5 ppm, which is attributed to one of the two protons of the molecule’s double bond. The J value (16 Hz) indicates the presence of a trans (E) configuration of the double bond. The second proton of the double bond appears in the aromatic region (7–8 ppm) as a doublet, which may not be clearly distinguishable in the spectrum due to the presence of aromatic hydrogens. Additionally, characteristic signals for the –CH2 protons of the molecule are observed around 4.5 ppm, appearing as two symmetrical multiplets. Subsequently, the analysis of the 13C NMR spectra in CDCl3 showed the most characteristic signals to be the carbonyl carbon appearing around 165 ppm, and the carbons of the –CH2 groups appearing around 60–70 ppm.
2.2. Physicochemical Studies
2.2.1. In Silico Determination of Drug-likeness and ADMET Properties
Drug discovery is an expensive, time-consuming and challenging procedure. Due to these disadvantages, in the last decades, the determination of human pharmacokinetic properties has been studied by in silico procedures that have replaced the experimental procedures in an early stage. In silico studies include the determination of ADMET properties and drug-likeness of the molecule [40].
Drug-likeness stands for the possibility of a molecule becoming an oral drug, and it is a qualitative method that predicts the bioavailability of the molecule. One of the most widely used approaches for evaluating drug-likeness is the rule of five developed by Lipinski et al. [41]. According to Lipinski’s rule, poor absorption of a molecule is related to the presence of more than five H-bond donors and ten H-bond acceptors. Furthermore, values of the molecular weight (MW) > 500 and calculated logP value > five lead to poor absorption as well [42,43].
We calculated the physicochemical and molecular properties to analyze the hybrids 5a–i, 6a–i, 9a–i, and 11 via the cheminformatics software tools of Molinspiration https://www.molinspiration.com/ (10 May 2025). According to Lipinski’s rule, all 28 synthesized compounds present druglikeness, with the exception of compounds 5h, 6h, 9b, 9e, 9g, 9h, and 9i, for which one violation is presented (the milogP value) (Table 2).
In drug design, another important parameter is the blood–brain barrier penetration of a molecule that can lead to side effects [44]. The calculation of BBB penetration was measured using preADME software https://preadmet.webservice.bmdrc.org/ (10 April 2025), which calculates the in vivo blood–brain barrier (BBB) penetration, often expressed as the ratio Cbrain/Cblood. The factors that influence BBB penetration value are lipophilicity (logP), TPSA and molecular weight [45]. When value Cbrain/Cblood is higher than 1, this indicates effective BBB penetration, with higher concentrations in the brain than in the blood. Such compounds are considered CNS-active. When value Cbrain/Cblood is between 0.1 to 1, that suggests partial penetration. The compound may have some CNS effects, depending on its pharmacodynamic properties. And finally, when value Cbrain/Cblood is lower than 0.1, that indicates poor BBB penetration. These compounds likely have limited CNS effects unless they are transported actively [46].
Regarding the tested analogues, it seems that almost half of them exhibit moderate absorption through the BBB (scores 0.1–1), while the other half shown low BBB penetration (scores < 0.1). Only compound 9g presents high BBB penetration (score > 1). All the above are depicted in Table 2.

Table 2.
Molecular properties prediction—Lipinski’s Rule of Five. The prediction is calculated by preADME [46] and Molinsiration [47] platforms.
Table 2.
Molecular properties prediction—Lipinski’s Rule of Five. The prediction is calculated by preADME [46] and Molinsiration [47] platforms.
| Compound | Milog P a | TPSA b | No Atoms | No O, N c | No OH, NH d | No Violations | No Rotational Bonds e | Volume f | MW g | logBB h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5a | 3.23 | 72.47 | 24 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 294.57 | 323.35 | 0.0909 |
| 5b | 4.21 | 72.47 | 28 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 338.56 | 373.41 | 0.0295 |
| 5c | 2.95 | 72.47 | 23 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 285.28 | 329.38 | 0.3054 |
| 5d | 2.31 | 85.61 | 23 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 276.14 | 313.31 | 0.2410 |
| 5e | 4.25 | 72.47 | 27 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 329.27 | 379.44 | 0.0369 |
| 5f | 3.61 | 85.61 | 27 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 320.13 | 363.37 | 0.0282 |
| 5g | 4.56 | 72.47 | 30 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 365.98 | 399.45 | 0.2139 |
| 5h | 5.54 | 72.47 | 34 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 409.97 | 449.51 | 0.0762 |
| 5i | 4.28 | 72.47 | 29 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 356.69 | 405.48 | 0.7968 |
| 6a | 3.29 | 88.00 | 25 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 7 | 306.86 | 338.36 | 0.0797 |
| 6b | 4.27 | 88.00 | 29 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 7 | 350.86 | 388.42 | 0.0980 |
| 6c | 3.01 | 88.00 | 24 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 7 | 297.58 | 344.39 | 0.0296 |
| 6d | 2.37 | 101.14 | 24 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 7 | 288.43 | 328.32 | 0.0286 |
| 6e | 4.32 | 88.00 | 28 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 7 | 341.57 | 394.45 | 0.0231 |
| 6f | 3.68 | 101.14 | 28 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 7 | 332.42 | 378.38 | 0.0287 |
| 6g | 4.63 | 88.00 | 31 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 8 | 378.27 | 414.46 | 0.2401 |
| 6h | 5.61 | 88.00 | 35 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 422.26 | 464.52 | 0.3068 |
| 6i | 4.35 | 88.00 | 30 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 8 | 368.98 | 420.49 | 0.0733 |
| 9a | 4.45 | 77.80 | 24 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 280.81 | 322.32 | 0.4173 |
| 9b | 5.43 | 77.80 | 28 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 324.80 | 372.38 | 0.0433 |
| 9c | 4.17 | 77.80 | 23 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 271.52 | 328.35 | 0.3747 |
| 9d | 3.53 | 90.94 | 23 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 262.38 | 312.28 | 0.3675 |
| 9e | 5.48 | 77.80 | 27 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 315.51 | 378.41 | 0.1693 |
| 9f | 4.83 | 90.94 | 27 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 306.37 | 362.34 | 0.1375 |
| 9g | 5.79 | 77.80 | 30 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 352.22 | 398.42 | 1.3975 |
| 9h | 6.77 | 77.80 | 34 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 396.21 | 448.48 | 0.2642 |
| 9i | 5.50 | 77.80 | 29 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 342.93 | 404.45 | 0.9812 |
| 11 | 3.78 | 121.17 | 29 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 338.03 | 416.41 | 0.1441 |
a Logarithm of partition coefficient between n-octanol and water (milog P); b topological polar surface area (TPSA) values expressed as Å2; c number of hydrogen bond acceptors (n-ON); d number of hydrogen bond donors (n-OHNH); e number of rotatable bonds (n-rotb); f molecular volume; g molecular weight; and h blood–brain barrier.
Another important parameter is the inhibition of Cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes. These are a group of enzymes that play a crucial role in the metabolism of drugs in the liver and other tissues. They are involved in the phase I metabolism of many drugs, which typically involves oxidation reactions, and can affect the pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and toxicity of a drug. Thus, the in silico prediction of metabolism is essential for assessing the risk of drug–drug interactions early, in the drug discovery process [48,49,50].
The prediction of CYP metabolism of the new hybrids using CypRules [51] is shown in Table 3. All compounds 5a–i and 6a–i do not inhibit the CYP2C19 enzyme, while all the furoxans 9a–i and 11 showed inhibition of this enzyme. In addition, compounds 9a–i and 11 showed inhibition of CYP2C9 enzyme while compounds 5a–i and 6a–i did not show any inhibition activity except the most lipophilic ones, 5g, 5h, 6g, and 6h. All compounds showed no inhibition activity for CYP2D6, while all of them are predicted to inhibit the CYP3A4 enzyme.

Table 3.
Prediction of the CYP metabolism of the new hybrids using the CypRules [51] platform.
Furthermore, toxicity is an important property to be considered in relation to discovery of new drugs. The potential toxicity of the tested compounds is predicted through the preADMET platform [46] in various tests. These tests are hERG inhibition, Carcinogenicity in Mouse, Carcinogenicity in Rat, Ames test and specifically in bacterial strains TA100_NA, TA100_10RLI, TA1535_NA and TA1535_10RLI.
hERG Inhibition
The hERG potassium channel (human Ether-à-go-go-Related Gene) plays a critical role in maintaining the proper electrical activity of the heart, specifically contributing to the repolarization phase of the cardiac action potential, the process by which the heart returns to its resting state following each contraction. Inhibition of this channel by a compound can result in QT interval prolongation on the electrocardiogram, potentially leading to life-threatening arrhythmia or even sudden cardiac death. For this reason, hERG inhibition is a key step in the assessment of the cardiotoxic potential of novel drug candidates’ prediction [50].
The hERG inhibitory potential of the newly synthesized compounds was predicted, and the results are summarized in Table 3. The table categorizes the compounds based on their predicted hERG inhibition risk correlated with the cause of cardiotoxicity [49].
Compounds 5g, 5h, 9a, 9b, 9e–9i, and 11 were predicted to be of low risk, suggesting minimal interaction with the hERG channel. In contrast, most of the 5-series compounds (except for 5g and 5h), as well as 9c, 9d, and selected compounds from the 6-series, were classified of moderate risk. Two compounds, 6b and 6i, are identified to induce severe cardiac arrhythmias.
Carcinogenicity in Mouse and Rat
Carcinogenicity refers to the potential of a chemical compound to induce neoplastic transformations in biological systems. Traditionally, the assessment of carcinogenicity involves long-term in vivo studies, typically lasting two years, in which mice or rats are chronically exposed to the test compound. The preADMET platform [46] enables in silico prediction of carcinogenic potential, based on models trained using data from the U.S. National Toxicology Program (NTP) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), derived from standardized long-term rodent bioassays [46].
The in silico predictions, summarized in Table 3, indicate that the majority of the tested compounds were predicted to be carcinogenic in mice, suggesting a high probability of tumorigenicity in these species. The only exception was compound 6a, which exhibited a negative carcinogenicity prediction.
Conversely, the predictions for rat models showed lower sensitivity. While ketone derivatives 5a–i and oxime derivatives 6a–i were consistently predicted to be carcinogenic, several furoxan-based compounds 9a–i demonstrated favorable results, suggesting a lower potential for carcinogenic liability.
These results highlight species-specific differences in predicted carcinogenic responses, with rats displaying lower sensitivity, particularly toward furoxan scaffold. These findings emphasize the necessity of performing cross-species evaluations when assessing the long-term toxicological risk of novel chemical entities, to ensure a more comprehensive and accurate risk assessment.
Ames Test
The Ames test is a biological assay used to assess the mutagenic potential of chemical compounds. The test uses specific strains of the bacterium Salmonella typhimurium that carry a mutation rendering them unable to synthesize the amino acid histidine. These bacteria are exposed to the test compound, and the ability of the compound to cause mutations—which reverts the mutation in the bacteria (allowing them to grow without histidine)—is predicted. A negative result in the Ames test is desirable, as it suggests that the substance does not cause mutations and is likely safe. A positive result indicates the substance is mutagenic, meaning it may cause genetic mutations and could potentially be harmful [52,53].
In this study, the mutagenic potential of the novel synthetic compounds 5a–i, 6a–i, and 11 was evaluated in silico. The preADMET platform predicts Ames test outcomes based on robust predictive models. As shown in Table 3, 26 out of the 27 compounds were predicted to be mutagenic, with only compound 5g yielding a non-mutagenic prediction.
The predominance of mutagenic predictions indicates a considerable genotoxic concern that warrants cautious interpretation, particularly in the context of drug development and experimental safety. Compound 5g appears to be the only candidate with a potentially safer mutagenic profile, although additional experimental validation is essential for a comprehensive risk assessment.
The in silico Ames test results from the preADMET platform [46] indicate a high mutagenic potential for most of the evaluated compounds, particularly after metabolic activation with liver enzymes. Ketone compounds 5a–i and oximes derivatives 6a–i were generally negative in the absence of metabolic activation (TA100_NA and TA1535_NA), suggesting low direct mutagenicity. However, they became mostly positive when metabolic activation was introduced (TA100_10RLI and TA1535_10RLI), indicating possible pro-mutagenic behavior. Furoxan derivatives 9a–i and 11 showed mixed results without activation but were positive after metabolism. Results are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Toxicity assessment of compounds 5a–i, 6a–i, 9a–i, and 11 using preADMET platform [46].
Among all tested compounds, only compound 5g remained consistently negative across all models, making it a potential candidate for further investigation. Nonetheless, additional in vitro and in vivo studies are essential to confirm these findings and to fully assess the safety profile of these compounds.
