Abstract
In this paper, we present a review of the intra-aortic balloon pump, as well as the usage of it in the medical field today. An intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) is a biomedical device that can assist the heart during unstable angina or after a heart attack. This pump is typically used in patients who suffer from ischemia of the heart tissue, due to an unbalanced level of myocardial oxygen supply or demand. Through counterpulsation, which is a technique to synchronize the external pumping of blood with the heart’s cycle, the device can balance the supply and demand of blood that is necessary for the heart to pump properly. The IABP is comprised of the following four components: a polyurethane balloon, a polyethylene or fiber-optic catheter, a transducer, and the intra-aortic balloon pump console. In the past, researchers have used other materials that have low biocompatibility and can cause complications within the body. This analysis will explain the complications and state changes that occurred due to them. Limitations of past designs and advantages of current designs will be acknowledged, for they can be used by researchers to enhance designs for the future. Consequently, the analysis of this device may lead to improved designs and treatment in the future for patients with cardiac conditions.
1. Introduction
The cardiovascular system is an imperative system in the human body, with the heart being a key organ for proper function. It allows for blood, oxygen, and nutrients to be delivered to different parts of the body [1]. The heart needs a specific amount of oxygen, so that it can continue to function properly (myocardial oxygen demand) and it also has a maximum amount of oxygen that can be provided by the blood (myocardial oxygen supply) [2]. If the heart does not have an accurate supply and demand balance, then it would be considered weak and in need of assistance. One suggestion physicians make for patients with a heart condition, such as heart failure, is the use of an intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) [3].
The IABP is a long and thin balloon that is able to control the blood flow through the aorta. The device attempts to balance out the supply and demand of blood and oxygen needed for the heart. To understand how the device works, it is necessary to gain knowledge on the fundamentals of hemodynamics and where the IABP will be incorporated. As Figure 1 shows [4], the blood flow through the heart begins with deoxygenated blood flowing into the right atrium (1), then the tricuspid valve opens and releases blood into the right ventricle (2), where it will then flow through the pulmonary valve and into the lungs where it will become oxygenated. The blood then flows into the left atrium and the mitral valve will open, allowing blood to flow into the left ventricle (3). The heart then pumps the blood through the aortic valve and into the aorta, to bring oxygenated blood to different parts of the body (4). The IABP joins this circulation in the aorta and takes a mechanical circulatory support approach to treat cardiac diseases [5].
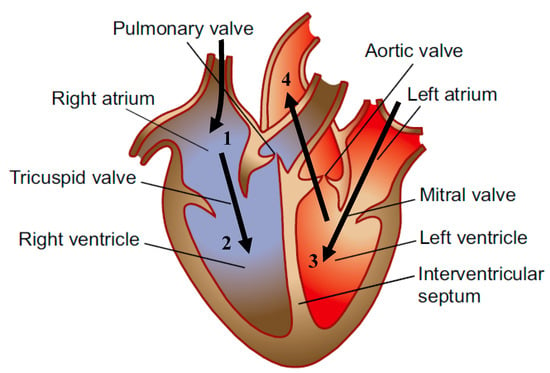
Figure 1.
Anatomy of the human heart [4].
The cardiovascular support that the IABP can accomplish is obtained through inflation and deflation of the balloon within the descending aorta. The presence of the IABP leads to hyperperfusion in the head and arms and hypoperfusion in the abdominal region and the lower portion of the body [5]. To place the balloon in the aorta, a catheter must be inserted into the femoral artery, which leads to a blockade of the artery in use during inflation. Complications can come from the obstruction of this artery, causing a displacement of the blood volume within the aorta, leading to a visceral and cerebral hyperperfusion. Clinically, different assist ratios can be used to improve perfusion to specific body parts. This allows the IABP to be useful for the treatment of many cardiac conditions like cardiogenic shock, left ventricular failure and unstable angina [6].
