Abstract
This study examines the preparation of several composites that are based on natural magnesium hydroxide (n-MDH) and various poly(ethylene-co-octene) polyolefin elastomers (POEs). Design of experiment (DoE) principles have been applied in order to optimize the mechanical, rheological, and flame-retardant properties of the final composites. DoE allows one to evaluate the influence of each variable on an experiment’s final properties. By increasing the density and crystallinity of the POE, a higher elastic modulus was obtained, which resulted in greater tensile strength and lower elongation at break. Improved flame retardant properties (as measured by the limiting oxygen index (LOI) and vertical burning tests) were obtained by increasing the amount of filler within the composite up to 65% and using a polymer with high crystallinity. More specifically, the best balance between mechanical, rheological, and flame retardant properties was provided by DoE using 63.75% n-MDH filler. The agreement between the predicted performance and the final properties of the composites has enabled the innovative use of DoE to provide reliable predictions about the final mechanical and flame retardant properties of the compounds that are used for low voltage electrical cable applications.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the use of halogen-free flame retardant (HFFR) compounds has attracted significant and increasing interest since they do not produce heavy smokes during combustion, thus reducing their toxicity and corrosion issues. In cable applications, HFFR polymer compounds are mainly based on ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) copolymers [1] and ethylene-octene or ethylene-butene copolymers, which are produced by metallocene catalysis, named ULDPE or more generally POE [2]. Both of these polymeric families are highly flexible, having low crystallinity, a melting point between 60 °C and 100 °C, and a broad array of molecular weights [3]. POEs are used in various industries, such as transport, building, textiles, electronics, and wires and cables [4].
POEs are compatible with most olefinic materials and are available in a wide range of grades to meet the most demanding processing and performance needs [5,6]. Notably, the low crystallinity and long chain branching content of certain POEs endow the polymers with the ability to withstand a large percentage of filler (as much as over 70% by weight), which is mandatory in order to achieve highly flame-retardant properties. Many strategies have been applied in order to improve polyolefin flame-retardancy by introducing specific additives that could intervene in the combustion mechanism, thus reducing both the fire risks and the fire hazards.
The most important commercial flame-retardants are metal hydroxides due to their combination of low cost, low smoke, and flame-retardancy. Inorganic hydroxide fillers have replaced the halogen-based fire retardants (FR) in many applications; the main FR agents that are used in polyolefin compounds for cables are aluminum hydroxide (ATH) and magnesium hydroxide (MDH) [7,8]. Notably, metal hydroxides (e.g., Al(OH)3 and Mg(OH)2) have many advantages, including their being halogen-free, environmentally friendly, and containing no corrosive or toxic decomposition products which prevents the emission of toxic fumes and their adverse general effects [9]. During the endothermal decomposition that is caused by the burning reaction, the metal hydroxides release water in the gas phase, thus diluting the oxygen in the flame area and cooling down the pyrolysis zone. They also form protective metal oxide layers on the polymer’s burning surface after the water-release, which decreases the heat feedback of the pyrolyzing polymer. However, the well-documented drawback of metal hydroxides is the high loading levels that are required for adequate flame-retardancy (up to 65–70% in weight), which often leads to processing difficulties and deterioration of the compound’s mechanical properties. Among metal hydroxides, magnesium hydroxide (MDH) shows a wider variety of applications, resulting in it being more versatile as a filler for linear low-density polyethylene and isotactic polypropylene matrices that need processing temperatures higher than 200 °C [10,11]. MDH is a crystalline powder that is obtained by a chemical process (in the case of synthetic MDH), by precipitation from seawater (in the case of seawater MDH), or by grinding naturally occurring brucite (in the case of natural MDH). Compared to ATH, all of the types of MDH offer several advantages, including higher decomposition temperature, reduced smoke levels, and reduced acidity of the smoke. Most of these traits come from the high surface and high basic reactivity MgO that is generated by the thermal decomposition of Mg(OH)2. Synthetic magnesium hydroxide is the most expensive mineral flame-retardant filler. It is available with different granulometry (d50 = 0.7–3.5 μm) and with a surface area of between 3–12 m2/g. It is used in very high-demand applications and in all polyolefins where the production can reach a very high temperature, such as 250 °C [12]. Natural magnesium hydroxide has been also used by researchers as a flame-retardant filler in polymeric materials with very promising results [13].
The present research aims to identify a final filler–polymer formulation by using a statistical approach to produce flame-retardant electrical cables with the best compromise between mechanical, rheological and flame-retardant properties. The relationships between the molecular characteristics of the raw materials and the final properties of the formulations were investigated with a focus on the effects that were provided by the polymer’s characteristics, such as the molecular weight, density and comonomer content. Five polymers were selected from among the commercially available poly(ethylene-co-octene) (POE) material that is supplied by Dow Chemical under the trade name ENGAGETM and characterized by different 1-octene comonomer contents, densities, and melt flow indexes (MFIs). Uncoated micronized brucite, a natural magnesium hydroxide (n-MDH), which was supplied by Europiren B.V, was selected for its excellent performance and for its natural origin. Moreover, MDH is non-toxic, environmentally friendly, and widely available [14].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The poly(ethylene-co-octene) polymers were supplied by Dow Chemical (Dow Europe GmbH, Horgen, Switzerland): ENGAGETM 8003 (d = 0.885 g/cm3 MFI 1 g/10 min 2.16kg @ 190 °C), ENGAGETM 8450 (d = 0.902 g/cm3 MFI 3 g/10 min 2.16kg@ 190 °C), ENGAGETM 8100 (d = 0.870 g/cm3, MFI 1 g/10 min 2.16kg @ 190 °C), ENGAGETM 8200 (d = 0.870 g/cm3, MFI 5 g/10 min 2.16 kg @ 190 °C), and ENGAGETM 8480 (d = 0.902 g/ cm3, MFI 1 g/10 min 2.16 kg @ 190 °C).
Micronized brucite Ecopiren 3.5 (hereinafter referred to as natural MDH or n-MDH) was supplied by Europiren (Rotterdam Science Tower, the Netherlands) at 92% purity, d50 (average particle size) = 3.5–4 μm, and a surface area of 11 m2/g.
The maleic anhydride modified ethylene copolymer (grafting degree 0.7–1.1 wt.%) [15] that was used as a maleated compatibilizer, FUSABOND N525TM (d = 0.880 g/cm3 MFI 3.7 g/10 min 2.16kg @ 190 °C), was supplied by Dow Chemical (Dow Europe GmbH, Horgen, Switzerland).
2.2. Preparation of Composite
To begin, 300 g of compound containing the 3 wt.% of the maleated compatibilizer and the required amount of n-MDH and POE were prepared in a twin-roll mixer at 140 °C for 10 min and then removed in the form of a sheet of around 1.4 mm thickness (Figure 1).
