- Article
Condensate Dark Stars Beyond the Mean-Field Approximation: The Lee–Huang–Yang Correction
- Grigoris Panotopoulos
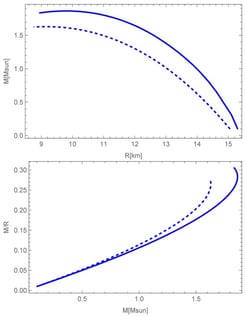
The paper investigates the structural properties of self-gravitating fluid spheres composed of a dilute, homogeneous, and ultracold Bose gas, assuming repulsive, short-range interactions. For the first time, the Lee–Huang–Yang (LHY) correction is incorporated to the standard polytropic equation-of-state with index , which extends beyond the Hartree mean-field approximation by accounting for quantum fluctuations. The findings indicate that this correction significantly affects the mass–radius relationships and other properties of condensate dark stars, such as the compactness factor and tidal Love numbers. Notably, the impact of the LHY correction is more pronounced for equations of state that support higher maximum stellar masses.
10 March 2026