-
 RASopathy and Sudden Cardiac Death: A Literature Review
RASopathy and Sudden Cardiac Death: A Literature Review -
 Drug Allergy in Hospitalized Patients: Three Years of Consultation Experience in a Tertiary Care Setting
Drug Allergy in Hospitalized Patients: Three Years of Consultation Experience in a Tertiary Care Setting -
 The Role of Microglial Activation in the Pathogenesis of Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies
The Role of Microglial Activation in the Pathogenesis of Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies -
 Polyoxometalates' Progress for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
Polyoxometalates' Progress for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
Journal Description
BioChem
BioChem
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on biochemistry published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, EBSCO and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 33.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
Regulatory Stipulations and Scientific Underpinnings for Inhaled Biologics for Local Action in the Respiratory Tract—Part II: A Characterization of Inhaled Biological Proteins
BioChem 2026, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem6010004 - 29 Jan 2026
Abstract
Following the discovery of therapeutic molecules and the identification of specific biological targets, preparation of regulatory dossiers entails extensive product development and characterization to support their safety, efficacy, and stability. We have examined the drug development and relevant regulatory considerations related to inhaled
[...] Read more.
Following the discovery of therapeutic molecules and the identification of specific biological targets, preparation of regulatory dossiers entails extensive product development and characterization to support their safety, efficacy, and stability. We have examined the drug development and relevant regulatory considerations related to inhaled biological proteins in the accompanying article. This review focuses on the characterization of locally acting inhaled biological proteins. Drug product characterization is a regulatory requirement, and it ensures drug product safety, efficacy, stability, and usability by the target populations. Together, these two articles provide a comprehensive discussion based on our review and analysis of the available open literature. We have attempted to fill gaps and simulate discussion of challenges following sound scientific pathways. This approach has the prospect of addressing regulatory expectations leading to rapid solutions to unmet medical needs. The robustness of characterization strategies and the development of analytical methods used in the in vitro testing for the evaluation of drug product attributes is assured through application of the Design-of-Experiment (DOE) and Quality-by-Design (QBD) approaches. Drug product characterization entails a variety of in vitro studies evaluating drug products for purity and contamination, and determination of drug delivery by the intended route of administration. Measurement of the proportion of the labeled amount per dose and the form suitable for delivery to the intended target sites is central to this assessment. For respiratory Drug–Device combination products, the testing may vary with the product designs. However, determination of the single-dose content, delivered-dose uniformity, aerodynamic particle size distribution, and device robustness when used by the target populations is common to all combination products. Characterization of aerosol plumes is limited to inhalation aerosols that produce specific aerosol clouds upon actuation. The flow rate dependency of devices is also examined. Product characterization also includes safety-related product attributes such as degradation products and leachables. For inhaled biological proteins, safety-related in vitro testing includes additional testing to assure maintenance of the three-dimensional structural integrity and the sustained biological activity of the drug substance in the formulation, during aerosolization and upon deposition. This article discusses various tests employed for regulatory-compliant product characterization. In addition, the stability testing and handling of possible changes during product development and post-approval are discussed.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Lactic Acid Bacteria: From Bioprocessing to Nanomedicine
by
Maryam Rezvani, Maria Manconi and Nejat Düzgüneş
BioChem 2026, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem6010003 - 27 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Lactic acid bacteria have long been recognized as pivotal microorganisms in food fermentation and health promotion. However, their significance has recently grown due to innovative applications in various fields, particularly at the intersection of biotechnology and nanotechnology. This study aimed to
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Lactic acid bacteria have long been recognized as pivotal microorganisms in food fermentation and health promotion. However, their significance has recently grown due to innovative applications in various fields, particularly at the intersection of biotechnology and nanotechnology. This study aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of these emerging applications. Methods: The latest scientific literature was drawn from online databases and thoroughly reviewed. The new nomenclature system based on the post-2020 reclassification was used for reports. Results: The current study highlighted the evolving role of lactic acid bacteria, beyond their traditional use as starter cultures for food fermentation, in newer challenges, including the production of high-value bioactive compounds through bioprocessing under optimal conditions to enhance the yield, underlining the involved genes and pathways. Furthermore, this review addressed the beneficial effects of lactic acid bacteria as probiotics, postbiotics, and paraprobiotics in the treatment of various diseases and disorders, their application in the production of functional foods, and the encapsulation of their bioproducts to produce advanced health-promoting functional ingredients. The potential use of lactic acid bacteria to synthesize metallic nanoparticles, minicells, and carbon dots was also explored, promising significant advancements in nanomedicine. Conclusions: This review could open a new horizon for leveraging the potential of lactic acid bacteria in biotechnology, food science, and nanomedicine. The multilateral perspective offered here would provide a foundation for future research and development to exploit the capabilities of lactic acid bacteria across these innovative fields.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in BioChem, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Quantum and Artificial Intelligence in Drugs and Pharmaceutics
by
Bruno F. E. Matarèse
BioChem 2026, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem6010002 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
The pharmaceutical industry faces a broken drug development pipeline, characterized by high costs, slow timelines and is prone to high failure rates. The convergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and quantum technologies is poised to fundamentally transform this landscape. AI excels in interpreting complex
[...] Read more.