Counterpulsation and the IABP date back to 1952, when Kantrowitz first described how to augment coronary blood flow using animal models [7]. In 1961, Moulopoulos developed a prototype of the IABP using a latex balloon and polyethylene catheter, that completed its job through counterpulsation [8]. A new development occurred in 1972 by A. Bregman, which was an IABP with two balloons that would block the distal blood flow and augment the proximal flow leading to the brain [9,10,11]. These discoveries enabled the use of the IABP on more than 5000 patients by 1976 [10,11,12]. Moreover, the IABP is able to improve ventricular performance by facilitating an increase in myocardial oxygen supply and decreasing myocardial oxygen demand [8]. Through the ages, scientists have recognized the many hemodynamic effects of IABP treatment, including a decrease in afterload on the heart and an increase in diastolic pressure in the aorta. [13]
2. IABP Architecture and Indications
The IABP has gone through immense advancements as science has progressed. The current design allows for many hemodynamic benefits, but only if proper sizing and equipment are in use. As Figure 2 shows, the IABP is inserted through the femoral artery; this procedure can be performed in the intensive care unit (ICU), catheterization lab, or in an operating room. It is moved to the proper position in the descending thoracic aorta by a threading technique [12]. To ensure that the procedure was performed correctly, a physician may use fluoroscopy as visualization within the body, or a radiograph film directly after [14]. After insertion, the electrocardiogram (ECG) on the console begins to read the heart’s cycle and will inflate the balloon with carbon dioxide or helium during the beginning of diastole [10,12,15]. Helium is typically chosen because it has shown to have faster gas retrieval and lower viscosity that allows for a larger volume to be held in the balloon [12]. This treatment method is known as counterpulsation and is defined as diastolic inflation and quick systolic deflation [16]. There will be an increase in arterial pressure, since the aortic valve has closed, and this allows for an increase in cardiac output. When the heart goes through systole the machine will have the IABP deflate, causing the diastolic pressure to decrease, ventricles to become tense, and increase stroke volume. The console has a frequency setting that is originally set at a 1:2 ratio, meaning every other heartbeat will be assisted [14]. Patients are weaned off the IABP rather than immediately stopped; this way they do not go into shock from the dependency on the pump [12].
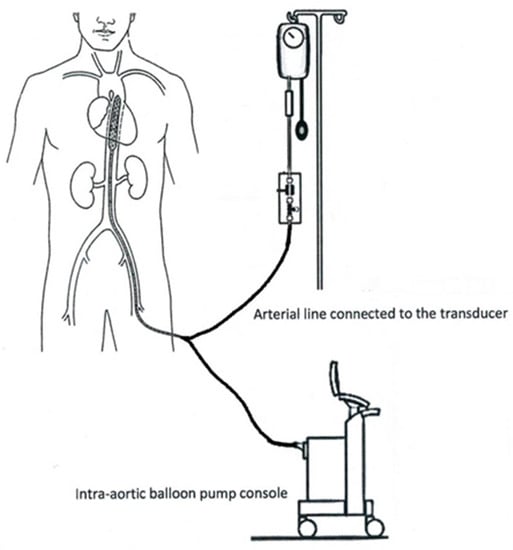
Figure 2.
Mechanical setup of the intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) [17].
The IABP is used for an array of heart conditions, but mainly high-risk patients with acute myocardial infarction and in cardiogenic shock [4]. Another popular condition for this form of treatment is high-risk that patients are undergoing artery bypass grafting surgery. Treatment using the IABP for patients with severe heart failure showed an increase in cerebral blood flow by 20% augmentation [18]. This increase in blood flow is thought to be an indirect result of the IABP, due to the displacement of blood volume, leading to an increase in coronary flow. For patients that suffer from ischemic stroke, a decrease in left ventricular afterload and increase in cerebral perfusion can be beneficial, which is one reason physicians use the IABP as a form of treatment [18]. Research has also shown that the pump can be used in patients who have undergone a transplant, by normalizing reduced cerebral blood flow. The main benefit that the IABP offers and physicians utilize is the ability to enhance cerebral blood flow in patients with severe cardiac conditions. This increase in cerebral blood flow is a result of the augmentation of diastolic cerebral blood flow that occurs during IABP treatment [18].
As all procedures do, counterpulsation using the IABP has complications that follow. There have been several serious complications reported like major bleeding, stroke, and systemic infections [16]. There is a higher rate of stroke for patients who undergo treatment with the pump. Research has shown that this could be due to a change in hemodynamics which leads to cerebral ischemia or hemorrhage [16]. Physicians combat the listed complications with blood transfusions, but technical modifications have also assisted. For example, there are new techniques that allow for a sheathless insertion with specific catheters, to reduce mechanical vascular complications [16]. The four main components of the IABP (the balloon, catheter, IABP console, and transducer) have all gone through extensive research and modifications over the years, leading to the current design [12].
