Abstract
Waste activated sludge (WAS), a byproduct of livestock wastewater treatment, poses significant disposal challenges due to its low biodegradability and potential environmental impact. Anaerobic digestion (AD) offers a sustainable approach for methane recovery and sludge stabilization. This study evaluates the biomethane potential (BMP) of WAS and its co-digestion with swine slurry (SS), water lily (Nymphaea spp.), and lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) shoot biomass to enhance methane yield. Batch BMP assays were conducted at substrate-to-inoculum (S/I) ratios of 1.0 and 0.5, with methane production kinetics analyzed using the modified Gompertz model. Mono-digestion of WAS yielded 259.35–460.88 NmL CH4/g VSadded, while co-digestion with SS, water lily, and lotus increased yields by 14.89%, 10.97%, and 16.89%, respectively, surpassing 500 NmL CH4/g VSadded. All co-digestion combinations exhibited synergistic effects (α > 1), enhancing methane production beyond individual substrate contributions. Lower S/I ratios improved methane yields and biodegradability, highlighting the role of inoculum availability. Co-digestion reduced the lag phase limitations of WAS and plant biomass, improving process efficiency. These findings demonstrate that co-digesting WAS with nutrient-rich co-substrates optimizes biogas production, supporting sustainable sludge management and renewable energy recovery in livestock wastewater treatment systems.
1. Introduction
The activated sludge process is a widely employed technology for treating a range of wastewater sources, including municipal, industrial, and agricultural effluents such as livestock wastewater. Although highly effective in removing contaminants, this process generates substantial quantities of solid byproducts, commonly referred to as biosolids or waste activated sludge (WAS). The management and disposal of these residuals pose increasing environmental and regulatory challenges, especially in the context of tightening solid waste management policies. Therefore, the development of sustainable and efficient strategies for handling sludge produced by the activated sludge process is essential [1].
With the expansion of livestock production, the Republic of Korea is facing growing environmental challenges associated with livestock waste disposal. Swine production is the predominant sector, commonly utilizing slatted-floor pit housing systems that generate slurry-type wastewater. Historically, government policies have prioritized the prevention of environmental pollution caused by livestock excreta. However, the Ministry of Environment has recently shifted its focus toward the valorization of livestock waste as a renewable energy resource. This policy transition aligns with national strategies that emphasize nutrient recycling and biogas production from livestock waste streams [2].
Anaerobic digestion (AD) has emerged as a sustainable and effective technology for managing waste activated sludge (WAS) generated from livestock wastewater treatment. This method is well-established in converting organic waste into renewable bioenergy while contributing to environmental sustainability. Compared to aerobic treatment processes, anaerobic digestion (AD) converts biodegradable organic matter into biogas under anaerobic conditions in sealed reactors, significantly reducing odor emissions and producing renewable methane as a bioenergy source as well as nutrient-rich digestate [3,4]. Although alternative sludge treatment methods—such as landfilling, incineration, or composting—are available, AD provides additional benefits by reducing sludge volume, stabilizing organic content, and minimizing environmental risks [5]. As an example, in South Korea, 20 out of 49 operational biogas facilities currently use sewage sludge as a primary feedstock [2,6].
Waste sludge derived from aerobic treatment of swine wastewater—characterized by high organic load is having potential as suitable substrate for AD. However, its mono-digestion offers limited energy recovery due to imbalanced nutrient composition and suboptimal biodegradability.
Recent advancements in anaerobic digestion (AD) have increasingly focused on co-digestion strategies to enhance biogas production and process stability to balance nutrient composition and improve biogas production. Co-digestion with other livestock wastes, such as pig manure, has been shown to enhance methane yield, improve nutrient balance, and stabilize the digestion process. Zhang et al. [7] demonstrated that co-digesting dewatered sewage sludge with pig manure increased methane production by 82.4%. Similarly, Renggaman et al. [8,9] reported that co-digestion of slaughterhouse waste with swine slurry enhanced methane yield by up to 75.5%, while simultaneously shortening the lag phase and improving the system’s buffering capacity. These findings highlight the potential of co-digesting livestock-derived waste as an effective strategy to maximize biogas recovery, improve process efficiency, and mitigate environmental impacts. On the other hand, a particular area of interest is co-digestion with invasive or underutilized plant species, such as water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) and giant reed (Arundo donax), which have gained attention due to their high biomass yield and potential to address environmental challenges. For instance, Oduor et al. [10] demonstrated that co-digesting water hyacinth with food waste significantly improved methane yields, leveraging the plant’s high carbon content to balance nutrient ratios. Similarly, studies on invasive aquatic plants like Egeria densa have shown enhanced biogas production when co-digested with sewage sludge, offering dual benefits of waste management and renewable energy recovery [11]. These approaches not only valorize otherwise problematic biomass but also align with circular bioeconomy principles by mitigating the ecological impact of invasive species while optimizing energy recovery from diverse resources.
In wastewater treatment—particularly for high-nutrient effluents such as swine wastewater—tertiary nutrient removal is critical for meeting regulatory discharge standards. Aquatic plants are increasingly used for this purpose. Floating and emergent macrophytes, such as Eichorrnia crassipes, Myriophyllum elatinoides, Miscanthus sacchariflorus, and Phragmites australis, have demonstrated the capacity to reduce nutrients and even antibiotic resistance genes in swine wastewater [10,12,13,14]. While Miscanthus and Phragmites are established bioenergy crops, water lily and lotus are primarily valued for their ornamental use.
In this study, water lily (Nymphaea spp.) and lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) were selected as co-substrates due to their efficacy in phytoremediation of nutrient-rich wastewater, as demonstrated by their ability to remove nitrogen and phosphorus in several published articles [15,16] and unpublished experiment by authors. These aquatic plants, cultivated in tertiary wastewater treatment systems, accumulate significant biomass with high carbon content, making them suitable for enhancing the carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratio in co-digestion with WAS. Unlike traditional bioenergy crops like Miscanthus, water lily and lotus are underutilized for biogas production, offering a novel approach to valorize phytoremediation byproducts while addressing waste management challenges. Moreover, the sustainability of phytoremediation systems depends on the downstream utilization of harvested biomass. While most studies focus on nutrient removal, few address the valorization of plant biomass. Integrating biomass energy recovery into treatment systems can significantly enhance their overall value. Recent studies have shown that co-digestion of aquatic plants or algae cultivated in wastewater with sludge can improve methane yields and digestion performance [14,17,18]. For instance, co-digestion of algae with sewage sludge increased methane production to 401 mL CH4/g VSadded, thereby enhancing both energy recovery and sludge management efficiency [18].
