Abstract
Estrogens play a crucial role in sexual development and fertility as well as many other physiological processes, and it is estrogen receptors that mediate the physiological responses. To study the role of the estrogen receptors in these processes, several genetic mouse models have been developed using different strategies, which also in some cases yield different results. Here, we summarize the models that have been made and their impact on fertility in relation to known cases of human estrogen receptor mutations.
Keywords:
Esr1; Esr2; estrogen receptor alpha; estrogen receptor beta; knockout mice; estrogen; fertility 1. Introduction
In this review, we focus on genetic animal models that have been created to study estrogen signaling and how fertility is affected in these models. The first generation of animal models targeting estrogen receptors were made by insertion of a neomycin cassette into a coding exon to interrupt the coding region; however, this strategy is not efficient, since there is a risk that the neomycin cassette can be spliced out, leaving partial receptor activity. Later mouse models developed have used the Cre/loxP system [1] to delete a specific exon to cause premature stop codons or delete specific domains from the receptor. This system can be used either to make germline deletions or conditional deletions. Several knock-in mouse lines with specific point mutations have also been made to determine the function of specific amino acids in the estrogen receptors. Recently, the CRISPR/Cas9 system [2] has been used to make large or specific deletions in the estrogen receptor genes. We will discuss how these different strategies to genetically target estrogen receptors yield different effects on male and female fertility in rodents in relation to known cases of human estrogen receptor mutations.
2. Estrogen Receptors
2.1. Overview
Physiological responses to estrogen are mediated by the two classic estrogen receptors, estrogen receptor alpha (ERα, NR3A1) and estrogen receptor beta (ERβ, NR3A2), and the G protein-coupled receptor 1 (GPER1) [3]. GPER1 mediates rapid non-genomic effects of estradiol (E2) but does not affect fertility in mice [4]. The human ERα gene, ESR1, was cloned in 1985 [5], and the ERβ gene, ESR2, was discovered in the laboratory of Jan-Åke Gustafsson and cloned from rat prostate in 1996 [6].
ERα and ERβ are nuclear receptors (NR) and belong to the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily of ligand-regulated transcription factors. Humans have 48 NRs and mice 49, and the ligands for NRs are generally small hydrophobic molecules, such as steroid hormones, retinoids, or metabolic intermediates, and regulate all aspects of life [7]. Ligand binding results in conformational changes that allow DNA binding and interaction with coregulator proteins, which affects gene transcription either positively or negatively, as reviewed in [8].
NRs have a conserved domain structure with a variable N-terminal domain that contains a constitutively active transcriptional activation function (AF-1) region, a DNA-binding domain (DBD), a flexible hinge region, and a ligand-binding domain (LBD), with a ligand-dependent AF-2 region in the C-terminal domain, as reviewed in [9]. The DBD consists of two zinc finger motifs that facilitate binding to specific regions in the genome, called hormone response elements (HRE). Steroid hormone receptors bind as homodimers, while most other NRs bind as heterodimers with the retinoid X receptor (RXR). Sequences responsible for dimerization are localized both in the DBD and the LBD. The LBD has a structurally conserved fold that upon agonist binding stabilizes a transcriptionally active conformation of the receptor, exposing a docking site for coactivators, that can modify the chromatin structure or interact directly with the transcription pre-initiation complex to facilitate transcription. In the absence of ligands or bound to antagonists, the LBD recruits corepressors that repress transcription [10]. The LBD is about 56% similar between ERα and ERβ, and both receptors bind E2 with high affinity. ERs can also bind to other estrogen metabolites and plant estrogens, called phytoestrogens, as well as synthetic ligands, although the affinity is lower than for E2 [11]. The DBD is 97% identical between ERα and ERβ and it directs binding to estrogen response elements (EREs) located in promoter and enhancer regions. The mouse ERα protein is 599 amino acids long with the DBD located at positions 184–265 and the LBD/AF2 at 315–599. Mouse ERβ contains 530 amino acids, with the DBD and LBD/AF2 at positions 149–214 and 264–530, respectively.
