Climate Crises Associated with Epidemiological, Environmental, and Ecosystem Effects of a Storm: Flooding, Landslides, and Damage to Urban and Rural Areas (Extreme Weather Events of Storm Daniel in Thessaly, Greece) †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
Modelling Techniques
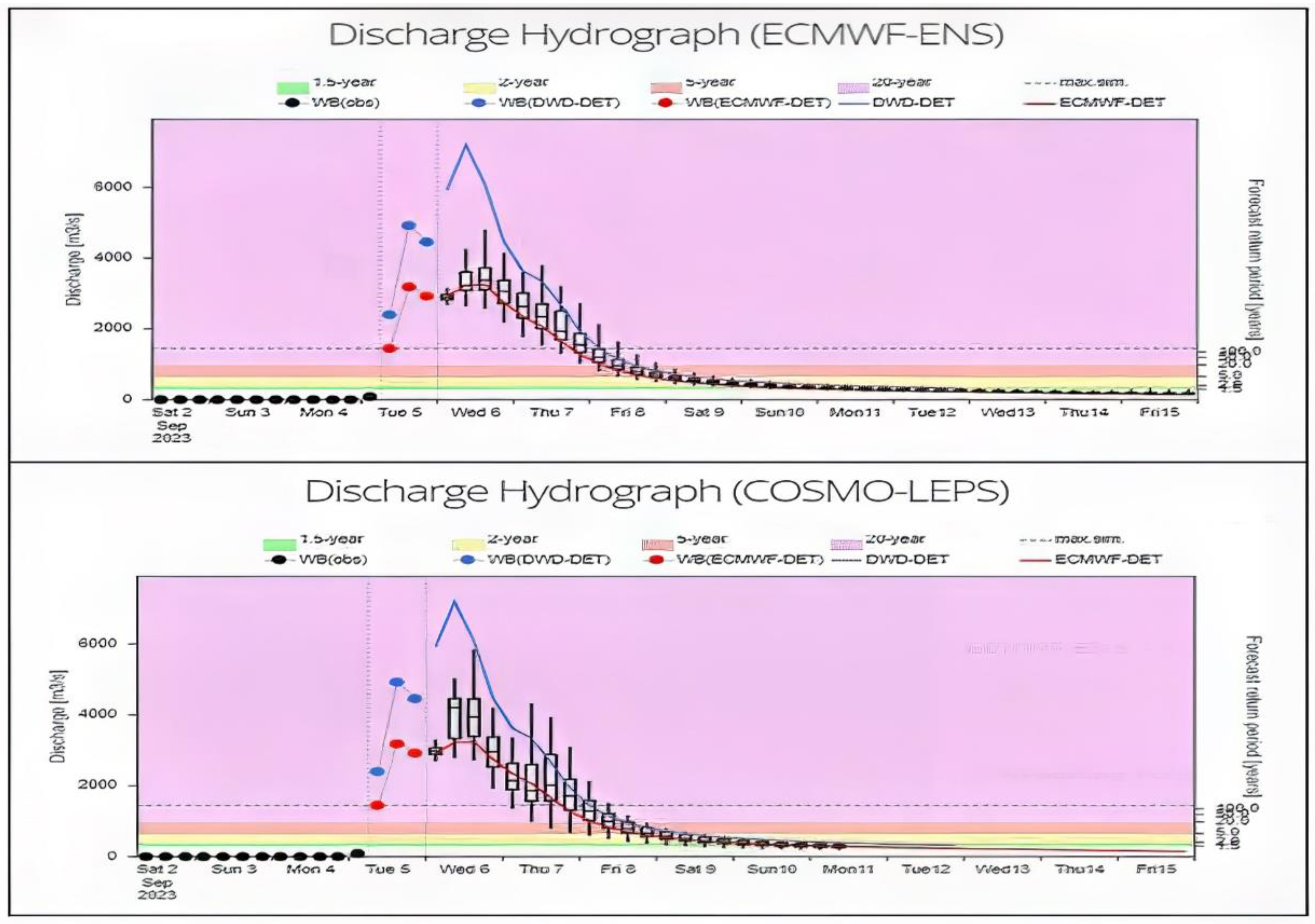
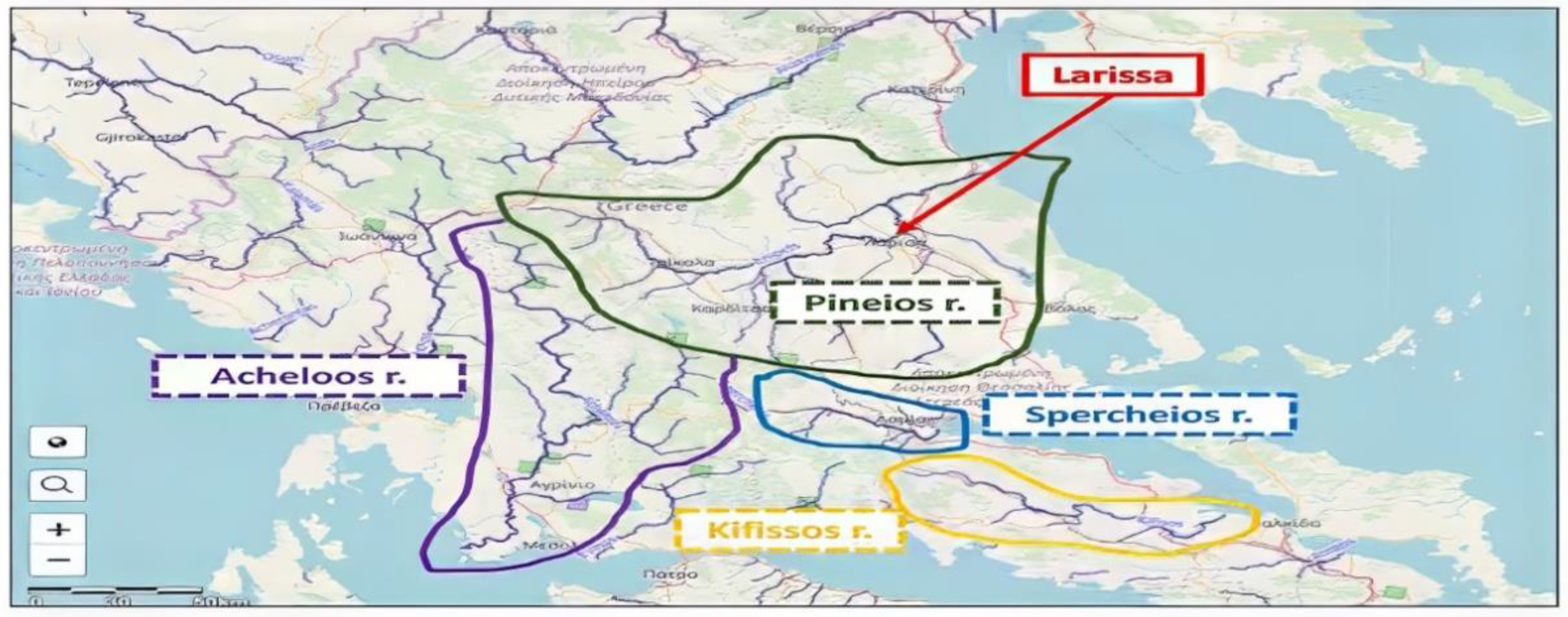
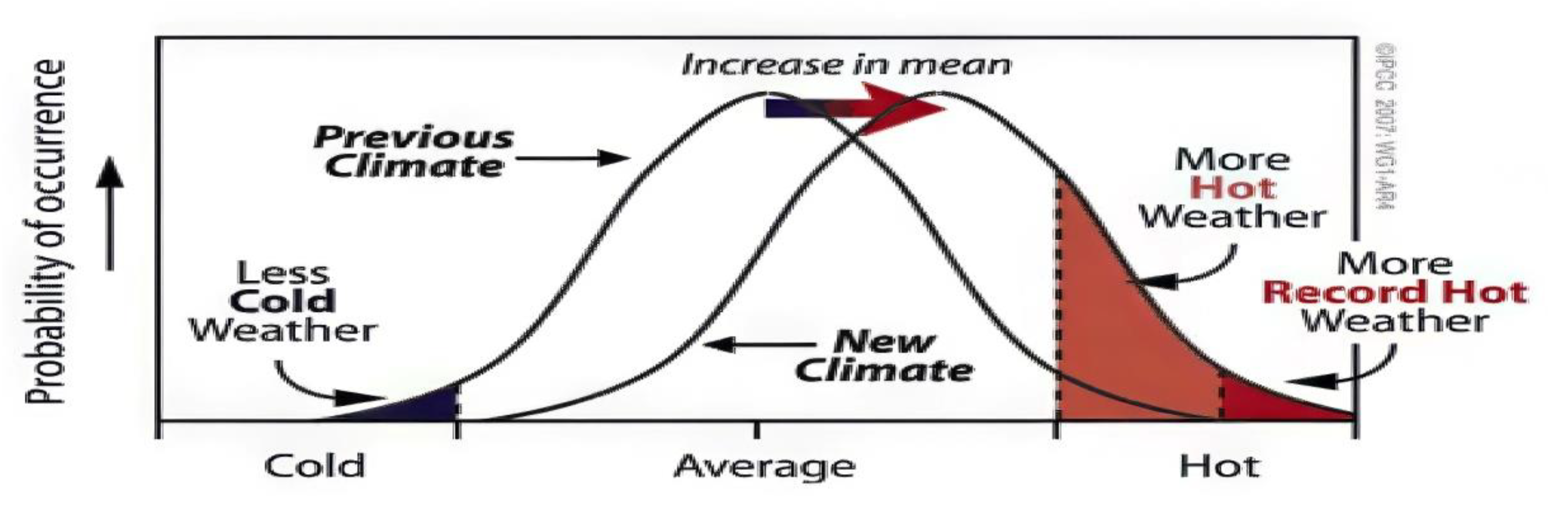