Furthermore, in drug design, descriptors such as TPSA are widely used to estimate ADME properties, since polar surface area strongly influences intestinal absorption and oral bioavailability. Therefore, the percentage of absorption (%ABS) was calculated with the equation below [54]:
%ABS = 109 − 0.345 TPSA
TPSA was calculated via Molinspiration platform [47] (Table 1). Results of the %ABS of the new molecules 5a–i, 6a–i, 9a–i, and 11 are shown in Table 5. The bioavailability of bioactive molecules is closely linked to their topological polar surface area (TPSA), a descriptor that correlates strongly with hydrogen bonding capacity [55]. The TPSA values of the hybrids ranged from 67.20 to 84 Å2, which are all below the commonly accepted threshold of 160 Å2, underlying a good oral bioavailability.

Table 5.
%ABS values of the new molecules 5a–i, 6a–i, 9a–i, and 11..
With the exception of hybrid 11, all the other hybrids presented a very high absorption, as indicated by their %ABS values derived from TPSA. Specifically, hybrids 5a–5i and 9a–9i exhibited %ABS values in the range of 77.6–84.0%, while hybrids 6a–6i ranged around 78.6%, all suggesting excellent intestinal absorption. Hybrid 11, with a TPSA of 121.17 Å2 and a %ABS of 66.2%, was the only compound with notably lower absorption supporting the suitability for oral administration.
Importantly, only the hybrids within the TPSA range of 72.47–90.94 Å2 are expected to be capable of crossing the blood–brain barrier.
2.3. Biological Evaluation
In the present study, the synthesized hybrids 5a–i, 6a–i, 9a–i, and 11 were evaluated for their in vitro activity as inhibitors of lipid peroxidation and soybean lipoxygenase. The hybrid oximes 6a–i and furoxans 9a–i and 11 that contain a NO donor moiety, were also evaluated for their ability to release NO, to inhibit COX-2 and albumin denaturation. Selected hydrids were tested for COX-1 inhibition. Finally, the selected hybrids 6c, 6i, 9e, 9g, and 9i were tested for their cytotoxic activity with MTT viability assay in various cancer cell lines.
2.3.1. In Vitro Lipid Peroxidation
Cell metabolism is a continuous source of reactive oxygen species (ROS), some of which are highly toxic. The body relies on enzymatic and non-enzymatic mechanisms to detoxify these compounds rapidly. However, their extreme reactivity and ability to initiate chain reactions can lead to pathological conditions. Studies have reported a marked increase in lipid peroxidation in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients, linking oxidative stress to the disease’s progression. Similarly, elevated levels of ROS and lipid peroxidation products have been observed in Parkinson’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, and Huntington’s disease, suggesting a common role of oxidative damage in neurodegeneration. In addition, oxidative stress is implicated in cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer, and chronic inflammatory conditions. Consequently, antioxidants that prevent lipid peroxidation in the brain and other tissues could hold significant therapeutic potential [56,57,58].
In the present study, the aim was to evaluate the anti-lipid peroxidation activities of the synthesized compounds 5a–i, 6a–i, 9a–i, and 11 and compare their efficacy to that of Trolox, a well-known antioxidant. Using the water-soluble compound 2,2′-azobis(2-amidinopropane) hydrochloride (AAPH), peroxyl radicals are generated through spontaneous thermal decomposition in vitro. This experimental setup imitated the lipid peroxidation processes occurring in cells due to radical activity allowing the investigation of the effectiveness of the tested compounds under conditions resembling cellular oxidative stress [56].
In general, within the compounds, the most potent anti-lipid peroxidation activity was shown by the derivatives 5g, 6b, 6g, 6h, 9a, 9f, 9g, 9h, and 11 with 89–97.7% inhibition activity that was comparable to the reference compound Trolox (93%) at 100 μM concentration. All the above compounds as well as compounds 9b and 9d have a better or similar activity to cinnamic acid (78%). All the compounds, except 5g, contain either an oxime or a furoxan group, indicating the presence of a moiety that can potentially act as a ROS scavenger. Furthermore, 5g, 6g, and 9g exhibited significant lipid peroxidation activity, highlighting the importance of this cinnamic derivative. Also, it seemed that higher lipophilicity leads to higher anti-lipid peroxidation activity, as the above compounds have lipophilicity values between 4.27 and 6.77. The anti-lipid peroxidation activity of all compounds 5a–i, 6a–i, 9a–i, and 11 is presented in Table 6.

Table 6.
Representation of the biological results of the new compounds 5a–i, 6a–i, 9a–i, and 11.
Perusal of the results among the hybrids of each group shows that for group 5 with R1 = H, the anti-lipid peroxidation activity seems to be almost equal for 5a ≥ 5c, whereas in 5b the naphthyl condensed derivative does not present any result under the experimental condition. It seems that among the heterocyclic compounds thienyl 5c presents antioxidant behavior whereas the furyl 5d not any. This is changed in 5f, the condensed benzofuryl in relation to 5d. We observed also that replacement of the phenyl ring by a naphthyl led to an inactive compound 5b as well as the presence of a benzothienyl ring in place of thienyl. The results are differentiated with the presence of R2 = phenyl as follows, 5h > 5b, 5i > 5c, 5g > 5a. It seems that for this group the presence of a R2 = phenyl substituent leads to enhancement.
For the group 6, the naphthyl-substituted derivative (compound 6b), is the most potent (6b > 6d > 6a) followed by the furyl and thienyl derivative. Subsequently, 6c as well as 6e and 6f—the two heteroaromatic condensed derivatives—are inactive. Among the R2 = phenyl substituted derivatives, only 6g and 6h are highly active.
The transformation of ketones 5 to oximes 6 is accompanied by an increase in some cases, e.g., 5a/6a, 5b/6b, 5d/6d, and 5h/6h.
The hybrids of group 9 present higher anti-lipid peroxidation activity (67–97%) with the exception of compound 9i. The presence of the phenyl furoxanyl group as well as of the phenylsulfonyl furoxanyl ring in 11 seems to play a crucial role.
2.3.2. In Vitro LOX Inhibition
Inhibition of lipoxygenases (LOXs) plays a crucial role in managing inflammation, as LOXs are enzymes involved in the metabolism of arachidonic acid, leading to the production of bioactive lipid mediators called leukotrienes. By inhibiting LOXs, it is possible to reduce the production of leukotrienes and other inflammatory mediators, thus reducing inflammation. This has therapeutic implications for various inflammatory conditions, such as asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel diseases [3,59].
In vitro anti-LOX activities were evaluated using soybean lipoxygenase isoenzyme-1 (SLOX-1), a commonly used model for mammalian LOXs [60]. SLOX-1 shows its activity at pH 9.0 and primarily catalyzes the formation of the 13-hydroperoxide derivative from the substrate (linoleic acid). The production of this derivative was monitored by its absorbance at 234 nm [61].
Compared to the reference compound NDGA, all tested compounds displayed lower potency (Table 6). The best inhibition activity was shown by compound 9a the furoxanyl representative with IC50 = 3.5 μΜ. Comparison of the two IC50 values of cinnamic acid (56 μM) and compound 9a, showed that the addition of the furoxanyl moiety plays a key role in the enhancement of the LOX inhibition. High potency is also shown by thiophene-oxime analogue 6c and by the double-bond-substituted furoxan compound 9h with IC50 = 10 μΜ. Compound 9h is the most lipophilic of all the tested compounds with milogP 6.77. Furthermore, the compounds 5h, 6a, 6g, and 9g showed better inhibition of LOX than cinnamic acid. These molecules, except 6a, contain a phenyl-substituted double bond in their structures and are highly lipophilic.
The study revealed distinct differences in lipoxygenase inhibition among the tested compounds. In group 5, only three compounds 5b, 5f, and 5h showed activity, with the lipophilic derivative 5h being the most potent (IC50 = 33 μM). Among them, two derivatives have the R1 = naphthyl group and one has a benzofuryl group. Both substituents offer to the overall lipophilicity and to the volume of the molecules. The presence of R2 = phenyl leads to higher inhibition (5b/5h). Within group 6, seven active compounds are yielded, suggesting that the oxime moiety may enhance enzyme interaction due to the oximes behavior to act as ligands with metals. Compound 6c, which contains a thiophene group on its structure, shows significant activity (IC50 = 10 μM). Among the furoxan derivatives, the simplest of all, 9a, demonstrated the best overall inhibition (IC50 = 3.5 μM), followed by 9h with IC50 = 10 μΜ, and R1 = naphthyl and R2 = phenyl groups. Significant results were given by 9b, 9c, and 9i with R1 substituents naphthyl and thienyl groups on the furoxan ring as well as compound 11 in which the sulfonyl furoxanyl substitution led to complete loss of activity. A phenyl group in R2 resulted to the potent inhibitor 9h compared to 9b R2 = H. The presence of the benzothienyl group led to an inhibitory activity 9e compared to 9c. No significant change was noticed when the furyl group was replaced by a benzofuryl group. Lipophilicity does not influence this biological activity.
2.3.3. In Vitro COX-2 and COX-1 Inhibition
Cyclooxygenase (COX) isoforms catalyze two key reactions. First, they convert arachidonic acid into prostaglandin G2 (PGG2). Then, through their peroxidase activity, PGG2 is reduced to prostaglandin H2 (PGH2). COX-1 isoform is constitutively expressed in most tissues, and it is involved in maintaining normal physiological functions like protecting the gastric lining, regulating renal blood flow, and platelet aggregation. COX-2 isoform is an inducible enzyme expressed during inflammation, pain, and fever; primarily involved in the production of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins [4,62].
Non-selective NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, aspirin) inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2, which can lead to side effects such as gastrointestinal irritation or ulcers due to COX-1 inhibition. Selective COX-2 inhibitors (e.g., celecoxib) target COX-2, reducing inflammation and pain with fewer gastrointestinal side effects [4,62].
Enzyme inactivation can occur due to the accumulation of hydroperoxides formed from arachidonic acid or other fatty acid substrates. In order to prevent this in the in vitro experiment used for testing COX inhibition activity of the new molecules, a co-substrate like N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine (TMPD) is included, as it undergoes co-oxidation by PGG2. The oxidized TMPD has a maximum absorbance at 590 nm. COX enzymes also depend on heme (Fe3+-protoporphyrin IX) as a cofactor, which can dissociate during purification. To ensure maximum enzyme activity, heme is added to the reaction mixture during the in vitro assay for ovine COX-2 inhibition and COX-1 inhibition [63].
None of the tested compounds 6a–i, 9a–i, and 11 have shown better activity than indomethacin, used as standard in COX-2 inhibition assay (Table 6). The best inhibitor is the compound 9e with IC50 = 8.25 μM with milogP value 5.48. Compound 6c has the second better IC50 value at 35 μM. Both compounds contain a sulfur atom at their structure in the cinnamic acid ring. Only compounds 6a, 6i, and 9i have shown inhibition in terms of IC50 values (IC50 = 100, 80, 70 μM, respectively) as COX-2 inhibitors (Figure 2).
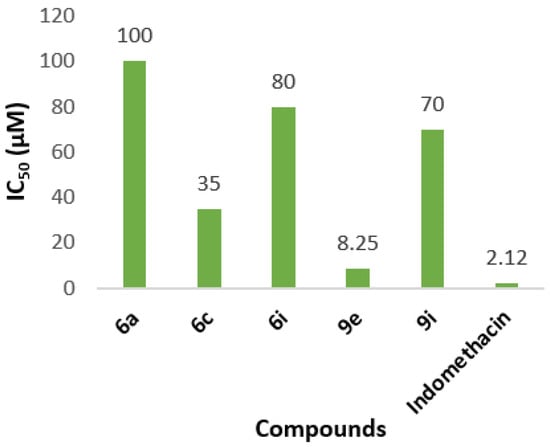
Figure 2.
IC50 values of the selected tested compounds with COX-2 inhibition activity.
Furthermore, to better clarify if the above compounds 6c, 6i, 9e, and 9i are selective COX-2 inhibitors, we tested them as COX-1 inhibitors (Table 6). Compounds 6c and 9e did not show any inhibition activity of COX-1 isoform and they are selective COX-2 inhibitors. The best COX-1 % inhibition activity has been presented by the compound 9i, while compound 6i showed lower inhibition activity, underlying the importance of the furoxan moiety for COX-1 inhibition activity. None of the compounds showed better activity compared to the reference standard SC-560 (100%) at 100 μΜ (Figure 3). Lipophilicity does not show any role.
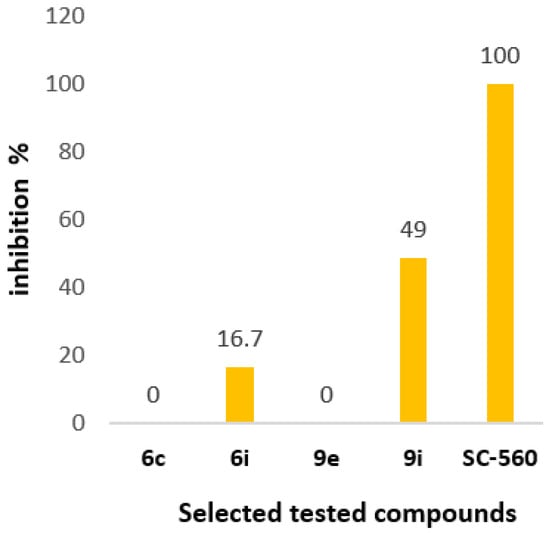
Figure 3.
