Definition
COVID-19 mRNA vaccines contain synthetic mRNA sequences encoded for the Spike proteins expressed on the surface of SARS-CoV-2, and utilize the host cells to produce specific antigens that stimulate both humoral and cellular immunities. Lipid nanoparticles are essential to facilitate the intracellular delivery of the mRNA to its action site, the ribosome, to fully exert its effect.
1. Introduction
In December 2019, a new contagious disease, later known as the coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), was first reported [1]. Since then, COVID-19 has rapidly spread across the globe, causing devastating medical, social, and economic consequences. In March 2020, the World Health Organisation (WHO) declared it a pandemic. There was a strong consensus that reliable vaccines are the most promising strategy to control the pandemic. Within a year after the disease outbreak, two messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) based vaccines became the first two vaccines to gain Emergency Use Authorisation (EUA) from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), bringing hope to billions of people on the planet. Two mRNA vaccines, BNT162b2 (Comirnaty®) and mRNA-1273, developed by Pifzer/BioNTech and Moderna, respectively, set the milestone in scientific history as the first-ever approved mRNA vaccines and opened a new era of mRNA-based approaches to prevent various diseases [2,3,4]. Never before have vaccines been developed and distributed in such a short period of time. A few more mRNA-based vaccines have reached various clinical stages of development (Table 1).

Table 1.
Examples of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 at various stages of development (updated on 4 August 2021).
The lightning-fast success of these mRNA vaccines are not only built on the extensive research in mRNA therapeutic application during the last decades, but also the major technical innovations in nanotechnology for intracellular delivery and advances in nanomedicine production. In this entry, we will first introduce the principles of the mRNA vaccines against COVID-19, followed by a detailed discussion on the roles of nanoparticles, in particular lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), in assisting the transportation of mRNA into the acting site of host cells to exert its effects. The manufacturing and storage requirements of these are also briefly outlined.
2. Mechanism of Action for COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines
Messenger RNA, first discovered by Brenner et al. in 1961 [6], is a single-stranded large molecule that makes a complimentary copy of one of the two DNA strands, and instructs the corresponding protein production in the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. In 1990, scientists at the University of Wisconsin demonstrated that injection of mRNA into mouse skeletal muscle resulted in persistent expression of encoded proteins, providing the first proof of the feasibility of mRNA vaccine [7]. Since then, mRNA vaccines have been researched substantially to tackle infectious disease and different types of cancer, with some reaching clinical trials [7]. The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic has undoubtedly sped up the approval of mRNA vaccines in human use [8].
An mRNA vaccine contains a synthetic mRNA sequence that encodes for a disease specific protein (antigen). In a SARS-CoV-2 RNA genome, there are four major viral proteins that are encoded, including the Spike, Envelope, Membrane, and Nucleocapsid proteins [8]. Among them, the Spike (S) protein attracts strong interest in vaccine development, since it is crucial for the virus to gain entry into the host cells [9]. The S protein exists as a precursor and is cleaved into two subunits, S1 and S2. The S1 subunit first binds to the host cell receptor, angiotensin converting enzyme II (ACE2) on the targeted lung cells, then sheds off, resulting in an irreversible conformational change of the S2 subunit. This structural change causes fusion of viral and cellular membranes and viral entry into the host cells, and ultimately initiates infection [9]. Both BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 contain modified mRNA encoded for the full-length S protein with two proline substitutions (K986P and V987P) to stabilise the protein in the pre-fusion conformation [8].
Both COVID-19 mRNA vaccines are administered via intramuscular injection, where they trigger a transient localized inflammatory response, and recruit different immune cells, primarily monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells to the injection site via the extensive network of blood vessels [8,10]. The mRNA molecules are taken up by those recruited immune cells and utilise the ribosomes of host cells to produce S proteins. The locally transfected antigen-presenting-cells (APCs), then migrate to the draining lymph nodes and present S antigen to the B cells and T cells. Once the S antigen is recognised and internalised by B cells, it activates B cells responses and generates a neutralizing antibody. Meanwhile, different T cells are generated via different pathways [11]. After post-translational modification in the host cells, the generated S protein can be degraded in the cytoplasm into fragments, which form a complex with major histocompatibility complex class-1 molecules (MHC class 1). This complex is transported to the cell surface, and eventually enables the induction of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells (cytotoxic T cells). Alternatively, the generated S protein can be released from the host cells, and taken up by other APCs, where they are degraded in the endosomes and the fragments are loaded onto MHC class 2 molecules. The complex is then presented on the cell surface, and leads to production of antigen-specific CD4+ helper T cells, which help B cells in making antigen specific antibodies [11]. Although the B cells promoted antibody production is the primary mechanism against SARS-CoV-2, coordination of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells with the antibody response contribute significantly to enhance the protection [8].