2.2. Genes
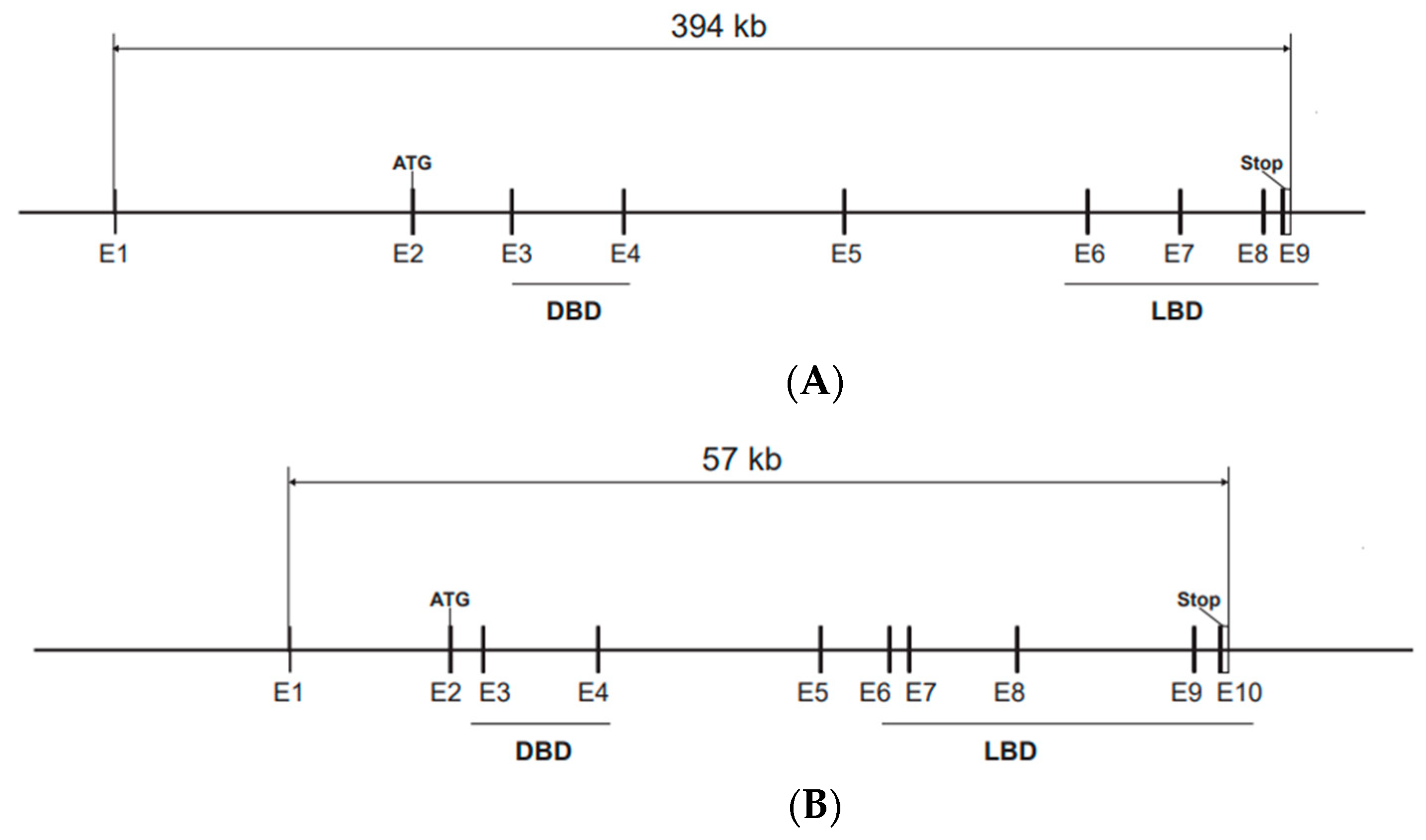
In mice, ERα and ERβ, encoded by the Esr1 and Esr2 genes, respectively, share a common genomic organization with the start codon in exon 2, according to the most used nomenclature, although alternative exons are present in both genes (Figure 1A,B). The sequences encoding the DBD are in exon 3 and exon 4, with one zinc finger in each of these exons [12]. Both Esr1 and Esr2 produce alternatively spliced mRNA transcripts [13,14]. Mouse Esr1 produce several mRNA variants with different 5′-untranslated regions by alternative promoter usage and alternative splicing [15]. The most common alternatively spliced Esr2 variant in mice and rats is ERβ-2, also called ERβ-ins, that has an extra exon in the region encoding the LBD, resulting in a lower affinity for ligands, and functions as a dominant negative receptor that represses estrogen signaling [16,17,18]. In humans, the splice variant ERβ-2, also called ERβ-cx, has a similar role [19]. The mouse Esr1 gene is localized on chromosome 10 and human ESR1 on chromosome 6, while the mouse Esr2 gene is localized on chromosome 12 and the human ortholog is on chromosome 14.
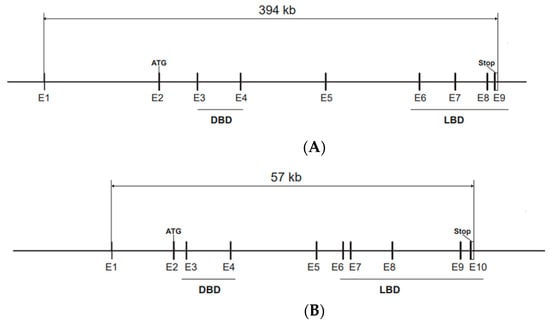
Figure 1.
Genomic structure of the Esr1 and Esr2 genes. Start and stop codons are indicated and the exons encoding the DBD and LBD are underlined. (A) The Esr1 gene is localized on chromosome 10 and spans 394 kb and 9 exons (E1–E9) according to reference sequence NM_007956.5, Esr1 transcript variant 1. The start codon (ATG) is located in exon 2 and the stop codon in exon 9. (B) The Esr2 gene is localized on chromosome 12 and spans 57 kb and contains 10 exons (E1–E10) according to reference sequence NM_207707.1, Esr2 transcript variant 1. This variant produces a protein with an insertion of 18 amino acids that results in decreased ligand-binding affinity. Esr2 transcript variant 2, that lacks exon 7, is the variant that has the highest transcriptional activation activity.
2.3. Expression Patterns of Esr1 and Esr2
Esr1 is expressed in reproductive organs, including the uterus, ovary, and testis, as well as several non-reproductive organs, including the pituitary, liver, mammary gland, bone, and hypothalamus [20,21]. The expression of mouse Esr2 is more restricted, with the highest protein levels in granulosa cells in the ovary and parts of the brain [22,23,24,25,26,27]. Rat and human ESR2 is expressed in more tissues, including prostate [6,23], and in humans the testis is the organ that expresses the highest levels of ERβ [22], suggesting species-specific functions of this receptor.
3. Animal Models
Several mouse models with disrupted Esr1 and Esr2 genes, resulting in compromised Esr expression, have been generated, and the mice are viable and grossly normal, but fertility is affected in both Esr1 and Esr2 null mutated mice. In addition, many Esr1 knock-in mouse lines have been developed. In these, mutations have been introduced in different parts of the Esr1 gene, resulting in different reproductive phenotypes. A summary of genetic mouse models with information about the roles of Esr1 and Esr2 on fertility is provided in Table 1.
3.1. Esr1 Mouse Models
The first Esr1 knockout mice were generated by insertion of a neomycin cassette into exon 3 and showed that female mice were infertile and male mice had reduced fertility [28]. More recent mouse models have used the Cre/LoxP system to excise Esr1 exon 3, that produces a frame-shift mRNA transcript with a premature stop codon short after the deleted exon, and the putative translated truncated protein lacks both the DBD and the LBD [29,30,31,32]. This mutation results in infertility in both male and female mice. The infertility in male knockout mice has been determined to be due to reduced expression of the Na+/H+ exchanger and water channel genes in the efferent ducts that connect the rete testis to the proximal portion of the duct of the epididymis, resulting in disrupted fluid reabsorption, causing a harmful environment, with increased pH and decreased luminal osmolality, that kills sperm [33,34,35]. Female knockout mice have increased E2 levels, no estrous cycle, a hypoplastic uterus, and hemorrhagic cysts in the ovaries. Esr1 knockout mice do not produce oocytes in response to superovulation [29]. The ovarian phenotype has been proposed to be due to elevated luteinizing hormone (LH) levels and hyperstimulation of the ovary as a result of aberrant estradiol feedback inhibition in the pituitary [36].