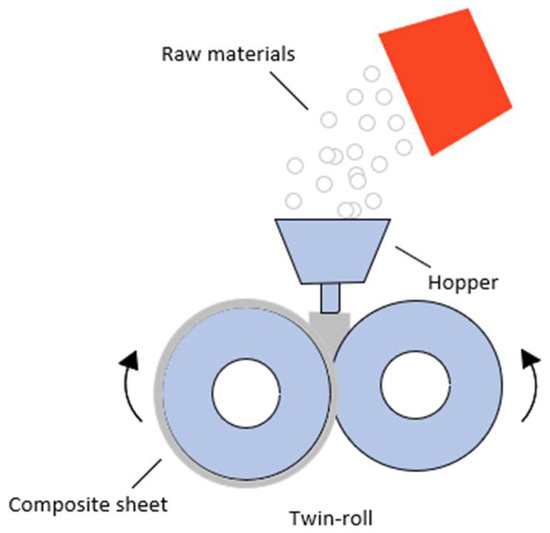
Figure 1.
Schematization of twin-roll mixer and preparation of composite.
Formulations that are frequently used in the cable industry were selected and investigated (Table 1) by varying the molecular characteristics of their polymer matrices (ethylene α-olefin copolymer) and their amounts of mineral filler.

Table 1.
Basic formulation of the composites.
Notably, the maleic anhydride modified ethylene copolymer has the function of reducing interphase tension with the n-MDH fillers in order to improve the performance properties of the polymer composite [16].
Stabilizer-protecting polyolefins usually contain a hindered phenolic primary antioxidant which significantly improves the thermo-oxidative stability of the polymer’s melting [17].
2.3. Characterization
The specimens for the MFI, density and mechanical tests were cut directly from the sheets. The mechanical properties were tested the day after compounding. The specimens for the LOI and vertical burning tests were prepared by hot pressing the prepared sheets following the compound orientation. For the LOI and the vertical burning tests, the thicknesses of the specimens were 3 and 1.5 mm, respectively.
The tensile properties were measured by using a Lloyd Instruments LS 500 dynamometer at a crosshead speed of 250 mm/min at room temperature. The width and thickness of the tensile test specimens were 3.0 mm and 2.0 mm ± 0.2 mm, respectively, and the stretched length was 20 mm ± 0.5 mm (according to the standard ISO 37 type 2).
The differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) (as measured by a Perkin Elmer Pyris 6 DSC) was performed on samples weighing from 10–20 mg. The values of the melting temperatures were recorded by the second heating curve of the DSC thermogram. The crystallization temperature was taken from the cooling curve of the DSC thermogram.
CAT (Chemometric Agile Tool, Gruppo di Chemiometria) was the software that was used for the data analysis of the DoE (design of experiment) [18,19].
The fire tests that were used for all of the investigated formulations were the limiting oxygen index (LOI) and vertical burning tests [14] For the determination of the limiting oxygen index, a burner flame was applied to the top of a vertically oriented bar, which was in a test column with a mixture of oxygen and nitrogen flowing. The LOI value represents the minimum concentration of oxygen (%) in the gas mixture that is necessary to support the combustion of the material that was initially held at room temperature. The initial concentration of oxygen was chosen arbitrarily. The specimens that were used were cut to dimensions of 100 × 6 × 3 mm, according to the standard ASTM D2863.
The vertical burning test was carried out on samples with dimension of 190 × 100 × 1.5 mm, with a graduation line marked at 150 mm [20]. Each specimen was fixed in a specimen holder and a Bunsen burner’s flame was applied at the bottom of the sample. The time that was necessary for the top of the flame to reach the graduation line was recorded (t1). This could be considered as a burning time measurement, which also considers the height (intensity) of the flame. Higher t1 values (up to the limit of self-extinguishing) indicated a lower burning rate and a lower height of the flame. A specially modified set up of this test was used for the determination of the characteristic burning time parameters and for the evaluation of the physical stability of the materials during combustion. The sufficiently large dimensions of the sample and the presence of the mask prevented the specimen from moving during the combustion process, leading to a clear identification of the stability of the material and its tendency to drip. The flame’s dimensions were determined by use of image analysis. The horizontal flame spread at the graduation line was determined by use of residue analysis.
2.4. Design of Experiment (DoE)
Design of experiment (DoE) is a suitable method that is used for studying the behavior of a system and it has been successfully introduced into industrial systems and research. DoE has built its principles from statistical and mathematical methods and it involves planning and performing a set of experiments in order to determine the effects of the input variables on the output responses. Experimental design is thus useful in the processes of designing new industrial products, finding the optimum values of a system, and predicting and characterizing the behavioral model of a system [21].
Within this study, DoE principles were applied to a variety of POEs that were combined with an n-MDH composite in order to find a method for evaluating the performances of the different formulations.
The density (d), melt flow index (MFI), and amount of filler in the formulation (filler) were selected as the independent variables of the model. The variation ranges of these factors were: density (x1) between 0.870–0.902 g/cm3, MFI (x2) between 1–5 g/10 min, and an amount of filler (x3) between 60–65%. The range of the variables that were selected complies with the characteristics that are required for the cable industry. The selected ternary system was studied through the application of DoE. CAT (Chemometric Agile Tool) is the software that was used to elaborate the data. The generic equation representing the correlation between the independent variables (x1, x2, x3) and the response (Y) is reported in Equation (1):
where β0, βi, βij and βii are the regression coefficients for the intercept, linear, interaction terms, and quadratic, respectively, which were calculated from the experimental data.
Y = β0 +Σβixi + Σβixixj + Σβiixi 2
In our case, the linear and interaction terms were considered; the linear terms relate to the direct influence of the components on the output responses and the second order terms represent the interaction between couples of variables. In the DoE, the domain of the study was limited between two levels: “lower level” and “upper level” (levels −1 and 1, respectively) [22,23]. The intersection of these factor levels gives an “experimental point” [24,25].
An 11-run experimental design was used in order to study the ternary FR system by choosing the formulations that are necessary for the statistical analysis of the different mechanical and flame-retardant parameters. Therefore, five ENGAGE TM polymers at the top and in the center of the experimental domain were selected for this study. The performance of the model was calculated by means of RMSECV (root mean square error in cross validation).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Characterization
Being that the mechanical properties of polymers and polymer composites are greatly affected by their crystallinity content, [26] thermal characterizations by differential scanning calorimetry of the ENGAGE-based matrices were accomplished and are reported in Figure 2.