% inhibition of the selected tested compounds as COX-1 inhibitors at 100 μM.
2.3.4. NO Release Ability
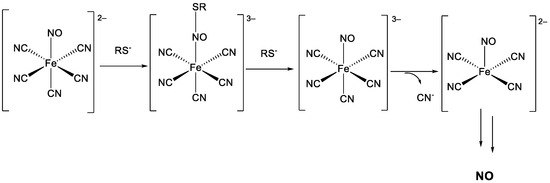
This assay evaluates the ability of nitrate esters to release nitric oxide (NO). First, sodium nitroprusside (SNP) reacts with the thiol compound, cysteine, which serves as a reducing agent (Scheme 5). The thiol donates electrons, facilitating the breakdown of the nitroprusside complex. Afterwards, the reaction leads to the formation of intermediate complexes, such as nitrosothiol species and the decomposition of these intermediates results in the release of nitric oxide (NO). According to the literature [64], measurements are conducted both in the presence and absence of the thiol agent, cysteine. No significant difference was observed between the two experimental conditions, and the results were reproducible. Sodium nitroprusside (SNP) was used as the reference compound [65].
Scheme 5.
Mechanism of NO release from SNP with thiol compound.
According to the experimental results (Table 6), the compounds 6a–i, which contain oxime moiety as an NO-donating group, did not exhibit significant nitric oxide (NO) releasing ability overall. Specifically, compounds 6b, 6c, 6d, 6e, and 6f displayed a slight ability to release NO, with low percentages ranging from 0.2% to 4%, while the remaining compounds 6a, 6g, 6h, and 6i showed no activity. These compounds were compared to the reference compound SNP, which demonstrates an NO release of 53% at 100 μΜ. Regarding compounds 9a–i and compound 11, which feature a furoxan moiety as an NO donor, the results showed that compounds 9a and 11 exhibited good NO-releasing ability, with percentages of 20% and 11%, respectively. Both compounds have a cinnamic acid moiety in their structure. Additionally, it appears that the substitution pattern on the furoxan ring influences its NO-donating ability, with the benzofuroxan structure proving to be the most effective. These compounds showed the highest activity among all the new compounds 6a–i, 9a–i, and 11, although their NO release was still lower than that of the reference SNP (53%) (Figure 4). However, the furoxan group proved to be more promising and effective than the oxime group, as indicated by the results.
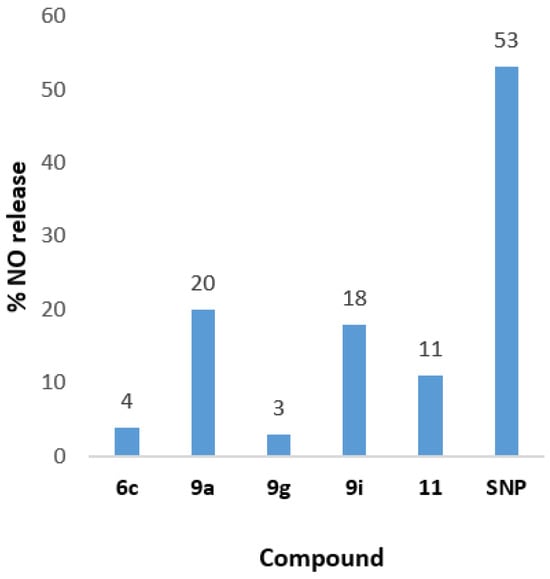
Figure 4.
In vitro NO-releasing ability of the compounds with the best activity.
2.3.5. In Vitro Inhibition of Albumin Denaturation
The ability of a compound to inhibit the thermal denaturation of albumin is considered an indicator of anti-inflammatory activity [66]. Heat exposure simulates conditions of cellular stress or inflammation, during which protein and tissue damage occur. Certain substances can protect proteins from denaturation upon heating by stabilizing their structure and preventing aggregation and precipitation.
The experimental results showed that almost all compounds 6a–i and 9a–i, as well as compound 11, did not exhibit inhibitory activity. The only exception was shown by compounds 6d and 6e, which demonstrated inhibition rates of 10% and 63.6%, respectively. These were the only compounds that showed activity in this assay. Notably, the thiol-containing compound 6e exhibited stronger inhibitory capacity than the reference compound acetylsalicylic acid (31%). The results of the assay are shown in Table 6.
2.3.6. MTT Assays on Cancer Cell Lines
The cytotoxic activity of five compounds was initially evaluated in HeLa (cervical cancer) and MCF-7 (breast cancer) cell lines using the MTT viability assay. As shown in Table 7, 6i exhibited the highest potency among all compounds tested, with EC50 values of 36.69 μM (HeLa) and 38.34 μM (MCF-7), following treatment for 48 h [67].

Table 7.
Half maximal effective concentration (EC50 values) of 6c, 6i, 9e, 9g, and 9i in HeLa and MCF-7 cancer cell lines.
Following these data, compound 6i was further tested in four additional cell lines: U251 and U87, which are derived from glioblastoma; MDA-MB-435, which originates from melanoma; and MDA-MB-231, which is derived from triple-negative breast cancer.
As shown in Table 8, this compound demonstrated the strongest cytotoxic effect in HeLa cell line (EC50 = 36.69 μM), while the lowest activity was observed in MDA-MB-435 (EC50 = 52.89 μM). In the remaining cell lines (U251, U87, and MDA-MB-231), EC50 values ranged from 40.94 to 45.44 μM, indicating moderate sensitivity.

Table 8.
Half maximal effective concentration (EC50 values) of compound 6i in HeLa, MCF-7, U251, U87, MDA-MB-435, and MDA-MB-231 cancer cell lines.
2.4. Computational Studies—Docking Simulation
2.4.1. Docking Studies on Soybean Lipoxygenase
The interactions at the molecular level between the ligands and soybean lipoxygenase were explored through molecular docking. Soybean lipoxygenase-1 crystal structure (PDB ID: 3PZW) was selected to rationalize the obtained biological results. The crystal structure of soybean lipoxygenase-1 (PDB ID: 3PZW) is lacking a co-crystallized ligand, requiring the identification of possible allosteric binding sites beyond the known iron-binding and substrate-binding regions, as reported in recent studies. Detsi, A. et al. [68] have identified three potential binding sites using SiteMap’s [69]. Researchers have found that Site 1 is located between the amino-terminal β-barrel (PLAT domain) and the α-helical domain, which houses the catalytic iron [70,71,72]. Sites 2 and 3 are also positioned within the α-helical domain. Additionally, Site 1 is recognized as a potential binding site in blind docking studies [70,71,72].
Based on the above research studies, blind docking was performed in addition to that of the active center encompassing all potential binding sites. The selected for synthesis candidates have been concluded that bind to Site 1 as previously reported [70,71,72]. Compound 9a being the most active in vitro within the series with an IC50 of 3.5 μΜ, develops hydrophobic interactions with the amino acids Val126, Phe143, Phe144, Val520, and π-cation interaction with Lys526 (Figure 5).
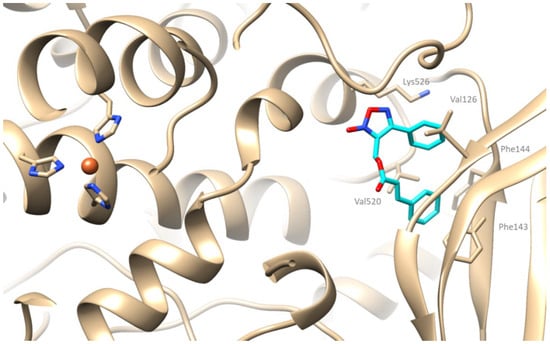
Figure 5.
Putative binding mode of compound 9a (depicted in cyan) bound to SLOX-1. Iron appears as an orange sphere.
2.4.2. Docking Studies on COX-2
Compound 9e, being the most potent in vitro among the series, presented a binding score of −9 kcal/mol. It seems to enter in the active cavity interacting hydrophobically with residues Thr62, Leu321, Ala485, Phe487, and Val492. Additionally, it develops two hydrogen bonds with His58 and Tyr324 and a salt bridge with His58 (Figure 6).
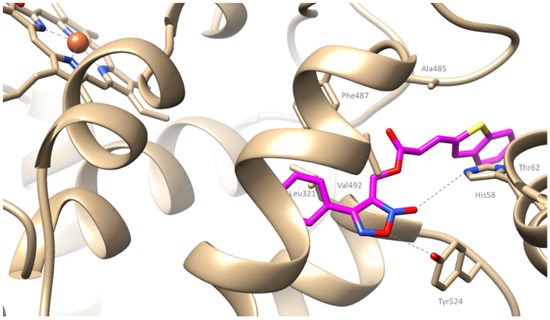
Figure 6.
Putative binding mode of compound 9e (depicted in magenta) bound to COX-2.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
Reagents were purchased from Acros® (Osaka, Japan), Alfa-Aesar® (Karlsruhe, Germany), Fluka® (Buchs, Switzerland), Fluorochem® (Hadfield, UK), Merck® (Darmstadt, Germany), Sigma-Aldrich® (Saint Louis, MO, USA), and TCI® (Tokyo, Japan). Solvents used were of analytical grade (Merck, Sigma-Aldrich, SDS (Hong Kong, China)). When required, drying of solvents was performed according to the standard literature procedures. Solvents used in column chromatography were distilled prior to use. Reactions involving moisture-sensitive reagents were carried out in oven-dried glassware under inert conditions. Anhydrous solvents and reagents were transferred using syringes. Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) was performed using pre-coated silica gel 60 F254 plates (code 5, Merck) to monitor reaction progress and product purification. Visualization of TLC plates was performed under UV light at 254 nm. Flash column chromatography was employed for the isolation or purification of products. Columns were packed with amorphous silica gel (SiO2, 70–230 mesh, Merck), and mobile phases were prepared as described in the corresponding procedures. Analytical samples were dried using appropriate low-pressure apparatus. Column chromatography was carried out using Silica gel 60 (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany).
Melting points were determined in capillary tubes using a MEL-Temp II apparatus (Lab. Devices, Holliston, MA, USA) and are uncorrected. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectra were recorded on an Agilent (Santa Clara, CA, USA) 500/54 DD2 spectrometer (500 MHz for 1H and 125 MHz for 13C) at the Department of Chemistry, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki. Samples were dissolved in deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO-d6) or deuterated chloroform (CDCl3). Chemical shifts (δ) are reported in parts per million (ppm) relative to the residual solvent peak as an internal standard. The following abbreviations are used for proton multiplicities: s (singlet), d (doublet), t (triplet), q (quartet), m (multiplet), br (broad), and combinations thereof. Coupling constants (J) are given in Hertz (Hz). High-resolution mass spectra (HRMS, ESI-MS) were obtained using a ThermoFisher Scientific LTQ Orbitrap Discovery MS (168 Third Avenue, Waltham, MA, USA). Theoretical fragments were calculated using the online tool available at https://www.sisweb.com/mstools/isotope.htm, 28 August 2025. Additional mass spectra were recorded using an LC-MS 2010 EV spectrometer (Shimadzu, Tokyo, Japan). Fragmentation patterns were predicted using PerkinElmer ChemDraw Professional 17.1 (PerkinElmer Informatics Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). All microwave irradiation experiments were carried out in CEM-Discover monomode microwave device. UV-Vis spectra were recorded on a Shimadzu PharmaSpec UV-1700 spectrophotometer (Kyoto, Japan) using 1 cm pathlength cuvette.
Biological assays were conducted using reagents including soybean lipoxygenase, sodium linoleate, 2,2′-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride (AAPH), human cyclooxygenase-2, albumin, Trolox, nordihydroguaiaretic acid (NDGA), N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine (TMPD), heme, cyclooxygenase-1, phosphate buffer (pH 7.4), L-cysteine, Griess reagent, and sodium nitroprusside (SNP), all purchased from Merck and Sigma-Aldrich. Cancer Cell Lines HeLa, MCF-7, U251, U87, MDA-MB-435, and MDA-MB-231 used in the biological experiments were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM).
