Journal Description
Poultry
Poultry
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on poultry health, welfare and productivity, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, EBSCO, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Agriculture, Dairy and Animal Science) / CiteScore - Q2 (Veterinary (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 34 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 10.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Poultry is a companion journal of Agriculture.
Impact Factor:
2.1 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.1 (2024)
Latest Articles
Matrix-Dosed Protease Supplementation Enhances Growth Performance, Nutrient Utilization, and Economic Return in Broiler Chickens
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 61; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040061 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
This study evaluated the effects of matrix-dosed protease supplementation on growth performance, nutrient utilization, intestinal morphology, serum biochemistry, carcass traits, and economic return in broiler chickens. A total of 240 Cobb 500 chicks were assigned to six dietary treatments (T0–T5) with four replicates
[...] Read more.
This study evaluated the effects of matrix-dosed protease supplementation on growth performance, nutrient utilization, intestinal morphology, serum biochemistry, carcass traits, and economic return in broiler chickens. A total of 240 Cobb 500 chicks were assigned to six dietary treatments (T0–T5) with four replicates of 10 birds each for 33 days. Protease supplementation, particularly with protease F at 250 g/tonne (T5), significantly increased body weight at day 7 (163.0 ± 1.4 g; p = 0.002) and day 21 (854.0 ± 7.0 g; p = 0.014), and improved the feed conversion ratio at day 33 (1.54 ± 0.01; p = 0.002). Birds in the T5 group consistently exhibited the highest serum total protein (p < 0.001 on Day 21; p = 0.002 on Day 33), albumin (p < 0.001 on both days), and creatinine (p < 0.001 on Day 21; p = 0.006 on Day 33), along with reduced low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels (p < 0.001 on Day 21; p = 0.002 on Day 33). Intestinal morphology was also enhanced, with villus height increasing to 874.0 ± 1.0 µm at day 21 and 931.0 ± 1.0 µm at day 33, accompanied by greater villus height-to-crypt depth ratios (11.23 ± 0.02 and 12.59 ± 0.01, respectively; p < 0.001). Moreover, apparent ileal digestibility of dry matter, crude protein, metabolizable energy, and amino acids were improved in T5 compared with the control and other treatments. Economic analysis showed the highest profit and return on investment (7.01%) in T5, followed by T4 and T2. These findings indicate that matrix-based protease supplementation enhances growth, nutrient absorption, and gut morphology while delivering substantial economic benefits, making it a cost-effective strategy for improving broiler productivity and profitability in commercial production systems.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Methods to Determine the True Ileal Calcium Digestibility of Animal Byproducts in Broiler Diets
by
Leonardo Willian de Freitas, Felipe Dilelis, Noédson de Jesus Beltrão Machado, Débora Vaccari Quaresma, Christiane Silva Souza, Ana Paula Silva Ton and Cristina Amorim Ribeiro de Lima
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 60; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040060 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Three experiments were conducted to evaluate methodologies and determine the digestibility of calcium (Ca) in ingredients of animal origin, using a completely randomized design. In the first experiment, the direct, regression, and substitution methods were compared to determine the true digestibility of calcium
[...] Read more.
Three experiments were conducted to evaluate methodologies and determine the digestibility of calcium (Ca) in ingredients of animal origin, using a completely randomized design. In the first experiment, the direct, regression, and substitution methods were compared to determine the true digestibility of calcium in fishmeal (FM). The true ileal digestibility coefficients (TIDCs) obtained were 0.7558 (substitution), 0.6856 (direct), and 0.6130 (regression). Compared with the regression method, the substitution method resulted in greater digestibility. In the second experiment, the TIDCs of three meat and bone meals (MBM) were evaluated by the direct method. The observed values were 0.6212 (MBM1), 0.5393 (MBM2), and 0.8181 (MBM3). The MBM3 resulted in greater digestibility, while there was no significant difference between MBM1 and MBM2. In the third experiment, the TIDC values of the calcium in three poultry byproduct meal (PBM) samples were determined by the direct method, with coefficients of 0.9440 (PBM1), 0.8673 (PBM2), and 0.9127 (PBM3). No significant differences were observed between the evaluated PBM. The substitution and direct methods were effective for FM. The TIDCs of the MBMs ranged from 0.5393 to 0.8181, whereas those of the offal meals ranged from 0.8673 to 0.9440, indicating the importance of considering the differences in calcium digestibility among the ingredients. The direct method is the most efficient and recommended method for estimating true Ca digestibility because of its simplicity and reduced need for analysis and animals. Individually evaluating each source of Ca in broiler feed formulations is essential because of the wide variation in digestibility between them.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Male Primary Sex Ratio Bias in Goose Eggs Early in the Laying Season: A Pilot Study
by
Valeriy G. Narushin, Michael N. Romanov, Darren K. Griffin, Sabine Klein, Attila Salamon, Sara Copeland, Cormac O’Shea and John P. Kent
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 59; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040059 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In bird eggs, the theoretical expectation of a primary sex ratio (at conception) of 50:50 males/females often fails to materialize. Using PCR technology for sex verification in this pilot study, we evaluated the primary sex ratio of 128 fertilized domestic goose eggs (
[...] Read more.