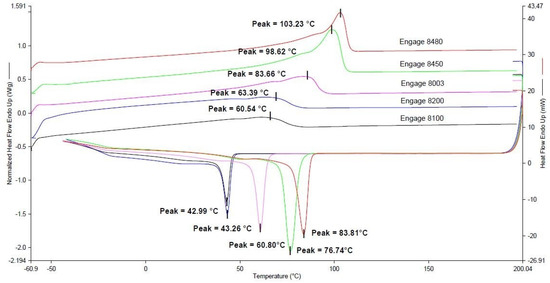
Figure 2.
First cooling and second heating DSC scans of ENGAGE 8480, ENGAGE 8450, ENGAGE 8003, ENGAGE 8200, and ENGAGE 8100.
From the Dow Chemical technical data sheets, it was possible to estimate the octene comonomer content that was used during the metallocene copolymerization process. The degree of crystallinity was calculated from ΔH°f using the Equation (2) [27] (the results of which were always greater than those that were reported by Dow [28]):
The physical structure and the properties of poly(ethylene-co-1-octene) are mainly controlled by the constitution of the macromolecule, i.e., the number of hexyl branches in the backbone. The concentration of the octene comonomer in poly(ethylene-co-octene) polymers has a predominant effect on their total crystallinity, crystal structure, and melting temperatures (Table 2). As the number of hexyl branches increases, the morphology of the crystals continuously changes from a lamellar structure, which is typical for a standard polyethylene, to a defect-rich, fringed-micellar arrangement that prevents the formation of a perfectly crystalline structure [29]. Notably, a higher density, higher melting peak, and greater melting enthalpy (ΔH°f) were found in the polymers with a higher crystallinity and a lower comonomer content. For example, ENGAGE 8480 showed the highest melting temperature and enthalpy, had a degree of crystallinity of 40%, a density of 0.902 g/cm3, and the lowest comonomer content of 5.9%. As reported by Kontou [30], poly(ethylene-co-octene) copolymers with densities less than 0.9 g/cm3 have no lamellae or spherulites, because the segmental length between branches is not long enough to crystallize by the conventional chain-folding process.

Table 2.
Data obtained from the DSC of ENGAGE 8480, 8450, 8003, 8200, and 8100, comonomer content, and degree of crystallinity obtained from literature.
3.2. Compatibilizer Optimization
A preliminary step in the optimization of the dosage of the maleated compatibilizer was accomplished. Six different formulations were prepared using ENGAGE 8003 as the POE with an intermediate density of 0.885 g/cm3, 60 wt.% of n-MDH, and with a variable 0–5 wt.% content of FUSABOND N525 as the maleated compatibilizer, with the aim to determine its influence on the mechanical properties of the final composites (Table 3).

Table 3.
Formulations vs. dosage of maleated compatibilizer %.
The samples were prepared and tested via stress–strain experiments that were in accordance with the ISO 37 type 2 test. The results have been reported and compared as a function of the dosage of the coupling agent in Figure 3 and Table 4.
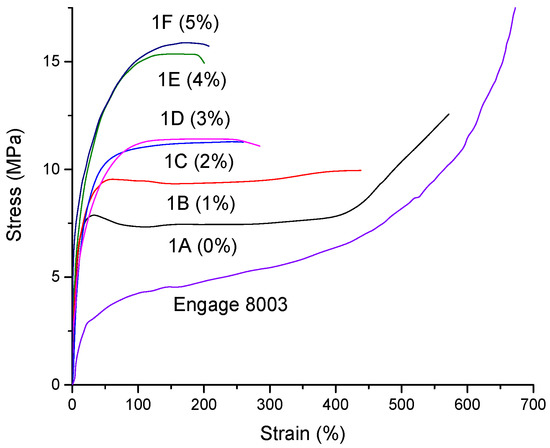
Figure 3.
Stress–strain curves of formulations 1A-1F based on ENGAGE 8003 and 60% of filler with different content of FUSABOND N525.

Table 4.
Properties (density, MFI, tensile strength, elongation at break, and Young’s modulus) of prepared samples 1a–1f based on ENGAGE 8003 and 60% of filler.
After the addition of the 60 wt.% of the mineral filler and in the absence of a coupling agent (i.e., 1A formulation containing ENGAGE 8003 and 0% coupling agent), the polymer matrix experienced an evident increase in its tensile strength at the expense of its elongation at break. An increase in the stress that was associated with stress hardening was also noted after the cold flow zone at 400% deformation in ENGAGE 8003 with and without filler.
Ethylene/α-olefin copolymers, such as ENGAGE 8003, with homogeneous branching distributions during the various phases at low stresses are free to slide, but at high stresses a large-scale orientation of the polymer chains in the amorphous phase crystalline lamellae occurs, resulting in the consequent strengthening of the material (Figure 3) [31].
The progressive addition of the FUSABOND N525 (Figure 3 and Table 4) strongly contributed to the decrease of the elongation at break and to the increase in the tensile strength due to an enhancement of the effective coupling interactions with the hydroxyl groups of the filler surface during the mixing process. This effect led to an increase in the mineral filler’s dispersion in the polymer matrix.
This result agrees with the literature, e.g., Lin [32] evaluated the effects of different compatibilizers on the mechanical properties of an EVA–MDH composite. They pointed out that the incorporation of PE-g-MAH increased the tensile strength at the expenses of the elongation at break. This response is possibly due to the effect of the carboxyl groups on maleic anhydride grafted polyethylene interacting with the hydroxyl groups of the magnesium hydroxide surface [33].
Polymer compounds that are used in electrical cables usually require 150% of elongation at break and 10 MPa or 12.5 MPa of tensile strength (for sheathing and insulating applications, respectively), therefore dosages of FUSABOND N525 that are higher than 3% were considered to be suitable (Figure 4) (per the reference standards CEI 20-11, BS7655 6.1, and DIN VDE 0207) [34]. This result is also confirmed by our previous work in which the 3% coupling agent was found to be the best compromise between mechanical and rheological properties [35].
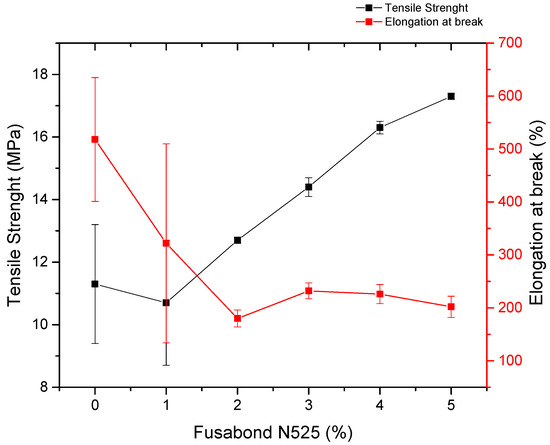
Figure 4.