2.1. Balloon
The first study on IABP took place in 1961 by S. Moulopoulos and associates [10]. The balloon that is used must be able to block the passage of blood in the aorta at certain times, meaning it has to be able to withstand the pressures within the heart. It should be made of a material that is not easy to pop or break and must be biocompatible. In 1962 [8], latex balloons were used to ensure that the device could close off the aorta properly. This changed in 1967 [11] when researchers started using the polyurethane balloons that were non-distensible, meaning that the material is structured to be less compliant under distention force and will undergo little change in dimension under the force [8,19,20,21]. This change also occurred because this material is synthetic and will not have issues with biocompatibility, whereas latex is a common allergen [22]. To this day, polyurethane balloons are still used, because they allow for a prolonged time span for counterpulsation. The IABP is a counterpulsation device, thus it needs to be able to sustain for a longer period of external pumping. The change from latex balloons to polyurethane balloons was needed because it created a safe and efficient IABP that otherwise could have had issues with failure [10]. A detrimental aspect of the IABP is the sizing of the balloon for each patient. Sizing is based upon the patient’s aorta, which can be sized differently in relation to age, weight, and size. The proper sizing of the balloon would be the size of the patient’s subclavian artery to their coeliac artery for length, and a diameter that is 95% of the diameter of their aorta [12]. The anatomical reasoning behind the diameter sizing is that 100% occlusion leads to the potential aortic wall and red blood cell damage [12]. To have a maximum hemodynamic gain, it is important to have the optimal occlusivity, as previously stated [12]. The position of the balloon with the aorta can create a disadvantage and loss of hemodynamic benefits. If the balloon is closer to the aortic valve, there will be a greater elevation in diastolic pressure. Placement of the tip of the balloon should be distal to the left subclavian artery, and the proximal end should lie above the renal vessels [10]. The current placement of the designs will allow for fewer difficulties and are important for satisfactory results [10,11].
2.2. Catheter
The IABP has a catheter that connects the balloon in the aorta to the monitoring machine and transducer outside the body. A catheter is a flexible tube that can be inserted into a narrow opening in the body, and can be used to remove or insert fluid. In this case, the catheter is used to bring the gas from the machine into the balloon or vice versa, for inflation and deflation. The catheter is important for monitoring the arterial pressure in the descending aorta, by use of a transducer [23]. During initial testing in 1961, researchers used a polyethylene catheter with holes in the side [10]. The catheter was designed to have the distal end occluded so that inflation and deflation occurred through the holes. This is important for the device to function properly because the catheter creates a closed system that allows for the proper air pressure and flows to the balloon to occur. Figure 3 shows the patent for a catheter and assembly for extracorporeal circulation, submitted in 1990 [24]. This goal of the design is to have a small resistance to blood flow of the blood from the vessels into the catheter body, along with reduced pressure loss. Therefore, Terumo and Sagae created a catheter with a hollow body and side holes, so that when it is used on the blood-drawing side the negative pressure applied will be distributed through the opening at the distal end and the side holes. This would reduce the risk of the catheter attempting to suck the blood vessel wall.
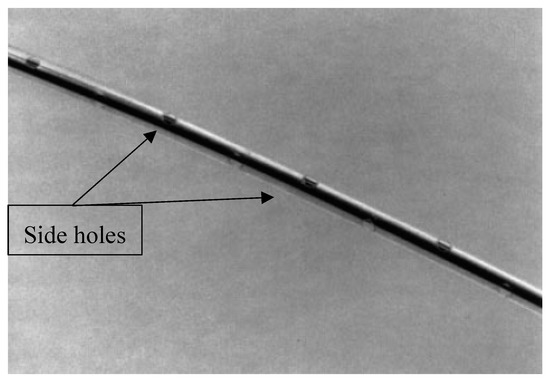
Figure 3.
Catheter design similar to that used in 1961, with multiple side holes [24].
Past designs have had issues with side holes, since they create an accessible site for foreign material to enter, as a sample is shown in Figure 3. Due to the size of the catheter, insertion became a troubling process that had complications. To better the process, 9 Fr 40 mL catheters were upgraded to smaller 7 Fr 40 mL ones in 2006 [25]. This change resulted in less obstruction and vascular complications, but the size was still a troubling issue. With time, engineers and researchers were able to design the first fiber-optic IABP catheter [26]. This new design allows better transmission with an abrasion-free material that coats the outside and is unaffected by dampening or noise [27]. Not all physicians use this new catheter, but it is a much-needed improvement of this medical device. Flexible fiberoptic catheters are able to monitor the blood oxygen saturation within the cardiovascular system. This new design allows physicians to calibrate in vivo without the danger of infections, lessening the potential for vascular complications in IABP treatment.