There are two types of mRNA vaccines, non-amplifying (either conventional or base modified) or self-amplifying mRNA vaccines [12]. While non-amplifying mRNA vaccines, such as BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 [8], only encode for the antigen that induces immune response, self-amplifying mRNA vaccines encodes for additional regions that allow them to self-replicate before protein production. Since the level of antigen expression is directly proportional to the number of mRNA delivered, non-amplifying COVID-19 mRNA vaccines require repeated administration to achieve an adequate immune response.
Compared with the conventional live attenuated, inactivated, or subunit vaccines, mRNA vaccines do not contain any infectious agents, thus are safer to administer even in an immunocompromised population [7]. Compared with DNA vaccines, mRNA vaccines do not integrate into host cell DNA, therefore, they have no potential to cause insertion-induced mutagenesis [13]. Instead, mRNA only transiently exists in the cell, and is degraded by natural cellular processes.
3. Efficacy and Safety of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines
A total of 43,548 volunteers participated in the multinational, placebo-controlled, observer-blinded trial to study the efficacy and safety of BNT162b2 during 2020 [14]. Two doses of the vaccine (30 µg each) given 21 days apart showed an astonishing 95% efficacy at least seven days after the second dose, with similar efficacy across different age, gender, race, ethnicity, baseline body-mass index, and comorbidity groups. Similarly, a phase 3 randomized, observer-blinded, placebo-controlled trial of 30,420 participants showed that mRNA-1273 given as two doses (100 µg each), 28 days apart resulted in a 94.1% efficacy at least 14 days after the second injection [15].
The reported safety profiles of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 were reassuring [14,15]. In general, more participants in the vaccine group reported adverse effects than the placebo group who received saline; however, the incidence of severe adverse effects were similar. The mostly reported local adverse reaction was mild-to-moderate pain at the injection site, which usually resolved within one to two days. The most commonly reported systematic adverse reactions were fatigue and headache [14,15]. Cases of severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) were reported during the roll out of both mRNA vaccines [16]. Although very rare, the consequences of anaphylaxis reactions can be fatal and cause considerable fear and hesitation in the general population. Of note, the active ingredient mRNA does not cause any allergic reactions; rather, it is likely the inactive ingredients in the formulation that stimulate an unwanted immune response [16]. BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 contain polyethylene glycol (PEG) that has been considered to induce anti-PEG antibodies. However, the link between the PEG and anaphylactic reactions to COVID-19 mRNA vaccines is yet to be established with scientific evidence [17]. Nevertheless, currently, the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advises all individuals with known severe allergic reaction to any of the components in the mRNA vaccines to avoid having the vaccines; and all other individuals should be monitored for 15 or 30 min after administration depending on the individuals previous allergic reaction to any vaccine or injectable therapy [16].
4. Mechanisms for Nanoparticle-Mediated Intracellular Delivery
4.1. The Need of Innovative Approach for Intracellular Delivery of mRNA
Despite their potential benefits, the initial development of mRNA vaccines did not attract much interest due to their intrinsic instability and the inefficient delivery into the host cells [5]. As mRNA has a large molecular size, an overall negative charge and water-loving nature, it struggles to cross the negatively charged lipid-loving cell membrane by diffusion [5]. In addition, as a self-defence mechanism, external mRNA is regarded as foreign materials by the host and is cleaved by ribonucleases (RNases) into small nucleotide units. The widely distributed RNase degrades the ‘naked’ mRNA outside the targeted cells and prevents it from entering into the cells. Therefore, only a small amount of mRNA is internalised via the caveolae/lipid raft-rich subdomain on the cell membrane, and subsequently accumulated in the lysosomes [18] where the majority of mRNA gets degraded. It was more recent innovations in nanotechnology for intracellular delivery that address those formidable obstacles [5] (Figure 1).
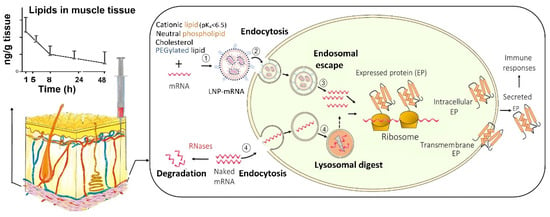
Figure 1.