Table 1.
Selected mouse lines with Esr mutations that affect fertility.
Table 1.
Selected mouse lines with Esr mutations that affect fertility.
| Mouse Line | Mutation | Cell Type/Effect | Fertility | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERKO | Neo insertion into | Global KO | F: infertile | [28] |
| Esr1 exon 3 | M: reduced | |||
| ERαKO, Ex3αERKO | Deletion of Esr1 exon 3 | Global KO | F: infertile | [29,30,31,32] |
| ERα−/− | M: infertile | |||
| ERαfl/fl;CamKIIα-Cre | Deletion of Esr1 exon 3 | Neurons | F: infertile | [37] |
| aP2-CreERαfl/fl | Deletion of Esr1 exon 3 | Adipocytes and | F: infertile | [38] |
| hypothalamus | M: fertile | |||
| ERαflox/flox αGSUcre | Deletion of Esr1 exon 3 | pituitary gonadotroph | F: infertile | [39] |
| UtEpiαERKO | Deletion of Esr1 exon 3 | uterine epithelial cells | F: infertile | [40] |
| WEd/d(Wnt7a-Cre) | Deletion of Esr1 exon 3 | uterine cells | F: infertile | [41] |
| Amhr2Cre/+;Esr1f/− | Deletion of Esr1 exon 3 | uterine stromal cells | F: reduced | [42] |
| NERKI+/− | E207A/G208A in ERα | no DNA binding, DN | F: infertile | [43] |
| M: fertile | ||||
| ERα(EAAE) | Y201E/K210A/K214A/R215E | no DNA binding | F: infertile | [44] |
| in ERα | M: infertile | |||
| ENERKI | G525L in ERα | no E2 binding | F: infertile | [45] |
| M: sub-fertile | ||||
| AF2ERKI | L543A/L544A in ERα | no E2 binding | F: infertile | [46] |
| M: fertile | ||||
| ERα C451A, NOER | C451A in ERα | no membrane ERα | F: infertile | [47,48,49] |
| M: sub-fertile | ||||
| ESR1Y541S/βActin-Cre | Y541S, inducible | constitutively active | F: infertile | [50] |
| M: infertile | ||||
| ERβ−/− | Neo insertion into | Global | F: reduced | [51] |
| Esr2 exon 3 | M: fertile | |||
| ErβKO | Replacement of Esr2 exon 3 | Global | F: reduced | [29] |
| with Neo | M: fertile | |||
| ERβSTL−/L−, Ex3βERKO | Deletion of Esr1 exon 3 | Global | F: reduced * | [52,53,54,55] |
| ERβ-Δex3, CERβKO | M: fertile * | |||
| Esr2ΔE1-10 | Deletion of Esr2 exon 1–10 | Global | F: sub-fertile | [24] |
| M: fertile | ||||
| Esr2Y55F/Y55F | Y55F in ERβ | reduced activity | F: reduced | [56] |
| αβERKO | Esr1/Esr2 double knockout | Global | F: infertile | [57] |
| ERKO × ERβ−/− | M: infertile | |||
| ERαβKO | Esr1/Esr2 double knockout | Global | F: infertile | [29] |
| ERαKO × ERβKO | M: infertile |
F, Female; M, Male; DN, dominant-negative function; * infertility has been reported.
For neuron-specific Esr1 deletion, ERαfl/fl CamKIIα-Cre mice have demonstrated a critical role for ERα in the estrogen positive feedback on gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neurons, where the lack of ERα results in infertility due to the absence of the pre-ovulatory gonadotropin surge [37]. In addition, an increased serum E2 level and infertility have been reported as a consequence of deletion of Esr1 in the hypothalamus using aP2-Cre or RIP-Cre transgenic mice, which directs Cre expression to adipocytes or the pancreas and hypothalamus [38,58]. Uterine-specific knockout mice that lack ERα in epithelial cells are infertile due to a lack of implantation [40,41], and mice with Esr1 deleted from uterine stromal cells have reduced fertility [42]. Finally, a critical role for ERα in the pituitary was further demonstrated since female pituitary-specific Esr1 knockout mice, ERαflox/flox αGSUcre, lack estrus cyclicity and the LH surge and are infertile [39]. In conclusion, studies indicate that it is ERα-mediated functions in the brain on several levels, in the uterus, and in the pituitary that are responsible for the infertility, rather than ERα’s effects on the ovary.
Mouse lines with entire ERα domains have been developed and showed that removal of the exons coding for the AF-1 domain or DBD or LBD results in infertility in both male and female mutated mice, as reviewed in [59]. Several mouse lines with Esr1 germline point mutations have been generated which display severe fertility deficits. A knock-in mouse line termed NERKI with mutations in Esr1, ERα E207A/G208A, that make ERα unable to bind to DNA, displayed infertility in female heterozygous mice. This mouse model showed the importance of the classical pathway, where ERs binds to DNA, but also nonclassical pathways, since the phenotype differed from the global ERα most strikingly in the uterus which displayed hyperplasia [43]. Another ERα DBD mutant knock-in mouse line termed EAAE, with the mutations Y201E, K210A, K214A, and R215E, displayed a phenotype similar to the global ERα knockout mice with infertility in both sexes when homozygous for the mutation [44]. Furthermore, ERα LBD is also needed for fertility, exemplified by an estrogen-non-responsive ERα knock-in mice (ENERKI) model with a point mutation in the LBD coding region, G525L [45]. This mutation resulted in a reduced response to endogenous estrogens and showed an anovulatory and hemorrhagic cystic follicle phenotype in female homozygous mice that in turn resulted in infertility [45]. Interestingly, the ENERKI mice do respond to the ERα-selective agonist propyl pyrazole triol (PPT), and treatment prevented the formation of hemorrhagic cysts.
