Abstract
Seafood contamination by heavy metals is a growing public health concern, particularly in regions like Tunisia where seafood is a major dietary component. This study assessed concentrations of cadmium (Cd), copper (Cu), lead (Pb), and zinc (Zn) in the muscle tissue of the red shrimp Parapenaeus longirostris, collected in 2023 from four coastal regions: Bizerte, Monastir, Kerkennah, and Gabes. Metal analysis was conducted using flame atomic absorption spectroscopy. This species was chosen due to its ecological and economic importance. The study sites were chosen based on their differing levels of industrial, urban, and agricultural influence, providing a representative overview of regional contamination patterns. Mean concentrations were 1.04 µg/g for Zn, 0.59 µg/g for Cu, 1.56 µg/g for Pb, and 0.21 µg/g for Cd (dry weight). Pb was the most prevalent metal across sites. Statistically significant variation was observed only for Cu (p = 0.0334). All metal concentrations were below international safety limits set by FAO/WHO and the European Union. Compared to similar studies, the levels reported were similar or slightly lower. Human health risk was evaluated using target hazard quotient (THQ), hazard index (HI), and cancer risk (CR) values. For adults, THQ ranged from 5.44 × 10−6 to 8.43 × 10−4, while for children it ranged from 2.40 × 10−5 to 3.72 × 10−3. HI values were also well below 1, indicating negligible non-carcinogenic risk. CR values for Cd and Pb in both adults and children fell within the acceptable risk range (10−6 to <10−4), suggesting no significant carcinogenic concern. This study provides the first field-based dataset on metal contamination in P. longirostris from Tunisia, contributing valuable insights for seafood safety monitoring and public health protection.
1. Introduction
With the expansion of anthropogenic activities such as industrial, agricultural, and mining operations, the concentration of contaminants, including potentially toxic elements, has significantly increased in environmental matrices like water, soil, and food [1,2]. Heavy metal pollution in marine environments has become a critical concern due to its persistence, bioaccumulation, and toxicological impacts on aquatic organisms and human health [2,3,4]. While some metals, such as copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), are essential in trace amounts for biological processes, others, like mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd), and lead (Pb), are highly toxic even at low concentrations [2,5].
The Mediterranean Sea, renowned for its biodiversity, faces increasing contamination from industrial, agricultural, and urban activities, leading to the accumulation of toxic trace elements in marine organisms [6]. The health risk posed by heavy metal contamination is a growing global concern, and various studies have focused on human exposure due to the consumption of contaminated seafood [2,3,7]. These pollutants are particularly concerning in crustaceans like shrimp, which are widely consumed and hold significant economic and nutritional value in the region. Shrimp serve as benthic feeders and can bioaccumulate metals through sediments and the food chain, increasing the risk of metal transfer to higher trophic levels, including humans [3,8,9]. Despite their importance, limited data are available on trace metal concentrations in shrimp populations along the African coasts of the Mediterranean, particularly in Tunisia. Previous studies in Tunisia have primarily focused on crabs, leaving a gap in understanding regarding metal accumulation in shrimp [10].
The consumption of heavy metals through seafood can pose both carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic health risks. To quantitatively assess the potential hazards associated with long-term exposure to chemical contaminants via shrimp consumption, several standardized metrics are employed. The Estimated Daily Intake measures the daily intake of metals through dietary exposure. To evaluate non-carcinogenic risks, the United States Environmental Protection Agency recommends the use of the target hazard quotient for individual metals, and the hazard index for cumulative exposure to multiple metals. Carcinogenic risks are assessed using cancer risk estimates, which incorporate cancer slope factors. These methods are widely recognized and have been validated in previous studies for assessing human health risks associated with seafood consumption [11,12,13,14,15,16].
Parapenaeus longirostris, the deep-water rose shrimp, is an economically significant crustacean species widely distributed in Mediterranean fisheries, including Tunisia. It is one of the most commercially exploited shrimp species in the region, contributing significantly to local fisheries and seafood markets. Ecologically, it plays a crucial role in benthic food webs, serving as both predator and prey in marine ecosystems. Its abundance, commercial relevance, and ability to integrate metal concentrations in its tissues make it a valuable bioindicator for monitoring marine contamination [17]. However, studies addressing trace element concentrations in this species remain scarce, especially in Tunisian waters.
In this context, the present study aims to evaluate the contamination levels of trace metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn) in Parapenaeus longirostris populations from Tunisia. Additionally, it seeks to assess the potential human health risks associated with consuming this species. While heavy metal contamination has been extensively studied in Mediterranean marine environments, research specifically targeting P. longirostris remains limited, particularly within the Mediterranean basin. To our knowledge, no previous studies have investigated trace metal accumulation in this species in Tunisian waters, making this the first study to provide such data. By addressing this gap, the study offers critical insights into metal contamination patterns in P. longirostris and contributes to a broader understanding of environmental pollution in the Mediterranean Sea. Furthermore, the assessment of human health risks related to shrimp consumption strengthens the relevance of this work for seafood safety and environmental management in the region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas
2.1.1. Bizerte Lagoon
The Bizerte Lagoon (Figure 1) is a Mediterranean coastal ecosystem in northern Tunisia (37°8′–37°14′ N; 9°46′–9°56′ E), covering about 150 km2 with an average depth of 7 m. It is connected to the Mediterranean Sea by a 6 km long channel and to Ichkeul Lake via the Tinja stream. The lagoon supports traditional fishing and aquaculture, particularly mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) and oysters (Ostrea edulis, Crassostrea gigas) [18]. The surrounding area includes major urban and industrial centers such as Bizerte, Menzel Bourguiba, and Menzel Jemil. These contribute significant anthropogenic pressures, including domestic and industrial effluents, agricultural runoff, and maritime traffic [19,20,21]. Industrial activities such as steel production, cement manufacturing, oil refining, and shipbuilding further contribute to the lagoon’s environmental degradation [21,22]. Several studies have documented the lagoon’s vulnerability to pollution, invasive species, and climate change, underscoring the urgent need for improved environmental management [23].
Figure 1.
Map displaying the areas sampled. Source: Google Maps https://www.google.com/maps (accessed on 2 May 2025).
2.1.2. Gulf of Gabes
The Gulf of Gabes (Figure 1), located in southeastern Tunisia, is characterized by a broad continental shelf and high marine productivity, contributing over 40% of the country’s national fish production [24]. The region is ecologically rich, with extensive Posidonia oceanica and Cymodocea nodosa seagrass meadows that support biodiversity, stabilize sediments, and enhance water quality. Despite its ecological importance, the Gulf faces intense anthropogenic pressures. Industrial zones in cities such as Sfax, Gabes, and Zarzis release untreated effluents into coastal waters, leading to habitat degradation and a decline in marine biodiversity [25].
2.1.3. Bay of Monastir
The Bay of Monastir (Figure 1), a semi-enclosed lagoon located on Tunisia’s eastern coast, spans a 38 km shoreline between Monastir and Bekalta [26]. It receives terrestrial input from local drainage systems, including Oued Essouk, Oued El Maleh, and nearby wastewater treatment plants. These inflows carry urban runoff, industrial discharges, and domestic effluents into the bay. Industrial activities such as ceramics, lead processing, textiles, and construction, combined with urbanization and aquaculture, have led to the accumulation of organic and inorganic pollutants. These pressures have resulted in eutrophication, algal blooms, and a decline in marine biodiversity [27].
2.1.4. Kerkennah Site
The Kerkennah Archipelago (Figure 1), located about 20 km off Sfax in the Gulf of Gabes, covers roughly 160 km2 and features shallow coastal waters (0–5 m depth), low currents, high salinity, and a mix of sandy and rocky substrates [28]. Shrimp samples were collected from Sidi Youssef port in Mellita, a key monitoring site for metal contamination. This site is the only navigation channel linking Sfax to Kerkennah and is affected by fishing, road traffic, and tourism activities [28].
2.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
Sampling across the four aquatic ecosystems was conducted in May 2023. Shrimp samples were collected from the Bizerte Lagoon, Monastir Bay, Kerkennah Island, and the Gulf of Gabes, with 100 individuals obtained from each site. The samples were collected from fishing landings, transported on ice, and stored in a cooler until they reached the laboratory, where they were preserved at −20 °C in a freezer. The shrimp collected from each station were divided into three pools. Upon arrival at the laboratory, each sample was subjected to biometric measurements. The total length was measured to the nearest 0.1 cm, and the total weight was recorded using a digital scale with a precision of 0.01 g. Following biometric analysis, the edible portion (flesh) of each shrimp was carefully separated from the exoskeleton. The flesh samples were then dried in an oven at 40 °C until a constant weight was obtained. Once dried, the samples were finely ground using a clean pestle and mortar to obtain a homogeneous powder for subsequent chemical analysis.