The pharmaceutical industry faces a broken drug development pipeline, characterized by high costs, slow timelines and is prone to high failure rates. The convergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and quantum technologies is poised to fundamentally transform this landscape. AI excels in interpreting complex data, optimizing processes and designing drug candidates, while quantum systems enable unprecedented molecular simulation, ultra-sensitive sensing and precise physical control. This convergence establishes an integrated, self-learning ecosystem for the discovery, development, and delivery of therapeutics. This framework co-designs strategies from molecular targeting to formulation stability, compressing timelines and enhancing precision, which may enable safer, faster, and more adaptive medicines.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Drug Delivery: Latest Advances and Prospects)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Long-Term Stability of Preservative-Free Urine Samples: Superior Biomolecular Integrity at −80 °C and in Lyophilized Form
by
Ranbala Kumari, Jasleen Kaur, Mishi Wasson, Deepika Trehan, Pawan Vasudeva, Niraj Kumar, Nitu Kumari and Usha Agrawal
BioChem 2026, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem6010001 - 25 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Proper storage of biofluids is critical to preserving their molecular integrity for downstream applications. This study investigates the effect of different storage temperatures on the stability of preservative-free urine samples over a two-year period. Methods: Urine samples were collected, aliquoted, and stored
[...] Read more.
Background: Proper storage of biofluids is critical to preserving their molecular integrity for downstream applications. This study investigates the effect of different storage temperatures on the stability of preservative-free urine samples over a two-year period. Methods: Urine samples were collected, aliquoted, and stored at −80 °C, −20 °C, 4 °C, and in lyophilized form. Samples were retrieved at 0, 6, 12, and 24 months for analysis. DNA, RNA, and protein were isolated and evaluated using agarose and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic acid quality was assessed using Nanodrop spectrophotometry and Bioanalyzer profiles. Results: A significant increase in pH and a concurrent decline in protein concentration were observed within the first six months at −20 °C and 4 °C. These changes plateaued after six months. Samples stored at −80 °C and in lyophilized form showed minimal variation in pH and retained higher protein stability. DNA quality, based on 260/280 and 260/230 ratios and electrophoretic band integrity, was well-preserved under these two conditions. RNA quality remained stable for up to 12 months but declined thereafter. Conclusions: Storage at −80 °C or in lyophilized form offers optimal preservation of protein concentration and nucleic acid quality in preservative-free urine samples over extended storage durations. However, lyophilization offers a cost-effective and logistically practical alternative, as samples can be stored at room temperature without the requirement of ultra-low freezers.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Frequency of HLA-A, -B, -DRB1, and -DQB1 Alleles in Moroccan Adult Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Case–Control Study
by
Khalid Laaziri, Abdelmajid Zyad, Fatima Ezzahra Lahlimi, Ouadii Abakarim, Illias Tazi, Ikram Brahim, Nadia Lakhouaja, Raja Hazime, El Mostafa Mtairag and Brahim Admou
BioChem 2025, 5(4), 44; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5040044 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common acute leukemia in adults, with over 50% of individuals succumbing to the disease annually. This study aimed to assess the correlation between human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in an
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common acute leukemia in adults, with over 50% of individuals succumbing to the disease annually. This study aimed to assess the correlation between human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in an adult Moroccan cohort. We included 60 persons with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who were eligible for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and compared them to a control group of 90 healthy adults. Methods: Patients and controls were subjected to HLA class I and II typing utilizing either sequence-specific primers (SSP) or sequence-specific oligonucleotides (SSO) in polymerase chain reaction-based methodologies. Results: The AML categories were predominantly represented by AML2, AML3, and AML4, comprising 36.66%, 30%, and 16.66%, respectively. We identified a notable correlation between HLA-A*11 (p = 0.003) and HLA-B*27 (p = 0.005) with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and for HLA class II allele groups, we detected an elevated frequency of HLA-DQB1*05 (p = 0.002) in adult AML patients. We identified a notable correlation between AML 2 and the allele groups examined, namely with HLA class I: HLA-A*11 (p = 0.0003) and HLA-B*27 (p = 0.00006). Conclusion: Our study suggests a potential association between specific HLA alleles and the development of AML specifically AML type 2 in adults. Further larger studies are needed to confirm these findings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Targeting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: Emerging Mechanisms and Therapeutics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
The Role of Microglial Activation in the Pathogenesis of Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies
by
Abba Musa Abdullahi, Shah Taha Sarmast and Usama Ishaq Abdulrazak
BioChem 2025, 5(4), 43; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5040043 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Microglial cells are the resident immune cells in the central nervous system (CNS) and constitute the brain’s innate immune system. They are the smallest of the glial cells and are derived from phagocytic white blood cells, fetal monocytes, which migrate from
[...] Read more.