Despite the established benefits of co-digesting WAS with livestock manure, the use of aquatic plant biomass, such as water lily and lotus, from phytoremediation systems remains underexplored. This study addresses this gap by evaluating the biomethane potential of these substrates and their synergistic effects in co-digestion with WAS. The objectives are to (1) assess the biomethane potential of WAS, swine slurry, water lily, and lotus shoot biomass, and (2) investigate the performance and synergistic effects of co-digestion systems to enhance anaerobic digestion efficiency, thereby promoting sustainable waste management and renewable energy recovery.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inoculum and Substrate
The inoculum used in this study was obtained from a mesophilic anaerobic digestion reactor treating swine slurry. Prior to experimentation, the inoculum was degassed to remove residual biogas [8,9]. The substrates for the biochemical methane potential (BMP) assays included swine slurry, waste activated sludge (WAS), and dried biomass of water lily (Nymphaea spp.) and lotus shoots (Nelumbo nucifera). Swine slurry was collected from a pit-type experimental housing facility. Water lily and lotus plants were cultivated using treated swine wastewater effluent from the Suwon experimental farm at Seoul National University, Republic of Korea. Biomass samples, consisting of dried leaves and stalks, were ground and passed through a 1 mm mesh sieve prior to use. WAS was collected from the sedimentation tank of a swine wastewater treatment system comprising anoxic and oxic reactors, a sedimentation tank, and a filtration unit. Characteristics of the inoculum and swine slurry were referenced from previously published data [8].
2.2. Substrate Characteristics Analysis
2.2.1. Total Solid, Volatile Solid, and Fixed Solid
Total solids (TS), volatile solids (VS), and fixed solids (FS) of the waste activated sludge were determined in accordance with APHA Standard Method 2540 [9,19]. Approximately 10 mL of a well-mixed sample was weighed and dried at 103–105 °C to measure TS, expressed either in mg/L (fresh weight) or as a percentage by weight. The dried residue was then combusted in a muffle furnace at 550 °C to determine VS and FS, reported as mg/L (fresh weight) or as a percentage of the dry weight.
2.2.2. Plant Biomass Characteristics Analysis
Dried plant biomass samples were used for compositional analysis. Volatile solids (VS) and fixed solids (FS) were determined using the loss-on-ignition (LOI) method [8]. Approximately 0.1–0.2 g of dried biomass was combusted in a muffle furnace at 550 °C for 2 h. The residual ash was recorded as fixed solids (FS), while the combusted portion represented the organic matter (VS), both expressed on a dry weight basis. Fiber fractions, including neutral detergent fiber (NDF), acid detergent fiber (ADF), and acid detergent lignin (ADL), were analyzed using the ANKOM F57 filter bag technique. About 0.5 g of dried sample was sealed in a filter bag and refluxed with NDF or ADF solution at 200 °C for 1.5 h. The bags were then rinsed with warm water until the rinse water was clear, soaked and washed in acetone, and dried at 105 °C for 2 h before final weighing. For ADL determination, the ADF-treated bags were subsequently immersed in 72% H2SO4 for 3 h with agitation every 30 min. After acid treatment, the bags were thoroughly rinsed with warm distilled water to neutral pH, washed with acetone, and dried at 105 °C. The contents of NDF, ADF, and ADL were calculated based on weight differences and reported on a dry matter basis.
2.2.3. Ultimate Analysis of Substrates
Ultimate (elemental) analysis was performed to quantify the carbon (C), hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), sulfur (S), and oxygen (O) content of the samples. Prior to analysis, samples were oven-dried and finely ground to pass through a 1 mm sieve. The C, H, N, and S contents were determined via high-temperature combustion at 1014 °C using a Flash EA 1112 Elemental Analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Germany). Oxygen content was measured separately using a Flash 2000 Elemental Analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Germany), following standardized procedures [8].
2.2.4. Fermentation Mass Characteristics
The characteristics of the fermentation mass, including the inoculum and co-digestion mixtures, were determined to assess the impact of substrate combinations on anaerobic digestion performance. The total solids (TS), volatile solids (VS), and carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratios for the fermentation mass are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
The characteristics of the fermentation mass.
2.3. Bio-Methane Potential (BMP) Assay of Waste Activated Sludge and Co-Digestion with Swine Slurry and Plant Biomass
The study comprised two experimental phases: Experiment I, which evaluated the biomethane potential (BMP) of individual substrates, and Experiment II, which assessed the effects of co-digestion (Table 2). For co-digestion experiments (setups 5–8), a substrate-to-inoculum (S/I) ratio of 0.5 was selected based on its superior methane yield in single-substrate tests (Section 3.2). The 1:1 and 1:2 ratios for SS + WAS (setups 5 and 6) were tested to evaluate the effect of varying WAS proportions (Table 2). For WL + WAS and LT + WAS (setups 7 and 8), a 1:2 ratio was chosen to optimize carbon input from plant biomass, without hindering the degradability due to lignocellulosic compounds of plant materials [20]. The S/I ratios of 0.5 and 1.0 were selected based on previous studies demonstrating that lower S/I ratios enhance methane production by increasing microbial activity and hydrolysis efficiency [21,22]. All treatments were performed in triplicate.

Table 2.
Biomethane potential experiment substrate and inoculum composition.
Figure 1 illustrates the experimental design for the BMP assays. The setup consisted of 250 mL serum bottles filled with substrate, inoculum, and distilled water to a working volume of 200 mL. Bottles were flushed with an N2/CO2 (80:20) gas mixture, sealed with rubber stoppers and aluminum crimps, and incubated at 35 °C [9]. Biogas production was measured using a calibrated glass syringe, and gas composition was analyzed via gas chromatography. A 50 mL aliquot was withdrawn from each bottle for subsequent analysis. Blank controls containing only inoculum and anaerobic medium were included to account for background biogas production.
