Abstract
The biting behavior of farmed fish on nylon netting raises concerns for microplastic accumulation in caged fish with potential influences on human health via consumption. Indeed, the reason for net biting is due to biofouling on the mesh being a tasty food that attracts fish. Hence, it is highly possible that a certain amount of microplastics from the mesh is ingested by fish, which can eventually enter the digestive system of humans through consumption. Caged fish may further receive microplastics from terrestrial flows or marine currents or through the food chain in the oceans. Therefore, the level of microplastic contamination in caged fish has been investigated by drawing a comparison with natural populations of Turkish and Iranian waters, in order to reveal the risks of microplastic transmission from fish to humans. Analyses of water samples, sediments, diets, zooplankton and fish tissues have been conducted and the amounts of microplastics in diets were evaluated. The identification of polymeric materials in collected microplastics was performed by FT-IR spectrometer, and Raman spectrometry was employed to determine the shape, size and polymer type of microplastics. Based on the preliminary results, the impact of cage nets on microplastic accumulation in fish digestive system and the interaction with human health risks upon consumption of contaminated fish have been assessed. The findings in this study may help to establish safe food strategies for future generations, with a healthy material selection approach in sustainable cage aquaculture management.
1. Introduction
Plastics are an inseparable material in the aquaculture industry due to the extensive use of plastic ingredients as the sole or main substance in the fabrication of fishing gear, nets and buckets, and other devices in breeding, hatching and cultivating. Moreover, huge amounts of plastic waste are discharged into the aquatic environment annually (Figure 1).
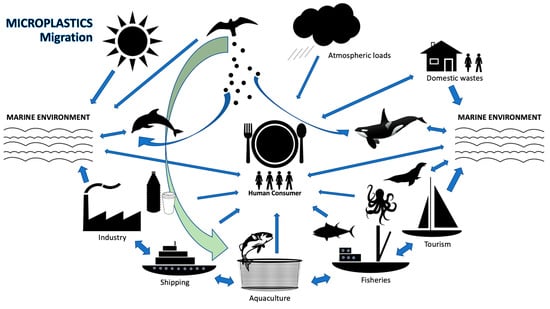
Figure 1.
Sources and ecological impacts of microplastic migration with interaction to human consumer.
Given the widespread occurrence of microplastics in marine species consumed by humans (particularly species in which the entire soft flesh is consumed, such as shellfish and fish) it is inevitable that human beings eating such foods might ingest at least some microplastics. Therefore, the level of microplastic (MPs) contamination in caged fish has been investigated via a comparison with natural populations of Turkish and Iranian waters, in order to reveal the risks of MPs transmission from fish to humans, which was conducted with the support of S the Ministry of Science, Research and Technology (MSRT, Iran).
The objectives of the study are as follow:
- Evaluate the presence and effects of plastic debris in cage-farmed fish species in Turkey and Iran;
- Evaluate the sources of MP contamination by studying the MP amount in the water body, bottom sediments, commercial feed, zooplankton and fish tissues;
- Assess the effects of cage net material on MP accumulation in fish digestive system and their connection with human health risks when consuming cage-farmed fish;
- Draw a comparison with fish possessing different foraging behaviors such as biting, chewing, etc., in terms of possible bio-accumulation of MPs on their edible tissues, and finally, assess the human health risks upon consumption of cage-farmed fish species.
2. Methodology
LSS Methodology
Fish material: Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) and Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) in Turkey, and Gilthead seabream (S. aurata) and Barramundi (Lates calcarifer) in Iran, from marine cages and natural environment.
Sites of study: Fish have been sampled from the harvest batch of the cage farm. Sampling sites were located off the Turkish coast of the Aegean Sea within the provinces of Aydın and Muğla, where the cage aquaculture facilities are dominated in Turkey. In Iran, sampling sites were located in the Persian Gulf off the coastal Provinces Hormozgan and Bushehr, which are the main cage farm areas. Additionally, wild fish from both study areas of Turkey and Iran, have been sampled through baited tackles from the natural environment in order to evaluate the level of MPs in fish.
The sampling periods in the present study comprise the summer and winter. Fish samples were taken from earlier identified locations of both countries were sieved using different mesh-sized sieves, washed, dried and weighed in laboratories. For the determination of the amounts of microplastics (MPs), analyses of water samples, sediments, fish diets, zooplankton and fish tissues have been conducted via alkaline-oxidation–chemical-digestion techniques for the extraction of microplastics from organics [1] and the amounts of microplastics in diets were evaluated [2]. The suspected microplastic particles from the samples were observed using a stereomicroscope.
Identification of polymeric materials in collected MPs was performed by FT-IR spectrometer, and Raman spectrometry was used to determine the polymer type of MPs.
