This review addresses current innovative approaches in the generation of waste-derived catalysts for chemical transformations.
Table 1 gives an overview of the presented articles. We divided the articles according to the waste type, recycled catalyst, recycling method, and applied catalytic reaction. The waste type is organized as e-waste, spent lithium-ion batteries, and wastewater from different sources. The recycled catalyst systems range from noble metals such as Au, Pd, and Ru to transition metals (oxides) such as Cu, Ni, CuNi, and LiNi
xMn
yCo
z oxides from used lithium-ion batteries. The methods for recycling and extracting the catalyst span a wide spectrum, from chemical, physical and mechanical processing to thermal treatment, and complexation-based methods, and methods based on functionalized nanoparticles. The applied reactions catalyzed by the recycled catalysts cover different organic syntheses such as cross-coupling, oxidation, or reduction.
2.1. Catalysts from e-Waste
E-waste covers a wide range of discarded electronic and electrical equipment and its components. It ranges from consumer electronics such as televisions and smartphones to more complex and larger equipment such as laptops, desktop computers, and servers. The metals found in these devices vary considerably in both composition and quantity. Base metals, including Al, Fe, Cu, Sn, Zn, Ni, and Pb, are ubiquitous in all forms of electronic waste. They are commonly found in wiring, structural elements, power supplies, and printed circuit boards (PCBs). In contrast, precious metals such as Au, Ag, and Pd are more selectively localized, mainly in specialized components such as electrical contacts, PCBs, and capacitors. The following studies have explored innovative methods to recover such metals and utilize them for catalysis.
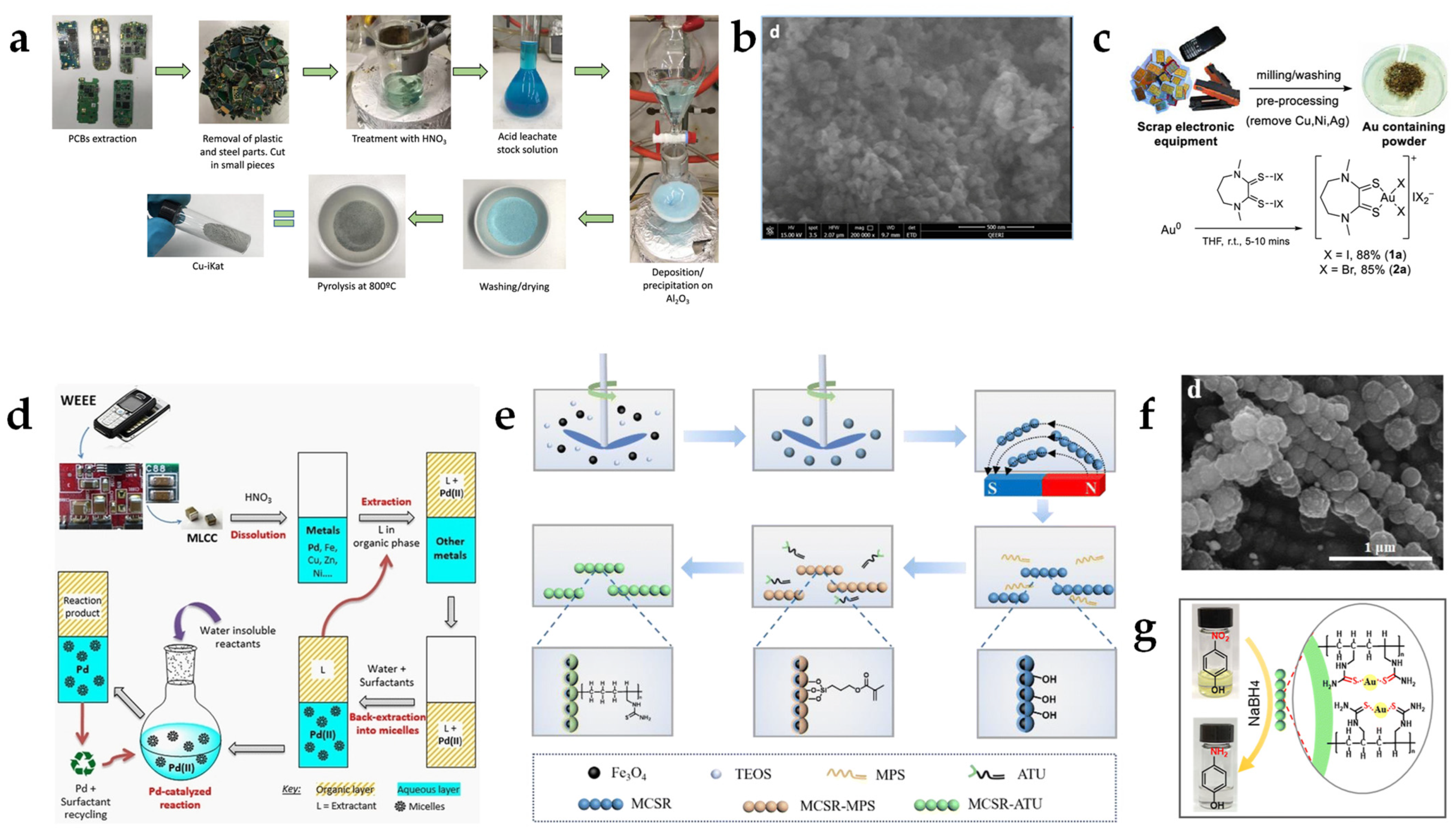
Ryabchuk et al. developed a feasible route for the valorization of base metals from low-quality PCBs that have low amounts of precious metals [
25]. The approach involved incorporating the abundant Cu present in PCBs into an alumina support and using this system as a catalyst. After leaching different metals such as Cu, Ni, Zn, Fe, Pb, Ag, and Sn from PCBs with 5 M HNO
3, non-noble metals were selectively deposited onto an alumina substrate by dropping the metal solution into an alkaline γ-Al
2O
3 suspension (
Figure 1a,b). Subsequent pyrolysis at 800 °C produced a Cu-based γ-Al
2O