The following software tools were used and are discussed in detail in the corresponding sections:
- AutoDockVina v.1.1.1 (The Scripps Research Institute), via the PyRx program [73]
- UCSF Chimera v.1.5.3 (University of California) [74]
- GROMACS toolkit v.4.6.5 [75]
- Modeller [76]
- OpenBabel v.2.2.3 [77]
- AmberTools [78]
- Molinspiration (https://www.molinspiration.com, accessed on 10 May 2025) [47]
- preADMET (https://preadmet.webservice.bmdrc.org/, accessed on 10 April 2025) [46]
3.2. Computational Studies
3.2.1. Molecular Docking Studies on Soybean Lipoxygenase
The protein structure (PDB ID: 3PZW) was visualized and pre-processed using UCSF Chimera (version 1.17) [79]. Water molecules and non-essential crystallographic components were removed via Chimera. Missing residues (Met1–Phe2–Ser3–Ala4–Gly5; Glu21–Val22–Asn23–Pro24–Asp25–Gly26–Ser27–Ala28–Val28–Asp29; Ile117–Ser118–Asn119–Gln120) were added using Modeller (v. 10.3) [80]. Hydrogen atoms and partial charges were incorporated using AmberTools 23 [81,82]. The iron center was assigned a +2.0 charge based on the 12–6 Lennard-Jones (LJ) non-bonded model [83]. Histidine residues (His499, His504, His690), which coordinate the iron, were modeled as neutral with δ-nitrogen protonation. The TIP3P water model was used for solvation, with the simulation box maintaining at least 12 Å between the solute and the box boundary. Ligand 3D structures were generated and minimized using OpenBabel (v. 3.1.1) [77] with the MMFF94 force field [84]. Ligand topologies and parameters were generated with ACPYPE [85], employing AnteChamber (AmberTools v. 22.10) [86]. Protein energy minimization was executed using GROMACS (v. 4.6.5) [87]. Ligand docking was carried out with AutoDock Vina (v. 1.2.3) [88], using a grid box centered at x = 1.35 Å, y = 14.3 Å, z = −34.60 Å, and with dimensions x = 100 Å, y = 70 Å, and z = 70 Å. The exhaustiveness was set to 10, with up to 20 docking modes generated. Docking outcomes were examined using UCSF Chimera.
3.2.2. Molecular Docking Studies on COX-2
Due to lack of ovine cyclooxygenase in the PDB, the human cyclooxygenase-2 (PDB code: 1CX2) was selected, due the high homology with the ovine COX-2 which was used in the in vitro experiments. The primary sequences of the two proteins were aligned using UniProt (www.uniprot.org) and the results showed 86.4% homology. The same procedure described above was used to conduct the molecular docking studies on the COX-2. The dimensions of the grid box used were 25 Å in all three axes. The analysis of the results was performed using UCSF Chimera. The docking calculations were carried out with an exhaustiveness value of 16 and maximum output of 20 docking poses.
3.3. Physicochemical Studies
3.3.1. In Silico Determination of miLogP
Lipophilicity was theoretically calculated as miLogP values by the Molinspiration software (https://www.molinspiration.com/ [47] (accessed on 10 May 2025).
3.3.2. In Silico Determination of ADMET Properties and Drug-likeness
All compounds were subjected to in silico evaluation analysis of their drug-likeness and ADMET properties.
3.4. Chemistry
3.4.1. Synthesis of N-(4-Acetylphenyl)-2-chloroacetamide (4) [34]
To a stirred solution of 4-aminoacetophenone (7) (0.79 mmol) in dichloromethane (1.2 mL), K2CO3 (2.22 mmol) was added under argon atmosphere. The reaction mixture was cooled down to 0 °C and chloroacetyl chloride (1.25 mmol) was added dropwise. The reaction mixture was allowed to stir at room temperature for 3 h. After completion of the reaction, the solvent was evaporated and the residue that obtained was washed with water and filtered to isolate compound 8. Yield: 72.2%; white solid; M.p. 152–153 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.37 (s, 1H), 8.01–7.96 (m, 2H), 7.70–7.66 (m, 2H), 4.22 (s, 2H), 2.59 (s, 3H) ppm.
3.4.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Hybrid Compounds 5a–i
To a stirred solution of the appropriate acid (1 eq) and compound 4 (1 eq) in DMF, triethylamine (2.3 eq) and potassium iodide (2.3 eq) were added. The reaction mixture was heated at 50 °C for 5 min under microwave at 50 W. After completion of the reaction, hydroxy ammonium solution 12% was added until pH = 12 and the residue that was filtered and washed with water to furnish compounds 5a–i.
2-((4-Acetylphenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl Cinnamate (5a)
Compound 5a was synthesized according to the general procedure from cinnamic acid 2a (37 mg, 0.25 mmol) and 4 (53 mg, 0.25 mmol) in dry DMF (0.3 mL). Yield: 16%; white solid; Rf: 0.48 (PE/EtOAc 6:4); M.p.: 157–159 °C; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M + Na]+ calculated for C19H17NO4: 346.34, found: 345.85, [M−H]− calculated for C19H17NO4: 322.34, found: 321.90; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.57 (s, 1H, NH), 6.98 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 6.83–6.71 (m, 5H), 6.48 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 3H), 5.79 (d, J = 16.1 Hz, 1H), 3.87 (s, 2H), 1.56 (s, 3H) ppm [36].
2-((4-Acetylphenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-3-(naphthalen-1-yl)acrylate (5b)
Compound 5b was synthesized according to the general procedure from cinnamic acid derivative 2b (50 mg, 0.25 mmol) and 4 (53 mg, 0.25 mmol) in dry DMF (0.3 mL). Yield: 32%; white solid; Rf: 0.28 (PE/EtOAc 6:4); M.p.: 162–164 °C; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [2M]+ calculated for C23H19NO4: 746.82, found: 746.80, [M−H]− calculated for C19H17NO4: 372.40, found: 371.90.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.56 (s, 1H), 8.55 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, 1H), 8.24 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.06 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 8.01 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.96 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.75 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.66 (ddd, J = 8.4, 6.8, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.60 (td, J = 7.7, 3.9 Hz, 2H), 6.84 (d, J = 15.8 Hz, 1H), 4.90 (s, 2H), 2.53 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 196.53, 166.12, 165.65, 142.80, 141.63, 133.32, 132.00, 130.90, 130.79, 130.56, 129.56, 128.80, 127.31, 126.39, 125.75, 125.58, 122.91, 119.88, 118.56, 62.86, 26.45 ppm.
2-((4-Acetylphenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-3-(thiophen-2-yl)acrylate (5c)
Compound 5c was synthesized according to the general procedure from cinnamic acid derivative 2c (53 mg, 0.25 mmol) and 4 (53 mg, 0.25 mmol) in dry DMF (0.3 mL). Yield: 37%; white solid; Rf: 0.28 (PE/EtOAc 6:4); M.p.: 155–158 °C; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [2M]+ calculated for C10H10NO3: 384.14, found: 383.90, [M−H]− calculated for C17H15NO4S: 328.36, found: 327.95.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.48 (s, 1H), 7.95 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.90 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, 1H), 7.77 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 7.73 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.61 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 6.40 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, 1H), 4.82 (s, 2H), 2.53 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 196.52, 166.10, 165.54, 142.75, 138.60, 138.17, 132.53, 131.99, 130.39, 129.54, 128.66, 118.57, 115.37, 62.70, 26.44 ppm.
2-((4-Acetylphenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-3-(furan-2-yl)acrylate (5d)
Compound 5d was synthesized according to the general procedure from cinnamic acid derivative 2d (111 mg, 0.80 mmol) and 4 (130 mg, 0.66 mmol) in dry DMF (3.7 mL). Yield: 34%; off-white solid; Rf: 0.20 (PE/EtOAc 7:3); M.p.: 156–159 °C; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C17H15NO5: 336.30, found: 335.80, [M−H]− calculated for C17H15NO5: 313.31, found: 311.90.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.49 (s, 1H), 7.94–7.88 (m, 3H), 7.71 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 2H), 7.55 (d, J = 15.5 Hz, 1H), 7.02 (s, 1H), 6.66 (s, 1H), 6.34 (d, J = 16.3 Hz, 1H), 4.80 (s, 2H), 2.51 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 196.98, 166.55, 166.08, 150.58, 146.79, 143.22, 132.53, 132.42, 130.00, 119.01, 117.11, 114.31, 113.37, 63.16, 26.90 ppm.
2-((4-Acetylphenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-3-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)acrylate (5e)
Compound 5e was synthesized according to the general procedure from cinnamic acid derivative 2e (90 mg, 0.44 mmol) and 4 (72 mg, 0.34 mmol) in dry DMF (2 mL). Yield: 24%; yellowish solid; Rf: 0.57 (PE/EtOAc 5:5); M.p.: 210–213 °C; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C21H17NO4S: 402.42, found: 401.85, [M−H]− calculated for C21H17NO4S: 378.42, found: 377.90.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.56 (s, 1H), 8.07–7.89 (m, 6H), 7.74 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.44 (t, J = 9.4 Hz, 2H), 6.45 (d, J = 15.8 Hz, 1H), 4.86 (s, 2H), 2.53 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 196.99, 166.48, 165.68, 143.22, 140.14, 139.75, 139.19, 139.16, 132.44, 130.77, 130.01, 127.14, 125.64, 125.27, 123.24, 119.03, 118.57, 63.31, 26.91 ppm.
2-((4-Acetylphenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-3-(benzofuran-2-yl)acrylate (5f)
Compound 5f was synthesized according to the general procedure from cinnamic acid derivative 2f (150 mg, 0.80 mmol) and 4 (130 mg, 0.61 mmol) in dry DMF (3.7 mL). Yield: 30%; white solid; Rf: 0.63 (PE/EtOAc 5:5); M.p.: 219–222 °C; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C21H17NO5: 386.36, found: 385.90, [M−H]− calculated for C21H17NO5: 362.36, found: 361.90.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.56 (s, 1H), 7.95 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.75 (t, J = 10.3 Hz, 4H), 7.64 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.49–7.41 (m, 2H), 7.31 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 6.61 (d, J = 15.8 Hz, 1H), 4.86 (s, 2H), 2.53 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 196.99, 166.44, 165.73, 155.47, 152.25, 143.22, 132.86, 132.44, 130.00, 128.45, 127.44, 124.12, 122.77, 119.04, 117.69, 113.22, 111.88, 63.34, 26.92 ppm.
2-((4-Acetylphenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-2,3-diphenylacrylate (5g)
Compound 5g was synthesized according to the general procedure from cinnamic acid derivative 2g (40 mg, 0.18 mmol) and 4 (29 mg, 0.14 mmol) in dry DMF (0.25 mL). Yield: 48%; white solid; Rf: 0.38 (PE/EtOAc 6:4); M.p.: 105–108 °C (decomposition); LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C25H21NO4: 422.44, found: = 421.90, [M−H]− calculated for C25H21NO4: 398.44, found: = 397.95.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.52 (s, 1H), 7.95 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.89 (s, 1H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.40 (dq, J = 12.8, 7.2 Hz, 3H), 7.25 (dq, J = 20.5, 7.2 Hz, 5H), 7.09 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 4.85 (s, 2H), 2.53 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 196.50, 166.52, 165.95, 142.77, 140.51, 135.39, 134.05, 131.94, 131.78, 130.35, 129.57 (d, J = 3.0 Hz), 129.46, 128.69, 128.38, 128.00, 118.42, 63.24, 26.43 ppm.
2-((4-Acetylphenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-3-(naphthalen-1-yl)-2-phenylacrylate (5h)
Compound 5h was synthesized according to the general procedure from cinnamic acid derivative 2h (100 mg, 0.36 mmol) and 4 (60 mg, 0.28 mmol) in dry DMF (0.5 mL). Yield: 52%; yellowish solid; Rf: 0.35 (PE/EtOAc 6:4); M.p.: 120–122 °C (decomposition); LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C29H23NO4: 472.15, found: = 471.90, [M−H]− calculated for C29H23NO4: 449.50, found: 447.95.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.59 (s, 1H), 8.47 (s, 1H), 8.08 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.99–7.93 (m, 3H), 7.84 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.75 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.67–7.55 (m, 2H), 7.30–7.19 (m, 4H), 7.16 (dd, J = 6.6, 3.1 Hz, 2H), 7.01 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.94 (s, 2H), 2.54 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 196.51, 166.44, 166.01, 142.79, 138.71, 134.86, 134.46, 132.97, 131.97, 131.73, 131.19, 129.93, 129.58, 128.95, 128.64, 128.06, 127.68, 127.58, 126.93, 126.34, 125.13, 123.85, 118.47, 63.38, 26.44 ppm.
2-((4-Acetylphenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-2-phenyl-3-(thiophen-2-yl)acrylate (5i)
Compound 5i was synthesized according to the general procedure from cinnamic acid derivative 2i (100 mg, 0.44 mmol) and 4 (72 mg, 0.34 mmol) in dry DMF (1 mL). Yield: 54%; brown solid; Rf: 0.35 (PE/EtOAc 6:4); M.p.: 137–140 °C (decomposition); LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C23H19NO4S: 428.46, found: 427.75.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.51 (s, 1H), 8.14 (s, 1H), 7.94 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.70 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.58 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 7.52–7.43 (m, 4H), 7.28 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 7.05 (t, J = 4.5 Hz, 1H), 4.81 (s, 2H), 2.53 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 196.57, 166.22, 166.04, 142.81, 137.67, 135.09, 134.80, 134.36, 132.28, 131.95, 129.89, 129.59, 129.16, 128.76, 128.64, 128.12, 127.03, 118.45, 63.11, 26.46 ppm.
3.4.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Hybrid Compounds 6a–i
To a stirred solution of the appropriate ketone derivative 5a–i (1 eq) in EtOH, sodium acetate (3.5 eq) and NH2OH·HCl (7 eq) were added. The reaction mixture is heated at 50 °C for 5–15 min under microwave at 50W. After completion of the reaction, water was added and the obtained residue was filtered to furnish compounds 6a–i.
