Abstract
Swarm unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) have been increasingly explored for maritime defense and security operations, particularly in scenarios requiring the rapid detection and interception of multiple attackers. The target detection reliability and defender–target assignment stability are significantly crucial to ensure quick responses and prevent mission failure. A key challenge in such missions lies in the assignment of targets among multiple defenders, where frequent reassignment can cause instability and inefficiency. This paper proposes a novel ETA-hysteresis-guided reinforcement learning (RL) framework for continuous multi-target hunting with swarm USVs. The approach integrates estimated time of arrival (ETA)-based task allocation with a dual-threshold hysteresis mechanism to balance responsiveness and stability in multi-target assignments. The ETA module provides an efficient criterion for selecting the most suitable defender–target pair, while hysteresis prevents oscillatory reassignments triggered by marginal changes in ETA values. The framework is trained and evaluated in a 3D-simulated water environment with multiple continuous targets under static and dynamic water environments. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves substantial measurable improvements compared to basic MAPPO and MAPPO-LSTM, including faster convergence speed (+20–30%), higher interception rates (improvement of +9.5% to +20.9%), and reduced mean time-to-capture (by 9.4–19.0%), while maintaining competitive path smoothness and energy efficiency. The findings highlight the potential of integrating time-aware assignment strategies with reinforcement learning to enable robust, scalable, and stable swarm USV operations for maritime security applications.
1. Introduction
Unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) have become a significant technology in the domain of autonomous maritime operations. Compared to conventional manned vessels, USVs offer several advantages in terms of endurance, risk reduction, and scalability, enabling persistent operations in challenging and hazardous environments [1]. Their applications span a wide range of fields, from oceanographic research and environmental monitoring [2,3] to maritime defense and security [4,5]. Over the past decade, the number of publications on swarm USV operation has grown almost exponentially [6]. This trend reflects the increasing interest in deploying multiple autonomous surface vessels (a paradigm recognized for its potential to address complex maritime missions).
The swarm USV concept corresponds to the autonomy level of USVs, as their effectiveness increasingly depends on the coordination capability and collective performance tasks within a group [7]. In addition, swarm USVs for threat handling leverage distributed intelligence, coordination, and adaptability. Swarm USVs can perform some fundamental tasks such as path planning [8,9], collision or obstacle avoidance [10,11], and formation control [12]. Inspired by nature’s biological swarms, these systems exploit local interactions and decentralized control to achieve collective behaviors such as group target tracking [13], area coverage [14], target interception [15], target encirclement task [5,16], and collaborative defense [17,18]. In the context of maritime security, swarms offer distinct advantages for countering asymmetric threats, including intruding vessels, pirates, or unmanned adversarial agents. Unlike single-agent approaches, swarm systems enhance robustness through redundancy, improve situational awareness through distributed sensing, and enable more dynamic strategies for interception and deterrence.
One emerging frontier in this area is the application of swarm USVs for multi-target hunting, where the swarm must identify, track, and neutralize multiple adversarial or high-value targets simultaneously. The research gap for swarm USV multi-target hunting is that these crucial tasks are still underexplored compared to other swarm USVs task operations such as formation control, collision avoidance, path planning, and target tracking [6]. Target hunting is inherently challenging due to the continuous and uncertain dynamics of the maritime domain. More studies focus on single-target [19,20,21] or fixed-number target hunting [22,23,24,25]. Traditional control and rule-based methods often fall short when addressing such high-dimensional, dynamic, and adversarial scenarios. Consequently, reinforcement learning (RL) has gained attraction as a promising approach, offering adaptability and the capability to learn effective policies through trial-and-error interactions. This study proposes ETA-hysteresis-based RL specifically for continuous multi-target hunting in static and dynamic water environments.
2. Related Works
Because the urgency of target hunting in the maritime sector has significantly increased, various studies and research have been conducted to gain effective target hunting methods. Numerous approaches have been used to determine the most effective and efficient method, ranging from traditional approaches to the latest advancements using deep reinforcement learning. Some studies adopt traditional approaches because of their simplicity and low computational cost while still achieving reasonably good results. Bai et al. (2025) applied a distributed extended state observer (DESO), data fusion algorithm, and integral backstepping sliding mode controller for target tracking control of multiple USVs [13]. Another research study used gradient-based control and event-triggered control for target tracking, formation control, and collision avoidance task [26]. Later, improved A* algorithm combined with binary tree traversal and biomimetic U-shaped formation was used for target hunting with path planning and obstacle avoidance tasks [27]. While these traditional approaches offer practical solutions with relatively low complexity, recent studies have increasingly shifted toward learning-based algorithms to address more dynamic and challenging maritime scenarios.