Background: Microglial cells are the resident immune cells in the central nervous system (CNS) and constitute the brain’s innate immune system. They are the smallest of the glial cells and are derived from phagocytic white blood cells, fetal monocytes, which migrate from the blood into the brain during development. On the other hand, epilepsy is a chronic condition defined as recurrent unprovoked seizures, with at least two seizures occurring over 24 h apart. Methods: To determine the role of microglial activation in the pathogenesis of drug-resistant epilepsy, we systematically searched published data for biomarkers of microglial activation from main databases including PubMed, PubMed Central, Scopus, Embase, Google Scholar, and Medline. Two research registries were also searched: the Cochrane Registry and clinicaltrial.gov. Data was collected after applying inclusion and exclusion criteria and studies were appraised critically. Both Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and regular keyword search strategies were employed. Results: Our systematic review shows significant elevation of biomarkers of microglial activation in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy, suggesting its role in the disease’s pathogenesis. Conclusions: Microglia cells are therefore considered as a special type of mononuclear phagocytes found in the CNS that plays important roles in both the brain’s immunity and homeostatic functions. The role of microglial activation in the pathogenesis of drug-resistant epilepsy is an active area of study, with potential therapies for drug-resistant epilepsy that target microglia currently being investigated.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Drug Allergy in Hospitalized Patients: Three Years of Consultation Experience in a Tertiary Care Setting
by
Christian P. Ratti, Alessandra Chiei Gallo, Francesca Barei, Alice Botta, Matteo Cavara, Eleonora Bono, Lea Caron, Valeria G. R. Ortolani and Enrico Iemoli
BioChem 2025, 5(4), 42; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5040042 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Drug hypersensitivity reactions (DHRs) are an important cause of morbidity in hospitalized patients, but their epidemiology and management in the inpatient setting are not well defined. Mislabeling of drug allergies may lead to inappropriate treatment and reduced antimicrobial stewardship. This study
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Drug hypersensitivity reactions (DHRs) are an important cause of morbidity in hospitalized patients, but their epidemiology and management in the inpatient setting are not well defined. Mislabeling of drug allergies may lead to inappropriate treatment and reduced antimicrobial stewardship. This study aimed to characterize the clinical profile, diagnostics, and management of inpatients referred for suspected drug allergy in a tertiary care hospital. Methods: We retrospectively reviewed all adult inpatients (≥18 years) at Luigi Sacco Hospital (Milan, Italy) who received allergology consultation between 1 June 2022 and 31 May 2025. Data on demographics, reaction type, culprit drugs, investigations, and management were collected. Immediate reaction severity was graded using the United States Drug Allergy Registry (USDAR) scale; delayed reactions were classified as severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs) or non-SCARs. Logistic regression identified predictors of severity. Results: Among 35,438 admissions, 334 patients (0.9%) were evaluated; median age was 65 years, 51.2% were female, 67.4% had atopic comorbidities, and 55.1% reported prior drug allergy. Immediate reactions occurred in 49.1%, delayed in 43.7%. Cutaneous involvement was present in 86.8%, anaphylaxis in 6.6%, and SCARs in 3.9%. Antibiotics—particularly β-lactams—were most often implicated. In multivariate analysis, antibiotic exposure and older age were linked to more severe immediate reactions, while the absence of atopy predicted SCARs. Desensitization was successfully performed in 16.2% of patients. Conclusions: DHRs in inpatients are frequent and often involve high-risk drugs. Structured inpatient allergology services and an “allergy stewardship” approach may reduce DHR-related risks, support optimal therapy, and improve antimicrobial use strategies in tertiary care settings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in BioChem, 2nd Edition)
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Polyoxometalates’ Progress for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
by
Manuel Aureliano, João Mateus and David Manjua Rijo
BioChem 2025, 5(4), 41; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5040041 - 20 Nov 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) signifies a devastating impact on the quality of life of patients and their families. At a biomolecular level, AD is characterized by the deposition of extracellular plaques of β-amyloid (Aβ), affecting language, spatial navigation, recognition abilities and memory. Among the
[...] Read more.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) signifies a devastating impact on the quality of life of patients and their families. At a biomolecular level, AD is characterized by the deposition of extracellular plaques of β-amyloid (Aβ), affecting language, spatial navigation, recognition abilities and memory. Among the selected 30 articles about polyoxometalates (POMs) and AD published from 2011 to 2025, pure POMs, hybrid POMs and POM nanoparticles can be found. The majority of POMs are polyoxotungstates (62%), the Keggin-type SiW11O39 being the most studied in AD. The main effect described is the inhibition of Aβ aggregates. Other effects include reversing the neurotoxicity induced by Aβ aggregates, decreasing ROS production and neuroinflammation, restoring memory and sequestering Zn2+ and Cu2+, among others, features that are well known to be associated with the pathology of AD. POMs have also shown the ability to induce the disaggregation of Aβ fibrils, particularly after irradiation, and to inhibit acetylcholinesterase activity at an nM range. Putting it all together, this review highlights a predominant trend in the exploration of POMs to act directly at the level of the formation and/or disaggregation of Aβ aggregates in the treatment of AD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in BioChem, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Converging Structural Biology and Nanotechnology to Decipher and Target Alzheimer’s Disease: From Atomic Insights to Clinical Translation