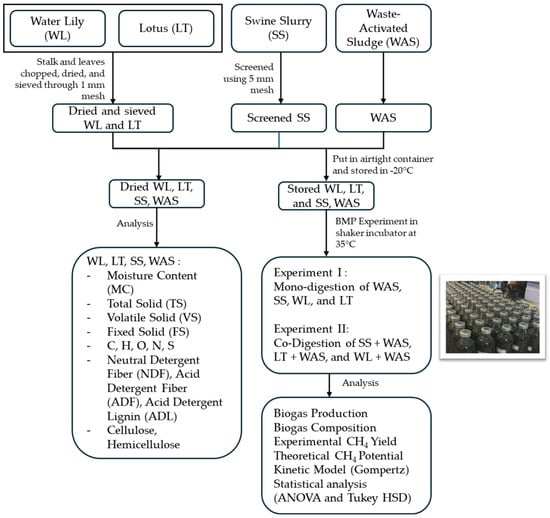
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of experimental design.
2.4. Theoretical Methane Potential Based on Ultimate Analysis
Theoretical methane potential (TMP) is a key parameter used to estimate the maximum methane yield of a substrate under standard temperature and pressure (STP) conditions (NmL CH4/g VSadded). TMP is calculated based on the elemental composition of the substrate (C, H, O, N, S). The empirical molecular formula (CaHbObNdSe) was determined, and methane production was estimated using the Buswell and Mueller equation (Equation (1)). The methane yield coefficient was calculated using Equation (2), and TMP (NmL CH4/g VSadded) was determined using Equation (3) [9,21].
2.5. Gas Production and Composition Analysis and Measurement
Biogas production was measured using the pressure displacement method with a calibrated glass syringe. The composition of the produced gas—specifically CO2, CH4, and N2—was analyzed by gas chromatography (Agilent Technologies) equipped with an HP-PLOT/Q capillary column and a thermal conductivity detector (TCD). The injector, oven, and detector temperatures were set at 40 °C, 35 °C, and 200 °C, respectively [8]. Daily methane production was calculated using Equation (4), while cumulative methane production was determined using Equation (5):
where is volume of methane at time t (mL); is volume of biogas at time t (mL); is concentration of methane at time t (%); and is cumulative methane production (mL).
The measured cumulative methane volume was standardized to conditions of 273 K and 1 atm. The standardized cumulative methane production was then used to calculate the experimental methane yield (EMY) using Equation (6):
where is normalized cumulative CH4 production (NmL); EMY is experimental CH4 yield (NmL/g VSadded); and VSadded is volatile solid of initial sample (g).
2.6. Kinetic Model
The first-order kinetic model exhibited a poorer fit compared to the modified Gompertz model. The Gompertz model is particularly well suited for biochemical methane potential (BMP) assays, as it accounts for the lag phase—an essential parameter when digesting complex organic substrates [9]. Therefore, kinetic modeling in this study was performed using the modified Gompertz equation (Equation (7)).
where G(t) represents the cumulative methane yield at a given digestion time t (NmL/g VSadded), G0 is the maximum methane yield of the substrate (NmL/g VSadded), Rmaxe denotes the maximum methane production rate (NmL/g VSadded per day), λ is the lag phase duration (days), t is the digestion time (days), and e is the base of the natural logarithm, approximately equal to 2.7183.
2.7. Biodegradability
The anaerobic biodegradability in anaerobic digestion assays is determined by comparing the experimental methane yield (EMY) to the theoretical methane potential (TMY) of the substrate. The anaerobic biodegradability (Ddeg) is calculated using Equation (8) [8,9]:
where EMY is experimental methane yield (NmL CH4/g VSadded) and TMP is theoretical methane potential (NmL CH4/g VSadded).
2.8. Synergistic Effect
The synergistic effect in co-digestion was quantified using Equation (9) [8,9]. MAS refers to the maximum methane yield (G0) of waste activated sludge (WAS) as determined by the modified Gompertz model (NmL CH4/g VSadded). The simulated G0 (Msim) of co-digested mixtures was calculated using Equation (10), incorporating the proportional contributions of WAS and co-substrates (SS, WL, or LT).
2.9. Statistical Analysis
Statistical differences among treatments were evaluated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test at a 95% confidence interval to identify significant differences in methane yields and kinetic parameters. All analysis was conducted using Microsoft Excel.
3. Results and Discussion
This study aimed to (1) evaluate the biomethane potential (BMP) of waste activated sludge (WAS), swine slurry (SS), water lily (WL), and lotus (LT) shoot biomass, and to (2) assess the synergistic effects of co-digesting WAS with SS, WL, or LT to enhance anaerobic digestion efficiency. The significance lies in addressing the disposal challenges of WAS while valorizing phytoremediation byproducts for renewable energy production. The results demonstrate that co-digestion significantly enhances methane yields, supporting sustainable sludge management in livestock wastewater treatment systems and contributing to circular bioeconomy principles by integrating nutrient recovery and biogas production [3,11].
3.1. Substrate Characteristics
Table 3 presents the characteristics of the substrates used in this study. The shoot biomass of both water lily and lotus exhibited higher volatile solids (VS) to total solids (TS) ratios compared to waste activated sludge (WAS) and swine slurry, indicating a greater proportion of organic matter. The total solids content of WAS was 6.6%, which falls within the reported range for municipal sewage sludge digestate, secondary sludge, waste activated sludge, and thickened waste activated sludge (0.2% to 10.5%) [23,24,25]. The VS content of WAS was 3.75%, with a VS/TS ratio of 0.57, suggesting a moderate level of organic matter.

Table 3.
Characteristics of substrates used in batch bio-methane potential (BMP) assay.
WAS consists of a complex mixture of organic and inorganic substances, microorganisms, extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), and water, contributing to its semi-rigid structural consistency [26]. This complexity makes WAS more resistant to microbial degradation. In contrast, water lily and lotus biomass contain higher VS content and greater carbon levels, which may enhance their suitability as substrates for anaerobic digestion.