In bird eggs, the theoretical expectation of a primary sex ratio (at conception) of 50:50 males/females often fails to materialize. Using PCR technology for sex verification in this pilot study, we evaluated the primary sex ratio of 128 fertilized domestic goose eggs (Anser anser) early in the laying season. Over 24 consecutive days of egg collection, 37% more males were found (58% males vs. 42% females). This male-biased trend gradually declined over the period, but an excess of males was still observed. Among the factors for predicting the male sex ratio bias in a particular goose was the egg weight, i.e., heavier eggs tended towards a male phenotype. The embryo sex of the first egg laid and the egg weight change dynamics over the laying period were also noted. The correlation between actual and predicted data was calculated, taking into account three parameters, and found to be 0.724. To explain the effect of an implicit random/non-random process more adequately, we introduced the concept of biased randomness. As well as being of academic interest, research on sex ratio bias is crucial for goose breeding/reproduction programs and important as a step towards understanding the physiological mechanisms that underly sex ratio bias in these animals.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Rearing Systems and Breeder Profile of a Local European Turkey Breed: The Case of the Andalusian Turkey
by
José Ignacio Salgado Pardo, Antonio González Ariza, Juan Vicente Delgado Bermejo, Ignacio Castro Castillo, Cecilio Barba Capote and María Esperanza Camacho Vallejo
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040058 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The present study provides a socio-economic characterization of an endangered turkey population in Europe for the first time, using the example of a southern Spanish population. To this end, 10 Andalusian turkey breeders were subjected to a 102-item survey, which included the following
[...] Read more.
The present study provides a socio-economic characterization of an endangered turkey population in Europe for the first time, using the example of a southern Spanish population. To this end, 10 Andalusian turkey breeders were subjected to a 102-item survey, which included the following sections: personal and educational profile, the role of women in breeding, availability and conditions of facilities, welfare conditions, other equipment, maintenance and hygiene, farm access, feeding management, reproductive and replacement management, mortality, market value, and motivations for breeding. The results exhibited a wide variety in the breeder and rearing system attributes. However, the respondents agreed that rearing local breeds was a non-professionalized hobby. Farmers have generally old facilities and makeshift equipment for breeding the animals, which show strong ancestral instincts and a low requirement for breeding. The main purpose of their rearing is for self-consumption; however, there is an established sale demand for meat associated with Christmas. Breeders show a strong emotional motivation for the preservation of this ancestral population, which shares the rearing system with other endangered breeds. Three different profiles of breeders, traditional, neo-rural, and new-peasant, are responsible for maintaining the population selflessly and without administrative support.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Classification of Broiler Breast Meat: Defining Red, Soft and Exudative Meat as a New Quality Class
by
Sara Kovačević, Nevena Grković, Branko Suvajdžić, Milijana Sindjić, Vladimir Dimitrijević, Zsolt Becskei and Nikola Čobanović
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 57; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040057 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study aimed to describe a new broiler meat quality class—red, soft, and exudative (RSE) meat—and to propose novel classification criteria. Two-step cluster analysis assigned 132 broilers into five meat quality classes using ultimate pH, drip loss, and L* values: pale, soft, and
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to describe a new broiler meat quality class—red, soft, and exudative (RSE) meat—and to propose novel classification criteria. Two-step cluster analysis assigned 132 broilers into five meat quality classes using ultimate pH, drip loss, and L* values: pale, soft, and exudative (PSE); pale, firm, and nonexudative (PFN); RSE; red, firm, and nonexudative (RFN); and dark, firm, and dry (DFD) meat. PSE meat showed the lowest plasma superoxide dismutase activity, highest malondialdehyde activity, greater live and carcass weights, higher breast and leg yields, the lowest initial and ultimate pH, highest initial temperature, the lightest colour (the highest L* and b* values, and the lowest a* value), and the greatest drip, thawing, and cooking losses. RFN meat had the highest superoxide dismutase activity, lowest malondialdehyde activity, and remained within the optimal range for ultimate pH, drip loss, and L* value, generally occupying a midpoint between PSE and DFD meat. RSE meat shared the poor water-holding capacity of PSE but differed by showing a colour similar to RFN and an optimal ultimate pH. PFN meat had firmness comparable to RFN, with appropriate water-holding capacity and optimal ultimate pH, but an undesirably pale colour resembling PSE. DFD meat displayed the highest initial and ultimate pH, lowest drip, thawing, and cooking losses, darkest colour (the lowest L* value), and lowest protein content. This study provides the first evidence of RSE meat in broilers and proposes a classification system based on ultimate pH, drip loss, and L* values to distinguish five quality classes. Further studies are required to validate these findings and develop preventive strategies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Supply Organ Development in Young Broilers in Response to Changing Dietary Fat and Amino Acids in the Starter Period
by
Edward Diehl, Ellen van Eerden, Masja Duijster and René Kwakkel
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 56; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040056 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Early growth in broilers depends on the rapid development of supply organs that enable nutrient use and support the growth of demand tissues such as muscle and bone. This study evaluated whether increasing dietary fat (and thereby AME) and amino acid concentration in
[...] Read more.
