Molecular Characterization and Pharmacology of Melatonin Receptors in Animals
Abstract
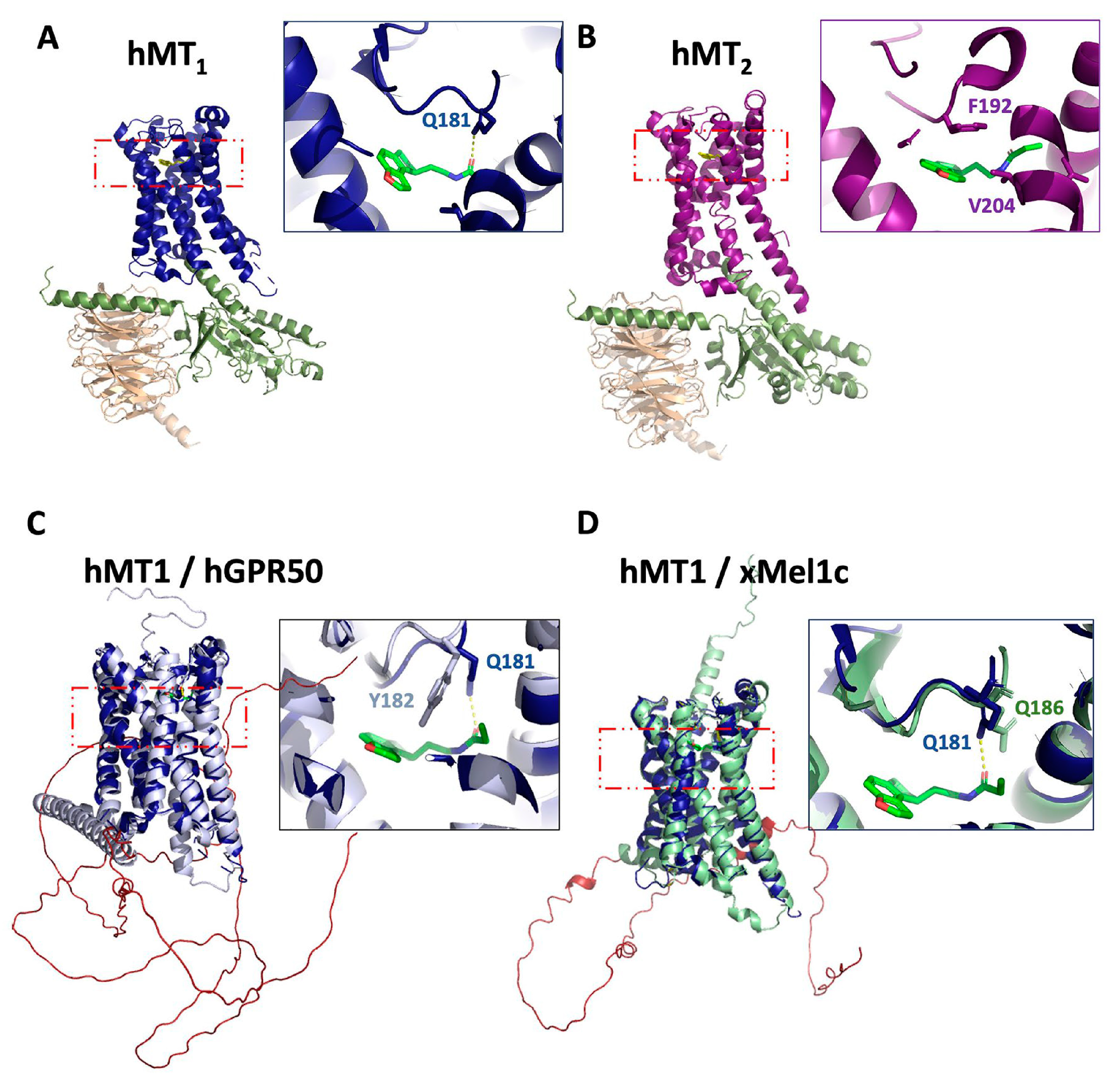
:1. Introduction
2. Cloning, Expression and Purification
2.1. Cloning
| pKi | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse MT1 | Mouse MT2 | Rat MT1 | Rat MT2 | Human MT1 | Human MT2 | Hamster MT1 | Hen Mel1c | |
| 4P-PDOT | 6.7 | 7.9 | 6.46 | 7.44 | 7.56 | 9.07 | 5.9 | 6.4 |
| Luzindole | 6.2 | 6.6 | 6.53 | 6.47 | 8.9 | 7.8 | 5.5 | 5.4 |
| MLT | 9.7 | 9.4 | 11.6 | 10 | 10.49 | 9.83 | 9.6 | 9.8 |
| S24268 | 6.9 | 5.2 | 5.72 | 5.96 | 7.89 | 7.15 | N/D | N/D |
| S20928 | 6.1 | 6.3 | 6.48 | 6.28 | 7.1 | 7.05 | 5.4 | N/D |
| S24773 | 6.8 | 7.8 | 6.72 | 8.25 | 6.9 | 7.7 | N/D | N/D |
2.2. Expression
2.3. Purification and Reconstitution
3. Melatonin Receptor Ligands
3.1. Labeled Tracers for Melatonin Receptor
3.2. Virtual Melatonin Receptor Ligand Search
3.3. Functional Characterization of Melatonin Receptors
3.4. Bias
3.5. Receptor-Associated Proteins
3.6. Antibodies
4. Drugs at Melatonin Receptors
5. Future Trends and Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boutin, J.A.; Audinot, V.; Ferry, G.; Delagrange, P. Molecular tools to study melatonin pathways and actions. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 26, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, D.C. Arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase: “The Timezyme”. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 4233–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reppert, S.M.; Weaver, D.R.; Godson, C. Melatonin receptors step into the light: Cloning and classification of subtypes. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1996, 17, 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakkuri, O.; Lämsä, E.; Rahkamaa, E.; Ruotsalainen, H.; Leppäluoto, J. Iodinated melatonin: Preparation and characterization of the molecular structure by mass and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 142, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudon, M.; Zisapel, N. Characterization of central melatonin receptors using 125 I-melatonin. FEBS Lett. 1986, 197, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan, M.J.; Takahashi, J.S.; Dubocovich, M.L. Characterization of 2-[125I]iodomelatonin binding sites in hamster brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1986, 132, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebisawa, T.; Karne, S.; Lerner, M.R.; Reppert, S.M. Expression cloning of a high-affinity melatonin receptor from Xenopus dermal melanophores. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 6133–6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reppert, S.M.; Weaver, D.R.; Cassone, V.M.; Godson, C.; Kolakowski, L.F. Melatonin receptors are for the birds: Molecular analysis of two receptor subtypes differentially expressed in chick brain. Neuron 1995, 15, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, Y.-J.; Park, J.-G.; Jeong, H.-B.; Takeuchi, Y.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-D.; Takemura, A. Expression of the melatonin receptor Mel(1c) in neural tissues of the reef fish Siganus guttatus . Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 147, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufourny, L.; Levasseur, A.; Migaud, M.; Callebaut, I.; Pontarotti, P.; Malpaux, B.; Monget, P. GPR50 is the mammalian ortholog of Mel1c: Evidence of rapid evolution in mammals. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levoye, A.; Dam, J.; Ayoub, M.A.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Couturier, C.; Delagrange, P.; Jockers, R. The orphan GPR50 receptor specifically inhibits MT1 melatonin receptor function through heterodimerization. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3012–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciech, S.; Ahmad, R.; Belaid-Choucair, Z.; Journé, A.-S.; Gallet, S.; Dam, J.; Daulat, A.; Ndiaye-Lobry, D.; Lahuna, O.; Karamitri, A.; et al. The orphan GPR50 receptor promotes constitutive TGFβ receptor signaling and protects against cancer development. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clement, N.; Renault, N.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Cecon, E.; Journé, A.-S.; Laurent, X.; Tadagaki, K.; Cogé, F.; Gohier, A.; Delagrange, P.; et al. Importance of the second extracellular loop for melatonin MT1 receptor function and absence of melatonin binding in GPR50. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 3281–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier, C.; Guenin, S.-P.; Riest-Fery, I.; Perry, T.J.; Legros, C.; Nosjean, O.; Simonneaux, V.; Grützner, F.; Boutin, J.A. Characterization of the Mel1c melatoninergic receptor in platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan, M.J.; Takahashi, J.S.; Dubocovich, M.L. 2-125Iiodomelatonin binding sites in hamster brain membranes: Pharmacological characteristics and regional distribution. Endocrinology 1988, 122, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosjean, O.; Ferro, M.; Coge, F.; Beauverger, P.; Henlin, J.M.; Lefoulon, F.; Fauchere, J.L.; Delagrange, P.; Canet, E.; Boutin, J.A. Identification of the melatonin-binding site MT3 as the quinone reductase 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 31311–31317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boutin, J.A.; Ferry, G. Is There Sufficient Evidence that the Melatonin Binding Site MT3 Is Quinone Reductase 2? J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 368, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabajee-Alibay, P.; Bonnaud, A.; Malpaux, B.; Delagrange, P.; Audinot, V.; Yous, S.; Boutin, J.A.; Stephan, J.-P.; Leprince, J.; Legros, C. A putative new melatonin binding site in sheep brain, MTx: Preliminary observations and characteristics. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2021, 380, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, S.Y.; Ng, N.; Pang, S.F. A molecular perspective of the genetic relationships of G-protein coupled melatonin receptor subtypes. J. Pineal Res. 1996, 20, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denker, E.; Ebbesson, L.O.E.; Hazlerigg, D.G.; Macqueen, D.J. Phylogenetic Reclassification of Vertebrate Melatonin Receptors To Include Mel1d. G3 2019, 9, 3225–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Labani, N.; Cecon, E.; Jockers, R. Melatonin Target Proteins: Too Many or Not Enough? Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stauch, B.; Johansson, L.C.; McCorvy, J.D.; Patel, N.; Han, G.W.; Huang, X.