2-((4-((E)-1-(Hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl cinnamate (6a)
Compound 6a was synthesized according to the general procedure from compound 5a (17 mg, 0.054 mmol) in EtOH (0.36 mL) for 5 min. Yield: 70%; white solid; Rf: 0.48 (PE/EtOAc 6:4); M.p.: 178–180 °C; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C19H18N2O4: 361.35, found: 360.85, [M+Na+MeOH]+ calculated for C19H18N2O4: 393.39, found: 392.90, [M−H]− calculated for C19H18N2O4: 337.35, found: 336.90.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.14 (s, 1H), 9.31 (s, 1H), 6.81–6.75 (m, 3H), 6.68–6.61 (m, 4H), 6.49 (dd, J = 4.9, 1.9 Hz, 3H), 5.79 (d, J = 16.1 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (s, 2H), 1.16 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.96, 165.72, 152.59, 145.54, 138.89, 134.02, 132.24, 129.14, 128.62, 126.21, 119.12, 117.56, 117.52, 62.81, 11.48 ppm.
2-((4-((E)-1-(Hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-3-(naphthalen-1-yl)acrylate (6b)
Compound 6b was synthesized according to the general procedure from compound 5b (20 mg, 0.054 mmol) in EtOH (0.36 mL) for 5 min. Yield: 85%; white solid; Rf: 0.5 (PE/EtOAc 6:4); M.p.: 165–168 °C; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M+H]+ calculated for C23H20N2O4: 389.1496, found: 389.1489, [M−H]− calculated for C23H20N2O4: 387.1345, found: 387.1342.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na+MeOH]+ calculated for C10H11N2O3: 262.11, found: 262.85, [M−H]− calculated for C19H18N2O4: 206.07, found: = 206.90.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.08 (s, 1H), 10.29 (s, 1H), 8.55 (d, J = 15.8 Hz, 1H), 8.24 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.04 (dt, J = 16.6, 7.9 Hz, 3H), 7.68–7.58 (m, 7H), 6.84 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, 1H), 4.87 (s, 2H), 2.13 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.66, 165.58, 152.38, 141.55, 138.83, 133.33, 132.12, 130.88, 130.80, 130.59, 128.80, 127.32, 126.40, 126.10, 125.76, 125.57, 122.93, 119.99, 119.01, 62.85, 11.37 ppm.
2-((4-((E)-1-(Hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-3-(thiophen-2-yl)acrylate (6c)
Compound 6c was synthesized according to the general procedure from compound 5c (18 mg, 0.054 mmol) in EtOH (0.36 mL) for 5 min. Yield: 80%; white solid; Rf: 0.48 (PE/EtOAc 5:5); M.p.: 170–172 °C; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ calculated for C17H16N2O4S: 345.0909, found: 345.0902, [M−H]− calculated for C17H16N2O4S: 343.0752, found: 343.0750.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na+MeOH]+ calculated for C17H16N2O4S: 399.11, found: 398.90, [M+Na]+ calculated for C17H16N2O4S: 367.07, found: 366.85, [M−H]− calculated for C17H16N2O4S: 343.07, found: 342.95.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.08 (s, 1H), 10.22 (s, 1H), 7.90 (d, J = 15.8 Hz, 1H), 7.77 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.61 (s, 5H), 7.17 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 6.39 (d, J = 15.8 Hz, 1H), 4.78 (s, 2H), 2.12 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.55 (d, J = 1.8 Hz), 152.36, 138.78, 138.63, 138.09, 132.49, 132.11, 130.34, 128.66, 126.06, 119.02, 115.48, 62.69, 11.36 ppm.
2-((4-((E)-1-(Hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-3-(furan-2-yl)acrylate (6d)
Compound 6d was synthesized according to the general procedure from compound 5d (18 mg, 0.054 mmol) in EtOH (0.36 mL) for 15 min. Yield: 94%; off-white solid; Rf: (PE/EtOAc 7:3) 0.13; M.p.: 185–187 °C; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M+H]+ calculated for C17H16N2O5: 329.1137, found: 329.1131, [M−H]− calculated for C17H17N2O5Ν2: 327.0981, found: = 327.0979.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C17H16N2O5: 351.10, found: 350.85, [M+ Na+MeOH]+ calculated for C17H16N2O5: 383.13, found: 382.85, [M−H]− calculated for C17H16N2O5: 327.10, found: 326.85.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.09 (s, 1H), 10.24 (s, 1H), 7.88 (s, 1H), 7.61 (t, J = 6.9 Hz, 4H), 7.40 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H), 7.25 (tt, J = 14.9, 7.5 Hz, 5H), 7.09 (d, J = 16.6 Hz, 2H), 4.78 (s, 2H), 2.12 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 187.19, 182.04, 165.65, 150.15, 146.34, 138.82, 132.00, 126.08, 119.03, 118.57, 116.61, 114.02, 112.93, 62.70, 11.37 ppm.
2-((4-((E)-1-(Hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-3-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)acrylate (6e)
Compound 6e was synthesized according to the general procedure from compound 5e (30 mg, 0.067 mmol) in EtOH (0.6 mL) for 5 min. Yield: 87%; yellowish solid; Rf: 0.18 (PE/EtOAc 7:3); M.p.: 177–179 °C; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M+H]+ calculated for C21H18N2O4S: 395.1065), found: 395.1057, [M−H]− calculated for C21H18N2O4S: 393.0909, found: 393.0904.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C21H18N2O4S: 417.09, found: 416.85, [M+Na+MeOH]+ calculated for C21H18N2O4S: 449.12, found: 449.00, [M−H]− calculated for C21H18N2O4S: 393.09, found: 392.90.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.06 (s, 1H), 10.23 (s, 1H), 7.73–7.69 (s, 2H), 7.61–7.59 (m, 5H), 7.42–7.39 (m, 2H), 7.29–7.26 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 6.58 (d, J = 15.9 Hz, 1H), 4.80 (s, 2H), 2.09 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.62, 165.45, 155.19, 152.53, 152.00, 138.94, 132.48, 132.30, 128.18, 127.15, 126.24, 123.84, 122.48, 119.22, 117.52, 112.85, 111.60, 63.05, 11.53 ppm.
2-((4-((E)-1-(Hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-3-(benzofuran-2-yl)acrylate (6f)
Compound 6f was synthesized according to the general procedure from compound 5f (30 mg, 0.082 mmol) in EtOH (2 mL) for 30 min. Yield: 87%; white solid; Rf: 0.16 (PE/EtOAc 7:3); M.p.: 222–225 °C (decomposition); HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M+H]+ calculated for C21H18N2O5: 379.1294, found: 379.1289, [M−H]− calculated for C21H18N2O5: 377.1137, found: 377.1135.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C21H18N2O5: 401.11, found: 400.85, [M+Na+MeOH]+ calculated for C21H18N2O5: 433.14, found: 432.85, [M−H]− calculated for C21H18N2O5: 377.11, found: 376.95.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.09 (s, 1H), 10.26 (s, 1H), 7.78–7.71 (m, 2H), 7.62 (s, 5H), 7.48–7.41 (m, 2H), 7.31 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 6.61 (d, J = 15.8 Hz, 1H), 4.83 (s, 2H), 2.13 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.45, 165.28, 155.02, 152.36, 151.83, 138.78, 132.32, 132.13, 128.02, 126.98, 126.07, 123.67, 122.31, 119.05, 117.35, 112.68, 111.43, 62.88, 11.37 ppm.
2-((4-((E)-1-(Hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-2,3-diphenylacrylate (6g)
Compound 6g was synthesized according to the general procedure from compound 5g (30 mg, 0.075 mmol) in EtOH (2 mL) for 15 min. Yield: 94%; white solid; Rf: 0.6 (PE/EtOAc 4:6); M.p.:185–187 °C (decomposition); HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M+H]+ calculated for C25H22N2O4: 415.1658, found: 415.1650, [M−H]− calculated for C21H18N2O5: 413.1501, found: 413.1499.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C25H22N2O4: 437.15, found: 436.85, [M−H]− calculated for C25H22N2O4: 413.15, found: 413.00.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.07 (s, 1H), 10.24 (s, 1H), 7.88 (s, 1H), 7.61 (t, J = 6.9 Hz, 4H), 7.40 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H), 7.25 (tt, J = 14.9, 7.5 Hz, 5H), 7.09 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 4.81 (s, 2H), 2.12 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 166.58, 165.47, 152.40, 140.52, 138.87, 135.48, 134.11, 132.07, 131.87, 130.41, 129.65, 129.51, 128.75, 128.44, 128.06, 126.15, 118.86, 63.28, 11.41 ppm.
2-((4-((E)-1-(Hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-3-(naphthalen-1-yl)-2-phenylacrylate (6h)
Compound 6h was synthesized according to the general procedure from compound 5h (30 mg, 0.067 mmol) in EtOH (0.6 mL) for 5 min. Yield: 87%; yellowish solid; Rf: 0.6 (PE/EtOAc 5:5); M.p.: 177–179 °C (decomposition); HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M+H]+ calculated for C29H24N2O4: 465.1814, found: 465.1806, [M−H]− calculated for C29H24N2O4: 463.1658, found: 463.1654.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C29H24N2O4: 487.16, found: 486.95, [M−H]− calculated for C29H24N2O4: 463.50, found: 463.00.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.08 (s, 1H), 10.32 (s, 1H), 8.46 (s, 1H), 8.08 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.95 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.84 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 4H), 7.61–7.55 (m, 2H), 7.30–7.20 (m, 4H), 7.20–7.12 (m, 2H), 7.01 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.90 (s, 2H), 2.13 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 166.91, 152.81, 147.33, 139.30, 139.11, 135.35, 134.98, 133.43, 132.23, 131.66, 130.40, 130.30, 129.39, 129.10, 128.51, 128.13, 128.04, 127.39, 126.81, 126.57, 125.59, 124.33, 119.33, 63.83, 11.82 ppm.
2-((4-((E)-1-(Hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl (E)-2-phenyl-3-(thiophen-2-yl)acrylate (6i)
Compound 6i was synthesized according to the general procedure from compound 5i (31 mg, 0.067 mmol) in EtOH 1 mL) for 15 min. Yield: 79%; yellow brown solid; Rf: 0.58 (PE/EtOAc 5:5); M.p.: 199–201 °C; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M+H]+ calculated for C23H20N2O4S: 421.1222, found: 421.1218, [M−H]− calculated for C23H20N2O4S: 419.1065, found: 419.1064.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C23H20N2O4S: 443.10, found: 442.85.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.08 (s, 1H), 10.21 (s, 1H), 8.14 (s, 1H), 7.60 (dt, J = 10.4, 6.2 Hz, 5H), 7.47 (h, J = 8.9, 8.0 Hz, 4H), 7.29 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 7.05 (q, J = 5.9, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 4.78 (s, 2H), 2.12 (s, 3H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 166.17, 165.45, 152.35, 138.81, 137.67, 135.02, 134.25, 132.20, 129.87, 129.11, 128.72, 128.58, 128.16, 126.98, 126.27, 126.08, 118.83, 63.09, 11.35 ppm.
3.4.4. Synthesis of 3-(Hydroxymethyl)-4-phenyl-1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide (8)
NaNO2 (1.8 g, 26.0 mmol, 7.0 eq) is gradually added to 5–10 °C over 2 h in a solution of cinnamyl alcohol (0.5 mL, 3.90 mmol, 1 eq) in AcOH (8 mL). The reaction mixture was then allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred for 24 h. Upon completion of the reaction, water was added, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (5×). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude oily product was purified by flash column chromatography with silica gel, using a mixture of PE/EtOAc (95:5 v/v) as the eluent to obtain compound 8. Yield: 62%; white solid; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.86–7.77 (m, 2H), 7.56 (q, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H), 4.75 (s, 2H), 2.76 (br, 1H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 156.97, 131.51, 129.55, 127.92, 126.30, 114.99, 53.48 ppm [37].
3.4.5. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Hybrid Compounds 9a–i
To a solution of the appropriate cinnamic acid 2a–i in dry DMF, the reagents EDCI·HCl, DMAP, and compound 8 were added. The reaction mixture was heated at 50 °C in a microwave oven at 50 W for 5–45 min. After completion of the reaction, water was added, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (×2). The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude yellow oily product was purified by flash column chromatography with silica gel, using a PE/EtOAc solvent mixture as eluent to isolate compounds 9a–i.