A different ERα LBD knock-in mouse model, AF2ERKI, with the ERα mutations L543A and L544A, displayed infertility in both male and female mice with similar phenotypes as in global ERα knockout mice [46,60]. Interestingly, this mutation changes antagonists to agonists and the male infertility can be restored by Tamoxifen treatment [46]. A mouse line with a Cre-inducible germline point mutation in the Esr1 LBD coding region, Y541S, corresponding to the human metastatic breast cancer mutation ESR1Y537S, resulted in constitutive activation of the receptor, which led to severe developmental defects in the reproductive organs that in turn resulted in infertility in both male and female mice and cysts detected in the uterus [50]. ERα non-genomic functions are mediated by a cell membrane-bound form of ERα that is directed to the cell membrane by the post-translational modification palmitoylation of a cysteine at position 451 in ERα, and position 447 in human ERα. The membrane-bound fraction of ERα interacts with the membrane protein caveolin-1 and acts together with membrane-associated kinases to mediate rapid effects of E2 [61]. Knock-in mouse models with a mutation of ERα cysteine 451 to alanine have been made independently by two research groups, and these two mouse lines, termed ERα C451A [47] and NOER [48], display severe effects on fertility in both female and male mice [47,48,49]. The female mice are infertile with ovaries lacking corpora lutea and have an excess of hemorrhagic follicles and increased luteinizing hormone levels. The phenotype of uteri was reported to be normal in ERα C451A mice but hypoplastic in NOER mice. The male phenotype is milder than the global ERα knockout and young males produce litters [49]. Finally, a targeted mutation, using the CRISPR/Cas9 technique, that specifically reduces the expression of an ovary-, uterus-, and pituitary-specific long variant of ERα (ERα-66), resulted in subfertility, an irregular estrus cycle, and defects in maintaining litters, although no obvious morphological or pathological changes were observed in the reproductive organs [62].
3.2. Esr2 Mouse Models
The first Esr2 knockout mouse line was made in the laboratories of Jan-Åke Gustafsson and Oliver Smithies by insertion of a neomycin cassette and stop codons into exon 3, encoding the DBD. These mice lack expression of full-length ERβ mRNA and displayed reduced female fertility, while male mice remained fertile [51]. Subsequent mouse models have used the Cre/loxP system to target exon 3, similar to what was done to generate Esr1 knockout mice [29,52,53,54,55]. Since targeting exon 3 may still produce low amounts of ERβ mRNA splice variants, later strategies have used the CRISPR/Cas9 system to delete the entire gene [24,63]. The overall conclusion from these studies is that male Esr2 knockout mice are fertile and female mice are sub-fertile, with fewer litters and reduced litter sizes. Interestingly, the complete deletion of the Esr2 gene results in not only female subfertility but also premature female infertility at around 6 months of age [24]. Transplantation experiments in which ovaries were transplanted from WT into Esr2 knockout mice restored the fertility in knockout females [64], which strongly supports that ERβ in the ovary is responsible for the effects on fertility and is in line with high levels of ERβ in the granulosa cells of the mouse ovary. Serum levels of E2 are normal in Esr2 knockout mice, but at the diestrus/proestrus stage of the estrous cycle, the levels have been reported to be lower than in WT mice [24,55,64] and it is likely that this affects the LH surge that is blunted in Esr2 knockout mice [55,64]. Furthermore, the ovaries of the Esr2 knockout mice display a reduced number of corpora lutea, a sign of reduced ovulation, as the most striking phenotype [24,29,51,55]. Analysis of gene expression in follicles and granulosa cells from Esr2 knockout mice have identified several genes with reduced expression that might explain the fertility defects. These include Cyp19a1, encoding the aromatase enzyme responsible for final stages of E2 biosynthesis, and after gonadotropin stimulation, the Lhcgr, Cyp11a1, and Ptgs2 genes were expressed at lower levels [53,65].
In superovulation experiments, Esr2 knockout mice produce less ovulating follicles in response to gonadotropin injections compared to their WT littermates [29,51,53,66]. Surprisingly, mice with a complete deletion of Esr2 do not show such superovulation deficits [24], which may suggest that the ovarian response to gonadotropins is not compromised upon total deletion of Esr2, and that the previous Esr2 knockout models targeting the exon 3 produce ovarian artefacts. ERβ has also been reported as expressed in GnRH-releasing neurons in the hypothalamus [67] that receive input from ERα- and Kiss1-positive afferent neurons. However, a clear role of ERβ in GnRH neurons has so far not been established, and likely the effect of ERβ on fertility is not mediated via its function in the adult brain.
In contrast to the many Esr1 knock-in mouse models, only one Esr2 knock-in model has been generated to our knowledge (Table 1). This mouse line has a point mutation in a tyrosine phosphorylation site in the N-terminal AF1 domain, Esr2Y55F/Y55F, and displays reduced female fertility and ovarian size [56]. The mutation was shown to reduce the Erβ chromatin binding to promoter regions. The involvement of Esr2 LBD or DBD in rodent fertility is, however, still not well-established, since there are no mice with point mutations in these regions. However, data from human patients with point mutations in the ESR2 gene suggest that both the LBD and DBD participate in male and female gonadal development and fertility (discussed in Section 4).
3.3. Esr1/Esr2 Double Knockouts
Mice that lack both Esr1 and Esr2, Esr1/Esr2 double knockouts, are viable, but both male and female mice are infertile with an ovarian phenotype different from the single knockouts, with structures similar to seminiferous tubules of the testis [29,57]. Interestingly, the adult, but not prepuberal, ovary exhibits follicles that lack oocytes but contain what appears to be seminiferous tube-like structures and Sertoli cells, normally found in testis, suggesting trans-differentiated follicles and a potential sex reversal [57]. Thus, a combined role of Esr1 and Esr2 may be needed to maintain oocyte integrity and prevent follicular degeneration.
3.4. Rat Esr1 and Esr2 Knockout Models
Knockout models of Esr1 and Esr2 have been made in rats using zinc finger nuclease genome targeting [68,69]. Both these models targeted and deleted exon 3, which encodes the DBD, similar to the mouse exon 3, and creates premature stop codons. The Esr1 rat knockout displays many phenotypes similar to the mouse Esr1 knockout, including infertility in both sexes, increased serum E2 levels, a hypoplastic uterus, and hemorrhagic cysts in the ovaries [68]. The phenotype in the null mutated rat Esr2 line is more severe than in mice, since females are infertile and do not produce oocytes in response to gonadotropin stimulation, while the males are fertile [69]. In addition, an exon 4-deleted rat model was made that mimics an endogenous splice variant encoding a transcript that lacks DNA-binding capacity. This rat model displays a similar phenotype as the null mutated rat, indicating that the regulation of female fertility depends on ERβ acting through binding to ERE motifs [69].
