Impact of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor on Aurora A Kinase and the G2/M Phase Pathway in Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice and In Vivo Treatment
2.2. Collection of Bone Marrow Cells
2.3. HSPC Isolation and Flow Cytometry
2.4. RNA Sequencing Library Construction and Transcriptomic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analyses
2.6. Data Availability
3. Results
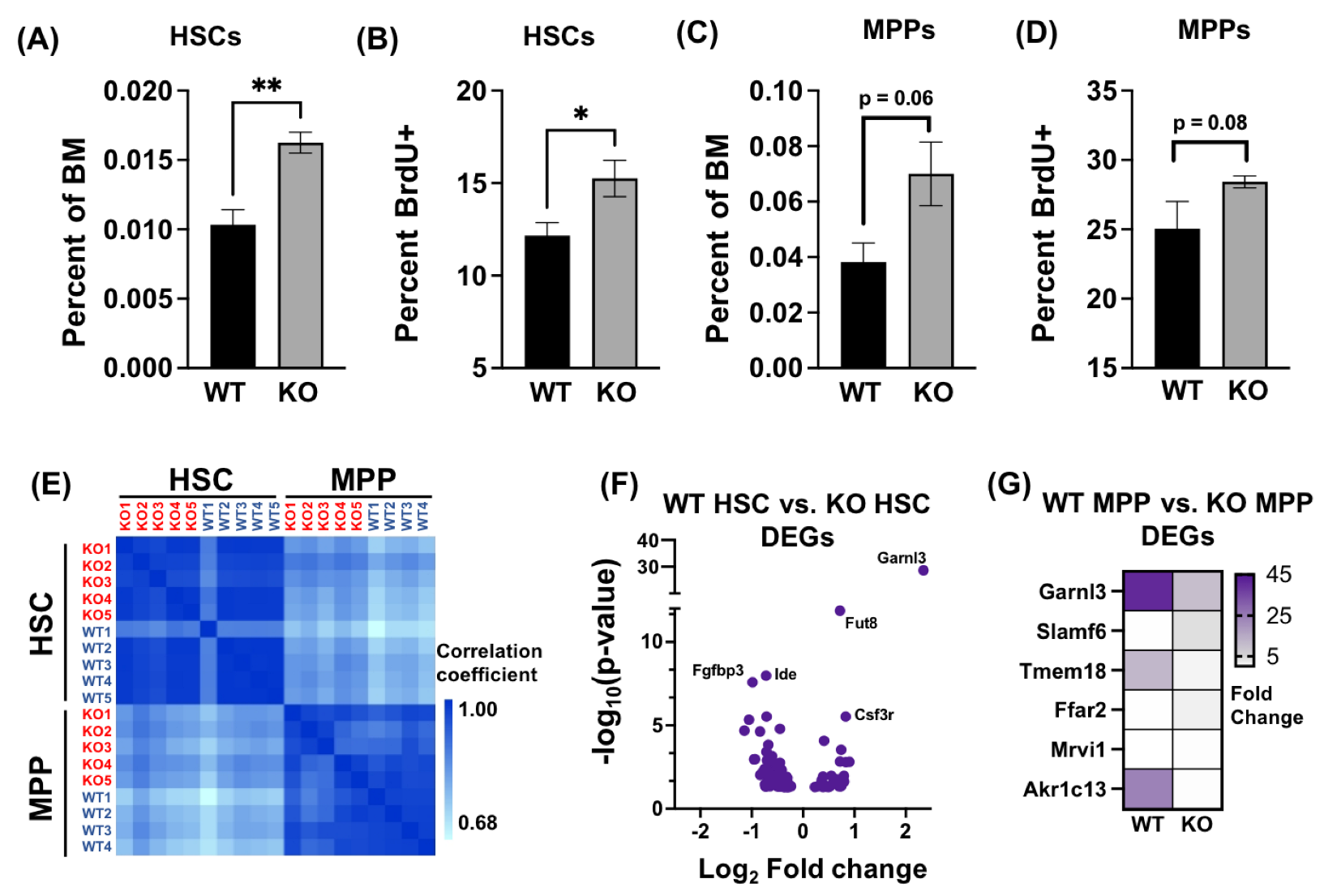
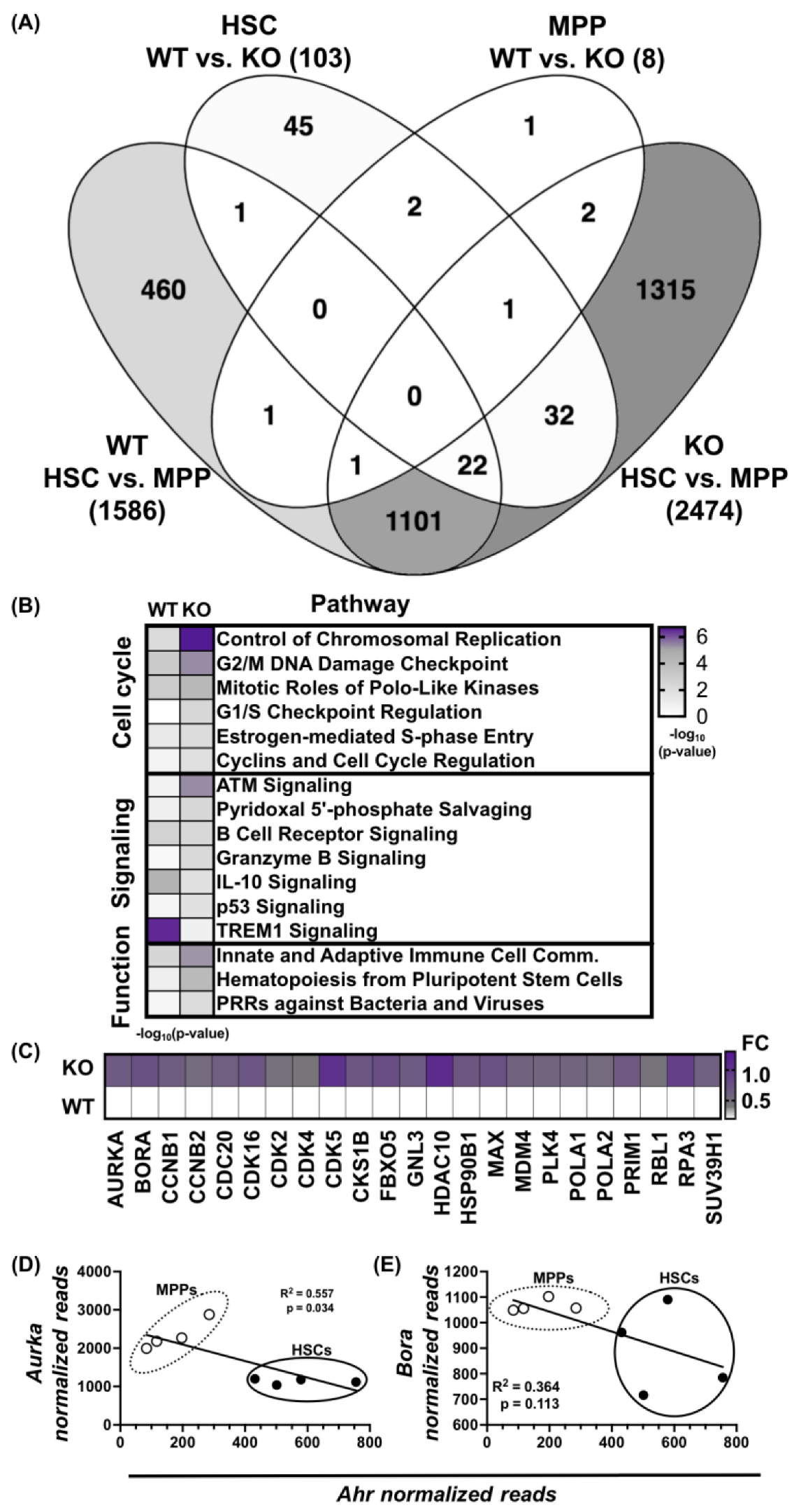
3.1. Absence of AHR Alters HSPC Transcriptome
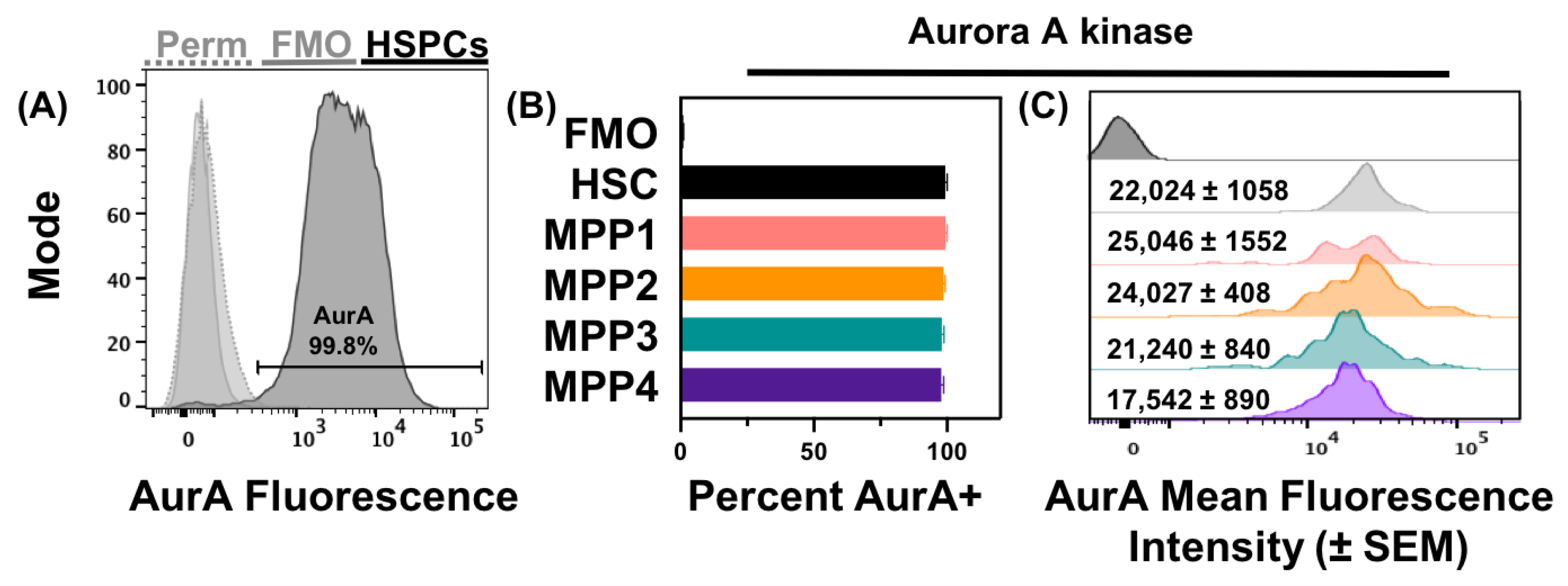
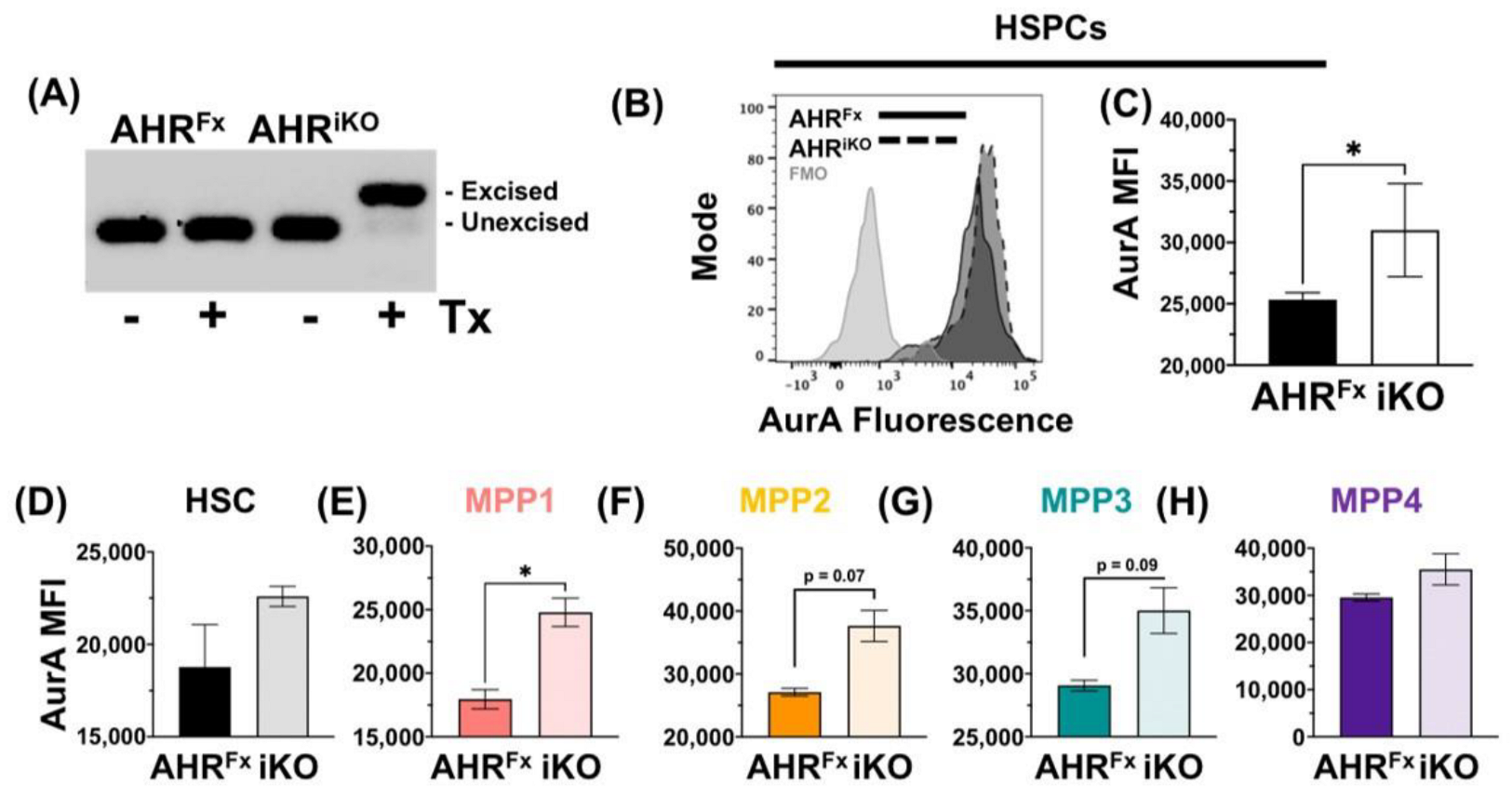
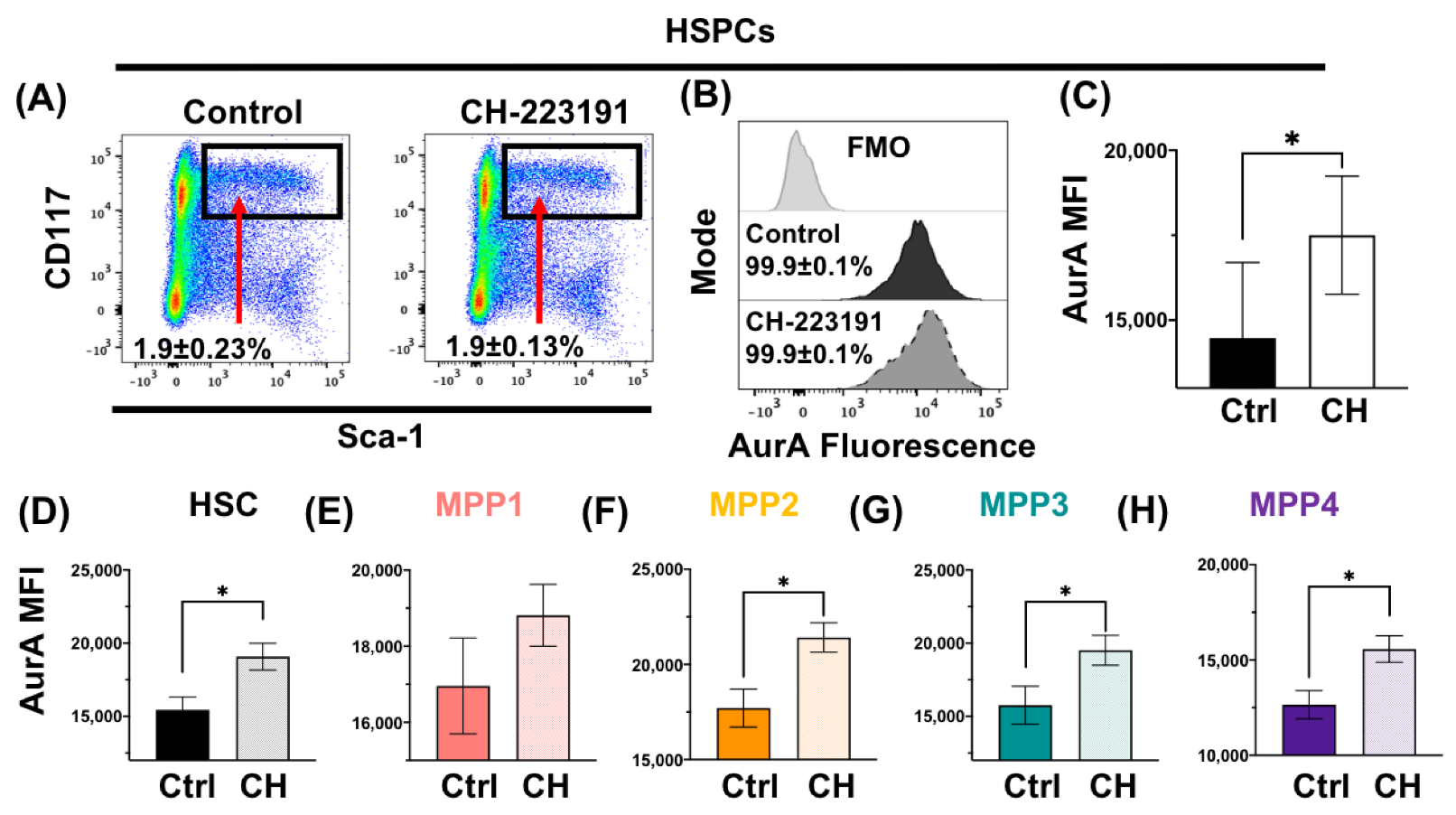
3.2. Acute Loss or Antagonism of AHR Results in Increased AurA in Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seita, J.; Weissman, I.L. Hematopoietic stem cell: Self-renewal versus differentiation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2010, 2, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, M.A.; Enver, T. The lineage commitment of haemopoietic progenitor cells. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1997, 7, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, K.; Klapproth, K.; Barile, M.; Flossdorf, M.; Holland-Letz, T.; Schlenner, S.M.; Reth, M.; Höfer, T.; Rodewald, H.-R. Fundamental properties of unperturbed haematopoiesis from stem cells in vivo. Nature 2015, 518, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Ramos, A.; Chapman, B.; Johnnidis, J.B.; Le, L.; Ho, Y.-J.; Klein, A.; Hofmann, O.; Camargo, F.D. Clonal dynamics of native haematopoiesis. Nature 2014, 514, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.L.; Baltimore, D. Regulation of stress-induced hematopoiesis. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2015, 22, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, S.; Chen, C.; Cheng, T. Cell cycle regulation of hematopoietic stem or progenitor cells. Int. J. Hematol. 2016, 103, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, B.; Osato, M. Stem cell exhaustion and leukemogenesis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 107, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.; Laurenti, E.; Trumpp, A. Balancing dormant and self-renewing hematopoietic stem cells. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2009, 19, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.J.; Scadden, D.T. The bone marrow niche for haematopoietic stem cells. Nature 2014, 505, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebert, D.W. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR): “Pioneer member” of the basic-helix/loop/helix per-Arnt-sim (bHLH/PAS) family of “sensors” of foreign and endogenous signals. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 67, 38–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.A.; Singh, K.P.; Welle, S.L.; Boule, L.A.; Lawrence, B.P.; Gasiewicz, T.A. Conditional deletion of Ahr alters gene expression profiles in hematopoietic stem cells. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.W.; Rozelle, S.S.; Leung, A.; Ubellacker, J.; Parks, A.; Nah, S.K.; French, D.; Gadue, P.; Monti, S.; Chui, D.H.; et al. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor directs hematopoietic progenitor cell expansion and differentiation. Blood 2013, 122, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasiewicz, T.A.; Singh, K.P.; Casado, F.L. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor has an important role in the regulation of hematopoiesis: Implications for benzene-induced hematopoietic toxicity. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2010, 184, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasiewicz, T.A.; Singh, K.P.; Bennett, J.A. The Ah receptor in stem cell cycling, regulation and quiescence. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1310, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Bennett, J.A.; Casado, F.L.; Walrath, J.L.; Welle, S.L.; Gasiewicz, T.A. Loss of aryl hydrocarbon receptor promotes gene changes associated with premature hematopoietic stem cell exhaustion and development of a myeloproliferative disorder in aging mice. Stem Cells Dev. 2014, 23, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, K.L.; Franchini, A.M.; Kern, H.G.; Lawrence, B.P. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulates murine hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis and influences lineage-biased stem and progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2021, 30, 970–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Garrett, R.; Casado, F.; Gasiewicz, T. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)-null allele mice have abnormal characteristics and functions of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2011, 20, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnisa, Z.; Singh, K.P.; Henry, E.C.; Donegan, C.L.; Bennett, J.A.; Gasiewicz, T.A. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor deficiency in an exon 3 deletion mouse model promotes hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and impacts endosteal niche cells. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 4536187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boitano, A.E.; Wang, J.; Romeo, R.; Bouchez, L.C.; Parker, A.E.; Sutton, S.E.; Walker, J.R.; Flaveny, C.A.; Perdew, G.H.; Denison, M.S.; et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonists promote the expansion of human hematopoietic stem cells. Science 2010, 329, 1345–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walisser, J.A.; Glover, E.; Pande, K.; Liss, A.L.; Bradfield, C.A. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent liver development and hepatotoxicity are mediated by different cell types. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17858–17863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madisen, L.; Zwingman, T.A.; Sunkin, S.M.; Oh, S.W.; Zariwala, H.A.; Gu, H.; Ng, L.L.; Palmiter, R.D.; Hawrylycz, M.J.; Jones, A.R.; et al. A robust and high-throughput Cre reporting and characterization system for the whole mouse brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Horimoto, H.; Kameyama, T.; Hayakawa, S.; Yamato, H.; Dazai, M.; Takada, A.; Kida, H.; Bott, D.; Zhou, A.C.; et al. Constitutive aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling constrains type I interferon-mediated antiviral innate defense. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; DeGroot, D.E.; Hayashi, A.; He, G.; Denison, M.S. CH223191 is a ligand-selective antagonist of the Ah (Dioxin) receptor. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 117, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.; Laurenti, E.; Oser, G.; van der Wath, R.C.; Blanco-Bose, W.; Jaworski, M.; Offner, S.; Dunant, C.F.; Eshkind, L.; Bockamp, E.; et al. Hematopoietic stem cells reversibly switch from dormancy to self-renewal during homeostasis and repair. Cell 2008, 135, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezas-Wallscheid, N.; Klimmeck, D.; Hansson, J.; Lipka, D.B.; Reyes, A.; Wang, Q.; Weichenhan, D.; Lier, A.; Von Paleske, L.; Renders, S.; et al. Identification of regulatory networks in HSCs and their immediate progeny via integrated proteome, transcriptome, and DNA methylome analysis. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 15, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roederer, M. Spectral compensation for flow cytometry: Visualization artifacts, limitations, and caveats. Cytom. J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2001, 45, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, A.; Green, J.; Pollard, J., Jr.; Tugendreich, S. Causal analysis approaches in ingenuity pathway analysis. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Czechowicz, A.; Seita, J.; Jiang, D.; Weissman, I.L. Clonal-level lineage commitment pathways of hematopoietic stem cells in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoedel, K.B.; Morcos, M.N.; Zerjatke, T.; Roeder, I.; Grinenko, T.; Voehringer, D.; Göthert, J.R.; Waskow, C.; Roers, A.; Gerbaulet, A. The bulk of the hematopoietic stem cell population is dispensable for murine steady-state and stress hematopoiesis. Blood 2016, 128, 2285–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Zhou, Z.; Yee, M.; Chu, C.