2.3. IABP Console
The console (monitoring machine) is where the source of gas originates for the IABP, and it is needed so that the balloon can inflate and deflate properly. It is also necessary for the monitoring system to be able to tell what phase is happening, so that the balloon does not inflate at the incorrect time and cause complications. The monitoring machine uses an electrocardiogram (ECG) to determine the phase that the heart is in and then inflates the balloon with helium when the aortic valve closes and there is in an increase in pressure and cardiac output [28,29,30]. Helium was not always used; in 1962 researchers chose to use carbon dioxide, but this gas moved slowly through the catheter [31]. One of the issues with carbon dioxide was that if there was a leakage or rupture of the catheter, it could cause an air embolus. Helium was chosen because of its low viscosity and ability to dissolve in the blood, meaning that the risk of an air embolus was resolved [12,29]. As stated before, the monitoring machine releases helium into the catheter based off the ECG graph that is shown on the monitor. It is able to recognize the isoelectric (T-P) interval and inflate the balloon, as well as the ventricular depolarization (QRS-T) interval to deflate the balloon [30]. The ECG was used in the first trial of the IABP; at that point in time, it was a 12-lead ECG, which is what we know and use today [31]. The only difference is that it is included in the monitoring system, rather than a separate component. Detection of the cardiac cycle is important, which is why the monitoring machine is so crucial, but a way to detect the pressure in the heart is just as important.
2.4. Transducers
Transducers were incorporated into the design of the IABP during the first testing in 1962 [11,15]. The function of it was to convert energy or signals from one form to another, which can then be displayed on a monitor for interpretation. For the IABP, it is important that blood pressure is continuously monitored because the dicrotic notch of the aortic blood pressure wave is used to time the inflation and deflation of the balloon [32]. The prior design was a fluid-filled transducer that was pre-calibrated, with a monitoring kit and flash device. This device had setbacks, like clotting the monitoring lines and reducing frequency response, which could then cause complications with knowing when to inflate or deflate the balloon [32]. Physicians can also use a micromanometer to determine the blood pressure, but they are very expensive devices and are prone to electrical disturbances.
There was a need in the field for a reliable and affordable transducer, to better the design of the IABP. A recent patent by Schock Williams and Walters shows a catheter with blood pressure sensors attached. The catheter has a micromanometer on the tip and a fluid-filled transducer attached to the end. The monitoring machine will read the signal from the micromanometer and can be compared to that of the transducer. Comparison of the mean blood pressure can be used to make the proper adjustments and better IABP treatment. As stated before, there is the risk of electrical disturbance from micromanometers, so the use of the additional transducer allows for proper signals to still be read. If the micromanometer is having difficulties, the transducer signals will be used instead [32]. This design will allow for more adequate results and advancements in treatment using the IABP.
3. Additional Counterpulsation Techniques
For patients that have chronic or acute heart conditions, there are many treatments in the medical field that can fit their specific needs. As stated prior, counterpulsation is a technique commonly used, which synchronizes the external pumping of blood with the phases of the heart to assist with circulation and decrease the overall work of the heart [27]. Currently, there are three forms of counterpulsation that are used in these patients; extracorporeal, percutaneous, and implantable counterpulsation. As Table 1 shows below, there are four different methods with the three combined techniques. Extracorporeal counterpulsation uses a method known as enhanced external counterpulsation to meet the patient’s needs. Percutaneous counterpulsation uses the intra-aortic balloon pump as the means to treat patients. Finally, implantable counterpulsation has three different methods that could be used; Cardioplus, C-pulse, and Symphony [33].

Table 1.
Counterpulsation Techniques [33].
Enhanced external counterpulsation has a pneumatic cuff that is placed on the patient’s lower legs, which inflates and deflates to the cardiac cycle (inflation during diastole and deflation during systole). This technique does not require surgical implantation or the use of anticoagulation regimens, but it does require multiple visits for treatment [33]. The IABP, as described earlier, is a balloon that is placed within patients descending aorta and works via counterpulsation. These counterpulsation devices inflate during diastole and quickly deflate during systole. This technique is made for short-term use and is beneficial both hemodynamically and metabolically. The location of the balloon and catheter, as well as biocompatibility issues, makes this method problematic. The implantable devices used for counterpulsation include the Cardioplus, C-pulse, and Symphony. The Cardioplus is an inflatable patch that is implanted into the heart. The C-pulse is a cuff that is wrapped around the patients ascending aorta [33]. The Symphony is a device implanted near the right axillary vein of the patient, in a pocket like a pacemaker. Each of these devices needs implantation but allows for on-demand and long-term assistance of the heart. The issue with these implanted devices is that if a patient needs surgery or a heart transplant later on in life, they may have complications or not be eligible. Overall, there are many counterpulsation techniques that can be used, and the method should be chosen based on the patients’ needs and the advantages each has.