3 catalyst with a Cu content of 5.7 wt%. The catalyst showed high catalytic activity for several reactions, including the hydrogenation of N-heterocycles and acetophenones, as well as deoxygenation and methanol synthesis via formamide hydrogenation, with moderate-to-high yields depending on the reaction investigated. Other synthesized supported catalysts, such as Cu on TiO
2, SiO
2, or MgO, showed no or negligible activity. In comparison to a CuO/γ-Al
2O
3 catalyst, the developed catalyst showed similar activity while requiring higher temperatures and higher catalyst loading. A shortcoming of this catalyst was that its catalytic activity dropped rapidly to 0% after its third use due to Cu leaching. Interestingly, the residual undeposited solid e-waste still contained precious metals, which could be utilized in further recycling processes.
McCarthy et al. have recently demonstrated that catalyst recovery must not focus primarily on recovering the metal of interest, but that complexed metal ions recovered from e-waste can also be used as effective homogeneous catalysts for various chemical reactions [
26]. The authors showcased this by extracting Au(III) with different complexing agents from old subscriber identity module (SIM) cards using a mild and efficient leaching method (
Figure 1c). The extraction process consisted of stripping the organic parts from SIM cards using tetrahydrofuran (THF), followed by the sequential removal of co-incorporated Cu and Ni metals. While Cu was oxidized with H
2O
2 in an ammoniacal sulfate solution, Ni was oxidized with HCl. Various synthesized dithiooxamide-derived leaching agents were evaluated to extract Au(III) as a complex under mild conditions. Further refining to recover elemental Au from the Au(III) complexes would not be economically feasible, according to the authors. Instead, the Au(III) complex was utilized directly as a catalyst. The catalyst’s efficacy was evaluated for various reactions, such as the cyclization of propargylic amides, the condensation of acetylacetone and
o-iodoanilin, addition reactions of electron-rich arenes and α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds, and oxidative C–C couplings of aryl silanes and arenes. For example, the cyclization reactions showed comparable yields to a benchmark catalyst after the use of an additive during the synthesis. The estimated cost of the recovered Au(III) catalyst was estimated to be less than half of a comparable commercially available catalyst (AuCl
3). This cost advantage would be amplified when considering the additional profit generated from co-produced Cu(II) and Ni(II) salts.