2.3. Chemical Analysis
The used method for detecting heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Zn, Pb) was adapted from that developed by Annabi et al. [29]. The concentration of heavy metals in the sample filtrates was determined using a flame atomic absorption spectrophotometer (Avanta GBC spectrometer, Australia), with acetylene gas and air serving as the fuel and oxidizer, respectively. A hollow cathode lamp was utilized as a light source for Zn, Cd, Pb and Cu at wavelengths of 213.9, 228.8, 283.3, and 248.3 nm, respectively, for the determination of each metal. The equipment underwent calibration using NIST-traceable atomic absorption standards for metals to establish a calibration curve. Linear calibration curves were established with linear regression values exceeding R2 > 0.989 ± 0.10. The limit of detection (LOD) for each metal was determined as follows: Cu 0.005 mg/L, Zn 0.003 mg/L, Cd 0.002 mg/L and Pb 0.013 mg/L. Heavy metal concentrations are expressed in µg/g dry weight. To prevent potential contamination, all glassware used in the experiments was thoroughly cleaned by immersing it in 10% nitric acid for 24 h, followed by thorough rinsing with deionized water prior to usage. Analytical-grade reagents sourced from Sigma-Aldrich (UK) were consistently employed throughout the analysis process. A reagent blank was analyzed alongside each batch of samples to account for any background contamination. The precision of the analytical procedure was assessed through triplicate analysis, and the relative standard deviation (%RSD) for each metal was calculated. The %RSD values obtained were found to be less than 10%. To conduct the repeatability test and verify the analytical method, shrimp samples were spiked with known concentrations of heavy metals. In each run, the samples underwent triplicate analysis. The spiked samples were then digested and analyzed using the same method employed for the original samples. The recovery values obtained ranged from 75% to 95%, indicating satisfactory accuracy across the measurements.
2.4. Pollution Assessment
The contamination level of shrimp by heavy metals was assessed using the Pollution Index (PI), which provides an indication of the pollution status of individual metals in biota. The PI was calculated according to the formula described by Adebiyi et al. [30]. It represents the quotient of the concentration of element x in the sample to the maximum permissible level of the element.
Cmetal represents the concentration of the metal in the sample, while Cstandard refers to the corresponding permissible limit or background value. Specifically, a PI value below 0.2 indicates a normal background level. A value between 0.2 and 0.6 suggests slight pollution, while a value between 0.6 and 1.0 indicates moderate pollution. A PI value equal to or greater than 1.0 reflects heavy pollution, indicating that it exceeds the permissible limits.
2.5. Health Risk Assessment
To assess possible health concerns linked to Parapenaeus longirostris consumption, several parameters were calculated. These include the following: Estimated Daily Intake (EDI), Estimated Weekly Intake (EWI), percentage of provisional tolerable weekly intake (%PTWI), maximum daily intake (MDI), maximum weekly intake (MWI), daily intake limit (CRlim), monthly consumption rate limit (CRmm), target hazard quotient (THQ), hazard index (HI), cancer risks (CR), and relative risk (RR). These calculations were conducted specifically for Zn, Cd, Cu and Pb.
2.5.1. Estimated Daily Intake
The EDI value was calculated according to the formula defined by Ben Ameur et al. [2], Miri et al. [31] and Tkachenko et al. [32].
EF and ED represent the exposure frequency (365 days per year) and exposure duration (60 years for adults and 10 years for children), respectively. FIR denotes the daily seafood consumption rate, estimated at 55.5 g/day for adults and 52.5 g/day for children, based on values reported in the literature [33,34,35]. CF is the conversion factor used to convert fresh weight to dry weight (0.2). Cm indicates the concentration of the metal in shrimp tissue (μg/g on a dry weight basis). WAB represents the average body weights, which are 15 kg for Tunisian children and 70 kg for Tunisian adults. Finally, TA refers to the total exposure time for non-carcinogenic effects, calculated as EF × ED.
2.5.2. Estimated Weekly Intake
The EWI was calculated using the equation developed by Ben Ameur et al. [2], Okbah et al. [7] and USEPA [36].
C refers to the concentration of the element in shrimp, IR represents the daily seafood consumption rate (grams per day), and BW denotes the body weight.
2.5.3. Percentage of Provisional Tolerable Weekly Intake
The %PTWI for each heavy metal was calculated using the equation described by Ben Ameur et al. [2], Miri et al. [31] and Abdel-Kader and Mourad [37].
EWI represents the Estimated Weekly Intake of metals (mg/kg body weight per week), while PTWI refers to the provisional tolerable weekly intake (mg/kg body weight per week).
2.5.4. Maximum Daily Intake
The MDI was determined on the basis of the equation outlined by Ben Ameur et al. [2] and Abdel-Kader and Mourad [37].
2.5.5. Maximum Weekly Intake
The MWI was evaluated using the formula reported by Ben Ameur et al. [2] and Abdel-Kader and Mourad [37].
MWI = MDI × 7
2.5.6. Daily Intake Limit
For assessing the carcinogenic effects of contaminants, the daily consumption rate limit (CRlim) for shrimp species was determined using the equation defined by Ben Ameur et al. [2], Miri et al. [31] and Berhanu et al. [38].
2.5.7. Maximum Acceptable Daily Intake
The CRlim of fish was determined for the non-carcinogenic risk associated with heavy metal contaminants using the equation described Ben Ameur et al. [2], Miri et al. [31] and Berhanu et al. [38].
CRlim represents the maximum permissible daily intake of contaminated shrimp (kg/day), while ARL denotes the acceptable lifetime risk threshold, set at 10−5 in this study. WAB refers to the average body weight of the consumer population (kg). CSF is the cancer slope factor (mg/kg/day)−1, RfD is the oral reference dose (mg/kg/day), and Cm indicates the concentration of metal in the edible portion of the shrimp (mg/kg).
2.5.8. Maximum Allowable Intake Rate
The CRmm of fish contaminated with heavy metals was determined using the formula outlined by Ben Ameur et al. [2], Okbah et al. [7] and Miri et al. [31].
CRmm represents the highest permissible consumption rate (meals per month), Tap refers to the average time span (30.44 days per month), and MS indicates the meal portion size (adults: 0.227 kg; children: 0.114 kg). A value higher than 16 meals/month was considered to present no obvious human health risk [36].
2.5.9. Target Hazard Quotient
The non-carcinogenic risks were assessed using the THQ calculation, as demonstrated in the equation reported by Ben Ameur et al. [2], Miri et al. [31] and Miri et al. [19], and Oros et al. [39].
A THQ value below 1 indicates no significant health risk for the exposed population. A THQ of 1 suggests that individuals may face potential non-carcinogenic health effects, with the likelihood of adverse impacts increasing as the THQ exceeds 1.
2.5.10. Hazard Index
The HI was determined by summing all the target hazard quotient values according to the equation defined by Ben Ameur et al. [2], Okbah et al. [7], Berhanu et al. [38] and Giri and Singh [40].
THQi represents the target hazard quotient for a specific metal, HI is the cumulative hazard index for all four metals analyzed in this study, and n corresponds to the total number of metals, which is 4.
2.5.11. Cancer Risks
The CR over a lifetime of Cd and Pb exposure was calculated following the formula reported by Ben Ameur et al. [2] and Miri et al. [31].
CSF refers to the cancer slope factor (mg/kg/day), while the remaining parameters are as previously defined. The USEPA has suggested an acceptable or tolerable cancer risk range for arsenic of 10−6 to 10−4 [41]. CR values below 10−6 are considered insignificant, values ranging between 10−6 and 10−4 are acceptable or tolerable, and values exceeding 10−4 indicate significant carcinogenic risk [39].
2.5.12. Relative Risk
The RR of contaminants for both carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic effects was determined using the equation defined by Ben Ameur et al. [2] and Miri et al. [31].