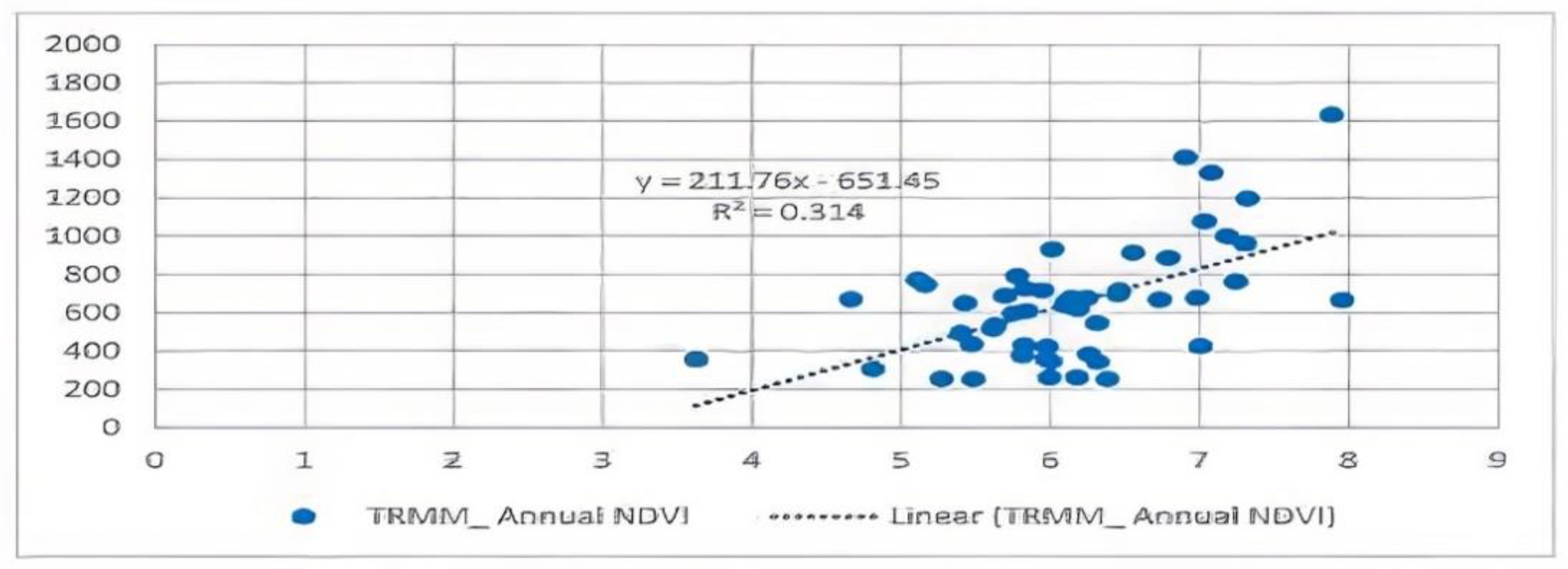
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Impacts
3.1.1. Extreme Weather
3.1.2. Storm Daniel
3.2. Addressing Response Efforts
- Search, Rescue Operations Cleanup, and Restoration: Immediate efforts must be made to save human lives and protect vulnerable wildlife. Removal of debris and contaminants from floodwaters and restoration of affected natural habitats are crucial. Implementation of erosion control measures are necessary to prevent further soil erosion and sedimentation.
- Monitoring, Research Policy, and Planning: Ongoing monitoring of the affected ecosystems is necessary to assess recovery progress and conduct research to understand the long-term impacts. Development or revision of policies related to land use, floodplain management, and disaster preparedness are necessary to reduce future risks [5,6,8,16,29].