3-((Cinnamoyloxy)methyl)-4-phenyl-1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide (9a)
Compound 9a was synthesized according to the general procedure for the preparation of the hybrid compounds from cinnamic acid 2a (20 mg, 0.14 mmol, 1.2 equiv), EDCI·HCl (40 mg, 0.21 mmol, 1.1 equiv), DMAP (26 mg, 0.21 mmol, 1.1 equiv), and compound 8 (22 mg, 0.11 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in dry DMF (1.7 mL), with a total reaction time of 5 min. After purification by flash column chromatography using a PE/EtOAc 95:5 v/v eluent mixture, compound 9a was obtained. Yield: 40%; yellow oily solid; Rf: 0.71 (PE/EtOAc 75:25); LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C18H14N2O4: 345.09, found: = 344.85, 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.76–7.73 (m, 2H), 7.71 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 7.60–7.49 (m, 5H), 7.43–7.37 (m, 3H), 6.43 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 5.28 (s, 2H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 166.03, 156.94, 147.02, 134.01, 131.56, 131.02, 129.58, 129.14, 128.44, 127.79, 126.22, 116.21 (d, J = 1.4 Hz), 111.52, 54.35 ppm.
3-(((3-(Naphthalen-1-yl)acryloyl)oxy)methyl)-4-phenyl-1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide (9b)
Compound 9b was synthesized according to the general procedure for the preparation of the hybrid compounds from cinnamic acid 2b (28 mg, 0.14 mmol, 1.2 equiv), EDCI·HCl (40 mg, 0.21 mmol, 1.1 equiv), DMAP (26 mg, 0.21 mmol, 1.1 equiv), and compound 8 (22 mg, 0.11 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in dry DMF (1.7 mL), with a total reaction time of 5 min. After purification by flash column chromatography using a PE/EtOAc 95:5 v/v eluent mixture, compound 9b was obtained. Yield: 66%; yellow oily solid; Rf: 0.66 (PE/EtOAc 75:25); HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M+H]+ calculated for C22H16N2O4: 373.1188, found: 373.1173, [M−H]− calculated for C22H16N2O4: 371.1032, found: 371.1036.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C22H16N2O4: 395.10, found: 394.85.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.56 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, 1H), 8.12 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.90 (dd, J = 18.7, 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.85–7.66 (m, 3H), 7.57 (h, J = 7.4 Hz, 5H), 7.52–7.44 (m, 1H), 6.53 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, 1H), 5.33 (s, 2H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.90, 156.93, 143.98, 133.79, 131.47, 131.24, 129.52, 128.97, 128.90, 127.84, 127.75, 126.42, 126.23, 125.49, 123.30, 123.28, 118.71, 118.62, 111.53, 54.43 ppm.
(E)-4-Phenyl-3-(((3-(thiophen-2-yl)acryloyl)oxy)methyl)-1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide (9c)
Compound 9c was synthesized according to the general procedure for the preparation of the hybrid compounds from cinnamic acid 2c (30 mg, 0.19 mmol, 1.2 equiv), EDCI·HCl (56 mg, 0.29 mmol, 1.8 equiv), DMAP (35 mg, 0.29 mmol, 1.8 equiv), and compound 8 (30 mg, 0.16 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in dry DMF (2.3 mL), with a total reaction time of 5 min. After purification by flash column chromatography using a PE/EtOAc 95:5 v/v eluent mixture, compound 9c was obtained. Yield: 50%; pink solid; Rf: 0.63 (PE/EtOAc 75:25); M.p.: 57–59 °C; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M+H]+ calculated for C16H12N2O4S: 329.0596, found: 329.0589, [M−H]− calculated for C16H12N2O4S: 327.0439, found: 327.0438.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C16H12N2O4S: 351.04, found: 350.85; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.79 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, 1H), 7.76–7.70 (m, 2H), 7.55 (q, J = 6.7, 6.2 Hz, 3H), 7.42 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.27 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 7.08–7.06 (m, 1H), 6.21 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, 1H), 5.26 (s, 2H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.88, 156.92, 139.28, 139.16, 131.96, 131.55, 129.57, 129.51, 128.40, 127.78, 126.20, 114.77, 111.51, 54.30 ppm.
(E)-3-(((3-(Furan-2-yl)acryloyl)oxy)methyl)-4-phenyl-1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide (9d)
Compound 9d was synthesized according to the general procedure for the preparation of the hybrid compounds from cinnamic acid 2d (30 mg, 0.19 mmol, 1.2 equiv), EDCI·HCl (60 mg, 0.32 mmol, 2.0 equiv), DMAP (39 mg, 0.32 mmol, 2.0 equiv), and compound 8 (31 mg, 0.16 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in dry DMF (2.5 mL), with a total reaction time of 10 min. After purification by flash column chromatography using a PE/EtOAc 95:5 v/v eluent mixture, compound 9d was obtained. Yield: 58%; yellow oily solid; Rf: 0.73 (PE/EtOAc 7:3); HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M+H]+ calculated for C23H20N2O4S: 313.0824, found: 313.0817.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C16H12N2O5: 335.06, found: 334.80.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.75–7.73 (m, 2H), 7.58–7.50 (m, 4H), 7.45–7.42 (m, 1H), 6.65 (d, J = 3.5 Hz, 1H), 6.48 (dt, J = 3.2, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 6.30 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, 1H), 5.25 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 2H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 166.07, 156.94, 150.60, 145.49, 132.92, 131.53, 129.55, 127.76, 126.18, 116.20, 113.64, 112.66, 111.52, 54.27 ppm.
(E)-3-(((3-(Benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)acryloyl)oxy)methyl)-4-phenyl-1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide (9e)
Compound 9e was synthesized according to the general procedure for the preparation of the hybrid compounds from cinnamic acid 2e (35 mg, 0.17 mmol, 1.3 equiv), EDCI·HCl (49 mg, 0.26 mmol, 2.0 equiv), DMAP (31 mg, 0.26 mmol, 2.0 equiv), and compound 8 (25 mg, 0.13 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in dry DMF (2 mL), with a total reaction time of 10 min. After purification by flash column chromatography using a PE/EtOAc 95:5 v/v eluent mixture, compound 9d was obtained. Yield: 57%; yellowish solid; Rf: 0.76 (PE/EtOAc 7:3); M.p.: 120–123 °C; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M+H]+ calculated for C20H14N2O4S: 379.0752, found: 379.0742, [M−H]− calculated for C20H14N2O4S: 377.0596, found: 377.0597.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C20H14N2O4S: 401.06, found: 400.80.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.89 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 7.82–7.70 (m, 4H), 7.57 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 3H), 7.49 (s, 1H), 7.38 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 6.28 (d, J = 17.4 Hz, 1H), 5.29 (s, 2H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.60, 156.92, 140.56, 139.87, 139.53, 139.02, 131.58, 129.89, 129.59, 127.79, 126.76, 126.16, 125.15, 124.80, 122.65, 117.22, 111.47, 54.42 ppm.
(E)-3-(((3-(Benzofuran-2-yl)acryloyl)oxy)methyl)-4-phenyl-1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide (9f)
Compound 9f was synthesized according to the general procedure for the preparation of the hybrid compounds from cinnamic acid 2f (40 mg, 0.21 mmol, 1.3 equiv), EDCI·HCl (60 mg, 0.32 mmol, 2.0 equiv), DMAP (39 mg, 0.32 mmol, 2.0 equiv), and compound 8 (31 mg, 0.16 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in dry DMF (2.5 mL), with a total reaction time of 10 min. After purification by flash column chromatography using a PE/EtOAc 95:5 v/v eluent mixture, compound 9f was obtained. Yield: 73%; white solid; Rf: 0.76 (PE/EtOAc 7:3); M.p.: 114–117 °C; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M+H]+ calculated for C20H14N2O5: 363.0981, found: 363.0975.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C20H14N2O5: 385.08, found: 384.85.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.77–7.75 (m, 2H), 7.61–7.55 (m, 5H), 7.48 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 1H), 7.40–7.37 (m, 1H), 7.28–7.24 (m, 1H), 6.98 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 6.57 (dd, J = 15.6, 1.9 Hz, 1H), 5.29 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 2H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.74, 156.94, 155.84, 151.92, 133.27, 131.57, 129.59, 128.34, 127.78, 127.07, 126.18, 123.64, 122.11, 116.68, 112.52, 111.62, 111.45, 54.45 ppm.
(E)-3-(((2,3-Diphenylacryloyl)oxy)methyl)-4-phenyl-1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide (9g)
Compound 9g was synthesized according to the general procedure for the preparation of the hybrid compounds from cinnamic acid 2g (42 mg, 0.19 mmol, 1.9 equiv), EDCI·HCl (48 mg, 0.25 mmol, 2.5 equiv), DMAP (18 mg, 0.25 mmol, 2.5 equiv), and compound 8 (21 mg, 0.10 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in dry DMF (2.5 mL), with a total reaction time of 45 min. After purification by flash column chromatography using a PE/EtOAc 92:8 v/v eluent mixture, compound 9g was obtained. Yield: 87%; yellow sticky solid; Rf: 0.68 (PE/EtOAc 75:25); M.p.: 91–94 °C; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M+H]+ calculated for C24H18N2O4: 399.1345, found: 399.1333, [M−H]− calculated for C24H18N2O4: 397.1188, found: 397.1184.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C24H18N2O4: 421.12, found: 420.85, [M−H]− calculated for C24H18N2O4: 397.12, found: 396.90.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.83 (s, 1H), 7.61 (dd, J = 7.1, 1.4 Hz, 2H), 7.58–7.51 (m, 1H), 7.46 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.35 (dd, J = 4.6, 2.0 Hz, 3H), 7.27–7.19 (m, 1H), 7.18–7.08 (m, 4H), 7.01 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 5.26 (s, 2H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 171.29, 166.88, 157.00, 142.49, 135.24, 134.21, 131.43, 131.07, 130.97, 129.73, 129.46, 128.97, 128.43, 128.25, 127.81, 126.19, 111.41, 54.92 ppm.
(E)-3-(((3-(Naphthalen-1-yl)-2-phenylacryloyl)oxy)methyl)-4-phenyl-1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide (9h)
Compound 9h was synthesized according to the general procedure for the preparation of the hybrid compounds from cinnamic acid 2h (52 mg, 0.19 mmol, 1.2 equiv), EDCI·HCl (72 mg, 0.38 mmol, 2.3 equiv), DMAP (46 mg, 0.38 mmol, 2.3 equiv), and compound 8 (30 mg, 0.16 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in dry DMF (1.2 mL), with a total reaction time of 45 min. After purification by flash column chromatography using a PE/EtOAc 95:5 v/v eluent mixture, compound 9h was obtained. Yield: 67%; yellow sticky solid; Rf: 0.66 (PE/EtOAc 75:25); M.p.: 114–117 °C; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M]+ calculated for C28H20N2O4: 448.1423, found: 448.1415, [M−H]− calculated for C28H20N2O4: 447.1345, found: 447.1338.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C28H20N2O4: 471.13, found: 470.85, [M−H]− calculated for C28H20N2O4: 447.13, found: 446.80.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.49 (s, 1H), 8.01 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.86–7.80 (m, 1H), 7.74–7.65 (m, 3H), 7.60–7.46 (m, 5H), 7.24–7.16 (m, 3H), 7.13 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.06 (dt, J = 6.6, 1.6 Hz, 2H), 6.95 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 5.36 (s, 2H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 168.15, 166.75, 140.67, 134.74, 133.52, 133.49, 132.11, 131.68, 131.50, 130.20, 129.52, 129.46, 128.86, 128.42, 128.00, 127.84, 127.18, 126.88, 126.32, 126.25, 125.13, 124.07, 111.44, 55.07 pm.
(E)-4-Phenyl-3-(((2-phenyl-3-(thiophen-2-yl)acryloyl)oxy)methyl)-1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide (9i)
Compound 9i was synthesized according to the general procedure for the preparation of the hybrid compounds from cinnamic acid 2i (44 mg, 0.19 mmol, 1.2 equiv), EDCI·HCl (72 mg, 0.38 mmol, 2.3 equiv), DMAP (46 mg, 0.38 mmol, 2.3 equiv), and compound 8 (30 mg, 0.16 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in dry DMF (1.2 mL), with a total reaction time of 5 min. After purification by flash column chromatography using a PE/EtOAc 95:5 v/v eluent mixture, compound 9i was obtained. Yield: 51%; brown oily solid; Rf: 0.63 (PE/EtOAc 75:25); HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M+H]+ calculated for C22H16N2O4S: 404.0831, found: 404.0827, [M−H]− calculated for C22H16N2O4S: 403.0752, found: 403.0749.; LC-MS (ESI, m/z): [M+Na]+ calculated for C22H16N2O4S: 427.07, found: 426.80.; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.03 (s, 1H), 7.59 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.4 Hz, 2H), 7.56–7.49 (m, 1H), 7.47–7.39 (m, 5H), 7.27–7.23 (m, 1H), 7.19–7.11 (m, 3H), 6.96–6.89 (m, 1H), 5.23 (s, 2H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 166.54, 157.03, 138.32, 135.77, 134.59, 134.41, 131.64, 131.42, 130.00, 129.44, 129.43, 128.87, 127.81, 127.74, 126.92, 126.19, 111.44, 54.83 ppm.