Tensile strength (MPa) and elongation at break (%) as a function of percentage of FUSABOND N525.
Moreover, the melt flow index (MFI, Table 2), which is a measurement of the resistance of a melting thermoplastic polymer to flowing, decreased from 7.4 ± 0.4 to 2.9 ± 0.1 g/10 min with the addition of the compatibilizer, thus suggesting the existence of effective interactions between compatibilizer and the POE matrix. Overall, considering these results, the 3 wt.% of the coupling agent was considered the best trade-off dosage, since it provided a good balance between the mechanical (tensile strength of 14.4 MPa, elongation at break 232%), and rheological properties (MFI 3.8 g/10 min) that were required.
3.3. Effect of POE Characteristics and Natural MDH Content on the Properties of HFFR Composites
Today there are a great number of low voltage electric cables that rely on raw materials that vary in their quality and performance. A great challenge is to develop methodologies and strategies that can help in the production of a stable product quality level that meets the minimum required standards. Chemometrics provides a tool for finding the optimum value of a certain responses or an adequate compromise if the requirements are in conflict.
We present here a general method that is based on the application of a multivariate approach to the study of a flame-retardant composite, which allows the analysis of different parameters, the relationship between the raw materials, and the end-product results.
The leverage was the first prediction that was taken into consideration and it can be calculated at any point of the experimental process.
The value of leverage multiplied by the experimental variance corresponds to the variance of the estimate of the response at that point. Therefore, a leverage of 1 means that the response can be predicted with the same accuracy as the actual experiment, while a leverage <1 means that the response can be predicted better than if a real experiment were performed at the same point [36].
From the iso-response surface and the contour plot that connects all of the points that have the same predicted response (Figure 5), we can observe how the leverage is lower than 1 in most of the experimental domains. The leverage grows in the upper right corner, indicating that the answer will have less confidence in that region (a zone which is outside of the experimental domain and therefore outside of the model).
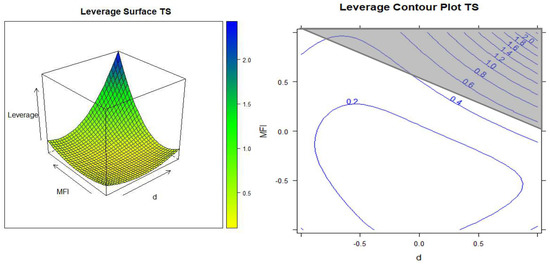
Figure 5.
Leverage surface and contour plot as a function of the density (d) and MFI.
The optimization of the mechanical and flame-retardant properties of the POEs were investigated by means of a multivariate analysis.
For this ternary system, 11 design formulation runs were performed relative to 10 different compositions and 1 formulation that was added from the validation test. Table 5 defines the experimental design as well as the main properties that were collected and the values of the normalized and dependent variables.

Table 5.
Properties (density, MFI, tensile strength, elongation at break, Young’s modulus) of prepared samples 1a–1f based on ENGAGE 8003 and 60% of filler.
The principal component analysis (PCA), which is outlined in Figure 6, was used in order to find correlations among the data of Table 5. Notably, PCA is a multivariate analysis method that is commonly used to express data in order to highlight the similarities and differences. The PCA allows the visualization of the variables that are responsible for the positive and negative correlations between the samples.
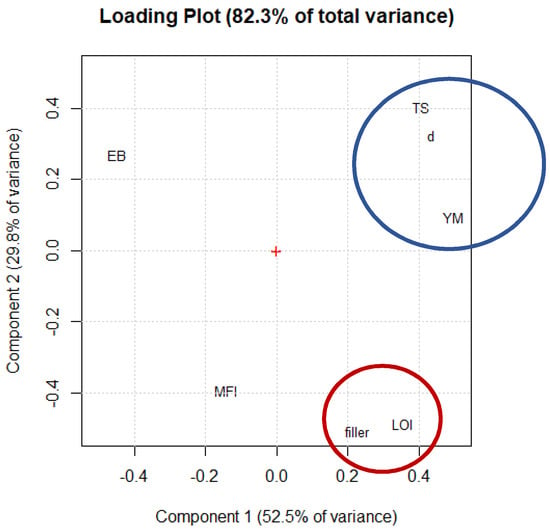
Figure 6.
PCA plot of the parameters.
It is possible to notice two different clusters in Figure 6: cluster 1 (blue circle), which is composed of tensile strength, Young’s modulus, and the density of the POE) and cluster 2 (red circle), the LOI and amount of filler). These positive correlations between the variables are in line with our expectations: in cluster 1 the increase in the density of the polymer matrix had led to an increase in both the tensile strength and Young’s modulus, while in cluster 2 the increase in the amount of filler content had led to an increase in the density of the compounds and in the flame-retardant properties (the LOI value). The variables in cluster 2 are also negatively correlated with the elongation at break. This is due to the high quantity of filler that is inside the compound that leads to a lowering of its mechanical properties. Concerning the statistical modelling of the data, Table 6 reports the values that were calculated for the set of regression coefficients that are involved in Equation (1) which describe the tensile strength, elongation at break and Young’s modulus (Y) as functions of the main parameters (x1, x2, x3), together with their statistical significances. The calculated coefficients for TS and YM indicate that these properties were positively affected by the increase in the density with significance at the 99% confidence level.

Table 6.
Coefficients of the model equation.
Following the report of the experimental plan to validate the model, three more tests were performed in the “central” point. All of the responses from the independent variable model were validated and therefore can be applied across all of the experimental domain. Considering the model’s validation, one of the three tests was selected (62.5% of filler and ENGAGETM 8003 d = 0.885 g/cm3 MFI 1 g/10 min 2.16 kg @ 190 °C) and was added to the model in order to improve its predictive capacity.
The multivariate analysis is therefore based on the samples that were prepared according to the 11 formulations that are reported in Table 5. The detailed analysis of the experimental and chemometric results is then reported.
3.4. Mechanical Properties
The five different POE samples that were investigated were filled with up to 60–65 wt.% of the flame-retardant filler and 3 wt.% of FUSABOND N525. These were subjected to tensile testing and the results, in terms of the tensile strength (TS), elongation at break (EB), and Young’s modulus (YM), are reported in Table 7.

Table 7.
Properties (tensile strength, elongation at break, and Young’s modulus) of the samples 1–11 with 3% of FUSABOND N525 filled with up to 60, 62.5, and 65 wt.% of filler.