All parameters have been defined previously. The risk to human health associated with shrimp consumption is expected to rise as the RR value increases.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The data related to the morphological study, as well as the results concerning heavy metal concentrations, were expressed as means ± standard deviations (SD). Statistical analysis was performed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) to compare group means, followed by Fisher’s Least Significant Difference (LSD) test to identify significant differences between specific pairs of means. The analyses were conducted using Stat View (version 5.0, by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA), and statistical significance was accepted at a p-value < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Study of Morphometric Parameters
Morphometric data (weight and length) collected from all examined individuals are reported in Figure 2. In Bizerte Lagoon (BL), shrimp exhibited an average weight of 4.38 g, ranging from 2.90 to 7.82 g, and an average length of 81.55 mm (66.04–109.30 mm). Individuals from Monastir Bay (MB) showed higher biometric values, with a mean weight of 6.71 g (3.38–14.56 g) and a mean length of 91.99 mm (73.08–120.03 mm). The largest specimens were recorded at Kerkennah Islands (KI), averaging 9.30 g in weight (5.28–14.16 g) and 93.92 mm in length (78.03–108.03 mm). In contrast, shrimp from the Gulf of Gabes (G) were generally smaller, with a mean weight of 4.67 g (2.69–11.89 g) and a mean length of 73.23 mm (6.70–98.08 mm). The regional average for this parameter is 6.27 g. The maximum total length was observed in Kerkennah, with an average of 93.92 mm, while the minimum value was found in Gabes, with an average of 73.23 mm. The regional average for this parameter is 85.20 mm.
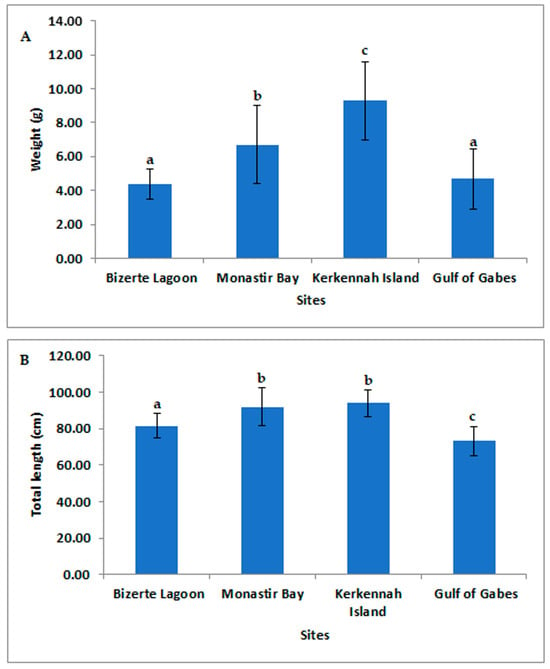
Figure 2.
Weight (A) and total length (B) of the red shrimp samples from the Bizerte Lagoon, Monastir Bay, Kerkennah Island and Gulf of Gabes. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences.
Statistical analysis revealed significant differences in biometric parameters across stations. For the physiological parameters, the inter-site comparison showed statistically significant differences in both total weight (p < 0.0001) and total length (p < 0.0001). For total weight, significant differences were observed between stations, except between Bizerte and Gabes (p = 0.2306). For total length, significant differences were found between stations, except between Monastir and Kerkennah (p = 0.3260).
3.2. Heavy Metal Concentrations
The concentrations of heavy metals analyzed in the muscle tissue of Parapenaeus longirostris are summarized in Figure 3. Among the four metals studied, Cu and Zn are essential elements required in small amounts, while Cd and Pb are non-essential and toxic even at low concentrations.

Figure 3.
Metal concentrations in the muscle of Parapenaeus longirostris across the different study sites.
In Bizerte Lagoon, Cd concentrations averaged 0.20 µg/g dry weight, ranging from 0.20 to 0.21 µg/g. Cu levels had a mean of 0.62 µg/g dry weight, with values between 0.59 and 0.64 µg/g. Zn concentrations averaged 0.99 µg/g dry weight, within a range of 0.92 to 1.06 µg/g, while Pb showed a mean of 1.79 µg/g dry weight, ranging from 1.54 to 2.05 µg/g. In Monastir Bay, Cd averaged 0.22 µg/g dry weight (0.21–0.23 µg/g), Cu was 0.71 µg/g dry weight (0.68–0.74 µg/g), Zn was 1.02 µg/g dry weight (0.91–1.12 µg/g), and Pb reached 1.63 µg/g dry weight (1.59–1.68 µg/g). At Kerkennah Island, Cd averaged 0.23 µg/g dry weight (0.22–0.25 µg/g), Cu was 0.52 µg/g dry weight (0.49–0.55 µg/g), Zn measured 1.12 µg/g dry weight (1.11–1.14 µg/g), and Pb averaged 1.66 µg/g dry weight (1.61–1.70 µg/g). In the Gulf of Gabes, Cd averaged 0.18 µg/g dry weight (0.17–0.19 µg/g), Cu was 0.50 µg/g dry weight (0.46–0.54 µg/g), Zn was 1.02 µg/g dry weight (1.01–1.03 µg/g), and Pb averaged 1.16 µg/g dry weight, with a range of 1.13 to 1.19 µg/g.
For all shrimp specimens studied in this work, the concentrations of metals ranked in decreasing order as follows: Pb > Zn > Cu > Cd. The average concentrations across all sites showed that Pb had the highest mean levels, ranging from 1.16 to 1.79 µg/g dry weight, followed by Zn (0.99–1.12 µg/g dry weight), Cu (0.50–0.71 µg/g dry weight), and Cd with the lowest values (0.18–0.23 µg/g dry weight). Specifically, the highest Cd concentration was recorded in specimens from Kerkennah (0.23 µg/g dry weight), whereas the lowest concentration was observed in those from Gabes (0.18 µg/g dry weight). The highest Cu concentration was observed in shrimp from Monastir (0.71 µg/g dry weight), while the lowest value was recorded in samples from Gabes (0.50 µg/g dry weight). The highest Zn concentration was found in samples from Kerkennah (1.12 µg/g dry weight), while the lowest concentration was detected in specimens from Bizerte (0.99 µg/g dry weight).
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Metal Concentrations Across Study Sites
Statistical analyses of the heavy metal concentrations recorded in this study revealed significant differences across the sampling sites. The p-values obtained were 0.0042, 0.004, <0.0001, and <0.0001 for Bizerte, Kerkennah, Monastir, and Gabes, respectively. A significant difference was observed in Cu concentrations (p = 0.0334). In contrast, no statistically significant differences were found for Cd (p = 0.1479), Zn (p = 0.5474), and Pb (p = 0.0888) between the studied sites.
In the Bizerte Lagoon, Pb showed the highest concentration in the samples, while Cd had the lowest. Statistically significant differences were observed among the four analyzed metals: Cd/Pb (p = 0.0010), Cd/Zn (p = 0.0134), Cu/Pb (p = 0.0032), and Pb/Zn (p = 0.0122). In Monastir Bay, Pb also showed the highest concentration, while Cd had the lowest. Statistically significant differences were found among the four metals: Cd/Cu (p = 0.0017), Cd/Pb (p < 0.0001), Cd/Zn (p < 0.0001), Cu/Zn (p = 0.0001), Cu/Pb (p < 0.0001), and Pb/Zn (p = 0.0002). At Kerkennah Island, Pb exhibited the highest concentration, while Cd showed the lowest. Statistically significant differences were observed between the four metals: Cd/Cu (p = 0.0044), Cd/Pb (p < 0.0001), Cd/Zn (p = 0.0007), Cu/Zn (p = 0.0241), Cu/Pb (p = 0.0004), and Pb/Zn (p = 0.0020). Similarly, in the Gulf of Gabes, Pb exhibited the highest concentration, while Cd showed the lowest. Statistically significant differences were noted among the four metals: Cd/Cu (p = 0.0010), Cd/Pb (p < 0.0001), Cd/Zn (p < 0.0001), Cu/Zn (p = 0.0002), Cu/Pb (p < 0.0001), and Pb/Zn (p = 0.0218).
3.4. Shrimp’s Level of Metal Pollution
The PI for the heavy metals in shrimp samples collected from the four sites was calculated to determine the extent of contamination/pollution associated with the red shrimp samples, and the results are presented in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4. The PI values for Cd were 0.20, 0.22, 0.23, and 0.18 for Bizerte Lagoon, Monastir Bay, Kerkennah Island, and Gulf of Gabes, respectively. In the case of Cu, the PI values are similar across the different locations, with a mean PI value of 0.22. Kerkennah Island exhibited the highest PI for Cd (0.23), indicating the highest contamination in this location. Bizerte Lagoon and Monastir Bay showed similar PI values (0.20 and 0.22, respectively), reflecting moderate contamination levels. The Gulf of Gabes recorded the lowest PI for Cd (0.18), suggesting it is less impacted by Cd pollution compared to the other sites. Zn and Cu concentrations were consistent across all sites, with values of 0.02 for Cu and 0.01 for Zn, suggesting minimal and almost uniform pollution across the regions. This indicates that Zn and Cu contamination is not significantly affecting these sites, and their levels are within acceptable or natural ranges. For Pb, Bizerte Lagoon showed the highest PI (0.90), indicating significant Pb contamination in this area. Monastir Bay and Kerkennah Island had similar PI values (0.82 and 0.83, respectively), pointing to moderate Pb pollution. The Gulf of Gabes recorded the lowest PI for Pb (0.58), suggesting it is less affected by Pb contamination.