Uptake of mRNA-loaded lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) following intramuscular injection versus naked mRNA into the host cells and the subsequent intracellular trafficking. (1) mRNA is incorporated into LNP, which is assembled from cationic, neutral, and PEGylated lipids as well as cholesterol; (2) mRNA-loaded LNPs are internalised into the host cell; and (3) within the cell, mRNA-loaded LNPs undergo endosome escape, and release mRNA for protein synthesis. In contrast, (4) naked mRNA can be partially internalised, but the majority is degraded in lysosomes. In addition, the extracellular mRNA is cleaved by the ribonucleases (RNases) while LNPs at the injection site protect of mRNA from RNases. LNPs provide extended local tissue exposure and the pharmacokinetic profile depends on various factors such as the lipids used and particle size.
Nanoparticles are nanoscale (1–1000 nm) vesicles that have been explored as non-viral vectors for the intracellular delivery of mRNA while protecting exogenous mRNA from RNase destruction [19]. Compared with viral vectors, non-viral vectors have the advantages of less immunogenicity, easier production, and higher efficiency to carry the mRNA [20]. Versatile nano-platforms have been investigated to deliver mRNA in the body, including LNPs, polymer-based nanoparticles, polymer-lipid hybrid nanoparticles, poly-peptides, protein derivatives mRNA complexes, and gold nanoparticles [16,19]. Among these vectors, LNPs are the most commonly used due to the relative ease of large scaled manufacture, their ability to deliver the encapsulated mRNA to ribosomes (via endosome escape), and flexibility for surface modification with a ligand for specific cell targeting, for example to enhance the uptake into dendritic cells [5,18]. LNPs are versatile drug delivery systems that have been investigated to tackle various disease, including infection and cancer [21]. As LNPs consist of at least one synthetic or natural lipid layer and an aqueous, oil, solid, or amorphous core [22], hydrophilic molecules, such as mRNA, small interference RNA (siRNA) and proteins can be entrapped within the LNP aqueous core, whereas lipophilic compounds can be incorporated into the lipid layers [18]. Thus, LNPs can be co-loaded with an immunopotentiator, also known as adjuvants, to enhance the immune response of the mRNA vaccine. The choice of LNPs for mRNA vaccine delivery has shifted from traditional liposomes, lipoplexes, and cationic nanoemulsions, to more advanced solid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers [20]. LNPs were employed not only by BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273, but also by other mRNA vaccines in the development of delivery carriers, which are listed in Table 1.
4.2. Formulation Compositions of Covid-19 mRNA Vaccines
The lipids in LNPs to ferry the mRNA are usually made of four typical components (Figure 1): an ionisable cationic lipid, a PEGylated lipid, a neutral phospholipid, and cholesterol. Table 2 lists the lipid components employed in BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273, and each of these different lipids serves distinct functions:

Table 2.
Lipid composition of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 [3,4,24].
(1) The ionisable cationic lipids show neutral or mild cationic charges at physiological pH, and become protonated (cationic) at low pH, therefore, an acid dissociation constant, or pKa around 6.5 is ideal. At acidic environment, these lipids are able to encapsulate the negatively charged mRNA through electrostatic interactions during LNPs formation; and in the physiological environment, it becomes neutral, preventing the rapid removal of the LNPs from the circulation, and reduces toxicity. The ionisable lipid was reported to be the primary driver of immunogenicity, pharmacokinetics of the LNPs, and tissue tolerability [23]. Increased biodegradability of the ionisable lipids leads to faster elimination of lipids in muscle, spleen, and liver without necessarily compromising the immune responses as little correlation between the protein expression and immunogenicity. In addition, more biodegradable ionisable lipids are removed from the injection site faster, thus less tissue irritancy [23]. Furthermore, depending on the lipid structure, some positively charged lipid can serve as a vaccine adjuvant and stimulate the innate immune response [20]. The ionisable lipids used in BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 are (4-hydroxybutyl)azanediyl)bis(hexane-6,1-diyl)bis(2-hexyldecanoate) (ALC-0315), and SM-102, respectively. The N:P molar ratio, defined as nitrogen (N) in the ionizable cationic lipid: phosphate (P) of the nucleotide, is approximately 6 for both vaccines [8,24].
(2) A PEGylated lipid consists of a hydrophilic polymer PEG conjugated to a lipid. In LNPs, the PEG chains anchored on the surface sterically stabilise the LNPs from aggregation, and prevent non-specific binding with proteins (opsonins) and removal by the reticuloendothelial system in the body [5]. However, the PEG layers could also inhibit the uptake by the targeted cells as well as interaction with the endosomal membrane, therefore, the PEG density on the LNP must be carefully tailored and are generally lower than 2% (mol) and the PEG chain length is limited to 2000.
