Epigenetics in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms and Acute Myeloid Leukemia
A topical collection in Cells (ISSN 2073-4409). This collection belongs to the section "Cellular Pathology".
Viewed by 30747Editor
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
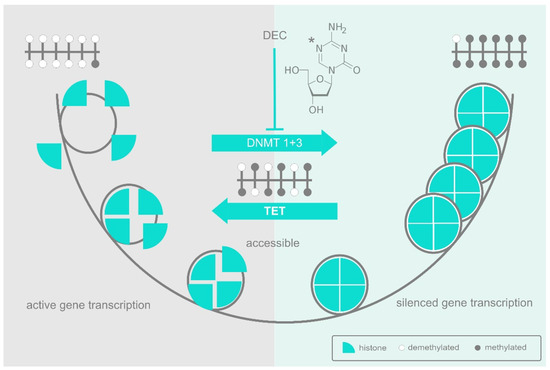
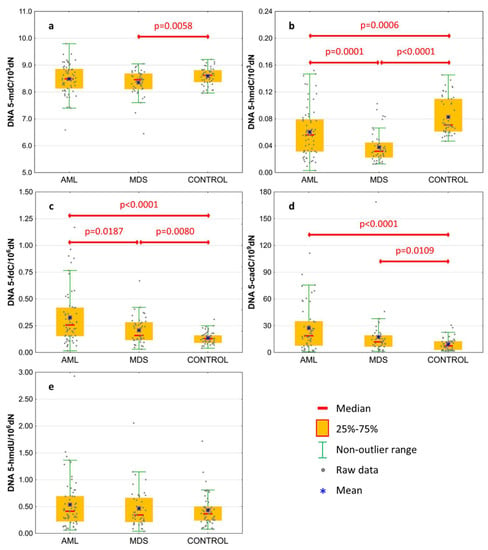
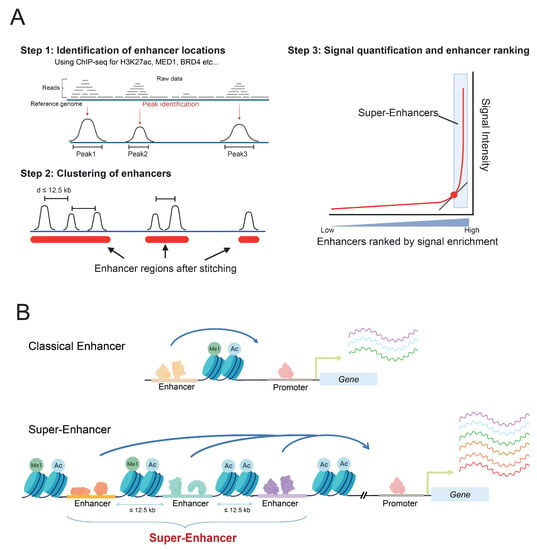
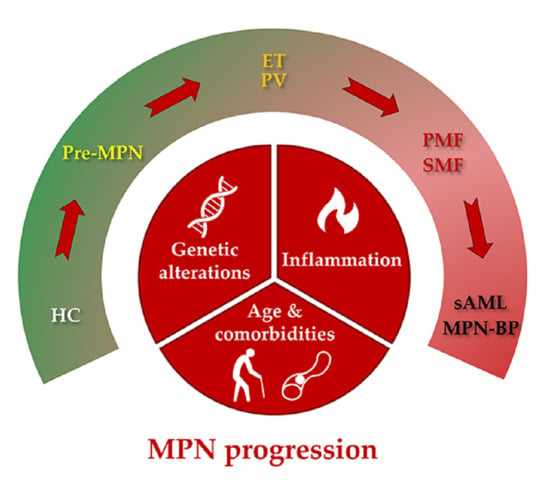
Research over the past years has revealed the increasingly intricate landscape of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN). Today it is well-appreciated that the heterogeneity of malignant cells in both diseases is triggered by sets of cytogenetic abnormalities and somatic mutations. Besides this genetic complexity, diversification in the epigenome has also been identified as a key player in both tumors. The multidimensional epigenetic picture integrates several layers of (dys)regulated DNA methylation, histone modification, and microRNA modulation. Indeed, abnormal epigenetic signatures, some of which may be linked to specific somatic mutations, frequently present in AML and MPN can profoundly disrupt the phenotype of hematopoietic cells. Furthermore, epigenetic (dys)regulation has emerged as an intersection of several key hallmarks of cancer such as immunology and metabolism.
Thus, understanding the functional link between genetic and epigenetic heterogeneity in AML and MPN, and what they contribute to the disease is an important area of research that would aid clinical decision-making and enhance drug development.
In this Topical Collection, we will discuss the current trends in epigenetic dysregulation in AML and MPN, their interactions with other cancer mechanisms, the interrelation between epigenetics and genetics, and the research on the development of drugs targeting epigenetic regulators, such as IDH1/2 inhibitors and BET proteins, as monotherapies or combination therapies in AML and MPN.
Dr. Haifa Kathrin Al-Ali
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- AML
- MPN
- epigenetics
- genes
- mutations
- therapy
- DANN methylation
- histone modification
- microRNA