4. Human Mutations in ESR1 and ESR2
Data on human loss-of-function ESR1 or ESR2 mutations are sparse, but identified cases confirm a role for these receptors in human reproduction. A male patient with a homozygous point mutation causing a premature stop codon before the sequences encoding the DBD in ESR1 has been identified [70]. The mutation resulted in abnormal bone maturation and mineralization, but seemingly normal testosterone levels and sperm count, although a lower sperm viability [70]. A female patient with a homozygous loss-of-function ESR1 variant, Q375H, affecting the LBD, was identified in 2013, with a lack of breast development, pelvic pain, increased serum E2 levels, and hemorrhagic ovarian cysts [71]. This phenotype resembles that of female Esr1 knockout mice. Similar phenotypes were reported from a family with another homozygous loss-of-function ESR1 mutation, R394H, affecting the LBD [72]. Recently, two sisters were identified with a homozygous loss-of-function ESR1 variant in the LBD, E385V, but displaying different severities of their ovarian and hormonal phenotypes, suggesting that different compensating mechanisms exist [73]. Three case studies with ESR2 mutations have been reported. The first study identifies a heterozygous ESR2 missense variant, A432D, in an exon encoding the LBD in a girl with primary amenorrhea [74]. The second describes a female patient with a heterozygous missense ESR2 mutation in the LBD, K314R, that was shown to produce a dominant negative form of ERβ that also affects the activity of ERα [75]. This patient displayed complete ovarian failure and a lack of puberty, as well as juvenile uterus, small ovaries, and severe osteoporosis due to the lack of E2-producing ovary function. Interestingly, E2 supplementation resulted in menarche and regular menses, as well as in an increased uterus volume and ovarian growth, however with a lack of follicles [75], which contrasts with E2 supplementation in ESR1 mutant females. This confirms animal model data showing that ERβ is important for fertility via its ovarian function rather than via any direct effect on the hypothalamus or pituitary. The third case study describes three patients with disorders or differences of sex development (46,XY DSD) [76]. One of these patients had a germline homozygous 3 bp deletion in the DBD encoding region of ESR2, N181del, and displayed an absence of gonads. The other two patients displayed different heterozygous missense mutations in the N-terminal region, G84V, and the LBD, L426R, coding sequence. However, the association of ESR2 variants with 46,XY DSD remains to be established since the clinical outcomes are different and the functions of the different ERβ variants are not fully understood [77]. Although these human studies confirm a role for ERs in human reproduction, they also suggest important species differences, where ESR2 mutations in humans appear to yield a more severe gonadal phenotype than in mouse models.
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Estrogen signaling via ERα and ERβ plays a key role for fertility in mice, rats, and humans. Null mutations of Esr1 lead to infertility in both mice and rats and in both males and females, and the phenotypes are comparable to what has been described in patients with homozygous loss-of-function mutations. Esr2 null mutations lead to reduced fertility in female mice and infertility in female rats. ESR2 mutations identified in patients suggest a more critical function of ESR2 on fertility in humans than in rodents. Thus, it appears that important species differences exist regarding ERβ’s role on fertility. However, this needs to be verified since the number of human cases is low and the function of most of these mutated variants is not fully understood when it comes to interactions with ERα or their transcriptional activity. The results from the 46,XY DSD patients suggest a role for ERβ in male gonadal development that is not seen in mouse models, and one explanation for this difference could be that humans express high levels of ERβ in testis that is not seen in rodents [22]. Identifying ERβ target genes in the ovary that can explain the reduced ovulation in ERβ-KO mice is an important future step to clarify the role of ERβ in fertility, and this may identify new targets for fertility treatment. Techniques such as Chip-Seq or single-cell sequencing may hold great promise to advance knowledge in this field. The roles of ERβ splice variants in fertility are not known, but the presence of two variants, that can either activate or repress E2-regulated transcriptional responses, suggests an important role for these in regulating fertility since the results from mouse models have shown that both enhanced and reduced estrogenic signaling affect fertility.