Early growth in broilers depends on the rapid development of supply organs that enable nutrient use and support the growth of demand tissues such as muscle and bone. This study evaluated whether increasing dietary fat (and thereby AME) and amino acid concentration in starter diets enhances supply organ development and growth performance in Cobb male broilers. A 2 × 2 factorial design compared two fat levels, corresponding to two AME levels (F− 2750 vs. F+ 3050 kcal/kg), and two standardized ileal digestible lysine levels (AA− 1.0% vs. AA+ 1.2%) in an ideal ratio, to other essential AAs during days 0–11. Higher amino acid concentration consistently improved body weight gain, feed efficiency, and nutrient utilization throughout the trial, whereas the benefits of higher AME were mainly observed during the first 11 days. Diets high in both fat and amino acids reduced early feed intake, suggesting satiety effects. The effects on supply organ development were limited; only the pancreas and small intestine exhibited treatment-related differences in relative weight or allometric growth. In conclusion, increased amino acid concentration in starter diets improved overall broiler performance and nutrient efficiency, whereas dietary fat provided only short-term benefits. These improvements were not consistently associated with morphological changes in supply organs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Poultry Nutrition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Functional Effects of Single-Stage vs. Multi-Stage Incubation Systems and Parental Flock Age on Embryonic Development, Oxidative Stress, and Performance of Male Broiler Chickens
by
Geise Linzmeier, Fernando de C. Tavernari, Aline Zampar, João V. Strapazzon, Paulo V. Oliveira, Roger Wagner, Aleksandro S. da Silva and Marcel M. Boiago
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 55; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040055 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
It is well established that both the age of the breeder hen and the type of incubator can influence the efficiency of the hatching process. However, there is a lack of information in the literature regarding the interaction between these two factors. This
[...] Read more.
It is well established that both the age of the breeder hen and the type of incubator can influence the efficiency of the hatching process. However, there is a lack of information in the literature regarding the interaction between these two factors. This study evaluated the effects of incubator type (multi-stage vs. single-stage) and breeder hen age (35 and 61 weeks) on the hatching parameters, embryonic oxidative stress, performance, carcass yield, and meat quality of male broiler chickens. The embryo livers from the multi-stage incubator presented significantly higher NADP oxidase (NOX) values (p = 0.022), indicating elevated oxidative stress. A significant interaction between breeder age and incubator type was observed for the thiol concentrations, with embryos from older hens incubated in the multi-stage system showing higher thiol levels compared to those from the single-stage system. Birds from these older breeders demonstrated increased breast yield, feed intake, and weight gain, without significant changes in feed conversion ratio. Additionally, the single-stage incubator was associated with reduced embryonic oxidative stress, lower egg weight loss during incubation, and improved early performance of chicks during the first week post-hatch. In conclusion, beyond the previously recognized benefits of single-stage incubation systems, our findings highlight their potential to mitigate oxidative stress in embryos, thereby enhancing early chick development.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Dietary Non-Essential Amino Acids to Lysine Ratio on Egg Performance and Body Composition of Brown-Egg Layers from 20 to 35 Weeks of Age
by
Gert Coertze, Rene Kwakkel, Laura Star and Christine Jansen van Rensburg
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 54; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040054 - 7 Nov 2025
Abstract
Limited published data are available on the ratio of digestible non-essential amino acid (DNEAA) to digestible lysine (DLys) for layers. The effect of different DNEAA-to-DLys ratios on performance parameters of Hy-Line Silver-Brown layers was studied from 20 to 35 weeks. Experimental design was
[...] Read more.
Limited published data are available on the ratio of digestible non-essential amino acid (DNEAA) to digestible lysine (DLys) for layers. The effect of different DNEAA-to-DLys ratios on performance parameters of Hy-Line Silver-Brown layers was studied from 20 to 35 weeks. Experimental design was randomized with ten dietary treatments of increasing concentrations of DNEAA-to-DLys ratio (10.61, 10.84, 11.08, 11.31, 11.54, 11.77, 12.00, 12.23, 12.46, 12.69). Average daily feed intake, total feed intake, laying rate, cumulative egg number, egg weight, hen body weight, feed conversion ratio, egg mass output, albumen weight, eggshell weight, yolk weight, eggshell breaking strength, eggshell thickness, carcass and feather weight, carcass protein, carcass fat, liver weight, and liver fat were recorded. Changing the DNEAA/DLys ratio did not affect production parameters. Yolk and yolk-to-egg weight decreased with an increase in DNEAA/DLys ratio, while albumen-to-yolk and albumen-to-egg weight increased. The DNEAA/DLys ratio did not affect carcass or liver composition, but liver and liver-to-body weight (%) decreased as the DNEAA/DLys ratio increased. Hy-Line Silver-Brown layers during peak production sustained egg production and quality even on the lowest ratio in this study. Low DNEAA/DLys ratios increased liver fat deposition.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Limestone Granulometry and Vitamin D Supplementation in Brown Laying Hens: Implications for Performance, Egg Quality, Bone Health, Thermoregulation, and Behavior in a Hot Environment
by
Carla Lourena Cardoso Macedo Lourenço, Débora Fonteles Lima, Angefferson Bento Evangelista, Alfredo Pinto Rodrigues, João Marcelo Lopes de Abreu, Ednardo Rodrigues Freitas, Carla Nágila Cordeiro, Cláudia Goulart de Abreu, Robson Mateus Freitas Silveira and Silvana Cavalcante Bastos Leite
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 53; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040053 - 5 Nov 2025
Abstract
This study evaluated the effects of limestone particle size and 25-hydroxycholecalciferol supplementation on performance, egg quality, digestive organ biometrics, bone characteristics, thermoregulatory responses, and behavior of brown laying hens reared under hot environmental conditions. The trial lasted five periods of 28 days. A
[...] Read more.