A similar approach was conducted by Lacanau et al. by extracting Pd from e-waste and utilizing Pd(II) as a catalyst, thus circumventing conventional isolation and purification steps [
27]. The authors integrated hydrometallurgy for the extraction of Pd and the use of surfactant-based aqueous systems for its direct application in a cross-coupling reaction (
Figure 1d). The waste of choice was multi-layer ceramic capacitors from computer motherboards and camera boards, where Pd is alloyed with Ag. After leaching with 3 M HNO
3, Pd was selectively extracted from the leaching solution with an organic extractant, either bis(2-ethylhexyl)sulfoxide or N,N′-dimethyl-N,N′-dibutyltetradecylmalonamide. Subsequently, one of the two tris-(hydroxymethyl)acrylamide-based surfactants developed was used to back-extract Pd(II) into an aqueous micellar solution. The aqueous micellar solution containing Pd(II) was employed in a Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction of an aryl halide and aryl boronic acid in water. The catalyst exhibited similar catalytic activity to conventional media prepared from commercial Pd(II) salt. The aqueous micellar Pd(II) solutions were found to be stable for months after back-extraction, as no Pd(II) hydrolysis was observed. This suggests that the micellar solutions can be stored and used for further experiments without significant degradation or loss of the catalyst. Additionally, the authors demonstrate that this process simplifies the recovery of Pd by avoiding several waste-generating steps, such as precipitation, burning, and electrowinning of Pd.
In the context of upcycling precious metals, Li et al. developed a sophisticated and highly selective adsorbent for recycling gold from e-waste [
28]. The leaching process involved immersing PCBs in a 10 M NaOH solution to remove the epoxy coating, followed by soaking in aqua regia. The approach employed capturing and reducing Au(III) ions in situ from the solution as Au(0) particles via a magnetic adsorbent functionalized with thiourea. The redox-active adsorbent was synthesized by functionalizing non-porous silica-coated magnetic Fe
3O
4 core stirring rods with thiourea through distillation-precipitation polymerization (
Figure 1e,f). The rapid adsorption kinetics and remarkable selectivity of the adsorbent rendered it an excellent candidate for practical Au recovery from complex waste solutions. Hence, the catalytic activity of the gold-loaded adsorbent was demonstrated for the hydrogenation of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol in the presence of NaBH
4 as a reducing agent (
Figure 1g). In comparison to several other supported Au catalysts, the catalyst exhibited exceptional reaction rates. Its high reusability without significant efficiency losses and ease of recovery by magnetic separation render it a promising method for sustainable catalysis. In a similar approach by their working group, Wu et al. also demonstrated the recovery of Pd(II) via functionalized magnetic particles for a Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction between bromobenzene and 4-formylphenylboronic acid with conversion efficiencies of up to 99% [
29].
Table 1.
Overview of the presented literature.
Table 1.
Overview of the presented literature.
| Waste Type | Recycled Catalyst | Recycling Method | Applied Catalytic Reaction | References |
|---|
| Electronic waste | Cu-based | Precipitation of acid leachate on Al2O3 and subsequent pyrolysis | Hydrogenation, deoxygenation, and hydrogenolysis reactions | Ryabchuk et al., 2021 [25] |
| Au(III) | Mild extraction with complexing agents | Set of different organic reactions | McCarty et al., 2022 [26] |
| Pd(II) | Selective extraction with extractants and surfactants | Cross-coupling | Lacanau et al., 2020 [27] |
| Au | In situ capture and reduction of Au ions by functionalized particles | Hydrogenation of 4-nitrophenol | Li et al., 2022 [28] |
| Spent lithium-ion batteries | LiNixMnyCozO2 | Pyrolysis of spent Li-ion battery black material | Oxidation of furans | Amarasekara et al., 2022 [30] |
| Oxidation of D-glucose to glycolic acid | Amarasekara et al., 2022b [31] |
| Decarboxylative dimerization of levulinic acid | Amarasekara et al., 2023 [32] |
| Reduced black mass of battery | Ball milling, calcination, and reduction with H2 | Hydrogenation of furfurals | Paone et al., 2022 [33] |
| Wastewater | Ni | Extraction with porous core-shell particles and calcination/reduction | Photothermal catalytic CO2-to-CO hydrogenation | Wang et al., 2022 [34] |
| Au | Selective adsorption by MOF and calcination/reduction with H2 | Electrochemical CO2 reduction | Zhu et al., 2022 [35] |
| Au, Pd | Selective adsorption by hybrid absorbent and calcination/reduction with H2 | Oxidation of 4-nitrophenol | Li et al. [36] |
| Pd | Selective Pd(II) extraction by porous polymer and NaBH4 reduction | Cross-coupling | Song et al., 2022 [37] |
| Pd | Electrochemical reduction of Pd(II) on carbon black particles | Cross-coupling and
electrocatalytic H2 generation | Oladeji et al., 2022 [38] |
| Pd | Extraction and in situ reduction of Pd(II) by a hybrid hydrogel | Cross-coupling | Slavik and Smith 2020 [39]
Piras et al., 2020 [40]
Albino et al., 2023 [41] |
| Ru on Nb–carbon support | Impregnation method followed by NaBH4 reduction | Hydrogenation of furfurals | Yao et al., 2022 [42] |
2.2. Catalyst from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), integral to modern energy storage, contain several elements and compounds in varying amounts, depending on the type of battery. They contain metals, often as their respective oxides, such as Li, Co, Ni, Mn, Fe, Al, and Cu, as well as non-metallic elements such as graphite and organic solvents, binders, and separators. As the global demand for LIBs increases rapidly, the resulting waste creates a need to recycle spent batteries into valuable materials. Currently, recycled catalysts from LIBs are mainly being investigated for their catalytic pollutant decontamination or water electrolysis capabilities. From the viewpoint of a circular economy approach together with an advancement of green chemistry, our focus is on articles that use the recycled catalytic materials from LIBs for the synthesis of organic molecules.
