Abstract
There are a variety of hydrogel-based bioinks commonly used in three-dimensional bioprinting. In this study, in the form of patent analysis, the state of the art has been reviewed by introducing what has been patented in relation to hydrogel-based bioinks. Furthermore, a detailed analysis of the patentability of the used hydrogels, their preparation methods and their formulations, as well as the 3D bioprinting process using hydrogels, have been provided by determining publication years, jurisdictions, inventors, applicants, owners, and classifications. The classification of patents reveals that most inventions intended for hydrogels used as materials for prostheses or for coating prostheses are characterized by their function or properties Knowledge clusters and expert driving factors show that biomaterials, tissue engineering, and biofabrication research is concentrated in the most patents.
1. Introduction
There are a variety of hydrogels commonly used in three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting, which is a process involving the deposition of cell-laden hydrogels (or bioinks) on a substrate (Figure 1). Hydrogels are synthetic matrices made up of a network of hydrophilic polymers that absorb water and/or biological fluids. They can be created from a large number of water-soluble materials, including synthetic polymers (e.g., polyethylene glycol, polylactic acid, etc.), proteins (e.g., collagen, gelatin, etc.), and polysaccharides (e.g., alginate, hyaluronic acid, etc.) [,,,].
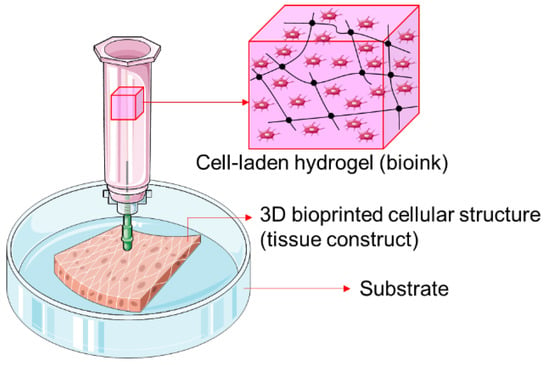
Figure 1.
Schema of 3D bioprinting process involving the deposition of cell-laden hydrogels (or bioinks) on a substrate to create 3D cellular structures for tissue engineering applications.
The 3D structure of these hydrogels is due to crosslinking, which forms an insoluble macromolecular network in the environmental fluid (Figure 2). The resemblance to different biological tissues, due to the elasticity and the presence of a large amount of water, allows the use of hydrogels in the regeneration of several types of damaged tissues (e.g., fibrin hydrogel is seeded with neural cells to regenerate brain tissue, keratinocytes are seeded in collagen hydrogel to regenerate skin tissue, etc.) [,].
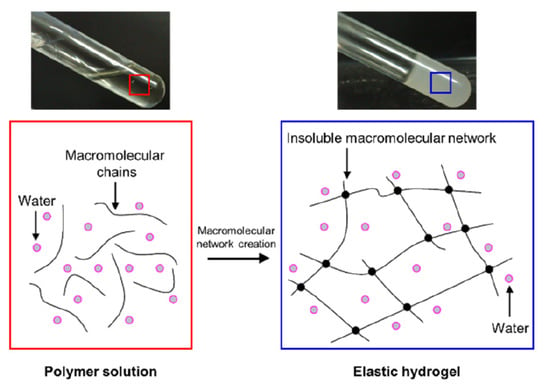
Figure 2.
Schema of hydrogel crosslinking, which forms an insoluble macromolecular network in the environmental fluid.
The first patent application concerning hydrogel-based bioinks was filed in 2005, and then granted in 2012 []. Through this patent, Forgacs et al. have invented an apparatus comprising, among others, a cartridge comprising one or more cell aggregates. Inventors have then proved the concept by bioprinting a fused ring structure by using cell aggregates and poly(N-(hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide)-based hydrogel as bioink [].
To promote the sufficiency of bioinks in 3D bioprinting, several researchers have investigated pathways to enhance bioink properties to meet bioprinting requirements, with several hydrogels developed. Research on hydrogels as bioinks is developing rapidly through the innovation and improvement of raw materials (synthetic and natural polymers), synthesis, and methods of preparation, as well as formulations and biofabrication processes. Moreover, more than 100 organizations (universities, academic institutes, companies, foundations, government bodies, etc.) around the world are currently involved in patent activity and filings concerning hydrogel-based bioinks. This trend is justified by the several advantages that hydrogels offer for bioprinting and biomedical applications. This is also evident from the increase in the number of patent applications filed each year worldwide in research and development in this area. For example, patent applications related to hydrogel-based bioinks have increased from 3 to 103, during the period from 2013 to 2020, respectively [].
This work in the form of patent analysis, which is a family of techniques for studying the information present within and attached to patents, describes the state of the art by introducing what has been innovated and patented in relation to hydrogel-based bioinks regarding to used hydrogels, their preparation methods and their formulations, as well as the 3D bioprinting process using hydrogels. Furthermore, this work gives a competitive analysis of the past, present and future trends in the hydrogel-based bioinks and leads to various recommendations that could help one to plan and innovate research strategy.