Most of the formulations met the standard requirements (tensile strength of 10–12 MPa and elongation at break of 150%) for cable applications (per IEC 2011, BS7655 6.1, and DIN VDE 0207). Some authors [37,38] have tried to find a good agreement between the amount of filler and the mechanical and fire-retardant properties, but at the moment there are no studies concerning composites that are loaded with a high amount of n-MDH (60–65%) and using poly(ethylene-co-octene) as a polymer matrix.
The mechanical properties (the tensile strength, elongation at break, and Young’s modulus) of the 11 formulations were analyzed from the results of their stress–strain curves, which are shown in Figure 7.
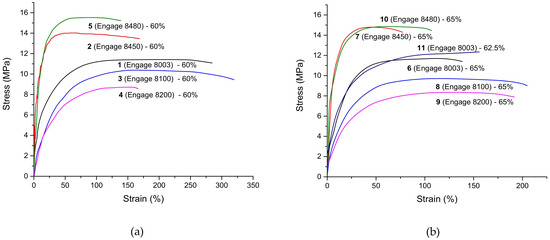
Figure 7.
(a) Stress–strain graphs of the samples 1–11 based on FUSABOND N525 with different ENGAGE (8480, 8450, 8003, 8100, and 8200), and (b) different amounts of filler n-MDH (60, 62.5, and 65%).
The mechanical properties of these compounds are mainly influenced by the type and amount of comonomer of the POE and by the distribution of the short chain branches (SCB). As the α-olefin content increases (and hence the density decreases), the number of consecutive ethylene units decreases and the crystallizable part of the copolymer becomes smaller [30,39].
Figure 7a evidences the role of the POE’s density (formulations 3 versus 5) in increasing its tensile strength (from 10.2 ± 0.3 MPa to 15.9 ± 0.4 MPa) and negatively impacting on its elongation at break (from 283 ± 24 to 133 ± 19, respectively).
The stress–strain graph that is shown in Figure 7b shows the same trend that has been reported previously. As reported in the literature [6], the increased crystallinity results in an improved modulus and yield stress and this is confirmed by the presently reported data. Actually, an enhancement of the MFI of the polymer matrix gives rise to a decrease in the tensile strength, specifically evidenced in the case of formulations 3 vs. 4 (from 10.2 ± 0.3 MPa to 9 ± 0.2 MPa) and 5 vs. 2 (from 15.9 ± 0.4 MPa to 14 ± 0.3 MPa).
Figure 8 reports the stress–strain curves of three formulations that were based on ENGAGE 8003 (d = 0.885 and MFI = 1.0) with 60, 62.5, and 65% filler composition, respectively.
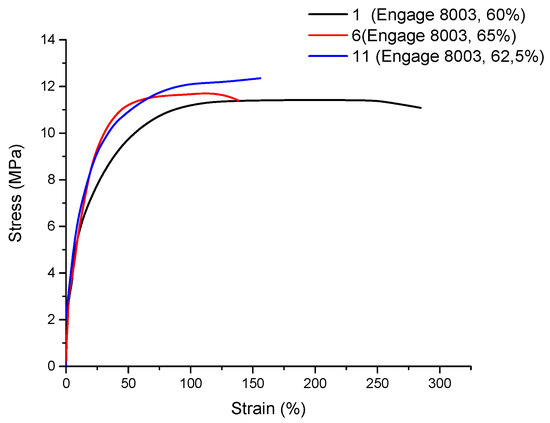
Figure 8.
Stress–strain graphs of formulation 1 (ENGAGE 8003, 60% filler), formulation 6 (ENGAGE 8003, 65% filler), and formulation 11 (ENGAGE 8003, 62.5% filler); all three formulations included 3% FUSABOND N525.
The reduced deformability of the POE’s matrix as a result of the increased filler content was possibly due to the filler–matrix interaction: adsorbed polymer chains on particles’ surfaces lead to higher rigidity (as indicated also by the higher Young’s modulus for these compositions), which leads to earlier fracture initiation and propagation [34].
In agreement with the literature [40], the introduction of a micronized mineral filler, such as natural magnesium hydroxide, leads to an increase in the Young’s modulus value (39.2 ± 4.3 MPa to 68.3 ± 5.5 MPa), yield strength (11.0 ± 0.3 MPa to 11.9 ± 0.3 MPa) and a decrease in the elongation at break (278 ± 15 to 147 ± 38) with increasing filler content.
The data that are reported in Table 5 were processed using CAT software (Chemometric Agile Tool) for the design of experiment (DoE) in order to describe the mechanical and flame-retardant (FR) properties as a function of the POE’s characteristics and its content of filler.
Figure 9a–c show the dependence of the tensile strength (TS), elongation at break (EB) and Young’s modulus (YM) on the density and the MFI that were measured with the intermediate amount of filler (x3 = 0).
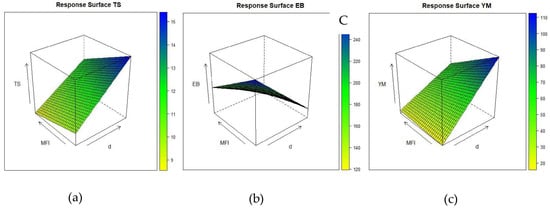
Figure 9.
Response surface of (a) tensile strength as a function of density (d) (x1), melt flow index (x2), and intermediate content of filler (x3 = 0); (b) elongation at break as a function of density (x1), melt flow index (x2), and intermediate content of filler (x3 = 0); (c) Young’s modulus as a function of density (x1), melt flow index (x2), and intermediate content of filler (x3 = 0).
In agreement with earlier works [41,42] that correlate the structure, morphology, and crystallinity of these POEs with their mechanical properties, it is known that the increase in the content of α-olefinic comonomers has a direct influence on the morphology of the melting polymer, with decreases in its crystallinity and density that lead to a drastic change in its mechanical properties. This is confirmed by the isoresponse surface wherein an enhancement of the polymer’s density gives rise to an increase in its tensile strength. Consequently, in agreement with the literature [43] and as confirmed by the model, the decrease in the level of crystallinity cooccurs with an increase in the elongation at break. Moreover, Young’s modulus has the same trend that is seen with the TS, as a matter of fact the independent variables that have the more significant and positive effects are the density and the amount of filler that is present. An improvement in the tensile strength leads to an increase in the slope of the elastic zone followed by an increase in Young’s modulus. Accordingly, the introduction of large quantities of filler results in an increase in Young’s modulus, the tensile strength, and a decrease in the elongation at break.