This study evaluated the effects of limestone particle size and 25-hydroxycholecalciferol supplementation on performance, egg quality, digestive organ biometrics, bone characteristics, thermoregulatory responses, and behavior of brown laying hens reared under hot environmental conditions. The trial lasted five periods of 28 days. A total of 270 Lohmann Brown Lite hens (48 weeks old) were allocated in a completely randomized design with a 2 × 2 + 1 factorial arrangement, comprising two limestone particle sizes (MGD 0.568 mm and MGD 1.943 mm) and two supplementation levels of vitamin D (2760 IU and 1380 IU), plus a control diet, totaling five treatments with six replicates each. The dietary treatments were as follows: (1) control diet without vitamin D supplementation; (2) 250 g vitamin D with 100% fine limestone; (3) 125 g vitamin D with 100% fine limestone; (4) 250 g vitamin D with 50% fine + 50% coarse limestone; and (5) 125 g vitamin D with 50% fine + 50% coarse limestone. Productive performance, egg quality, organ biometrics, bone traits, thermoregulatory variables, and behavioral indicators were measured. Data were analyzed by ANOVA, followed by Tukey test (5%), considering the factorial model. There was no interaction between the factors for any parameter evaluated. There was an effect of shift on thermoregulatory variables. The other variables were not influenced by the treatments. These findings indicate that the tested limestone particle sizes can be incorporated in the diets of brown laying hens without affecting performance, egg quality, bone integrity, thermoregulation, or behavior, regardless of vitamin D supplementation, under hot climatic conditions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Poultry Nutrition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploration of the Antibacterial Mechanism of the Aqueous Extract of Bidens pilosa L. Against the Avian Pathogen Escherichia coli
by
Beiwen Zhang, Xiaobing Li, Hongxi Li, Chengzhen Weng, Xinxin Huang, Yuhang Jiang, Longxin Qiu and Hongbo Chen
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 52; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040052 - 29 Oct 2025
Abstract
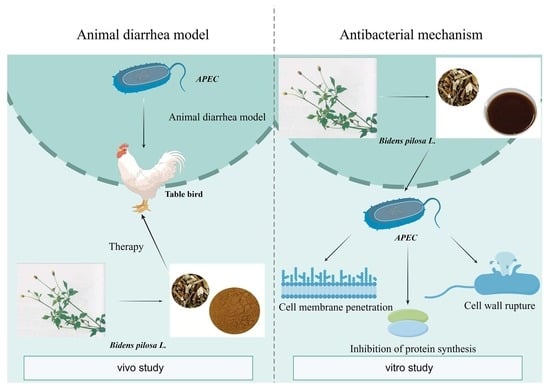
Bidens pilosa L. extract (BPE), a traditional medicine known for its antimicrobial properties, has not been thoroughly investigated for its potential against avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC), a major pathogen responsible for severe economic losses and high mortality in poultry. This study aimed
[...] Read more.
Bidens pilosa L. extract (BPE), a traditional medicine known for its antimicrobial properties, has not been thoroughly investigated for its potential against avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC), a major pathogen responsible for severe economic losses and high mortality in poultry. This study aimed to comprehensively assess the antibacterial activity of BPE against APEC through both in vivo and in vitro experiments and to explore its underlying mechanisms. In a chicken infection model, BPE treatment led to an 80% cure rate and 20% mortality, in contrast to the 90% diarrhea and 70% mortality observed in the untreated model group. BPE also significantly alleviated intestinal tissue damage and reduced serum levels of inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-1β (p < 0.01). In vitro analyses revealed a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 625 mg/mL. BPE dose-dependently suppressed bacterial motility, swarming, and biofilm formation (p < 0.01) and markedly increased membrane permeability, indicated by elevated release of nucleic acids, proteins, and alkaline phosphatase (p < 0.001). Moreover, PCR results showed that treatment with BPE at 1/2 MIC for 24 h significantly downregulated multiple virulence-associated genes, including aatA, papC, ibeB, vat, ompA, iss, fyuA, and irp2 (p < 0.01). These results demonstrate that BPE exerts its anti-APEC effects by damaging cell membrane integrity, inhibiting biofilm formation and motility, and suppressing virulence gene expression. Our findings support the potential of BPE as a natural alternative for controlling APEC infections and contribute a scientific basis for the use of traditional herbal medicine in combating bacterial diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Trends in Antimicrobial Resistance and Its Mitigation in Global Poultry Industry)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Colistin, ESBL, and Multidrug Resistance in Escherichia coli Across the Broiler Production Chain in Karnataka, India
by
Mohammad Nasim Sohail, Srikrishna Isloor, Doddamane Rathnamma, S. Chandra Priya, Belamaranahally M. Veeregowda, Nagendra R. Hegde, Csaba Varga and Nicola J. Williams
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 51; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040051 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
The emergence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) across the broiler production chain holds significant economic, animal, and public health implications. This study investigated phenotypic resistance to 13 antimicrobials and the presence of 35 antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) in Escherichia coli (n = 291)
[...] Read more.