Interestingly, the analysis revealed that waste activated sludge (WAS) contained higher measured levels of cellulose- and hemicellulose-like fractions compared to swine slurry. This outcome is likely attributable to the use of the Van Soest method, which was originally developed for plant-based materials and may not accurately characterize the complex composition of sludge. Thus, the fractions identified as “cellulose-like” and “lignin-like” in WAS are more likely to represent structurally analogous compounds rather than true plant-derived fibers.
Mottet et al. [27] fractionated solid material from municipal wastewater treatment into hemicellulose-like, cellulose-like, and lignin-like components to evaluate WAS degradability. In the present study, the total proportion of these cellulosic- and lignin-like fractions in WAS appears to be overestimated. Previous reports have suggested that sewage sludge can contain over 20% cellulose [28]; however, this generally refers to primary sludge, which often includes materials such as toilet paper that elevate cellulose content. More recent findings [29] indicate that the cellulose-like fraction in WAS is approximately 9%, while hemicellulose- and lignin-like fractions are about 15% and 9%, respectively.
The C/N ratios of the substrates ranged from 7.72 (WAS) to 13.64 (LT), which are lower than the commonly recommended range of 15–25 for optimal anaerobic digestion [20]. The lower C/N ratios in WAS and SS are attributed to their high nitrogen content, primarily from microbial biomass and organic waste, respectively. Despite these suboptimal ratios, co-digestion with carbon-rich aquatic biomass (WL and LT) improved the overall C/N balance, reducing the risk of ammonia inhibition. Previous studies have shown that co-digestion can effectively mitigate the limitations of low C/N ratios by enhancing nutrient balance and microbial activity, thereby improving methane yields [30,31].
3.2. Methane Production of Waste Activated Sludge, Swine Slurry, and Plant Biomass at Different S/I Ratio
The substrate-to-inoculum (S/I) ratio is a critical factor influencing the anaerobic digestion process. The commonly used S/I ratio in batch anaerobic assays is 1, based on volatile solids (VS) [23]. However, lower S/I ratios have been reported to enhance methane production in some cases; for example, Chynoweth et al. [32] observed increased methane yields using plant biomass at an S/I ratio of 0.5 VS/VS. In this study, single substrates were tested at S/I ratios of 1 and 0.5. The experimental cumulative methane yield (EMY) increased significantly (p < 0.05) as the S/I ratio decreased across all substrates, indicating that S/I ratio markedly affects methane production. Recent research supports these findings, Khadka et al. [22] demonstrated that at lower S/I ratio biogas yield is higher during mesophilic digestion of food waste, and studies on co-digestion of lignocellulosic biomass (Phragmites australis) with food waste also recommend S/I ratios of 1 or less [33].
Lowering the S/I ratio is known to improve the hydrolysis phase of anaerobic digestion by providing a higher inoculum concentration relative to substrate, which accelerates microbial activity. However, excessively low S/I ratios can cause accumulation of acidic intermediates, potentially inhibiting the process. In this study, evaluation of S/I ratios at 1.0 and 0.5 revealed a statistically significant increase (p < 0.05) in cumulative methane yield at the lower ratio. These results suggest that greater inoculum availability enhances microbial activity and promotes more efficient substrate degradation, consistent with recent studies emphasizing the importance of optimizing the S/I ratio to maximize anaerobic digestion efficiency.
The experimental methane yields (EMY) for all single substrates are presented in Table 4. The EMY of waste activated sludge (WAS) was 259.35 and 460.88 NmL CH4/g VSadded at S/I ratios of 1 and 0.5, respectively, representing the lowest methane yield among the substrates tested. This lower performance is attributed to WAS having the lowest carbon content (Table 3) and inherently low biodegradability. The majority of organic compounds in WAS originate from microbial cells with robust cell membranes and glycan–peptide-linked cell walls that resist enzymatic degradation. Consequently, hydrolysis of these complex structures is a rate-limiting step in the anaerobic digestion of WAS [34]. Efficient degradation of these microbial cells remains a major challenge for the treatment and utilization of waste activated sludge.

Table 4.
Empirical chemical formulas, theoretical methane potential (TMP), experimental methane yield (EMY), and anaerobic degradability (Ddeg) of single substrates at substrate-to-inoculum (S/I) ratios of 1.0 and 0.5. Substrates: WAS (waste activated sludge), SS (swine slurry), WL (water lily), LT (lotus). Values are means ± standard deviation (SD). Different lowercase letters within a row indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
Swine slurry exhibited EMYs of 317.83 and 524.45 NmL CH4/g VSadded at S/I ratios of 1 and 0.5, respectively. As a widely studied substrate, these values align well with previously reported methane yields ranging from 347 to 487.9 mL CH4/g VSadded [7,35,36,37]. Compared to WAS, swine slurry produced significantly higher methane yields by approximately 55% at S/I 1 and 53% at S/I 0.5, with statistical significance confirmed at both ratios (p < 0.05). Despite swine slurry having lower volatile solids content than WAS (Table 3), its VS fraction is more readily biodegradable, highlighting that the quality and composition of organic matter, rather than quantity alone, critically influence biogas production.
For water lily, EMYs were 393.13 and 434.7 NmL CH4/g VSadded at S/I ratios of 1 and 0.5, respectively, while lotus biomass yielded 375.25 and 492.96 NmL CH4/g VSadded. Both plant biomasses produced comparable methane yields, with no statistically significant difference at S/I 1 (p > 0.05). However, at S/I 0.5, the difference between water lily and lotus became significant (p < 0.05), indicating that the substrate-to-inoculum ratio affects methane production differently depending on plant species.
Table 4 also summarizes the empirical chemical formulas of the four substrates and their theoretical methane potentials (TMPs) derived from ultimate analysis. Swine slurry showed the highest TMP, whereas water lily had the lowest. The TMP of swine slurry was significantly greater than that of water lily (p < 0.05), while no significant differences were observed among the TMP values for WAS, lotus, and swine slurry.
Degradability values near or above 100% for lotus at S/I 0.5 (104.6%) may result from contributions of degradable volatile solids from the inoculum and potential underestimation of TMP due to trace sulfur in plant biomass. Such anomalies have been reported in low S/I ratio systems, where high inoculum loads enhance apparent degradability [38,39]. Co-digestion of WAS with complementary substrates significantly enhanced methane yield, with improvements of 14.89% (SS), 10.97% (WL), and 16.89% (LT) compared to WAS mono-digestion. These findings align with studies reporting increased methane yields through co-digestion, such as a 40% increase with swine manure and sewage sludge [40], highlighting the role of nutrient balance in enhancing biogas production.
