Abstract
The ground-based monitoring of the lower ionosphere by studying the perturbations of the subionospheric propagation of very-low-frequency/low-frequency (VLF/LF) signals is important in the research of a wide variety of geophysical and Sun/space extreme phenomena. Such perturbations are identified as anomalies in the signal received from the VLF/LF transmitters operating worldwide for military purposes, time code broadcasting, etc. Especially for the study of local ionosphere-influencing phenomena, such as earthquakes, volcanoes, typhoons, etc., the monitoring of several subionospheric propagation paths is necessary. However, it is very difficult to find in the market (or reproduce) hardware (HW) for wide-band VLF/LF receivers that could receive many different transmitters, while the involved software (SW) is mainly proprietary. Aiming to provide a low-cost and easy-to-build alternative for the scientists involved in this research field, we suggest a VLF/LF receiver setup based on amateur radio open-source HW and SW. Its key components are the so-called “mini-whip” active antenna and the freeware “SpectrumLab” and “GPS2Time”. The full HW schematics and all settings of the employed SW configuration for the proposed VLF/LF receiver setup are provided in the article. To check the reliability of the proposed receiver setup, two almost identical VLF/LF radio receivers were installed in the prefecture of Attica in Greece, in June and September of 2021, respectively. Examples of ionospheric perturbations due to different phenomena (solar flares, earthquakes, and a magnetic storm) are provided to show the ability of the proposed receiver setup to provide reliable data for ionosphere-related research.
1. Introduction
The study of Earth’s ionosphere in association with different extreme phenomena has become a very interesting topic in recent years. Many scientists around the world have made significant progress in studying imprints of extreme phenomena in the ionosphere by using various observation techniques, e.g., [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. For this reason, the ionosphere is known to be a useful “tool” for studying disturbances that are caused by such phenomena.
Specifically, very-low-frequency/low-frequency (VLF/LF) ground-based monitoring of the ionosphere is a widely used method in many studies, searching for anomalies in the VLF/LF receiver amplitude and phase of the signal that are related to sudden ionospheric disturbances (SIDs) generated from the Sun [9]. These disturbances are caused by solar energetic particles (SEPs) and solar flares, which lead to fast transient plasma changes in the ionosphere, more intensively at the sunlight hemisphere [10,11]. The F, D, and E ionospheric layers are affected by the solar extreme ultra-violet (EUV) and X-ray radiation due to enhancement of the ionization process during the occurrence of these phenomena [12].
Moreover, geomagnetic storms are very important extreme phenomena that are reflected in global disturbances in the ionosphere, middle atmosphere, and troposphere [13,14]. They enhance the speed and density of solar wind and are related to shock waves [15,16]. Geomagnetic storms can increase the profile of electron density in the lower ionosphere (D and E layers) and especially in the auroral zone, leading to radio wave absorption and the significant disappearance of MF/HF transmitted signals [16,17]. This strong increment in the electron density profile is a result of energetic particle precipitation [16]. It should be noted that the penetration of energetic particle precipitation into the lower ionosphere and also in the middle atmosphere is accompanied by a loss of energy due to the emission of X-ray “bremsstrahlung” radiation [16]. VLF/LF radio wave propagation is disturbed by geomagnetic storms. They can cause ionospheric disturbances that result in changes in VLF/LF signal amplitude and phase. Other factors that can ionize the ionosphere and affect VLF/LF signals are galactic gamma-ray bursts, which are produced far away from the solar system [18], as well as lightning-induced energetic particle precipitations and direct heating due to intensive lightning discharges and transient luminous events (TLEs) [19,20,21].
Another ionosphere-related concept that has been intensively investigated during the last three decades is the lithosphere–atmosphere–ionosphere (LAIC) coupling, aiming at possible short-term earthquake (EQ) prediction [22,23,24,25,26]. Specifically, many VLF/LF anomalies have been identified prior to EQs in many studies, through the analysis of the characteristics of VLF/LF receiver signals (amplitude and phase), by using various analysis methods [5,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. It should also be noted that criticality analysis has successfully been performed on VLF/LF data, identifying criticality indications in the lower ionosphere prior to significant (M > 5.5) EQs, indicating that the ionosphere is in critical state prior to the EQ, as happens for the EQ preparation zone in the lithosphere [30,38].
It is evident that the study of a specific geophysical or solar–space phenomenon by monitoring the ionosphere is a complex problem because the ionosphere is affected by a large number of such phenomena.
In this work, we introduce a VLF/LF receiver design based on amateur radio open-source hardware (HW) and software (SW) for the monitoring of the lower ionosphere. We aim to provide a cost-effective, but also scientifically reliable, solution for researchers that are interested in the study of geophysical and solar–space phenomena that perturb the lower ionosphere. We present in detail the proposed receiver setup, both in terms of HW and SW, providing all required information for one to reproduce it (online available supplementary material is complementary to the provided information). In order to check the reliability of the proposed receiver setup, two almost identical VLF/LF radio receivers were installed in the prefecture of Attica in Greece, in June and September of 2021, respectively. The first one is located in a suburban area to the east of Athens, and the second one is located in a forest area to the west of Athens, close to the urban complex of Athens. These two VLF/LF stations are able to receive signals from many VLF and LF transmitters. Using the recordings of these two stations, we present examples of identified perturbations associated with different phenomena that occurred during the time period 1 September 2021–30 April 2022. Specifically, we present results associated with three solar flares of “X”, “M”, and “C” class, respectively, three EQs (M > 5.5) that happened in the southeastern Mediterranean, and one geomagnetic storm. The perturbations associated with the EQs and the geomagnetic storm were identified using the statistical method known as the “nighttime fluctuation method” (NFM) [39,40], while the effect of solar flares is identified directly on the amplitude of the recorded signals. The identified disturbances of the lower ionosphere are indicative of the quality of the data acquired by the proposed VLF/LF receiver setup.
The remainder of the article is organized as follows: Section 2 provides information on the HW and SW of the receiver design, while in Section 3, the two installations in Attica are presented. In Section 4, we provide key information about the NFM statistical analysis method, and in Section 5, we present the results obtained regarding different ionosphere-influencing phenomena. Finally, in Section 6, we summarize the conclusions.
2. Receiver Design
Receivers “listening” to VLF/LF signals are rare since the commercial demand for receivers in these frequency bands is low. The literature review for open HW and SW VLF/LF receiving systems that cover frequencies up to 90 kHz yielded very few solutions. These are low-end designs, mainly by amateur associations [41,42,43,44,45], which perform basic functions below the frequency of 30 kHz. There are also commercial receivers [39,46,47,48], for which very little information is available about their design and which are very few (and lately not available), due to the limited demand that does not justify mass production. Moreover, there are some designs by research groups [49,50,51], which, unfortunately, are also difficult, or even impossible, to acquire, while detailed information for the complete VLF/LF receiver setup is usually missing for one to reproduce them. Different VLF/LF networks, using different receivers, have been developed in various geographical areas, such as the Hi-SEM network in Japan [39,52], the European VLF/LF Radio Monitoring Network (INFREP) [46,47,48], and the South America VLF NETwork (SAVNET) [50,53]. AWESOME receivers [54,55,56] are also popular but are no longer available. Finally, it has to be mentioned that, as the computing power of PCs continuously increases, the VLF/LF receiver design focus has eventually been shifted from the HW to SW [18,19,20], restricting the specialized HW to the antenna–preamplifier–filters system. It has to be noted that the most popular SW for VLF/LF receivers are also commercial products [57,58,59].
From the abovementioned aspects, it is clear that it is very difficult to find in the market (or reproduce) the HW for wide-band VLF/LF receivers, while the involved SW is mainly proprietary. To provide an easy-to-build, flexible, but also reliable, alternative for researchers focusing on the study of the lower ionosphere, we hereby suggest a VLF/LF receiver setup based on amateur radio open-source HW and SW. We aimed to provide a cost-effective wideband HW solution that anyone can build by combining low-cost, commercially (online) available parts, or even by reproducing the critical parts (i.e., antenna, preamplifier, and preamplifier’s power supply) at one’s own lab from the electronic-component-level available design information. As for the necessary SW, all used programs should be open-source or freeware and their necessary settings should also be provided.
During the time period from September 2020 to February 2021, various possible receiver solutions were tested. Two categories stood out: software-defined-radio-based (SDR) and sound-card-based ones. The number of available SDR-based receivers is continuously increasing nowadays. These use the PC’s computational power for all the stages to deliver and process signals. External (or internal) soundcards, on the other hand, are very sophisticated nowadays. Many models of high-end, very-low-noise (external or internal) soundcards can be found in the market at low prices. For frequencies up to 90 kHz, the soundcard solution (with a sampling rate of 192 kHz) was chosen. A high-end soundcard is cheaper than a high-end SDR receiver, while a soundcard solution demands less computational power from the host PC.
2.1. Hardware
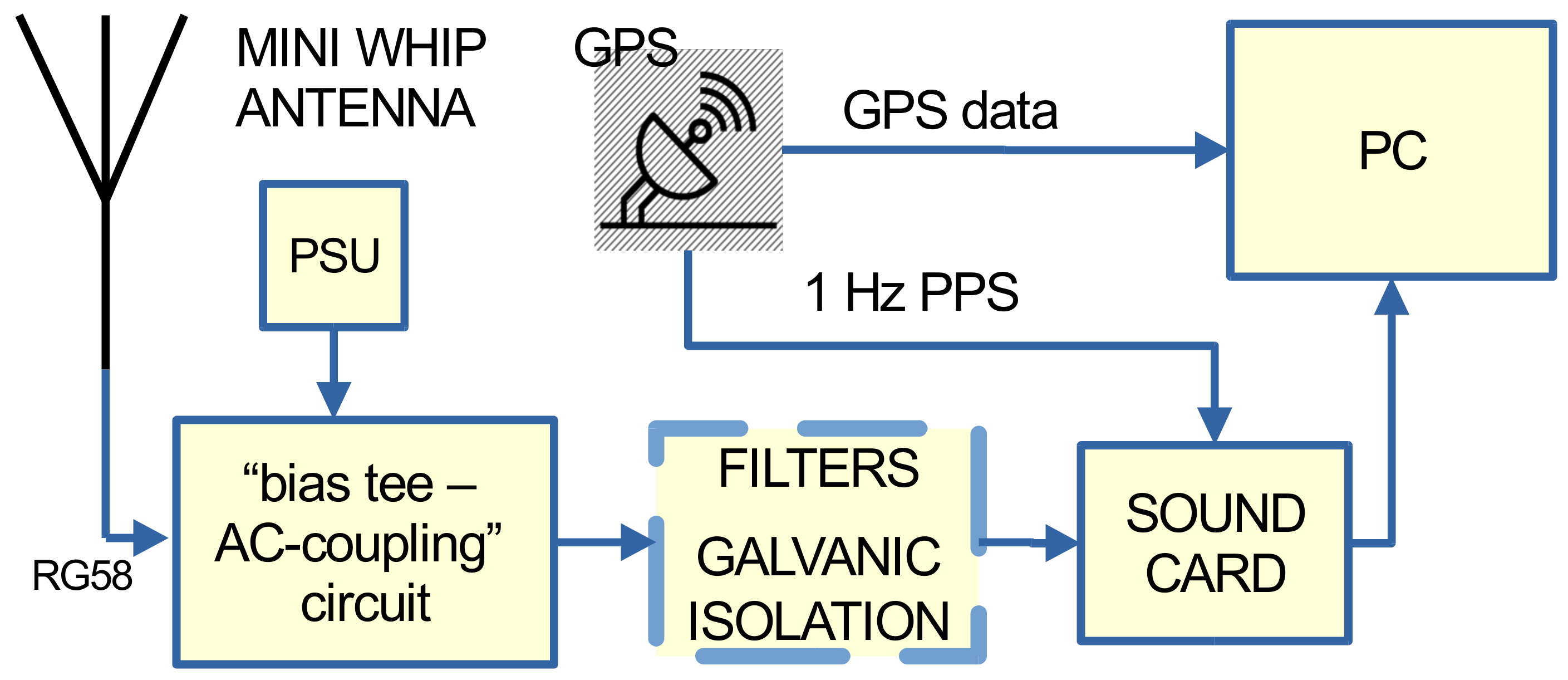
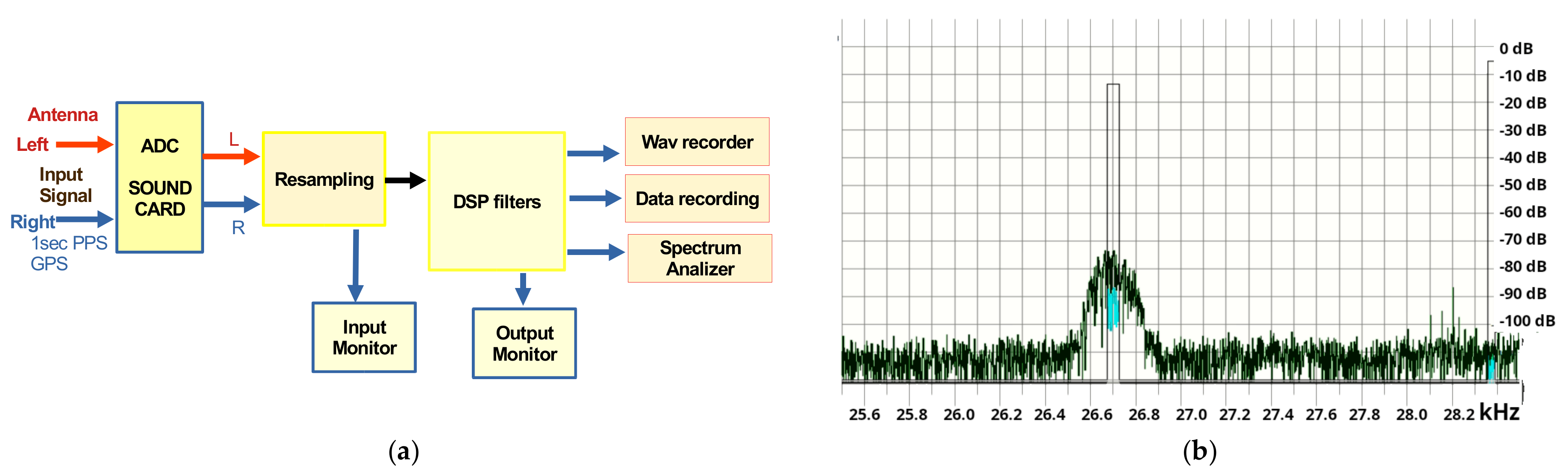
All the necessary hardware of the proposed VLF/LF receiver design is shown in Figure 1. It consists of an active antenna, a “bias tee–AC coupling” circuit, a 12 V power supply for the antenna, filters, galvanic isolators, a GPS receiver with a 1 Hz PPS (1 pulse per second) output, a soundcard (for the analog to digital conversion (ADC) of the antenna and GPS signals), and a personal computer (PC) for the signal processing. An essential part of the setup is the antenna. Usually, VLF/LF receivers use homemade loop antennas since they aim at recording only one or a few VLF stations transmitting below 30 kHz. Such antennas are suitable only for narrowband applications. As loop antennas are practically a coil of many turns, they receive only the magnetic component of the electromagnetic field and their pattern is not isotropic. Wideband receivers, aiming at monitoring multiple transmitters, use wire antennas. As a half-wave wire antenna suitable for VLF/LF frequencies must be a few km in length, such a solution is usually not adopted. Small-size wire antennas (a few meters or only one meter long) with the addition of a high-gain preamplifier are usually employed instead, e.g., [39,57]. However, this kind of antenna is sensitive to electrical discharges.
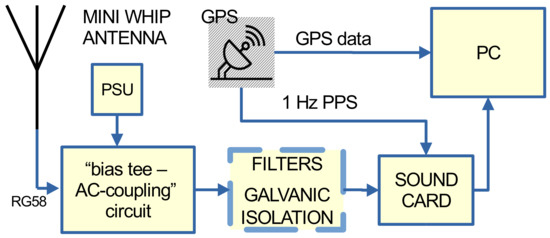
Figure 1.
Block diagram of the proposed VLF/LF receiver. The active antenna combined with a low-noise external (or internal) soundcard are the most important stages of the receiver. The rest of the stages serve for performance optimization and signal processing.