(3) Neutral lipids are responsible for forming the backbone of the lipid layer and maintain the LNP structure. 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DSPC) was used in both of the currently approved COVID-19 mRNA vaccines. It is a saturated lipid with a high melting point, therefore, is able to produce a stable LNPs [20].
(4) Cholesterol in the LNP formulation acts as a stabilising agent of the particles as well as limiting non-specific LNP-protein interactions [20].
4.3. How Does LNPs Assist mRNA Delivery into the Ribosomes Inside Cells
Following intramuscular injection, LNPs provide extended local tissue exposure at the injection site [18]. A typical pharmacokinetic profile is shown in Figure 1. The pharmacokinetics of LNP vaccines depend on their particle size, surface charge, and colloidal stability of LNPs as well as the biodegradability of the ionisable cationic lipid [23]. These factors in turn determine cellular uptake and lymphatic trafficking as well as the exposure to liver and spleen [18]. LNPs smaller than 150 nm could be drained via afferent lymphatic vessels while larger LNPs are readily phagocytosed by immune cells and then trafficked to the lymph nodes. However, complexity associated with identifying the best formulation parameters as lymphatic drainage and transfection potency are not the only parameters determining the immune response.
LNPs have two major roles in mRNA delivery; mediating the uptake of mRNA into the targeted host cell and promoting the release of mRNA from endosome into the cytoplasm, thus improve the bioavailability of mRNA to ribosomes where mRNA produces proteins (antigen) (Figure 1). In addition, LNPs encapsulate the mRNA within the core, thus protecting the mRNA from being degraded by the extracellular RNases [10].
LNPs facilitate the cellular uptake of the mRNA via various endocytosis routes, for example, clathrin- and caveolae-mediated endocytosis [5,22]. The efficiency of the internalization largely depends on the selection of lipids, degree of PEGylation, particle size, and surface charge of the nanoparticles. After endocytosis, LNPs are first entrapped inside the endosomes. The ionisable cationic lipids play a crucial role in promoting the endosomal escape of mRNA. Within the acidic environment of the endosome (pH < ~6.5) the ionisable lipids become protonated. Those positively charged lipids form ion pairs with the negatively charged phospholipids in the endosome membrane, disrupt the bilayer structure and result in endosomal escape [18]. In addition, inclusion of cholesterol in the LNP structure may contribute to the fusion of the LNPs with the endosome, and promotes the release of mRNA into the cytoplasm [20]. However, the current LNPs generally have a low degree of endosome escape (<2%), and the exact mechanisms remain unclear [5]. Therefore, more research is required for further improvement.
5. Manufacturing and Stability
5.1. Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines at large scale consists of three major steps. These steps include the purification of viral DNA, transcription of the DNA into mRNA, and assembly of the mRNA vaccines. Once the mRNA molecules are purified and subjected to rigorous testing, they were incorporated into the LNPs via a modified ethanol injection nanoprecipitation method [5,25]. Briefly, all oily lipid components were mixed with ethanol; and mRNA was mixed with water. The lipids and mRNA solutions were mixed in acidic buffer (pH 4–5) through a set of pumps with a highly controlled flow rate at each phase. Due to the low pH in the mixture, the lipids were positively charged, and easily came into contact with the negative charged mRNA strands via electric attraction. The lipids readily encapsulate mRNAs into the vesicles with high encapsulation efficiencies. The newly formed vaccine mixture were then neutralised to physiological pH value, filtered to remove ethanol and other impurities, and finally sterilised and frozen to be shipped across the globe [25].
5.2. Stability and Storage
As nucleic acids, all mRNA are intrinsically prone to degradation via a number of reactions, for example hydrolysis of N-glycosidic bonds (depurination) or phospho-diester bonds, oxidation of nucleobases or sugar moieties [26]. Even a small change in the structure could alter its translation performance. Both Pfizer/Biotech and Moderna’s vaccines have stringent storage requirements (Table 3) and need to be thawed before administration.

Table 3.
Stability and storage requirement of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 vaccines [3,4].