Learning-based algorithms offer more effective strategies for target hunting because of their capability to iteratively improve the solution through experience. Some studies implement nature-based optimization algorithms for target hunting tasks. Sun et al. (2022) proposed self-organizing control with artificial potential field (APF) algorithms for target interception tasks [28]. Moreover, other studies used deep learning approaches for target hunting and target tracking tasks. They implemented OR-LSTM (Obstacle-Relation Long Short-Term Memory) [29] and YOLOv5 with adaptive extended Kalman filter (AEKF) [30]. In addition to swarm USVs, many studies on multi-target hunting have also been conducted using other types of vehicles or robotic platforms [31,32]. These learning-based methods demonstrate the potential of machine learning and deep learning to enhance target hunting performance, paving the way for more adaptive solutions such as reinforcement learning.
Numerous studies have demonstrated the applicability of reinforcement learning due to its ability to adaptively learn from the environment and design reward mechanisms that enhance the efficiency of swarm USVs in performing multi-target hunting tasks. Early implementation of the multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) using swarm USV defenders is for hunting single targets [19,20,21]. Other studies applied multi-agent reinforcement learning [22,23] for cooperative multi-target hunting and dynamic navigation. Moreover, Xue et al. (2025) proposed MSA-MADDPG (multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient) with multi-head self-attention for multi-USV hunting tasks [24]. Another study proposed end-to-end DRL method for guidance and control of USV for target tracking in ocean environment [25]. However, most studies prioritize discussing single target hunting or multi-target hunting strategies with a fixed number of targets. Moreover, convergence speed remains a key challenge in the development of learning algorithms. Therefore, this paper proposes ETA-hysteresis-based RL specifically for continuous multi-target hunting to produce a learning algorithm that accelerates convergence speed and improves the interception rate performance of swarm USV.
Continuous multi-target hunting in static and dynamic maritime environments requires a control strategy that can both assign targets reliably and generate adaptive pursuit behaviors under uncertainty. Traditional methods such as rule-based control, A* [27], or k-means assignment can select targets but cannot learn real-time pursuit strategies or remain robust under disturbances like waves, drag, and current. Likewise, existing MARL methods (e.g., MAPPO [19,20,21], MADDPG [24], attention-based RL) lack explicit assignment stability, often leading to redundant clustering and frequent target switching. In addition to autonomous systems, other related stability challenges under dynamic environments have also been identified in other fields, such as traffic flow and cyber-physical systems. Zhai et al. proposed a multi-phase lattice hydrodynamic model with a continuous self-stabilizing control protocol to suppress oscillatory behavior under malicious