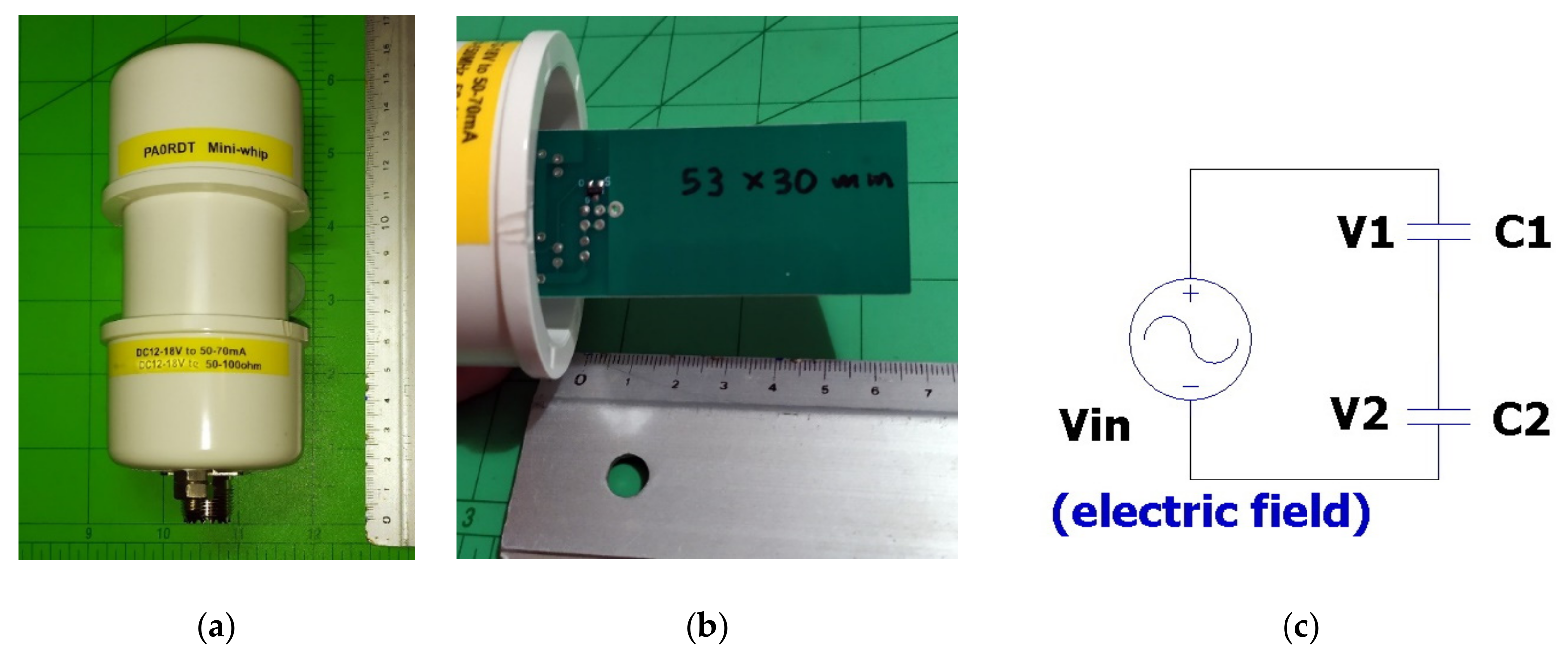
In our case, an active antenna (Figure 2) was chosen to capture frequencies from 3 to 90 kHz. A key advantage, beyond the small size, is the high-gain and low-noise preamplification and filtering directly on the antenna. One can reproduce it at one’s own lab using the electronic-component-level available design information [60] or it can be purchased on the internet via the code “PA0RDT Mini-Whip antenna”. It is a minimalistic design (Figure 3), only 15 cm long, and can efficiently replace a wire antenna a few meters long. It is inexpensive and can be purchased from a wide variety of online stores because it is very popular among radio amateurs. Currently, the price starts from EUR 25 and it consists of two parts, the active antenna and its power supply.
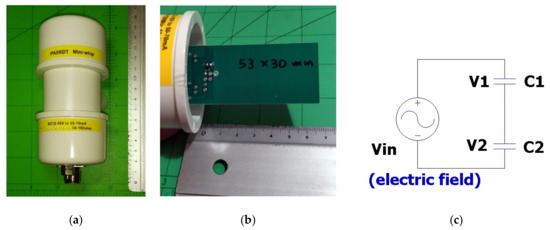
Figure 2.
Mini-whip active antenna is an active antenna that is a few cm long. At VHF/LF frequencies, it acts as a capacitor to the ground, capacitively coupling to the electrical field of the electromagnetic signal. (a) An example of a mini-whip active antenna that is commercially available through online stores (“PA0RDT Mini-Whip antenna”). (b) The copper plate of the antenna has dimensions 53 mm × 30 mm. (c) Electrical model of the mini-whip active antenna; C1 represents the antenna’s capacitance to Earth, and C2 the input capacitance of the first stage of the antenna preamplifier (see JFET in Figure 3).
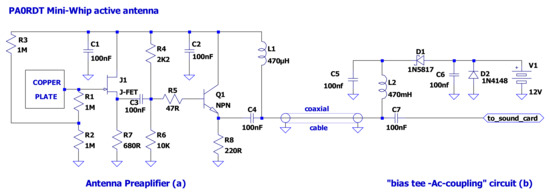
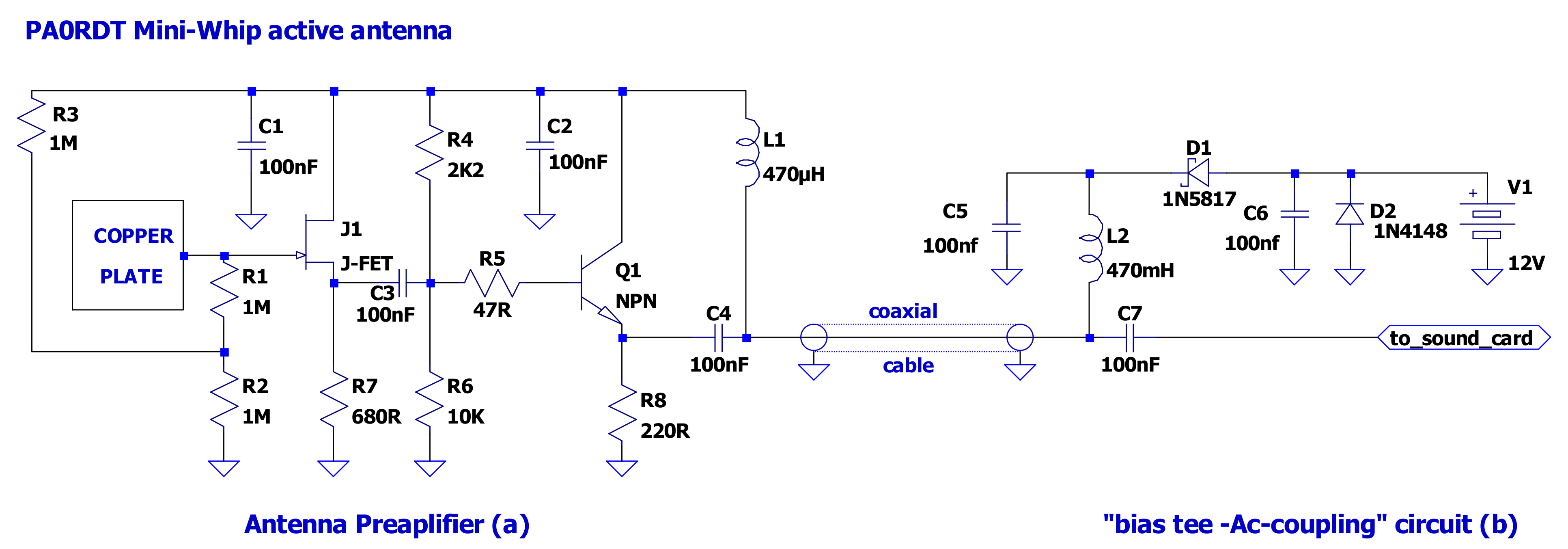
Figure 3.
The schematic of the PA0RDT Mini-Whip antenna, consisting of two parts: (a) the antenna preamplifier (placed on the top of the mast), which receives the electrical component of the electromagnetic field, using a copper plate as the half part of a capacitor to the Earth, and (b) the “bias tee—AC coupling” circuit (placed close to the soundcard), which provides the preamplifier with the necessary supply voltage to operate (bias tee), while it AC-couples (through the capacitor C7) the antenna signal to the soundcard. In our implementation, J1 is the JFET MMBFJ310 but 2N3819 or equivalent can also be used, while Q1 is the NPN-type BJT 2N5109 but 2N3866 or equivalent can also be used.
In contrast to loop antennas, the mini-whip receives the electrical portion of the electromagnetic signal. The simplified electrical model of Figure 2c helps to illustrate its principle of operation. The antenna is coupled to the electric field through the C1 capacitor and to the amplifier through the C2 capacitor. These two form a voltage divider [61]. Increasing C1′s value (by using a copper plate of longer perimeter in the antenna [62]) or/and lowering C2′s value (e.g., by choosing a lower input capacitance JFET; see Figure 3), the received signal strength is increased. At very high frequencies (VHF), the mini-whip antenna works as a typical half-wave antenna, but at lower frequencies, its behavior is completely different. At VLF/LF, it behaves as the half part (one plate) of a capacitor, while the other part (plate) is the Earth. What it receives is the electrical component of the electromagnetic field, as a result of capacitive coupling to a capacitor having the Earth as one of its plates. This means that very good grounding is essential during installation.
Figure 3 shows the full schematic diagram of the mini-whip antenna system. It is split into two parts. One is the active antenna (copper plate and preamplifier) and is placed over the mast, while the other is the “bias tee–AC coupling” circuit, feeding the necessary power supply to the active antenna and the alternating current (AC) coupling to the ADC stage (soundcard), and is placed close to the soundcard. The sensor is the copper plate. The longer the perimeter of the plate is, the higher the capacitance to Earth [62] and the higher the received signal strength. However, if there are strong local radio transmitters, it is better to keep the antenna’s plate small to avoid parasitic phenomena. The design relies on a very high input resistance and very low input capacitance preamplifier, by using a JFET transistor in the first stage [60]. In this case, the effective input capacitance of the preamplifier is practically the capacitance of the capacitor formed between the copper plate and the Earth. The NPN-type BJT transistor circuit forms a voltage buffer stage (voltage follower) that offers impedance matching to low impedance loads. At ~400 kHz, the antenna noise is approximately −90 dBm [63]. Experiments have shown that a shortened antenna such as this has no impact on antenna sensitivity [63]. The second part of the antenna is a small circuit that feeds the necessary direct current (DC) voltage, which is produced by a power supply unit (PSU), to the antenna (bias tee) and AC-couples the signal to the ADC stage (soundcard). The PSU can be any commercially available unit producing a 12 V DC output, capable of providing at least 50 mA output current. However, low-noise linear PSUs are strongly preferable, since the preamplifier is very sensitive to noise. Even a 12 V battery can be used as the PSU of the antenna, since the power consumption is low (48 mA).
For the connections of the active antenna to the “bias tee–AC coupling” circuit and of this circuit to the soundcard, a 50 Ohm coaxial cable such as RG58 or a 75 Ohm coaxial cable such as RG59 is sufficient. In a noisy EM environment, galvanic isolation and filters can be added between the “bias tee–AC coupling” circuit and the soundcard to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
The active antenna part is placed on the top of the mast. The top 0.5 m part of the mast is made of an electrical isolator material, such as PVC, while the rest of the mast is made of a conductive material that is well grounded, since this is essential for less noise reception. A long enough electrical isolator between the active antenna and the (grounded) conductive part of the mast is necessary for the active antenna copper plate to act as one plate of the capacitor, the other plate of which is the Earth. At VLF/LF frequencies, the polarization of the mini-whip antenna is always vertical [61].
As already mentioned, there is an optional stage of filters. These are recommended in the case of strong local AM/MF/LF/VLF broadcasts. Restricting the bandwidth of the signal reaching the soundcard, by excluding strong local broadcasts, protects the soundcard from saturation. The type of filter depends on the frequencies of the local broadcasts. Moreover, galvanic isolation can reduce local noise originating from nearby operating electrical equipment. It is simply a 1:1 toroid transformer, which breaks the ground loop effect between the soundcard and the antenna. Its effect is considerable against the noise produced by the switch-mode PSU of the PC. Furthermore, it protects the receiver against discharges from the antenna. In this design, an AOR GT-1 transformer is used (cost ~EUR 50).
Experiments with various types of soundcards showed that for VLF/LF signals, low-noise and high-sampling-frequency soundcards can do an excellent job. In the two VLF/LF receivers that have been installed (see Section 3), a “Focusrite Scarlet 2i2” was chosen for the ACH station, and a “Behringer U-Phoria umc202hd” for the GER station. These two soundcards are of similar key technical characteristics, i.e., both are 24-Bit, 192 kHz very-low-noise soundcards, having high dynamic range. These cards cost ~EUR 100 each. One channel is connected to the antenna, while the other channel is connected to a 1 Hz high-accuracy pulse of the GPS receiver. This pulse is used to resample via software the soundcard and also for accurately measuring the phase of the received signals.
The final stage is a PC. In our case, a low-end PC is used with an Intel® Celeron Quad Core J1900 CPU, 4 GB memory, and a 500 GB hard disc. All software is run under a free license and needs a Windows 7 or later operating system.
2.2. Software
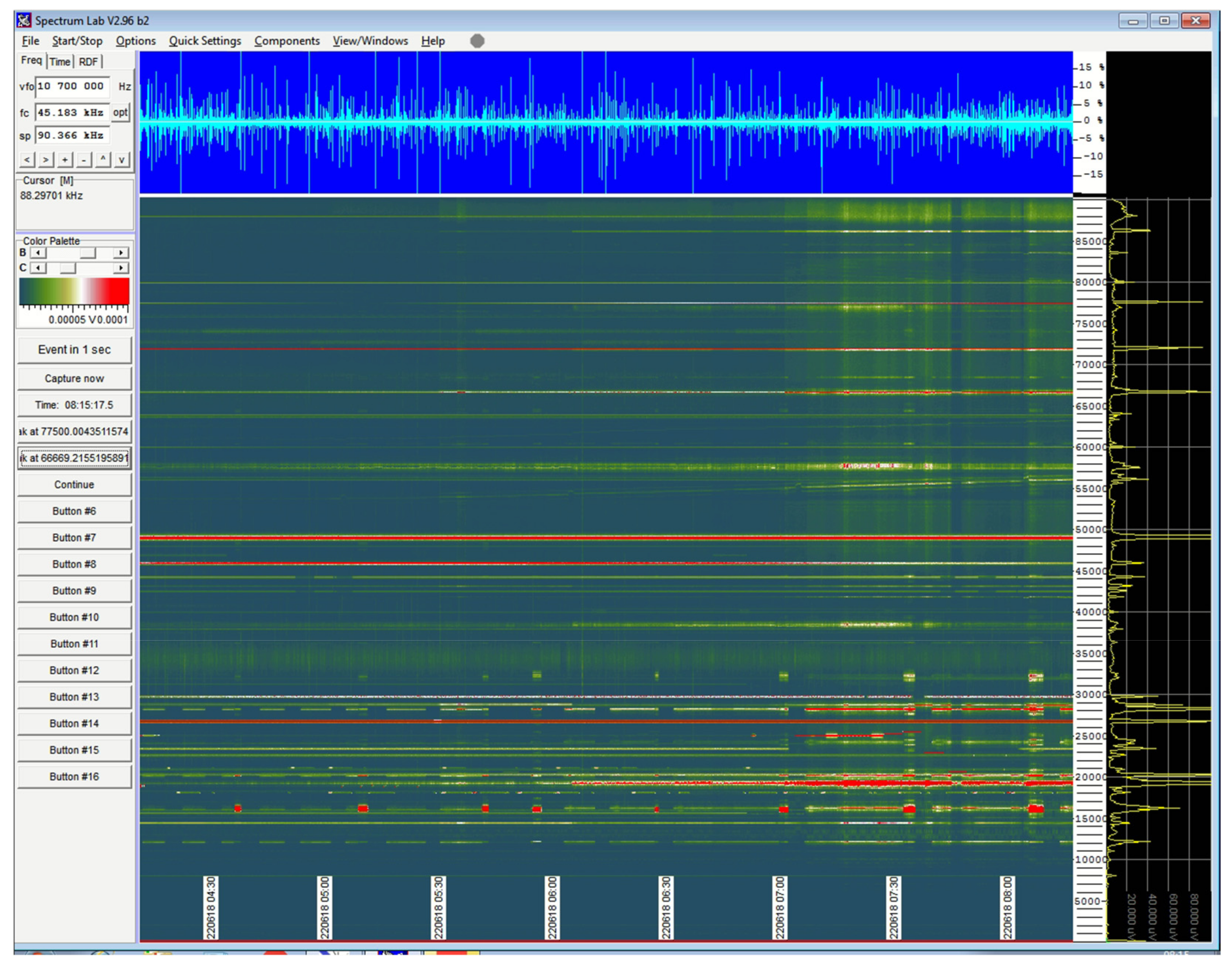
The main SW used is DL4YHF’s Amateur Radio Software: Audio Spectrum Analyzer [59] “SpectrumLab”, which is a freeware program very popular among radio amateurs. It is designed to analyze signals acquired via a soundcard. It can record and replay these signals as WAV-type audio files. The spectrogram, i.e., the temporal variation of the spectrum of the acquired waveforms, can be observed in the form of a fully configurable, so-called “waterfall”, display (Figure 4).
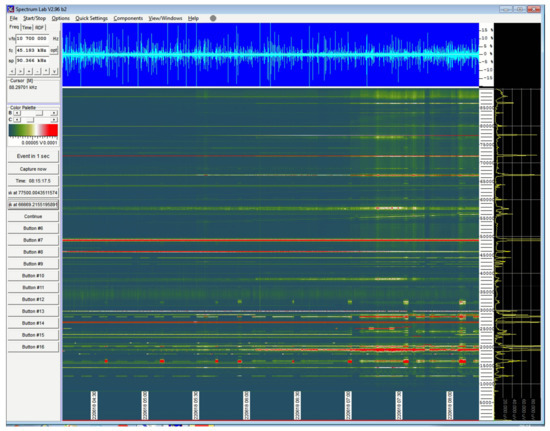
Figure 4.