by
Akshata Yashwant Patne, Imtiyaz Bagban and Meghraj Vivekanand Suryawanshi
BioChem 2025, 5(4), 40; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5040040 - 18 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the leading cause of dementia, is defined by two pathological hallmarks, amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and hyperphosphorylated tau tangles—both now structurally resolved at near-atomic precision thanks to cryo-EM. Despite decades of research, effective disease-modifying therapies remain elusive, underscoring the need for
[...] Read more.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the leading cause of dementia, is defined by two pathological hallmarks, amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and hyperphosphorylated tau tangles—both now structurally resolved at near-atomic precision thanks to cryo-EM. Despite decades of research, effective disease-modifying therapies remain elusive, underscoring the need for innovative interdisciplinary approaches. This review synthesizes recent advances in structural biology and nanotechnology, highlighting their synergistic potential in revolutionizing AD diagnosis and treatment. Cryo-EM and NMR have revolutionized our understanding of Aβ/tau polymorphs, revealing structural vulnerabilities ripe for therapeutic targeting—yet clinical translation remains bottlenecked by the blood–brain barrier (BBB). Concurrently, nanotechnology offers groundbreaking tools, including nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for blood–brain barrier (BBB) penetration, quantum dot biosensors for early Aβ detection, and CRISPR-nano platforms for APOE4 gene editing. We discuss how integrating these disciplines addresses critical challenges in AD management—from early biomarker detection to precision therapeutics—and outline future directions for translating these innovations into clinical practice.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Deamidation at N53 Causes SOD1 Structural Instability and Excess Zn Incorporation
by
Eric Zanderigo, Phyllis Schram, Owen Rogers, Mikayla McLaughlin, Colin A. Smith and Alison L. O’Neil
BioChem 2025, 5(4), 39; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5040039 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Approximately 20% of familial ALS (fALS) cases are linked to mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1). Through a gain function, SOD1 misfolding exerts a toxic effect on motor neurons, leading to their degradation and ALS symptomology in both fALS cases and
[...] Read more.
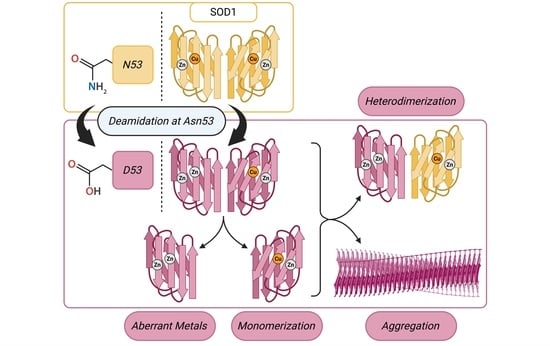
Background/Objectives: Approximately 20% of familial ALS (fALS) cases are linked to mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1). Through a gain function, SOD1 misfolding exerts a toxic effect on motor neurons, leading to their degradation and ALS symptomology in both fALS cases and sporadic ALS (sALS) cases with no known genetic cause. To further our understanding of SOD1-ALS etiology, identifying motor neuron-specific SOD1 post-translational modifications (PTMs) and studying their structural influence is necessary. To this end, we have conducted a study on the influence of the deamidation of Asn53, a PTM proximal to key stabilizing motifs in SOD1, which has scarcely been addressed in the literature to date. Methods: Deamidation to N53 was identified by tandem mass spectrometry of SOD1 immunoprecipitated from motor neuron (MN) cultures derived from wild-type (WT) human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). WT SOD1 and N53D SOD1, a mutant mimicking the deamidation, were expressed in Escherichia coli and purified for in vitro analyses. Differences between species were measured by experiments probing metal cofactors, relative monomer populations, and aggregation propensity. Furthermore, molecular dynamics experiments were conducted to model and determine the influence of the PTM on SOD1 structure. Results: In contrast to WT, N53D SOD1 showed non-native incorporation of metal cofactors, coordinating more Zn2+ cofactors than total Zn-binding sites, and more readily adopted monomeric forms, unfolded, and aggregated with heating, possibly while releasing coordinated metals. Conclusions: Deamidation to N53 in SOD1 encourages the adoption of non-native conformers, and its detection in WT MN cultures suggests relevance to sALS pathophysiology.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
RASopathy and Sudden Cardiac Death: A Literature Review
by
Cecilia Salzillo and Andrea Marzullo
BioChem 2025, 5(4), 38; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5040038 - 7 Nov 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
RASopathies are a heterogeneous group of genetic syndromes caused by germline mutations in genes encoding proteins of the RAS/MAPK pathway, which are essential in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation and survival. Although characterized by common phenotypic manifestations such as craniofacial dysmorphism, congenital
[...] Read more.