2. Resources and Analysis
2.1. Resources and Research Methods
The supported field codes used in this study were based on the Patentscope search service of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) [,] and The Lens patent data set []. During the search, different keywords and related terms were used, and patents were searched according to title, abstract, and claims. The search was then filtered to include only documents with an application date until 2020.
2.2. Analysis of the Patentability of Hydrogel-Based Bioinks
The search indicates that 119 patent documents have been found. Generally, it encompasses patent applications and granted patents. In relation to hydrogel-based bioinks, the found patent documents are classed as: 103 patent applications and 16 granted patents.
Here, we will review the state of the art by introducing what has been patented in relation to hydrogel-based bioinks. We then provide a detailed analysis of the patentability of the used hydrogels, their preparation methods and their formulations, as well as the 3D bioprinting process, following these sections:
- Publication year;
- Jurisdictions;
- Inventors;
- Applicants;
- Owners;
- Patent classifications.
3. Results
3.1. Publication Year
The date on which a patent document is published, thereby making it part of the state of the art. For hydrogel-based bioinks, 119 patent documents have been found until 2020. The year 2013 saw the registration of three patent documents only (exclusively patent applications). However, the year 2020 recorded 31 patent documents (24 patent applications and 7 granted patents). The maximum number of patent applications (25) was recorded in 2019. However, the maximum number of granted patents (7) was recorded in 2020.
3.2. Jurisdictions
An applicant, or first mentioned applicant in the case of joint applicants, can file an application for patent at the appropriate Patent Office (e.g., European Patent Office (EPO), United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO), Korean Intellectual Property Office (KIPO), China National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA), etc.) under whose jurisdiction he normally resides, has his domicile, has a place of business, or the place from where the invention actually originated. For hydrogel-based bioinks, the top 10 jurisdictions of filled patents until 2020 are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Jurisdictions (top 10) of resulted patents as a function of patent documents and patent contribution (%) of hydrogel-based bioinks.
The United States through the USPTO encompasses 32 patent documents, with a higher patent contribution per total of ~26.9%. On the other hand, the global system for filing patent applications, known as the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) and administered by WIPO, encompasses 26 patent documents with a patent contribution per total of ~21.8%, as well as China through the CNIPA, encompasses 25 patent documents with a patent contribution per total of ~13.4%. Finally, the EPO, through which patent applications are filed regionally (Europe), encompasses six patent documents with a patent contribution per total of ~5%.
3.3. Inventors
The inventor is a natural person designated for a patent application. In several cases, the inventor can also be the applicant, and there may be more than one inventor per patent application [].
For hydrogel-based bioinks, the top 10 inventors until 2020 are presented in Table 2. The inventors, Murphy Keith and Dorfman Scott, from the United States, are ranked as the co-first inventors, having recorded 18 patent documents each. In second place, the inventor, Law Richard Jin, from the United States, has recorded 13 patent documents.

Table 2.
Inventors (top 10) of resultant patents as a function of patent documents for hydrogel-based bioinks.
All the found patent documents of these three above inventors concern the healthcare company Organovo INC (Solana Beach, CA, USA) as applicants and/or owners. It specializes in the design and development of human tissues for in vitro and therapeutic applications, such as preclinical testing and drug discovery research, by utilizing 3D bioprinting technology.
3.4. Applicants
The applicant is a person (i.e., a natural person) or an organization (i.e., a legal entity) that has filed a patent application. In several cases, the applicant can also be the inventor, and there may be more than one applicant per patent application [].
For hydrogel-based bioinks, the top 10 applicants until 2020 are presented in Table 3. Regarding this top 10, all applicants are considered as organizations: companies, foundations, academic institutions, or universities.

Table 3.
Applicants (top 10) of resultant patents as a function of patent documents for hydrogel-based bioinks.
The company Organovo INC (Solana Beach, CA, USA), as a legal entity, is ranked as the first applicant who has recorded 19 patent documents. In second place, the company Cellink AB (Gothenburg, Sweden), as a legal entity, has recorded 10 patent documents. Thirdly, the company Inventia Life Science PTY LTD (Alexandria, Australia), as a legal entity, has recorded seven patent documents.
3.5. Owners
The assignee, or patent owner, is a person (i.e., a natural person) or an organization (i.e., a legal entity) to whom the inventor or applicant assigned the right to a patent. The patent owner has the right, for a period limited to the duration of the patent term, to protect his brainchild. The patent system prohibits others from making, using, or selling the invention without the inventor’s permission, or it requires others to use the invention under terms agreed upon with the inventor [].
For hydrogel-based bioinks, the top 10 owners until 2020 are presented in Table 4. Regarding this top 10, all owners are considered organizations: companies, universities, foundations, or government bodies.

Table 4.
Owners (top 10) of resultant patents as a function of patent documents for hydrogel-based bioinks.