Author Contributions
I.N., writing the manuscript, review and editing, visualization; P.A., writing the manuscript, review and editing, visualization. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Karolinska Institute and I.N. is in part funded by the National Institutes of Health (R01AG065209).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sauer, B.; Henderson, N. Site-Specific DNA Recombination in Mammalian Cells by the Cre Recombinase of Bacteriophage P1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 5166–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome Engineering Using the Crispr-Cas9 System. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyster, K.M. The Estrogen Receptors: An Overview from Different Perspectives. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1366, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prossnitz, E.R.; Hathaway, H.J. What Have We Learned About Gper Function in Physiology and Disease from Knockout Mice? J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 153, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, P.; Green, S.; Greene, G.; Krust, A.; Bornert, J.M.; Jeltsch, J.M.; Staub, A.; Jensen, E.; Scrace, G.; Waterfield, M. Cloning of the Human Estrogen Receptor Cdna. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 7889–7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper, G.G.; Enmark, E.; Pelto-Huikko, M.; Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J.A. Cloning of a Novel Receptor Expressed in Rat Prostate and Ovary. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 5925–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Thummel, C.; Beato, M.; Herrlich, P.; Schütz, G.; Umesono, K.; Blumberg, B.; Kastner, P.; Mark, M.; Chambon, P.; et al. The Nuclear Receptor Superfamily: The Second Decade. Cell 1995, 83, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, M.G.; Lunyak, V.V.; Glass, C.K. Sensors and Signals: A Coactivator/Corepressor/Epigenetic Code for Integrating Signal-Dependent Programs of Transcriptional Response. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1405–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronemeyer, H.; Gustafsson, J.; Laudet, V. Principles for Modulation of the Nuclear Receptor Superfamily. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 950–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldring, N.; Pike, A.; Andersson, S.; Matthews, J.; Cheng, G.; Hartman, J.; Tujague, M.; Strom, A.; Treuter, E.; Warner, M.; et al. Estrogen Receptors: How Do They Signal and What Are Their Targets. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 905–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, G.G.; Carlsson, B.; Grandien, K.; Enmark, E.; Haggblad, J.; Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J.A. Comparison of the Ligand Binding Specificity and Transcript Tissue Distribution of Estrogen Receptors Alpha and Beta. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Burch, P.E.; Cooney, A.J.; Lanz, R.B.; Pereira, F.A.; Wu, J.; Gibbs, R.A.; Weinstock, G.; Wheeler, D.A. Genomic Analysis of the Nuclear Receptor Family: New Insights into Structure, Regulation, and Evolution from the Rat Genome. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kos, M.; O’Brien, S.; Flouriot, G.; Gannon, F. Tissue-Specific Expression of Multiple Mrna Variants of the Mouse Estrogen Receptor Alpha Gene. FEBS Lett. 2000, 477, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowski, S.; Kalita, K.; Kaczmarek, L. Estrogen Receptor Beta. Potential Functional Significance of a Variety of Mrna Isoforms. FEBS Lett. 2002, 524, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Sakuma, Y. Complex Organization of the 5′-Untranslated Region of the Mouse Estrogen Receptor Alpha Gene: Identification of Numerous Mrna Transcripts with Distinct 5′-Ends. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 125, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Leygue, E.; Dotzlaw, H.; Murphy, L.C.; Watson, P. Estrogen Receptor-Beta Mrna Variants in Human and Murine Tissues. Mol Cell. Endocrinol. 1998, 138, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Endoh, H.; Sasaki-Iwaoka, H.; Kanou, H.; Shimaya, E.; Hashimoto, S.; Kato, S.; Kawashima, H. A Novel Isoform of Rat Estrogen Receptor Beta with 18 Amino Acid Insertion in the Ligand Binding Domain as a Putative Dominant Negative Regular of Estrogen Action. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 246, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Toresson, G.; Xu, L.; Koehler, K.F.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Dahlman-Wright, K. Mouse Estrogen Receptor Beta Isoforms Exhibit Differences in Ligand Selectivity and Coactivator Recruitment. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 7936–7944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, S.; Inoue, S.; Watanabe, T.; Orimo, A.; Hosoi, T.; Ouchi, Y.; Muramatsu, M. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of Human Estrogen Receptor Betacx: A Potential Inhibitor Ofestrogen Action in Human. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 3505–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couse, J.F.; Lindzey, J.; Grandien, K.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Korach, K.S. Tissue Distribution and Quantitative Analysis of Estrogen Receptor-Alpha (Eralpha) and Estrogen Receptor-Beta (Erbeta) Messenger Ribonucleic Acid in the Wild-Type and Eralpha-Knockout Mouse. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 4613–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irsik, D.L.; Carmines, P.K.; Lane, P.H. Classical Estrogen Receptors and Eralpha Splice Variants in the Mouse. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, S.; Sundberg, M.; Pristovsek, N.; Ibrahim, A.; Jonsson, P.; Katona, B.; Clausson, C.M.; Zieba, A.; Ramstrom, M.; Soderberg, O.; et al. Insufficient Antibody Validation Challenges Oestrogen Receptor Beta Research. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, H.; Otsuka, M.; Kanaya, M.; Higo, S.; Hattori, Y.; Ozawa, H. Applicability of Anti-Human Estrogen Receptor Beta Antibody Ppz0506 for the Immunodetection of Rodent Estrogen Receptor Beta Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonson, P.; Apolinario, L.M.; Shamekh, M.M.; Humire, P.; Poutanen, M.; Ohlsson, C.; Nalvarte, I.; Gustafsson, J.A. Generation of an All-Exon Esr2 Deleted Mouse Line: Effects on Fertility. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 529, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, M.; Hattori, Y.; Higo, S.; Otsuka, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Ozawa, H.; Ishii, H. Optimized Mouse-on-Mouse Immunohistochemical Detection of Mouse Esr2 Proteins with Ppz0506 Monoclonal Antibody. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2022, 55, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, S.K.; Tag, C.G.; Kessel, J.C.; Antonson, P.; Weiskirchen, R. Immunohistochemical Detection of Estrogen Receptor-Beta (ErΒ) with Ppz0506 Antibody in Murine Tissue: From Pitfalls to Optimization. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maioli, S.; Leander, K.; Nilsson, P.; Nalvarte, I. Estrogen Receptors and the Aging Brain. Essays Biochem. 