3. Results
This is an ongoing research project between Turkey and Iran. The expected modes of implementation of the results can be summarized as follows:
- Evaluate the presence and effects of plastic debris in cage-farmed fish in Iran and Turkey;
- Assess the human health risks due to the consumption of fish;
- Assess the effects of plastic litter on the marine food chain, aquaculture and fishing activities and their connection with human health;
- Assess the effects of cage net material on microplastic accumulation in fish digestive system and their connection with human health risks when consuming farmed fish;
- Assess the impacts of cage aquaculture farms on the surrounding marine ecosystem in terms of microplastic litter via ingestion by fish;
- Address issues related to food safety for future generations;
- Address issues related to safe aquaculture production via an environmentally friendly approach;
- Address issues related to the selection of proper net materials for food safety in aquaculture facilities;
- Address issues related to sustainable aquaculture activities.
4. Discussion/Conclusions
It is known that there are microplastics (MPs) in many environments and species, and aquaculture system products are no exception, in which food supply and safety are important concerns. The drastically increase of industrial activities and the accumulation of plastic products in the marine ecosystem poses a severe threat to human health via the food chain and seafood for human consumers [3]. It has been underlined that the presence of MPs shows variations among species as well as between the gills and gastrointestinal tracts of fish, which were reported to originate from different sources of anthropogenic activities [4]. Further, MP ingestion was found to increase with the time of exposure, however, these increases did not influence the muscle tissues in gilthead seabream [5]. Among several sources of MPs, fishmeal used in aqua-diets has been featured to the foreground [6], which is likely contaminated by the actual species used for fishmeal production [2], where the wild fish captured for fishmeal production is also exposed to a variety of MPs through the trophic chain as MPs were identified in zooplankton (Daphnia magna) in the ocean as well [7].
To control MPs pollution, it is important to detect and analyze the MPs that currently contaminate these areas. Therefore, when detecting MPs in aquaculture environments, it is necessary to clarify the sources and fates of MPs within them [8]. In order to better evaluate the quality and safety of aquaculture products and to control the input of MPs in aquaculture environments and promote the sustainable and healthy development of aquaculture, clarification regarding the relationship between MPs, aquaculture products and their potentially detrimental impacts on human and ecological health is needed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.E., M.Y. and A.V.; methodology, S.E. and A.V.; validation, S.E., A.V. and M.E.; formal analysis, S.Y., A.V., M.E. and B.E.; investigation, S.E., A.V., S.Y., M.E. and B.E.; resources, S.E., M.Y., Y.B.; data curation, S.E., A.V., S.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, S.E., M.Y., Y.B.; writing—review and editing, S.E., A.V., M.Y., Y.B.; visualization, S.E. and A.V.; supervision, S.E. and A.V.; project administration, S.E. and A.V.; funding acquisition, S.E. and A.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK-Ankara, Turkey) ARDEB 1001 (Project Number: 121N183) (Turkey) and the Ministry of Science, Research and Technology of Iran (MSRT-Tehran, Iran).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All samples used in this study were collected from the harvest batch of commercial facilities, hence no ethical approval needed for this study.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent has been obtained from all individual participants involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The authors declare that data can be provided by corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK-Ankara) and the Ministry of Science, Research and Technology of Iran (MSRT-Tehran) are acknowledged for the financial support of this study. The authors would like to thank MSci students Ayşenil BAYIZIT and Aisen CHASAN for their laboratory studies, and Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University (Turkey), Eskişehir Technical University (Turkey), and Shiraz University (Iran) for their support of research and laboratory facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
There is no conflict of interests for publishing this study.
References
- Munno, K.; Helm, P.A.; Jackson, D.A.; Rochman, C.; Sims, A. Impacts of temperature and selected chemical digestion methods on microplastic particles. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gündoğdu, S.; Eroldoğan, O.T.; Evliyaoğlu, E.; Turchini, G.M.; Wu, X.G. Fish out, plastic in: Global pattern of plastics in commercial fishmeal. Aquaculture 2021, 534, 736316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Occurrence and ecological impact of micro plastics in aquaculture ecosystems. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiguo, Z.; Di, S.; Chong, W.; Yuliang, C.; Shaolin, X.; Peiqin, K.; Guohuan, X.; Huijuan, T.; Jixing, Z. Characteristics and differences of microplastics ingestion for farmed fish with different water depths, feeding habits and diets. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomar, C.; Sanz-Martín, M.; Compa, M.; Rios-Fuster, B.; Alvarez, E.; Ripolles, V.; Valencia, J.M.; Deudero, S. Microplastic ingestion in reared aquaculture fish: Biological responses to low-density polyethylene controlled diets in Sparus aurata. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelvetro, V.; Corti, A.; Bianchi, S.; Giacomelli, G.; Manariti, A.; Vinciguerra, V. Microplastics in fish meal: Contamination level analyzed by polymer type, including polyester (PET), polyolefins, and polystyrene. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 115792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, R.; Gürses, R.K.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishida, Y.; Kimoto, T.; Kitagawa, S.; Iiguni, Y.; Ohtani, H. Pyrolysis-GC–MS analysis of ingested polystyrene microsphere content in individual Daphnia magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 15298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; Opportunities and Challenges, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Pub: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).