3.3. Gompertz Kinetic Model and Co-Digestion Experiment
The modified Gompertz kinetic model was employed to estimate key anaerobic digestion parameters—maximum methane yield (G0), maximum methane production rate (Rm), and lag phase duration (λ)—with results summarized in Table 5. Model performance was evaluated by comparing experimental methane yields with simulated values for both single substrates and co-digestion systems (Figure 2 and Figure 3). High coefficients of determination (R2 values between 0.94 and 0.99) demonstrate strong correlations, confirming the model’s robustness. These findings align with previous studies [7,41], and more recent research using diverse feedstocks such as vegetable crop residues, agricultural waste, rice straw, pig manure, water hyacinth, and food waste have also reported similarly high R2 values [10,42,43,44], further supporting the Gompertz model’s applicability for predicting methane production kinetics across various organic and lignocellulosic substrates.

Table 5.
Gompertz kinetic model parameters.
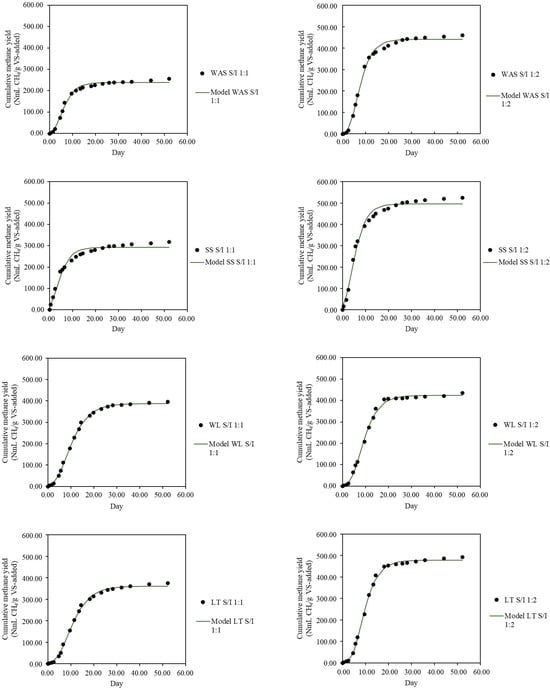
Figure 2.
Comparison of maximum methane yield (G0) predicted by the Gompertz model and experimental methane yield (EMY) for single-substrate experiments at substrate-to-inoculum (S/I) ratios of 1.0 and 0.5. Substrates: WAS (waste activated sludge), SS (swine slurry), WL (water lily), LT (lotus).
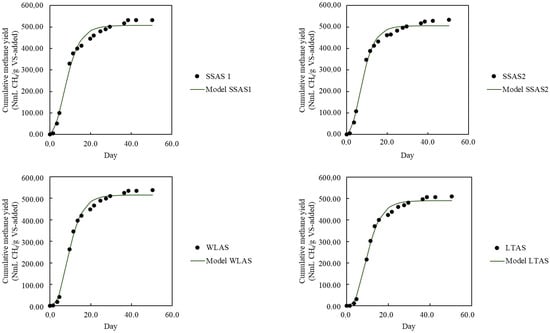
Figure 3.
Comparison of maximum methane yield (G0) predicted by the Gompertz model and experimental methane yield (EMY) for co-digestion experiments at an S/I ratio of 0.5. Combinations: SSAS 1 (swine Slurry + WAS, 1:1), SSAS 2 (swine slurry + WAS, 1:2), WLAS (water lily + WAS, 1:2), LTAS (lotus + WAS, 1:2).
The lowest maximum methane production rate (Rm) was observed for mono-digestion of waste activated sludge (WAS) at an S/I ratio of 1. However, Rm improved at the lower S/I ratio of 0.5 and in co-digestion treatments. These enhancements are likely due to the higher inoculum-to-substrate ratio, which increases microbial abundance and accelerates substrate degradation. Additionally, co-digestion can synergistically promote anaerobic digestion by improving nutrient balance and substrate biodegradability, resulting in higher methane yields. A lower S/I ratio means more microbes relative to substrate, facilitating faster conversion and enhancing the methane production rate. Co-digestion has also been shown to improve process stability and efficiency by balancing nutrients and enhancing the breakdown of complex substrates, enabling faster bioconversion [26,33].
The lag phase in anaerobic digestion reflects the period during which microbial communities acclimate to new substrates, particularly the initial hydrolysis of complex organics. In this study, swine slurry exhibited the shortest lag phase (0.11 days) at an S/I ratio of 1:1, indicating rapid microbial adaptation. This contrasts with findings by Zhang et al. [7], who reported lag phases of 6.9 days for pig manure and 1.8 days for dewatered sewage sludge using the Gompertz model. The discrepancy likely stems from differences in physicochemical properties; swine slurry has higher moisture content and contains more readily degradable, soluble compounds, promoting faster microbial utilization and fermentation [7,26].
In contrast, WAS exhibited a longer lag phase, likely due to its lower content of easily accessible organics and the structural resistance imposed by microbial cell walls and extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) [23,34]. EPS, composed of tightly bound proteins and carbohydrates, forms a dense, semi-rigid matrix that resists enzymatic attack, delaying methane production. Similarly, plant-based biomass showed prolonged lag phases, reflecting the difficulty methanogens face in hydrolyzing lignocellulosic materials, especially when the inoculum is not previously adapted to fibrous substrates [45,46].
Swine slurry’s shorter lag phase is attributed to its higher content of free water and soluble biodegradable compounds, facilitating microbial metabolism [44]. The inoculum’s prior exposure to similar substrates also plays a critical role in shortening the lag phase [25]. Co-digestion of WAS with swine slurry slightly reduced the lag phase, though the difference was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). Conversely, co-digestion of WAS with plant biomass significantly increased the lag phase, likely due to the combined effect of WAS’s recalcitrant matrix and the fibrous nature of plant biomass, which together prolong microbial adaptation.