RASopathies are a heterogeneous group of genetic syndromes caused by germline mutations in genes encoding proteins of the RAS/MAPK pathway, which are essential in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation and survival. Although characterized by common phenotypic manifestations such as craniofacial dysmorphism, congenital heart defects, and growth retardation, an aspect of great clinical relevance is the increased risk of sudden cardiac death, especially in relation to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) and ventricular arrhythmias. Pathogenic variants in genes such as RAF1, RIT1, PTPN11, BRAF and SHOC2 have been associated with phenotypes with increased incidence of HCM, sometimes with early onset and a rapidly evolving course. The literature highlights the importance of early identification of patients at risk; however, specific surveillance protocols and follow-up strategies are defined in expert guidelines. This literature review aims to provide an updated overview of the main RASopathies with cardiac involvement, highlighting the genotype-phenotype correlations, the pathogenic mechanisms underlying sudden cardiac death, and current diagnosis, monitoring, and prevention strategies. The aim is to promote greater clinical awareness and encourage a multidisciplinary approach aimed at reducing mortality in these rare genetic conditions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in BioChem, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Muscle Mechanics in Metabolic Health and Longevity: The Biochemistry of Training Adaptations
by
Mike Tabone
BioChem 2025, 5(4), 37; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5040037 - 30 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Skeletal muscle is increasingly recognized as a dynamic endocrine organ whose secretome—particularly myokines—serves as a central hub for the coordination of systemic metabolic health, inflammation, and tissue adaptation. This review integrates molecular, cellular, and physiological evidence to elucidate how myokine signaling translates mechanical
[...] Read more.
Skeletal muscle is increasingly recognized as a dynamic endocrine organ whose secretome—particularly myokines—serves as a central hub for the coordination of systemic metabolic health, inflammation, and tissue adaptation. This review integrates molecular, cellular, and physiological evidence to elucidate how myokine signaling translates mechanical and metabolic stimuli from exercise into biochemical pathways that regulate glucose homeostasis, lipid oxidation, mitochondrial function, and immune modulation. We detail the duality and context-dependence of cytokine and myokine actions, emphasizing the roles of key mediators such as IL-6, irisin, SPARC, FGF21, and BAIBA in orchestrating cross-talk between muscle, adipose tissue, pancreas, liver, bone, and brain. Distinctions between resistance and endurance training are explored, highlighting how each modality shapes the myokine milieu and downstream metabolic outcomes through differential activation of AMPK, mTOR, and PGC-1α axes. The review further addresses the hormetic role of reactive oxygen species, the importance of satellite cell dynamics, and the interplay between anabolic and catabolic signaling in muscle quality control and longevity. We discuss the clinical implications of these findings for metabolic syndrome, sarcopenia, and age-related disease, and propose that the remarkable plasticity of skeletal muscle and its secretome offers a powerful, multifaceted target for lifestyle interventions and future therapeutic strategies. An original infographic is presented to visually synthesize the complex network of myokine-mediated muscle–organ interactions underpinning exercise-induced metabolic health.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
AI-Assisted Identification of the Functional Residues of Ginsenoside Biosynthesis-Associated UGTs
by
Kisook Jung, Narae Kim, Chaelin Park and Jaewook Kim
BioChem 2025, 5(4), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5040036 - 14 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Ginsenosides, one of the most pharmaceutically valuable chemical compounds in Panax ginseng, are synthesized with several enzymes, including UGTs. UGTs determine absorbability and physiological function upon consumption. Thus, understanding the functional residues of ginsenoside biosynthesis-associated UGTs is crucial for enhancing
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Ginsenosides, one of the most pharmaceutically valuable chemical compounds in Panax ginseng, are synthesized with several enzymes, including UGTs. UGTs determine absorbability and physiological function upon consumption. Thus, understanding the functional residues of ginsenoside biosynthesis-associated UGTs is crucial for enhancing the production of valuable ginsenoside varieties. Methods: We collected the UGT homologs of high sequence similarity from two rate-limiting steps of the biosynthetic pathway. The 3D structures of these proteins were predicted using the AlphaFold3 model. The ligand-binding interactions of these UGTs were examined using SwissDock and CB-Dock2. Enzyme kinetics were analyzed with MPEK. Using these tools, we performed in silico mutagenic analyses to identify the functional residues of UGTs in detail. Results: We elucidated the molecular mechanisms of experimentally verified functional residues in UGTs, many of which were associated with optimal ligand interaction angles that expose target carbons. We also identified putatively important amino acid residues that mediate ligand interactions and modulate reaction kinetics by more than 25%. In this study, residues at positions 62, 224, 397, and 398 were shown to significantly influence enzyme kinetics. Conclusions: Our study provides the first structural analysis of the functional residues of ginsenoside biosynthetic UGTs based on their 3D structures. We identified several key amino acid residues essential for proper ginsenoside biosynthesis: (1) residues determining ligand interactions, (2) residues modulating ligand binding angles, and (3) residues affecting reaction kinetics. Our findings demonstrate an effective approach to identifying functional residues in plant enzymes and present valuable UGT candidates for future experimental validation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in BioChem, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: A Narrative Review
by
Charles F. Manful, Eric Fordjour, Emmanuel Ikumoinein, Lord Abbey and Raymond Thomas
BioChem 2025, 5(4), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5040035 - 6 Oct 2025
Cited by 6
Abstract
Oxidative stress and inflammation are deeply interconnected processes implicated in the onset and progression of numerous chronic diseases. Despite promising mechanistic insights, conventional antioxidant and anti-inflammatory therapies such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and dietary antioxidants have shown limited and inconsistent success in long-term clinical
[...] Read more.