In this context, Amarasekara et al. reported innovative approaches to enhance the value of biomass-derived compounds through conversion by recycled catalysts from spent LIBs [
30,
31,
32]. The recycling of LIBs for reuse as catalysts involved a discharging and mechanical dismantling process (
Figure 2a). Interfering organic residues, e.g., binders, were removed by pyrolyzing the cathode and anode black material at 600 °C. After grinding and sieving, the resulting powder of LiNi
xMn
yCo
zO
2/C was used as a catalyst (
Figure 2b). The authors demonstrated the practicability of this catalyst for the transformation of different biomass-derived substrates, namely the oxidation of cellulose-derived furans to their corresponding carboxylic acids [
30], the oxidation of D-glucose to glycolic acid [
31], and the decarboxylative dimerization of levulinic acid [
32]. For example, the oxidation of furans, including furan-2-aldehyde, 5-hydroxymethyl furfural, and 5,5′-[oxybis(methylene)]bis [2-furaldehyde], achieved moderate-to-high yields ranging from 82% to 97% depending on the substrate used. The catalyst showed robust reusability over four cycles under optimized conditions for the oxidation of furan-2-aldehyde, with a slight decrease in yield from 97% to 86% while maintaining full conversion.
Amarasekara et al. finalized their recycled catalyst by oxidizing it at 600 °C, resulting in an oxide catalyst. In contrast, Paone et al. included a reduction step in the recycling of LIBs, leading to the partial production of catalytically active metal particles (
Figure 2c) [
33]. Similar to Amarasekara et al., after the mechanical separation, the black mass, consisting of metal oxides and graphite, was sieved, ball-milled, and calcinated at 600 °C for 6 h. However, additionally, the material was reduced at 500 °C for 6 h under hydrogen flow in the last step. The final catalyst particles consisted mainly of Co and Ni metals and oxides of Mn and Al. The catalyst was demonstrated for selective reduction reactions of biomass-derived furfural and other aldehydes and ketones. The catalyst was showcased for direct hydrogenation with H
2 as well as for milder and safer transfer hydrogenation using 2-propanol as both the solvent and hydrogen donor. Furfural was successfully converted to furfuryl alcohol in 90 min at 120 °C using H
2 in 2-propanol. The conversion of furfural under transfer hydrogenation conditions using 2-propanol as the solvent and proton donor resulted in a 70% yield. At temperatures above 150 °C, the yield increased to 98%, achieving similar results as the H
2 route. The catalyst was able to convert other substrates, namely 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, benzaldehyde, acetophenone, and cyclohexanone, with varying yields, indicating a broader possible scope of substrates. These findings highlight the importance of the reduction of the black mass to metallic Co and Ni as a necessary step for the hydrogenation reaction.