Table 1.
The estimated EDI, EWI, PTWI %, MDI, MWI, estimated CRlim (carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic), CRmm, THQ, CR and RR of Cd, Cu, Zn and Pb in Parapenaeus longirostris muscle from Bizerte Lagoon consumed by an adult and a child.

Table 2.
The estimated EDI, EWI, PTWI %, MDI, MWI, estimated CRlim (carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic), CRmm, THQ, CR and RR of Cd, Cu, Zn and Pb in Parapenaeus longirostris muscle from Monastir Bay consumed by an adult and a child.

Table 3.
The estimated EDI, EWI, PTWI %, MDI, MWI, estimated CRlim (carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic), CRmm, THQ, CR and RR of Cd, Cu, Zn and Pb in Parapenaeus longirostris muscle from Kerkennah Island consumed by an adult and a child.

Table 4.
The estimated EDI, EWI, PTWI %, MDI, MWI, estimated CRlim (carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic), CRmm, THQ, CR and RR of Cd, Cu, Zn and Pb in Parapenaeus longirostris muscle from Gulf of Gabes consumed by an adult and a child.
3.5. Health Risk Assessment Related to the Consumption of Parapenaeus longirostris
Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 show that the Estimated Daily Intake (EDI) and Estimated Weekly Intake (EWI) of trace elements were ranked as follows: Pb > Zn > Cu > Cd in Bizerte Lagoon, Monastir Bay, and Gulf of Gabes, and Pb > Zn > Cd > Cu in Kerkennah Island. The study also compared the consumption of Parapenaeus longirostris muscle between children and adults across the four studied lagoons. The results revealed that the Estimated Weekly Intake (EWI) values for all detected metals in shrimp were below the provisional tolerable weekly intake (PTWI) limits established by relevant regulatory bodies (Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4). The contribution of heavy metals from shrimp consumption was less than 1% of the PTWI, except for Pb.
Among the metals, Pb contributed the most to the PTWI across all the studied areas, while Zn (from Bizerte Lagoon and Monastir Bay) and Cu (from Kerkennah Island and Gulf of Gabes) showed the lowest contributions.
The monthly fish meal size based on non-carcinogenic effects was also calculated, and the results are shown in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4. For contaminated fish from Bizerte Lagoon, the meal size due to exposure to Cd, Cu, Zn, and Pb ranges from 18.35 to 2844.48 meals per month for adults and from 7.83 to 1213.72 meals per month for children. For fish from Monastir Bay, the meal size ranges from 2760.82 to 20.16 meals per month for adults and from 8.60 to 1178.02 meals per month for children, based on exposure to Cd, Cu, Zn, and Pb. In Kerkennah Island, the meal size ranges from 19.79 to 2514.32 meals per month for adults and from 8.44 to 1072.84 meals per month for children. In the Gulf of Gabes, the meal size ranges from 28.32 to 2760.82 meals per month for adults and from 12.08 to 1178.02 meals per month for children.
The target hazard quotient of heavy metals through Parapenaeus longirostris consumption by the average Tunisian adult and child is presented in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4. The mean concentrations of Cd and Zn in Parapenaeus longirostris were used to compute the THQ and hazard index for metals in shrimp. It was observed that the metals’ THQ values declined in the following order in Bizerte Lagoon and Gulf of Gabes (for both adults and children): Pb > Cd > Cu > Zn. In Kerkennah Island and Monastir Bay, the THQ values of metals in fish are ranked as follows for both children and adults: Cd > Pb > Cu > Zn.
The hazard index was <1 for adults (1.20 × 10−3 for Bizerte Lagoon, 4.74 × 10−4 for Monastir Bay, 4.85 × 10−4 for Kerkennah Island, and 8.70 × 10−4 for Gulf of Gabes) and <1 for children (5.32 × 10−3 for Bizerte Lagoon, 5.15 × 10−3 for Monastir Bay, 2.14 × 10−3 for Kerkennah Island, and 3.84 × 10−3 for Gulf of Gabes).
The carcinogenic risk values for Cd, due to exposure from the consumption of Parapenaeus longirostris, were 2.08 × 10−5, 2.29 × 10−5, 2.39 × 10−5, and 1.87 × 10−5 for adults in Bizerte Lagoon, Kerkennah Island, Monastir Bay, and the Gulf of Gabes, respectively. For children, the CR values were 1.11 × 10−6, 1.01 × 10−4, 1.05 × 10−4, and 8.26 × 10−5, respectively. Regarding Pb, the CR values for adults were 2.51 × 10−7, 2.28 × 10−6, 2.33 × 10−7, and 1.63 × 10−6 in Bizerte Lagoon, Kerkennah Island, Monastir Bay, and the Gulf of Gabes, respectively. For children, the CR values were 1.11 × 10−6, 1.01 × 10−6, 1.03 × 10−5, and 7.18 × 10−6.
The non-carcinogenic risk (RR) values for consuming shrimp contaminated with Cd, Cu, Zn, and Pb are presented in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4. In Bizerte Lagoon, the highest and lowest RR values were 5.11 × 10−1% and 3.30 × 10−3% of the total risk for Pb and Zn, respectively. In Monastir Bay, the highest and lowest RR values were 3.40 × 10−3% and 4.66 × 10−1% of the total risk for Pb and Zn, respectively.
4. Discussion
This research aimed to examine the levels of heavy metals in the edible muscle tissues of a commercially significant shrimp species sold in the Tunisian market, as data on heavy metal contamination in shrimp from this area are scarce. To the best of our knowledge, no previous study has investigated heavy metal concentrations in Parapenaeus longirostris collected from the Tunisian coast. The study of heavy metal concentrations in crustaceans is crucial for managing ecosystems and safeguarding human health through consumption.
4.1. Heavy Metal Content and Level of Pollution in Shrimp
The variability in metal concentrations across the study sites can be attributed to a combination of site-specific anthropogenic activities and environmental factors. The higher levels of Pb observed across all study sites compared to Cd, Cu, and Zn could be attributed to its persistence in sediments, limited natural degradation, and historical legacy from leaded gasoline and paints, all of which likely contribute to its increased bioavailability to benthic organisms such as Parapenaeus longirostris. For instance, the elevated Pb levels observed in Bizerte Lagoon are likely the result of intensive industrial activities, heavy shipping traffic, and urban wastewater discharges in this highly developed coastal area. Similarly, the higher Cu concentrations detected in Monastir Bay may be associated with urban runoff, mariculture operations, and the use of copper-based antifouling paints in boat maintenance. In contrast, the relatively lower concentrations of metals, especially Cu and Cd, measured in the Gulf of Gabes may be explained by greater hydrodynamic dispersion, remoteness from major industrial centers, and less urbanization. In addition, natural variables such as salinity, temperature, sediment characteristics, and organic matter content also influence metal bioavailability and their subsequent accumulation in shrimp tissues.
These spatial differences in contamination levels carry important practical implications for various stakeholders. Environmental monitoring agencies should intensify surveillance efforts in hotspots such as Bizerte and Monastir to track contamination trends and assess the effectiveness of existing pollution control measures. Public health authorities can use these findings to develop site-specific seafood consumption advisories, especially targeting vulnerable groups like children and pregnant women. Fisheries managers may need to consider harvest restrictions or spatial planning measures to minimize exposure risks and maintain product quality. For policy-makers, these results underscore the need to strengthen regulations on industrial discharges, improve wastewater treatment infrastructure, and implement better coastal land-use practices. Additionally, advancing integrated coastal zone management strategies could help reconcile environmental protection with ongoing economic activities such as fisheries, tourism, and urban expansion.