Physician recommendation for IABP treatment has declined due to controversy and an increase in complication rates [13,34]. The efficiency and safety for patients with acute myocardial infarction with or without cardiogenic shock have sparked controversy, but studies have shown no clear distinction on what treatment options would be beneficial [13]. Those who do recommend the IABP prefer it for its easy percutaneous insertion [34]. Technical complications may come with any treatment, but for the IABP, the insertion techniques and duration of treatment are major drawbacks. Table 2 shows a summary of the complications related to insertion, treatment duration, and biocompatibility for IABP treatment, as well as the benefits of the treatment.

Table 2.
Technical Complications and Advantages.
4. Future Use of the IABP
The intra-aortic balloon pump has been used for many cardiac conditions in the past forty years. Normally, the device is used for issues like unstable angina, arrhythmia, and myocarditis [5]. The research that is currently being completed is for use of the IABP before surgeries, or for conditions that do not commonly use the IABP for treatment. Some researchers have proposed that the IABP can be used as perioperative support in high-risk cardiac surgeries, which would mean that if a patient had a heart transplant, the IABP could reduce stress on the body once the new heart has been implanted [30,35]. This is important because heart transplants can be tough on the body, and the surgeons want to make sure it is compatible with the body. If it gets some assistance there is less stress on the patient, and hopefully the transplant would incorporate into the body properly. Another proposed idea for the IABP is to use it for treatment of left ventricular distention on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [30,35]. An extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is a form of life support that is typically used in babies, children, and adults with heart conditions. It is a form of a heart–lung bypass, which means it will take over the function of the heart and lungs during surgery. Researchers think that the IABP will help with the swelling of the ventricle during this process. This would mean that there would be lower chances of adverse reactions during this bypass process. Overall, it seems that the future of the IABP has to do with if it will be approved for use in patients with other disorders, other than the typical heart conditions listed. Researches have shown great effort to use the pump for different perspectives that may assist patients in an outstanding way.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aneta, S. Physics of the human cardiovascular system. Contemp. Phys. 1999, 40, 31–55. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, K.T.; Janicki, J.S. The metabolic demand and oxygen supply of the heart: Physiologic and clinical considerations. Am. J. Cardiol. 1979, 44, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, O.; Pae, W.E.; Daily, B.B.; Pierce, W.S. Ventriculoarterial coupling with intra-aortic balloon pump in acute ischemic heart failure. J. Thorac Cardiovasc. Surg. 1999, 117, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shah, S.; Gnanasegaran, G.; Sundberg-Cohon, J.; Buscombe, J. The Heart: Anatomy, Physiology and Exercise Physiology. In Integrating Cardiology for Nuclear Medicine Physicians; Movahed, A., Gnanasegaran, G., Buscombe, J., Hall, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, M.V.; Gramigna, V.; Fragomeni, G. A CFD investigation of intra-aortic balloon pump assist ratio effects on aortic hemodynamics. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 39, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremper, R.S. Intra-aortic balloon pump therapy—A primer for perioperative nurses. AORN J. 2006, 84, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, M.; Zacharowski, K. Principles of intra-aortic balloon pump counterpulsation. Contin. Educ. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain 2009, 9, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulopoulos, S.; Stamatelopoulos, S.; Petrou, P. Intraaortic balloon assistance in intractable cardiogenic shock. Eur. Heart J. 1986, 7, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clauss, R.H.; Missier, P.; Reed, G.E.; Tice, D. Assisted circulation by counter-pulsation with an intraaortic balloon Methods and effects. In Annual Conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology; Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Parissis, H.; Graham, V.; Lampridis, S.; Lau, M.; Hooks, G.; Mhandu, P.C. IABP: History-Evolution-Pathophysiology-Indications: What We Need to Know. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, K. Origins of intraaortic balloon pumping. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1990, 50, 672–674. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, K.T.; Janicki, J.S. Intraaortic balloon counterpulsation: A review of physiological principles, clinical results, and device safety. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1974, 17, 602–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, S.K.; Buiten, L.; Esposito, M.L.; Paruchuri, V.; Mullin, A.; Breton, C.; Patel, A.R. Acute Hemodynamic Effects of Intra-Aortic Balloon Counterpulsation Pumps in Advanced Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2017, 23, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbara, B.H. Intra-aortic Balloon Pump. Essential 2010, 165, 459–468. [Google Scholar]