2.3. Catalysts from Wastewater
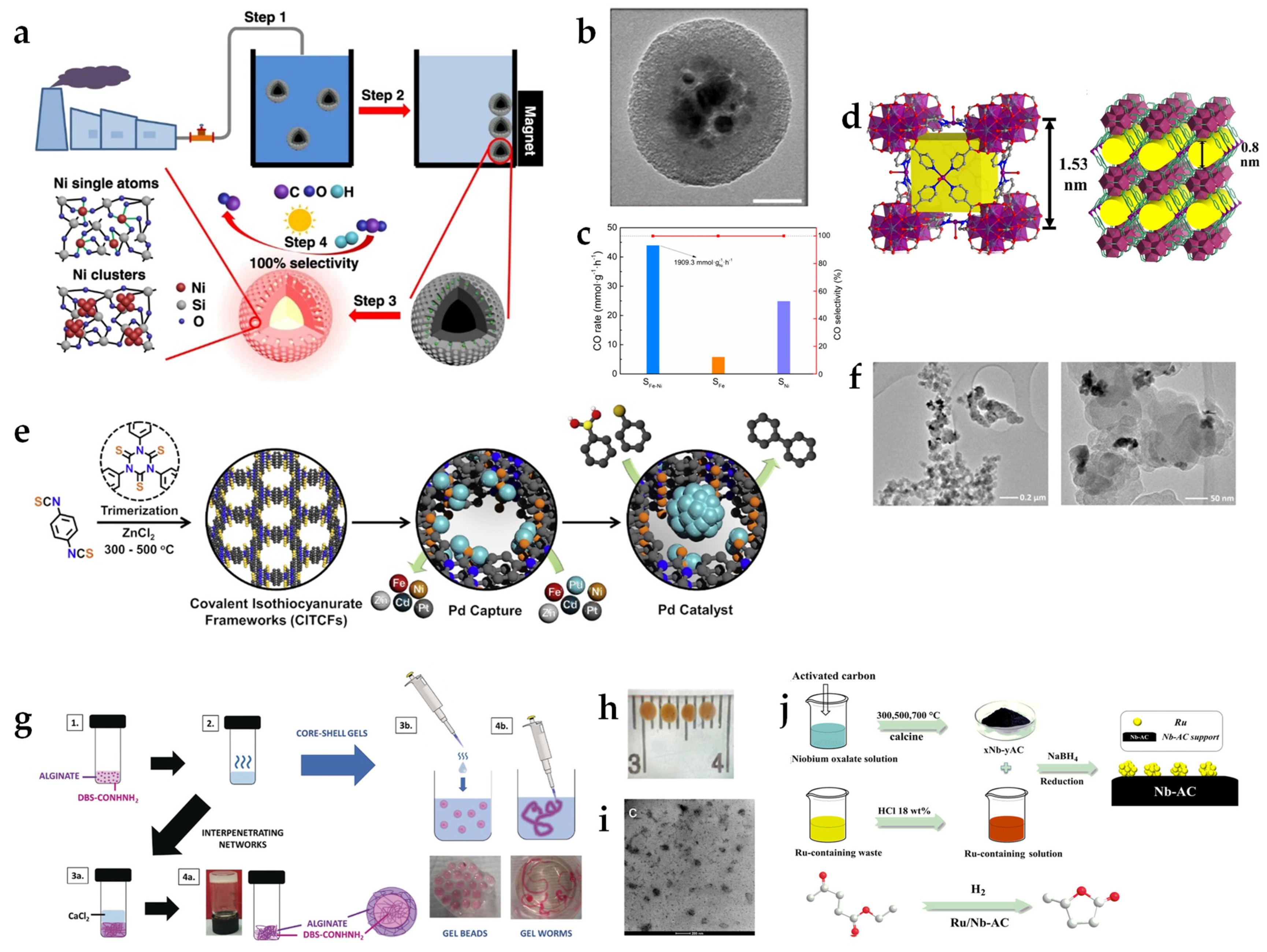
Metal-contaminated wastewaters, whether from industrial effluents or urban runoff, are known for their potential toxicity, posing acute and chronic risks to both human health and ecosystems. The mandatory removal of hazardous metals from wastewater often requires a high energy input and can result in the release of secondary pollutants. Such processes, while effective, come with their own environmental costs, amplifying the challenge of sustainable wastewater treatment. However, the simultaneous sequestration and transformation into useful catalysts enable these environmental liabilities to be converted into promising tools for green chemistry. Due to the concurrent presence of metal ions in wastewater, the key obstacle to the recovery of metals from wastewater is the creation of highly selective adsorbents for specific metal ions. This is mainly achieved by porous 3D networks with a functionalized surface. By utilizing such sophisticated architectures, the formation of metal particles is scaled down to particle sizes at the nanoscale, enabling faster reaction rates. This section will present several innovative approaches that focus on such strategies.