SpectumLab “waterfall” display of the raw signal received by the active antenna (before the application of any filters). The waveform of the signal (top), as well as the temporal variation in the spectrum, i.e., the spectrogram (bottom), and the current instant of the spectrum (right) are observed here. This view can be periodically captured and saved as a picture for later review. Scroll rate and display colors are configurable. Signal strength is represented by color-coding. Predefined and customized display templates can be applied.
The configuration of SpectumLab’s signal analysis and display is done through fifteen menu cards permitting the adjustment of almost every aspect. As multiple instants of this program can run on the same PC, the input device menu permits one to select the input–output sound devices from multiple soundcards and sets the working sampling rate. Any information shown on the screen can be fully modified by the user through four menu cards. The settings of the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) menu are crucial for the operation of the system. Specifically, two parameters are important: the FFT size (available rage: 32—2,097,152) and the FFT window function (available options: Rectangle, Hamming, Hann, Gauss, Nuttall, and various Flat Top windows). For a selected sampling frequency of the soundcard, , the FFT size, , determines the step of the produced resulting spectrum, also known as FFT-bin-size, as , and therefore the equivalent noise bandwidth (ENBW). Increasing the FFT size, the ENBW is reduced and therefore the noise power in each FFT-bin is reduced. If one chooses the maximum available FFT length, , for , the time window, i.e., the minimum necessary time period to collect and record samples on which the FFT is going to be applied, is which is actually the minimum sampling period of the spectrum. If one needs a spectrum sampling period ≤ 1 s, for , should choose , e.g., . However, then, the ENBW increases from 91.5527 mHz to 1.46484 Hz, degrading the SNR by 12 dB. This is a trade-off that one should always keep in mind. Up to 40 markers can be defined on the frequency layer, usually to show the station’s position over the frequency axis. The system menu adjusts memory, time-zone, and calibration issues. All the configuration settings are saved as a TXT file.
Signal processing is user-determined by means of interconnected components (blocks) in a virtual interactive circuit. The user can select which kinds of blocks (e.g., input–output devices, resampling, signal monitors, spectral analysis, recording “devices”, bandpass digital filters, 50 or 60 Hz harmonics’ elimination filters, delay line, hard limiter, noise blanker, dc reject, fixed gain, automatic gain control (AGC), etc.) will be involved, as well as the parameters of each block. Figure 5a shows the processing stages that have been used for the proposed VLF/LF receiver design, while an example of the graphically defined narrowband filters that are applied to the acquired spectrum at each frequency of interest is depicted in Figure 5b. The only processing applied in the proposed design is narrowband bandpass filtering around each frequency of interest, as well as an appropriate fixed gain per filter.
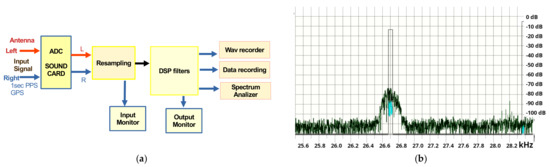
Figure 5.
(a) Block diagram of the SpectrumLab signal processing used in the proposed VLF/LF receiver design. (b) DSP filter block applies multiple narrowband bandpass filters (one per frequency of interest), adjusting also the signal strength of each monitored VLF/LF transmitter.
One can set up to 40 narrowband bandpass filters, for which data can be collected. Digital filtering is performed in real-time for each VLF/LF transmitter’s frequency, permitting the continuous monitoring of their amplitude variation and the phase variation for up to 8 or 9 of them (depending on the available processing power of the host PC). After processing the received signal, the software can store the results for the monitored frequencies in CSV-type files. The format of each row of the file is fully customizable. Stored data can be the min, max, or mean value, as well as user-defined functions over each one of the user-defined narrow frequency bands. There are also available functions yielding normalized values over the entire frequency range. Through the scheduled actions, all user-selected data per monitored frequency can be recorded automatically in files once per day or every few hours.
Table 1 summarizes the key settings of the employed SpectrumLab configuration for the proposed VLF/LF receiver setup, while the full settings are provided in the online available supplementary material for this article.

Table 1.
Key settings of SpectrumLab for the suggested VLF/LF receiver setup. In the example, an external (USB-connected) Focusrite Scarlet 2i2 soundcard is used for the acquisition of the signal received by the active antenna (left channel), while a 1 PPS synchronization pulse from the GPS receiver is also acquired by the soundcard (right channel). The spectrum sampling period in this example is 15 s. The monitored transmitters are shown in Table 2. Full settings of the suggested VLF/LF setup are provided in the online available supplementary material for this article.
For better performance, the suggested VLF/LF receiver setup uses a GPS receiver that delivers a 1 Hz PPS time reference to the soundcard for synchronization purposes. Alternatively, this synchronization can be performed by monitoring one of the time code transmitters, such as RBU (66.666 kHz) or DCF-77 (77.5 kHz) (for receivers installed in Europe). The time reference is used to resample the soundcard-acquired signal in order to eliminate any drift between the real and nominal sampling rates. Phase variation recording needs such accuracy. The internal signal detector of SpectrumLab measures continuously the input signal sampling rate, compares it to the reference time signal, and, if necessary, corrects the sample rate to the nominal. For accurate phase measurements, it is advised that the minimum sampling period of the spectrum is > 10 s. Phase variation can be plotted by the “plot panel”, which can display phase changes in real time and also record them in CSV-like files.
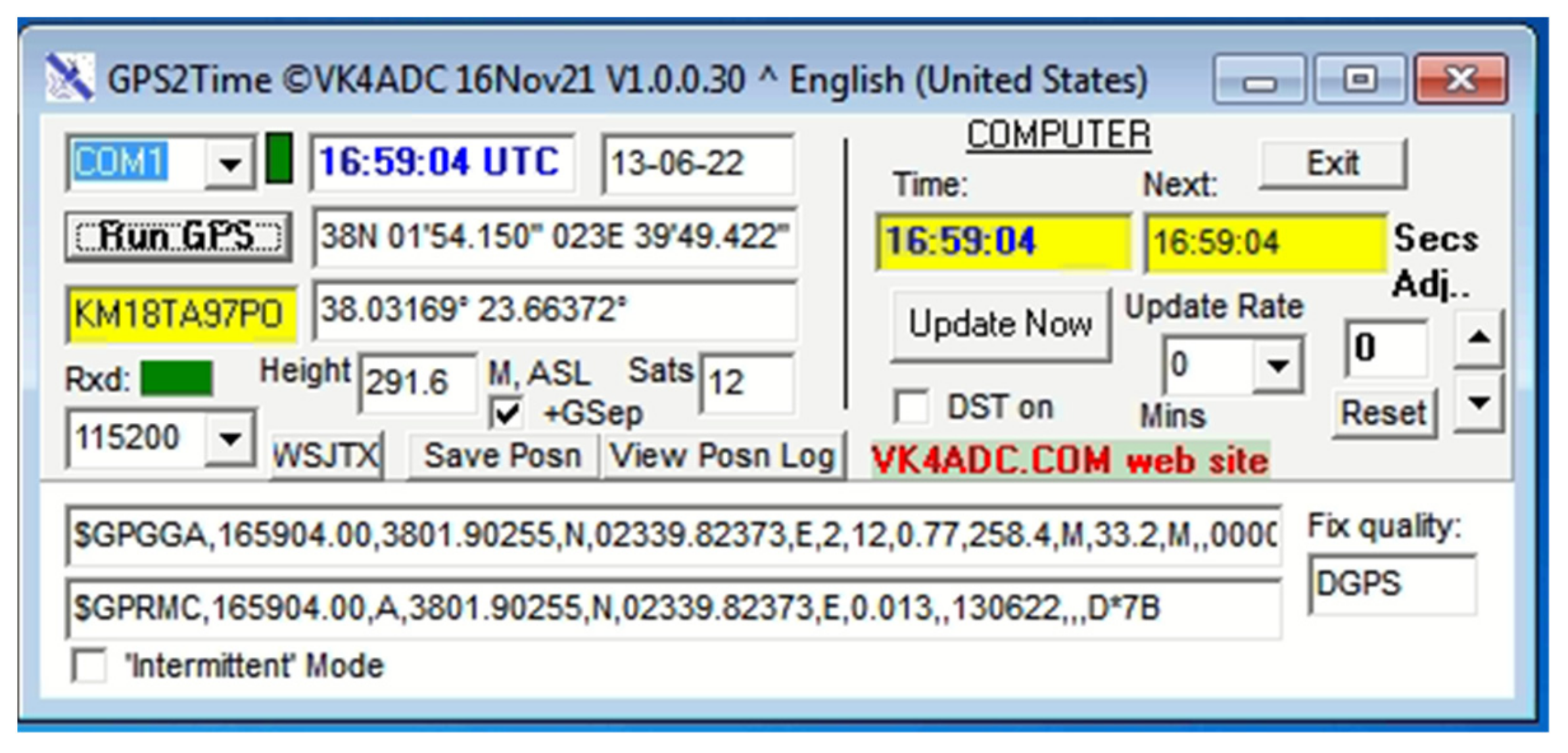
The GPS receiver calibrates the computer’s real-time clock (RTC) for more accurate calculations over frequencies with the aid of a freeware program called GPS2Time (Figure 6), which must run with administrator rights. Since the higher the baud rate is, the higher the accuracy of time setting is, we set the baud rate at 115,200. For continual calibration of the PC’s RTC, it is necessary to set the update rate to zero.
Figure 6.
Freeware GPS2Time, which continuously synchronizes the PC’s RTC for better accuracy.

Table 2.
Transmitters monitored by the GER and ACH VLF/LF receivers installed in Attica (Greece). Note that the mentioned transmitters’ powers have been acquired from different literature and online sources, while for some transmitters (denoted by “?”), no information was found.
Table 2.
Transmitters monitored by the GER and ACH VLF/LF receivers installed in Attica (Greece). Note that the mentioned transmitters’ powers have been acquired from different literature and online sources, while for some transmitters (denoted by “?”), no information was found.
| No. | Frequency (kHz) | Power (kW) | Call Name | Country | Coordinates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16.400 | 350 [37] | JNX | Norway | 66°58′56.41″ N, 13°52′20.9″ E 66.982337°, 13.872471° |
| 2 | 20.270 | 43 [64] | ICV | Italy | 40°55′22.4″ N, 9°43′55.39″ E 40.922889°, 9.732052° |
| 3 | 23.400 | 800 [37] | DHO-38 | Germany | 53°5′14.43″ N, 7°36′31.15″ E 53.087341°, 7.608652° |
| 4 | 24.000 | 1000 [37] | NAA | USA | 38°52′4.15″ N, 77°4′44.76″ W 38.86782°, −77.0791° |
| 5 | 26.700 | ~100 [64] | TBB | Turkey | 37°24′33.91″ N, 27°19′30.98″ E 37.40942°, 27.325273° |
| 6 | 29.700 | ? | ISR | Israel | 30°58′32.51″ N, 35°5′55.21″ E 30.975696°, 35.098668° |
| 7 | 37.500 | 100 [65] | NRK | Iceland | 63°51′3″ N, 22°27′6″ W 63.850833°, −22.451667° |
| 8 | 44. 200 | ? | SRC | Sweden | 57°6′15.0012″ N, 12°22′30″ E 57.104167°, 12.375° |
| 9 | 45.900 | 250 [65] | NSY | Italy | 37°7′32.35″ N, 14°26′10.77″ E 37.125654°, 14.436325° |
| 10 | 49.000 | ? | SXA | Greece | 38°8′42.67″ N, 24°1′10.93″ E 38.145186°, 24.019703° |
| 11 | 60.000 | 17 [65] | MSF | UK | 54°54′36″ N, 3°16′48″ W 54.91°, −3.28° |
| 12 | 62.600 | ? | FUG | France | 43°23′12.47″ N, 2°05′50.60″ E 43.386798°, 2.097388° |
| 13 | 63.850 | ? | FTA-63 | France | 48°32′49.776″ N, 2°34′56.172″ E 48.54716°, 2.58227° |
| 14 | 65.800 | ? | FUE | France | 48°38′15.62″ N, 4°21′2.61″ W 48.637672°, −4.350725° |
| 15 | 66.666 | 10 [65] | RBU | Russia | 56°44′0″ N, 37°39′48″ E 56.733333°, 37.663333° |
| 16 | 77.500 | 50 [65] | DCF-77 | Germany | 50°0′51.24″ N, 9°0′41.35″ E 50.014234°, 9.011487° |
3. Installations
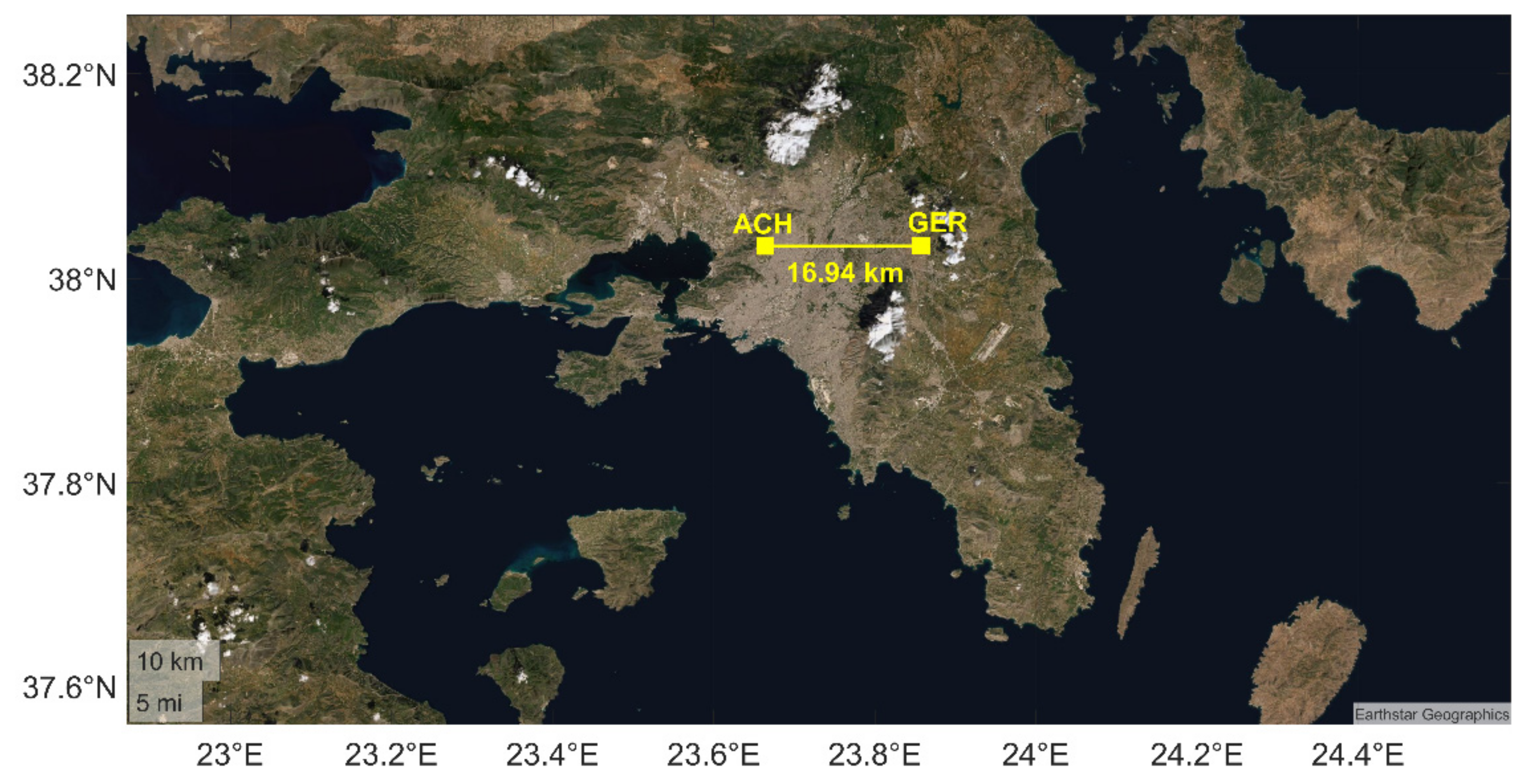
In order to check the reliability of the proposed VLF/LF receiver setup, two identical receivers have been installed in Attica, Greece, and have been experimentally operated since June and September of 2021, respectively. The first one is located in the suburban area of Gerakas, to the east of Athens (call sign: “GER”, geographical coordinates: (38.03° Ν, 23.85° E)), while the second one is located in a forest area to the west of Athens, called “Aspra Chomata” (call sign: “ACH”, geographical coordinates: (38.03° N, 23.66° E)), close to the urban complex of Athens. The distance between the two stations is ~17 km (Figure 7).