In general, Pb was identified as the most accumulated metal, while Cd showed the lowest accumulation in shrimp. These findings align with earlier studies that reported high Pb concentrations in shrimp, crabs, fish, Ulva lactuca, mullet, and oysters from Pulicat Lake, India [42]. The variation in metal accumulation rates may be attributed to factors such as metabolic activity, exposure pathways, metal mobility, bioavailability, and the type of chelating agents present in the water and sediment of Pulicat Lake [42]. Furthermore, environmental variables like pH, temperature, salinity, nutrient levels, organic matter, organic carbon, and overall ecosystem conditions play a significant role in influencing metal bioavailability and bioaccumulation rates [42]. Ra et al. [8] reported that aquatic species, such as shrimp, frequently accumulate higher concentrations of heavy metals like Pb, Cd, arsenic, and Hg compared to other metals.
The main sources of contamination along the coast of Monastir could include the processing industries of fishing products, dairy industries, textile industries, and wastewater treatment plants. For the Bizerte Lagoon, the primary sources of pollution from these xenobiotics could include wastewater discharge from sewage treatment plants (both domestic and industrial), agricultural runoff (fertilizers and pesticides), the spreading of residual sludge from sewage treatment facilities, various industries (such as Bizerte Cement Company, the sugar refining plant in Bizerte, Tunisian Refining Industries in Bizerte, Tunisian Lubricants Company in Bizerte, metallurgical industries, STIR, SOTULUB, and the Tunisian Company for Mechanical and Naval Construction and Repair ‘SOCOMENA’), domestic heating (wood, coal, oil, or gas), automobile traffic (combustion of automotive fuel), incineration of household waste, and fishing activities. In contrast, since the Kerkennah Islands lack significant industrial activity and urban development, the primary sources of pollution by metals are likely to be traditional and illegal fishing activities, as well as oil-related industrial activities, including extraction and production. Consequently, the coastal environment of these islands is exposed to industrial effluents, atmospheric emissions, and crude oil, all of which may carry toxic pollutants. However, for all four studied sites, natural sources resulting from the alteration and weathering of rocks from the earth’s crust should not be overlooked.
The degree of heavy metal contamination in organisms can be assessed using the Pollution Index (PI) [43]. The PI offers an evaluation of the overall toxicity status of the sample, reflecting the contribution of the metals under study (Pb, Cd, Cu, Zn).
The PI values can be categorized into four pollution levels: PI < 0.2 (no major pollution), 0.2 < PI < 0.6 (minor pollution), 0.6 < PI < 1 (moderate pollution), and PI > 1 (severe pollution) [44]. Based on these classifications, the contamination level for Cd in most areas is considered minor pollution, with no major pollution observed in the Gulf of Gabes. For Cu and Zn, the contamination level across all sites is classified as no major pollution. Pb contamination is classified as moderate pollution in Bizerte Lagoon, Monastir Bay, and Kerkennah Island, while the Gulf of Gabes shows minor pollution.
Seafood, including pink shrimp, represents an important source of protein for human populations living near the Tunisian coasts. These populations may be at risk of exposure to elevated levels of metals, especially when consuming large quantities of seafood. To assess the safety of the metal levels found in Parapenaeus longirostris samples, the average values recorded in this study for the four heavy metals were compared with the threshold values established by international standards. Given the impact of metals on human health, the muscle tissue of shrimp is studied more extensively than other organs, as it represents the portion typically consumed [45].
To the best of our knowledge, there are currently no specific Tunisian food safety standards for metal concentrations in seafood. Therefore, the results obtained for the muscle samples were compared with limit values and guidelines reported in the literature for human consumption, based on wet weight measurements. To facilitate the comparison, the values were standardized to μg/g wet weight before analysis. In this study, the concentrations of Cd, Cu, Zn, and Pb in the red shrimp muscle did not exceed the permissible levels for crustaceans as established by European Community legislation [46], nor did they surpass the maximum permissible limits for crustaceans in Bangladesh, the European Union, New Zealand, or Turkey [45]. Moreover, their concentrations in all analyzed specimens were lower than the maximum limits recommended by the FAO and WHO in 1984 [47] (Cd: 1 mg/kg; Zn: 100 mg/kg; Pb: 2 mg/kg fresh weight). Thus, there is no serious health risk associated with the consumption of Cd, Cu, Zn, and Pb bioaccumulated in the analyzed shrimp species.
4.2. Human Health Risk Assessment
The comparison of the lower EDI values with the Provisional Tolerable Daily Intake (PTDI) thresholds for all analyzed heavy metals (expressed in µg kg body weight−1 day−1) indicates that the consumption of Parapenaeus longirostris does not pose any significant risk to consumers. The PTDI values are as follows: Cu: 500; Zn: 1000; Cd: 1; and Pb: 3.75 [48].
Although the contributions from the metals are minimal, they could become more significant if other food items consumed by adults also contain elevated levels of these metals. The results of this study showed that the EDI, EWI, and PTWI% for adults were all below the PTWI levels set by the FAO/WHO [49]. Based on these findings, the study recommends that children should consume no more than 8.38 g/day or 58.66 g/week of Parapenaeus longirostris muscle from Bizerte Lagoon, less than 9.20 g/day or 64.42 g/week from Monastir Bay, less than 9.04 g/day or 63.25 g/week from Kerkennah Island, and less than 12.93 g/day or 90.52 g/week from the Gulf of Gabes.
For adults, the recommended intake should be less than 39.11 g/day or 273.74 g/week from Bizerte Lagoon, less than 42.94 g/day or 300.61 g/week from Monastir Bay, less than 42.17 g/day or 295.18 g/week from Kerkennah Island, and less than 60.34 g/day or 422.41 g/week from the Gulf of Gabes.
The average Estimated Daily Intake and Estimated Weekly Intake values in this study are lower than the provisional tolerable weekly intake standards established by JECFA [50], suggesting that consuming the analyzed seafood species poses no health risks to humans.
Based on the data presented in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4, the daily consumption rate limits for contaminated shrimp from Bizerte Lagoon, based on non-carcinogenic effects, range from 0.14 to 21.21 kg/day for adults and from 0.03 to 4.55 kg/day for children. For Monastir Bay, the daily consumption rate limits range from 0.15 to 20.59 kg/day for adults and from 0.03 to 4.41 kg/day for children. For Kerkennah Island, the daily consumption rate limits range from 0.15 to 18.75 kg/day for adults and from 0.03 to 4.02 kg/day for children. In the Gulf of Gabes, the daily consumption rate limits range from 0.21 to 20.59 kg/day for adults and from 0.05 to 4.41 kg/day for children.
The findings showed that each metal’s individual mean HQ values were less than one (1), indicating no harmful impact on either adults or children consuming the studied shrimp species from all the investigated areas. In addition, the obtained HI values were lower than one, indicating non-carcinogenic combined effects. The CR values for both Cd and Pb were lower than the accepted range (10−4 to 10−6), indicating that consumption of shrimp from these four aquatic ecosystems poses no significant carcinogenic risk.
Based on the RR values, Pb exposure presents the greatest concern related to shrimp consumption among residents in all four study areas.
Cadmium is a highly toxic heavy metal classified as a human carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. It tends to accumulate in vital organs such as the kidneys and liver, leading to renal dysfunction and bone demineralization with prolonged exposure. Cd also bioaccumulates in aquatic organisms, posing a potential health hazard through seafood consumption. In this study, THQ values for Cd in both adults and children remained well below the USEPA safety threshold of 1, suggesting negligible non-carcinogenic risk. The cumulative HI, which accounts for the combined toxicity of all assessed metals including Cd, was also below 1 across all sites, further confirming the low overall health risk from shrimp consumption. Additionally, Cd concentrations in shrimp samples were below the maximum permissible limits established by international standards. Although the CR values for Cd fell within the acceptable range of 10−6 to 10−4, indicating a low carcinogenic threat, particular attention should be paid to children, who are more vulnerable to long-term toxic effects. These findings underscore the importance of ongoing monitoring and adherence to safe consumption levels to protect public health.
Copper is an essential trace element involved in crucial biological processes such as enzymatic activity and iron metabolism. However, excessive Cu intake may result in adverse health effects, including gastrointestinal distress, liver damage, and nephrotoxicity. In this study, THQ values for Cu in both adults and children remained below the USEPA threshold of 1, indicating low non-carcinogenic risk. The cumulative HI values, which include Cu exposure, were also below 1 across all age groups and sampling locations. Measured Cu concentrations were well within the maximum tolerable limits established by international health authorities. Since Cu is not classified as carcinogenic, a CR calculation was not applicable. These results suggest that Cu levels in shrimp from the study sites are within acceptable safety margins for human consumption.