-Y.; Lopez, A.M.; Lunger, V.A.; Solleti, S.K.; Resseguie, E.; Buczynski, B.; Mariani, T.J.; et al. The genome-wide transcriptional response to neonatal hyperoxia identifies Ahr as a key regulator. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 307, L516–L523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formosa, R.; Borg, J.; Vassallo, J. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) is a potential tumour suppressor in pituitary adenomas. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2017, 24, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.P.; Li, H.; Mitchell, K.A.; Joshi, A.D.; Elferink, C.J. Ah Receptor–Mediated Suppression of Liver Regeneration through NC-XRE–Driven p21”Cip1” Expression. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 85, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlowe, J.L.; Puga, A. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor, cell cycle regulation, toxicity, and tumorigenesis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 96, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Seyedhosseini, F.S.; Behnampour, N.; Yazdani, Y. Indole-3-carbinol induces G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through aryl hydrocarbon receptor in THP-1 monocytic cell line. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2017, 37, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, P.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Hou, H.H.; Hsu, S.P.; Juan, S.H. Molecular mechanisms of p21 and p27 induction by 3-methylcholanthrene, an aryl-hydrocarbon receptor agonist, involved in antiproliferation of human umbilical vascular endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 215, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.-I.; Wang, Q.; Fan, Y.; Xia, Y.; Puga, A. Pluripotency factors and Polycomb Group proteins repress aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression in murine embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2014, 12, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.-I.; Fan, Y.; de Gannes, M.; Wang, Q.; Xia, Y.; Puga, A. Repression of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor is required to maintain mitotic progression and prevent loss of pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 2825–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, E.F.; Jang, H.S.; Pearce, M.; Kerkvliet, N.I.; Kolluri, S.K. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is required for induction of p21cip1/waf1 expression and growth inhibition by SU5416 in hepatoma cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamouchene, H.; Arlt, V.M.; Giddings, I.; Phillips, D.H. Influence of cell cycle on responses of MCF-7 cells to benzo[a]pyrene. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes-Ellerbe, S.; Knudsen, K.E.; Puga, A. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin blocks androgen-dependent cell proliferation of LNCaP cells through modulation of pRB phosphorylation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, C.S.; Desai, A. Tension sensing by Aurora B kinase is independent of survivin-based centromere localization. Nature 2013, 497, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducat, D.; Zheng, Y. Aurora kinases in spindle assembly and chromosome segregation. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 301, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marumoto, T.; Honda, S.; Hara, T.; Nitta, M.; Hirota, T.; Kohmura, E.; Saya, H. Aurora-A kinase maintains the fidelity of early and late mitotic events in HeLa cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 51786–51795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Chen, R.; Chen, X.; Huang, B.; Lin, R.; Xie, X.; Chen, J.; Jiang, J.; Deng, Y.; Wen, J. AhR regulates the expression of human cytochrome P450 1A1 (CYP1A1) by recruiting Sp1. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 4215–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denison, M.S.; Pandini, A.; Nagy, S.R.; Baldwin, E.P.; Bonati, L. Ligand binding and activation of the Ah receptor. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2002, 141, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rico, F.J.; Vicente-García, C.; Fernández, A.; Muñoz-Santos, D.; Montoliu, L.; Morales-Hernández, A.; Merino, J.M.; Román, A.-C.; Fernández-Salguero, P.M. Alu retrotransposons modulate Nanog expression through dynamic changes in regional chromatin conformation via aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Epigenetics Chromatin 2020, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikha, P.; Lee, D.A. The role of AhR in transcriptional regulation of immune cell development and function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2020, 1873, 188335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula Borges, D.; Dos Santos, A.W.A.; Paier, C.R.K.; Júnior, H.L.R.; Costa, M.B.; Farias, I.R.; de Oliveira, R.T.G.; da Frota França, I.G.; Cavalcante, G.M.; Magalhães, S.M.M.; et al. Prognostic importance of Aurora Kinases and mitotic spindle genes transcript levels in Myelodysplastic syndrome. Leuk. Res. 2018, 64, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazit, R.; Garrison, B.S.; Rao, T.N.; Shay, T.; Costello, J.; Ericson, J.; Kim, F.; Collins, J.J.; Regev, A.; Wagers, A.J.