-P.; Gati, C.; Batyuk, A.; Slocum, S.T.; Ishchenko, A.; et al. Structural basis of ligand recognition at the human MT1 melatonin receptor. Nature 2019, 569, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.C.; Stauch, B.; McCorvy, J.D.; Han, G.W.; Patel, N.; Huang, X.-P.; Batyuk, A.; Gati, C.; Slocum, S.T.; Li, C.; et al. XFEL structures of the human MT2 melatonin receptor reveal the basis of subtype selectivity. Nature 2019, 569, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Jockers, R. Structure-Based Virtual Screening Accelerates GPCR Drug Discovery. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elisi, G.M.; Scalvini, L.; Lodola, A.; Bedini, A.; Spadoni, G.; Rivara, S. In silico drug discovery of melatonin receptor ligands with therapeutic potential. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2022, 17, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.H.; Miyauchi, H.; Inoue, A.; Raimondi, F.; Tsujimoto, H.; Kusakizako, T.; Shihoya, W.; Yamashita, K.; Suno, R.; Nomura, N.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of the human MT1-Gi signaling complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lu, Q.; Guo, Q.; Teng, M.; Gong, Q.; Li, X.; Du, Y.; Liu, Z.; Tao, Y. Structural basis of the ligand binding and signaling mechanism of melatonin receptors. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadi, M.; Anyango, S.; Deshpande, M.; Nair, S.; Natassia, C.; Yordanova, G.; Yuan, D.; Stroe, O.; Wood, G.; Laydon, A.; et al. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database: Massively expanding the structural coverage of protein-sequence space with high-accuracy models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D439–D444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Ali, S.; Manghwar, H.; Saqib, S.; Ullah, F.; Ayaz, A.; Zaman, W. Melatonin Function and Crosstalk with Other Phytohormones under Normal and Stressful Conditions. Genes 2022, 13, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, N.; Iqbal, S.; Hayat, F.; Raziq, A.; Ayaz, A.; Zaman, W. Melatonin in Micro-Tom Tomato: Improved Drought Tolerance via the Regulation of the Photosynthetic Apparatus, Membrane Stability, Osmoprotectants, and Root System. Life 2022, 12, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldo Acosta, M.; Cano, A.; Hernández-Ruiz, J.; Arnao, M.B. Melatonin as a Possible Natural Safener in Crops. Plants 2022, 11, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reppert, S.M.; Weaver, D.R.; Ebisawa, T. Cloning and characterization of a mammalian melatonin receptor that mediates reproductive and circadian responses. Neuron 1994, 13, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reppert, S.M.; Godson, C.; Mahle, C.D.; Weaver, D.R.; Slaugenhaupt, S.A.; Gusella, J.F. Molecular characterization of a second melatonin receptor expressed in human retina and brain: The Mel1b melatonin receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8734–8738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roca, A.L.; Godson, C.; Weaver, D.R.; Reppert, S.M. Structure, characterization, and expression of the gene encoding the mouse Mel1a melatonin receptor. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 3469–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pozo, D.; Delgado, M.; Fernandez-Santos, J.M.; Calvo, J.R.; Gomariz, R.P.; Martin-Lacave, I.; Ortiz, G.G.; Guerrero, J.M. Expression of the Mel1a-melatonin receptor mRNA in T and B subsets of lymphocytes from rat thymus and spleen. FASEB J. 1997, 11, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gauer, F.; Schuster, C.; Poirel, V.-J.; Pévet, P.; Masson-Pévet, M. Cloning experiments and developmental expression of both melatonin receptor Mel1A mRNA and melatonin binding sites in the Syrian hamster suprachiasmatic nuclei. Mol. Brain Res. 1998, 60, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailliet, F.; Audinot, V.; Malpaux, B.; Bonnaud, A.; Delagrange, P.; Migaud, M.; Barrett, P.; Viaud-Massuard, M.-C.; Lesieur, D.; Lefoulon, F.; et al. Molecular pharmacology of the ovine melatonin receptor: Comparison with recombinant human MT1 and MT2 receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 67, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audinot, V.; Bonnaud, A.; Grandcolas, L.; Rodriguez, M.; Nagel, N.; Galizzi, J.-P.; Balik, A.; Messager, S.; Hazlerigg, D.G.; Barrett, P.; et al. Molecular cloning and pharmacological characterization of rat melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 2007–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devavry, S.; Legros, C.; Brasseur, C.; Cohen, W.; Guenin, S.-P.; Delagrange, P.; Malpaux, B.; Ouvry, C.; Cogé, F.; Nosjean, O.; et al. Molecular pharmacology of the mouse melatonin receptors MT1 and MT2. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 677, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogé, F.; Guenin, S.P.; Fery, I.; Migaud, M.; Devavry, S.; Slugocki, C.; Legros, C.; Ouvry, C.; Cohen, W.; Renault, N.; et al. The end of a myth: Cloning and characterization of the ovine melatonin MT(2) receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 1248–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gautier, C.; Dufour, E.; Dupré, C.; Lizzo, G.; Caignard, S.; Riest-Fery, I.; Brasseur, C.; Legros, C.; Delagrange, P.; Nosjean, O.; et al. Hamster Melatonin Receptors: Cloning and Binding Characterization of MT1 and Attempt to Clone MT2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Tam, P.C.; Poon, A.M.; Brown, G.M.; Pang, S.F. 2-125Iiodomelatonin-binding sites in the human kidney and the effect of guanosine 5′-O-(3-thiotriphosphate). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Ayre, E.A.; Pang, S.F. 125Iiodomelatonin binding sites in mammalian and avian kidneys. Biol. Signals 1993, 2, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier, C.; Theret, I.; Lizzo, G.; Ferry, G.; Guénin, S.-P.; Boutin, J.A. Why Are We Still Cloning Melatonin Receptors? A Commentary. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2550, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legros, C.; Dupré, C.; Brasseur, C.; Bonnaud, A.; Bruno, O.; Valour, D.; Shabajee, P.; Giganti, A.; Nosjean, O.; Kenakin, T.P.; et al. Characterization of the various functional pathways elicited by synthetic agonists or antagonists at the melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2020, 8, e00539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boutin, J.A.; Legros, C. The five dimensions of receptor pharmacology exemplified by melatonin receptors: An opinion. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2020, 8, e00556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boutin, J.A.; Witt-Enderby, P.A.; Sotriffer, C.; Zlotos, D.P. Melatonin receptor ligands: A pharmaco-chemical perspective. J. Pineal Res. 2020, 69, e12672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier, C.; Bothorel, B.; Ciocca, D.; Valour, D.; Gaudeau, A.; Dupré, C.; Lizzo, G.; Brasseur, C.; Riest-Fery, I.; Stephan, J.-P.; et al. Gene expression profiling during hibernation in the European hamster. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, K.; Michaux, J.; Lebedev, V.; Yigit, N.; Colak, E.; Ivanova, N.; Poltoraus, A.; Surov, A.; Markov, G.; Maak, S.; et al. Molecular phylogeny of the Cricetinae subfamily based on the mitochondrial cytochrome b and 12S rRNA genes and the nuclear vWF gene. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2006, 39, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, D.R.; Liu, C.; Reppert, S.M. Nature’s knockout: The Mel1b receptor is not necessary for reproductive and circadian responses to melatonin in Siberian hamsters. Mol. Endocrinol. 1996, 10, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becker-André, M.; Wiesenberg, I.; Schaeren-Wiemers, N.; André, E.; Missbach, M.; Saurat, J.H.; Carlberg, C. Pineal gland hormone melatonin binds and activates an orphan of the nuclear receptor superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 28531–28534, Erratum in J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 16707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero, G.; Rodella, L.F.; Nardo, L.; Giugno, L.; Cocchi, M.A.; Borsani, E.; Reiter, R.J.; Rezzani, R. A comparison of melatonin and α-lipoic acid in the induction of antioxidant defences in L6 rat skeletal muscle cells. Age 2015, 37, 9824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.-C.; Lu, K.-C.; Lin, G.-J.; Hsieh, H.-Y.; Chu, P.; Lin, S.-H.; Sytwu, H.-K. Melatonin enhances endogenous heme oxygenase-1 and represses immune responses to ameliorate experimental murine membranous nephropathy. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, T.; Feng, D.; Zhou, B.; Bai, L.; Yin, Y. Melatonin Suppresses LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress in Dendritic Cells for Inflammatory Regulation via the Nrf2/HO-1 Axis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; An, S.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Yu, B.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lin, B.; Lin, X.; Gao, Y. Melatonin suppresses ferroptosis via activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in the mouse model of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 112, 109162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, A.; Clark, J.; Fedo, J.; Sementilli, A.; Fragoso, Y.D.; McCaffery, P. Retinoic Acid Signalling in the Pineal Gland Is Conserved across Mammalian Species and Its Transcriptional Activity Is Inhibited by Melatonin. Cells 2023, 12, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, D.N.; Otchere, A.; Patel, J.H.; Uddin, R.; Pollock, N.L.; Routledge, S.J.; Rothnie, A.J.; Slack, C.; Poyner, D.R.; Bill, R.M.; et al. Expression and purification of recombinant G protein-coupled receptors: A review. Protein Expr. Purif. 2020, 167, 105524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, L.; Kugler, V.; Wagner, R. Expression of Eukaryotic Membrane Proteins in Pichia pastoris. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1432, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logez, C.; Berger, S.; Legros, C.; Banères, J.-L.; Cohen, W.; Delagrange, P.; Nosjean, O.; Boutin, J.A.; Ferry, G.; Simonin, F.; et al. Recombinant human melatonin receptor MT1 isolated in mixed detergents shows pharmacology similar to that in mammalian cell membranes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godson, C.; Reppert, S.M. The Mel1a melatonin receptor is coupled to parallel signal transduction pathways. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Tanaka, G.; Masuda, S.; Ogasawara, J.; Sakurai, T.; Kizaki, T.; Ohno, H.; Izawa, T. Melatonin promotes adipogenesis and mitochondrial biogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Meng, J.; Long, J.; Li, L.; Qiu, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.V.; Ren, P.-G. Orphan receptor GPR50 attenuates inflammation and insulin signaling in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. FEBS Open Bio 2022, 13, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munmun, F.; Mohiuddin, O.A.; van Hoang, T.; Burow, M.E.; Bunnell, B.A.; Sola, V.M.; Carpentieri, A.R.; Witt-Enderby, P.A. The role of MEK1/2 and MEK5 in melatonin-mediated actions on osteoblastogenesis, osteoclastogenesis, bone microarchitecture, biomechanics, and bone formation. J. Pineal Res. 2022, 73, e12814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logez, C.; Damian, M.; Legros, C.; Dupré, C.; Guéry, M.; Mary, S.; Wagner, R.; M’Kadmi, C.; Nosjean, O.; Fould, B.; et al. Detergent-free Isolation of Functional G Protein-Coupled Receptors into Nanometric Lipid Particles. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Rao, B.D.; Jafurulla, M. Solubilization of G protein-coupled receptors: A convenient strategy to explore lipid-receptor interaction. Methods Enzymol. 2015, 557, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hothersall, J.D.; Jones, A.Y.; Dafforn, T.R.; Perrior, T.; Chapman, K.L. Releasing the technical ‘shackles’ on GPCR drug discovery: Opportunities enabled by detergent-free polymer lipid particle (PoLiPa) purification. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1944–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amati, A.; Graf, S.; Deutschmann, S.; Dolder, N.; Von Ballmoos, C. Current problems and future avenues in proteoliposome research. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 1473–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jockers, R.; Maurice, P.; Boutin, J.A.; Delagrange, P. Melatonin receptors, heterodimerization, signal transduction and binding sites: What’s new? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legros, C.; Devavry, S.; Caignard, S.; Tessier, C.; Delagrange, P.; Ouvry, C.; Boutin, J.A.; Nosjean, O. Melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors display different molecular pharmacologies only in the G-protein coupled state. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaulieu, J.