Zinc is another essential micronutrient required for various physiological functions, including immune defense, DNA replication, and wound healing. Although Zn deficiency is a known health concern, overexposure can cause nausea, vomiting, and immune suppression. In this study, THQ values for Zn in both adults and children were all well below the USEPA risk threshold of 1. The cumulative HI remained under 1, indicating low risk from combined metal exposure. Moreover, Zn concentrations in shrimp did not exceed internationally accepted limits. As Zn is not considered carcinogenic, the CR metric was not applicable. These findings support the conclusion that Zn exposure from shrimp consumption poses no significant health risk.
Lead is a well-documented neurotoxicant with no known physiological benefit in humans. Chronic Pb exposure, especially in children, can impair cognitive development and cause lasting neurological damage. In this study, THQ values for Pb in both adults and children remained below the USEPA safety benchmark of 1, indicating a low non-carcinogenic risk. The overall HI, including Pb, was also below 1, suggesting acceptable cumulative exposure levels. Pb concentrations across all shrimp samples did not exceed the permissible limits defined by international guidelines. The CR values for Pb were within the tolerable range (10−6 to 10−4), indicating limited carcinogenic concern. Nonetheless, given the increased sensitivity of children to Pb toxicity, sustained surveillance and appropriate dietary recommendations remain essential.
The health risk assessment results indicate that the levels of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn in Parapenaeus longirostris from the Tunisian coast pose no significant non-carcinogenic or carcinogenic risks to human consumers. These findings carry important practical implications. From a public health perspective, the data support the continued consumption of this shrimp species from the studied regions, reassuring both consumers and public authorities. However, regular biomonitoring remains essential to detect any future increases in metal contamination, particularly in areas experiencing industrial or agricultural expansion.
For local fisheries, these results offer valuable insight into the current environmental quality and may help guide sustainable harvesting practices and export safety certification. Promoting responsible aquaculture and limiting pollution inputs (e.g., from fertilizers, urban runoff, or marine traffic) will be crucial in preserving this favorable status.
4.3. Comparison of Metal Concentrations Derived from Literature Data
The bioaccumulation of heavy metals in shrimp muscle has been investigated in several studies. To better illustrate and evaluate the impact of marine pollution and its consequences on marine organisms along the Tunisian coasts, we conducted a comparative study involving different shrimp species. These species are used as sentinel organisms to assess the contamination level of Parapenaeus longirostris in the studied sites.
Table 5 presents the concentrations of metals in shrimp muscle tissues from various regions worldwide (μg/g dry weight). The Zn levels observed in Parapenaeus longirostris in this study are comparable to those reported for Penaeus merguiensis from Indonesia [51] and Macrobrachium felicinum from Nigeria [52], but are lower than the values recorded for Penaeus monodon from Bangladesh [53], Palaemon longirostris from Pakistan [54], and P. monodon from Malaysia [55]. These discrepancies could reflect differences in industrialization levels, agricultural runoff, and urban wastewater management between regions. For instance, elevated Zn levels in South and Southeast Asia could be linked to intensive aquaculture practices and industrial effluents.

Table 5.
Metal concentrations in shrimp muscle from various regions worldwide (ug/g dry weight).
Likewise, Cu concentrations in our samples are lower than those found in Penaeus indicus from Egypt [56], P. indicus from India [57], and Litopenaeus stylirostris from the Gulf of California [58], but are comparable to those reported for Fenneropenaeus merguiensis from the Persian Gulf [59]. This variability may be attributed to regional differences in copper-based antifouling paint usage, mining runoff, or sewage discharge.
In terms of Pb, concentrations in our samples are within the range of values reported for Penaeus species from the Malay Peninsula [60], Parapenaeus longirostris from Algeria [61], and P. monodon from the Sundarbans, India [62], but are lower than those observed in Penaeus semisulcatus from Turkey [63]. The higher Pb levels in these latter regions are often linked to intense port activity, petrochemical discharges, and inadequate waste regulation.
Similarly, Cd levels in our samples are consistent with those reported for Metapenaeus ensis from China [64], although they are lower than concentrations found in P. californiensis from Mexico [65], Penaeus species from Kenya [66] and P. merguiensis from the Persian Gulf [67]. These differences may stem from variations in phosphate industry discharge, sediment characteristics, or regulatory effectiveness in managing cadmium emissions.
Overall, the observed discrepancies in metal concentrations emphasize the role of local anthropogenic pressures, environmental regulations, and ecological dynamics in shaping contamination profiles. The results from Tunisia contribute valuable reference data for the southern Mediterranean, a region where such assessments remain relatively scarce.
5. Conclusions
This study represents the first assessment of trace metal concentrations (Cd, Zn, Cu, and Pb) in the muscle tissue of Parapenaeus longirostris from four Tunisian coastal regions. The results revealed the presence of all four metals across the sites, with concentrations remaining below internationally accepted safety thresholds. P. longirostris continues to be a relevant bioindicator due to its ecological and commercial significance.
Although Pb was the most abundant metal detected, health risk assessments (THQ, HI, CR, EDI) indicated no significant carcinogenic or non-carcinogenic risk for both adults and children. Pollution indices also suggested low to moderate contamination levels, without reaching thresholds of severe pollution.
While this study provides insights into the levels and associated risks of selected heavy metals, it is important to acknowledge that mercury, a critical contaminant in seafood, was not analyzed due to analytical limitations. Future investigations should include Hg to ensure a more comprehensive and robust assessment of potential health risks. To safeguard public health and ensure sustainable seafood consumption, we recommend that public health authorities implement regular biomonitoring programs focusing on key commercial species like Parapenaeus longirostris, enforce stricter controls on industrial and urban discharges in coastal areas, establish national seafood safety guidelines aligned with international standards, and raise awareness among local consumers regarding safe consumption frequencies, particularly for vulnerable groups. Such measures would support early detection of environmental contamination, improve risk management strategies, and promote more informed and safer seafood consumption practices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: W.B.A.; supervision: W.B.A.; methodology: W.B.A., A.A. and M.M.; sample collection: K.R.; sampling preparation and instrumental analysis: W.B.A. and K.R.; formal analysis: W.B.A., A.A. and M.M.; writing—original draft, W.B.A.; writing—review and editing: W.B.A., A.A., K.R. and M.M.; project administration: W.B.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all members of the Life Sciences Department of the Faculty of Sciences of Gabes, University of Gabes, for providing reagents and scientific technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Cd | Cadmium |
| Cu | Copper |
| Pb | Lead |
| Zn | Zinc |
| Hg | Mercury |
| NIST | National Institute of Standards and Technology |
| LOD | Limit of Detection |
| RSD | Relative Standard Deviation |
| PI | Pollution Index |
| EDI | Estimated Daily Intake |
| EWI | Estimated Weekly Intake |
| %PTWI | Percentage of Provisional Tolerable Weekly Intake |
| MDI | Maximum Daily Intake |
| MWI | Maximum Weekly Intake |
| CRlim | Daily Intake Limit |
| CRmm | Monthly Consumption Rate Limit |
| THQ | Target Hazard Quotient |
| HI | Hazard Index |
| CR | Cancer Risks |
| RR | Relative Risk |
| EF | Exposure Frequency |
| ED | Exposure Duration |
| FIR | Food Ingestion Rate |
| CF | Conversion Factor |
| WAB | Weight of Average Body |
| TA | Total exposure time |
| USEPA | United States Environmental Protection Agency |
| IR | Ingestion Rate |
| BW | Body Weight |
| ARL | Acceptable Risk Level |
| CSF | Cancer Slope Factor |
| RfD | Oral Reference Dose |
| Tap | Average Time Span |
| MS | Meal Size |
| THQi | Target Hazard Quotient |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| LSD | Least Significant Difference |
| p-value | Probability value |
| STIR | Société Tunisienne des Industries de Raffinage |
| SOTULUB | Société Tunisienne de Lubrifiants |
| SOCOMENA | Société de Construction Mécanique et Navale |
| MPI | Metal Pollution Index |
References