Oxidative stress and inflammation are deeply interconnected processes implicated in the onset and progression of numerous chronic diseases. Despite promising mechanistic insights, conventional antioxidant and anti-inflammatory therapies such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and dietary antioxidants have shown limited and inconsistent success in long-term clinical applications due to challenges with efficacy, safety, and bioavailability. This review explores the molecular interplay between redox imbalance and inflammatory signaling and highlights why conventional therapeutic translation has often been inconsistent. It further examines emerging strategies that aim to overcome these limitations, including mitochondrial-targeted antioxidants, Nrf2 activators, immunometabolic modulators, redox enzyme mimetics, and advanced delivery platforms such as nanoparticle-enabled delivery. Natural polyphenols, nutraceuticals, and regenerative approaches, including stem cell-derived exosomes, are also considered for their dual anti-inflammatory and antioxidant potential. By integrating recent preclinical and clinical evidence, this review underscores the need for multimodal, personalized interventions that target the redox-inflammatory axis more precisely. These advances offer renewed promise for addressing complex diseases rooted in chronic inflammation and oxidative stress.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Targeting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: Emerging Mechanisms and Therapeutics)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Application Potential of Lysinibacillus sp. UA7 for the Remediation of Cadmium Pollution
by
Yue Liang, Peng Zhao, Haoran Shi and Feiyan Xue
BioChem 2025, 5(4), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5040034 - 2 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Cadmium (Cd) pollution poses a significant environmental challenge. Microbially induced carbonate precipitation (MICP), an advanced bioremediation approach, relies on the co-precipitation of soluble metals with the microbial hydrolysate from urea. This study isolated a urease-producing strain and evaluated its Cd remediation
[...] Read more.
Background: Cadmium (Cd) pollution poses a significant environmental challenge. Microbially induced carbonate precipitation (MICP), an advanced bioremediation approach, relies on the co-precipitation of soluble metals with the microbial hydrolysate from urea. This study isolated a urease-producing strain and evaluated its Cd remediation potential. Methods: The isolated strain UA7 was identified through 16S rDNA gene sequencing. Urease production was enhanced by optimizing the culture conditions, including temperature, dissolved oxygen levels—which were affected by the rotational speed and the design of the Erlenmeyer flask, and the concentration of urea added. Its Cd remediation efficacy was assessed both in water and soil. Results: UA7 was identified as Lysinibacillus sp., achieving peak urease activity of 188 U/mL. The immobilization rates of soluble Cd reached as high as 99.61% and 63.37%, respectively, at initial concentrations of 2000 mg/L in water and 50 mg/kg in soil. The mechanism of Cd immobilization by strain UA7 via MICP was confirmed by the microstructure of the immobilized products with attached bacteria, characteristic absorption peaks, and the formed compound Ca0.67Cd0.33CO3, which were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The Cd-remediation effect of strain UA7, which reduces lodging in wheat plants, prevents the thinning and yellowing of stems and leaves, and hinders the transition of soluble Cd to the above-ground parts of the plant, was also demonstrated in a pot experiment. Conclusions: Therefore, Lysinibacillus sp. UA7 exhibited high potential for efficiently remediating contaminated Cd.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Biochemical Programming of the Fungal Cell Wall: A Synthetic Biology Blueprint for Advanced Mycelium-Based Materials
by
Víctor Coca-Ruiz
BioChem 2025, 5(4), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5040033 - 1 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The global transition to a circular bioeconomy is accelerating the demand for sustainable, high-performance materials. Filamentous fungi represent a promising solution, as they function as living foundries that transform low-value biomass into advanced, self-assembling materials. While mycelium-based composites have proven potential, progress has
[...] Read more.