-M.; Borrelli, E.; Carlsson, A.; Caron, M.G.; Civelli, O.; Espinoza, S.; Fisone, G.; Gainetdinov, R.R.; Grandy, D.K.; Kebabian, J.W.; et al. Dopamine receptors (version 2019.4) in the IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology Database. GtoPdb CITE 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grailhe, R.; Grabtree, G.W.; Hen, R. Human 5-HT(5) receptors: The 5-HT(5A) receptor is functional but the 5-HT(5B) receptor was lost during mammalian evolution. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 418, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beukers, M.W.; Klaassen, C.H.W.; De Grip, W.J.; Verzijl, D.; Timmerman, H.; Leurs, R. Heterologous expression of rat epitope-tagged histamine H2 receptors in insect Sf9 cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 122, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pockes, S.; Wifling, D.; Keller, M.; Buschauer, A.; Elz, S. Highly Potent, Stable, and Selective Dimeric Hetarylpropylguanidine-Type Histamine H2 Receptor Agonists. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 2865–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molinari, E.J.; North, P.C.; Dubocovich, M.L. 2-[125I]Iodo-5-methoxycarbonylamino-N-acetyltryptamine: A selective radioligand for the characterization of melatonin ML2 binding sites. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 301, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, L.; Cohen, W.; Delagrange, P.; Boutin, J.A.; Nosjean, O. Molecular and cellular pharmacological properties of 5-methoxycarbonylamino-N-acetyltryptamine (MCA-NAT): A nonspecific MT3 ligand. J. Pineal Res. 2010, 48, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legros, C.; Brasseur, C.; Delagrange, P.; Ducrot, P.; Nosjean, O.; Boutin, J.A. Alternative Radioligands for Investigating the Molecular Pharmacology of Melatonin Receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 356, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legros, C.; Matthey, U.; Grelak, T.; Pedragona-Moreau, S.; Hassler, W.; Yous, S.; Thomas, E.; Suzenet, F.; Folleas, B.; Lefoulon, F.; et al. New radioligands for describing the molecular pharmacology of MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8948–8962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gbahou, F.; Cecon, E.; Viault, G.; Gerbier, R.; Jean-Alphonse, F.; Karamitri, A.; Guillaumet, G.; Delagrange, P.; Friedlander, R.M.; Vilardaga, J.-P.; et al. Design and validation of the first cell-impermeant melatonin receptor agonist. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 2409–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gbahou, F.; Levin, S.; Tikhonova, I.G.; Somalo Barranco, G.; Izabelle, C.; Ohana, R.F.; Jockers, R. Luminogenic HiBiT Peptide-Based NanoBRET Ligand Binding Assays for Melatonin Receptors. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2022, 5, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somalo-Barranco, G.; Serra, C.; Lyons, D.; Piggins, H.D.; Jockers, R.; Llebaria, A. Design and Validation of the First Family of Photo-Activatable Ligands for Melatonin Receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 11229–11240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, R.; Barnes, N.M.; Baxter, G.; Bockaert, J.; Branchek, T.; Butler, A.; Cohen, M.L.; Dumuis, A.; Eglen, R.M.; Göthert, M.; et al. 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptors (version 2019.4) in the IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology Database. GtoPdb CITE 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantarini, M.; Rusciano, D.; Amato, R.; Canovai, A.; Cammalleri, M.; Monte, M.D.; Minnelli, C.; Laudadio, E.; Mobbili, G.; Giorgini, G.; et al. Structural Basis for Agonistic Activity and Selectivity toward Melatonin Receptors hMT1 and hMT2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, R.M.; Kang, H.J.; McCorvy, J.D.; Glatfelter, G.C.; Jones, A.J.; Che, T.; Slocum, S.; Huang, X.-P.; Savych, O.; Moroz, Y.S.; et al. Virtual discovery of melatonin receptor ligands to modulate circadian rhythms. Nature 2020, 579, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Huang, X.P.; Grandner, J.M.; Johansson, L.C.; Stauch, B.; McCorvy, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Roth, B.; Katritch, V. Structure-based discovery of potent and selective melatonin receptor agonists. Elife 2020, 9, e53779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCord, C.P.; Allen, F.P. Evidences associating pineal gland function with alterations in pigmentation. J. Exp. Zool. 1917, 23, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lerner, A.B.; Case, J.D.; Takahashi, Y.; Lee, T.H.; Mori, W. Isolation of melatonin, the pineal gland factor that lightens melanocytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Robison, G.A.; Liddle, G.W.; Butcher, R.W.; Nicholson, W.E.; Baird, C.E. Role of cyclic AMP in mediating the effects of MSH, norepinephrine, and melatonin on frog skin color. Endocrinology 1969, 85, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.H.; Sekura, R.D.; Rollag, M.D. Pertussis toxin blocks melatonin-induced pigment aggregation in Xenopus dermal melanophores. J. Comp. Physiol. B 1987, 157, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugden, D. Effect of putative melatonin receptor antagonists on melatonin-induced pigment aggregation in isolated Xenopus laevis melanophores. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 213, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugden, D. N-acyl-3-amino-5-methoxychromans: A new series of non-indolic melatonin analogues. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 254, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filadelfi, A.M.; Castrucci, A.M. Melatonin desensitizing effects on the in vitro responses to MCH, alpha-MSH, isoproterenol and melatonin in pigment cells of a fish (S. marmoratus), a toad (B. ictericus), a frog (R. pipiens), and a lizard (A. carolinensis), exposed to varying photoperiodic regimens. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Physiol. 1994, 109, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolesi, G.E.; Atkinson-Leadbeater, K.; Mackey, E.M.; Song, Y.N.; Heyne, B.; McFarlane, S. The regulation of skin pigmentation in response to environmental light by pineal Type II opsins and skin melanophore melatonin receptors. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2020, 212, 112024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubocovich, M.L. Characterization of a retinal melatonin receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1985, 234, 395–401. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, K.; Tosini, G. Assessing the Role of Melatonin in the Modulation of Visual Functions in the Mouse. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2550, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatfelter, G.C.; Sosa, J.; Hudson, R.L.; Dubocovich, M.L. Methods to Assess Melatonin Receptor-Mediated Phase-Shift and Re-entrainment of Rhythmic Behaviors in Mouse Models. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2550, 391–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydon, L.; Petit, L.; De Coppet, P.; Barrett, P.; Morgan, P.; Strosberg, A.D.; Jockers, R. Polymorphism and signalling of melatonin receptors. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 1999, 39, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecon, E.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Jockers, R. Functional Investigation of Melatonin Receptor Activation by Homogenous cAMP Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2550, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbier, R.; Jockers, R. GTPγS Binding Assay for Melatonin Receptors in Mouse Brain Tissue. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2550, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, A.; Jockers, R. Measuring Protein-Protein Interactions of Melatonin Receptors by Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET). Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2550, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plouffe, B.; Karamitri, A.; Flock, T.; Gallion, J.M.; Houston, S.; Daly, C.A.; Bonnefond, A.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Le Gouill, C.; Froguel, P.; et al. Structural Elements Directing G Proteins and β-Arrestin Interactions with the Human Melatonin Type 2 Receptor Revealed by Natural Variants. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2022, 5, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupré, C.; Legros, C.; Boutin, J.A. Functionality of Melatonin Receptors: Recruitment of β-Arrestin at MT1. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2550, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegron, A.; Huh, E.; Deupi, X.; Sokrat, B.; Gao, W.; Le Gouill, C.; Canouil, M.; Boissel, M.; Charpentier, G.; Roussel, R.; et al. Identification of Key Regions Mediating Human Melatonin Type 1 Receptor Functional Selectivity Revealed by Natural Variants. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 1614–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamitri, A.; Plouffe, B.; Bonnefond, A.; Chen, M.; Gallion, J.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Hegron, A.; Boissel, M.; Canouil, M.; Langenberg, C.; et al. Type 2 diabetes-associated variants of the MT2 melatonin receptor affect distinct modes of signaling. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaan6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cecon, E.; Oishi, A.; Jockers, R. Melatonin receptors: Molecular pharmacology and signalling in the context of system bias. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 3263–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Cecon, E.; Karamitri, A.; Gao, W.; Gerbier, R.; Ahmad, R.; Jockers, R. Melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptor ERK signaling is differentially dependent on Gi/o and Gq/11 proteins. J. Pineal Res. 2020, 68, e12641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roka, F.; Brydon, L.; Waldhoer, M.; Strosberg, A.D.; Freissmuth, M.; Jockers, R.; Nanoff, C. Tight association of the human Mel(1a)-melatonin receptor and G(i): Precoupling and constitutive activity. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 56, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydon, L.; Roka, F.; Petit, L.; de Coppet, P.; Tissot, M.; Barrett, P.; Morgan, P.J.; Nanoff, C.; Strosberg, A.D.; Jockers, R. Dual signaling of human Mel1a melatonin receptors via G(i2), G(i3), and G(q/11) proteins. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 2025–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, P.; Kenakin, T.; Alexander, S.P.H.; Bermudez, M.; Bohn, L.M.; Breinholt, C.S.; Bouvier, M.; Hill, S.J.; Kostenis, E.; Martemyanov, K.A.; et al. Community guidelines for GPCR ligand bias: IUPHAR review 32. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 3651–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenakin, T. Emergent Concepts of Receptor Pharmacology. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2019, 260, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotta, L.A.; Mokrosiński, J.; Mendes de Oliveira, E.; Li, C.; Sharp, S.J.; Luan, J.; Brouwers, B.; Ayinampudi, V.; Bowker, N.; Kerrison, N.; et al. Human Gain-of-Function MC4R Variants Show Signaling Bias and Protect against Obesity. Cell 2019, 177, 597–607.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hablitz, L.M.; Molzof, H.E.; Abrahamsson, K.E.; Cooper, J.M.; Prosser, R.A.; Gamble, K.L. GIRK Channels Mediate the Nonphotic Effects of Exogenous Melatonin. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 14957–14965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McArthur, A.J.; Hunt, A.E.; Gillette, M.U. Melatonin action and signal transduction in the rat suprachiasmatic circadian clock: Activation of protein kinase C at dusk and dawn. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piano, I.; Baba, K.; Gargini, C.; Tosini, G. Heteromeric MT1/MT2 melatonin receptors modulate the scotopic electroretinogram via PKCζ in mice. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 177, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbier, R.; Ndiaye-Lobry, D.; Martinez de Morentin, P.B.; Cecon, E.; Heisler, L.K.; Delagrange, P.; Gbahou, F.; Jockers, R. Pharmacological evidence for transactivation within melatonin MT2 and serotonin 5-HT2C receptor heteromers in mouse brain. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, A.; Cecon, E.; Jockers, R. Melatonin Receptor Signaling: Impact of Receptor Oligomerization on Receptor Function. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 338, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A.S.; Avet, C.; Normand, C.; Mancini, A.; Inoue, A.; Bouvier, M.; Gloriam, D.E. Common coupling map advances GPCR-G protein selectivity. Elife 2022, 11, e74107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daulat, A.M.; Maurice, P.; Jockers, R. Recent methodological advances in the discovery of GPCR-associated protein complexes. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benleulmi-Chaachoua, A.; Chen, L.; Sokolina, K.; Wong, V.; Jurisica, I.; Emerit, M.B.; Darmon, M.; Espin, A.; Stagljar, I.; Tafelmeyer, P.; et al. Protein interactome mining defines melatonin MT1 receptors as integral component of presynaptic protein complexes of neurons. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, P.; Daulat, A.M.; Broussard, C.; Mozo, J.; Clary, G.; Hotellier, F.; Chafey, P.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Ferry, G.; Boutin, J.A.; et al. A generic approach for the purification of signaling complexes that specifically interact with the carboxyl-terminal domain of G protein-coupled receptors. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 1556–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benleulmi-Chaachoua, A.; Hegron, A.; Le Boulch, M.; Karamitri, A.; Wierzbicka, M.; Wong, V.; Stagljar, I.; Delagrange, P.; Ahmad, R.; Jockers, R. Melatonin receptors limit dopamine reuptake by regulating dopamine transporter cell-surface exposure. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 4357–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollinger, S.; Hepler, J.R. Cellular regulation of RGS proteins: Modulators and integrators of G protein signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 527–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernstein, L.S.; Ramineni, S.; Hague, C.; Cladman, W.; Chidiac, P.; Levey, A.I.; Hepler, J.R. RGS2 binds directly and selectively to the M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor third intracellular loop to modulate Gq/11alpha signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 21248–21256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hague, C.; Bernstein, L.S.; Ramineni, S.; Chen, Z.; Minneman, K.P.; Hepler, J.R. Selective inhibition of alpha1A-adrenergic receptor signaling by RGS2 association with the receptor third intracellular loop. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 27289–27295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgoussi, Z.; Leontiadis, L.; Mazarakou, G.; Merkouris, M.; Hyde, K.; Hamm, H. Selective interactions between G protein subunits and RGS4 with the C-terminal domains of the mu- and delta-opioid receptors regulate opioid receptor signaling. Cell. Signal. 2006, 18, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, P.; Daulat, A.M.; Turecek, R.; Ivankova-Susankova, K.; Zamponi, F.; Kamal, M.; Clement, N.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Bettler, B.; Galès, C.; et al. Molecular organization and dynamics of the melatonin MT1 receptor/RGS20/G(i) protein complex reveal asymmetry of receptor dimers for RGS and G(i) coupling. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 3646–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, J.-L.; Daulat, A.M.; Maurice, P.; Levoye, A.; Migaud, M.; Brydon, L.; Malpaux, B.; Borg-Capra, C.; Jockers, R. The PDZ protein mupp1 promotes Gi coupling and signaling of the Mt1 melatonin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 16762–16771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayoub, M.A.; Couturier, C.; Lucas-Meunier, E.; Angers, S.; Fossier, P.; Bouvier, M.; Jockers, R. Monitoring of ligand-independent dimerization and ligand-induced conformational changes of melatonin receptors in living cells by bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 21522–21528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayoub, M.A.; Levoye, A.; Delagrange, P.; Jockers, R. Preferential formation of MT1/MT2 melatonin receptor heterodimers with distinct ligand interaction properties compared with MT2 homodimers. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, K.; Benleulmi-Chaachoua, A.; Journé, A.-S.; Kamal, M.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Dussaud, S.; Gbahou, F.; Yettou, K.; Liu, C.; Contreras-Alcantara, S.; et al. Heteromeric MT1/MT2 melatonin receptors modulate photoreceptor function. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamal, M.; Gbahou, F.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Daulat, A.M.; Benleulmi-Chaachoua, A.; Luka, M.; Chen, P.; Kalbasi Anaraki, D.; Baroncini, M.; La Mannoury Cour, C.; et al. Convergence of melatonin and serotonin (5-HT) signaling at MT2/5-HT2C receptor heteromers. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 11537–11546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oishi, A.; Karamitri, A.; Gerbier, R.; Lahuna, O.; Ahmad, R.; Jockers, R. Orphan GPR61, GPR62 and GPR135 receptors and the melatonin MT2 receptor reciprocally modulate their signaling functions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beedle, A.M.; McRory, J.E.; Poirot, O.; Doering, C.J.; Altier, C.; Barrere, C.; Hamid, J.; Nargeot, J.; Bourinet, E.; Zamponi, G.W. Agonist-independent modulation of N-type calcium channels by ORL1 receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, R.M.; You, H.; Hameed, S.; Altier, C.; Mezghrani, A.; Bourinet, E.; Zamponi, G.W. Heterodimerization of ORL1 and opioid receptors and its consequences for N-type calcium channel regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Massagué, J. TGFbeta in Cancer. Cell 2008, 134, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raynaud, P.; Gauthier, C.; Jugnarain, V.; Jean-Alphonse, F.; Reiter, E.; Bruneau, G.; Crépieux, P. Intracellular VHHs to monitor and modulate GPCR signaling. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1048601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-H.; Ursinus, J.; Zhou, J.-N.; Scheer, F.A.J.L.; Ai-Min, B.; Jockers, R.; van Heerikhuize, J.; Swaab, D.F. Alterations of melatonin receptors MT1 and MT2 in the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus during depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 148, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaskan, E.; Ayoub, M.A.; Ravid, R.; Angeloni, D.; Fraschini, F.; Meier, F.; Eckert, A.; Müller-Spahn, F.; Jockers, R. Reduced hippocampal MT2 melatonin receptor expression in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 38, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, P.; Sözer-Topcular, N.; Jockers, R.; Ravid, R.; Angeloni, D.; Fraschini, F.; Eckert, A.; Müller-Spahn, F.; Savaskan, E. Pineal and cortical melatonin receptors MT1 and MT2 are decreased in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Histochem. 2006, 50, 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.-H.; Zhou, J.