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis Identifies Regulators of Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2013, 1, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenson, B.; Crispino, J.D. The aurora kinases in cell cycle and leukemia. Oncogene 2015, 34, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goroshchuk, O.; Kolosenko, I.; Vidarsdottir, L.; Azimi, A.; Palm-Apergi, C. Polo-like kinases and acute leukemia. Oncogene 2019, 38, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.X.; Liu, R.; Jin, S.Q.; Fan, F.Y.; Zhan, Q.M. Overexpression of Aurora-A kinase promotes tumor cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Cell Res. 2006, 16, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goepfert, T.M.; Adigun, Y.E.; Zhong, L.; Gay, J.; Medina, D.; Brinkley, W.R. Centrosome amplification and overexpression of aurora A are early events in rat mammary carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4115–4122. [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier, N.; Sicheri, F.; Pintard, L. Aurora A kinase activation: Different means to different ends. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e202106128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentil, M.; Hugues, P.; Desterke, C.; Telliam, G.; Sloma, I.; Souza, L.E.B.; Baykal, S.; Artus, J.; Griscelli, F.; Guerci, A.; et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) is a novel druggable pathway controlling malignant progenitor proliferation in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.; Zulick, E.; Skvir, N.; Vanuytsel, K.; Morrison, T.A.; Naing, Z.H.; Wang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Chui, D.H.; Steinberg, M.H.; et al. Notch and aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling impact definitive hematopoiesis from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 1004–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Sheng, B.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, K.; Xiao, W.; Yang, H. Role of AhR in positive regulation of cell proliferation and survival. Cell Prolif. 2016, 49, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Leo, E.M.; Lorenzo-Martín, L.F.; Román, Á.C.; Bustelo, X.R.; Merino, J.M.; Fernández-Salguero, P.M. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor controls skin homeostasis, regeneration, and hair follicle cycling by adjusting epidermal stem cell function. Stem Cells 2021, 39, 1733–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolluri, S.K.; Weiss, C.; Koff, A.; Göttlicher, M. p27Kip1 induction and inhibition of proliferation by the intracellular Ah receptor in developing thymus and hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1742–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elizondo, G.; Fernandez-Salguero, P.; Sheikh, M.S.; Kim, G.-Y.; Fornace, A.J.; Lee, K.S.; Gonzalez, F.J. Altered cell cycle control at the G2/M phases in aryl hydrocarbon receptor-null embryo fibroblast. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Kurita, H.; Carreira, V.; Ko, C.-I.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Biesiada, J.; Medvedovic, M.; Puga, A. Ah receptor activation by dioxin disrupts activin, BMP, and WNT signals during the early differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells and inhibits cardiomyocyte functions. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 149, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahim, M.; Smith, R.; Safe, S. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor gene silencing with small inhibitory RNA differentially modulates Ah-responsiveness in MCF-7 and HepG2 cancer cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 63, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, F.K.B.; Jensen, T.L.; Rapin, N.; Aslan, D.; Wilhelmson, A.S.; Pundhir, S.; Rehn, M.; Paul, F.; Giladi, A.; Hasemann, M.S.; et al. Differences in Cell Cycle Status Underlie Transcriptional Heterogeneity in the HSC Compartment. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 766–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucella, J.N.; Upadhaya, S.; Reizis, B. The Source and Dynamics of Adult Hematopoiesis: Insights from Lineage Tracing. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 36, 529–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, M.A.; Schroeder, T. Hematopoiesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. 2012, 4, a008250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, C.; Rannug, A. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Barrier Organ Physiology, Immunology, and Toxicology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-C.; Chang, L.-H.; Huang, S.-S.; Huang, Y.-J.; Chih, C.-L.; Kuo, H.-C.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lee, I.H. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulates stroke-induced astrogliosis and neurogenesis in the adult mouse brain. J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Duran, A.; Carvajal-Gonzalez, J.M.; Mulero-Navarro, S.; Santiago-Josefat, B.; Puga, A.; Fernandez-Salguero, P.M. Fitting a xenobiotic receptor into cell homeostasis: How the dioxin receptor interacts with TGFβ signaling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, M.; Fabbrocini, G.; Martora, F.; Picone, V.; Morelli, P.; Patruno, C. Role of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation in Inflammatory Chronic Skin Diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, C.; Staley, S.; Wilson, K.; Rutkovsky, A.; Wisniewski, P.; Dopkins, N.