The global transition to a circular bioeconomy is accelerating the demand for sustainable, high-performance materials. Filamentous fungi represent a promising solution, as they function as living foundries that transform low-value biomass into advanced, self-assembling materials. While mycelium-based composites have proven potential, progress has been predominantly driven by empirical screening of fungal species and substrates. To unlock their full potential, a paradigm shift from empirical screening to rational design is required. This review introduces a conceptual framework centered on the biochemical programming of the fungal cell wall. Viewed through a materials science lens, the cell wall is a dynamic, hierarchical nanocomposite whose properties can be deliberately tuned. We analyze the contributions of its principal components—the chitin–glucan structural scaffold, the glycoprotein functional matrix, and surface-active hydrophobins—to the bulk characteristics of mycelium-derived materials. We then identify biochemical levers for controlling these properties. External factors such as substrate composition and environmental cues (e.g., pH) modulate cell wall architecture through conserved signaling pathways. Complementing these, an internal synthetic biology toolkit enables direct genetic and chemical intervention. Strategies include targeted engineering of biosynthetic and regulatory genes (e.g., CHS, AGS, GCN5), chemical genetics to dynamically adjust synthesis during growth, and modification of surface chemistry for specialized applications like tissue engineering. By integrating fungal cell wall biochemistry, materials science, and synthetic biology, this framework moves the field from incidental discovery toward the intentional creation of smart, functional, and sustainable mycelium-based materials—aligning material innovation with the imperatives of the circular bioeconomy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Deep Generative Modeling of Protein Conformations: A Comprehensive Review
by
Tuan Minh Dao and Taseef Rahman
BioChem 2025, 5(3), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5030032 - 15 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Proteins are dynamic macromolecules whose functions are intricately linked to their structural flexibility. Recent breakthroughs in deep learning have enabled accurate prediction of static protein structures. However, understanding protein function is more complex. It often requires access to a diverse ensemble of conformations.
[...] Read more.
Proteins are dynamic macromolecules whose functions are intricately linked to their structural flexibility. Recent breakthroughs in deep learning have enabled accurate prediction of static protein structures. However, understanding protein function is more complex. It often requires access to a diverse ensemble of conformations. Traditional sampling techniques exist to help with this. These include molecular dynamics and Monte Carlo simulations. These techniques can explore conformational landscapes. However, they have limitations as they are often limited by high computational cost and suffer from slow convergence. In response, deep generative models (DGMs) have emerged as a powerful alternative for efficient and scalable protein conformation sampling. Leveraging architectures such as variational autoencoders, normalizing flows, generative adversarial networks, and diffusion models, DGMs can learn complex, high-dimensional distributions over protein conformations directly from data. This survey on generative models for protein conformation sampling provides a comprehensive overview of recent advances in this emerging field. We categorize existing models based on generative architecture, structural representation, and target tasks. We also discuss key datasets, evaluation metrics, limitations, and opportunities for integrating physics-based knowledge with data-driven models. By bridging machine learning and structural biology, DGMs are poised to transform our ability to model, design, and understand dynamic protein behavior.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Osteoporosis: Focus on Bone Remodeling and Disease Types
by
Chiara Castellani, Erica De Martino and Paolo Scapato
BioChem 2025, 5(3), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5030031 - 11 Sep 2025
Cited by 3
Abstract
Osteoporosis is a common skeletal disease that leads to increased bone fragility, associated with increased risk of fracture and consequent significant morbidity and mortality, and is a global public health problem. It results from a chronic imbalance in bone remodeling, where bone resorption
[...] Read more.
Osteoporosis is a common skeletal disease that leads to increased bone fragility, associated with increased risk of fracture and consequent significant morbidity and mortality, and is a global public health problem. It results from a chronic imbalance in bone remodeling, where bone resorption by osteoclasts exceeds bone formation by osteoblasts. Aging, hormonal changes, comorbidities, and drugs influence the process that leads to osteoporosis. In this review, we delve into the pathogenesis of primary and secondary osteoporosis after a summary of the normal physiology of bone homeostasis. Primary osteoporosis includes postmenopausal osteoporosis, driven largely by estrogen deficiency, and age-related (senile) osteoporosis, associated with reduced bone formation. An insight into male osteoporosis and osteoporosis treatment is also provided. Secondary osteoporosis can derive from underlying conditions, such as endocrine disorders, chronic inflammatory and genetic diseases, or prolonged use of glucocorticoids. Clinically, osteoporosis is often unacknowledged, underlining the importance of early risk assessment and diagnosis. A thorough understanding of the disease, its subtypes, and its underlying pathogenetic mechanisms is essential for early diagnosis and individualized treatment, all targeted to effective fracture prevention.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in BioChem, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessOpinion
An Opinion on the Supplementation of Folic Acid 1 mg + Iron (Ferrous Sulfate) 90 mg in the Prevention and Treatment of Anemia
by
João Gomes, Joana Brandão Silva, César Vinícius José and Hugo Ribeiro