-N.; van Heerikhuize, J.; Jockers, R.; Swaab, D.F. Decreased MT1 melatonin receptor expression in the suprachiasmatic nucleus in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaskan, E.; Olivieri, G.; Brydon, L.; Jockers, R.; Kräuchi, K.; Wirz-Justice, A.; Müller-Spahn, F. Cerebrovascular melatonin MT1-receptor alterations in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 308, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savaskan, E.; Olivieri, G.; Meier, F.; Brydon, L.; Jockers, R.; Ravid, R.; Wirz-Justice, A.; Müller-Spahn, F. Increased melatonin 1a-receptor immunoreactivity in the hippocampus of Alzheimer’s disease patients. J. Pineal Res. 2002, 32, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savaskan, E.; Wirz-Justice, A.; Olivieri, G.; Pache, M.; Kräuchi, K.; Brydon, L.; Jockers, R.; Müller-Spahn, F.; Meyer, P. Distribution of melatonin MT1 receptor immunoreactivity in human retina. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2002, 50, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer, P.; Pache, M.; Loeffler, K.U.; Brydon, L.; Jockers, R.; Flammer, J.; Wirz-Justice, A.; Savaskan, E. Melatonin MT-1-receptor immunoreactivity in the human eye. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 86, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, D.C.; Easley, S.E.; Asch, B.B.; Cheney, R.T.; Brydon, L.; Jockers, R.; Winston, J.S.; Brooks, J.S.; Hurd, T.; Asch, H.L. Differential expression of high-affinity melatonin receptors (MT1) in normal and malignant human breast tissue. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2002, 118, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-H.; Zhou, J.-N.; Balesar, R.; Unmehopa, U.; Bao, A.; Jockers, R.; van Heerikhuize, J.; Swaab, D.F. Distribution of MT1 melatonin receptor immunoreactivity in the human hypothalamus and pituitary gland: Colocalization of MT1 with vasopressin, oxytocin, and corticotropin-releasing hormone. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 499, 897–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wamelen, D.J.; Aziz, N.A.; Anink, J.J.; van Steenhoven, R.; Angeloni, D.; Fraschini, F.; Jockers, R.; Roos, R.A.C.; Swaab, D.F. Suprachiasmatic nucleus neuropeptide expression in patients with Huntington’s Disease. Sleep 2013, 36, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angeloni, D.; Longhi, R.; Fraschini, F. Production and characterization of antibodies directed against the human melatonin receptors Mel-1a (mt1) and Mel-1b (MT2). Eur. J. Histochem. 2000, 44, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Savaskan, E.; Jockers, R.; Ayoub, M.; Angeloni, D.; Fraschini, F.; Flammer, J.; Eckert, A.; Müller-Spahn, F.; Meyer, P. The MT2 melatonin receptor subtype is present in human retina and decreases in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2007, 4, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Canul, M.; Palazzo, E.; Dominguez-Lopez, S.; Luongo, L.; Lacoste, B.; Comai, S.; Angeloni, D.; Fraschini, F.; Boccella, S.; Spadoni, G.; et al. Selective melatonin MT2 receptor ligands relieve neuropathic pain through modulation of brainstem descending antinociceptive pathways. Pain 2015, 156, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Sanchez, R.; Comai, S.; Lacoste, B.; Bambico, F.R.; Dominguez-Lopez, S.; Spadoni, G.; Rivara, S.; Bedini, A.; Angeloni, D.; Fraschini, F.; et al. Promotion of non-rapid eye movement sleep and activation of reticular thalamic neurons by a novel MT2 melatonin receptor ligand. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 18439–18452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sengupta, A.; Baba, K.; Mazzoni, F.; Pozdeyev, N.V.; Strettoi, E.; Iuvone, P.M.; Tosini, G. Localization of melatonin receptor 1 in mouse retina and its role in the circadian regulation of the electroretinogram and dopamine levels. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jilg, A.; Bechstein, P.; Saade, A.; Dick, M.; Li, T.X.; Tosini, G.; Rami, A.; Zemmar, A.; Stehle, J.H. Melatonin modulates daytime-dependent synaptic plasticity and learning efficiency. J. Pineal Res. 2019, 66, e12553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Bretaño, A.; Suen, T.-C.; Baba, K.; DeBruyne, J.; Tosini, G. Melatonin receptor heterodimerization in a photoreceptor-like cell line endogenously expressing melatonin receptors. Mol. Vis. 2019, 25, 791–799. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Bretaño, A.; Baba, K.; Janjua, U.; Piano, I.; Gargini, C.; Tosini, G. Melatonin partially protects 661W cells from H2O2-induced death by inhibiting Fas/FasL-caspase-3. Mol. Vis. 2017, 23, 844–852. [Google Scholar]
- Posa, L.; De Gregorio, D.; Lopez-Canul, M.; He, Q.; Darcq, E.; Rullo, L.; Pearl-Dowler, L.; Luongo, L.; Candeletti, S.; Romualdi, P.; et al. Supraspinal melatonin MT2 receptor agonism alleviates pain via a neural circuit that recruits mu opioid receptors. J. Pineal Res. 2022, 73, e12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecon, E.; Ivanova, A.; Luka, M.; Gbahou, F.; Friederich, A.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Keller, P.; Knoch, K.; Ahmad, R.; Delagrange, P.; et al. Detection of recombinant and endogenous mouse melatonin receptors by monoclonal antibodies targeting the C-terminal domain. J. Pineal Res. 2019, 66, e12540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stazi, M.; Negro, S.; Megighian, A.; D’Este, G.; Solimena, M.; Jockers, R.; Lista, F.; Montecucco, C.; Rigoni, M. Melatonin promotes regeneration of injured motor axons via MT1 receptors. J. Pineal Res. 2021, 70, e12695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamouda, H.O.; Chen, P.; Levoye, A.; Sözer-Topçular, N.; Daulat, A.M.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Ravid, R.; Savaskan, E.; Ferry, G.; Boutin, J.A.; et al. Detection of the human GPR50 orphan seven transmembrane protein by polyclonal antibodies mapping different epitopes. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 43, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batailler, M.; Mullier, A.; Sidibe, A.; Delagrange, P.; Prévot, V.; Jockers, R.; Migaud, M. Neuroanatomical distribution of the orphan GPR50 receptor in adult sheep and rodent brains. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2012, 24, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidibe, A.; Mullier, A.; Chen, P.; Baroncini, M.; Boutin, J.A.; Delagrange, P.; Prevot, V.; Jockers, R. Expression of the orphan GPR50 protein in rodent and human dorsomedial hypothalamus, tanycytes and median eminence. J. Pineal Res. 2010, 48, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marczynski, T.J.; Yamaguchi, N.; Ling, G.M.; Grodzinska, L. Sleep induced by the administration of melatonin (5-methoxyn-acetyltryptamine) to the hypothalamus in unrestrained cats. Experientia 1964, 20, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubauer, D.N. A review of ramelteon in the treatment of sleep disorders. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2008, 4, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lôo, H.; Hale, A.; D’haenen, H. Determination of the dose of agomelatine, a melatoninergic agonist and selective 5-HT(2C) antagonist, in the treatment of major depressive disorder: A placebo-controlled dose range study. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2002, 17, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delagrange, P.; Boutin, J.A. Therapeutic potential of melatonin ligands. Chronobiol. Int. 2006, 23, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Stein, M.B. Update on treatments for anxiety-related disorders. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2022, 36, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaiana, G.; Gupta, S.; Chiodo, D.; Davies, S.J.C.; Haederle, K.; Koesters, M. Agomelatine versus other antidepressive agents for major depression. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 12, CD008851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, S.; Corruble, E.; Hale, A.; Lemoine, P.; Montgomery, S.A.; Quera-Salva, M.-A. Antidepressant efficacy of agomelatine versus SSRI/SNRI: Results from a pooled analysis of head-to-head studies without a placebo control. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 28, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, A.; Furukawa, T.A.; Salanti, G.; Chaimani, A.; Atkinson, L.Z.; Ogawa, Y.; Leucht, S.; Ruhe, H.G.; Turner, E.H.; Higgins, J.P.T.; et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs for the acute treatment of adults with major depressive disorder: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet 2018, 391, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Traynor, K. Tasimelteon approved for circadian disorder in blind adults. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2014, 71, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, G.; Comai, S. Differential Function of Melatonin MT1 and MT2 Receptors in REM and NREM Sleep. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garfinkel, D.; Laudon, M.; Nof, D.; Zisapel, N. Improvement of sleep quality in elderly people by controlled-release melatonin. Lancet 1995, 346, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortesi, F.; Giannotti, F.; Sebastiani, T.; Panunzi, S.; Valente, D. Controlled-release melatonin, singly and combined with cognitive behavioural therapy, for persistent insomnia in children with autism spectrum disorders: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. J. Sleep Res. 2012, 21, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servant, G.; Kenakin, T.; Zhang, L.; Williams, M.; Servant, N. The function and allosteric control of the human sweet taste receptor. Adv. Pharmacol. 2020, 88, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenakin, T. Biased signaling as allosteric probe dependence. Cell. Signal. 2021, 79, 109844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Westhuizen, E.T.; Valant, C.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A. Endogenous allosteric modulators of G protein-coupled receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 353, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferry, G.; Chabrol, E.; Boutin, J.A. Nanobodies in the Pharmaceutical Industry: Possible Trends. Adv. Nanotechnol. 2022, 27, 61–82. [Google Scholar]


| Compound | pKd |
|---|---|
| [3H]-MLT | |
| hMT₁ | 10.23 |
| hMT₂ | 9.46 |
| 2-[12⁵I]-MLT | |
| hMT₁ | 10.69 |
| hMT₂ | 10.16 |
| [12⁵I]-SD6 | |
| hMT₁ | 10.85 |
| hMT₂ | 10.18 |
| [12⁵I]-S70254 | |
| hMT₁ | No Aff |
| hMT₂ | 9.61 |
| [12⁵I]-DIV880 | |
| hMT₁ | No Aff |
| hMT₂ | 9.65 |
| ICOA-9 (BODIPY-FL dye) | |
| hMT₁ | 5.76 a |
| hMT₂ | 7.41 a |
| ICOA-13 (BODIPY-FL dye) | |
| hMT₁ | 4.97 a |
| hMT₂ | 5.48 a |
| PBI-8192 (BODIPY NanoBRET 590 dye) | |
| hMT₁ | No Aff b |
| hMT₂ | 7.26 b |
| PBI-8238 (BODIPY NanoBRET 590 dye) | |
| hMT₁ | 6.38 b |
| hMT₂ | No Aff b |
| Antibody Target | Host | Epitope | Antibody Source | IHC/IF | WB | IP | Reported Cross-Reactivity | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MT1 | rabbit | last 19 aa hMT1 | Brydon et al. [97] | 1:100 | 5 μg/mL | 1:40 | h (not m, r, ham) | transfected cells |
| rabbit | last 9 aa hMT1 | Angeloni et al. [148] | 1:100 | — | — | h | transfected cells | |
| rabbit | last 19 aa mMT1 | Sengupta et al. [152] | 1:500 | 1:500 | — | m | KO mice tissue | |
| goat | not provided | Santa Cruz #SC13186 | 1:200 | 1:500 | — | m | KO mice tissue | |
| rabbit | residues 223–236 of ICL3 | Alomone #AMR-031 | 1:500 | 1:200 | — | m, (h, r) a | similar IF staining pattern b | |
| mouse | entire Cter mMT1 | Cecon et al. [98] | 10 μg/mL | 2 μg/mL | 1 μg/mL | m (h, r for some antibodies) | transfected cells, KO mice tissue | |
| MT2 | rabbit | last 9 aa hMT1 | Angeloni et al. [148] | 1:1000 | 1:500 | 1:500 | h, r (not m) | transfected cells, KO mice tissue |
| goat | not provided | Santa Cruz #SC13177 | 1:200 | 1:500 | — | m | KO mice tissue, KO 661W cell line | |
| rabbit | residues 232–246 of ICL3 | Alomone #AMR-032 | 1:250 | 1:2000 | — | m, (r) a | similar IF staining pattern c | |
| mouse | entire Cter mMT1 | Cecon et al. [98] | 10 μg/mL | 2 μg/mL | 1 μg/mL | m (h, r for some antibodies) | transfected cells, KO mice tissue | |
| GPR50 | rabbit | last 13 aa hGPR50, oGPR50 | Hamouda et al. [159] | 1:150–1:2000 | 1:1000 | 4–10 μg/mL | h, m, o, r | transfected cells, KO mice tissue |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cecon, E.; Boutin, J.A.; Jockers, R. Molecular Characterization and Pharmacology of Melatonin Receptors in Animals. Receptors 2023, 2, 127-147. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2020008
Cecon E, Boutin JA, Jockers R. Molecular Characterization and Pharmacology of Melatonin Receptors in Animals. Receptors. 2023; 2(2):127-147. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2020008
Chicago/Turabian StyleCecon, Erika, Jean A. Boutin, and Ralf Jockers. 2023. "Molecular Characterization and Pharmacology of Melatonin Receptors in Animals" Receptors 2, no. 2: 127-147. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2020008
APA StyleCecon, E., Boutin, J. A., & Jockers, R. (2023). Molecular Characterization and Pharmacology of Melatonin Receptors in Animals. Receptors, 2(2), 127-147. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2020008