The emergence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) across the broiler production chain holds significant economic, animal, and public health implications. This study investigated phenotypic resistance to 13 antimicrobials and the presence of 35 antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) in Escherichia coli (n = 291) isolated across three broiler production chains (broiler breeder farms, hatcheries, commercial broiler farms, and retail meat shops). An extremely high phenotypic resistance (>70%) to doxycycline, ciprofloxacin, and cefpodoxime, and very high resistance (50–70%) to ampicillin, cefotaxime, gentamicin, and ceftazidime was observed. In addition, 97% of isolates were multidrug-resistant (resistant to ≥1 drug in ≥3 antimicrobial classes), 42% were extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producers, 65% were resistant to third-generation cephalosporins (3GCR), and 21% were resistant to colistin. The Poisson regression model revealed no significant difference in AMR among broiler production stages, except for colistin. Among 35 ARGs tested, 24 (67%) were detected at least once. The most prevalent were tetA, blaTEM, qnrB, qnrS, and aac(6′)-Ib-cr, while qnrD, sul2, blaOXA, and blaCTX-M were detected at lower levels (1–7%). All five tested mcr genes (mcr-1 to mcr-5) were identified in commercial farms and retail shops. No blaNDM, tetB, tetC, tetD, tetM, qnrC, aac(3)-IIa (aacC2), aph(3)-IIa (aphA2), or aac(6′)-Ib genes were found. A strong correlation was observed between AMR phenotypes and ARGs. High AMR among E. coli in broiler production poses significant One Health risks, with widespread MDR, ESBL production, and resistance to critically important antimicrobials. Prudent antimicrobial use, enhanced surveillance and education, farm biosecurity, and One Health strategies are crucial in mitigating these threats.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Trends in Antimicrobial Resistance and Its Mitigation in Global Poultry Industry)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Inclusion of Tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) Residual Oil in Diets for Commercial Hens on Productive Performance, Physiological Parameters and Egg Quality
by
Thiago de Souza, João Paulo Ferreira Rufino, Pablo Garcia Dias, Laiane Ferreira de Souza, Kaisa Freitas de Araújo, Maria Fernanda da Silva Gomes, Maiko Willas Soares Ribeiro, Francisco Alberto de Lima Chaves, Philip Dalbert da Silva Castro, Joel Lima da Silva Junior, Marco Antonio de Freitas Mendonça, Joana Maia Mendes, Emerson Silva Lima, Angela Maria Comapa Barros, Carlos Alexandre Góes Farias, Juliano Carneiro Ramos, Ronner Joaquim Mendonça Brasil, Felipe Dilelis de Resende Sousa, Adriano Teixeira de Oliveira, Suelen Miranda dos Santos and Noedson de Jesus Beltrão Machadoadd
Show full author list
remove
Hide full author list
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 50; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040050 - 22 Oct 2025
Abstract
The increasing demand for sustainable and cost-effective animal feed alternatives has stimulated the use of agro-industrial by-products in poultry diets. This study evaluated the effects of tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) residual oil (TRO), derived from aquaculture waste, on productive performance, physiological responses,
[...] Read more.
The increasing demand for sustainable and cost-effective animal feed alternatives has stimulated the use of agro-industrial by-products in poultry diets. This study evaluated the effects of tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) residual oil (TRO), derived from aquaculture waste, on productive performance, physiological responses, and egg quality in commercial laying hens. A total of 144 Hisex Brown hens were assigned to diets containing 0%, 1.5%, 3.0%, or 4.5% TRO for 63 days. While TRO inclusion did not affect overall productivity, moderate levels (1.5% and 3.0%) improved egg weight, yolk pigmentation, and internal quality (Haugh unit). Hematological and biochemical parameters indicated metabolic adaptations, with increased cholesterol and decreased triglycerides in treated groups. The yolk fatty acid profile revealed higher omega-3 content with TRO inclusion, but lipid oxidation (TBARS) also increased, especially at higher levels. Sensory evaluation showed reduced aroma and flavor acceptability in eggs from hens fed 3.0% and 4.5% TRO. These findings suggest that moderate TRO inclusion can enhance egg nutritional value and support sustainable aquaculture waste reuse, though excessive levels may compromise product acceptability. Optimal inclusion levels should be further explored to balance metabolic benefits, oxidative stability, and consumer preferences.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Black Cumin (Nigella sativa) as a Healthy Feed Additive for Broiler Production: A Focused Review
by
Sanjida Akter, Giovana M. Longhini, Md Saidul Haque, Yuhua Z. Farnell and Yuxiang Sun
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 49; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040049 - 10 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Following restrictions on antibiotic growth promoters in poultry production, there is growing interest in natural feed additives that support health and productivity. Among these, black cumin (Nigella sativa) has emerged as a promising candidate due to its antioxidant, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory
[...] Read more.