To reduce the extended lag phase observed during co-digestion of waste activated sludge (WAS) and plant biomass, substrate pre-treatment is often necessary. Pre-treatment methods—chemical, physical, or biological—aim to increase the bioavailability of organic matter, facilitating microbial conversion and thus shortening the lag phase [47]. Such treatments are known to enhance substrate degradability and improve biogas production. For example, intermediate thermal hydrolysis has been reported to increase the hydrolysis rate constant and methane yield by up to fourfold in WAS–wheat straw co-digestion systems [48]. Likewise, mechanical, chemical, and hydrothermal pre-treatments significantly improve the accessibility of lignocellulosic biomass, accelerating enzymatic degradation and boosting biogas output [49]. These findings, building on earlier work by Bjerg Nielsen et al. [47], emphasize the critical role of tailored pre-treatment strategies in optimizing anaerobic digestion performance.
Co-digestion of WAS with complementary substrates such as swine slurry (SS), water lily (WL), and lotus (LT) significantly enhanced the experimental methane yield (EMY) compared to mono-digestion of WAS. Methane yield improvements of 14.89%, 10.97%, and 16.89% were observed for co-digestion with SS, WL, and LT, respectively. Although there was a modest increase in lag phase duration, these results highlight the potential of co-digestion to enhance biogas production.
Previous studies corroborate these findings. For instance, co-digestion of municipal sewage sludge with swine manure increased biogas production by nearly 40% when swine manure was added at 30% by volume [40]. Similarly, co-digestion of municipal WAS with Egeria densa grass improved methane potential [11]. Oduor et al. [10] reported enhanced methane production from co-digesting food waste with aquatic biomass, particularly water hyacinth, demonstrating the benefits of mixed substrates in improving anaerobic digestion efficiency. Conversely, Wang et al. [50] observed that co-digestion of sewage sludge with Eleusine indica grass negatively affected methane production, underscoring the importance of substrate compatibility and optimal mixing ratios.
In this study, neither WL nor LT showed inhibitory effects and both improved biogas production, suggesting their compatibility with WAS in co-digestion systems. The observed increase in methane yield after co-digestion likely results from improved substrate characteristics, notably a more balanced carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratio. Plant biomass contains higher carbon content compared to WAS, and mixing WAS with carbon-rich agricultural residues generally enhances methane yields by optimizing the C/N balance and overall biodegradability [20,30]. Maintaining an appropriate C/N ratio can mitigate volatile fatty acid accumulation and ammonia inhibition, thereby stabilizing the anaerobic digestion process [11].
Water lily and lotus biomass may contain bioactive compounds, such as phenolics and saponins, which could potentially inhibit microbial activity in anaerobic digestion. However, no inhibitory effects were observed in this study, likely due to the low concentrations of these compounds in the processed biomass and the buffering capacity of the co-digestion system. Previous studies have noted that phenolic compounds in aquatic plants can be mitigated through dilution or microbial adaptation in co-digestion systems [45].
In lab-scale BMP assays, the inoculum was degassed to remove residual biogas, ensuring accurate measurement of methane production from the substrates. In large-scale continuous or semi-continuous systems, fresh substrate is typically added to active digesters containing non-degassed inoculum, which may retain residual biogas. However, this is unlikely to significantly alter methane yield trends, as microbial communities in continuous systems are well-adapted to the substrate. Studies suggest that the synergistic effects observed in batch co-digestion systems, such as those in this study, are generally translatable to larger scales, though process optimization (e.g., hydraulic retention time) is critical [25,31].
3.4. Synergistic Effect of Substrate Co-Digestion
Co-digestion of waste activated sludge (WAS) with swine slurry, water lily, or lotus biomass resulted in a notable increase in methane yield compared to the mono-digestion of WAS. As shown in Table 6, the synergy coefficients (α-values) for all co-digestion combinations exceeded 1, indicating positive synergistic interactions that enhanced biogas production. This synergistic effect was supported by both the maximum methane yield (G0) values derived from the Gompertz model and the calculated methane potential (CMP) based on the individual substrate contributions.

Table 6.
Synergistic or antagonistic effects (α) produced from co-digestion.
These improvements are commonly attributed to improved nutrient balance and physicochemical compatibility between co-substrates, which help to overcome the inherent limitations of WAS—particularly its low carbon content and recalcitrant organic compounds [44,51]. For example, co-digesting WAS with high-carbon biomass optimizes the carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratio, a critical factor for stable methanogenesis that helps prevent ammonia inhibition and acidification [38,50]. Moreover, the synergistic effect may also arise from the complementary microbial communities and enhanced enzymatic activities during co-digestion, which collectively improve substrate biodegradability and digestion efficiency [43,48].
The synergistic effects observed in co-digestion likely result from enhanced microbial community dynamics, with complementary substrates promoting diverse methanogenic populations. Studies suggest that co-digestion of WAS with carbon-rich biomass fosters syntrophic interactions between hydrolytic and methanogenic bacteria, improving process efficiency [43]. The use of water lily and lotus biomass as co-substrates is promising due to their high potential shoot biomass yield in phytoremediation systems, based on calculation 5–8 ton FW/ha for Lotus and 8–20 t FW/ha for water lily depending on planting density and other factors. Economically, these plants are advantageous especially when the plants are integrated with tertiary wastewater treatment reducing harvesting costs compared to dedicated bioenergy crops. However, processing costs (e.g., drying and grinding) may impact feasibility, necessitating further cost–benefit analyses to optimize large-scale implementation [11,14].
