-
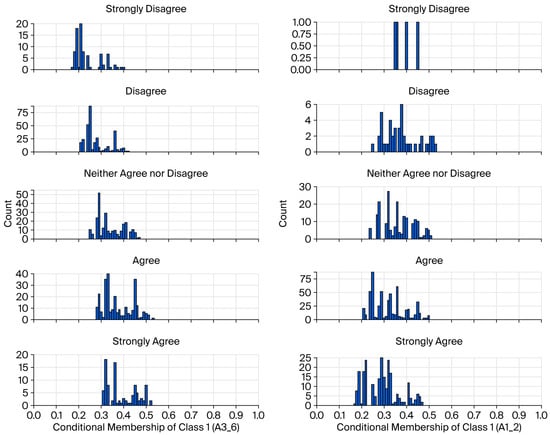
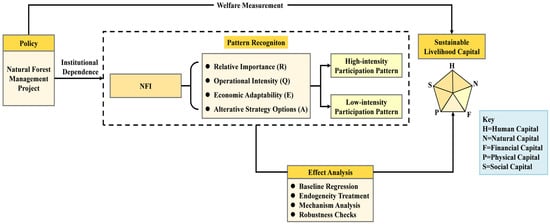
 Between Old Law and New Practice: The Policy–Implementation Gap in Türkiye’s Forest Governance Transition
Between Old Law and New Practice: The Policy–Implementation Gap in Türkiye’s Forest Governance Transition -
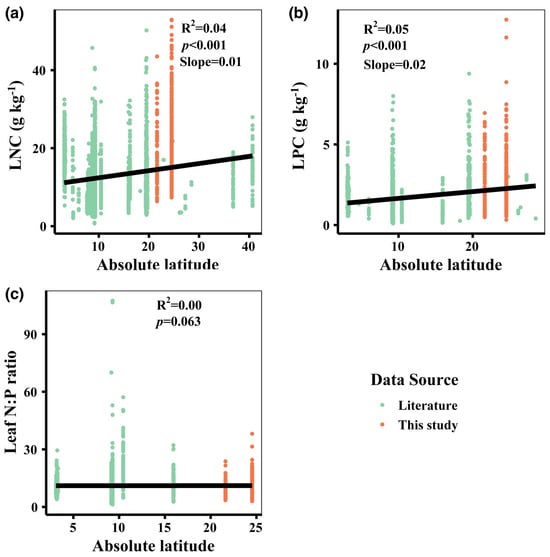
 Host-Specific Fungal Assemblages, Dominated by Ophiostomatoid Taxa, in Scots Pine Bark Beetles from Slovakia Revealed by Metabarcoding
Host-Specific Fungal Assemblages, Dominated by Ophiostomatoid Taxa, in Scots Pine Bark Beetles from Slovakia Revealed by Metabarcoding -
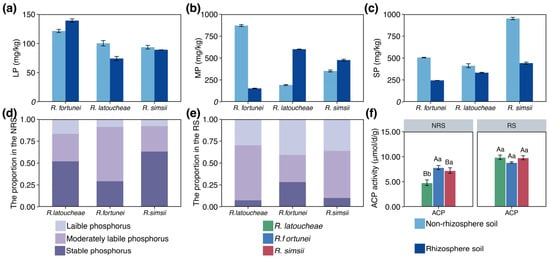
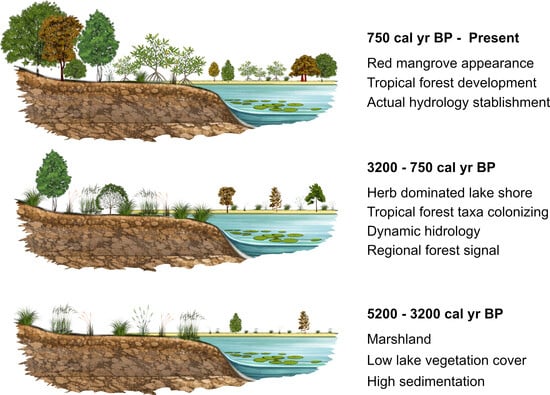
 Mixed-Species Afforestation Increases Deep Soil Water Consumption on the Semi-Arid Loess Plateau
Mixed-Species Afforestation Increases Deep Soil Water Consumption on the Semi-Arid Loess Plateau -
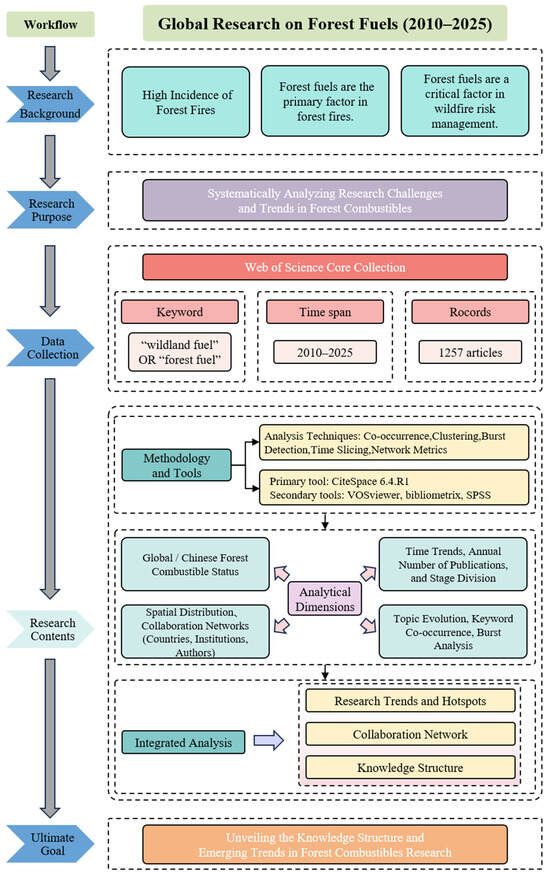
 Interactive Visualizations of Integrated Long-Term Monitoring Data for Forest and Fuels Management on Public Lands
Interactive Visualizations of Integrated Long-Term Monitoring Data for Forest and Fuels Management on Public Lands -
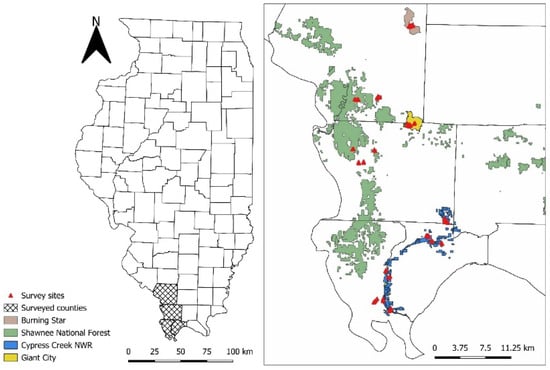
 Entomopathogenic Fungi from Minnesota Are Virulent Against Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), Adults in a Laboratory Autodissemination Device Assay
Entomopathogenic Fungi from Minnesota Are Virulent Against Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), Adults in a Laboratory Autodissemination Device Assay
Journal Description
Forests
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), Ei Compendex, GEOBASE, PubAg, AGRIS, PaperChem, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Forestry) / CiteScore - Q1 (Forestry)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Forests.
- Journal Cluster of Ecosystem and Resource Management: Forests, Diversity, Fire, Conservation, Ecologies, Biosphere and Wild.
Latest Articles
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
MDPI Launches the Michele Parrinello Award for Pioneering Contributions in Computational Physical Science

Meet Us Online at the 5th International Electronic Conference on Forests–Forests at the Crossroads: Integrating Ecology, Technological Innovation, and Governance (IECF 2026), 14–16 September 2026

Topics
Deadline: 31 March 2026
Deadline: 31 May 2026
Deadline: 16 June 2026
Deadline: 30 June 2026
Conferences

Special Issues
Deadline: 10 March 2026
Deadline: 10 March 2026
Deadline: 10 March 2026
Deadline: 20 March 2026