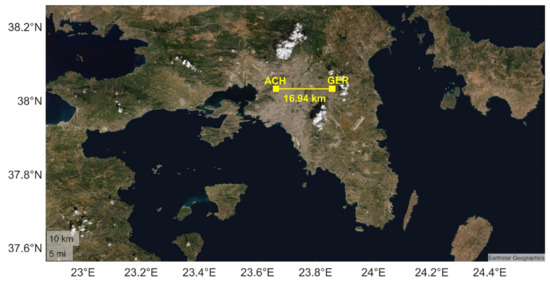
Figure 7.
Satellite image of the prefecture of Attica in Greece. The two VLF/LF stations (ACH and GER) are depicted with yellow squares, while the distance between them is shown to be 16.94 km.
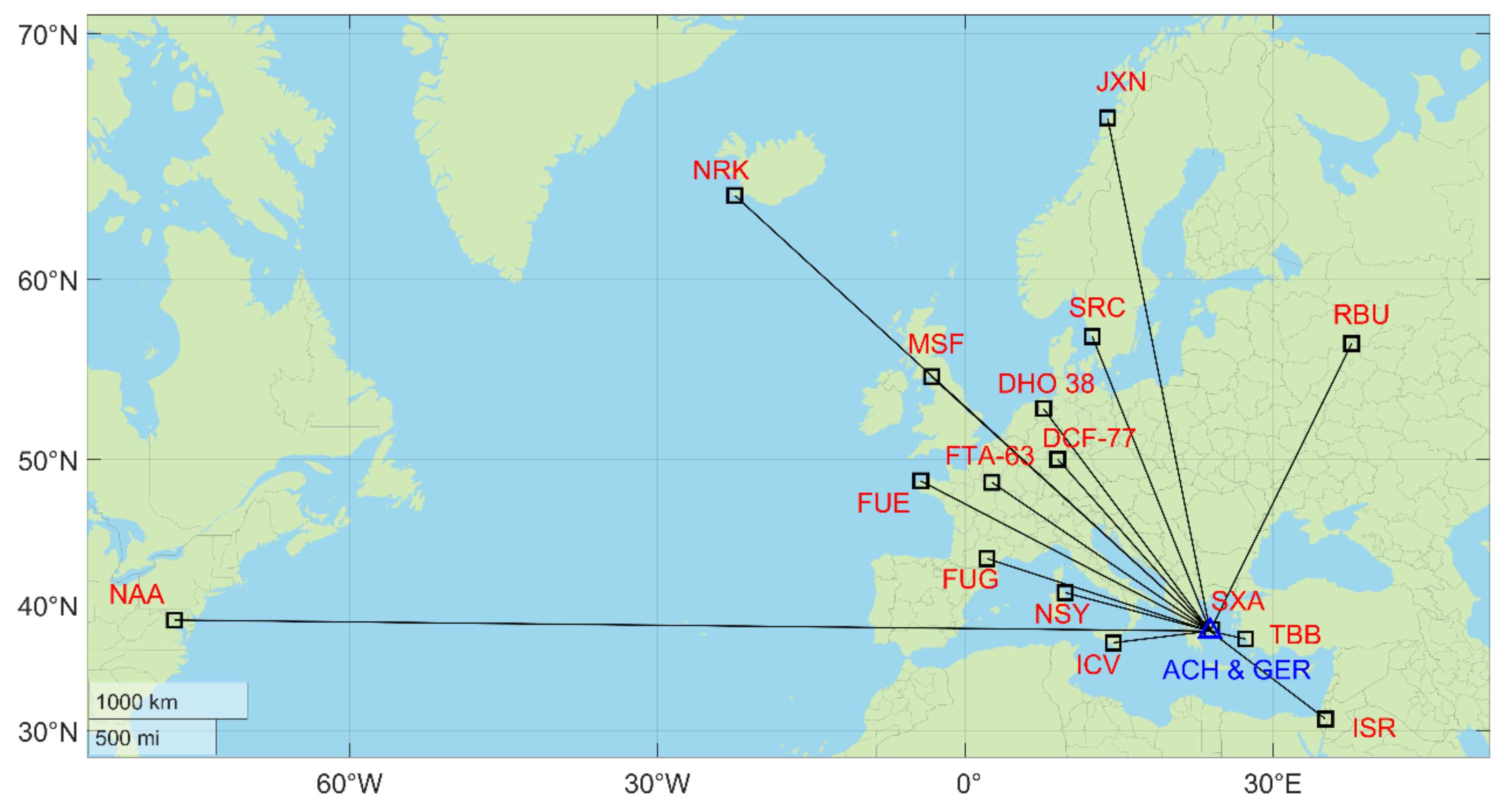
Both monitor the sixteen stations shown in Table 2 (see also Figure 8) and also the background noise at a few narrow frequency bands where no known VLF/LF transmissions or local interference take place (in our case, e.g., 3 kHz, 10 kHz, 59 kHz, 85 kHz). The scope of monitoring the background noise is to set a reference that permits one to check whether a transmitter has interrupted transmission, especially for distant/weak signals. It is advised that, at any new location, one should carefully select the background noise frequencies so that they are not affected by any narrowband transmissions or any local interference.
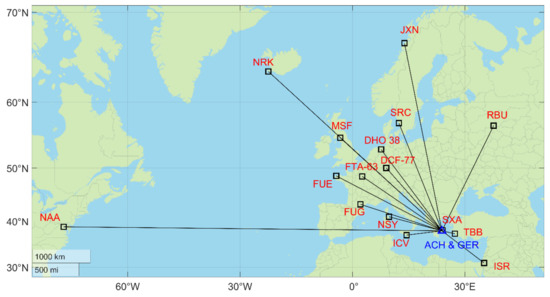
Figure 8.
Map showing the locations along with the call signs of all of the transmitters that are monitored by the ACH and GER VLF/LF receivers. The blue triangle denotes the location of the two receivers, whereas the black squares indicate the locations of the monitored transmitters.
It has to be mentioned that the only differences between the VLF/LF receiver installations are: (a) the type of the external soundcard used, which are of similar specifications (see Section 2.1), and (b) the spectrum sampling period (for GER, it is 30 s, and for ACH, it is 15 s). This has been intentionally done to check whether such deviations in the setup can lead to notably different performance.
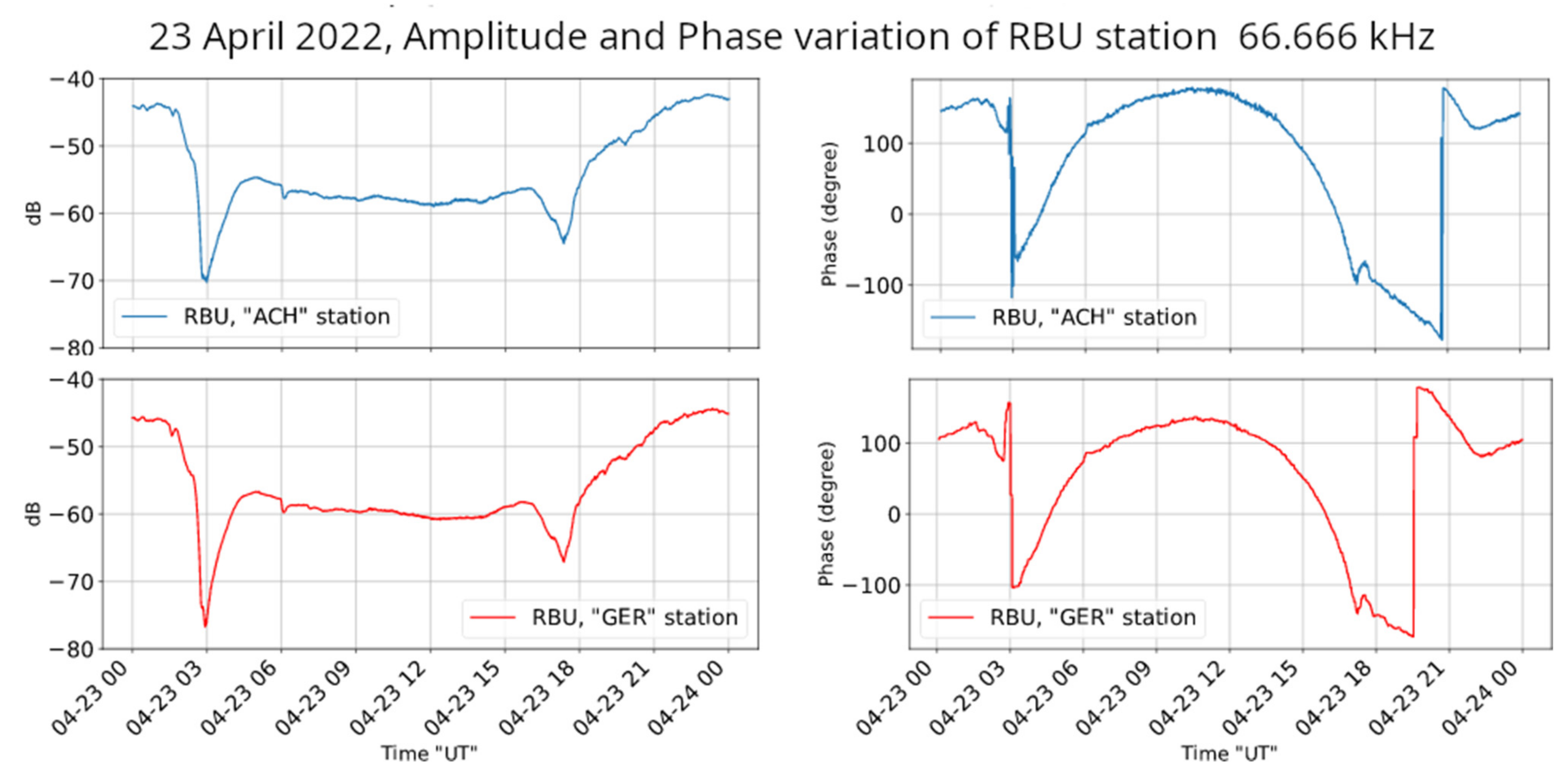
Figure 9 shows a sample of the daily variation in the amplitude and phase of the same transmitter (RBU) as acquired by the two VLF/LF receivers. One can observe that there are no notable differences between the amplitudes of the received signals, while there is a small difference in their phases during the terminator times’ transitions. It is noted that phase measurements are very “sensitive” to different factors, such as small HW differences (in the case of ACH and GER receivers, there is a difference in the used soundcards), a small change in the frequency of a transmitter (it is very common that VLF/LF transmitters slightly change their frequency, while a change even at mHz level can lead to a drift in the measured phase), changes in the level of the received signal (the lower the received signal, i.e., the lower the SNR, the more difficult it is to accurately calculate the phase), and the presence of electric discharges (during lightning activity, which affects all the acquired spectrum, the SNR is degraded, leading to a higher possibility of inaccurate phase measurements).
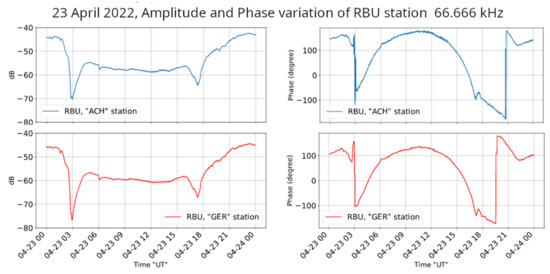
Figure 9.
Amplitude (left panels), in dB, and phase (right panels), in degrees, ±180° wrapped, of the reception from the transmitter RBU on 23 April 2022, by the ACH and GER VLF/LF receivers. The diurnal variation in the amplitude of the signals is almost identical, while small differences are found in the diurnal variation in the phase of the signals.
4. Nighttime Fluctuation Method
In this section, we briefly present the VLF/LF statistical analysis method called the “nighttime fluctuation method” (NFM) [39,40]. The D ionospheric layer disappears after the sunset and the amplitude of the signal is stronger during the nighttime due to smaller absorptions compared to the day. Therefore, we initially extract the nighttime amplitude data (in dB) from the diurnal variation in the amplitude data, by defining the nighttime time interval so that it has an adequate margin from the local minima of sunrise and sunset terminators. Secondly, we estimate the residual variation in the amplitude of the signal ( defined as , where is the signal of the amplitude at the time , and is calculated over a window of days around the day of interest (including the day of interest). The applied window has the ability to enhance the short-term variations and reduce the long-term ones. Subsequently, we calculate the daily values for the three statistical parameters, ““ (trend), “” (dispersion), and “” (nighttime fluctuation), as follows:
where represents the mean value of , and and are the endpoints of the chosen nighttime interval (starting and ending time points);
where the is actually the standard deviation of , and
After the calculation of the daily-valued time series of the three statistical quantities, we compute the normalized values , as , where and are the mean value and the standard deviation of days around the day of interest, respectively. Any statistical anomaly in these daily-valued time series that exceeds could possibly be related to an EQ preparation process or a geomagnetic storm [30,39,40], or to any other phenomenon that can influence the lower ionosphere. In fact, this method has recently been applied extensively to identify ionospheric anomalies prior to EQs as an increase in and decrease in and , e.g., [28,30,39]. It should be mentioned that, generally, the usage of a day window around the day of interest includes information from the “future”, so this is appropriate only for a posteriori analysis [30]. For “real-time” analysis, one should use single-sided windows.
5. Identified Perturbations
In the following, we present examples of ionospheric anomalies possibly related to extreme events, such as solar flares, geomagnetic storms, and EQs, which were possible to be detected by the VLF/LF receivers of the proposed setup that were installed in Attica, Greece (see Section 3), as evidence of the reliability of the proposed VLF/LF receiver setup.
Concerning solar flares, we present receptions from different transmitters for three cases of “M” and “X” class flares that happened on 28 October 2021, as well as one case of a “C” class flare that happened on 09 April 2022. A sudden increase in the amplitude of the signal is observed in these four cases, whereas the identification of the C class flare shows that the sensitivity of the system is able to capture even such a minor flare.
In regard to EQs, we present NFM analysis (see Section 4) results around the time of occurrence of three significant EQs (M > 5.5) that took place in the southeast Mediterranean (two on Crete Island and one close to Karpathos Island) between 27 September 2021 and 19 October 2021. We discuss the obtained results in terms of other ionosphere-influencing phenomena, including weather ones, such as typhoons, cyclones, weather fronts, tornadoes, and large thunderstorm systems, which produce atmospheric gravity waves (AGW) in the troposphere [66].
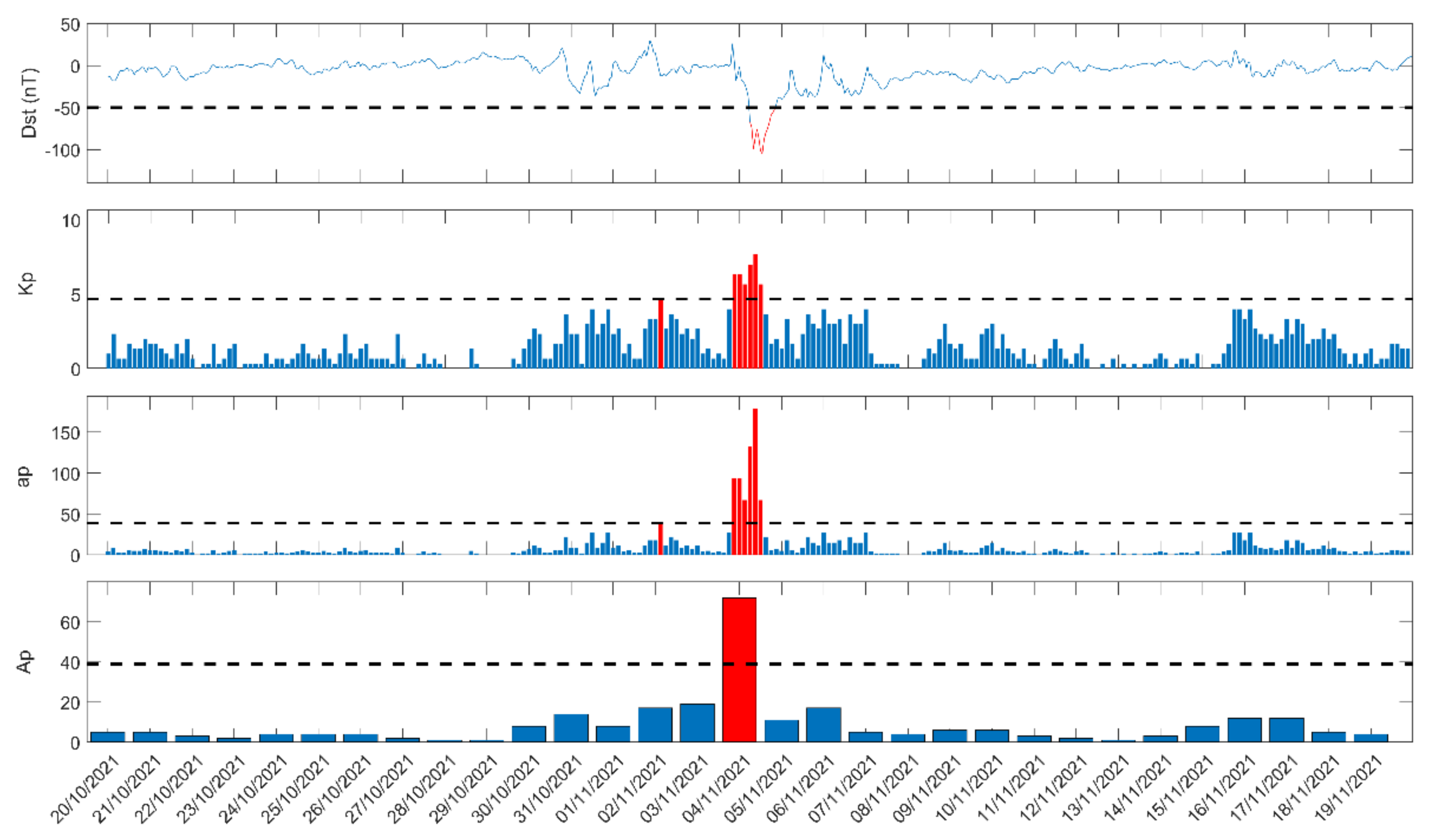
Finally, we show the magnetic storm’s effect on the received signal, by presenting the NFM analysis (see Section 4) results around the time period in which an intense geomagnetic storm (minimum Dst = −105 nT) occurred on 4 November 2021.