3.4.6. Synthesis of the 4-(2-(Cinnamoyloxy)ethoxy)-3-(phenylsulfonyl)-1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide (11)
To a solution of cinnamic acid 2a (44 mg, 0.19 mmol, 1.2 equiv) in dry DMF (1.2 mL), the reagents EDCI·HCl (72 mg, 0.38 mmol, 2.3 equiv), DMAP (46 mg, 0.38 mmol, 2.3 equiv), and compound 10 (30 mg, 0.16 mmol, 1.0 equiv) were added. The reaction mixture was heated at 50 °C in a microwave oven at 50 W for 5 min. After completion of the reaction, water was added, and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (×2). The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude yellow oily product was purified by flash column chromatography with silica gel, using a PE/EtOAc 95:5 v/v solvent mixture as eluent, to isolate compound 11. Yield: 61%; yellow solid; Rf: 0.52 (PE/EtOAc 7:3); M.p.: 55–57 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.07–8.05 (m, 1H), 7.75 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 7.70 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.60–7.50 (m, 4H), 7.42 (q, J = 3.7 Hz, 3H), 6.47 (d, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 4.72–4.70 (m, 2H), 4.63–4.61 (m, 2H) ppm.; 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 166.48, 158.70, 146.00, 138.01, 135.64, 134.07, 130.70, 129.66, 129.01, 128.59, 128.22, 117.04, 69.00, 61.33 ppm [38].
3.5. Biological In Vitro Assays
For the in vitro assays, a 10 mM stock solution of the tested compounds was prepared in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and subsequently diluted with the appropriate buffer to achieve the desired concentrations. Each experiment was conducted in triplicate or more, with the standard deviation of absorbance remaining within 10%. The compounds were found to be stable under the in vitro experimental conditions. Their stability was studied with TLC and spectroscopically with NMR.
3.5.1. In Vitro Inhibition of Linoleic Acid Lipid Peroxidation
An in vitro assay was performed following previously established protocols [89]. The compound 2,2′-Azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride (AAPH) was used as a controlled source of thermally generated alkylperoxy free radicals. The formation of conjugated diene hydroperoxides through the oxidation of sodium linoleate in an aqueous dispersion at 37 °C was measured by monitoring absorbance at 234 nm. The results were compared with the reference compound, Trolox (93%) (Table 6).
3.5.2. In Vitro Inhibition of Soybean Lipoxygenase
An in vitro study was conducted following a previously reported method [90]. The tested compounds were dissolved in DMSO (100 µM) and incubated at room temperature with 0.1 mL of sodium linoleate as the substrate and 0.2 mL of soybean lipoxygenase solution in Tris-HCl buffer (pH 9.0). The conversion of sodium linoleate to 13-hydroperoxylinoleic acid was monitored by measuring absorbance at 234 nm and compared to the standard inhibitor NDGA (IC50 = 0.45 µM) (Table 6). Different concentrations ranging from 100 µM to 1 µM were tested to determine IC50 values.
3.5.3. In Vitro Inhibition of Ovine Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)
The in vitro COX-2 inhibitory activity was assessed using arachidonic acid (AA) as a substrate and N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine (TMPD) as a co-substrate in a Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.5), following the reported method [89]. To the test tube, 10 µL of the compound dissolved in DMSO was added to a mixture containing 730 µL of Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.5), 50 µL of heme, 10 µL of COX-2 enzyme, and 100 µL of TMPD. The absorbance was measured at 590 nm. Subsequently, 100 µL of AA was added, followed by a second 5-min incubation at 37 °C with vigorous shaking, and the absorbance was measured again at 611 nm. Different concentrations (ranging from 100 µM to 1 µM) were tested to determine IC50 values. A blank determination was conducted as a negative control. Results were compared against the standard inhibitor Indomethacin, as shown in Table 6.
3.5.4. In Vitro Inhibition of COX-1
Cyclooxygenase (COX) activity was measured using arachidonic acid (AA) as the substrate and N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylphenylenediamine (TMPD) as the co-substrate following the reported method [90]. The reaction mixture (1 mL) consisted of 0.75 mM heme, 128 mM TMPD, 80 mM AA, and 1.5 mg of enzyme in 0.1 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.5). The substrate oxidation was monitored at room temperature by recording the increase in absorbance at 590 nm. Absorbance due to the spontaneous oxidation of TMPD was subtracted from the initial oxidation rate observed in the presence of AA. The inhibitory activity of the test compounds at a concentration of 100 μM was evaluated after a 6-min pre-incubation with the enzyme in the presence of heme and TMPD. The reaction was initiated by adding AA measured again at 611 nm. SC-560 was used as the reference COX-1 inhibitor (Table 6).
3.5.5. In Vitro Determination of NO Release with Griess Reagent
The compounds (from a 10 mM stock solution in DMSO, final concentration 100 μM) are added (20 μL) to each test tube. Then, 2 mL of phosphate buffer solution (pH 7.4) is added. L-cysteine, used as the thiol agent, is added to the mixture at a final concentration of 0.5 mM. The solution is incubated at 37 °C for 60 min, after which 1 mL is removed and mixed with 250 μL of Griess reagent (4 g sulfanilamide, 0.2 g N-(1-naphthyl)-ethylenediamine dihydrochloride, and 10 mL of H3PO4 solution, final volume adjusted to 100 mL). The mixture is allowed to stand for 10 min at room temperature, and the absorbance of the produced compound is measured at 540 nm. Sodium nitroprusside (SNP) is used as the reference compound. The results are presented as the release of NO2− (% NO2− (mol/mol)) induced by the compounds in the presence of L-cysteine (Table 6).
3.5.6. In Vitro Inhibition of Albumin
Inhibition of albumin denaturation was measured following the reported method [66]. In a test tube, 1 mL of bovine serum albumin solution (fraction V, 1% w/v in phosphate buffer, pH 7.4) and 100 μL of the test compound solution were added sequentially. The mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 15 min, followed by heating at 60 °C for 10 min. After cooling to room temperature, the absorbance was measured at 660 nm. DMSO was used as the blank, and the results were compared to acetylsalicylic acid, which served as the reference compound (Table 6).
3.5.7. MTT Assays on Cancer Cell Lines
Cell Culture
HeLa, MCF-7, U251, U87, MDA-MB-435, and MDA-MB-231 cancer cell lines were maintained in incubators at 37 °C with 5% CO2 in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS) and antibiotics/antimycotics. All cell lines used in this study originate from the Laboratory of Biochemistry, Department of Chemistry, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki. They are low-passage, mycoplasma-free cancer cell lines that have been extensively used over the past 25 years in numerous studies across various fields of cancer research, including drug cytotoxicity testing.
MTT Assays
All cell lines tested were seeded in 96-well plates at a concentration of 6 × 103 cells per well, except HeLa, which were seeded at 3 × 103 cells per well. The day after, cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of the compounds for 48 h. Cell viability was determined using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, a colorimetric assessment of cellular metabolic activity as described previously [67]. Absorbance values from treated samples were normalized to those of untreated controls, which were assigned to a 100% viability value. The half-maximal effective concentration (EC50), defined as the concentration of treatment resulting in a 50% reduction in cell viability relative to controls, was subsequently calculated. As a positive control, doxorubicin exhibited an IC50 value of approximately 500 nM following 48 h of exposure in HeLa cells as determined by the MTT assay. The results are shown in Table 7 and Table 8.
4. Conclusions
In this study, 28 new cinnamic acid hybrids were synthesized, 19 of which incorporated a nitric oxide donor moiety (oxime or furoxan). Computational studies confirmed the ability of the selected compounds 9a and 9e to interact with LOX and COX-2, in agreement with the in vitro results. In addition, in silico analyses indicated that most derivatives fulfilled drug-likeness criteria, with some exceptions in lipophilicity and blood–brain barrier permeability.
Biological evaluations revealed several potent inhibitors of lipid peroxidation (e.g., 5g, 6g, 9a, 9h, 11), with activity comparable to Trolox, while compound 9a displayed also a remarkable LOX inhibitory activity (IC50 = 3.5 μM). Furthermore, compound 9e showed selective inhibition of COX-2, whereas 6e exhibited significant inhibition of albumin denaturation activity, surpassing that of aspirin. Compound 9i is a double COX-1/COX-2 inhibitor. Notably, some furoxan derivatives (9a, 11) demonstrated efficient nitric oxide release, in higher proportions than the corresponding oximes. Regarding anticancer potential, compound 6i exhibited the strongest cytotoxic activity, with EC50 values ranging from 36–45 μM across multiple cancer cell lines, highlighting its potential as a promising lead for further development.
Overall, these findings support that cinnamic acid-based hybrids bearing oxime and furoxan moieties represent promising multi-target agents with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cytotoxic properties. These results are important to enhance our knowledge for good candidates for anticancer agents. Further investigation will follow to delineate the possible mechanism. In the literature, cinnamic acid has reported to demonstrate anticancer activity by inducing apoptosis, inhibiting cell proliferation, and inhibiting with pathways crucial for tumor growth and metastasis [11,12]. Its anticancer effects are partly due to its ability to damage DNA, block signaling pathways, and act as a potent antioxidant. However, the clinical application of cinnamic acid is currently limited due to poor water solubility and membrane permeability. Thus, we believe that the herein presented hybrids will offer some interesting ideas to skip these problems. Among them, compounds 9a, 9e, and 6i emerged as the most active candidates and may serve as lead compounds for further research, whereas 9i could be subjected to structural modifications to lead to a COX-2 inhibitor.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules30234582/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.H.-L. and I.-C.T.; methodology, I.-C.T., E.N., and I.S.; software, I.-C.T., D.H.-L., and E.P.; validation, I.-C.T. and D.H.-L.; investigation, I.-C.T.; data curation, I.-C.T., D.H.-L., and K.C.P.; writing—original draft preparation, I.-C.T.; writing—review and editing, D.H.-L., E.P., and E.N.; supervision, D.H.-L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The synthesized compounds are available from the laboratory of Pharmaceutical chemistry, under the responsibility of Hadjipavlou-Litina.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Douka M., for taking the LC-MS.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fleit, H.B. Chronic Inflammation. Pathobiol. Hum. Dis. Dyn. Encycl. Dis. Mech. 2014, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punchard, N.A.; Whelan, C.J.; Adcock, I. The Journal of Inflammation. J. Inflamm. 2004, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rådmark, O.; Werz, O.; Steinhilber, D.; Samuelsson, B. 5-Lipoxygenase: Regulation of expression and enzyme activity. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, F.A. Cyclooxygenase Enzymes: Regulation and Function. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 10, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelombitko, M.A. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Inflammation: A Minireview. Mosc. Univ. Biol. Sci. Bull. 2018, 73, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1126–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, J. Reactive oxygen species and inflammation. Comptes Rendus Seances Soc. Biol. Fil. 1993, 187, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumenacker, J.S.; Hanafy, K.A.; Murad, F. Regulation of nitric oxide and soluble guanylyl cyclase. Brain Res. Bull. 2004, 62, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirino, G.; Distrutti, E.; Wallace, J.L. Nitric oxide and inflammation. Inflamm. Allergy-Drug Targets 2006, 5, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroux, F.S.; Pavlick, K.P.; Hines, I.N.; Kawachi, S.; Harada, H.; Bharwani, S.; Hoffman, J.M.; Grisham, M.B. Role of nitric oxide in inflammation. Acta. Physiol. Scand. 2001, 173, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwizhi, N.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Cinnamic Acid Derivatives and Their Biological Efficacy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Multi-Target Cinnamic Acids for Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Modeling Studies. Molecules 2018, 24, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivasiv, V.; Albertini, C.; Gonçalves, A.E.; Rossi, M.; Bolognesi, M.L. Molecular Hybridization as a Tool for Designing Multitarget Drug Candidates for Complex Diseases. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1694–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosquesi, P.L.; Melo, T.R.F.; Vizioli, E.O.; Santos, J.L.D.; Chung, M.C. Anti-Inflammatory Drug Design Using a Molecular Hybridization Approach. Pharmaceuticals 2011, 4, 1450–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Joubert, J.; Malan, S.F. Recent Developments in Drug Design of NO-donor Hybrid Compounds. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1175–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasfi, A.A.M.; Al-Masoudi, N.A.; Saeed, B.A.; Winter, R.; Pannecouque, C. Synthesis, In Vitro Anti-HIV Activity, Cytotoxicity, and Computational Studies of Some New Steroids and Their Pyrazoline and Oxime Analogues. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 46, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E.; Zhuang, C.; Chen, F.E. Privileged scaffold inspired design of novel oxime-biphenyl-DAPYs in treatment of HIV-1. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 99, 103825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Ellah, H.S.; Abdel-Aziz, M.; Shoman, M.E.; Beshr, E.A.M.; Kaoud, T.S.; Ahmed, A.S.F.F. New 1,3,4-oxadiazole/oxime hybrids: Design, synthesis, anti-inflammatory, COX inhibitory activities and ulcerogenic liability. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 74, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Ellah, H.S.; Abdel-Aziz, M.; Shoman, M.E.; Beshr, E.A.M.; Kaoud, T.S.; Ahmed, A.S.F.F. Novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole/oxime hybrids: Synthesis, docking studies and investigation of anti-inflammatory, ulcerogenic liability and analgesic activities. Bioorg. Chem. 2016, 69, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koikov, L.N.; Alekseeva, N.V.; Lisitza, E.A.; Krichevsky, E.S.; Grigoriev, N.B.; Danilov, A.V.; Severina, I.S.; Pyatakova, N.V.; Granik, V.G. Oximes, amidoximes and hydroxamic acids as nitric oxide donors. Mendeleev Commun. 