3.5. Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI)
The flame-retardant efficiency of POE-based composites that are filled with n-MDH has been evaluated with the limiting oxygen index (LOI). The LOI can be still considered the most-used FR test in the industrial world as an indicator of the flammability of materials: a higher LOI value indicates superior flame-retardancy [10]. Generally, LOI values go from 16–18% O2 for highly flammable compounds (like pure PE or PP) up to >90% O2 for virtually incombustible materials. In HFFR compounds that are used for the insulation and sheathing of cables, the typical LOI range is from 25% to 48% O2 [44]
As for the other composite properties, the fire-retardant performance depends strongly on the nature, origin and chemical characteristics of the fillers and polymers, and especially their interactions. The obtained results are reported in Table 8.

Table 8.
Data obtained from LOI of formulations 1–11, with 3% of FUSABOND N525 filled up to 60–65 wt.% n-MDH.
As expected, the LOI values slightly increased with the addition of the fillers to the POE due to the flame retardant-effect of the magnesium hydroxide.
Figure 10a shows the dependence of the LOI on the density and MFI at an intermediate amount of filler (x3 = 0) and Figure 10b shows the dependence of the LOI on the density and amount of filler at intermediate values of the MFI (x2 = 0).
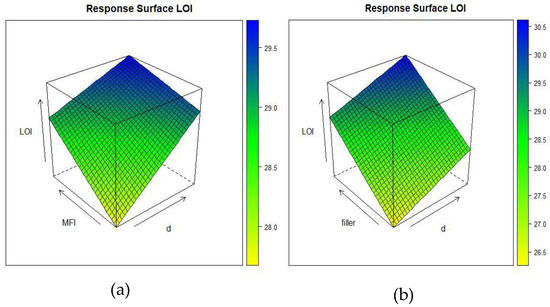
Figure 10.
Response surface of (a) LOI as a function of density (d) (x1), melt flow index (x2), and intermediate amount of filler (x3 = 0); (b) LOI as a function of density (x1), amount of filler (x3), and intermediate value of melt flow index (x2 = 0). This shows the dependence of the LOI on the density and amount of filler at intermediate values of MFI (x2 = 0).
The same trend was reported by the model, i.e., the isoresponse curves show that the LOI values increased with the increase in the amount of the filler content. Notably, the statistical coefficients indicate (Table 6) that the LOI is effectively influenced by all three of the variables, with that which was associated with the filler loading (x3) being the most significant. Further, the viscosity of the composite increased due to the filler’s affects the LOI experiment. The higher viscosity of the composite avoids dripping and the material shows a reduced ability to disperse heat. Moreover, it is possible to notice an improvement in the LOI with the polymer density at the same level of filler content, i.e., from 27% (formulation 3) to 29% (formulation 5).
3.6. Best Operating Conditions
The DoE was also inspected for its validity by comparing the experimental values and the fitted values that were provided by the model for each output datum, as shown in Figure 11. The data showed that the model provided an accurate description of the experimental data, indicating a connection between the dependent and independent variables.
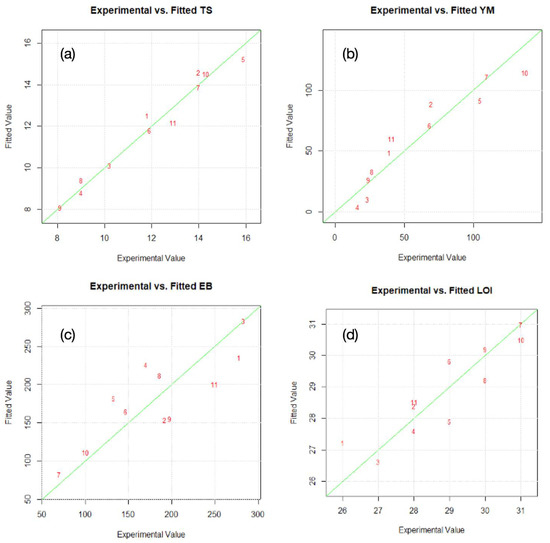
Figure 11.
Comparison of experimental value and fitted data for the output model parameters for (a) tensile strength TS; (b) Young’s modulus YM; (c) elongation at break EB; and (d) limited oxygen index LOI.
The values that were predicted by the multivariate model that was associated with each dependent variable are in good agreement with the values that were observed experimentally. The results highlight that there are tendencies in the linear regression fit (Figure 11) and the model accurately explains the experimental range that was studied. On this account, the model was found to be adequate for predicting the optimized production of HFFR compounds from the range of the preparation variables that was studied.
The above study shows that the mechanical and fire-retardant properties of HFFR compounds are more highly influenced by the density of the main polymer and the amount of filler that is present in the composite. DoE numerical optimization tools were then used in order to evaluate the best molecular properties of the polymer matrix and the most appropriate proportion of flame-retardant additives that was required in order to produce the best desired output. In order to obtain a product with the stringent specifications that were required, as previously reported, [34] the following limitations were defined:
- (1)
- 150% of elongation at break.
- (2)
- 10 MPa or 12.5 MPa of tensile strength (for sheathing and insulating applications, respectively).
Figure 12 shows the formulations that were predicted by the DoE model for the three variables that were studied in this case, with elongation at break values that are greater than 150%.
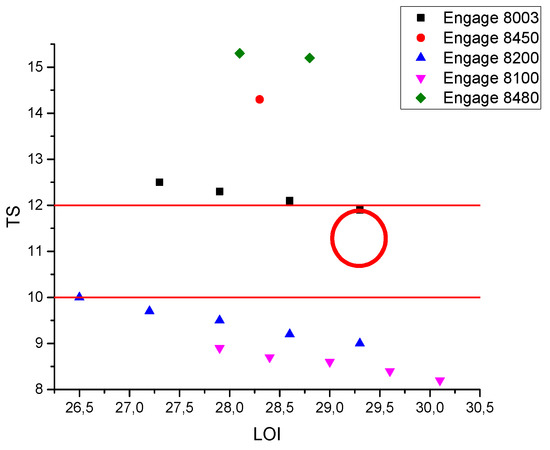
Figure 12.
Formulations with the highest desirability predicted by the DOE model and the output values of tensile strength and LOI at >150% of elongation at break, according to standard reference.
Depending on the specifications that were previously considered for sheathing and insulating applications, the present model is able to predict the best formulations in terms of the tensile strength (TS) and high flame-retardant properties (high LOI).
The formulation that was identified by the model to be the best compromised (red circle in Figure 12) the properties for both sheathing and insulating (TS 11.99 EB 166 LOI 29.3) and involved 63.75% n-MDH filler and ENGAGE 8003 (Figure 12). This result eventually demonstrated that the statistical analysis was reliable in its ability to optimize the production of HFFR compounds with the best compromise between mechanical, rheological, and fire-retardant properties.