5.1. Solar Flares
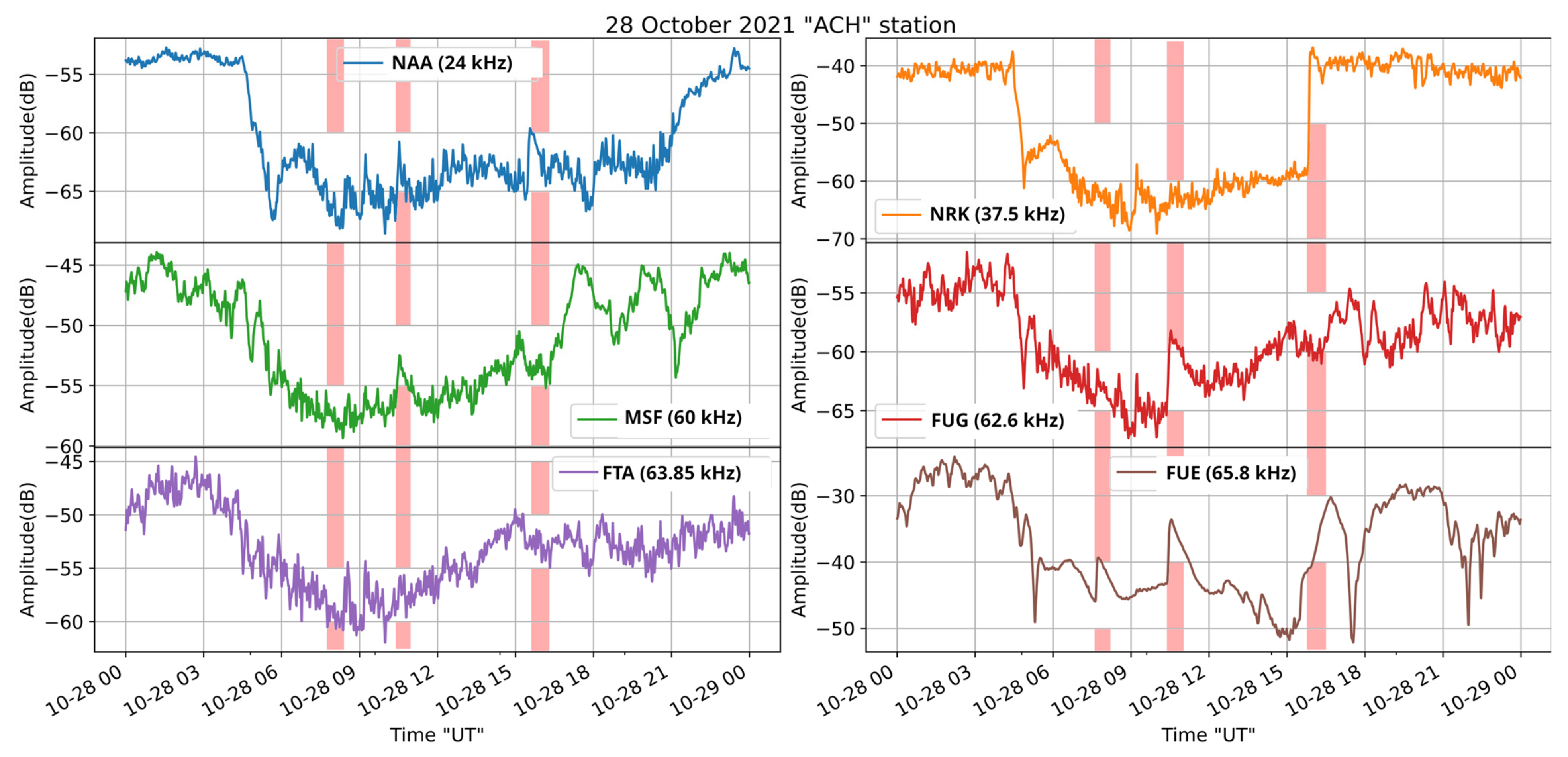
On 28 October 2021, there were three powerful solar flare events: at 7:40 UTC, a M1.4 class; at 10:28 UTC, a M2.2 class; and at 15:35 UTC, a X1 class. The receiver recorded ionospheric abnormalities during the period of these phenomena in the reception amplitude of more than one of the monitored transmitters, confirming their global character. The result was a change in the amplitude of the signal of distantly measured radio stations. As already mentioned, the Sun’s activity is the main reason for SID. Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12 show the received amplitudes from different transmitters during the occurrence of the studied M1.4, M2.2, and X1 solar flares. Specifically, Figure 10 shows the signals received from transmitters located far west of the receiver, Figure 11 depicts signals from transmitters close to the longitude of the receiver and west of it, whereas Figure 12 shows signals from transmitters close to the longitude of the receiver and east of it. By comparing Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12, one can observe that the reception more clearly appearing to be disturbed by all three solar flares is the signal from FUE, where the disturbance amplitude is monotonously increased with the solar flare strength (Figure 10).
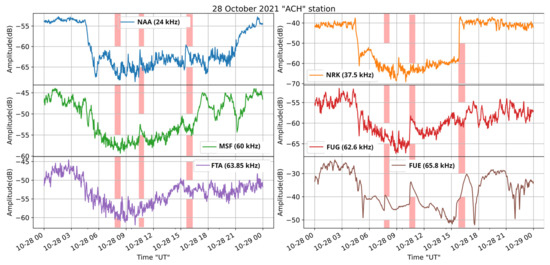
Figure 10.
Received amplitude at the ACH receiver on 28 October 2021, for the transmitters NAA, MSF, FUG, FTA-63, and FUE, located far west from the longitude of the receiver. The vertical bars indicate the time period of occurrence of the M1.4, M2.2, and X1 solar flares, in this time order. FUE signal shows the clearest disturbance due to all three of them.
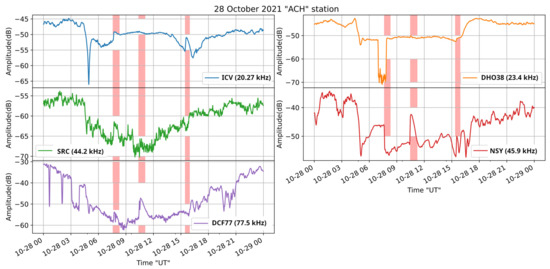
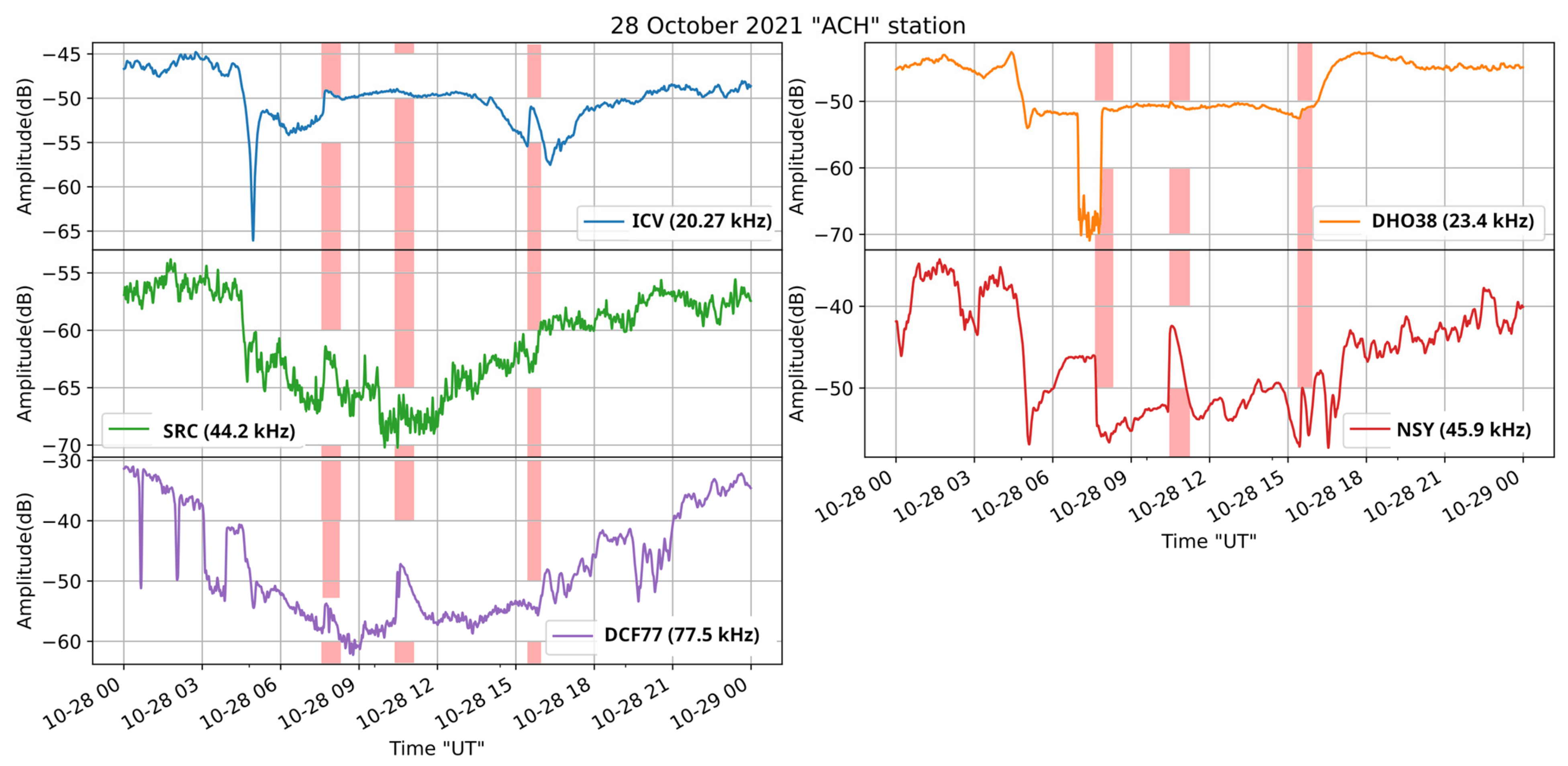
Figure 11.
Received amplitude at the ACH receiver on 28 October 2021, for the transmitters ICV, DHO-38, SRC, NSY, and DCF-77, located at the longitude of the receiver and west of it. The vertical bars indicate the time period of occurrence of the M1.4, M2.2, and X1 solar flares, in this time order.
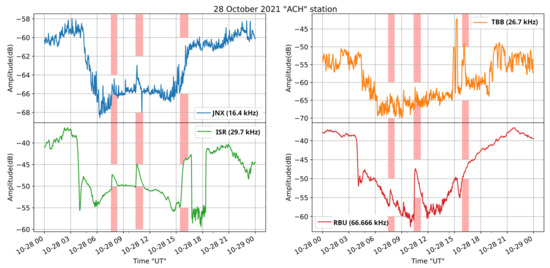
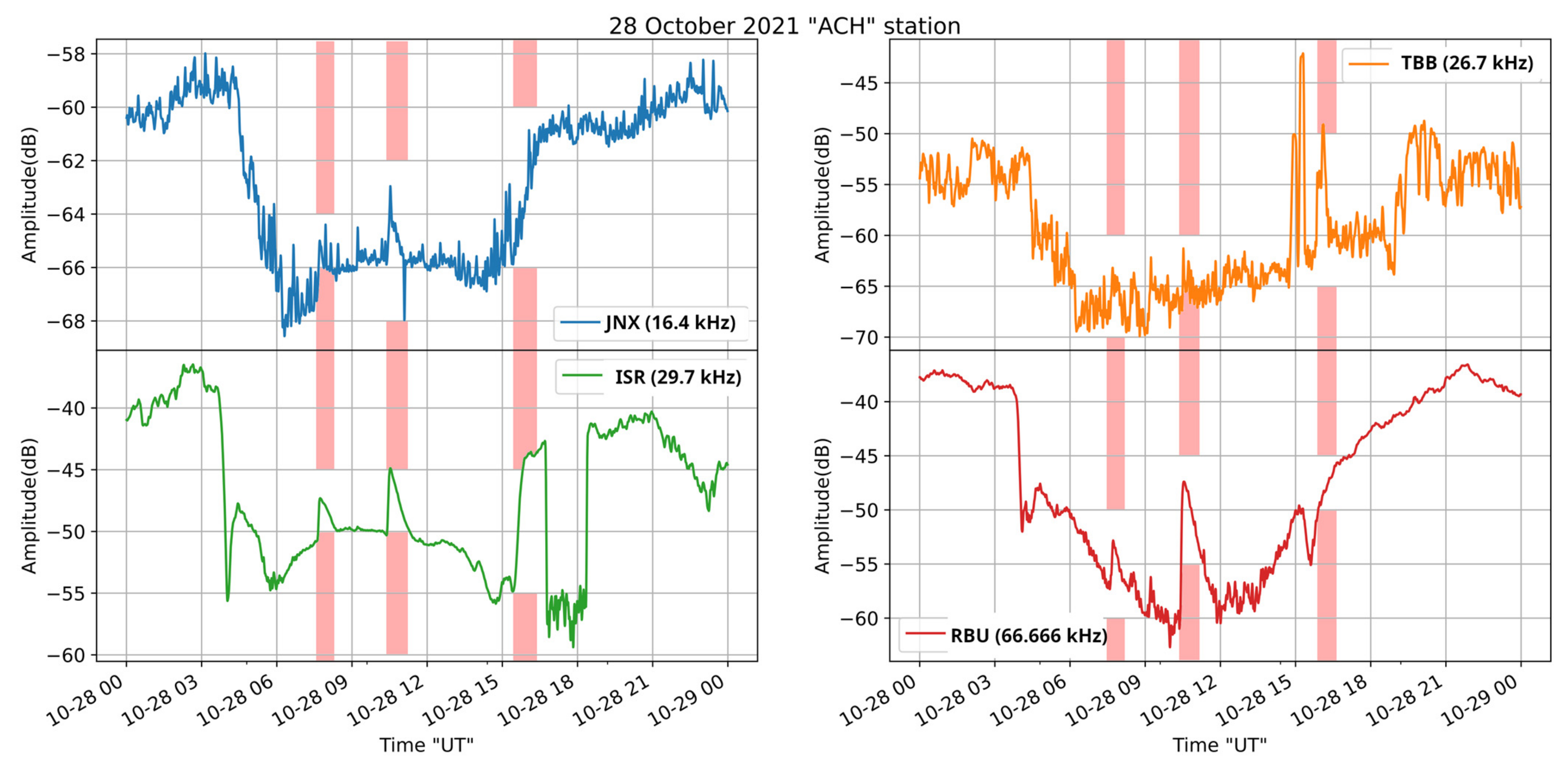
Figure 12.
Received amplitude at the ACH receiver on 28 October 2021, for the transmitters JNX, TBB, ISR, and RBU, located at the longitude of the receiver and east of it. The vertical bars indicate the time period of occurrence of the M1.4, M2.2, and X1 solar flares, in this time order.
One would expect that all long propagation paths to the west of the receiver (Figure 10) should present imprints of all three solar flares, since all three of them fall within the daytime part of the received signal. However, this is not true, probably due to the low level (close to the level of background noise) of the received signals for all of these stations, except FUE. Nevertheless, the M2.2 solar flare’s effect seems to be imprinted in the signals from FUG, MSF, and NAA, while disturbances possibly due to the X1 event, but shifted in time in relation to X1′s occurrence, can be observed in the signals from NAA and MSF.
Figure 11 shows that the reception from transmitters located close to the longitude of the receiver and to the west of it was disturbed by the M2.2 solar flare, which occurred at the middle of the daytime part of the signals, as clearly shown for NSY and DCF-77. On the contrary, the receptions from ICV, DHO-38, and SRC do not seem to present any imprint of the M2.2 flare. The X1 solar flare occurred close to the sunset terminator time of these propagation paths and therefore it is not easy to discriminate any influence on the received signals. Nevertheless, ICV, NSY, and DCF-77 seem to present disturbances due to the X1 solar flare. Finally, the M1.4 solar flare occurrence time matches the disturbances of ICV, SRC, and DCF-77. However, in the case of SRC and DCF-77, it has to be noted that the signal is of low level and noisy.