BioChem 2025, 5(3), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5030030 - 8 Sep 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Introduction: Anemia, characterized by a reduction in hemoglobin concentration, is a widespread health concern globally, impacting individuals across various demographics. Iron deficiency, often compounded by inadequate folic acid levels, is a primary driver. This review aims to consolidate current evidence and offer a
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Anemia, characterized by a reduction in hemoglobin concentration, is a widespread health concern globally, impacting individuals across various demographics. Iron deficiency, often compounded by inadequate folic acid levels, is a primary driver. This review aims to consolidate current evidence and offer a practical recommendation regarding the role of folic acid 1 mg + iron (ferrous sulfate) 90 mg supplementation in both preventing and treating anemia. Objective: We aimed to provide a comprehensive review and recommendation regarding the use of folic acid 1 mg + iron (ferrous sulfate) 90 mg supplementation in the prevention and treatment of anemia in adults, based on current evidence and clinical experience. Methods: A thorough literature review was conducted, encompassing studies, guidelines, and meta-analyses related to iron deficiency, anemia, and folic acid supplementation. This review incorporated data from sources such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the European Hematology Association (EHA), and Cochrane Database. Clinical experience of the authors was also taken into account. Results: Anemia, a prevalent hematological condition, affects a significant portion of the global population. The risk factors for iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia include age, menstruation, pregnancy, dietary restrictions, chronic diseases, and inflammatory conditions. Accurate diagnosis of anemia involves reticulocyte count, morphological classification, and identification of the underlying etiology. Oral iron salts, particularly ferrous sulfate, are the first-line treatment for uncomplicated iron deficiency anemia, with lower doses or alternate-day dosing improving tolerability. Adequate folic acid availability is crucial for erythropoiesis, and supplementation is safe and enhances treatment response, especially in mixed deficiency anemia. A fixed-dose combination of folic acid 1 mg + iron (ferrous sulfate) 90 mg is effective and well-tolerated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia, mixed nutritional anemia, and iron deficiency without anemia in adults. Conclusions: Based on extensive scientific evidence and clinical experience, the combination of folic acid 1 mg + iron (ferrous sulfate) 90 mg is a valuable therapeutic option for the prevention and treatment of anemia. This combination should be indicated for iron and folic acid deficiency during pregnancy, lactation, and the postpartum period and for the prophylaxis and treatment of anemia during pregnancy and in adults in general. This approach enables correction of folate deficiencies, optimizing treatment response and ensuring sufficient folic acid levels, particularly in cases of incomplete adherence or missed doses, and is critical during pregnancy to minimize the risk of neural tube defects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in BioChem, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Trifecta of CD-19 Receptor, IgG4 Disease and the Mitigate Trials
by
Rahul Jain, Bipneet Singh, Palak Grover, Jahnavi Ethakota, Sakshi Bai, Gurleen Kaur and Merritt Bern
BioChem 2025, 5(3), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5030029 - 7 Sep 2025
Abstract
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a subacute, progressive, multisystemic autoinflammatory condition which presents with nonspecific symptoms like weight loss, fatigue and myalgia, and is marked by lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates rich in IgG4-positive plasma cells. IgG4-RD can involve various organs including the pancreas, bile ducts, thyroid,
[...] Read more.
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a subacute, progressive, multisystemic autoinflammatory condition which presents with nonspecific symptoms like weight loss, fatigue and myalgia, and is marked by lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates rich in IgG4-positive plasma cells. IgG4-RD can involve various organs including the pancreas, bile ducts, thyroid, salivary and lacrimal glands, retroperitoneum, kidneys, lungs and CNS, often mimicking malignancy. A rigorous literature review was conducted. Articles on IgG4 disease, CD-19 and the MITIGATE trials were studied and included in the review. Glucocorticoids remain first-line therapy, but adverse effects and relapses are common. Rituximab, an anti-CD20 agent, is effective but may leave CD20-negative plasmablasts intact, contributing to relapse. In contrast, CD19-targeting therapies like inebilizumab offer more comprehensive B-cell depletion, including plasmablasts, potentially reducing relapses, fibrosis progression and long-term organ damage. MITIGATE trials showed promise in the use of an anti-CD-19 agent in preventing IgG4 disease flares and prolonging the time to first flare.
Full article
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Foods, IJMS, Nutrients, Biomolecules, BioChem, Molecules
Bioactive Compounds with Application Potentials in Nutraceuticals and Nutricosmetics: Focus on Mechanism of Action and Application Science—2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Hyun-Gyun Yuk, Caili Fu, Lin Chen, Pujie ShiDeadline: 31 December 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
BioChem
Targeting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: Emerging Mechanisms and Therapeutics
Guest Editors: Hicham Wahnou, Riad El Kebbaj, Youness LimamiDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
BioChem
Translational Medicine: From Gene Discovery to Drug Discovery
Guest Editors: Talat Nasim, Khaled Habas, Merve Yuzbasioglu Baran, Maria Osei-WusuansaDeadline: 30 June 2026
Special Issue in
BioChem
Drug Delivery: Latest Advances and Prospects
Guest Editors: Xueying Zhao, Xue MiDeadline: 30 September 2026
Special Issue in
BioChem
Feature Papers in BioChem, 3rd Edition
Guest Editors: Buyong Ma, Manuel AurelianoDeadline: 31 December 2026