3.7. Vertical Burning Test
For the evaluation of the flame performance of the composite, a vertical burning test was realized in addition to the measurement of the LOI. In industrial applications, vertical burning tests are widely used for flammability analysis as a screening procedure because they provide an efficiency indication quite rapidly [14]. Generally, vertical burning tests provide information on the rate of a fire’s spread and about the dripping tendency of flaming parts. FR materials often must reach specific fire safety standards that have been established for plastic components. To satisfy the fire safety requirements, the presence of flaming drops is taken in account within EN 50399 as adopted by European Construction Products Regulation (CPR) [45]
In our case, great attention was also given to the evaluation of the stability and cohesion of the material during combustion. This is one of the key properties for materials that are used in the field of cables, roofing, and transportation applications: materials are considered safer when they do not produce any flaming droplets.
The DIN 4102 B2 setting was useful for observing the combustion characteristics of the material. In this work, the vertical combustion tests were performed using a laboratory scale test (DIN 4102 B2 modified). A specially modified configuration of this test was used for the determination of the characteristic parameters of the burning time and for the estimation of the physical stability of the materials, as evaluated by the presence of burning drops.
Table 9 shows the experimental results of the 11 formulations that were obtained from the vertical combustion test.

Table 9.
Vertical burning test of formulations 1–11, with 3% of FUSABOND N525, filled up to 60–65 wt.% of filler.
The values that are reported in Table 9 evidence the role of n-MDH in increasing flame retardancy. All of the results of the vertical tests in the studied system highlight the strong effect of the fillers, in accordance with the results of previous works [14].
The role of POE’s crystallinity and the probable role of its melting temperature is less obvious. As previously mentioned, the melting temperatures of ENGAGE 8480 and 8450 are higher than those of ENGAGE 8003, 8200, and 8100. Actually, the experimental results suggest that POEs with lower density and lower melting temperatures give the HFFR compounds a higher tendency to drip. Moreover, the higher melting temperature of the polymer is reflected in the results of sample 7, which is characterized by a self-extinguishing behavior with no dripping.
4. Conclusions
The design of experiment method that was adopted here has been exploited in order to study the effects of the different molecular properties (MFI and density) of polymers and the effects of different amounts of filler on POE composites. A wide variety of parameters were studied for the design of experiment, such as the tensile strength, elongation at break, and Young’s modulus for measuring the mechanical properties and the limiting oxygen index and vertical burning tests for measuring the fire properties.
It has been demonstrated that 3 wt.% of maleated coupling agent is required in order to achieve good mechanical properties (TS 14.4 EB 232) that satisfy the characteristics that are required for the final application. Our studies have shown that an improvement in the flame-retardant properties (as measured by the LOI and vertical burning test) is obtained by increasing the amount of filler that is in the composite (60%, 62.5%, and 65%). Better flame-retardant properties are also obtained from polymers with a higher degree of crystallinity. More specifically the best flame-retardant ability, with a LOI of 31%, was eventually determined in the case of ENGAGE 8450 with 65 wt.% of n-MDH. Moreover, in the case of ENGAGE 8480 with 65 wt.% of n-MDH, the best flame-retardant properties, self-extinguishing behavior and no dripping were identified.
Actually, regarding the mechanical properties, the significant role of the POE’s density (or, in other words, its crystallinity) in increasing the tensile strength from 10.2 MPa to 15.9 MPa and negatively impacting on the elongation at break from 283% to 133%, respectively, was demonstrated. A good balance between mechanical, rheological and flame-retardant properties can be reached by varying the molecular properties of POE and the content of n-MDH. More specifically, the present model provided an optimized recipe for a formulation that is characterized by the best compromise between mechanical, rheological, and fire-retardant properties (TS 11.99 EB 166 LOI 29.3) for sheathing and insulating applications, in compliance with the relevant requirements.
Overall, this model represents the innovative use of a method that is able to offer a practical way for studying, modelling, and characterizing the influence of pertinent parameters that are involved in the response of flame-retardant compounds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.; formal analysis, M.M. and S.H.; investigation, M.M.; data curation, M.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.; writing—review and editing, A.P.; supervision, A.P. and G.R.; project administration, C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Dow Europe, Europiren B.V., and Silma S.r.l are kindly acknowledged for supplying the raw materials ENGAGE®, Ecopiren® and Silmaprocess®, respectively, and related information.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- El Hage, R.; Viretto, A.; Sonnier, R.; Ferry, L.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.-M. Flame retardancy of ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) using new aluminum-based fillers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batistini, A. New polyolefin plastomers and elastomers made with insite™ technology: Structure-property relationship and benefits in flexible thermoplastic applications. Macromol. Symp. 1995, 100, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chum, P.S.; Swogger, K.W. Olefin polymer technologies—History and recent progress at The Dow Chemical Company. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 797–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basuli, U.; Chaki, T.K.; Naskar, K. Influence of Engage® copolymer type on the properties of Engage®/silicone rubber-based thermoplastic dynamic vulcanizates. Express Polym. Lett. 2008, 2, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijada, R.; Dupont, J.; Miranda, M.S.L.; Scipioni, R.B.; Galland, G.B. Copolymerization of ethylene with 1-hexene and 1-octene: Correlation between type of catalyst and comonomer incorporated. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1995, 196, 3991–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanke, A.G.; Galland, G.B.; Freitas, L.; da Jornada, J.A.H.; Quijada, R.; Mauler, R.S. Influence of the comonomer content on the thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of metallocene ethylene/1-octene copolymers. Polymer 1999, 40, 5489–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luks, A.; Sauerwein, R. Halogen Free and Flame Retardant Elastomeric Cable Compounds with Submicron Sized Fillers Hal-ogen Free and Flame Retardant Elastomeric Cable Compounds with Submicron Sized Fillers. In Proceedings of the 57th IWCS Conference: Proceedings of the International Wire & Cable Symposium (IWCS), Providence, RI, USA, 9–12 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, N.L. Inorganic hydroxides and hydroxycarbonates: Their function and use as flame retardants. In Fire Retardency of Polymeric Materials. Marcel! Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 285–352. [Google Scholar]
- Fire Retardancy of Polymeric Materials. 2000, pp. 1–26. Available online: https://books.google.im/books?hl=en&lr=&id=BOIlen8ZqP4C&oi=fnd&pg=PR3&dq=fire+retardant+additives&ots=BF9afG_po9&sig=qsjEsr15wDURQUcTNj47L461EDo&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=fireretardantadditives&f=false (accessed on 31 December 2010).