2021, 65, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubahn, D.B.; Moyer, J.S.; Golding, T.S.; Couse, J.F.; Korach, K.S.; Smithies, O. Alteration of Reproductive Function but Not Prenatal Sexual Development after Insertional Disruption of the Mouse Estrogen Receptor Gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11162–11166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, S.; Krust, A.; Gansmuller, A.; Dierich, A.; Chambon, P.; Mark, M. Effect of Single and Compound Knockouts of Estrogen Receptors Alpha (Eralpha) and Beta (Erbeta) on Mouse Reproductive Phenotypes. Development 2000, 127, 4277–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wolfe, A.; Wang, X.; Chang, C.; Yeh, S.; Radovick, S. Generation and Characterization of a Complete Null Estrogen Receptor Alpha Mouse Using Cre/Loxp Technology. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2009, 321, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, S.C.; Kissling, G.E.; Fieselman, K.E.; Jayes, F.L.; Gerrish, K.E.; Korach, K.S. Biological and Biochemical Consequences of Global Deletion of Exon 3 from the Er Alpha Gene. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 4660–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonson, P.; Omoto, Y.; Humire, P.; Gustafsson, J.A. Generation of Eralpha-Floxed and Knockout Mice Using the Cre/Loxp System. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 424, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, E.M.; Washburn, T.F.; Bunch, D.O.; Goulding, E.H.; Gladen, B.C.; Lubahn, D.B.; Korach, K.S. Targeted Disruption of the Estrogen Receptor Gene in Male Mice Causes Alteration of Spermatogenesis and Infertility. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 4796–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, R.A.; Bunick, D.; Lee, K.H.; Bahr, J.; Taylor, J.A.; Korach, K.S.; Lubahn, D.B. A Role for Oestrogens in the Male Reproductive System. Nature 1997, 390, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, R.A.; Cooke, P.S. Estrogen in the Male: A Historical Perspective. Biol. Reprod. 2018, 99, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis Hewitt, S.; Couse, J.F.; Korach, K.S. Estrogen Receptor Transcription and Transactivation: Estrogen Receptor Knockout Mice: What Their Phenotypes Reveal About Mechanisms of Estrogen Action. Breast Cancer Res. 2000, 2, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintermantel, T.M.; Campbell, R.E.; Porteous, R.; Bock, D.; Grone, H.J.; Todman, M.G.; Korach, K.S.; Greiner, E.; Perez, C.A.; Schutz, G.; et al. Definition of Estrogen Receptor Pathway Critical for Estrogen Positive Feedback to Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Neurons and Fertility. Neuron 2006, 52, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonson, P.; Matic, M.; Portwood, N.; Kuiper, R.V.; Bryzgalova, G.; Gao, H.; Windahl, S.H.; Humire, P.; Ohlsson, C.; Berggren, P.-O.; et al. Ap2-Cre-Mediated Inactivation of Estrogen Receptor Alpha Causes Hydrometra. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieske, M.C.; Kim, H.J.; Legan, S.J.; Koo, Y.; Krust, A.; Chambon, P.; Ko, C. Pituitary Gonadotroph Estrogen Receptor-Alpha Is Necessary for Fertility in Females. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winuthayanon, W.; Hewitt, S.C.; Orvis, G.D.; Behringer, R.R.; Korach, K.S. Uterine Epithelial Estrogen Receptor Alpha Is Dispensable for Proliferation but Essential for Complete Biological and Biochemical Responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19272–19277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.; Laws, M.J.; Bagchi, I.C.; Bagchi, M.K. Uterine Epithelial Estrogen Receptor-Alpha Controls Decidualization Via a Paracrine Mechanism. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winuthayanon, W.; Lierz, S.L.; Delarosa, K.C.; Sampels, S.R.; Donoghue, L.J.; Hewitt, S.C.; Korach, K.S. Juxtacrine Activity of Estrogen Receptor Alpha in Uterine Stromal Cells Is Necessary for Estrogen-Induced Epithelial Cell Proliferation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakacka, M.; Ito, M.; Martinson, F.; Ishikawa, T.; Lee, E.J.; Jameson, J.L. An Estrogen Receptor (Er)Alpha Deoxyribonucleic Acid-Binding Domain Knock-in Mutation Provides Evidence for Nonclassical Er Pathway Signaling in Vivo. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 2188–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlbory-Dieker, D.L.; Stride, B.D.; Leder, G.; Schkoldow, J.; Trolenberg, S.; Seidel, H.; Otto, C.; Sommer, A.; Parker, M.G.; Schutz, G.; et al. DNA Binding by Estrogen Receptor-Alpha Is Essential for the Transcriptional Response to Estrogen in the Liver and the Uterus. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkevicius, K.W.; Burdette, J.E.; Woloszyn, K.; Hewitt, S.C.; Hamilton, K.; Sugg, S.L.; Temple, K.A.; Wondisford, F.E.; Korach, K.S.; Woodruff, T.K.; et al. An Estrogen Receptor-Alpha Knock-in Mutation Provides Evidence of Ligand-Independent Signaling and Allows Modulation of Ligand-Induced Pathways in Vivo. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 2970–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arao, Y.; Hamilton, K.J.; Ray, M.K.; Scott, G.; Mishina, Y.; Korach, K.S. Estrogen Receptor Alpha Af-2 Mutation Results in Antagonist Reversal and Reveals Tissue Selective Function of Estrogen Receptor Modulators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14986–14991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlanmerini, M.; Solinhac, R.; Abot, A.; Fabre, A.; Raymond-Letron, I.; Guihot, A.-L.; Boudou, F.; Sautier, L.; Vessières, E.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Mutation of the Palmitoylation Site of Estrogen Receptor Alpha in Vivo Reveals Tissue-Specific Roles for Membrane Versus Nuclear Actions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E283–E290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedram, A.; Razandi, M.; Lewis, M.; Hammes, S.; Levin, E.R. Membrane-Localized Estrogen Receptor Alpha Is Required for Normal Organ Development and Function. Dev. Cell 2014, 29, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjappa, M.K.; Hess, R.A.; Medrano, T.I.; Locker, S.H.; Levin, E.R.; Cooke, P.S. Membrane-Localized Estrogen Receptor 1 Is Required for Normal Male Reproductive Development and Function in Mice. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 2909–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simond, A.M.; Ling, C.; Moore, M.J.; Condotta, S.A.; Richer, M.J.; Muller, W.J. Point-Activated Esr1(Y541s) Has a Dramatic Effect on the Development of Sexually Dimorphic Organs. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krege, J.H.; Hodgin, J.B.; Couse, J.F.; Enmark, E.; Warner, M.; Mahler, J.F.; Sar, M.; Korach, K.S.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Smithies, O. Generation and Reproductive Phenotypes of Mice Lacking Estrogen Receptor Beta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15677–15682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antal, M.C.; Krust, A.; Chambon, P.; Mark, M. Sterility and Absence of Histopathological Defects in Nonreproductive Organs of a Mouse Erbeta-Null Mutant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2433–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, A.K.; Rodriguez, K.F.; Hamilton, K.J.; Stockton, P.S.; Reed, C.E.; Korach, K.S. The Absence of Er-Beta Results in Altered Gene Expression in Ovarian Granulosa Cells Isolated from in Vivo Preovulatory Follicles. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 2174–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maneix, L.; Antonson, P.; Humire, P.; Rochel-Maia, S.; Castaneda, J.; Omoto, Y.; Kim, H.J.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.A. Estrogen Receptor Beta Exon 3-Deleted Mouse: The Importance of Non-Ere Pathways in Erbeta Signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5135–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novaira, H.J.; Negron, A.L.; Graceli, J.B.; Capellino, S.; Schoeffield, A.; Hoffman, G.E.; Levine, J.E.; Wolfe, A.; Wondisford, F.E.; Radovick, S. Impairments in the Reproductive Axis of Female Mice Lacking Estrogen Receptor Beta in Gnrh Neurons. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 315, E1019–E1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Yang, J.; Dubeau, L.; Hu, Y.; Li, R. A Phosphotyrosine Switch in Estrogen Receptor Beta Is Required for Mouse Ovarian Function. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 649087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couse, J.F.; Hewitt, S.C.; Bunch, D.O.; Sar, M.; Walker, V.R.; Davis, B.J.; Korach, K.S. Postnatal Sex Reversal of the Ovaries in Mice Lacking Estrogen Receptors Alpha and Beta. Science 1999, 286, 2328–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonson, P.; Nalvarte, I.; Varshney, M.; Xu, L.; Windahl, S.H.; Humire, P.; Ohlsson, C.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Dahlman-Wright, K. Identification of Proteins Highly Expressed in Uterine Fluid from Mice with Hydrometra. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 466, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, S.C.; Korach, K.S. Estrogen Receptors: New Directions in the New Millennium. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arao, Y.; Hamilton, K.J.; Goulding, E.H.; Janardhan, K.S.; Eddy, E.M.; Korach, K.S. Transactivating Function (Af) 2-Mediated Af-1 Activity of Estrogen Receptor Alpha Is Crucial to Maintain Male Reproductive Tract Function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21140–21145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acconcia, F.; Ascenzi, P.; Bocedi, A.; Spisni, E.; Tomasi, V.; Trentalance, A.; Visca, P.; Marino, M. Palmitoylation-Dependent Estrogen Receptor Alpha Membrane Localization: Regulation by 17beta-Estradiol. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Dickey, J.E.; Rodeghiero, S.R.; Toth, B.A.; Kelly, M.J.; Deng, Y.; Singh, U.; Deng, G.; Jiang, J.; Cui, H. Hypomorphism of a Novel Long Eralpha Isoform Causes Severe Reproductive Dysfunctions in Female Mice. Endocrinology 2022, 163, bqac160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, M.; Wu, W.F.; Montanholi, L.; Nalvarte, I.; Antonson, P.; Gustafsson, J.A. Ventral Prostate and Mammary Gland Phenotype in Mice with Complete Deletion of the Erbeta Gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 4902–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayes, F.L.; Burns, K.A.; Rodriguez, K.F.; Kissling, G.E.; Korach, K.S. The Naturally Occurring Luteinizing Hormone Surge Is Diminished in Mice Lacking Estrogen Receptor Beta in the Ovary. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 90, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmen, J.M.; Couse, J.F.; Elmore, S.A.; Yates, M.M.; Kissling, G.E.; Korach, K.S. In Vitro Growth and Ovulation of Follicles from Ovaries of Estrogen Receptor (Er)Alpha and Erbeta Null Mice Indicate a Role for Erbeta in Follicular Maturation. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couse, J.F.; Yates, M.M.; Deroo, B.J.; Korach, K.S. Estrogen Receptor-Beta Is Critical to Granulosa Cell Differentiation and the Ovulatory Response to Gonadotropins. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3247–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrabovszky, E.; Shughrue, P.J.; Merchenthaler, I.; Hajszan, T.; Carpenter, C.D.; Liposits, Z.; Petersen, S.L. Detection of Estrogen Receptor-Beta Messenger Ribonucleic Acid and 125i-Estrogen Binding Sites in Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone Neurons of the Rat Brain. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 3506–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumi, M.A.; Dhakal, P.; Kubota, K.; Chakraborty, D.; Lei, T.; Larson, M.A.; Wolfe, M.W.; Roby, K.F.; Vivian, J.L.; Soares, M.J. Generation of Esr1-Knockout Rats Using Zinc Finger Nuclease-Mediated Genome Editing. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1991–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumi, M.A.K.; Singh, P.; Roby, K.F.; Zhao, X.; Iqbal, K.; Ratri, A.; Lei, T.; Cui, W.; Borosha, S.; Dhakal, P.; et al. Defining the Role of Estrogen Receptor Beta in the Regulation of Female Fertility. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 2330–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.P.; Boyd, J.; Frank, G.R.; Takahashi, H.; Cohen, R.M.; Specker, B.; Williams, T.C.; Lubahn, D.B.; Korach, K.S. Estrogen Resistance Caused by a Mutation in the Estrogen-Receptor Gene in a Man. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaynor, S.D.; Stradtman, E.W., Jr.; Kim, H.-G.; Shen, Y.; Chorich, L.P.; Schreihofer, D.A.; Layman, L.C. Delayed Puberty and Estrogen Resistance in a Woman with Estrogen Receptor Alpha Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, V.; Kherra, S.; Francou, B.; Fagart, J.; Viengchareun, S.; Guéchot, J.; Ladjouze, A.; Guiochon-Mantel, A.; Korach, K.S.; Binart, N.; et al. Familial Multiplicity of Estrogen Insensitivity Associated with a Loss-of-Function Esr1 Mutation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcour, C.; Khawaja, N.; Gonzalez-Duque, S.; Lebon, S.; Talbi, A.; Drira, L.; Chevenne, D.; Ajlouni, K.; de Roux, N. Estrogen Receptor Alpha Inactivation in 2 Sisters: Different Phenotypic Severities for the Same Pathogenic Variant. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e2553–e2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Zare-Abdollahi, D.; Ebrahim-Habibi, A.; Matin, N. Estrogen Receptor Mutation in a Girl with Primary Amenorrhea. Clin. Genet. 2013, 83, 497–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang-Muritano, M.; Sproll, P.; Wyss, S.; Kolly, A.; Hurlimann, R.; Konrad, D.; Biason-Lauber, A. Early-Onset Complete Ovarian Failure and Lack of Puberty in a Woman with Mutated Estrogen Receptor Beta (Esr2). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 3748–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baetens, D.; Güran, T.; Mendonca, B.B.; Gomes, N.L.; De Cauwer, L.; Peelman, F.; Verdin, H.; Vuylsteke, M.; Van der Linden, M.; Stoop, H.; et al. Biallelic and Monoallelic Esr2 Variants Associated with 46,Xy Disorders of Sex Development. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElreavey, K.; Bashamboo, A. Monogenic Forms of Dsd: An Update. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2021, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).