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.; Busbee, P.B. AhR expression on both Rorc-specific immune cells and Vil1-expressing colonic epithelial cells are essential for I3C-mediated protection against colitis. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 17-04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boule, L.A.; Burke, C.G.; Jin, G.-B.; Lawrence, B.P. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling modulates antiviral immune responses: Ligand metabolism rather than chemical source is the stronger predictor of outcome. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, Á.C.; Carvajal-Gonzalez, J.M.; Merino, J.M.; Mulero-Navarro, S.; Fernández-Salguero, P.M. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the crossroad of signalling networks with therapeutic value. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 185, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franchini, A.M.; Vaughan, K.L.; Bhattacharya, S.; Singh, K.P.; Gasiewicz, T.A.; Lawrence, B.P. Impact of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor on Aurora A Kinase and the G2/M Phase Pathway in Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells. Receptors 2023, 2, 100-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2010006
Franchini AM, Vaughan KL, Bhattacharya S, Singh KP, Gasiewicz TA, Lawrence BP. Impact of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor on Aurora A Kinase and the G2/M Phase Pathway in Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells. Receptors. 2023; 2(1):100-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranchini, Anthony M., Keegan L. Vaughan, Soumyaroop Bhattacharya, Kameshwar P. Singh, Thomas A. Gasiewicz, and B. Paige Lawrence. 2023. "Impact of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor on Aurora A Kinase and the G2/M Phase Pathway in Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells" Receptors 2, no. 1: 100-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2010006
APA StyleFranchini, A. M., Vaughan, K. L., Bhattacharya, S., Singh, K. P., Gasiewicz, T. A., & Lawrence, B. P. (2023). Impact of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor on Aurora A Kinase and the G2/M Phase Pathway in Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells. Receptors, 2(1), 100-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2010006