- Mahmudiono, T.; Esfandiari, Z.; Zare, A.; Sarkhoshkalat, M.; Mehri, F.; Fakhri, Y. Concentration of Potentially Toxic Elements in Fillet Shrimps of Mediterranean Sea: Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Health Risk Assessment. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ameur, W.; Annabi, A.; Ben Said, S.; Marini, M. First Assessment of Consumer Health Risks from Metal Accumulation in Fish from the Bizerte and Ghar El Melh Lagoons: The Case of Sarpa salpa (Linnaeus, 1758). Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2025, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oros, A.; Galatchi, M. Long-Term Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation in Sprat (Sprattus sprattus) from the Romanian Black Sea: Ecological and Human Health Risks in the Context of Sustainable Fisheries. Fishes 2025, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.-H.; Wang, Z.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Qi, X.-H.; Cao, P.-T.; Li, Q.; Wang, W.-J.; Wang, P.; Yang, Y. Organ-Level Concentrations of Heavy Metals (Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd, Hg and Pb) in Five Aquatic Organisms from Lianyungang in China and Associated Heath Risk Assessment. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 139, 107089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, K.; Charoenpong, C.; Bureekul, S.; Wang, X.; Sompongchaiyakul, P. Heavy Metal Contamination in Marine Fish from the Andaman Sea: Influence of Habitat and Health Risk Assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 210, 117299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosn, M.; Mahfouz, C.; Chekri, R.; Khalaf, G.; Guérin, T.; Jitaru, P.; Amara, R. Seasonal and Spatial Variability of Trace Elements in Livers and Muscles of Three Fish Species from the Eastern Mediterranean. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12428–12438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okbah, M.A.A.; Dango, E.A.S.; Zokm, G.M.E. Heavy Metals in Fish Species from Mediterranean Coast, Tripoli Port (Libya): A Comprehensive Assessment of the Potential Adverse Effects on Human Health. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2018, 22, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, W.-J.; Yoo, H.J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Yun, T.; Soh, B.; Cho, S.Y.; Joo, Y.; Lee, K.-W. Heavy Metal Concentration According to Shrimp Species and Organ Specificity: Monitoring and Human Risk Assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Miras, J.J.; Sanchez-Muros, M.J.; Renteria, P.; De Carrasco, C.G.; Roca-Perez, L.; Boluda-Navarro, M.; Pro, J.; Martín, J.A.R. Potentially Toxic Element Bioaccumulation in Consumed Indoor Shrimp Farming Associated with Diet, Water and Sediment Levels. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 121794–121806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dghim, A.; Ben Ameur, W.; Annabi, A. Assessment of the Accumulation of Trace Metals and Oxidative Stress Response Biomarkers in the Portunid Portunus segnis. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Luo, X.; Yu, D.; He, C.; Cao, W.; He, L.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Fang, G. Risk Assessment of As, Cd, Cr, and Pb via the Consumption of Seafood in Haikou. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, A.; Qazi, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Ahmad, O.; Nazir, M.M.; Bhatti, M.B.; Hussain, N.; Sherzada, S. Heavy Metals Concentration and Human Health Risk Assessment in Selected Shrimp Species of Pakistan. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2025, 18, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.B.; Bhuiyan, N.Z.; Kasem, A.; Hossain, M.K.; Sultana, S.; Nur, A.-A.U.; Yu, J.; Albeshr, M.F.; Arai, T. Heavy Metals in Four Marine Fish and Shrimp Species from a Subtropical Coastal Area: Accumulation and Consumer Health Risk Assessment. Biology 2022, 11, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Hossain, M.B.; Choudhury, T.R.; Yu, J.; Rana, M.S.; Noman, M.A.; Hosen, M.M.; Paray, B.A.; Arai, T. Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Cultured Shrimp and Aquaculture Sludge. Toxics 2022, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayati, N.V.; Prudent, P.; Asia, L.; Vassalo, L.; Torre, F.; Widowati, I.; Sabdono, A.; Syakti, A.D.; Doumenq, P. Assessment of the Ecological and Human Health Risks from Metals in Shrimp Aquaculture Environments in Central Java, Indonesia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 41668–41687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Dong, K.F.; Xiao, G.; Ma, D. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Aquatic Organisms (Fishes, Shrimp and Crabs) and Health Risk Assessment in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 159, 111505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skordas, K.; Lolas, A.; Gounari, C.; Georgiou, K.; Neofitou, N.; Vafidis, D. Trace Element Content and Potential Human Health Risk from Consumption of the Deep-Water Rose Shrimp Parapenaeus longirostris (Crustacea: Decapoda) from Pagasitikos Gulf, Greece. J. Chem. Health Risks 2022, 12, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaaboub, N.; Martins, M.V.A.; Terroso, D.L.; Helali, M.A.; Béjaoui, B.; El Bour, M.; Boukef-BenOmrane, I.; Pereira, A.L.; Dardon, U.; Ennouri, R.; et al. Geochemical and mineralogical fingerprints of the sediments supply and early diagenetic processes in the Bizerte Lagoon (Tunisia). J. Sediment. Environ. 2016, 1, 432–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ameur, W.; Hanen, G.; Ben Hassine, S.; Safouen, G.; El Megdiche, Y.; Mhadhbi, T.; Annabi, A.; Touil, S.; Driss, M.R. Bioaccumulation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Solea Solea from Bizerte and Ghar El Melh Lagoons (Tunisia) and Human Health Risk Assessment. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2021, 56, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MeHSIP-PPIF (2013) Études de Faisabilité—Dépollution Intégrée du lac de Bizerte. Mediterranean Hot Spot Investment Programme—Project Preparation and Implementation Facility, Technical Assistance Funded by the European Union—FEMIP Support Fund. Final Version Published September 2013. Available online: http://www.ecopact.tn/sites/default/files/2022-05/Etude-de-Faisabilite-Bizerte.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Khammassi, M.; Jourde, J.; Zaabar, W.; Laabidi, S.; Sauriau, P.-G.; Achouri, M.S. Inventory and New Records of Benthic Amphipods from Macrophytes and Fine Sand Communities of the Bizerte Lagoon (Tunisia, SW Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2019, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ameur, W.; El Megdiche, Y.; Ennaceur, S.; Mhadhbi, T.; Ben Hassine, S.; Annabi, A.; De Lapuente, J.; Driss, M.R.; Borràs, M.; Eljarrat, E. Biomarkers Responses and Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Their Methoxylated Analogs Measured in Sparus aurata from the Lagoon of Bizerte, Tunisia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 38618–38632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdaoui, B.; Ennouri, R.; Fatnassi, M.; Zarrouk, H.; Romdhane, N.; Chalghaf, M.; Mili, S. Review of the Situation of Tunisian Lagoon of Bizerta Using Marine Spatial Planning as a Key to Sustainable Blue Growth. J. Biomed. Res. Environ. Sci. 2022, 3, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karray, S. Etude Écotoxicologique et Phylogéographique de la Coque Cerastoderma glaucum Issue du Golfe de Gabès: Réponse Adaptative (In Situ et In Vivo) au Stress Métallique et Structure Génétique. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Sfax, Sfax, Tunisie, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chouba, L.; Mzoughi-Aguir, N. Les métaux traces (Cd, Pb, Hg) et les hydrocarbures totaux dans les sédiments superficiels de la frange côtière du golfe de Gabès. INSTM Bull. Mar. Freshw. Sci. 2006, 33, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiari, N.; Atoui, A.; Khalil, N.; Charef, A.; Aleya, L. Dynamics of Sediments along with Their Core Properties in the Monastir-Bekalta Coastline (Tunisia, Central Mediterranean). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 134, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahim, M.; Atoui, A.; Ben Ali, M.R. Sedimentary Dynamics in Monastir Bay of the Tunisian Water. INSTM Bull. Mar. Freshw. Sci. 2017, 44, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouchene, K.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Ksibi, M. Types, Occurrence, and Distribution of Microplastics and Metals Contamination in Sediments from South West of Kerkennah Archipelago, Tunisia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 46477–46487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, A.; El Mouadeb, R.; Herrel, A. Distinctive Accumulation Patterns of Heavy Metals in Sardinella aurita (Clupeidae) and Mugil Cephalus (Mugilidae) Tissues. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 2623–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebiyi, F.M.; Ore, O.T.; Ogunjimi, I.O. Evaluation of Human Health Risk Assessment of Potential Toxic Metals in Commonly Consumed Crayfish (Palaemon hastatus) in Nigeria. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, M.; Akbari, E.; Amrane, A.; Jafari, S.J.; Eslami, H.; Hoseinzadeh, E.; Zarrabi, M.; Salimi, J.; Sayyad-Arbabi, M.; Taghavi, M. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Intake Due to Fish Consumption in the Sistan Region, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, H.; Kurhaluk, N.; Kasiyan, O.; Kamiński, P. Dietary Nutrients and Health Risks from Exposure to Some Heavy Metals through the Consumption of the Farmed Common Carp (CYPRINUS CARPIO). J Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Integrated Risk Information System. 2008. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/risk/recordisplay.cfm?deid=2776 (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Mohiuddin, M.; Hossain, M.B.; Ali, M.M.; Kamal Hossain, M.; Habib, A.; Semme, S.A.; Rakib, M.R.J.; Rahman, M.A.; Yu, J.; Al-Sadoon, M.K.; et al. Human Health Risk Assessment for Exposure to Heavy Metals in Finfish and Shellfish from a Tropical Estuary. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 102035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakma, S.; Rahman, M.A.; Jaman, M.N.; Al-Azim; Nag, S.K.; Ali, M.K.; Hoque, M.S.; Chakma, K. Assessing Trace Elements Bioaccumulation in Coastal River Fish and Shellfish: Implications for Human Health and Risk Evaluation. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2025, 203, 1859–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Guidance for Assessing Chemical Contamination Data for Use in Fish Advisories II Risk Assessment and Fish Consumption Limits. EPA/823–B94-004. United States Environmental Protection Agency Washington. 2000. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-06/documents/volume2.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Abdel-Kader, H.H.; Mourad, M.H. Estimation of Cadmium in Muscles of Five Freshwater Fish Species from Manzalah Lake, and Possible Human Risk Assessment of Fish Consumption (Egypt). Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berhanu, G.; Lemma, H.; Mekonnen, S.; Dadi, D. Heavy Metals in Wastewater and Fish Collected from Waste Stabilization Pond and Human Health Risks in Southwestern Ethiopia. Front. Environ. Health 2024, 3, 1386827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbinah, R.T.; Boadi, N.O.; Saah, S.A.; Agorku, E.S.; Badu, M.; Kortei, N.K. Cancer Risk from Heavy Metal Contamination in Fish and Implications for Public Health. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 24162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Singh, A.K. Human Health Risk and Ecological Risk Assessment of Metals in Fishes, Shrimps and Sediment from a Tropical River. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 2349–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demissie, S.; Mekonen, S.; Awoke, T.; Teshome, B.; Mengistie, B. Examining Carcinogenic and Noncarcinogenic Health Risks Related to Arsenic Exposure in Ethiopia: A Longitudinal Study. Toxicol. Rep. 2024, 12, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batvari, B.P.D.; Sivakumar, S.; Shanthi, K.; Lee, K.-J.; Oh, B.-T.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Kamala-Kannan, S. Heavy Metals Accumulation in Crab and Shrimps from Pulicat Lake, North Chennai Coastal Region, Southeast Coast of India. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2016, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahity, T.; Islam, M.R.U.; Bhuiyan, N.Z.; Choudhury, T.R.; Yu, J.; Noman, M.A.; Hosen, M.M.; Quraishi, S.B.; Paray, B.A.; Arai, T.; et al. Heavy Metals Accumulation in Tissues of Wild and Farmed Barramundi from the Northern Bay of Bengal Coast, and Its Estimated Human Health Risks. Toxics 2022, 10, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, H. The Size Screening Could Greatly Degrade the Health Risk of Fish Consuming Associated to Metals Pollution—An Investigation of Angling Fish in Guangzhou, China. Toxics 2023, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytekin, T.; Kargın, D.; Çoğun, H.Y.; Temiz, Ö.; Varkal, H.S.; Kargın, F. Accumulation and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Tissues of the Shrimp and Fish Species from the Yumurtalik Coast of Iskenderun Gulf, Turkey. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 364, 5–24. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2006:364:0005:0024:EN:PDF (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Biswas, C.; Soma, S.S.; Rohani, M.F.; Rahman, M.H.; Bashar, A.; Hossain, M.S. Assessment of heavy metals in farmed shrimp, Penaeus monodon sampled from Khulna, Bangladesh: An inimical to food safety aspects. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaansa-Ansah, E.E.; Nti, S.O.; Opoku, F. Heavy Metals Concentration and Human Health Risk Assessment in Seven Commercial Fish Species from Asafo Market, Ghana. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO. Summary of Evaluations Performed by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA 1956-2003)(First through Sixty First Meetings); ILSI Press International Life Sciences Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- JECFA. Summary and Conclusions of the 61st Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA); JECFA/61/SC; JECFA: Rome, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Soegianto, A. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Some Commercial Animals Caught from Selected Coastal Waters of East Java, Indonesia. Res. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2008, 4, 881–885. [Google Scholar]
- Opuene, K.; Agbozu, I. Relationships Between Heavy Metals in Shrimp (Macrobrachium felicinum) and Metal Levels in The Water Column and Sediments of Taylor Creek. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2008, 2, 343–348. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.; Khan, Y. Trace metals in Penaeid shrimp and Spiny lobster from the Bay of Bengal. Sci. Asia 2001, 27, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miramand, P.; Guyot, T.; Rybarczyk, H.; Elkaim, B.; Mouny, P.; Dauvin, J.C.; Bessineton, C. Contamination of the Biological Compartment in the Seine Estuary by Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn. Estuaries 2001, 24, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Jusoh, N.R.; Ghani, I.A. Trace Metal Concentrations in Marine Prawns off the Malaysian Coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1995, 31, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahdy, H.H.H.; Abdallah, A.M.; Tayel, F. Assessment of Heavy Metals and nonessential content of some edible and soft tissues. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2007, 33, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurti, J.R.V.N. Concentration of metals in shrimps and crabs from Thane- Bassein creek system, Maharastra. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 1999, 28, 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Frías-Espericueta, M.G.; Izaguirre-Fierro, G.; Valenzuela-Quiñonez, F.; Osuna-López, J.I.; Voltolina, D.; López-López, G.; Muy-Rangel, M.D.; Rubio-Castro, W. Metal Content of the Gulf of California Blue Shrimp Litopenaeus stylirostris (Stimpson). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 79, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baboli, M.J.; Velayatzadeh, M. Determination of heavy metals and trace elements in the muscles of marine shrimp, Fenneropenaeus merguiensis from Persian Gulf, Iran. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2013, 23, 786–791. [Google Scholar]
- Everaarts, J.M.; Boon, J.P.; Kastoro, W.; Fischer, C.V.; Razak, H.; Sumanta, I. Copper, Zinc and Cadmium in Benthic Organisms from the Java Sea and Estuarine and Coastal Areas around East Java. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1989, 23, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdennour, C.; Smith, B.D.; Boulakoud, M.S.; Samraoui, B.; Rainbow, P.S. Trace metals in marine, brackish and freshwater prawns (Crustacea, Decapoda) from northeast Algeria. Hydrobiologia 2000, 432, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guhathakurta, H.; Kaviraj, A. Heavy Metal Concentration in Water, Sediment, Shrimp (Penaeus monodon) and Mullet (Liza parsia) in Some Brackish Water Ponds of Sunderban, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çoğun, H.; Yüzereroğlu, T.A.; Kargin, F.; Firat, Ö. Seasonal Variation and Tissue Distribution of Heavy Metals in Shrimp and Fish Species from the Yumurtalik Coast of Iskenderun Gulf, Mediterranean. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 75, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, C.C.M.; Li, X.D.; Zhang, G.; Wong, C.S.C.; Zhang, W.L. Heavy Metal and Pb Isotopic Compositions of Aquatic Organisms in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 138, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez-Osuna, F.; Tron-Mayen, L. Distribution of Heavy Metals in Tissues of the Shrimp Penaeus californiensis from the Northwest Coast of Mexico. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1995, 55, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everaarts, J.M.; Nieuwenhuize, J. Heavy Metals in Surface Sediment and Epibenthic Macroinvertebrates from the Coastal Zone and Continental Slope of Kenya. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1995, 31, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourang, N.; Dennis, J.H. Distribution of Trace Elements in Tissues of Two Shrimp Species from the Persian Gulf and Roles of Metallothionein in Their Redistribution. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everaarts, J.M.; Swennen, C. Heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Cd, Pb) in some benthic invertebrate species and in sediment from three coastal areas in Thailand and Malaysia. Sci. Asia 1987, 13, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, F.G.; Sharma, V.K.; Mendoza, Q.A.; Hernandez, R. Metals in Fish and Shrimp of the Campeche Sound, Gulf of Mexico. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 67, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell, G.; Ramos, C.; Tarazona, J.V. Heavy Metals in Shrimp Culture Areas from the Gulf of Fonseca, Central America. II. Cultured Shrimps. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1998, 60, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Salam, H.; Hamdi, S.A.H. Heavy Metals Monitoring Using Commercially Important Crustacean and Mollusks collected from Egyptian and Saudi Arabia Coasts. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2014, 2, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abdennour, C. Copper, zinc and haemocyanin concentrations in four caridean decapods (Crustacea): Size relationships. Hydrobiologia 1997, 346, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, L.; Goyette, D. Metals in Northeast Pacific Coastal Sediments and Fish, Shrimp, and Prawn Tissues. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1989, 20, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).