1998, 8, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferioli, R.; Folco, G.C.; Ferretti, C.; Gasco, A.M.; Medana, C.; Fruttero, R.; Civelli, M.; Gasco, A. A new class of furoxan derivatives as NO donors: Mechanism of action and biological activity. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 114, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasco, A.; Fruttero, R.; Sorba, G.; Di Stilo, A.; Calvino, R. NO donors: Focus on furoxan derivatives. Pure Appl. Chem. 2004, 76, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Geromichalos, G.; Papageorgiou, A. Anticancer activity and quantitative-structure activity relationship (QSAR) studies of a series of antioxidant/anti-inflammatory aryl-acetic and hydroxamic acids. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2009, 74, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heravi, M.M.; Asadi, S.; Azarakhshi, F. Recent Applications of Doebner, Doebner-von Miller and Knoevenagel-Doebner Reactions in Organic Syntheses. Curr. Org. Synth. 2014, 11, 701–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Bergmann, E.D. The Reaction of Acetals with Malonic Acid and its Derivatives. A Contribution to the Knowledge of the Knoevenagel–Doebner Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 3452–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotopoulos, I.; Pontiki, E.; Litina, D.H. Targeting Inflammation with Conjugated Cinnamic Amides, Ethers and Esters. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2018, 17, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Gao, S.J.; Zhang, M.T.; Jia, J.; Chen, F.X.; Chen, C.L.; Yang, P.F.; Mao, J.L. Synthesis, configurational analysis and antiviral activities of novel diphenylacrylic acids with caffeic acid as the lead compound. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1291, 136016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csankó, K.; Illés, L.; Felföldi, K.; Kiss, J.T.; Sipos, P.; Pálinkó, I. CH⋯S hydrogen bonds as the organising force in 2,3-thienyl- and phenyl- or 2,3-dithienyl-substituted propenoic acid aggregates studied by the combination of FT-IR spectroscopy and computations. J. Mol. Struct. 2011, 993, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Lei, N.; Miao, Z.; Sheng, C.; Zhuang, C.; Yao, J.; Zhang, W. β-alanine-DBU: A highly efficient catalytic system for knoevenagel-doebner reaction under mild conditions. Chin. J. Chem. 2012, 30, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obushak, M.D.; Pokhodylo, N.T.; Ostapiuk, Y.V.; Matiychuk, V.S. Synthesis of 3-Substituted (6-[(E)-2-(1-Benzofuran-2-yl)ethenyl][1,2,4]triazolo [3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazoles. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2007, 183, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, H.; Sun, M. Discovery of a novel piperlongumine analogue as a microtubule polymerization inhibitor with potent anti-angiogenic and anti-metastatic efficacy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 243, 114738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellassoued, M.; Lensen, N.; Bakasse, M.; Mouelhi, S. Two-carbon homologation of aldehydes via silyl ketene acetals: A new stereoselective approach to (E)-alkenoic acids. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 8785–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upare, A.A.; Gadekar, P.K.; Sivaramakrishnan, H.; Naik, N.; Khedkar, V.M.; Sarkar, D.; Choudhari, A.; Roopan, S.M. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of (E)-5-styryl-1,2,4-oxadiazoles as anti-tubercular agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 86, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthwal, A.; Thakur, B.K.; Rawat, M.S.M.; Rawat, D.S.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Synthesis, Characterization and In Vitro Anticancer Activity of C-5 Curcumin Analogues with Potential to Inhibit TNF-α-Induced NF-B Activation. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 524161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsopka, I.C.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. 2-((4-((E)-1-(Hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl Cinnamate. Molbank 2021, 2021, M1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.; Nazir, Y.; Ashraf, Z.; Rafique, H.; Afzal, S.; Mumtaz, A.; Hassan, M.; Ali, A.; Afzal, K.; Yousuf, M.R.; et al. Synthesis, computational studies, tyrosinase inhibitory kinetics and antimelanogenic activity of hydroxy substituted 2-[(4-acetylphenyl)amino]-2-oxoethyl derivatives. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 1562–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.; Nash, K.; Tackie-Yarboi, E.; Kostrevski, A.; Novak, A.; Raghavan, A.; Tulsulkar, J.; Alhadidi, Q.; Wamer, N.; Langenderfer, B.; et al. Furoxans (Oxadiazole-4 N-oxides) with Attenuated Reactivity are Neuroprotective, Cross the Blood Brain Barrier, and Improve Passive Avoidance Memory. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 4593–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, Y.; Ji, H.; Peng, S.; Tian, J. Novel nitric oxide-releasing derivatives of farnesylthiosalicylic acid: Synthesis and evaluation of antihepatocellular carcinoma activity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3251–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.D.; Shao, L.H.; Wang, Q.T.; Bai, Y.; Li, N.; Yang, G.; Li, Y.P.; Bian, X.L. Design, synthesis and evaluation of phenylfuroxan nitric oxide-donor phenols as potential anti-diabetic agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 89, 103000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norinder, U.; Bergström, C.A.S. Prediction of ADMET Properties. ChemMedChem 2006, 1, 920–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A. Lead- and drug-like compounds: The rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2004, 1, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, L.; Kerns, E.H.; Carter, G.T. Strategies to assess blood-brain barrier penetration. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2008, 3, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, I.F.; Teixeira, A.L.; Pinheiro, L.; Falcao, A.O. A Bayesian approach to in Silico blood-brain barrier penetration modeling. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PreADMET|Prediction of ADME/Tox—Just Another BMDRC Sites Site. Available online: https://preadmet.webservice.bmdrc.org/ (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Molinspiration Cheminformatics. Available online: https://molinspiration.com/ (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Dmitriev, A.V.; Rudik, A.V.; Karasev, D.A.; Pogodin, P.V.; Lagunin, A.A.; Filimonov, D.A.; Poroikov, V.V. In Silico Prediction of Drug-Drug Interactions Mediated by Cytochrome P450 Isoforms. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- De Graaf, C.; Vermeulen, N.P.E.; Feenstra, K.A. Cytochrome P450 in silico: An integrative modeling approach. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 2725–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelkonen, O.; Mäenpääj, J.; Taavitsainen, P.; Rautio, A.; Raunio, H. Inhibition and induction of human cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes. Xenobiotica 1998, 28, 1203–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.-Y.; Su, B.-H.; Tu, Y.-S.; Lin, C.; Lin, O.A.; Tseng, Y.J. CypRules: A rule-based P450 inhibition pre-diction server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1869–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrecht, A.; Muster, W.; Brigo, A.; Kansy, M.; Weiser, T.; Singer, T. Comparative evaluation of in silico systems for ames test mutagenicity prediction: Scope and limitations. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.; Li, J.; Malcomber, S.; Moore, C.; Scott, A.; White, A.; Carmichael, P. Integrated in silico approaches for the prediction of Ames test mutagenicity. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2012, 26, 1017–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, P.; Rohde, B.; Selzer, P. Fast calculation of molecular polar surface area as a sum of fragment-based contributions and its application to the prediction of drug transport properties. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 3714–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, S.; Doerksen, R.J. Topological polar surface area: A useful descriptor in 2D-QSAR. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Samadi, A.; Unzeta, M.; Marco-Contelles, J. Analysis of the antioxidant properties of differently substituted 2- and 3-indolyl carbohydrazides and related derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 63, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankovska, I.M.; Klymenko, O.O.; Gonchar, O.O.; Karasevich, N.V.; Karaban, I.M. Interplay of oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases: Mechanisms and treatment strategies. Neurophysiology 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.Z.; Souayah, N. Oxidative Stress: Pathological Driver in Chronic Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisastra, R.; Dekker, F.J. Inflammation, Cancer and Oxidative Lipoxygenase Activity are Intimately Linked. Cancers 2014, 6, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigge, S.T.; Boyington, J.C.; Gaffney, B.J.; Amzel, L.M. Structure conservation in lipoxygenases: Structural analysis of soybean lipoxygenase-1 and modeling of human lipoxygenases. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 1996, 24, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Synthesis and pharmacochemical evaluation of novel aryl-acetic acid inhibitors of lipoxygenase, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 5819–5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, J.R.; Botting, R.M. Anti-inflammatory drugs and their mechanism of action. Inflamm. Res. 1998, 47 (Suppl. S2), 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noti, V.; Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Development of Novel Pyrrole Derivatives and Their Cinnamic Hybrids as Dual COX-2/LOX Inhibitors. Molecules 2023, 28, 7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.N.; Dasgupta, T.P. Mechanism of Nitric Oxide Release. I. Two-electron Reduction of Sodium Nitroprusside by l-cysteine in Aqueous Solution. Inorg. React. Mech. 2002, 3, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Broderick, M.; Fein, H. Measurement of Nitric Oxide Production in Biological Systems by Using Griess Reaction Assay. Sensors 2003, 3, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, S.; Kamboj, P.; Alam, O.; Amir, M. 1,2,4-Triazole-based benzothiazole/benzoxazole derivatives: Design, synthesis, p38α MAP kinase inhibition, anti-inflammatory activity and molecular docking studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 81, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigala, I.; Tsamis, K.I.; Gousia, A.; Alexiou, G.; Voulgaris, S.; Giannakouros, T.; Kyritsis, A.P.; Nikolakaki, E. Expression of SRPK1 in gliomas and its role in glioma cell lines viability. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 8699–8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulou, I.; Tzani, A.; Polyzos, N.I.; Karadendrou, M.A.; Kritsi, E.; Pontiki, E.; Liargkova, T.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Zoumpoulakis, P.; Detsi, A. Exploring the 2′-Hydroxy-Chalcone Framework for the Development of Dual Antioxidant and Soybean Lipoxygenase Inhibitory Agents. Molecules 2021, 26, 2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khatabi, K.; El-Mernissi, R.; Aanouz, I.; Ajana, M.A.; Lakhlifi, T.; Khan, A.; Wei, D.Q.; Bouachrine, M. Identification of novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitors through 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation targeting Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mol. Model. 2021, 27, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Lipoxygenase inhibitors: A comparative QSAR study review and evaluation of new QSARs. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28, 39–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavridis, E.; Bermperoglou, E.; Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. 5-(4H)-Oxazolones and Their Benzamides as Potential Bioactive Small Molecules. Molecules 2020, 25, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulou, I.; Diassakou, A.; Kavetsou, E.; Kritsi, E.; Zoumpoulakis, P.; Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Detsi, A. Novel quinolinone–pyrazoline hybrids: Synthesis and evaluation of antioxidant and lipoxygenase inhibitory activity. Mol. Divers. 2021, 25, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UCSF Chimera Home Page. Available online: https://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera/ (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- GROMACS 4.6.5 Online Reference. Available online: https://manual.gromacs.org/archive/4.6.6/online.html (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- About MODELLER. Available online: https://salilab.org/modeller/ (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An Open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AmberTools25. Available online: https://ambermd.org/AmberTools.php (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiser, A.; Šali, A. MODELLER: Generation and Refinement of Homology-Based Protein Structure Models. Methods Enzym. 2003, 374, 461–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Aktulga, H.M.; Belfon, K.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cisneros, G.A.; Cruzeiro, V.W.D.; Forouzesh, N.; Giese, T.J.; Gotz, A.W.; Gohlke, H.; et al. AmberTools. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 63, 6183–6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Piana, S.; Palmo, K.; Maragakis, P.; Klepeis, J.L.; Dror, R.O.; Shaw, D.E. Improved side-chain torsion potentials for the Amber ff99SB protein force field. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2010, 78, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Roberts, B.P.; Chakravorty, D.K.; Merz, K.M. Rational design of particle mesh ewald compatible lennard-jones parameters for +2 metal cations in explicit solvent. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 2733–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgren, T.A. Merck molecular force field. I. Basis, form, scope, parameterization, and performance of MMFF94. J. Comput. Chem. 1996, 17, 490–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashrey, M.K.; Bakr, R.O.; Fayed, M.A.A.; Refaey, R.H.; Nissan, Y.M. Pharmacophore based virtual screening for natural product database revealed possible inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Virology 2022, 570, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Automatic atom type and bond type perception in molecular mechanical calculations. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2006, 25, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Kutzner, C.; Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E. GRGMACS 4: Algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peperidou, A.; Kapoukranidou, D.; Kontogiorgis, C.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Multitarget Molecular Hybrids of Cinnamic Acids. Molecules 2014, 19, 20197–20226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Litinas, K.; Nicolotti, O.; Carotti, A. Design, synthesis and pharmacobiological evaluation of novel acrylic acid derivatives acting as lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase-1 inhibitors with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).