- Hull, R.; Witkowski, A.; Hollingbery, L. Fire retardant action of mineral fillers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hornsby, P. Fire retardant fillers for polymers. Int. Mater. Rev. 2001, 46, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jancar, J.; Fekete, E.; Hornsby, P.R.; Jancar, J.; Pukánszky, B.; Rothon, R.N. (Eds.) Mineral Fillers in Thermoplastics I; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.H.; Lee, Y.B.; Bae, J.W.; Jho, J.Y.; Nam, B.U.; Chang, D.-H.; Yoon, S.-H.; Lee, K.-J. Tensile properties and stress whitening of polypropylene/polyolefin elastomer/magnesium hydroxide flame retardant composites for cable insulating application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 2311–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.I.; Haurie, L.; Formosa, J.; Chimenos, J.M.; Antunes, M.; Velasco, J. Characterization of poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) (EVA) filled with low grade magnesium hydroxide. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graft Polymer. Material Comparison; Graft Polymer: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2013; pp. 253–254. Available online: http://i.materialise.com/materials/compare (accessed on 30 April 2021).
- Passaglia, E.; Corsi, L.; Aglietto, M.; Ciardelli, F.; Michelotti, M.; Suffredini, G. One-step functionalization of an ethylene/propylene random copolymer with two different reactive groups. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 87, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschweng, B.; Tátraaljai, D.; Földes, E.; Pukánszky, B. Natural antioxidants as stabilizers for polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 145, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malegori, C.; Mustorgi, E. Analytical Chemistry and Chemometrics Group, Department of Pharmacy, University of Genova: An update. NIR News 2020, 31, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, B.; Caponigro, V.; Ardini, F. Experimental Design Step by Step: A Practical Guide for Beginners. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 52, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardelli, A.; Ruggeri, G.; Calderisi, M.; Lednev, O.; Cardelli, C.; Tombari, E. Effects of poly(dimethylsiloxane) and inorganic fillers in halogen free flame retardant poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) compound: A chemometric approach. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 2536–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, M. Experimental design and response surface methodology in energy applications: A tutorial review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 151, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D. Design and Analysis of Experiments. 2012. Available online: https://www.amazon.de/Design-Analysis-Experiments-Author-Montgomery/dp/B00XV4CQTU/ref=sr_1_11?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=1479835758&sr=1-11&keywords=design+and+analysis+of+experiments (accessed on 30 April 2012).
- Iordache, O. Design of Experiments. Underst. Complex Syst. 2012, 3923, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessaissia, F.Z.; Zegaoui, A.; Boutoubat, M.; Allouache, H.; Aillerie, M.; Charles, J.-P. The DoE method as an efficient tool for modeling the behavior of monocrystalline Si-PV module. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1968, 030059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemi, A.P.; Procter, C. E-commerce and entrepreneurship in SMEs: Case of myBot. J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 2018, 25, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minick, J.; Moet, A.; Hiltner, A.; Baer, E.; Chum, S.P. Crystallization of very low density copolymers of ethylene with α-olefins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1995, 58, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanke, A.G.; Galland, G.B.; Neto, R.B.; Quijada, R.; Mauler, R.S. Influence of the type and the comonomer contents on the mechanical behavior of ethylene/α-olefin copolymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow Chemicals, ENGAGE TM Polyolefin Elastomers Product Selection Guide, Data Sheet. (n.d.) 1–4. Form No. 777-088-01E-0819. Available online: https://www.dow.com/content/dam/dcc/documents/en-us/catalog-selguide/777/777-088-01-engage-polyolefin-elastomer-product-selection-guide.pdf?iframe=true (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- And, R.A.; Wunderlich, B. Analysis of the Degree of Reversibility of Crystallization and Melting in Poly(ethylene-co-1-octene). Macromolecules 2000, 33, 9076–9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontou, E.; Niaounakis, M.; Spathis, G. Thermomechanical behavior of metallocene ethylene-α-olefin copolymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 2477–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, D.; Cho, K.; Woo, T.; Lee, B.H.; Choe, S. Blends of ethylene 1-octene copolymer synthesized by Ziegler-Natta and metal-locene catalysts. I. Thermal and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.S.; Bunker, S.P.; Whaley, P.D.; Cogen, J.M.; Bolz, K.A.; Alsina, M.F. Evaluation of Metal Hydroxides and Coupling Agents for Flame Resistant Industrial Cable Applications. In Proceedings of the 54th IWCS/FOCUS Conference: International Wire & Cable Symposium (IWCS), Providence, RI, USA, 13–16 November 2005; p. 229. [Google Scholar]
- Jančář, J.; Kučera, J. Yield behavior of PP/CaC03 and PP/Mg(OH)2 composites. II: Enhanced interfacial adhesion. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1990, 30, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camino, G.; Maffezzoli, A.; Braglia, M.; De Lazzaro, M.; Zammarano, M. Effect of hydroxides and hydroxycarbonate structure on fire retardant effectiveness and mechanical properties in ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 74, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haveriku, S.; Meucci, M.; Badalassi, M.; Cardelli, C.; Ruggeri, G.; Pucci, A. Optimization of the Mechanical Properties of Polyolefin Composites Loaded with Mineral Fillers for Flame Retardant Cables. Micro 2021, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leardi, R. Experimental design in chemistry: A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 652, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Flame retardancy and smoke suppression of magnesium hydroxide filled polyethylene. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2003, 41, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahabi, H.; Laoutid, F.; Movahedifar, E.; Khalili, R.; Rahmati, N.; Vagner, C.; Cochez, M.; Brison, L.; Ducos, F.; Ganjali, M.R.; et al. Description of complementary actions of mineral and organic additives in thermoplastic polymer composites by Flame Retardancy Index. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 2056–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehanobish, K.; Patel, R.M.; Croft, B.A.; Chum, S.P.; Kao, C.I. Effect of chain microstructure on modulus of ethylene–α-olefin copolymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 51, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Fracture behavior and deformation mechanism of polypropylene/ethylene-octene copolymer/magnesium hydroxide ternary phase composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 98, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, R.; Godehardt, R.; Lebek, W.; Frangov, S.; Michler, G.H.; Radusch, H.-J. Morphology and micromechanical properties of ethylene/1-octene copolymers and their blends with high density polyethylene. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2005, 16, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.; Hussein, I.A.; Aldalbahi, A.; Parvez, A.; Soares, J.B.P. Synthesis of Metallocene Catalyzed Ethylene 1,7-Octadiene Copolymer: Effect of Copolymerization on Polymer Properties. Macromol. Res. 2018, 26, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, B.; Rogunova, M.; Chum, S.P.; Hiltner, A.; Baer, E. Classification of homogeneous copolymers of propylene and 1-octene based on comonomer content. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 4357–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypych, G. Flammability of Filled Materials. In Handbook of Fillers; ChemTec Pub.: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2016; pp. 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, E.; Stöcklein, W.; Klack, P.; Schartel, B. Assessing the reaction to fire of cables by a new bench-scale method. Fire Mater. 2016, 41, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).