Regarding the transmitters located at the longitude of the receiver and east of it (Figure 12), one can observe that while the M2.2 is imprinted in all of them, the X1 solar flare is not depicted since it occurred close to the sunset terminator. The peak of TBB during the X1 solar flare could be related to this, but the signal of the specific station was low during this particular day and thus we cannot offer a definitive conclusion. Moreover, ISR was probably turned off for a few hours after the X1 solar flare, so the peak appearing close to the time of occurrence of the X1 flare is not a disturbance; it only appears so because of the sudden stop in the transmission. As far as the M1.4 solar flare is concerned, one can clearly see its effect on the signals of ISR and RBU, while the corresponding small peaks in the signals of JNX cannot be decisively attributed to the M1.4 solar flare since the signal is too low, at the level of noise.
Summarizing the results, it is concluded that the M2.2 class solar flare had a stronger impact on the received amplitudes than the X1 class one. This is because the M2.2 solar flare happened at 12.28 EEST (local time of the receiver), when the Sun was almost at the maximum of its orbit, leading to a stronger SID than that of the X1 class solar flare, which happened at 17:35 EEST, close to the sunset (18:30 EEST), and therefore close to the sunset terminator minimum of the reception. Moreover, a milder effect on the receptions is observed for the M1.4 class event that occurred at 05:40 EEST local time, before sunrise (07:16 EEST), for similar reasons.
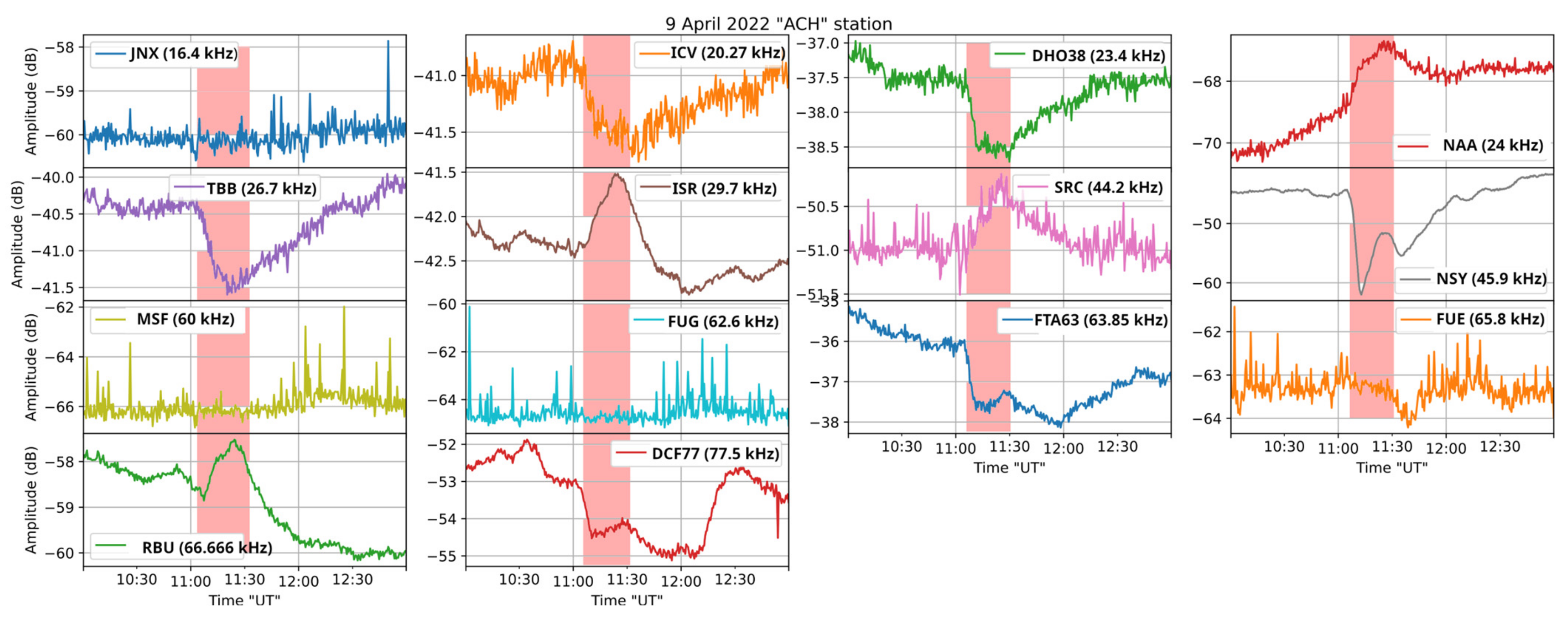
In order to determine the minimum solar flare class that can be detected in the receptions of more than one monitored transmitter, we checked all diurnal variations for all received transmitters from September 2021 to April 2022, and we concluded that a C4.7 class was able to disturb 10 of the monitored frequencies. On 9 April 2022, at 11:24 UTC, a C4.7 class solar flare occurred and concurrently the signal level of the transmitters NAA, ISR, SCR, and RBU was suddenly increased, while the signal level of the transmitters ICV, DHO-38, TBB, NSY, FTA, and DCF-77 was suddenly decreased (Figure 13), indicating that the proposed VLF/LF receiver can detect solar flares at least down to C4.7 class. It is noted that during the specific time period, the signal level of the transmitters JNX, MSF, FUG, and FUE was particularly low.
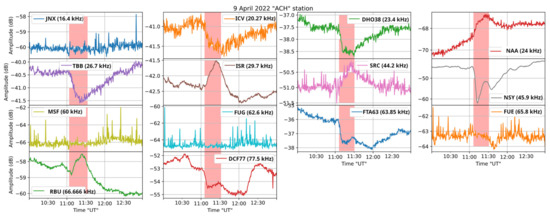
Figure 13.
Zoom-in of the received amplitude at the ACH receiver on 9 April 2022, around the time of occurrence of a C4.7 class solar flare, for the transmitters JNX, ICV, DHO-38, NAA, TBB, ISR, SRC, NSY, MSF, FUG, FTA-63, FUE, RBU, and DCF-77. The vertical bars indicate the time period of occurrence of the C4.7 solar flare.
5.2. Earthquakes
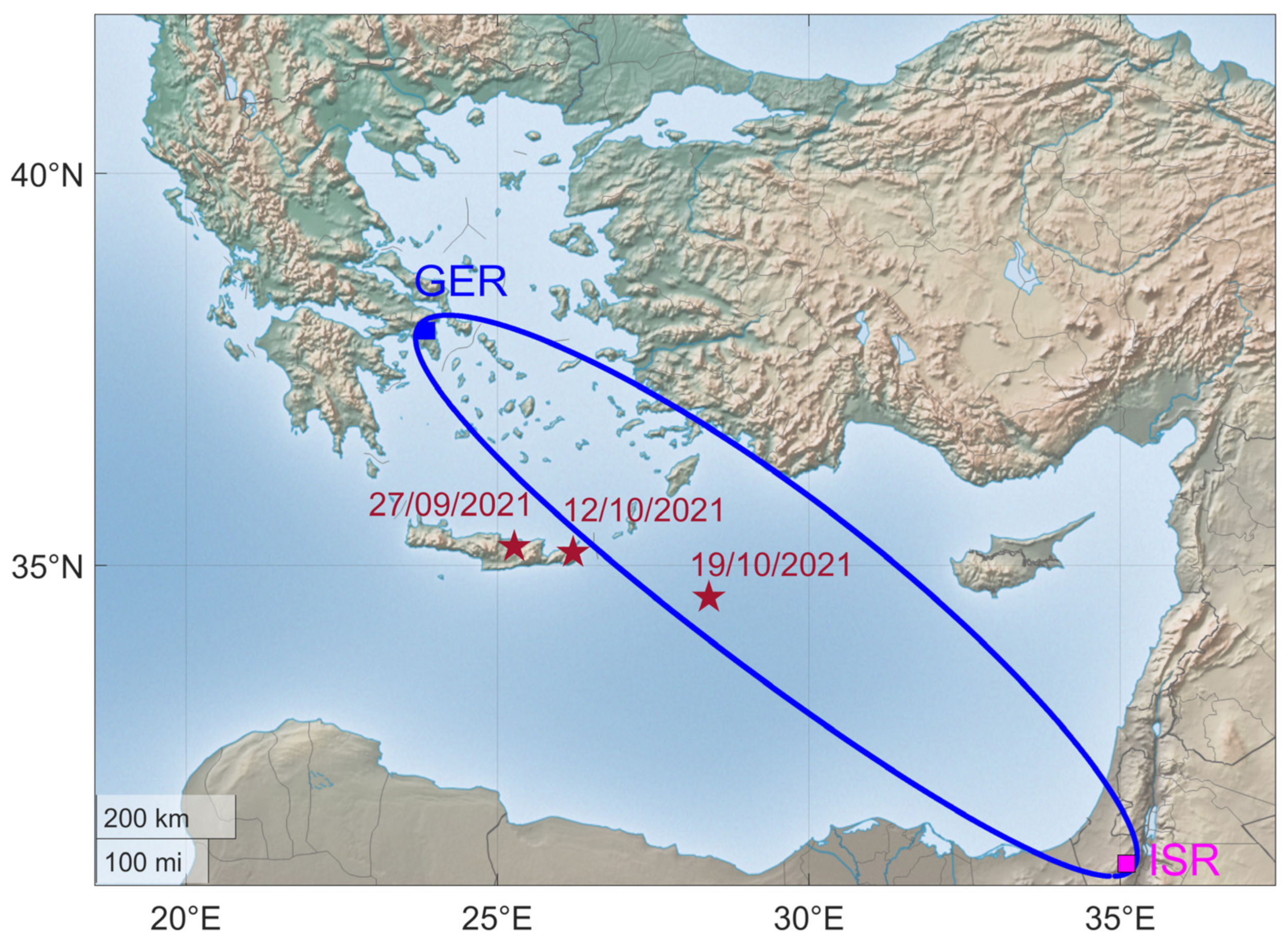
As already mentioned in Section 1, in this article, we investigate three recent EQs that happened in the southeastern Mediterranean on September and October of 2021. For this reason, we used the VLF data received from the ISR transmitter, which is located southeast of Athens, in Negev (Israel). We used only data acquired by the receiver GER, since the receiver ACH was unfortunately intermittently operating from 1 September 2021 to 14 November 2021, initially due to setup optimization experiments and later on due to lightning damage. All the details about the three EQs as acquired from the Institute of Geodynamics of the National Observatory of Athens (https://www.gein.noa.gr/en/services-products/earthquake-catalogs/ (accessed on 23 July 2022)) are presented in Table 3. More precisely, the epicenters of the first two of them, in chronological order, were located in the eastern part of Crete Island and the third one was located in the southeastern offshore region of Karpathos Island. In Figure 14, we present the subionospheric propagation path ISR-GER, along with the epicenters of the abovementioned EQs. Moreover, it is noted that these EQs had significant magnitudes, M > 5.5, and hence are considered able to disturb the lower ionosphere within or very close to the borders of the fifth Fresnel zone of the ISR-GER propagation path [29,39].

Table 3.
List of examined EQs in southeastern Mediterranean.
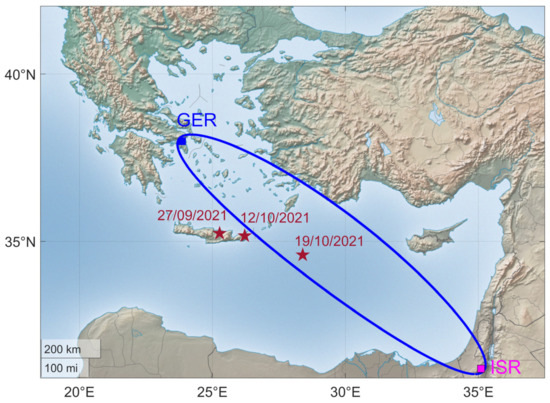
Figure 14.
Map of eastern Mediterranean. The fifth Fresnel zone of the propagation path ISR-GER is indicated, as well as the epicenters and dates of the studied EQs (Table 3).
It is mentioned that when studying ionospheric anomalies in possible relation to EQs, one should also check for any other phenomena that could have a contaminating impact on the obtained results. This includes both global phenomena, such as geomagnetic storms and M and X class flares, and local phenomena, such as volcanos, tsunamis, and a variety of weather phenomena (typhoons, cyclones, weather fronts, tornadoes, and large thunderstorm systems), which can affect the ionosphere [66,67,68,69]. Specifically, for possible geomagnetic storms, we checked the geomagnetic indices Dst, Kp, ap, and Ap from the World Data Center for Geomagnetism of Kyoto (https://wdc.kugi.kyoto-u.ac.jp/wdc/Sec3.html (accessed on 23 July 2022)). For possible solar flares, we checked the data on solar X-ray flux from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (https://www.swpc.noaa.gov/products/goes-x-ray-flux (accessed on 23 July 2022)). Moreover, for possibly erupted volcanoes, we checked the Global Volcanism Program of the Smithsonian Institution (https://volcano.si.edu/search_eruption.cfm (accessed on 23 July 2022)). Finally, regarding possible thunderstorms, we checked the parameter of convective available potential energy (commonly abbreviated as CAPE), as an indication of atmospheric instability, by observing its distribution in the map from the Ventusky search engine (https://www.ventusky.com (accessed on 23 July 2022)), the data of which are provided by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD), while lightning activity was checked using the “Blitzortung.org” lightning detection network (https://www.blitzortung.org/en/historical_maps.php (accessed on 23 July 2022)) and “lightningmaps.org” (https://www.lightningmaps.org/ (accessed on 23 July 2022)).
In this study, we applied the NFM analysis method (see Section 4) by selecting a wide time period from 15 September 2021 to 31 October 2021 to examine the three EQs of interest (see Table 3) that happened on eastern Crete Island and the offshore southeastern region of Karpathos Island. We used the nighttime interval from 00:00 to 05:00 LT (21:00–02:00 UTC) of the VLF amplitude data, after removing any nighttime amplitude excerpts of the signal that were artificial anomalies due to transmitter operation disruptions.
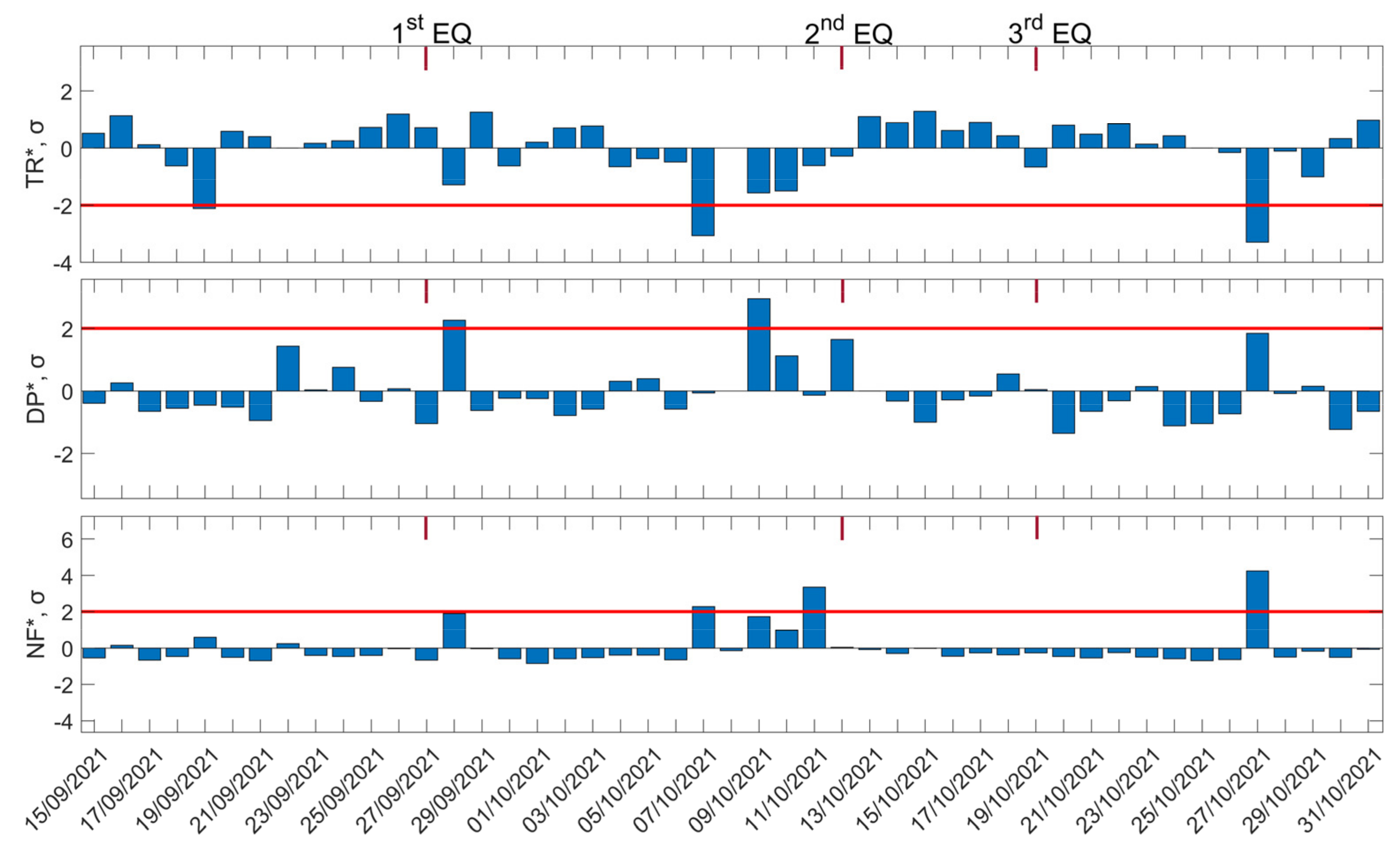
In Figure 15, we present the three normalized statistical parameters for the abovementioned time period. As is evident from Figure 15, there was a decrement in , exceeding –2σ, on 19 September 2021, 8 days before the M5.8 EQ of 27 September 2021, while the enhancement in (exceeding the +2σ threshold) and (slightly below the +2σ threshold) on 28 September 2021 could possibly be attributed to the specific EQ as well, since the second EQ (M6.2, 12 October 2021) occurred 2 weeks later and, therefore, it is considered unlikely to be related to it.