Following restrictions on antibiotic growth promoters in poultry production, there is growing interest in natural feed additives that support health and productivity. Among these, black cumin (Nigella sativa) has emerged as a promising candidate due to its antioxidant, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory properties. Most studies report that black cumin, in the form of whole seeds, seed meal, or seed oil, improves body weight gain and feed conversion ratio, enhances antioxidant and immune status, and provides additional benefits on lipid profiles, liver enzymes, and cecal microbial balance. This review provides a focused synthesis of recent studies (2014–2025) on black cumin supplementation in broiler chickens, considering its various forms (whole seeds, seed meal, seed oil, and nano-formulations) and production contexts (healthy, heat-stressed, and disease-challenged birds). Specifically, this review compares responses across different forms and doses, evaluates effects on growth performance, immune function, gut health, antioxidant status, liver metabolism, and meat and carcass quality, and highlights inconsistencies among studies. Additionally, it identifies key research gaps to guide future investigations, including optimal dosing, long-term safety, and practical applications in commercial production. Overall, black cumin shows potential as a natural alternative to antibiotics, but further standardized, large-scale studies are needed to confirm its efficacy and feasibility in sustainable poultry farming.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Relationship Between Animal Welfare Metrics, Production, Slaughter, and Economic Gain in Poultry Farming
by
Deivid Kelly Barbosa, Vivian A. R. C. Heiss, Maria F. C. Burbarelli, Leonardo O. Seno, Rodrigo G. Garcia, Rita T. R. Pietramale and Fabiana R. Caldara
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 48; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040048 - 2 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Animal welfare (AW) is increasingly being discussed and mandated in chicken production, both by current Brazilian legislation and by importing markets. Industries continually seek greater financial returns, and within this context, it has been observed that the proper implementation of animal welfare principles
[...] Read more.
Animal welfare (AW) is increasingly being discussed and mandated in chicken production, both by current Brazilian legislation and by importing markets. Industries continually seek greater financial returns, and within this context, it has been observed that the proper implementation of animal welfare principles effectively reduces losses by minimizing carcass condemnations due to injuries, thereby significantly contributing to in-creased profitability. The economic impact of non-compliance with these welfare standards in broiler production is well documented in the scientific literature. However, the same level of concern is not observed regarding the financial impact on integrated producers, who supply the raw materials. The present study aims to systematically map, contextualize, quantify, and qualitatively analyze articles evaluating the implementation of animal welfare in industrial broiler production and its impact on the financial returns of producers and integrated companies. The primary descriptor used was “animal welfare.” To quantify the relevant articles, the Proknow-C method was applied, followed by a similarity analysis using VoSViewer® software version 1.6.19 for systematic content evaluation. Descriptor combinations were led by animal welfare, followed by broiler pro-duction, poultry production, slaughter, economy, and rural producers. Although a significant number of articles address AW, those focused exclusively on chicken production are far fewer, declining even more when carcass condemnations are considered. Only six studies included the descriptor “economic,” and just three included “producer.” The con-tent of these nine studies was systematically reviewed, with two excluded and seven selected for discussion. Among the seven analyzed studies, none specifically examined the economic impact of AW implementation for the producer, clearly highlighting a significant research gap.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Caprylic Acid on the Cecal Colonization of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Heidelberg and the Cecal Microbiome in Broiler Chickens
by
Shijinaraj Manjankattil, Dhananjai Muringattu Prabhakaran, Anup Kollanoor Johny, Claire Peichel, Divek V. T. Nair, Grace Dewi, Jason Langlie, Trevor J. Gould and Annie M. Donoghue
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 47; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040047 - 1 Oct 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study determined the efficacy of in-feed supplementation of a medium-chain fatty acid, caprylic acid (CA), on the cecal colonization of multidrug-resistant (MDR) Salmonella Heidelberg (SH) and its effect on the cecal microbiome of commercial broilers. A total of 24, 4-week-old commercial Ross
[...] Read more.
This study determined the efficacy of in-feed supplementation of a medium-chain fatty acid, caprylic acid (CA), on the cecal colonization of multidrug-resistant (MDR) Salmonella Heidelberg (SH) and its effect on the cecal microbiome of commercial broilers. A total of 24, 4-week-old commercial Ross 708 chickens were randomly allocated to two replicates of four treatment groups in eight BSL2 isolators (3 birds/isolator): Negative control (NC), Positive Control (PC), Antibiotic group (AB), and caprylic acid (CA) groups. The birds received a Salmonella-free standard corn–soy-based diet, with the broilers in the AB receiving 50 g/ton bacitracin methylene disalicylate, and the CA group receiving caprylic acid (1% w/w), in feed from days 1 to 35. All birds, except those in the NC group, were challenged with ~3.7 log10 CFU of MDR SH/5 mL by crop gavage on day 29. Cecal samples were collected 7 days after the challenge for SH recovery by direct plating and enrichment, as well as for DNA extraction for 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. Compared to the PC group, a 3.6 log10 CFU/g reduction in SH was observed in the CA group (p < 0.05). Although no significant effect of CA on cecal microbial composition was observed, a significant difference in taxonomic α- and β-diversities was observed in the AB. CA also resulted in significant differences in hub taxa compared to PC in the network association analysis, indicating a potential role for microbiome modulation in its mechanism of action.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Biosecurity Gaps and Food Production Practices in Subsistence and Differentiated Backyard Poultry Systems in Central Chile
by
Víctor Marambio, Francisca Di Pillo, Cecilia Baumberger, Cristobal Oyarzún, Pablo Galdames, Tamara Palma, Pedro Jimenez-Bluhm, Javiera Cornejo, Stacey Schultz-Cherry and Christopher Hamilton-West
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 46; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040046 - 30 Sep 2025
Abstract
Backyard poultry systems (BPS) are the most widespread form of animal production worldwide, contributing to household economies and improving food availability. However, limited biosecurity measures and close human–animal interactions raise concerns regarding zoonotic disease transmission. In recent years, consumer-driven motivations have given rise
[...] Read more.