The company Organovo INC (Solana Beach, CA, USA), as a legal entity, is ranked as the first owner, having recorded eight patent documents. In second place, the company Cellink AB (Gothenburg, Sweden), as a legal entity, has recorded three patent documents. As for the podium of the third place, it is shared between eight legal entities that are: Inventia Life Science PTY LTD (Alexandria, Australia), Medical University of South Carolina (Charleston, SC, USA), Advanced Solutions Life Sciences LLC (Louisville, KY, USA), Texas A&M University System (College Station, TX, USA), MUSC Foundation for Research Development (Charleston, SC, USA), Revotek CO LTD (Lewes, DE, USA), Board of Regents of the University of Texas System (Austin, TX, USA), and Curators of the University of Missouri (Columbia, MO, USA), with two patent documents each.
3.6. Patent Classifications
The International Patent Classification (IPC) is a hierarchical system in the form of codes, which divides all technology areas into a range of sections, classes, subclasses, groups, and subgroups. It is an international classification system that provides standard information to categorize inventions and evaluate their technological uniqueness [,].
For hydrogel-based bioinks, the top 10 IPC codes until 2020 are presented in Table 5. The most IPC code corresponds to A61K9/52 which is a subgroup of materials for prostheses or for coating prostheses characterized by their function or physical properties. More specifically, it concerns hydrogels or hydrocolloids. This subgroup recorded, alone, 38 patent documents. The second IPC code corresponds to A61L27/38, which is a subgroup of materials for prostheses or for coating prostheses containing ingredients of undetermined constitution or reaction products thereof, such as animal cells, has recorded 34 patent documents.

Table 5.
IPC codes (top 10) of resulted patents concerning hydrogel-based bioinks as a function of patent documents with the meaning of each IPC code [].
4. Conclusions
This patent analysis concerned only the innovation and improvement of hydrogel-based bioinks until 2020. A detailed analysis of the patentability of the used hydrogels, their preparation methods and their formulations, as well as the 3D bioprinting process using hydrogels, have been provided. During the search, 119 patent documents were found (103 patent applications and 16 granted patents). The United States was ranked first with 32 patent documents, and 2020 was the year with the maximum number of patent documents (31).
The innovation and improvement of hydrogel-based bioinks concerned raw materials (synthetic and natural polymers), synthesis and methods of preparation, as well as formulations and fabrication processes. Based on the patent classification, all filled patents and most inventions are intended for materials for prostheses or for coating prostheses, characterized firstly by their function or physical properties, such as hydrogels or hydrocolloids, and containing secondly ingredients of undetermined constitution or reaction products thereof, such as animal cells. Knowledge clusters and expert driving factors show that research based on additive manufacturing products, processes, and materials specially adapted for additive manufacturing is concentrated in the most patents.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/IOCPS2021-11239/s1.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available within this article content.
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges the World Intellectual Property Organization for the Patentscope search service and the Cambia Institute for The Lens patent data set used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares that this article content has no conflict of interest. The author has no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in this article.
References
- Zhang, S.; Huang, D.; Lin, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X. Cellulose Nanocrystal Reinforced Collagen-Based Nanocomposite Hydrogel with Self-Healing and Stress-Relaxation Properties for Cell Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2400–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehm, K.D.; Madihally, S.V. Bioprinted chitosan-gelatin thermosensitive hydrogels using an inexpensive 3D printer. Biofabrication 2017, 10, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, L.K.; Huebner, P.; Fisher, M.B.; Spang, J.T.; Starly, B.; Shirwaiker, R.A. 3D-Bioprinting of Polylactic Acid (PLA) Nanofiber–Alginate Hydrogel Bioink Containing Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1732–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skardal, A.; Zhang, J.; Prestwich, G.D. Bioprinting vessel-like constructs using hyaluronan hydrogels crosslinked with tetrahedral polyethylene glycol tetracrylates. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6173–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Abelseth, E.; de la Vega, L.; Willerth, S.M. Bioprinting a novel glioblastoma tumor model using a fibrin-based bioink for drug screening. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 12, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.; Singh, G.; Trasatti, J.P.; Bjornsson, C.; Xu, X.; Tran, T.N.; Yoo, S.-S.; Dai, G.; Karande, P. Design and Fabrication of Human Skin by Three-Dimensional Bioprinting. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2013, 20, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forgacs, G.; Jakab, K.; Neagu, A.; Mironov, V. Self-assembling Cell Aggregates and Methods of Making Engineered Tissue Using the Same. Granted Patent U.S. 8241905 B2, 14 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- World Intellectual Property Organization. Patentscope. Available online: https://patentscope.wipo.int (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- World Intellectual Property Organization. Patentscope Fields Definition. Available online: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/help/fieldsHelp.jsf (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Cambia Institute. The Lens Patent Data Set. Version 8.0.14. Available online: https://www.lens.org (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- European Patent Office. Espacenet Glossary. Version 1.24.1. Available online: https://worldwide.espacenet.com/patent (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- World Intellectual Property Organization. What Is Intellectual Property? Frequently Asked Questions: Patents. Available online: https://www.wipo.int/patents/en/faq_patents.html (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- World Intellectual Property Organization. IPC Publication. IPCPUB v8.5. Available online: https://www.wipo.int/classifications/ipc/ipcpub (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- World Intellectual Property Organization. Guide to the International Patent Classification (IPC). Available online: https://www.wipo.int/edocs/pubdocs/en/wipo_guide_ipc_2020.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).