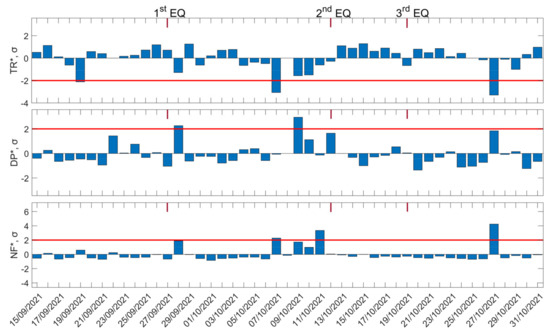
Figure 15.
Time evolution of three statistical quantities, , , and , of the NFM analysis method for the subionospheric path GER-ISR is shown in the top, middle, and bottom panels, respectively. The time period represented in the figure is from 15 November 2021 to 31 October 2021. Red solid horizontal lines indicate the corresponding +2σ/−2σ limits; σ is calculated for the whole studied period of each panel. The dates of three EQs are shown on top of each panel by the red vertical line segments, marked on the top panel as “1st EQ”, “2nd EQ”, and “3rd EQ”.
Moreover, anomalies were identified between 7 October 2021 and 11 October 2021, a few days before the second EQ. Specifically, on 7 October 2021, there was a significant anomaly in both and (but not in ), exceeding the +2σ and –2σ limits, respectively, that may be associated with the second EQ (12 October 2021). An enhancement in , on 09 October 2021, was observed ~3 days before the second EQ, but there was no statistically significant (i.e., exceeding –2σ and +2σ, respectively) anomaly in and . Moreover, on 11 October 2021, we could observe an enhancement in , exceeding the +2σ threshold 1 day before the second EQ (12 October 2021). However, it has to be noted that, during this specific date, there was a moderate storm (moderate to strong atmospheric instability in terms of CAPE parameter) with lightning activity in the studied area, which could possibly have affected the VLF propagation of the subionospheric path of ISR-GER.
Although the abovementioned statistical anomalies occurred only 1–1.5 weeks before the third EQ (M6.1, 19 October 2021), and even though the third EQ was well within the fifth Fresnel zone of the ISR-GER propagation path, they are unlikely to be related to the third EQ; it is more likely to be related to the second EQ. The reasons, beyond the longer time distance, are that the third EQ had a far deeper hypocenter (58 km) than the second one (8 km) and the third EQ’s epicenter was in the sea, ~130 km from the nearest coast (south coast of Karpathos Island), while the second one was very close (~22 km) to the eastern coast of Crete Island.
Finally, a decrease in and an increase in , exceeding +2σ and −2σ, respectively, was observed on 27 October 2021, while the only phenomena found that could possibly be responsible for this anomaly were moderate atmospheric instability with lightning activity at the western borders of the fifth Fresnel zone of the ISR-GER propagation path.
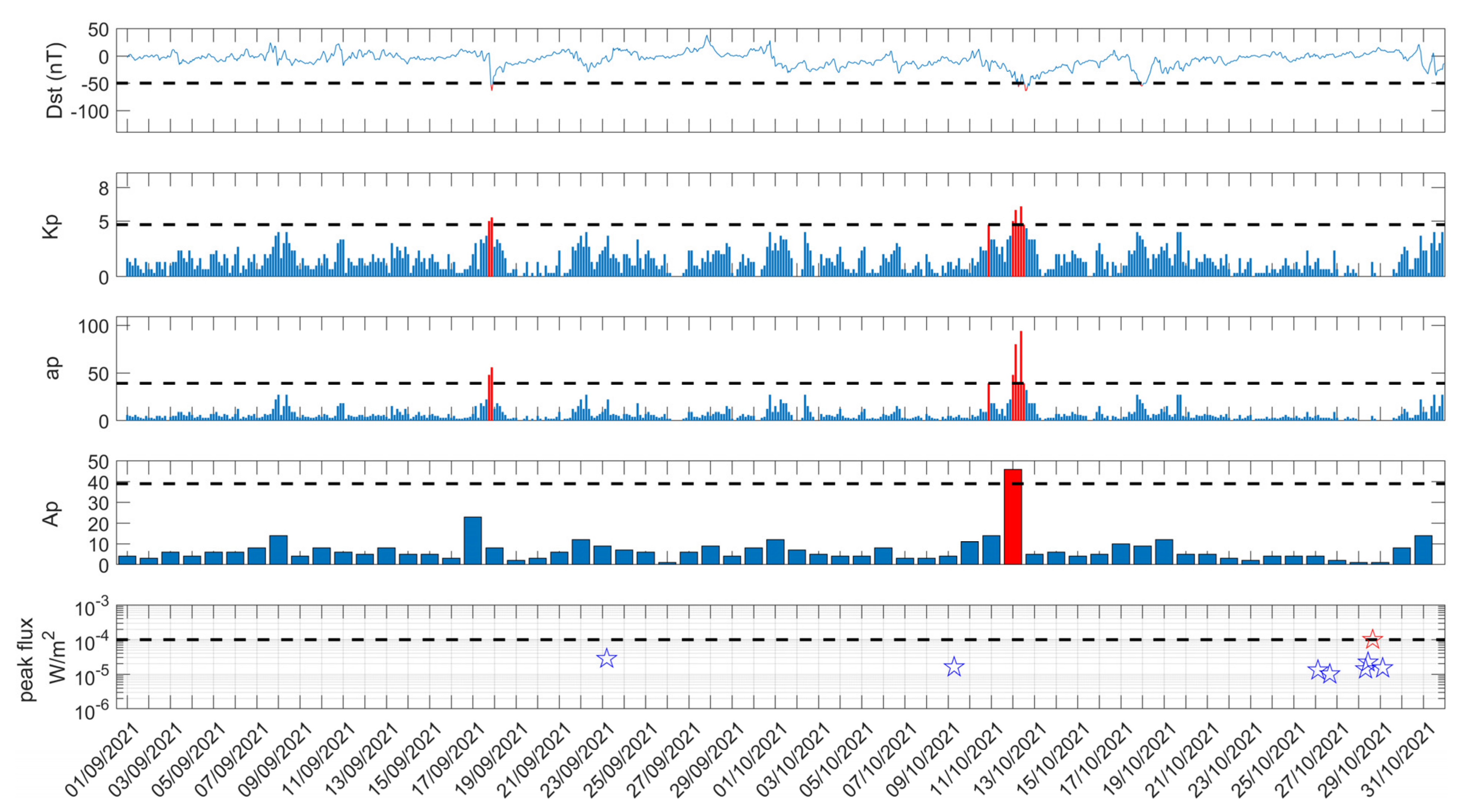
In terms of space/Sun phenomena (Figure 16), the only geomagnetic storms found were 2-week ones (~−50 nT), on 18 September 2021 and 12 October 2021, which are not considered to have influenced the results, while an X1 solar flare happened on 28 October 2021, close to the sunset terminator (see also Section 5.1), and less intense solar flares happened on 23 September, 9 September, 26 October, and 28 October 2021; none of them are considered to have contaminated the results, since nighttime data have been used (the used signal excerpts do not show any influence of the specific solar flares). Moreover, no eruptions of nearby located volcanos happened during the studied time period.
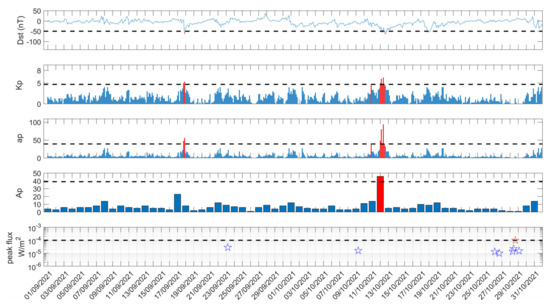
Figure 16.
Geomagnetic indices Dst, Kp, ap, and Ap, as well as solar flares during the time period 1 September 2021–31 October 2021. Red colored parts indicate values exceeding the thresholds marked by the horizontal black dashed lines.
5.3. Geomagnetic Storm
In this section, we investigate a geomagnetic storm by analyzing the VLF/LF subionospheric propagation data with NFM (see Section 4). In Figure 17, we present in four panels the following geomagnetic indices, each one of them available in a different sampling period: Dst (1 h), Kp (3 h), ap (3 h), and Ap (1 day), for the time period from 20 October 2021 to 19 November 2021. As is clear from Figure 17, the minimum value of the Dst index, −105 nT, was observed on 4 November 2021, indicating an intense storm, while, on the same day, the three other geomagnetic indices also increased, exceeding the corresponding thresholds, e.g., max Kp = 8, indicating a “G4”, i.e., severe, event.
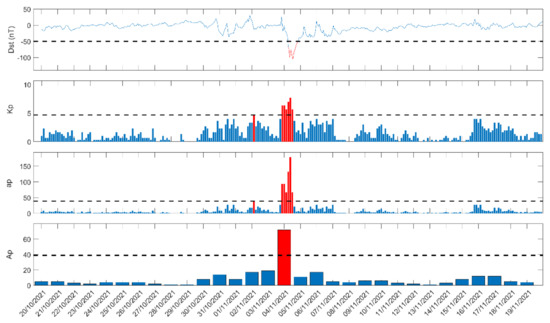
Figure 17.
Geomagnetic indices of Dst (value per 1 h), Kp (1 value per 3 h), ap (1 value per 3 h), Ap (1 value per day) are shown for the time period from 20 October 2021 to 19 November 2021. The horizontal dashed black line in each of the panels indicates the threshold for a moderate geomagnetic storm for each index. Red colored parts indicate values exceeding each threshold.
Tatsuta et al. [40] have reported the existence of lower ionospheric anomalies during geomagnetic storms on three statistical parameters of the NFM analysis method using nighttime VLF/LF data from long-distance high-latitude subionospheric propagation paths. Specifically, they reported that high-latitude subionospheric propagation paths are more sensitive to the impact of geomagnetic storms due to electron density enhancement in the D layer caused by high-energy auroral electron precipitation [40,70,71]. The result of this effect was a decrease in , which is related to a decrease in the nighttime amplitude, as well as an increase in and , associated with the fluctuation of the amplitude [40]. Thus, we expect that the effect of the abovementioned geomagnetic storm should be evident in at least one of the high-latitude-covering subionospheric propagation paths that is monitored by the proposed receiver.
In this direction, we used for the NFM analysis the nighttime amplitude data from 23:00 LT to 05:00 LT of the transmitter NRK, which is located in Grindavik (Iceland) (see Table 2), as recorded by the receiver GER. As usual, we removed from the signal all excerpts containing any type of artificial amplitude anomaly before applying the NFM. The subionospheric propagation path NRK-GER covers an area that extends from high latitudes to mid-latitudes, with directions from northwest to southeast.
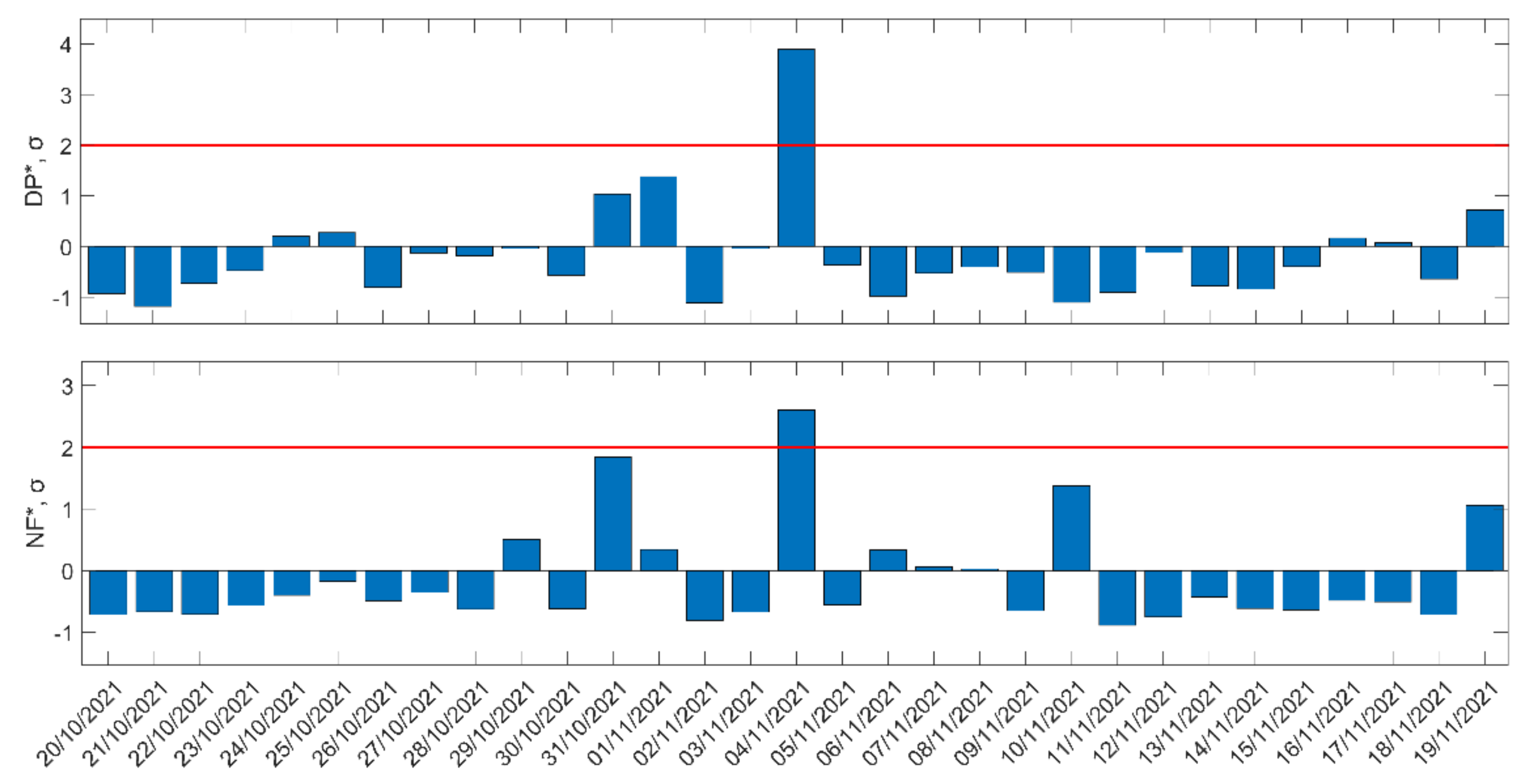
In Figure 18, we show the NFM analysis results for the time period from 20 October 2021 to 19 November 2021, similarly to Figure 17. As is evident from Figure 18, an anomaly on 4 November 2021 was observed in and , while did not show any anomaly. These anomalies exactly coincide with the geomagnetic storm on 4 November 2021. Finally, there was no other global or local disturbance on 4 November 2021, so it is considered that these anomalies were probably caused by the geomagnetic storm of 4 November 2021.
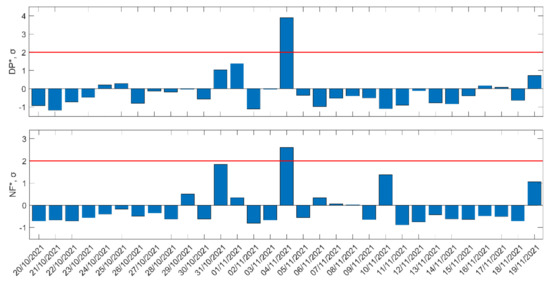
Figure 18.
Daily variations in the two statistical quantities, , , for the subionospheric path GER-ISR, for the time period from 20 October 2021 to 19 November 2021. Red solid horizontal lines indicate the corresponding +2σ/−2σ limits; σ is calculated for the whole studied period in each panel.
6. Conclusions
Although the ground-based monitoring of the lower ionosphere focusing on VLF/LF subionospheric propagation path perturbations is important in the research of a wide variety of geophysical and Sun/space extreme phenomena, the procurement/reproduction of appropriate VLF/LF receivers, especially wideband ones, is very difficult.
As a low-cost, open-source (HW/SW) solution, we presented a complete VLF/LF receiver setup, providing all the necessary information for one to build it. The key components of the specific receiver are popular among radio amateurs: the “mini-whip” active antenna, and “SpectrumLab” and “GPS2Time” freeware.