4. Discussion
Implications for Research and Practice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adamopoulos, I.; Frantzana, A.; Adamopoulou, J.; Syrou, N. Climate Change and Adverse Public Health Impacts on Human Health and Water Resources. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Meteorology, Climatology and Atmospheric Physics—COMECAP 2023, Athens, Greece, 25–29 September 2023; p. 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, I.; Frantzana, A.; Syrou, N. Epidemiological surveillance and environmental hygiene, SARS-CoV-2 infection in the community, urban wastewater control in Cyprus, and water reuse. J. Contemp. Stud. Epidemiol. Public Health 2023, 4, ep23003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padulano, R.; Costabile, P.; Rianna, G.; Costanzo, C.; Mercogliano, P.; Del Giudice, G. Comparing Different Modelling Strategies for the Estimation of Climate Change Effects on Urban Pluvial Flooding. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 21, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulou, J.; Frantzana, A.; Adamopoulos, I. Addressing water resource management challenges in the context of climate change and human influence. Eur. J. Sustain. Dev. Res. 2023, 7, em0223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Climate Change Made Deadly Floods in Libya and Greece More Extreme: EBSCO Host. Available online: https://web.p.ebscohost.com/ehost/detail/detail?vid=31&sid=3cd51567-1bcd-4e46-b59a-2427515a1f1d%40redis&bdata=JnNpdGU9ZWhvc3QtbGl2ZQ%3d%3d#AN=172026262&db=bsu (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- World Meteorological Organization—WMO. Storm Daniel Leads to Extreme Rain and Floods in Mediterranean, Heavy Loss of Life in Libya; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Brief Communication: Storm Daniel Flood Impact in Greece 2023: Mapping Crop: EBSCO Host. Available online: https://web.p.ebscohost.com/ehost/detail/detail?vid=9&sid=6ca79037-3f47-4b61-bbcc-d795a4fb8ba2%40redis&bdata=JnNpdGU9ZWhvc3QtbGl2ZQ%3d%3d#AN=172961890&db=eih (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Tsagkaris, C.; Bartkova, J.; Saridi, M.; Panagopoulos, P.; Zil-E-Ali, A. Climate Crisis as an Opportunity for Socially and Environmentally Sensitive Surgical Preparedness: The Major Needs of Minors in Greece. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2023. Available online: http://www.jpedsurg.org/article/S002234682300581X/fulltext (accessed on 10 December 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamopoulos, I.; Syrou, N.; Adamopoulou, J. Greece’s current water and wastewater regulations and the risks they pose to environmental hygiene and public health, as recommended by the European Union Commission. Eur. J. Sustain. Dev. Res. 2024, 8, em0251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M.; Skordoulis, M.; Kyriakopoulos, P. Public Perceptions of Flood and Extreme Weather Early Warnings in Greece. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Duan, A. The energy and water cycles under climate change. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, I.; Syrou, N.; Adamopoulou, J.; Mijwil, M. Southeast Mediterranean and Middle Eastern Countries Are Experiencing Impacts from the Climate Crisis, Extreme Weather Events, and the Conventional Method of Water Use: A Comprehensive Scoping Study. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4746621 (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- Diakakis, M.; Skordoulis, M.; Savvidou, E. The relationships between public risk perceptions of climate change, environmental sensitivity and experience of extreme weather-related disasters: Evidence from Greece. Water 2021, 13, 2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, M.S.; Al-Jayyousi, O.R. Brackish water desalination: An alternative for water supply enhancement in Jordan. Desalination 1999, 124, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groupeware Bigbang 40 Data-Sinanet. Isipranbiente.it. Available online: https://groupware.sinanet.isprambiente.it/bigbang-data/library/bigbang40 (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Landis, W.G.; Durda, J.L.; Brooks, M.L.; Chapman, P.M.; Menzie, C.A.; Stahl, R.G., Jr.; Stauber, J.L. Ecological Risk Assessment in the Context of Global Climate Change. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Summary for Policymakers. In Global Warming of 1.5 °C: IPCC Special Report on Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C above Pre-Industrial Levels in Context of Strengthening Response to Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Flood Awareness System. Available online: https://www.copernicus.eu/en/european-flood-awareness-system (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Major Upgrade of the European Flood Awareness System, ECMWF. Available online: https://www.ecmwf.int/en/newsletter/166/meteorology/major-upgrade-european-flood-awareness-system (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Allamano, P.; Claps, P.; Laio, F. Global warming increases flood risk in mountainous areas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L24404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extreme Weather. Available online: https://www.e-education.psu.edu/meteo469/book/export/html/133 (accessed on 7 December 2023).
