Therapeutic Potential of Essential Oils and Their Bioactive Compounds Against Colon Cancer: Focus on Colon-Specific Micro- and Nanocarriers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Colon Cancer and Conventional Therapies
3. Essential Oils and Their Bioactive Compounds’ Potential for Colon Cancer Treatment
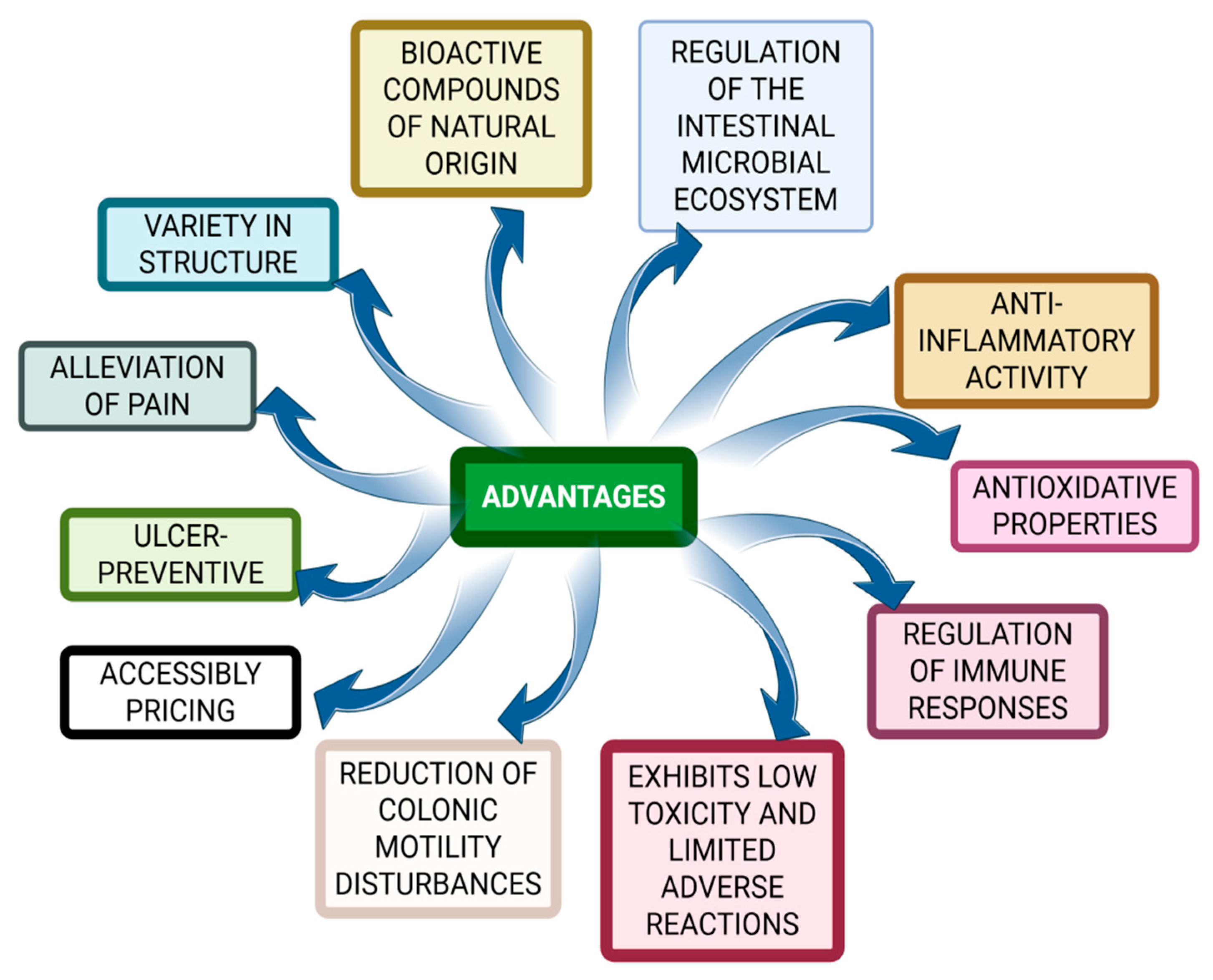
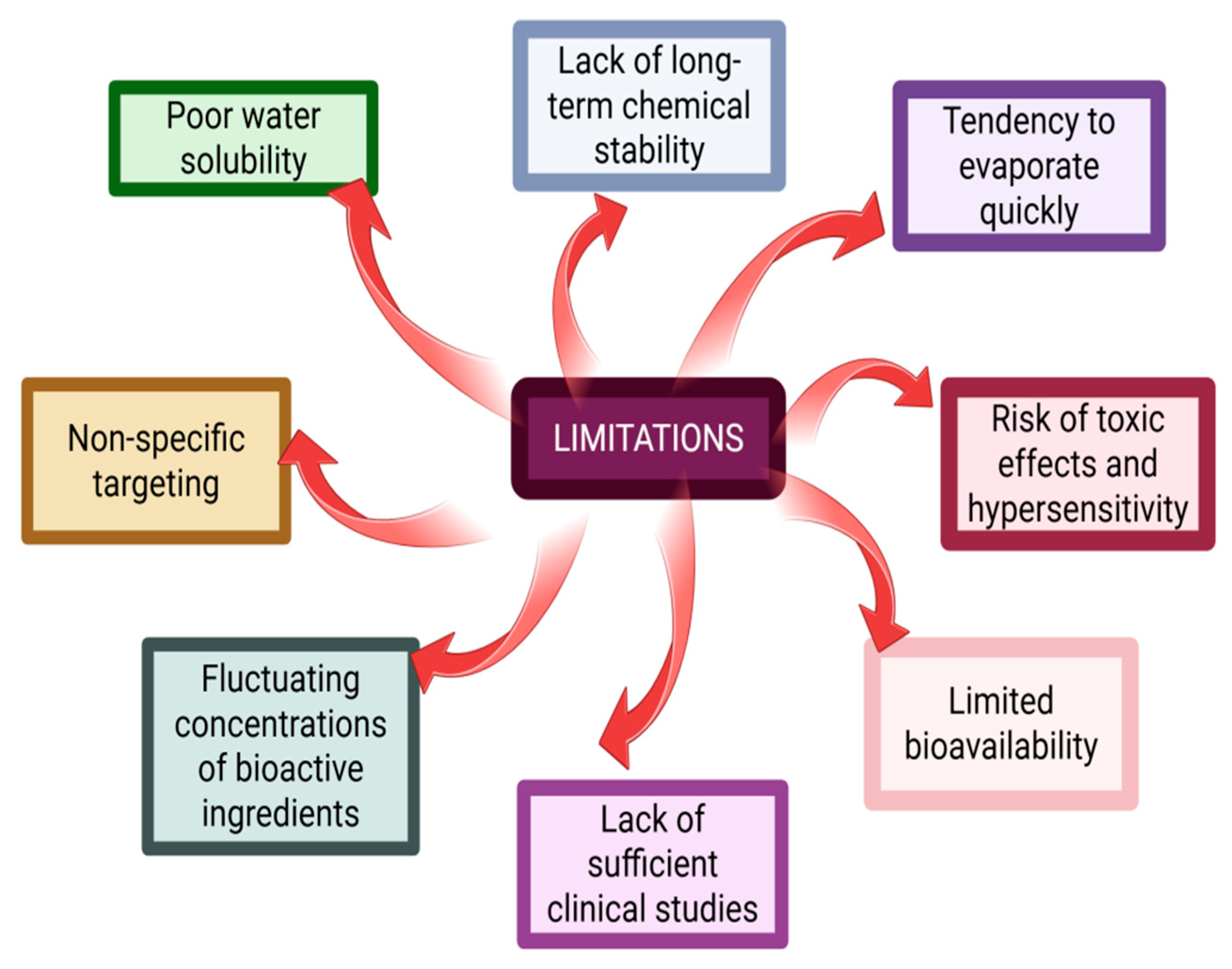
4. Encapsulation Strategies for Colon-Targeted Delivery of EOs and Their Bioactive Compounds: Advantages, Limitations, and Progress by Incorporating Essential Oils into Specific Colon-Targeted Drug Delivery Systems
4.1. Microencapsulation Approaches
4.2. Nanoencapsulation Approaches
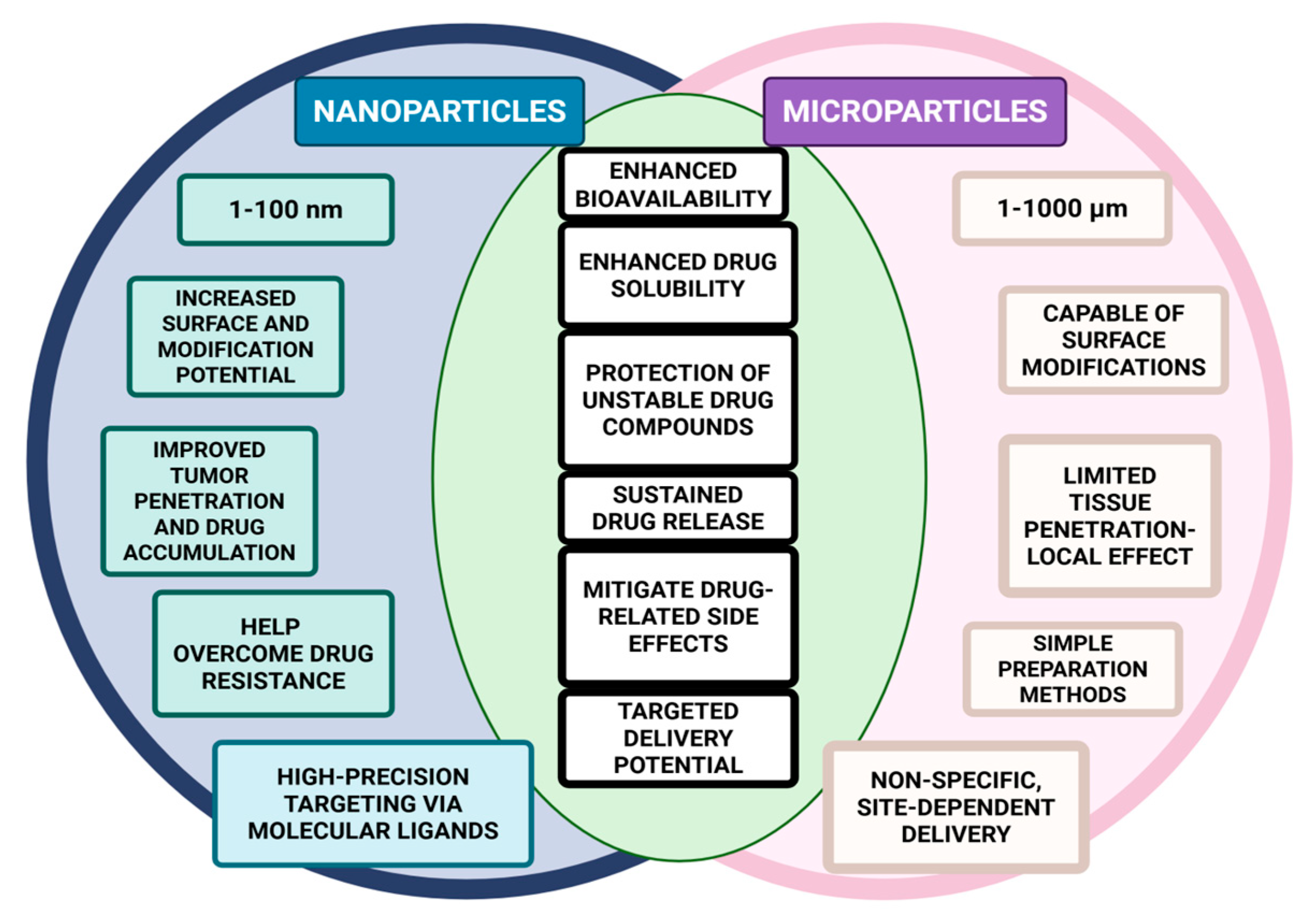
4.3. Comparison Between Micro- and Nano-Scaled Colon-Targeted Delivery Systems
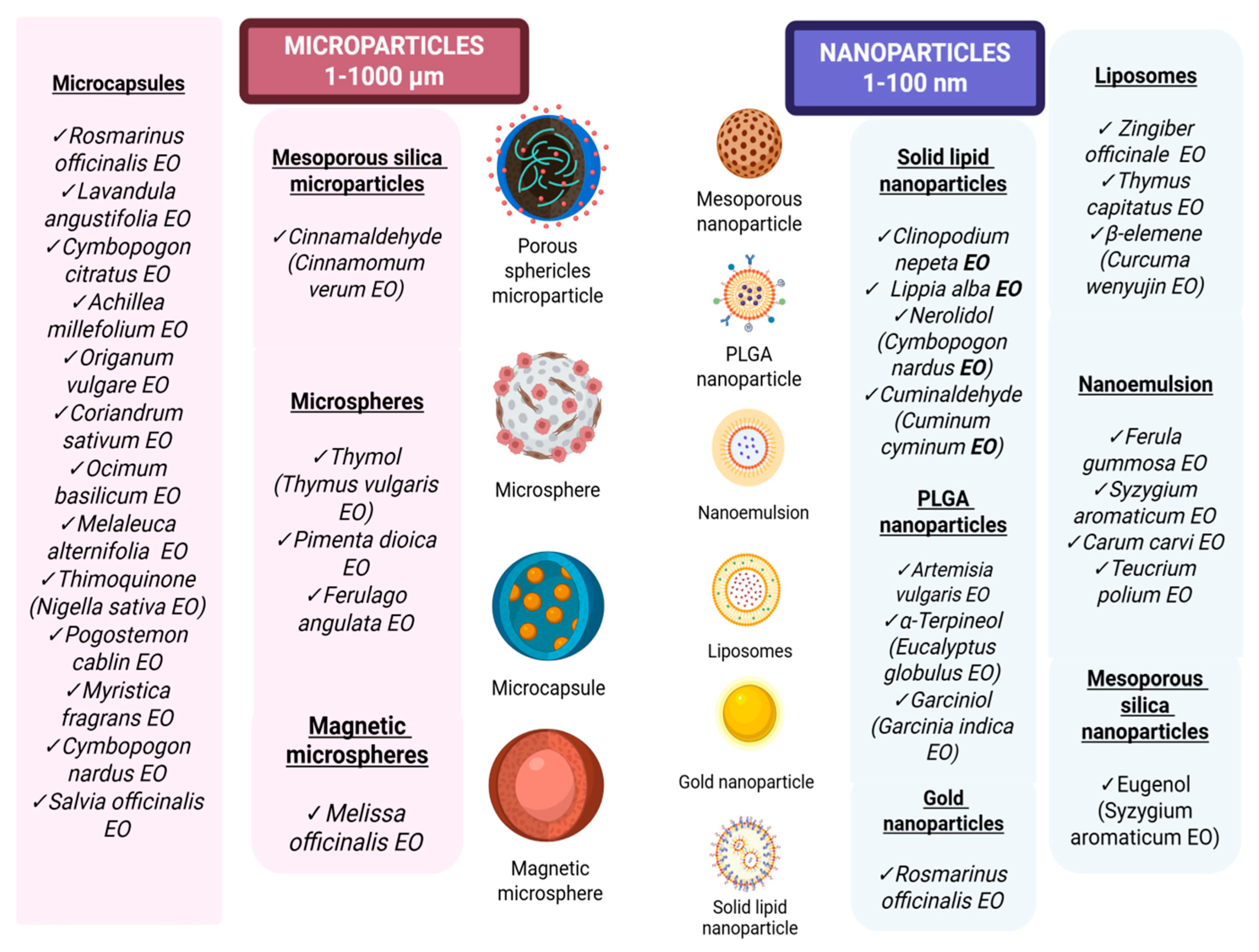
5. Advanced Micro- and Nano-Delivery Systems for Colon-Specific Targeting of Essential Oils and Their Bioactive Compounds
6. Advanced Drug Delivery Systems’ Potential to Improve the Outcomes of CC Treatment
6.1. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Novel EO’s Drug Delivery Strategies in CC Cell Lines
6.2. Effect of Advanced Combinations of EOs and Cytotoxic Agents in the Treatment of CC
7. Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CC | Colon cancer |
| EO | Essential oil |
| EOs | Essential oils |
| BAC | Bioactive compound |
| GIT | Gastrointestinal tract |
| CDDS | Colon-specific drug delivery systems |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| CA | Carnosic acid |
| KRAS | Kirsten rat sarcoma |
| MPs | Microparticles |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| SLNs | Solid lipid nanoparticles |
| NEs | Nanoemulsions |
| EPI | Epirubicin |
| EPR | Enhanced permeability and retention effect |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| eNPs–EUG | Enzyme-responsive nanoparticles encapsulating eugenol |
References
- Liang, Z.; Xie, H.; Shen, W.; Shao, L.; Zeng, L.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Q.; Zhai, X.; Li, K.; Qiu, Z.; et al. The Synergism of Natural Compounds and Conventional Therapeutics against Colorectal Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2022, 27, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douaiher, J.; Ravipati, A.; Grams, B.; Chowdhury, S.; Alatise, O.; Are, C. Colorectal Cancer—Global Burden, Trends, and Geographical Variations. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 115, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicki, T.; Ruszkowska, M.; Danielewicz, A.; Niedźwiedzka, E.; Arłukowicz, T.; Przybyłowicz, K.E. A Review of Colorectal Cancer in Terms of Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Development, Symptoms and Diagnosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzoli, S.; Alarcón-Zapata, P.; Seitimova, G.; Alarcón-Zapata, B.; Martorell, M.; Sharopov, F.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Dize, D.; Yamthe, L.R.T.; Les, F.; et al. Natural Essential Oils as a New Therapeutic Tool in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbarnejad, T.; Saidijam, M.; Moradkhani, S.; Najafi, R. Methanolic Extract of Boswellia Serrata Exhibits Anti-Cancer Activities by Targeting Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase-1 in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017, 131, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; the International Natural Product Sciences Taskforce; Orhan, I.E.; Banach, M.; Rollinger, J.M.; Barreca, D.; Weckwerth, W.; Bauer, R.; et al. Natural Products in Drug Discovery: Advances and Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunarkar-Patil, P.; Kaleem, M.; Mishra, R.; Ray, S.; Ahmad, A.; Verma, D.; Bhayye, S.; Dubey, R.; Singh, H.; Kumar, S. Anticancer Drug Discovery Based on Natural Products: From Computational Approaches to Clinical Studies. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Lu, C.; Wang, H. α-Linalool from Coriander Root Inhibits the Proliferation and Invasion of a Human Gastric Cancer Cell Line. Clin. Cancer Investig. J. 2023, 12, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouAitah, K.; Lojkowski, W. Nanomedicine as an Emerging Technology to Foster Application of Essential Oils to Fight Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabrahim, O.A.A.; Lababidi, J.M.; Fritzsche, W.; Azzazy, H.M.E.-S. Beyond Aromatherapy: Can Essential Oil Loaded Nanocarriers Revolutionize Cancer Treatment? Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 5511–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awais Khan, R.M.; Akhtar, S.; J Edagwa, B.; Shahnaz, G.; Rehman, S.U.; Rahdar, A.; Kharaba, Z. Doxycycline Monohydrate and Azelaic Acid Co-Loaded Nanoemulgel for the Treatment of Facial Rosacea: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 98, 105894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvioni, L.; Rizzuto, M.A.; Bertolini, J.A.; Pandolfi, L.; Colombo, M.; Prosperi, D. Thirty Years of Cancer Nanomedicine: Success, Frustration, and Hope. Cancers 2019, 11, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Akash, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Nowrin, F.T.; Akter, T.; Shohag, S.; Rauf, A.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; Simal-Gandara, J. Colon Cancer and Colorectal Cancer: Prevention and Treatment by Potential Natural Products. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 368, 110170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale-Ahmad, A.; Kazemi, S.; Daraei, A.; Sepidarkish, M.; Moghadamnia, A.A.; Parsian, H. pH-Sensitive Nanoformulation of Acetyl-11-Keto-Beta-Boswellic Acid (AKBA) as a Potential Antiproliferative Agent in Colon Adenocarcinoma (in Vitro and in Vivo). Cancer Nanotechnol. 2024, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Mitra, A.; Pathak, S.; Prasad, S.; Zhang, A.S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.-F.; Banerjee, A. Recent Advancements, Limitations, and Future Perspectives of the Use of Personalized Medicine in Treatment of Colon Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, S.; Larson, D.W. Targeted Therapy for Colorectal Cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 31, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Khatoon, S.; Khan, M.J.; Abu, J.; Naeem, A. Advancements and Limitations in Traditional Anti-Cancer Therapies: A Comprehensive Review of Surgery, Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy, and Hormonal Therapy. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, U.; Dey, A.; Chandel, A.K.S.; Sanyal, R.; Mishra, A.; Pandey, D.K.; De Falco, V.; Upadhyay, A.; Kandimalla, R.; Chaudhary, A.; et al. Cancer Chemotherapy and beyond: Current Status, Drug Candidates, Associated Risks and Progress in Targeted Therapeutics. Genes Dis. 2023, 10, 1367–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Albalawi, R.; Pottoo, F.H. Trends in Targeted Delivery of Nanomaterials in Colon Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 227–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolba, M.F. Revolutionizing the Landscape of Colorectal Cancer Treatment: The Potential Role of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 2996–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaviyarasan, V.; Das, A.; Deka, D.; Saha, B.; Banerjee, A.; Sharma, N.R.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Pathak, S. Advancements in Immunotherapy for Colorectal Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Review of Strategies, Challenges, and Future Prospective. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2024, 40, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, M.; Bitgen, N.; Onder, G.O.; Gurbuz, P.; Yay, A. Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis and Inflammation Response of Melissa Officinalis and Thymus Vulgaris in SW480 Colon Cancer Cells. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 162, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, S.; Staynova, R.; Koleva, N.; Ivanov, K.; Grekova-Kafalova, D. Public Perception and Usage Trends of Essential Oils: Findings from a Nationwide Survey. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmeeta, A.; Adhikary, S.; Dharshnaa, V.; Swarnamughi, P.; Ummul Maqsummiya, Z.; Banerjee, A.; Pathak, S.; Duttaroy, A.K. Plant-Derived Bioactive Compounds in Colon Cancer Treatment: An Updated Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodenak-Kladniew, B.; Castro, M.A.; Gambaro, R.C.; Girotti, J.; Cisneros, J.S.; Viña, S.; Padula, G.; Crespo, R.; Castro, G.R.; Gehring, S.; et al. Cytotoxic Screening and Enhanced Anticancer Activity of Lippia alba and Clinopodium nepeta Essential Oils-Loaded Biocompatible Lipid Nanoparticles against Lung and Colon Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, N.; Mantha, A.K.; Mittal, S. Essential Oils and Their Constituents as Anticancer Agents: A Mechanistic View. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 154106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.-K.; Tan, L.; Chan, K.-G.; Lee, L.-H.; Goh, B.-H. Nerolidol: A Sesquiterpene Alcohol with Multi-Faceted Pharmacological and Biological Activities. Molecules 2016, 21, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luca, T.; Napoli, E.; Privitera, G.; Musso, N.; Ruberto, G.; Castorina, S. Antiproliferative Effect and Cell Cycle Alterations Induced by Salvia officinalis Essential Oil and Its Three Main Components in Human Colon Cancer Cell Lines. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Li, X.; Cao, Y.; Qi, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, H. Carvacrol Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2015, 26, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Yan, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G. Geraniol and Geranyl Acetate Induce Potent Anticancer Effects in Colon Cancer Colo-205 Cells by Inducing Apoptosis, DNA Damage and Cell Cycle Arrest. J. BUON 2018, 23, 346–352. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M.; Grewal, K.; Jandrotia, R.; Batish, D.R.; Singh, H.P.; Kohli, R.K. Essential Oils as Anticancer Agents: Potential Role in Malignancies, Drug Delivery Mechanisms, and Immune System Enhancement. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Otaibi, W.A.; AlMotwaa, S.M. Oxaliplatin-Loaded Nanoemulsion Containing Teucrium polium L. Essential Oil Induces Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cell Lines through ROS-Mediated Pathway. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 2190–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drif, A.I.; Yücer, R.; Damiescu, R.; Ali, N.T.; Abu Hagar, T.H.; Avula, B.; Khan, I.A.; Efferth, T. Anti-Inflammatory and Cancer-Preventive Potential of Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L.): A Comprehensive In Silico and In Vitro Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrocelli, G.; Farabegoli, F.; Valerii, M.C.; Giovannini, C.; Sardo, A.; Spisni, E. Molecules Present in Plant Essential Oils for Prevention and Treatment of Colorectal Cancer (CRC). Molecules 2021, 26, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, S.; Pashova, S.; Dyankov, S.; Georgieva, Y.; Ivanov, K.; Benbassat, N.; Koleva, N.; Bozhkova, M.; Karcheva-Bahchevanska, D. Chemical Composition and Future Perspectives of Essential Oil Obtained from a Wild Population of Stachys germanica L. Distributed in the Balkan Mountains in Bulgaria. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 2023, 4275213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashova, S.; Karcheva-Bahchevanska, D.; Ivanov, K.; Ivanova, S. Genus Stachys—Phytochemistry, Traditional Medicinal Uses, and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2024, 29, 5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechkova, B.; Karcheva-Bahchevanska, D.; Ivanov, K.; Todorova, V.; Benbassat, N.; Penkova, N.; Atanassova, P.; Peychev, L.; Hrischev, P.; Peychev, Z.; et al. A Study of the Chemical Composition, Acute and Subacute Toxicity of Bulgarian Tanacetum Parthenium Essential Oil. Molecules 2023, 28, 4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, S.; Dzhakova, Z.; Staynova, R.; Ivanov, K. Salvia verticillata (L.)—Biological Activity, Chemical Profile, and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.; Maraei, R.; Rezk, A.; Diab, A. Phytochemical Constitutes and Biological Activities of Essential Oil Extracted from Irradiated Caraway Seeds (Carum carvi L.). Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2023, 99, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhoglova, V.; Ivanov, K.; Karcheva-Bahchevanska, D.; Koleva, N.; Bozhkova, M.; Benbassat, N.; Ivanova, S. Salicornia europaea L. and Suaeda maritima (L.) Dumort: Bioactive Compounds and Future Perspectives. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2024, 38, 2326291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, P.; Tirillini, B.; Akhtar, M.S.; Dimitriu, L.; Bricchi, E.; Bertuzzi, G.; Venanzoni, R. Essential Oil with Anticancer Activity: An Overview. In Anticancer Plants: Natural Products and Biotechnological Implements; Akhtar, M.S., Swamy, M.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 207–231. ISBN 978-981-10-8063-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, S.; Nalbantova, V.; Benbassat, N.; Dzhoglova, V.; Dzhakova, Z.; Koleva, N.; Vasilev, V.; Grekova-Kafalova, D.; Ivanov, K. Comparison between the Chemical Composition of Essential Oils Isolated from Biocultivated Salvia Rosmarinus Spenn. (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and Some Commercial Products. Pharmacia 2025, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheljazkov, V.D.; Cantrell, C.L.; Semerdjieva, I.; Radoukova, T.; Stoyanova, A.; Maneva, V.; Kačániová, M.; Astatkie, T.; Borisova, D.; Dincheva, I.; et al. Essential Oil Composition and Bioactivity of Two Juniper Species from Bulgaria and Slovakia. Molecules 2021, 26, 3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambara Murthy, K.N.; Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Patil, B.S. D-Limonene Rich Volatile Oil from Blood Oranges Inhibits Angiogenesis, Metastasis and Cell Death in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Life Sci. 2012, 91, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianfaglione, K.; Blomme, E.E.; Quassinti, L.; Bramucci, M.; Lupidi, G.