- Article
Predicting the Remaining Useful Life of Ship Shafting Using Bayesian Networks with Asymmetric Probability Distributions
- Peng Dong,
- Ge Han and
- Luwen Yuan
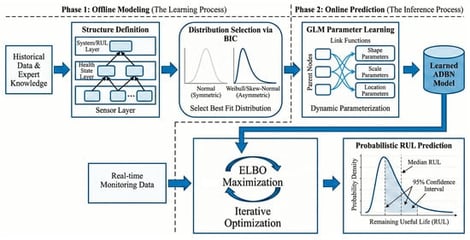
Accurately predicting the remaining useful life (RUL) of ship shafting is crucial for ensuring navigation safety and optimizing operation and maintenance. Traditional Bayesian Network (BN) methods are usually based on the assumption of symmetric distributions. They struggle to effectively characterize common statistical properties such as asymmetry and heavy tails during the shafting degradation process, leading to biases in prediction results. To address this issue, this study proposes an Asymmetric Distribution Bayesian Network (ADBN) method. The method consists of three key components. Firstly, each node selects the optimal asymmetric distribution form based on the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) to better fit data characteristics. Secondly, a Generalized Linear Model (GLM) is used to associate distribution parameters (e.g., location, scale, shape) with parent node states, enabling the conditional distribution to adaptively evolve with the system degradation process. Finally, to tackle the complex inference problem under asymmetric distributions, an approximate algorithm based on stochastic gradient variational inference is designed to ensure prediction timeliness. Experimental results show that the ADBN method outperforms traditional Gaussian networks in terms of Mean Absolute Error in the early, middle, and late stages of RUL prediction, and can provide more accurate prediction intervals. This research offers a probabilistic approach that better aligns with actual statistical properties for modeling ship shafting degradation.
4 March 2026