Wang et al. introduced a novel approach for extracting Ni from widely available electroplating wastewater and built it into an advanced photothermal catalyst for converting CO
2 to CO, which is a significant reaction step in numerous chemical transformations [
34]. The group employed a core-shell adsorbent comprising a magnetic Fe
3O
4 core encapsulated by two layers: a dense SiO
2 layer that protected the core as an etching barrier in the acidic wastewater and an outer layer of amine-functionalized mesoporous SiO
2 that could efficiently scavenge Ni(II) from the wastewater (
Figure 3a,b). Upon reaching adsorption equilibrium, the Ni(II) captured alongside the adsorbent was magnetically isolated. This assembly was subsequently calcined and reduced under H
2, yielding a core-shell catalyst with highly dispersed Ni in the mesoporous SiO
2 layer. In its practical application, the catalyst excelled in the reverse water–gas shift reaction, underlining the potential of waste-derived materials for carbon capture and utilization strategies. The catalyst demonstrated not only high CO production rates and selectivity but also remarkable stability and a reduced CO
2 footprint compared to the conventional thermocatalytic pathway. The catalyst’s performance can be ascribed to the Fe
3O
4 core’s light-harvesting and high photo-to-thermal conversion efficiency (
Figure 3c). This resulted in temperatures of up to 400 °C under concentrated light, primarily driving a thermochemical reaction route. The SiO
2 shell confines the energy due to its thermal insulation properties while also functioning as a support for Ni particles. Wang et al.’s innovative catalyst displayed a higher CO production rate than commercial Cu-ZnO-Al
2O
3 catalysts and other reported photothermal catalysts. The consistent chemical composition of the catalyst across three different waste solutions indicates a stable absorption performance of the particles despite the varying mixtures of Ni(II) wastewater used.
In a separate study on CO
2 reduction, Zhu et al. presented a novel Metal–Organic Framework (MOF) for the selective adsorption of AuCl
4− from solution and its subsequent transformation into an active electrochemical catalyst [
35]. The synthesis of the MOF was carried out via solvothermal synthesis using ZrCl
4, Ni(NO
3)
2, and isonicotinic acid in DMF as precursors. The MOF exhibited a high surface area of 1570 m
2/g and a high Au(III) capacity of 415 mg/g. The immersion of the MOF in an artificial e-waste solution containing AuCl
4−, followed by calcination at 200 °C under a H
2/Ar atmosphere, resulted in Au nanoparticles uniformly dispersed within the MOF network with adjustable Au particle sizes between 2.4 and 4.4 nm depending on the initial AuCl
4− concentration (
Figure 3d). The selectivity for Au(III) adsorption was notably robust. Despite the presence of competing metal ions such as Fe, Ni, Cu, Co, Zn, and Mn at concentrations an order of magnitude greater than AuCl
4−, the interference of the adsorption was minimal. The Au/MOF system proved to be highly efficient for the electrochemical reduction of CO
2 to CO with a Faradaic efficiency of 95%, maintaining its performance for 15 h with a minor decrease in activity (−13%) and efficiency (−7%). This breakthrough underscores the multifaceted potential of MOFs to obtain low-cost and high-performance size-adjustable Au-based catalysts from wastewater.
The ability of MOFs to scavenge precious metals from complex wastewater mixtures was also demonstrated by Li et al. with a hybrid absorbent for the selective recovery of Au and Pd for the catalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol [
36]. The hybrid adsorbent consisted of a functional graphene foam linked with a Cu-based MOF. The graphene foam was activated at 120 °C for 12 h and functionalized with 4,4′-thiodibenzenethiol at 40 °C with a reaction time of 48 h, yielding a thiol-functionalized graphene foam (FGF). To synthesize the MOF@FGF hybrid, the FGF was modified with a benzene-1,4-dithiol linker and subsequently mixed with an ammoniacal cupric nitrate solution, washed, and dried. The prepared hybrid absorbent was able to recover Au(III) and Pd(II) from artificial wastewater with recovery rates of 90.4% over five cycles and high adsorption capacities of 3715 mg/g for Au(III) and 3345 mg/mg for Pd(II) at concentrations ranging from 20 mg/L to 2000 mg/L. The addition of potentially interfering ions of Ag(I), Li(I), Pt(II), Co(II), Fe(II), Cu(II), Al(III), Sb(III), Fe(III), and Sn(IV) at 200 mg/L did not result in a significant reduction of Au(III) and Pd(II) adsorption. The synthesis of the carbon-supported metal nanoparticle catalysts involved calcination at 800 °C under N
2 and H
2 for 2 h, which generated particles with sizes between 2 nm and 5 nm. To prove the catalytic efficiency, a catalytic oxidation of 4-nitrophenol via peroxymonosulfate activation was used as a model reaction.