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Maggi, F. Cytotoxic Essential Oils from Eryngium campestre and Eryngium amethystinum (Apiaceae) Growing in Central Italy. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1700096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, K. Polyamine Metabolism and Gene Methylation in Conjunction with One-Carbon Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, A.K.; Bahuguna, A.; Paul, S.; Kang, S.C. Thymol Elicits HCT-116 Colorectal Carcinoma Cell Death Through Induction of Oxidative Stress. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 17, 1942–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, D.; Richardson, A.J.; Zweifel, B.; Wallace, R.J.; Gratz, S.W. Genoprotective Effects of Essential Oil Compounds Against Oxidative and Methylated DNA Damage in Human Colon Cancer Cells. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1979–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larbi, B.A.M.; Naima, B.; Elsharkawy, E.R.; Neghmouche, N.S. Phytochemical Characterization, In-Vitro Cytotoxic and Antibacterial Activity of Cotula cinerea (Delile) Vis Essential Oil. J. Nat. Remedies 2018, 18, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Yadav, S.S.; Kumar, S.; Narashiman, B. A Review on Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Clinical Research of Dietary Spice Cuminum cyminum L. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 5007–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunohara, Y.; Nakano, K.; Matsuyama, S.; Oka, T.; Matsumoto, H. Cuminaldehyde, a Cumin Seed Volatile Component, Induces Growth Inhibition, Overproduction of Reactive Oxygen Species and Cell Cycle Arrest in Onion Roots. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 289, 110493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwa, N.; Chauhan, R.; Chauhan, A.; Kumar, M.; Ramniwas, S.; Mathkor, D.M.; Saini, A.K.; Tuli, H.S.; Haque, S.; Slama, P. Garcinol in Gastrointestinal Cancer Prevention: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, E.; Ghorbani, S.; Safi, M.; Seyyed Sani, N.; Firouzi Amoodizaj, F.; Heidari, M.; Chavoshi, R.; Hajazimian, S.; Isazadeh, A.; Heidari, M. Inhibition of Colorectal Cancer Cell Line CaCo-2 by Essential Oil of Eucalyptus Camaldulensis Through Induction of Apoptosis. Acta Med. Iran. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wei, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zuo, H.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Z.; Hao, M.; et al. Carnosic Acid: An Effective Phenolic Diterpenoid for Prevention and Management of Cancers via Targeting Multiple Signaling Pathways. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 206, 107288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barni, M.V.; Carlini, M.J.; Cafferata, E.G.; Puricelli, L.; Moreno, S. Carnosic Acid Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration Capacity of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Sun, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, F.; Chen, H.; Xia, D.; Xu, E.; Lai, M.; Wu, Y.; et al. Mutations of Key Driver Genes in Colorectal Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Qiu, J.; Pan, C.; Tang, Y.; Chen, M.; Song, H.; Yang, J.; Hao, X. Potential Roles and Molecular Mechanisms of Bioactive Ingredients in Curcumae Rhizoma against Breast Cancer. Phytomedicine 2023, 114, 154810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Geng, Y.-D.; Wang, B.; Feng, X.-J.; Chen, Z.-L.; Wei, W.; Jiang, L. β-Elemene Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy in Colorectal Cancer Cells through Regulating the ROS/AMPK/mTOR Pathway. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2022, 20, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Liu, S.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Pan, T.; Yan, L.; Feng, J.; et al. Combinative Treatment of β-Elemene and Cetuximab Is Sensitive to KRAS Mutant Colorectal Cancer Cells by Inducing Ferroptosis and Inhibiting Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transformation. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5107–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yammine, J.; Chihib, N.-E.; Gharsallaoui, A.; Ismail, A.; Karam, L. Advances in Essential Oils Encapsulation: Development, Characterization and Release Mechanisms. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 3837–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turek, C.; Stintzing, F.C. Stability of Essential Oils: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turek, C.; Stintzing, F.C. Impact of Different Storage Conditions on the Quality of Selected Essential Oils. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Pan, W.; Su, Y.; Yang, Y. Physical and Antimicrobial Properties of Thyme Oil Emulsions Stabilized by Ovalbumin and Gum Arabic. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajic Stevanovic, Z.; Sieniawska, E.; Glowniak, K.; Obradovic, N.; Pajic-Lijakovic, I. Natural Macromolecules as Carriers for Essential Oils: From Extraction to Biomedical Application. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevanović, Z.D.; Bošnjak-Neumüller, J.; Pajić-Lijaković, I.; Raj, J.; Vasiljević, M. Essential Oils as Feed Additives—Future Perspectives. Molecules 2018, 23, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alu’datt, M.H.; Alrosan, M.; Gammoh, S.; Tranchant, C.C.; Alhamad, M.N.; Rababah, T.; Zghoul, R.; Alzoubi, H.; Ghatasheh, S.; Ghozlan, K.; et al. Encapsulation-Based Technologies for Bioactive Compounds and Their Application in the Food Industry: A Roadmap for Food-Derived Functional and Health-Promoting Ingredients. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 101971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, F.; Nirmal, N.; Wang, P.; Jin, H.; Grøndahl, L.; Li, L. Recent Advances in Essential Oils and Their Nanoformulations for Poultry Feed. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila Gandra, E.; Radünz, M.; Helbig, E.; Dellinghausen Borges, C.; Kuka Valente Gandra, T. A Mini-Review on Encapsulation of Essential Oils. J. Anal. Pharm. Res. 2018, 7, 00205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Lin, Z.; Li, W.; Qin, Y.; Sun, Q.; Ji, N.; Xie, F. The Construction of Sodium Alginate/Carboxymethyl Chitosan Microcapsules as the Physical Barrier to Reduce Corn Starch Digestion. Foods 2024, 13, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.; Weisany, W.; Hosseini, S.E.; Ghasemlou, M. Mechanisms of Nanoencapsulation to Boost the Antimicrobial Efficacy of Essential Oils: A Review. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 150, 109655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhariha, M.; Rafati, A.A.; Garmakhany, A.D.; Asl, A.Z. Nanoencapsulation Enhances Stability, Release Behavior, and Antimicrobial Properties of Sage and Thyme Essential Oils. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 18373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Bajracharya, R.; Min, J.Y.; Han, J.-W.; Park, B.J.; Han, H.-K. Strategic Approaches for Colon Targeted Drug Delivery: An Overview of Recent Advancements. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curcio, C.; Greco, A.S.; Rizzo, S.; Saitta, L.; Musumeci, T.; Ruozi, B.; Pignatello, R. Development, Optimization and Characterization of Eudraguard®-Based Microparticles for Colon Delivery. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulbake, A. Insight to Drug Delivery Aspects for Colorectal Cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, K.; Bai, B.; Gao, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Xie, B. Orally Administrable Therapeutic Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 670124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iswandana, R.; Putri, K.S.S.; Larasati, S.A.; Gunawan, M.; Putri, F.A. Delivery of Potential Drugs to The Colon: Challenges and Strategies. Indones. J. Pharm. 2022, 33, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifisha Basumatary, M.Z.A. Development of the Formulation and Assessment of Colon Targeted Drug Delivery or Oral Administered Prednisolone. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 3, 9172–9213. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/15225136 (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Mohajeri, S.; Moayedi, S.; Mohajeri, S.; Yadegar, A.; Haririan, I. Targeting Pathophysiological Changes Using Biomaterials-Based Drug Delivery Systems: A Key to Managing Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1045575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choukaife, H.; Seyam, S.; Alallam, B.; Doolaanea, A.A.; Alfatama, M. Current Advances in Chitosan Nanoparticles Based Oral Drug Delivery for Colorectal Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 3933–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Shah, T.; Amin, A. Therapeutic Opportunities in Colon-Specific Drug-Delivery Systems. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 2007, 24, 147–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, J.; Da Silva, G.S.; Velho, M.C.; Beck, R.C.R. Eudragit®: A Versatile Family of Polymers for Hot Melt Extrusion and 3D Printing Processes in Pharmaceutics. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wu, X.; Cao, D. Eudragit L/HPMCAS Blend Enteric-Coated Lansoprazole Pellets: Enhanced Drug Stability and Oral Bioavailability. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ibrahim, I.M. Advances in Polysaccharide-Based Oral Colon-Targeted Delivery Systems: The Journey So Far and the Road Ahead. Cureus 2023, 15, e33636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaniga, A.; Moutaharrik, S.; Filippin, I.; Foppoli, A.; Palugan, L.; Maroni, A.; Cerea, M. Time-Based Formulation Strategies for Colon Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidon, S.; Brown, J.E.; Dave, V.S. Colon-Targeted Oral Drug Delivery Systems: Design Trends and Approaches. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, C.; McCoubrey, L.E.; Basit, A.W. Advances in Colon-Targeted Drug Technologies. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2025, 41, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga, R.D.S.D.; Aparecida Da Silva-Buzanello, R.; Corso, M.P.; Canan, C. Essential Oils Microencapsulated Obtained by Spray Drying: A Review. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2019, 31, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Osorno, D.M.; López-Jaramillo, M.C.; Caicedo Paz, A.V.; Villa, A.L.; Peresin, M.S.; Martínez-Galán, J.P. Recent Advances in the Microencapsulation of Essential Oils, Lipids, and Compound Lipids through Spray Drying: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, V.I.; Parente, J.F.; Marques, J.F.; Forte, M.A.; Tavares, C.J. Microencapsulation of Essential Oils: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shendge, R.S.; Zalte, T.S.; Khade, S.B. Polymeric Microspheres Redefining the Landscape of Colon-Targeted Delivery: A Contemporary Update. Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 2024, 11, 100156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collnot, E.-M.; Ali, H.; Lehr, C.-M. Nano- and Microparticulate Drug Carriers for Targeting of the Inflamed Intestinal Mucosa. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Dubey, R.; Omrey, P.; Vyas, S.P.; Jain, S.K. Development and Characterization of Colon Specific Drug Delivery System Bearing 5-ASA and Camylofine Dihydrochloride for the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis. J. Drug Target. 2010, 18, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlatti, B.; Souza Bergo, P.L.D.; Fernandes Da Silva, M.F.D.G.; Batista, J.; Rossi, M. Polymeric Nanoparticle-Based Insecticides: A Controlled Release Purpose for Agrochemicals. In Insecticides—Development of Safer and More Effective Technologies; Trdan, S., Ed.; InTech: Houston, TX, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-953-51-0958-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pavoni, L.; Perinelli, D.R.; Bonacucina, G.; Cespi, M.; Palmieri, G.F. An Overview of Micro- and Nanoemulsions as Vehicles for Essential Oils: Formulation, Preparation and Stability. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jampilek, J.; Kralova, K. Anticancer Applications of Essential Oils Formulated into Lipid-Based Delivery Nanosystems. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Filho, J.G.; Miranda, M.; Ferreira, M.D.; Plotto, A. Nanoemulsions as Edible Coatings: A Potential Strategy for Fresh Fruits and Vegetables Preservation. Foods 2021, 10, 2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommasi, F.; Esfandiari, N. Liposomal Nanomedicine: Applications for Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Huang, Q. Liposomes for Tumor Targeted Therapy: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, M.S.; Johnson, M.P.; Najahi-Missaoui, W. Targeted Liposomal Drug Delivery: Overview of the Current Applications and Challenges. Life 2024, 14, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüdtke, F.L.; Silva, T.J.; Da Silva, M.G.; Hashimoto, J.C.; Ribeiro, A.P.B. Lipid Nanoparticles: Formulation, Production Methods and Characterization Protocols. Foods 2025, 14, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.D.C.V.; Muehlmann, L.A. Characteristics and Preparation of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. J. Nanotheranostics 2024, 5, 188–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, S.; Mitragotri, S. Challenges Associated with Penetration of Nanoparticles across Cell and Tissue Barriers: A Review of Current Status and Future Prospects. Nano Today 2014, 9, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieložná, J.; Mikušová, V.; Mikuš, P. Advances in the Delivery of Anticancer Drugs by Nanoparticles and Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. X 2024, 8, 100281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enin, H.A.A.; Alquthami, A.F.; Alwagdani, A.M.; Yousef, L.M.; Albuqami, M.S.; Alharthi, M.A.; Alsaab, H.O. Utilizing TPGS for Optimizing Quercetin Nanoemulsion for Colon Cancer Cells Inhibition. Colloids Interfaces 2022, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Cabanillas Lomelí, M.; Tijerina-Sáenz, A.; García-Hernández, D.G.; Hernández-Salazar, M.; Salas García, R.; González-Llerena, J.L.; Verde-Star, M.J.; Cordero-Díaz, A.; Heya, M.S. Colon Cancer: Overview on Improved Therapeutic Potential of Plant-Based Compounds Using Nanotechnology. Sci. Pharm. 