Backyard poultry systems (BPS) are the most widespread form of animal production worldwide, contributing to household economies and improving food availability. However, limited biosecurity measures and close human–animal interactions raise concerns regarding zoonotic disease transmission. In recent years, consumer-driven motivations have given rise to non-traditional BPS with differential attributes (BPS-DA), yet there is limited knowledge about their food production practices. This study aimed to characterize and compare practices across 25 BPS and 25 BPS-DA in the Metropolitan Region using surveys, interviews, and direct observations of egg collections and poultry slaughters. Eggs were the main animal product in both systems, with women primarily responsible for care. Poultry slaughter was reported exclusively in BPS (60%), generally performed under inadequate hygienic conditions and without veterinary oversight. These practices, (poultry slaughter, food production and handling), may considerably increase the risk of human exposure to zoonotic pathogens, such as avian influenza viruses. In contrast, BPS-DA prioritized birds as companion animals (60%), free-range rearing (68%), and hobby-based production (80%). While both systems showed limited biosecurity, significant differences were found in the use of dedicated footwear (p = 0.01; V = 0.35), egg collection sites (p = 0.04; V = 0.29), and refrigeration (p = 0.004; V = 0.41). Veterinary access was limited in both (32% in BPS; 44% in BPS-DA). These findings highlight critical gaps in health management and underscore the need for context-specific educational and regulatory strategies for safer backyard poultry production.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biosecurity in Poultry)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Molecular Characterization of Fowl Adenovirus from Brazilian Poultry Farms
by
André Salvador Kazantzi Fonseca, Diéssy Kipper, Nilo Ikuta and Vagner Ricardo Lunge
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 45; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040045 - 28 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Fowl adenovirus (FAdV) can cause different poultry diseases with economic losses in the broilers and layers commercial farms. FAdV is currently classified into five species and 12 serotypes, disseminated in poultry flocks worldwide. The present study aimed to identify FAdV species and serotypes
[...] Read more.
Fowl adenovirus (FAdV) can cause different poultry diseases with economic losses in the broilers and layers commercial farms. FAdV is currently classified into five species and 12 serotypes, disseminated in poultry flocks worldwide. The present study aimed to identify FAdV species and serotypes in Brazilian poultry farms. A total of 678 chicken flocks from the main Brazilian poultry-producing regions were evaluated for FAdV infection between 2020 and 2023. FAdV was detected by a real-time PCR targeting 52K gene and further genotyped by partial sequencing of the hexon gene followed by phylogenetic analyses. The results demonstrated that FAdV was detected in 72 flocks (10.6%). In 46 of these samples, FAdV species and serotypes could be identified, including three main species: Aviadenovirus ventriculi (FAdV-A = 15), Aviadenovirus gallinae (FAdV-D = 15) and Aviadenovirus hepatitidis (FAdV-E = 16). Phylogenetic analysis based on 173 partial hexon sequences (including sequences from this study, 44 previously sequenced in Brazil, and 86 data from other countries) revealed five separate clades for FAdV species. All Brazilian FAdVs were classified into the same three species reported above (FAdV-A = 19, FAdV-D = 34, FAdV-E = 37), and also in well-supported subclades for each serotype: FAdV-A1 (n = 19), FAdV-D9 (n = 1), FAdV-D11 (n = 33), FAdV-E6 (n = 1), FAdV-E8a (n = 33), FAdV-E8b (n = 3). Amino acid substitutions in the hyper variable regions (1, 2 and 3) and conserved motifs of the Hexon protein were further analyzed, enabling discrimination between closely related serotypes. This study demonstrates the circulation of different FAdVs in Brazil, highlighting FAdV-A1, FAdV-D9, FAdV-D11, FAdV-E6, FAdV-E8a and FAdV-E8b. The findings reported here also indicate genetic and amino acid diversity in the Hexon protein of the FAdVs in Brazilian poultry farms, which are of importance for molecular surveillance and poultry diseases control strategies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Gut Microbiota—Campylobacter jejuni Crosstalk in Broiler Chickens: A Comprehensive Review
by
Bereket Dessalegn, Motuma Debelo, Michael Hess and Wageha A. Awad
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 44; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040044 - 25 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The interaction between gut microbiota and C. jejuni in the guts of broiler chickens is essential for the bacterium’s growth and potential pathogenicity. Recent findings highlighted the significance of modifying gut microbiota in relation to higher C. jejuni colonization rates and improved immune
[...] Read more.
The interaction between gut microbiota and C. jejuni in the guts of broiler chickens is essential for the bacterium’s growth and potential pathogenicity. Recent findings highlighted the significance of modifying gut microbiota in relation to higher C. jejuni colonization rates and improved immune responses. This study suggested that a varied and balanced microbiota aids in decreasing and preventing C. jejuni proliferation via mechanisms including competitive exclusion, the synthesis of antimicrobial peptides, and the modulation of the chicken immune response. C. jejuni demonstrates adaptability in the gut environment by encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria while inhibiting others, improving the way it acquires nutrients, and modifying the transcriptional response of its virulence factors. The dynamic nature of these microbiota communities has caused differences in the results of how gut microbiota and C. jejuni proliferation interact. Understanding the relationships between gut microbiota and C. jejuni is critical for developing strategies to mitigate the impact of C. jejuni in broiler chickens. This review compiles information on the relationships between gut microbiota and C. jejuni proliferation in broiler chickens and offers commentary on how the findings could improve gut health and food safety.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Precision Livestock Farming: YOLOv12-Based Automated Detection of Keel Bone Lesions in Laying Hens
by
Tommaso Bergamasco, Aurora Ambrosi, Vittoria Tregnaghi, Rachele Urbani, Giacomo Nalesso, Francesca Menegon, Angela Trocino, Mattia Pravato, Francesco Bordignon, Stefania Sparesato, Grazia Manca and Guido Di Martino
Poultry 2025, 4(4), 43; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4040043 - 24 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Keel bone lesions (KBLs) represent a relevant welfare concern in laying hens, arising from complex interactions among genetics, housing systems, and management practices. This study presents the development of an image analysis system for the automated detection and classification of KBLs in slaughterhouse
[...] Read more.
