- Article
Beyond Detection: Comparing State-Based Newborn Screening Methods for Effective Mucopolysaccharidosis I Diagnosis
- Rithika Thampy,
- Nishitha R. Pillai and
- Amy Gaviglio
- + 4 authors
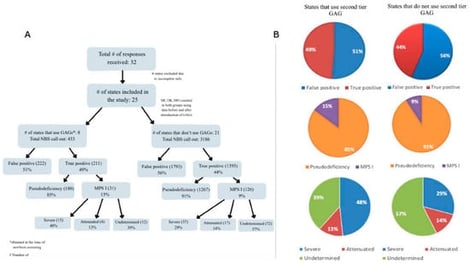
Mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I) results in the accumulation of glycosaminoglycans (GAG) and, for the purposes of newborn screening, is differentiated into two forms: severe (Hurler syndrome) versus attenuated (encompassing Scheie and Hurler-Scheie syndromes). MPS I was added to the federal Recommended Uniform Screening Panel for newborn screening (NBS) in 2016, and as of December 2025, 45 of 54 programs in the United States (US) screen for MPS I. Within the newborn screening program, a second-tier analysis of GAG is thought to reduce false-positive rates, particularly through mitigating the detection of pseudodeficiency. However, there have been some concerns that the use of second-tier GAG analysis might inadvertently result in missed detection of attenuated cases. A survey of all US NBS programs was conducted requesting data on the total number of screen-positive NBS results for MPS I as well as the final diagnostic outcome from these results. Diagnostic outcomes after screening were classified as false-positive, pseudodeficiency, severe MPS I, attenuated MPS I, and MPS I of undetermined phenotype. Additionally, information on testing methodologies and dates of MPS I NBS implementation was collected. Responses were obtained from 32 NBS programs. The cohort of screening programs utilizing second-tier blood spot GAG determinations detected a higher proportion of severe cases than those not using this second-tier test (48% vs. 29%). The proportion of attenuated cases remained consistent between both groups (13% vs. 14%). The proportion of pseudodeficiency detection was only slightly lower in the cohort using second-tier GAG analysis (85% vs. 91%). Second-tier GAG analysis appears to reduce the detection of false-positive cases and improves the resolution of severe MPS I cases, though the proportion of pseudodeficiency was only slightly lower compared to the programs that do not use second-tier GAG analysis. Currently, the proportion of attenuated cases is comparable between the two cohorts, but the higher number of “undetermined phenotype” cases may eventually shift the balance toward states not using GAG analysis once the type is determined.
3 March 2026