4. Conclusions
Co-digestion of waste activated sludge (WAS) with swine slurry (SS), water lily (WL), or lotus (LT) shoot biomass significantly enhanced biomethane potential, achieving methane yields exceeding 500 NmL CH4/g VSadded and demonstrating synergistic effects (α > 1). A substrate-to-inoculum (S/I) ratio of 0.5 optimized methane production and biodegradability compared to 1.0, highlighting the importance of inoculum availability. These findings support the integration of phytoremediation byproducts into anaerobic digestion systems for sustainable sludge management and renewable energy recovery. Future research should explore optimum plant biomass incorporation in anaerobic digestion process, microbial community dynamics in co-digestion systems, the agronomic potential of digestate as fertilizer, and the energy cost–benefit of biomass pre-processing to enhance scalability and economic feasibility.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.R., H.L.C. and S.I.A.S.; Data curation, H.L.C. and S.I.A.S.; Formal analysis, S.I.A.S., A.R. and A.S.; Funding acquisition, H.L.C.; Investigation, S.I.A.S. and H.L.C.; Methodology, S.I.A.S., H.L.C. and A.R.; Project administration, S.I.A.S. and H.L.C.; Resources, S.I.A.S.; Software, S.I.A.S. and A.S.; Supervision, H.L.C.; Validation, S.I.A.S., A.R. and H.L.C.; Visualization, S.I.A.S.; Writing—original draft, S.I.A.S., H.L.C. and A.R.; Writing—review and editing, S.I.A.S., H.L.C., A.R. and A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (iPET), project number 116049-3, Ministry of Agriculture, Feed, and Rural Affairs, Republic of Korea. S.I.A.S. also want to thank Seoul National University (SNU) Lecture & Research Scholarship, SNU Merit-based Scholarship, and Cargill Inc. for the financial support she received during her doctoral program.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to express their gratitude to Seoul National University (SNU) Global Scholarship, SNU Lecture & Research Scholarship, SNU Merit-based Scholarship, and Farmsco Co., Ltd. for the financial support the author received during his doctoral program.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
List of Abbreviations
| AD | Anaerobic Digestion |
| BMP | Biochemical Methane Potential |
| WAS | Waste Activated Sludge |
| SS | Swine Slurry |
| WL | Water Lily (Nymphaea spp.) |
| LT | Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) |
| S/I | Substrate-to-Inoculum Ratio |
| VS | Volatile Solids |
| TS | Total Solids |
| FS | Fixed Solids |
| EMY | Experimental Methane Yield |
| TMP | Theoretical Methane Potential |
| C/N | Carbon-to-Nitrogen Ratio |
| NDF | Neutral Detergent Fiber |
| ADF | Acid Detergent Fiber |
| ADL | Acid Detergent Lignin |
| G0 | Maximum Methane Yield (Gompertz) |
| Rmax | Maximum Methane Production Rate |
| λ | Lag Phase Duration |
| Ddeg | Anaerobic Biodegradability |
| α | Synergy Coefficient |
References
- Manea, E.E.; Bumbac, C. Sludge Composting—Is This a Viable Solution for Wastewater Sludge Management? Water 2024, 16, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, H.Y.; Kim, Y. Comparison of domestic and European Union statutes and management policies for livestock excretion. Clean Technol. 2024, 30, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranjpe, A.; Saxena, S.; Jain, P. A review on performance improvement of anaerobic digestion using co-digestion of food waste and sewage sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 338, 117733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Vander Elst, M.; Smets, I.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Baeyens, J.; Deng, Y. Reviewing Improved Anaerobic Digestion by Combined Pre-Treatment of Waste-Activated Sludge (WAS). Sustainability 2024, 16, 6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, M.; Nasab, H.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Ebrahimi, A.A. Evaluation of the efficiency of dry anaerobic digester in the production of biogas and fertilizer using activated sludge and plant waste. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Yoon, Y.M.; Kim, C.H.; Giersdorf, J. Status of biogas technologies and policies in South Korea. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 3430–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wei, Q.; Wu, S.; Qi, D.; Li, W.; Zuo, Z.; Dong, R. Batch anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure with dewatered sewage sludge under mesophilic conditions. Appl. Energy 2014, 128, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renggaman, A.; Choi, H.L.; Sudiarto, S.I.A.; Febrisiantosa, A.; Ahn, D.H.; Choung, Y.W.; Suresh, A. Biochemical Methane Potential of Swine Slaughter Waste, Swine Slurry, and Its Codigestion Effect. Energies 2021, 14, 7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renggaman, A.; Choi, H.L.; Sudiarto, S.I.A.; Suresh, A.; Jeon, Y.C. Biomethane Potential of Beef Cattle Slaughterhouse Waste and the Impact of Co-Digestion with Cattle Feces and Swine Slurry. Fermentation 2024, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduor, W.W.; Wandera, S.M.; Murunga, S.I.; Raude, J.M. Enhancement of anaerobic digestion by co-digesting food waste and water hyacinth in improving treatment of organic waste and bio-methane recovery. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, G.; Lu, X.; Kobayashi, T.; Li, Y.Y.; Xu, K.; Zhao, Y. Mesophilic anaerobic co-digestion of waste activated sludge and Egeria densa: Performance assessment and kinetic analysis. Appl. Energy 2015, 148, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudiarto, S.I.A.; Renggaman, A.; Choi, H.L. Floating aquatic plants for total nitrogen and phosphorus removal from treated swine wastewater and their biomass characteristics. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, R.; He, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, R.; Zheng, C.; Pan, D.; Fang, H.; Wu, X. Integrating livestock and aquatic plant towards mitigating antibiotic resistance transmission from swine wastewater. npj Clean Water 2025, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudiarto, S.I.A.; Choi, H.L.; Renggaman, A. Application of Phytoremediation for Total Nitrogen and Total Phosphorus Removal from Treated Swine Wastewater and Bio-methane Potential of the Biomass. J. Korea Org. Resour. Recycl. Assoc. 2015, 23, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abd Rasid, N.S.; Naim, M.N.; Man, H.C.; Bakar, N.A.; Mokhtar, M.N. Evaluation of surface water treated with lotus plant; Nelumbo nucifera. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jain, A.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Yugandhar, P.; Xu, Y.; Sun, S.; Hu, F. Differential efficacy of water lily cultivars in phytoremediation of eutrophic water contaminated with phosphorus and nitrogen. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 171, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.C.; Gonçalves, P.R.; Nobre, A.; Alves, M.M. Biomethanation potential of macroalgae Ulva spp. and Gracilaria spp. and in co-digestion with waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohutskyi, P.; Keller, T.A.; Phan, D.; Parris, M.L.; Li, M.; Richardson, L.; Kopachevsky, A.M. Co-digestion of Wastewater-Grown Filamentous Algae with Sewage Sludge Improves Biomethane Production and Energy Balance Compared to Thermal, Chemical, or Thermochemical Pretreatments. Front. Energy Res. 2019, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renggaman, A.; Choi, H.L.; Suresh, A. Underground anaerobic digester to solve the energy balance problem in temperate regions: A pilot study. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2015, 31, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibro, M.K.; Ancha, V.R.; Lemma, D.B. Impacts of anaerobic co-digestion on different influencing parameters: A critical review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaseelan, V.N. Anaerobic digestion of biomass for methane production: A review. Biomass Bioenergy 1997, 13, 83–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, A.; Parajuli, A.; Dangol, S.; Thapa, B.; Sapkota, L.; Carmona-Martínez, A.A.; Ghimire, A. Effect of the substrate to inoculum ratios on the kinetics of biogas production during the mesophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste. Energies 2022, 15, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potdukhe, R.M.; Sahu, N.; Kapley, A.; Kumar, R. Co-digestion of waste activated sludge and agricultural straw waste for enhanced biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 15, 100769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarina, R.; Mezule, L. Opportunities for resource recovery from Latvian municipal sewage sludge. Heliyon 2023, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabii, A.; El Sayed, A.; Ismail, A.; Aldin, S.; Dahman, Y.; Elbeshbishy, E. Optimizing the Mixing Ratios of Source-Separated Organic Waste and Thickened Waste Activated Sludge in Anaerobic Co-Digestion: A New Approach. Processes 2024, 12, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Z.; Dai, X. Perspective on enhancing the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottet, A.; François, E.; Latrille, E.; Steyer, J.P.; Déléris, S.; Vedrenne, F.; Carrère, H. Estimating anaerobic biodegradability indicators for waste activated sludge. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 160, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, S.I.; Miyata, N.; Iwahori, K. Recovery of biomass cellulose from waste sewage sludge. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2002, 4, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; van Lier, J.B.; de Kreuk, M. Digestibility of waste aerobic granular sludge from a full-scale municipal wastewater treatment system. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Pandey, R.; Aryal, N.; Lohani, S.P. Recent advances in co-digestion conjugates for anaerobic digestion of food waste. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, I.D.; Rosa, A.P.; Almeida, G.K.; Rocha, D.N.; Neves, T.D.; Borges, A.C. Integrated Assessment of Methane Production from the Co-Digestion of Swine Wastewater and Other Organic Wastes. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chynoweth, D.P.; Turick, C.E.; Owens, J.M.; Jerger, D.E.; Peck, M.W. Biochemical methane potential of biomass and waste feedstocks. Biomass Bioenergy. 1993, 5, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Iraqi, A.R.; Gandhi, B.P.; Folkard, A.M.; Barker, P.A.; Semple, K.T. Influence of inoculum to substrate ratio and substrates mixing ratio on biogas production from the anaerobic co-digestion of Phragmites australis and food waste. Bioenergy Res. 2024, 17, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Hua, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, C.; Wu, B.; Dai, X. Impediments to bioaccessibility in the anaerobic digestion of waste activated Sludge: An in-depth review of challenges and influencing factors. Energy Environ. Sustain. 2025, 1, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonmati, A.; Flotats, X.; Mateu, L.; Campos, E. Study of thermal hydrolysis as a pretreatment to mesophilic anaerobic digestion of pig slurry. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, K.J.; Jang, A.M.; Yim, S.K.; Kim, I.S. The effects of digestion temperature and temperature shock on the biogas yields from the mesophilic anaerobic digestion of swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Cao, W.; Liu, R. Kinetics of methane production from swine manure and buffalo manure. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 177, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.M.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, K.S.; Kim, C.H. Effects of substrate to inoculum ratio on the biochemical methane potential of piggery slaughterhouse wastes. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, F.; Fernández-Cegrí, V.; De la Rubia, M.A.; Borja, R.; Béline, F.; Cavinato, C.; Ganesh, R. Biochemical methane potential (BMP) of solid organic substrates: Evaluation of anaerobic biodegradability using data from an international interlaboratory study. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 86, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowski, S.; Domański, J.; Weatherley, L. Anaerobic co-digestion of swine and poultry manure with municipal sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafle, G.K.; Kim, S.H.; Sung, K.I. Ensiling of fish industry waste for biogas production: A lab scale evaluation of biochemical methane potential (BMP) and kinetics. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 127, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, W.; Sun, M.; Xu, X.; Zhang, B.; Sun, Y. Evaluation of biochemical methane potential and kinetics on the anaerobic digestion of vegetable crop residues. Energies 2018, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almomani, F.; Bhosale, R.R. Enhancing the production of biogas through anaerobic co-digestion of agricultural waste and chemical pre-treatments. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, B.; An, X.; Shen, F.; An, W.; Zhang, Q. Anaerobic co-digestion of rice straw and pig manure pretreated with a cellulolytic microflora: Methane yield evaluation and kinetics analysis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 579405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyi-Loh, C.E.; Lues, R. Anaerobic digestion of lignocellulosic biomass: Substrate characteristics (challenge) and innovation. Fermentation 2023, 9, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaweesuk, A.; Artnaseaw, A.; Benjapiyaporn, C. Optimization of methane production through co-digestion of pig manure with napier grass. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2025, 26, 100931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerg-Nielsen, M.; Ward, A.J.; Møller, H.B.; Ottosen, L.D.M. Influence on anaerobic digestion by intermediate thermal hydrolysis of waste activated sludge and co-digested wheat straw. J. Waste Manag. 2018, 72, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhong, C.; Gao, M.; Shi, D.; He, Q.; Gu, L. Effects of hydrothermal pretreatment on the mono-and co-digestion of waste activated sludge and wheat straw. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, B.J.; Nakhate, S.P.; Gupta, R.K.; Chavan, A.R.; Singh, A.K.; Khardenavis, A.A.; Purohit, H.J. A comprehensive review on the pretreatment of lignocellulosic wastes for improved biogas production by anaerobic digestion. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 3429–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Hidaka, T.; Tsumori, J. Enhancement of anaerobic digestion of shredded grass by co-digestion with sewage sludge and hyperthermophilic pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudzanani, K.; Iyuke, S.E.; Daramola, M.O. Co-digestion of wastewater treatment sewage sludge with various biowastes: A comparative study for the enhancement of biogas production. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 2172–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).