A similar nanocage approach was presented by Song et al., who developed porous polyisothiocyanurates, termed covalent isothiocyanurate framework (CITCF), for Pd adsorption [
37]. This approach enabled the recovery of Pd(II) from artificial wastewater, followed by the reduction of Pd(II) to Pd particles within the polymer and their subsequent use as a catalyst for the Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction. CITCFs were synthesized by heating a mixture of 1,4-phenyl-diisothiocyanate and ZnCl
2 (
Figure 3e) in a sealed ampoule at 300–500 °C. The resulting material was thoroughly washed and purified through various solvents and dried overnight at 90 °C. The CITCFs exhibited high surface areas of up to 1589 m
2/g. Due to the thiourea sites in the framework, the extraction from artificial wastewater containing PdCl
42− showed a high Pd(II) capacity of 909 mg/g. The reduction of Pd(II) within the polymer matrix was achieved by treatment with NaBH
4 and subsequent washing and drying steps, resulting in Pd particle sizes of 1.49 nm. The high thermal and chemical stability of the material, coupled with its exceptional selectivity for Pd(II)—notably five times greater than for Pt(IV) and significantly higher than for other transition metals like Ni, Fe, Zn, and Cd—emphasizes its potential for selective metal recovery. The catalytic activity of Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions was confirmed using both Pd(II) and Pd(0) within the polymer, with the reduced Pd particles giving superior results. Several reactions with bromobenzene derivatives and phenylboronic acid derivatives were carried out under optimized conditions, displaying exclusive selectivity and high yields between 81.6% and 99.9%. Over five catalytic cycles, the catalyst exhibited no loss of activity and no reduction in surface area, demonstrating its robustness as an environmentally friendly waste-derived catalyst.
Figure 3.
Catalysts from wastewater. (
a) Preparation of Ni-based catalyst for water–gas shift reaction. (
b) TEM image of catalyst particle. Scale bar: 50 nm. (
c) CO production rate and CO selectivity for different compositions of the catalyst in a batch reactor. Adapted from Wang et al. [
34]. Used under CC BY 4.0. (
d) MOF. Reproduced (adapted) with permission from Zhu et al. [
35]. Copyright 2020, Wiley. (
e) Synthesis of porous polyisothiocyanurate network for Pd capture. Reprinted from Song et al. [
37]. Copyright 2022, with permission from Elsevier. (
f) Pd nanoparticles on carbon black nanoparticles after nanoimpact deposition. Scale bar (left image): 0.2 µm; scale bar (right image): 50 nm. Adapted from Oladeji et al. [
38]. Used under CC BY 4. (
g) Preparation of gelatinous Pd scavenger network and beads: (
1) Suspending DBS-CONHNH
2 in alginate solution, (
2) heating for complete dissolution, (
3a) adding dissolved CaCl
2, (
4a) forming of a gel network. Alternatively, a solution of CaCl
2 can be added dropwise or in a continuous stream to form (
3b) beads or (
4b) strings. Adapted from Piras et al. [
39] Used under CC BY 4.0. (
h) Image of Pd-loaded gel beads. (
i) TEM image of Pd nanoparticles encapsulated in the hydrogel. Adapted from Albino et al. [
41]. Used under CC BY 4.0. (
j) Preparation of Ru/Nb–carbon catalyst. Reprinted (adapted) with permission from Yao et al. [
42]. Copyright 2022 American Chemical Society.
Figure 3.
Catalysts from wastewater. (
a) Preparation of Ni-based catalyst for water–gas shift reaction. (
b) TEM image of catalyst particle. Scale bar: 50 nm. (
c) CO production rate and CO selectivity for different compositions of the catalyst in a batch reactor. Adapted from Wang et al. [
34]. Used under CC BY 4.0. (
d) MOF. Reproduced (adapted) with permission from Zhu et al. [
35]. Copyright 2020, Wiley. (
e) Synthesis of porous polyisothiocyanurate network for Pd capture. Reprinted from Song et al. [
37]. Copyright 2022, with permission from Elsevier. (
f) Pd nanoparticles on carbon black nanoparticles after nanoimpact deposition. Scale bar (left image): 0.2 µm; scale bar (right image): 50 nm. Adapted from Oladeji et al. [
38]. Used under CC BY 4. (
g) Preparation of gelatinous Pd scavenger network and beads: (
1) Suspending DBS-CONHNH
2 in alginate solution, (
2) heating for complete dissolution, (
3a) adding dissolved CaCl
2, (
4a) forming of a gel network. Alternatively, a solution of CaCl
2 can be added dropwise or in a continuous stream to form (
3b) beads or (
4b) strings. Adapted from Piras et al. [
39] Used under CC BY 4.0. (
h) Image of Pd-loaded gel beads. (
i) TEM image of Pd nanoparticles encapsulated in the hydrogel. Adapted from Albino et al. [
41]. Used under CC BY 4.0. (
j) Preparation of Ru/Nb–carbon catalyst. Reprinted (adapted) with permission from Yao et al. [
42]. Copyright 2022 American Chemical Society.