- Kantrowitz, A.; Freed, P.S.; Tachi, H.; Suzuki, A. Electrocardiographic Measurement Method for Controlling an Intra-aortic Balloon Pump. U.S. Patent No. 4,809,681, 7 May 1989. [Google Scholar]
- De Waha, S.; Desch, S.; Eitel, I.; Fuernau, G.; Lurz, P.; Sandri, M.; Thiele, H. Reprint of “Intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation—Basic principles and clinical evidence”. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 61, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connie, L.; Gurung, R. Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump—A Thing of the Past? Kai Tiaki Nurs. N. Z. 2019, 25, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Pfluecke, C.; Christoph, M.; Kolschmann, S.; Tarnowski, D.; Forkmann, M.; Jellinghaus, S.; Ibrahim, K. Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP) Counterpulsation Improves Cerebral Perfusion in Patients with Decreased Left Ventricular Function. Perfusion 2014, 29, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warshaw, E.M. Latex allergy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1998, 39, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schock, R.B.; Williams, J.; Walters, D.A. Intra-Aortic Balloon Catheter Having a Dual Sensor Pressure Sensing System. U.S. Patent No. 6,616,597, 9 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- EP2049181A1—Catheter Balloons with Integrated Non-Distensible Seals. Google Patents. Google. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/EP2049181A1 (accessed on 6 February 2019).
- Perera, D. Elective intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation during high-risk percutaneous coronary intervention: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2010, 304, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, D.L.; Bates, S. Intra Aortic Balloon Pumping: How to Stay on Course. Am. J. Nurs. 1990, 90, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, H.H.; Ladd, M.E.; Hilfiker, P.R.; Paul, G.G.; Ha, S.W.; Debatin, J.F. Autoperfused balloon catheter for intravascular MR imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 9, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, G.; Morra, L.; Castaldi, G.; Maschietto, L.; Gripshi, F.; Fabris, E.; Perkan, A.; Benussi, B.; Sinagra, G.; Pappalardo, A. Preoperative Intra-Aortic Counterpulsation in Cardiac Surgery: Insights From a Retrospective Series of 588 Consecutive High-Risk Patients. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2018, 32, 2077–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majd, A.; Lindsay, J. A Brief Review: History to Understand Fundamentals of Electrocardiography. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2012, 2, 1438310. [Google Scholar]
- Jonathan, W.; Hoff, R.; Kaushansky, Y. Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump Condensation Prevention System. U.S. Patent No. 6,210,319, 3 April 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zantos, G.N.; Hanlon-Pena, P. Adaptive Real Time ECG Triggering and Uses Thereof. U.S. Patent No. 8,204,582, 19 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Papaioannou, T.G.; Stefanadis, C. Basic principles of the Intraaortic balloon pump and mechanisms affecting its performance. ASAIO J. 2005, 51, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeling, W.B.; Williams, M.L.; Slaughter, M.S.; Zhao, Y.; Puskas, J.D. Off-pump and on-pump coronary revascularization in patients with low ejection fraction: A report from the society of thoracic surgeons national database. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 96, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elghazzawi, Z. Apparatus and Method for Distinguishing Heart Beats from Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump Beats. U.S. Patent No. 5,365,933, 22 November 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Schock, R.B.; Williams, J.; Walters, D.A. US7229403B2—Intra-Aortic Balloon Catheter Having a Dual Sensor Pressure Sensing System. U.S. Patent No 7,229,403, 12 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Black, M.C.; Schumer, E.M.; Rogers, M.; Trivedi, J.; Slaughter, M.S. Sunshine Heart C-Pulse: Device for NYHA Class III and ambulatory Class IV heart failure. Future Cardiol. 2016, 12, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralabos, P.; Alan, S.; Al-Alao, B. Intra aortic balloon pump: Literature review of risk factors related to complications of the intraaortic balloon pump. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2011, 6, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Huu, A.L.; Shum-Tim, D. Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump: Current Evidence & Future Perspectives. Future Cardiol. 2018, 14, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).