Keel bone lesions (KBLs) represent a relevant welfare concern in laying hens, arising from complex interactions among genetics, housing systems, and management practices. This study presents the development of an image analysis system for the automated detection and classification of KBLs in slaughterhouse videos, enabling scalable and retrospective welfare assessment. In addition to lesion classification, the system can track and count individual carcasses, providing estimates of the total number of specimens with and without significant lesions. Videos of brown laying hens from a commercial slaughterhouse in northeastern Italy were recorded on the processing line using a smartphone. Six hundred frames were extracted and annotated by three independent observers using a three-scale scoring system. A dataset was constructed by combining the original frames with crops centered on the keel area. To address class imbalance, samples of class 1 (damaged keel bones) were augmented by a factor of nine, compared to a factor of three for class 0 (no or mild lesion). A YOLO-based model was trained for both detection and classification tasks. The model achieved an F1 score of 0.85 and a mAP@0.5 of 0.892. A BoT-SORT tracker was evaluated against human annotations on a 5 min video, achieving an F1 score of 0.882 for the classification task. Potential improvements include increasing the number and variability of annotated images, refining annotation protocols, and enhancing model performance under varying slaughterhouse lighting and positioning conditions. The model could be applied in routine slaughter inspections to support welfare assessment in large populations of animals.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns and Resistance Genes of Enterococci from Broiler Chicken Litter
by
Tam T. Tran, Niamh Caffrey, Haskirat Grewal, Yuyu Wang, Rashed Cassis, Chunu Mainali, Sheryl Gow, Agnes Agunos, Sylvia Checkley and Karen Liljebjelke
Poultry 2025, 4(3), 42; https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4030042 - 12 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Enterococci, commonly found in the normal intestinal flora of humans and animals, have emerged as an important human pathogen. A total of 184 isolates (88 isolates in 2015 and 96 isolates in 2016) were collected from 46 flocks. Two predominant enterococcus species were
[...] Read more.
Enterococci, commonly found in the normal intestinal flora of humans and animals, have emerged as an important human pathogen. A total of 184 isolates (88 isolates in 2015 and 96 isolates in 2016) were collected from 46 flocks. Two predominant enterococcus species were identified: Enterococcus faecalis (59%) and Enterococcus faecium (~39%). Resistance to penicillin was significantly decreased in the overall enterococci community, while it remained unchanged in the multi-class drug resistant (MDR) community. We identified the emeA and efrAB genes, which encode efflux pump systems, in 93% (26/28) of the MDR isolates with (intermediate) resistance to levofloxacin. The ermB gene was present in all MDR strains with resistance to erythromycin. The lsa gene was detected in 87% (84/97) of the MDR isolates with resistance to quinupristin/dalfopristin. About 82.2% of MDR strains in 2015 and 100% of MDR strains in 2016 carried the insertion sequence IS256, which is known to be associated with AMR genes, conferring resistance to erythromycin, gentamicin and vancomycin in enterococci. These results support the need for monitoring AMR in Gram-positive bacteria in poultry production, specifically in broiler chicken farms, to complement current AMR data, and develop a timely intervention framework.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agriculture, Dairy, Poultry, Veterinary Sciences, Animals
Practical Methods for Accommodating Behavioral Needs and Improving the Wellbeing of Farm Animals: 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Temple Grandin, Kurt VogelDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Animals, Dairy, Genes, Agriculture, Poultry, Ruminants, Veterinary Sciences
Application of Reproductive and Genomic Biotechnologies for Livestock Breeding and Selection: 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Manuel García-Herreros, Pedro Manuel AponteDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topic in
Agriculture, Animals, Poultry, Ruminants
The Environmental Footprint of Animal Production
Topic Editors: Giulia Ferronato, Vincenzo LopreiatoDeadline: 31 May 2026
Topic in
Agriculture, Animals, Antibiotics, Microorganisms, Poultry, Pathogens, Veterinary Sciences, Biologics
Advances in Infectious and Parasitic Diseases of Animals
Topic Editors: Felipe M. Salvarani, Sheyla Farhayldes Souza Domingues, Júlia Angélica Gonçalves Da SilveiraDeadline: 31 December 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Poultry
Current Research and Key Issues in Poultry Immunology
Guest Editors: Dieter Liebhart, Christine JansenDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Poultry
Recent Trends in Antimicrobial Resistance and Its Mitigation in Global Poultry Industry
Guest Editors: Ilias Giannenas, Vasudevan GowthamanDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Poultry
Biosecurity in Poultry
Guest Editors: Maria Pia Franciosini, Guido GrilliDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Poultry
Basic and Applied Aspects of Incubation Oriented to the Needs of the Embryos
Collection Editor: Barbara Tzschentke