6. Conclusions
The COVID-19 pandemic has ravaged the world, leaving scientists with no choice but to accelerate the development of potent and cost-effective vaccines. This milestone achievement with BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 has opened up an exciting new era for mRNA vaccines to control communicable diseases. This would have not been possible without the break-through innovations in the nanoparticle mediated drug delivery. Nanoparticles, in particular lipid nanoparticles, help guard the mRNA to circumvent the major obstacles in cellular uptake and intracellular trafficking, and to allow the vaccines to fully elicit its immune responses.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, Y.G.; supervision, Z.W. and A.N.S.; writing—review and editing, Z.W., A.N.S. and K.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Entry Link on the Encyclopedia Platform
Abbreviations
| ACE2 | Angiotensin converting enzyme II |
| APCs | Antigen presenting cells |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease-2019 |
| DSPC | 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
| EUA | Emergency Use Authorisation |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| LNPs | Lipid nanoparticles |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| mRNA | Messenger ribonucleic acid |
| PEG | Poly(ethylene glycol) |
| RNases | Ribonucleases |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| WHO | World Health Organisation |
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, Y.N. BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine: First approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration. FDA Briefing Document: Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/144434/download (accessed on 3 May 2021).
- European Medicines Agency. Comirnaty: EPAR-Product Information. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/comirnaty-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2021).
- Wu, Z.; Li, T. Nanoparticle-mediated cytoplasmic delivery of messenger RNA vaccines: Challenges and future perspectives. Pharm. Res. 2021, 38, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, S.; Jacob, F.; Meselson, M. An unstable intermediate carrying information from genes to ribosomes for protein synthesis. Nature 1961, 190, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. mRNA vaccines-a new era in vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, R.; Lentacker, I.; De Smedt, S.C.; Dewitte, H. The dawn of mRNA vaccines: The COVID-19 case. J. Control. Release 2021, 333, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, T.; Peng, H.; Sterling, S..; Walsh, R., Jr.; Rawson, S.; Rits-Volloch, S.; Chen, B. Distinct conformational states of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Science 2020, 369, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Zhang, C.; Walker, P.G.; Dong, Y. Formulation and delivery technologies for mRNA vaccines. In Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wadhwa, A.; Aljabbari, A.; Lokras, A.; Foged, C.; Thakur, A. Opportunities and challenges in the delivery of mRNA-based vaccines. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakney, A.K.; Ip, S.; Geall, A.J. An update on self-amplifying mRNA vaccine development. Vaccines 2021, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzler, M.A.; Weiner, D.B. DNA vaccines: Ready for prime time? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.; Thomas, S.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerji, A.; Wickner, P.G.; Saff, R.; Stone, C.A.; Robinson, L.B.; Long, A.A.; Wolfson, A.R.; Williams, P.; Khan, D.A.; Phillips, E.; et al. mRNA vaccines to prevent COVID-19 disease and reported allergic reactions: Current evidence and suggested approach. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhawt, M.; Abrams, E.M.; Oppenheimer, J.; Leek, T.K.V.; Mack, D.P.; Singer, A.G.; Shaker, M. The COVID-19 pandemic in 2021: Avoiding overdiagnosis of anaphylaxis risk while safely vaccinating the world. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichumuth, A.M.; Oberli, M.; Jaklenec, A.; Langer, R.B.D. mRNA vaccine delivery using lipid nanoparticles. Ther. Deliv. 2016, 7, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, C.; Fotin-Mleczek, M.; Roth, G.; Becker, C.; Dam, T.C.; Verdurmen, W.P.R.; Brock, R.; Probst, J.; Schlake, T. Protein expression from exogenous mRNA: Uptake by receptor-mediated endocytosis and trafficking via the lysosomal pathway. RNA Biol. 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldosari, B.N.; Alfagih, I.M.; Almurshedi, A.S.; Hinrichs, J. Lipid nanoparticles as delivery systems for RNA-based vaccines. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Y. Nanoscale platforms for messenger RNA delivery. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 11, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, K.J.; Benenato, K.E.; Jacquinet, E.; Lee, A.; Woods, A.; Yuzhakov, O.; Himansu, S.; Deterling, J.; Geilich, B.M.; Ketova, T.; et al. Optimization of lipid nanoparticles for intramuscular administration of mRNA vaccines. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenmaker, L.; Witzigmann, D.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Verbeke, R.; Kersten, G.; Jiskoot, W.; Crommelin, D.J.A. mRNA-lipid nanoparticle COVID-19 vaccines: Structure and stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, K.S.; Edwards, D.K.; Leist, S.R.; Abiona, O.M.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Gillespie, R.A.; Himansu, S.; Schäfer, A.; Ziwawo, C.T.; DiPiazza, A.T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine design enabled by prototype pathogen preparedness. Nature 2020, 586, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crommelin, D.J.A.; Anchordoquy, T.J.; Volkin, D.B.; Jiskoot, W.; Mastrobattista, E. Addressing the cold reality of mRNA vaccine stability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).