2024, 93, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulthana, W.M.; Ibrahim, N.E.-S.; Osman, N.M.; Seif, M.M.; Hassan, A.K.; Youssef, A.M.; El-Feky, A.M.; Madboli, A.A. Evaluation of the Biological Efficiency of Silver Nanoparticles Biosynthesized Using Croton tiglium L. Seeds Extract against Azoxymethane Induced Colon Cancer in Rats. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 1369–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoni, L.; Pavela, R.; Cespi, M.; Bonacucina, G.; Maggi, F.; Zeni, V.; Canale, A.; Lucchi, A.; Bruschi, F.; Benelli, G. Green Micro- and Nanoemulsions for Managing Parasites, Vectors and Pests. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoubrey, L.E.; Favaron, A.; Awad, A.; Orlu, M.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Colonic Drug Delivery: Formulating the next Generation of Colon-Targeted Therapeutics. J. Control. Release 2023, 353, 1107–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, B.; Wu, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Han, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, P.; Chen, X.; Huang, X.; Li, G.; et al. Preparation, Characterization, Pharmacokinetics and Anticancer Effects of PEGylated β-Elemene Liposomes. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, S.; Karole, A.; Mudavath, S.L. Fabrication, Physicochemical Characterization and In Vitro Anticancer Activity of Nerolidol Encapsulated Solid Lipid Nanoparticles in Human Colorectal Cell Line. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 215, 112520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poyatos-Racionero, E.; González-Álvarez, I.; Sánchez-Moreno, P.; Sitia, L.; Gatto, F.; Pompa, P.P.; Aznar, E.; González-Álvarez, M.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Marcos, M.D.; et al. Lactose-Gated Mesoporous Silica Particles for Intestinal Controlled Delivery of Essential Oil Components: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassu, G.; Nieddu, M.; Bosi, P.; Trevisi, P.; Colombo, M.; Priori, D.; Manconi, P.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E.; Boatto, G. Encapsulation and Modified-Release of Thymol from Oral Microparticles as Adjuvant or Substitute to Current Medications. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berraaouan, D.; Essifi, K.; Addi, M.; Hano, C.; Fauconnier, M.-L.; Tahani, A. Hybrid Microcapsules for Encapsulation and Controlled Release of Rosemary Essential Oil. Polymers 2023, 15, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turasan, H.; Sahin, S.; Sumnu, G. Encapsulation of Rosemary Essential Oil. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, M.Y.; Ibrahim, E.H. Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) and Rosmarinus Officinalis Extract and Their Potentials to Prompt Apoptosis and Arrest Cell Cycle in HT-29 Colon Cancer Cells. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 102304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Székely-Szentmiklósi, I.; Rédai, E.M.; Szabó, Z.-I.; Kovács, B.; Albert, C.; Gergely, A.-L.; Székely-Szentmiklósi, B.; Sipos, E. Microencapsulation by Complex Coacervation of Lavender Oil Obtained by Steam Distillation at Semi-Industrial Scale. Foods 2024, 13, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Alencar, D.D.; De Souza, E.L.; Da Cruz Almeida, E.T.; Da Silva, A.L.; Oliveira, H.M.L.; Cavalcanti, M.T. Microencapsulation of Cymbopogon Citratus D.C. Stapf Essential Oil with Spray Drying: Development, Characterization, and Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities. Foods 2022, 11, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Székely-Szentmiklósi, I.; Rédai, E.M.; Kovács, B.; Gergely, A.-L.; Albert, C.; Szabó, Z.-I.; Székely-Szentmiklósi, B.; Sipos, E. Investigation of Yarrow Essential Oil Composition and Microencapsulation by Complex Coacervation Technology. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, C.; Cotârlet, M.; Alexe, P.; Dima, S. Microencapsulation of Essential Oil of Pimento [Pimenta dioica (L) Merr.] by Chitosan/k-Carrageenan Complex Coacervation Method. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 22, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Xi, X.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.; Han, X.; Wang, J. Preparation and Characterization of Active Films Based on Oregano Essential Oil Microcapsules/Soybean Protein Isolate/Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alirezaei, M.; Ghobeh, M.; Es-haghi, A. Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid)(PLGA)-Based Nanoparticles Modified with Chitosan-Folic Acid to Delivery of Artemisia vulgaris L. Essential Oil to HT-29 Cancer Cells. Process Biochem. 2022, 121, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz, F.; Soltanshahi, M.; Khosravani, F.; Bakhshiyan, F.; Ghanbari, A.; Hassanzadeh, S.; Amirpour, M.; Ghalamfarsa, G. Thymol-Loaded Liposomes Effectively Induced Apoptosis and Decreased EGFR Expression in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 5157–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosrat, T.; Tabrizi, M.H.; Etminan, A.; Irani, M.; Zarei, B.; Rahmati, A. In Vitro and In Vivo Anticancer Activity of Ferula Gummosa Essential Oil Nanoemulsions (FGEO-NE) for the Colon Cancer Treatment. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 4166–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, A.V.M.; Karimi, E.; Oskoueian, E.; Mohammad, G.R.K.S.; Shafaei, N. Synthesis, Characterization and Cytoxicity Evaluation of Syzygium aromaticum L. Bud (Clove) Essential Oil Nanoemulsion. Res. Sq. 2021. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-952488/v1 (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Khatamian, N.; Homayouni Tabrizi, M.; Ardalan, P.; Yadamani, S.; Darchini Maragheh, A. Synthesis of Carum carvi Essential Oil Nanoemulsion, the Cytotoxic Effect, and Expression of Caspase 3 Gene. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijewantha, N.; Sane, S.; Eikanger, M.; Antony, R.M.; Potts, R.A.; Lang, L.; Rezvani, K.; Sereda, G. Enhancing Anti-Tumorigenic Efficacy of Eugenol in Human Colon Cancer Cells Using Enzyme-Responsive Nanoparticles. Cancers 2023, 15, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basholli Salihu, M.; Haloci, E.; Kryeziu, T.; Ahmeti, J.; Zogjani, B.; Bağcı, U.; Lupci, V.; Jakupi, X.; Zimmer, A.; Shala, A. Nanoemulsion of Thymus Capitatus and Origanum Vulgare Essential Oil: Stability, Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Properties. J. Res. Pharm. 2025, 29, 852–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, I.; Motallebi Moghanjoghi, A.; Sharafati Chaleshtori, R.; Ataee, M.; Khaledi, A. Nanoemulsification of Rose (Rosa damascena) Essential Oil: Characterization, Anti-Salmonella, In Vitro Cytotoxicity to Cancer Cells, and Advantages in Sheep Meat Application. J. Food Qual. 2023, 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almnhawy, M.; Jebur, M.; Alhajamee, M.; Marai, K.; Tabrizi, M.H. PLGA-Based Nano-Encapsulation of Trachyspermum ammi Seed Essential Oil (TSEO-PNP) as a Safe, Natural, Efficient, Anticancer Compound in Human HT-29 Colon Cancer Cell Line. Nutr. Cancer 2021, 73, 2808–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimipour, E.; Abedini, M.; Handali, S. Targeted Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Formulation for Colon Cancer Treatment and Cytotoxicity Assessment Using HT29 Cell Line. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2023, 18, e135987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, M.H.; Aljadani, M.A.; Mahassni, S.H. Carrying Epirubicin on Nanoemulsion Containing Algae and Cinnamon Oils Augments Its Apoptotic and Anti-Invasion Effects on Human Colon Cancer Cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 2463–2472. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Bhattacharya, S. Recent Advances in Nanomedicine Preparative Methods and Their Therapeutic Potential for Colorectal Cancer: A Critical Review. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1211603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H. Advances in Controllable Release Essential Oil Microcapsules and Their Promising Applications. Molecules 2023, 28, 4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gvozdeva, Y.; Georgieva, P. Therapeutic Potential of Essential Oils and Their Bioactive Compounds Against Colon Cancer: Focus on Colon-Specific Micro- and Nanocarriers. BioChem 2025, 5, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5030026
Gvozdeva Y, Georgieva P. Therapeutic Potential of Essential Oils and Their Bioactive Compounds Against Colon Cancer: Focus on Colon-Specific Micro- and Nanocarriers. BioChem. 2025; 5(3):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5030026
Chicago/Turabian StyleGvozdeva, Yana, and Petya Georgieva. 2025. "Therapeutic Potential of Essential Oils and Their Bioactive Compounds Against Colon Cancer: Focus on Colon-Specific Micro- and Nanocarriers" BioChem 5, no. 3: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5030026
APA StyleGvozdeva, Y., & Georgieva, P. (2025). Therapeutic Potential of Essential Oils and Their Bioactive Compounds Against Colon Cancer: Focus on Colon-Specific Micro- and Nanocarriers. BioChem, 5(3), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5030026