Two VLF/LF receivers of the suggested setup were installed in the prefecture of Attica in Greece, on June and September of 2021, respectively. These two receivers, the only difference in which is the soundcard used, monitor 16 different VLF/LF transmitters, recording almost identical signals for each one of them.
Examples of identified perturbations due to solar flares (down to C4.7 class), strong earthquakes (M > 5.5), and an intense geomagnetic storm (max Dst < −100 nT) are presented as evidence for the appropriateness of the proposed receiver setup for research focusing on global and local ionosphere-influencing phenomena. Specifically, three solar flares that happened on 28 October 2021—an M1.4 class at 7:40 UTC, an M2.2 class at 10:28 UTC, and an X1 class at 15:35 UTC—were successfully identified as sudden ionospheric disturbances (SIDs) in the received amplitude from multiple transmitters, while even an SID due to a C4.7 class solar flare that occurred on 9 April 2022, at 11:24 UTC, was also possible to be identified. Moreover, the perturbation due to an intense geomagnetic storm (minimum Dst = −105 nT) that occurred on 4 November 2021 was successfully identified, while the disturbances possibly related to three EQs (M5.8, 27 November 2021, depth = 10 km; M6.3, 12 October 2021, depth = 8 km; M6.1, 19 October 2021, depth = 58 km) that happened in the southeastern Mediterranean, as well as to other ionosphere-influencing phenomena during the specific time period, were carefully studied.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/foundations2030044/s1; Software configuration S1: Setup of “Spectrum Lab” and “GPS2Time” SW for the suggested VLF/LF receiver.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M.P., F.M. and D.D.; methodology, S.M.P.; software, F.M., D.Z.P., S.M.P. and D.D.; validation, D.D. and D.Z.P.; formal analysis, D.Z.P. and F.M.; investigation, F.M.; resources, S.M.P., F.M. and D.D.; writing—original draft preparation, F.M., D.Z.P. and S.M.P.; writing—review and editing, F.M., D.Z.P., S.M.P. and D.D.; visualization, F.M. and D.Z.P.; supervision, S.M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The VLF/LF data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. All other data are publicly available from the sources mentioned in the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Hellenic Telecommunications and Post Commission for hosting our receiver ACH at their fixed surveillance station at the “Aspra Chomata” location; the Institute of Geodynamics of the National Observatory of Athens for the seismic catalogs; the World Data Center for Geomagnetism of Kyoto for the geomagnetic indices Dst, Kp, ap, and Ap data; the USA National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration for the solar X-ray flux data; the Global Volcanism Program of the Smithsonian Institution for the volcano eruption data; the Ventusky search engine, the USA National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and the Deutscher Wetter-dienst (DWD) for the CAPE parameter data, as well as Blitzortung.org and lightningmaps.org for the lightning activity data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Alcay, S. Ionospheric response to extreme events and its effects on precise point positioning. Indian J. Phys. 2022, 79, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolarski, A.; Srećković, V.A.; Mijić, Z.R. Response of the Earth’s lower ionosphere to solar flares and lightning-induced electron precipitation events by analysis of VLF Signals: Similarities and differences. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lei, J.; Luan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhong, J.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Lin, L. Responses of the D region Ionosphere to solar flares revealed by MF radar measurements. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2019, 182, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Ni, B.B.; Gu, X.D.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Yang, G.B.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.N. First observations of low latitude whistlers using WHU ELF/VLF receiver system. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2016, 60, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Kundu, S.; Ghosh, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Yang, S.-S.; Hayakawa, M.; Chakraborty, S.K.; Chakrabarti, S.; Sasmal, S. Contaminated effect of geomagnetic storms on pre-seismic atmospheric and ionospheric anomalies during Imphal earthquake. Open J. Earthq. Res. 2020, 9, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krypiak-Gregorczyk, A. Ionosphere response to three extreme events occurring near Spring Equinox in 2012, 2013 and 2015, observed by regional GNSS-Tec Model. J. Geod. 2018, 93, 931–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisdom, J.B.; Yushau, S.M.; Muhammad, G.; Kangiwa, U.M.; Mustapha, A.; Olatunji, O.M. Monitoring of sudden ionospheric disturbance (SID) with 0–50 KHz frequency receiver over Aliero, Nigeria. Int. J. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2021, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, A.D.; Konstantinova, A.V. Detailed analysis of the behavior of the F2-layer critical frequency prior to geomagnetic storms. 3. dependence on the storm intensity. Heliogeophys. Res. 2021, 29, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, W.M.; Thomson, N.R. Solar flare induced ionospheric D-region enhancements from VLF phase and amplitude observations. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2004, 66, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.P. Ionospheric Effects of Solar Flares, 1st ed.; Reidel Publishing Company: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, A.V.; Yeh, H.-C. Geomagnetic signatures of sudden ionospheric disturbances during extreme solar radiation events. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2008, 70, 1971–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.F. Empirical models of Solar Flare X Ray and EUV emission for use in studying their E and F region effects. J. Geophys. Res. 1976, 81, 4745–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastovicka, J. Effects of geomagnetic storms in the lower Ionosphere, middle Atmosphere and Troposphere. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 1996, 58, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, A.D.; Lastovicka, J. Effects of geomagnetic storms on the Ionosphere and Atmosphere. Int. J. Geomagn. Aeron. 2001, 2, 209–224. [Google Scholar]
- Lastovicka, J. Solar wind and high energy particle effects in the middle atmosphere. In Handbook for MAP; International Council of Scientific Unions: Williamsburg, VA, USA, 1989; Volume 29, 119p. [Google Scholar]
- Kozyra, J.U.; Crowley, G.; Emery, B.A.; Fang, X.; Maris, G.; Mlynczak, M.G.; Niciejewski, R.J.; Palo, S.E.; Paxton, L.J.; Randall, C.E.; et al. Response of the upper/middle Atmosphere to coronal holes and powerful high-speed solar wind streams in 2003. In Recurrent Magnetic Storms: Corotating Solar Wind Streams; Geophysical Monograph; Tsurutani, B., McPherron, R., Gonzalez, W., Lu, G., Sobral, J., Gopalswamy, N., Eds.; AGU: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; Volume 167, 319p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenette, D.L.; Datlowe, D.W.; Robinson, R.M.; Schumaker, T.L.; Vondrak, R.R.; Winningham, J.D. Atmospheric energy input and ionization by energetic electrons during the geomagnetic storm of 8–9 November 1991. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1993, 20, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.T.; Raulin, J.P.; Bertoni, F.C.P.; Fagundes, P.R.; Chau, J.; Schuch, N.J.; Hayakawa, M.; Hobara, Y.; Terasawa, T.; Takahashi, T. First very low frequency detection of short repeated bursts from magnetar SGR J 1550-5418. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 721, L24–L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, U.S.; Carpenter, D.L.; Helliwell, R.A.; Katsufrakis, J.P. Subionospheric VLF/LF phase perturbations produced by lightning whistler induced particle precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 90, 7457–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, U.S.; Shafer, D.C.; Yip, W.Y.; Orville, R.E. Subionospheric VLF signatures of nighttime D-region perturbations in the vicinity of lightning discharges. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 11455–11472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobara, Y.; Iwasaki, N.; Hayashida, T.; Hayakawa, M.; Ohta, K.; Fukunishi, H. Interrelation between ELF transients and ionospheric disturbances in association with sprites and elves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulinets, S.A.; Boyarchuk, K. Ionospheric Precursors of Earthquakes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; 315p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Izutsu, J.; Schekotov, A.; Yang, S.-S.; Solovieva, M.; Budilova, E. Lithosphere–Atmosphere–Ionosphere coupling effects based on multiparameter precursor observations for February–March 2021 earthquakes (M~7) in the offshore of Tohoku area of Japan. Geoscience 2021, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, O.A.; Hayakawa, M. Seismo Electromagnetics and Related Phenomena: History and Latest Results; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 2008; 189p. [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin, V.V.; Chmyrev, V.; Hayakawa, M. Electrodynamic Coupling of Lithosphere-Atmosphere-Ionosphere of the Earth; NOVA Science Pub. Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015; 355p. [Google Scholar]
- Ouzounov, D.; Pulinets, S.; Hattori, K.; Taylor, P. Pre-Earthquake Processes: A Multidisciplinary Approach to Earthquake Prediction Studies; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2018; 365p. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, M.; Kasahara, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Muto, F.; Horie, T.; Maekawa, S.; Hobara, Y.; Rozhnoi, A.A.; Solovieva, M.; Molchanov, O.A. A statistical study on the correlation between lower ionospheric perturbations as seen by subionospheric VLF/LF propagation and earthquakes. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, A09305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhnoi, A.; Solovieva, M.; Molchanov, O.A.; Hayakawa, M. Middle latitude LF (40 kHz) phase variations associated with earthquakes for quiet and disturbed geomagnetic conditions. Phys. Chem. Earth 2004, 29, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhnoi, A.; Solovieva, M.; Hayakawa, M. VLF/LF signals method for searching for electromagnetic earthquake precursors. In Earthquake Prediction Studies: Seismo Electromagnetics; Hayakawa, M., Ed.; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 2013; pp. 31–48. [Google Scholar]
- Politis, D.Z.; Potirakis, S.M.; Contoyiannis, Y.F.; Biswas, S.; Sasmal, S.; Hayakawa, M. Statistical and criticality analysis of the lower Ionosphere prior to the 30 October 2020 Samos (Greece) earthquake (M6.9), based on VLF electromagnetic propagation data as recorded by a new VLF/LF receiver installed in Athens (Greece). Entropy 2021, 23, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, S.; Horie, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Sawaya, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Hayakawa, M.; Sasaki, H. A statistical study on the effect of earthquakes on the Ionosphere, as based on the subionospheric LF of propagation data in Japan. Ann. Geophys. 2006, 24, 2219–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M. VLF/LF radio sounding of ionospheric perturbations associated with earthquakes. Sensors 2007, 7, 1141–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Molchanov, O.A. Effect of earthquakes on lower Ionosphere as found by subionospheric VLF propagation. Adv. Space Res. 2000, 26, 1273–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, O.A.; Hayakawa, M.; Ondoh, T.; Kawai, E. Precursory effects in the subionospheric VLF signals for the Kobe earthquake. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1998, 105, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Chakrabarti, S.K.; Sasmal, S. Precursory effects in the nighttime VLF signal amplitude for the 18 January 2011 Pakistan earthquake. Indian J. Phys. 2012, 86, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Sasmal, S.; Basak, T.; Chakrabarti, S.K.; Samanta, A. Comparative study of the possible lower ionospheric anomalies in very low frequency (VLF) signal during Honshu, 2011 and Nepal, 2015 earthquakes. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 1596–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppelbaum, L.V. VLF-Method of Geophysical Prospecting: A non-conventional system of processing and interpretation (implementation in the Caucasian ore deposits). ANAS Trans. Earth Sci. 2021, 2, 16–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politis, D.; Potirakis, S.M.; Hayakawa, M. Criticality analysis of 3-year-long VLF subionospheric propagation data possibly related to significant earthquake events in Japan. Nat. Hazards 2020, 102, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M. Probing the Lower Ionospheric Perturbations Associated with Earthquakes by Means of Sub-Ionospheric VLF/LF propagation. Earthq. Sci. 2011, 24, 609–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsuta, K.; Hobara, Y.; Pal, S.; Balikhin, M. Sub-ionospheric VLF signal anomaly due to geomagnetic storms: A statistical study. Ann. Geophys. 2015, 33, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An Improved Gyrator Tuned VLF Receiver. Available online: https://www.aavso.org/improved-gyrator-tuned-vlf-receiver (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- VLF Receiver for SIDs. Available online: https://sites.google.com/site/radioastronomydm2/sids/vlf-receivers-for-sids (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- UKRAA Very Low Frequency (VLF) Receiver. Available online: https://www.ukraa.com/store/categories/vlf-range/vlf-receiver (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- Inspire VLF-3 Radio Receiver Kit. Available online: https://theinspireproject.org/default.asp?contentID=3 (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- EXPLORER E202. A Simple but Effective Portable Device for Natural Radio Signal Reception by Renato Romero. Available online: http://www.vlf.it/romero2/explorer-e202.html (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- Biagi, P.F.; Maggipinto, T.; Righetti, F.; Loiacono, D.; Schiavulli, L.; Ligonzo, T.; Ermini, A.; Moldovan, I.A.; Moldovan, A.S.; Buyuksarac, A.; et al. The European VLF/LF radio network to search for earthquake precursors: Setting up and natural/man-made disturbances. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeberis, C.; Zaharis, Z.; Xenos, T.; Spatalas, S.; Stratakis, D.; Maggipinto, T.; Colella, R.; Biagi, P.F. Evaluation of disturbances detected on a VLF/LF receiver inside the preparation zone of a sequence of earthquakes. In Proceedings of the 19th EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 23–28 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gheorghita, M.; Suciu, E.; Moldovan, A.; Moldovan, I. Testing a new installed VLF/LF radio receiver for seismic precursors’ monitoring in Romania. Rom. J. Phys. 2010, 55, 830–840. [Google Scholar]
- Suryadi; Abdullah, M.; Husain, H. Development of VLF receiver for remote sensing of low atmospheric activities. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Space Science and Communication, Port Dickson, Malaysia, 26–27 October 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raulin, J.P.; Correia de Matos David, P.; Hadano, R.; Saraiva, A.C.V.; Correia, E.; Kaufmann, P. The south America VLF NETwork (SAVNET): Development, installation status, first results. Geofis. Int. 2009, 48, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusnandar; Kusmadi; Najmurrokhman, A.; Sunubroto; Chairunnisa; Munir, A. Development of High Sensitivity Amplifier for VLF Receiver Application. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics (ICEEI), Denpasar, Indonesia, 10–11 August 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potirakis, S.M.; Asano, T.; Hayakawa, M. Criticality Analysis of the Lower Ionosphere Perturbations Prior to the 2016 Kumamoto (Japan) Earthquakes as Based on VLF Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Data Observed at Multiple Stations. Entropy 2018, 20, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanes, J.E.; Raulin, J.; Macotela, E.L.; Day, W.R.G. Estimating the VLF modal interference distance using the South America VLF Network (SAVNET). Radio Sci. 2015, 50, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.B.; Gross, N.C.; Higginson-Rollins, M.A.; Marshall, R.A.; Gołkowski, M.; Liles, W.; Rockway, R.J. The lower ionospheric VLF/LF response to the 2017 Great American Solar Eclipse observedacross the continent. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3348–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NaitAmor, S.; Ghalila, H.; Cohen, M.B. TLEs and early VLF events: Simulating the important impact of transmitter-disturbance-receiver geometry. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurses, B.V.; Whitmore, K.T.; Cohen, M.B. Ultra-sensitive broadband “AWESOME” electric field receiver for nanovolt low- frequency signals. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2021, 92, 024704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UltraMSK: A VLF Radio Receiver. Available online: https://www.ultramsk.com (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- SOFTPAL LF Receiver. Available online: http://www.lfsoftpal.com (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- DL4YHF’s Amateur Radio Software: Audio Spectrum Analyzer “Spectrum Lab”. Available online: https://www.qsl.net/dl4yhf/spectra1.html (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- Bakker, R. The pa0rdt-Mini-Whip. Available online: http://dl1dbc.net/SAQ/Mwhip/pa0rdt-Mini-Whip.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- De Boer, P.J. Fundamentals of the MiniWhip Antenna. Available online: http://www.pa3fwm.nl/technotes/tn07.html (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- De Boer, P.J. Capacitance of ANTENNA elements. Available online: http://www.pa3fwm.nl/technotes/tn08b.html (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- Bakker, R. The PA0RDT-Mini-Whip an Active Receiving Antenna for 10 kHz to 20 MHz. Available online: http://dl1dbc.net/SAQ/Mwhip/Article_pa0rdt-Mini-Whip_English.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- Meredith, N.P.; Horne, R.B.; Clilverd, M.A.; Ross, J.P. An investigation of VLF transmitter wave power in the inner radiation belt and slot region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 5246–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radio Frequencies & Transmitter Maps Worldwide. Available online: https://fmscan.org/index.php (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- Laštovička, J. Forcing of the Ionosphere by waves from below. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2006, 68, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhnoi, A.; Solovieva, M.; Levin, B.; Hayakawa, M.; Fedun, V. Meteorological effects in the lower ionosphere as based on VLF/LF Signal Observations. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 2671–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egoshin, A.A.; Ermak, V.M.; Zetzer, Y.I.; Kozlov, S.I.; Kudryavtsev, V.P.; Lyakhov, A.N.; Poklad, Y.V.; Yakimenko, E.N. Influence of meteorological and wave processes on the lower ionosphere during solar minimum conditions according to the data on Midlatitude VLF-LF propagation. Izv. Phys. Solid Earth 2012, 48, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salut, M.M.; Abdullah, M.; Graf, K.L.; Cohen, M.B.; Cotts, B.R.; Kumar, S. Long recovery VLF perturbations associated with lightning discharges. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, A08311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummer, S.A.; Bell, T.F.; Inan, U.S.; Zanetti, L.J. VLF remote sensing of the auroral electrojet. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 5381–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummer, S.A.; Bell, T.F.; Inan, U.S. VLF remote sensing of high-energy auroral particle precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 7477–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).