![Suschem 05 00003 g003]()
An innovative method for the upcycling of a noble metal was presented by Oladeji et al. via impact electrochemistry for the recovery of Pd from solution and its subsequent use as a catalyst [
38]. The authors used the nanoimpact technique to generate carbon-supported Pd catalysts from artificial wastewater with low concentrations of PdCl
2. The synthesis involved the collision of carbon black nanoparticles (CB NPs) with an electrode immersed in wastewater, leading to the reduction and irregular deposition of Pd onto the surface of the nanoparticles (
Figure 3f). In the absence of CB NPs, the recovery rate of Pd(II) was about 65%. However, upon their addition, this rate increased to 85%. Notably, the introduction of CB NPs during chronoamperometric experiments considerably reduced the background deposition on the electrode. To demonstrate the catalytic properties of the resulting material, both a Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction of phenylboronic acid with iodobenzene and an electrocatalytic hydrogen generation were carried out in a proof of concept. Although insights into the selectivity of the nanoimpact method for Pd were not reported, this approach highlights the capability of electrochemical techniques for metal extraction and catalyst production from wastewater.
Another promising strategy to recover Pd from wastewater was demonstrated by Smith et al. [
39,
40,
41]. The key concept revolves around the use of a gelatinous material for the selective capture of Pd from aqueous solutions and the subsequent use of Pd as a catalyst. The hybrid hydrogels developed have a high affinity and specificity for Pd(II) ions and can reduce Pd(II) to Pd(0). Such an approach is particularly relevant when considering recycling Pd-rich wastewater. The catalytic active material was prepared by encapsulation of Pd nanoparticles via an in situ reduction of Pd(II) in a hybrid hydrogel made from an acylhydrazide-functionalized 1,3:2,4-dibenzylidenesorbitol (DBS-CONHNH
2) low-molecular-weight gelator combined with a polymer gelator such as alginate (
Figure 3g,h). The Pd(II) solution used was an acidic PdCl
2 solution mimicking wastewater. The catalytic material could be prepared either as a catalytic gel block [
39] or as catalytic gel beads/worms [
40]. In particular, the catalytic beads prepared with agarose as the polymer gelator were mechanically more stable, easier to reuse, and not prone to Pd leaching compared to the gel block and the beads/worms prepared with alginate (
Figure 3i) [
41]. The beads also demonstrated thermal stability up to 99 °C and showed three-time reusability after filtering and washing. These Pd-enclosing materials were extensively demonstrated to be effective catalysts for cross-coupling reactions, including Sonogashira and Heck [
39,
40] and Suzuki–Miyaura [
41] reactions, under environmentally friendly and mild conditions with high yields.
Yao et al. developed a novel method for fabricating Ru-based catalysts using Ru-rich waste from lignite depolymerization processes [
42]. The recycled catalyst showed comparable efficiencies to conventional Ru catalysts in the hydrogenation of ethyl levulinate to γ-valerolactone, maintaining its activity across multiple cycles. The catalyst synthesis was achieved via an impregnation method in which a Nb–carbon support was mixed with Ru-containing wastewater, stirred for 2 h, and then directly reduced with NaBH
4 solution in an ice bath for 2 h. The Nb–carbon support itself was synthesized by mixing Nb oxalate with activated carbon, followed by drying, grinding, and calcination in an inert atmosphere (
Figure 3j). The catalyst was applied to a broad substrate scope and proved to be an effective catalyst for reducing saturated aldehydes and ketones to their corresponding alcohols. However, it exhibited limitations in the hydrogenation of aromatic compounds, particularly benzaldehyde and acetophenone, where the yields were significantly reduced due to complete ring hydrogenation or deoxygenation side reactions.