- Mazzoglio, P.; Ganora, D.; Claps, P. Long-Term Spatial and Temporal Rainfall Trends over Italy. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 21, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus Emergency Management Service Directorate Space, Security and Migration, European Commission Joint Research Centre (EC JRC). Available online: https://emergency.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 5 October 2023).
- World Meteorological Organization. Available online: https://wmo.int/media/news/storm-daniel-leads-extreme-rain-and-floods-mediterranean-heavy-loss-of-life-libya (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Utembe, W.; Sanabria, N.M. Occupational and Environmental Chemical Risk Assessment in a Changing Climate: A Critical Analysis of the Current Discourse and Future Perspectives. In Proceedings of the 4th International Electronic Conference on Environmental Research and Public Health—Climate Change and Health in a Broad Perspective, Online, 15–30 October 2022; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- METEO 469-FROM Meteorology to Mitigation: Understanding Global Warming. Available online: https://www.e-education.psu.edu/meteo469/node/112 (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Finotti, A.R.; Susin, N.; Finkler, R.; Silva, M.D.; Schneider, V.E. Development of A Monitoring Network of Water Resources in Urban Areas as a Support for Municipal Environmental Management. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 182, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, W.D.; Bonta, J.; Thurston, H.; Warnemuende, E.; Smith, D.R. Impacts of impervious surface on watershed hydrology: A review. Urban Water J. 2005, 2, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottle, N.D.; Batten, L. Reclaiming Urban Waterfronts through Green Stormwater Solutions. Int. J. Environ. Cult. Econ. Soc. Sustain. Annu. Rev. 2012, 7, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global Change and the Ecology of Cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, I.; Syrou, N.; Lamnisos, D.; Boustras, G. Cross-sectional nationwide study in occupational safety & health: Inspection of job risks context, burn out syndrome and job satisfaction of public health Inspectors in the period of the COVID-19 pandemic in Greece. Saf. Sci. 2023, 158, 105960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, I.P. Job Satisfaction in Public Health Care Sector, Measures Scales and Theoretical Background. Eur. J. Environ. Public Health 2022, 6, em0116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, I.; Lamnisos, D.; Syrou, N.; Boustras, G. Public health and work safety pilot study: Inspection of job risks, burn out syndrome and job satisfaction of public health inspectors in Greece. Saf. Sci. 2022, 147, 105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, C.; Gargiulo, C.; Papa, R.; Carpentieri, G. Vulnerability and Exposure of Mediterranean Coastal Cities to Climate Change-Related Phenomena. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyes, P.D.; McElwee, M.K.; Miller, H.D.; Clark, B.W.; Van Tiem, L.A.; Walcott, K.C.; Erwin, K.N.; Levin, E.D. The toxicology of climate change: Environmental contaminants in a warming world. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 971–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasmeen, Z.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Hussain, S.; Haroon, Z.; Amin, S.; Waqas, M.S. Downscaling of Satellite Rainfall Data Using Remotely Sensed NDVI and Topographic Datasets. In Proceedings of the 1st International Precision Agriculture Pakistan Conference 2022 (PAPC 2022)—Change the Culture of Agriculture, Rawalpindi, Pakistan, 22–24 September 2022; p. 40. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adamopoulos, I.; Frantzana, A.; Syrou, N. Climate Crises Associated with Epidemiological, Environmental, and Ecosystem Effects of a Storm: Flooding, Landslides, and Damage to Urban and Rural Areas (Extreme Weather Events of Storm Daniel in Thessaly, Greece). Med. Sci. Forum 2024, 25, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025007
Adamopoulos I, Frantzana A, Syrou N. Climate Crises Associated with Epidemiological, Environmental, and Ecosystem Effects of a Storm: Flooding, Landslides, and Damage to Urban and Rural Areas (Extreme Weather Events of Storm Daniel in Thessaly, Greece). Medical Sciences Forum. 2024; 25(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025007
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdamopoulos, Ioannis, Aikaterini Frantzana, and Niki Syrou. 2024. "Climate Crises Associated with Epidemiological, Environmental, and Ecosystem Effects of a Storm: Flooding, Landslides, and Damage to Urban and Rural Areas (Extreme Weather Events of Storm Daniel in Thessaly, Greece)" Medical Sciences Forum 25, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025007
APA StyleAdamopoulos, I., Frantzana, A., & Syrou, N. (2024). Climate Crises Associated with Epidemiological, Environmental, and Ecosystem Effects of a Storm: Flooding, Landslides, and Damage to Urban and Rural Areas (Extreme Weather Events of Storm Daniel in Thessaly, Greece). Medical Sciences Forum, 25(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025007