cyber-attacks, highlighting the role of stabilization mechanisms in adversarial environments [33]. A similar study was conducted by Chen et al. for analyzing large-scale vehicle trajectory data and showed that frequent lane-changing decisions and interaction patterns strongly influence system-level stability and efficiency [34]. They conceptually reinforce the importance of stability-aware coordination and switching suppression, which directly motivates the hysteresis-based target assignment. Therefore, this paper adopts ETA-hysteresis-based RL because it combines the strengths of both domains: ETA provides fast and interpretable target selection, hysteresis suppresses oscillatory reassignments, and RL learns smooth, cooperative navigation policies that adapt to dynamic water conditions. This approach offers more stable coordination, faster convergence, and higher interception efficiency than alternative methods. The details of proposed method will be explained in Section 4.
3. Problem Formulation
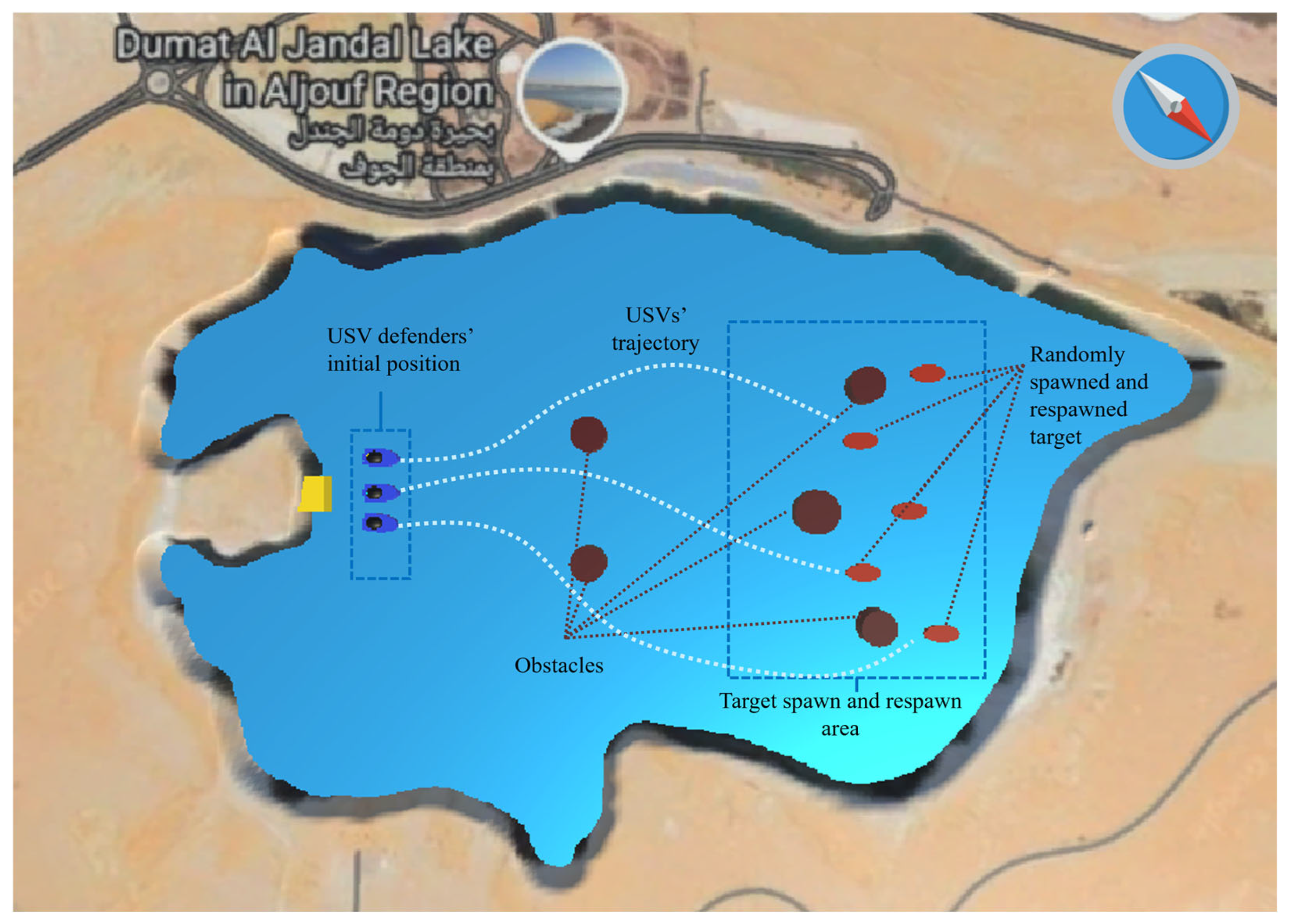
In a continuous multi-target hunting USV swarm scenario, defender USVs are set for hunting (interception) task for five attacker USV targets . For clarity and consistency, variables and mathematical symbols used in the problem formulation are summarized in Table 1. The number of defenders and attacker agents is flexible and can be modified based on the needs of the experimental setup or real-world deployment. Each target intercepted by the defender is immediately respawned at a new random position within the simulation area. Thus, this scenario provides a continuous system: there are always five active targets to be hunted in turn. Figure 1 illustrates the swarm USV defender and target in the experimental environment. The simulation environment map is based on real-world water environment shape of Dumat Al Jandal Lake in Saudi Arabia.

Table 1.
Summary of notations used in problem formulation.
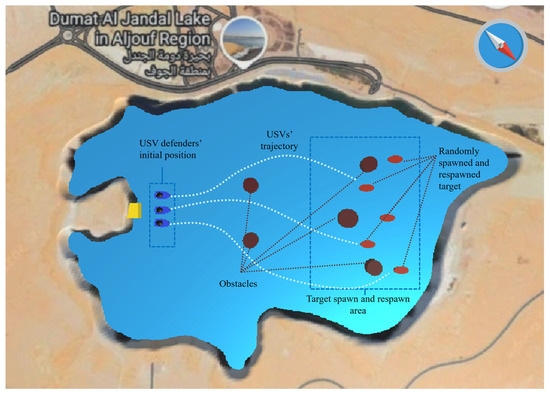
Figure 1.
Illustration of the swarm USV defender and target in the experimental environment.
The main challenges that arise in continuous multi-target hunting include the target assignment, interception control, and assignment stability. For the target assignment, swarm USV without coordination, multiple defenders can pursue the same target, leaving others unguarded. Moreover, for the interception control, once a target is assigned, each defender must generate efficient movement control to pursue and engage the attacker while avoiding obstacles. Finally, for the assignment stability, if targets change frequently due to dynamic positioning, switching thrashing can occur. Therefore, a hysteresis mechanism is used to ensure stable assignment.
3.1. Problem Definition
Let denote the position of defender and the position and target . The Euclidean distance follows this equation:
The assignment problem becomes the following:
Thus, defenders are allocated to minimize travel time with a hysteresis penalty for switching targets, where is the maximum speed of defender .
3.2. Swarm USV Kinematics
The kinematics is implemented in the Unity 3D simulation platform including the following:
- Translationwith .
- Rotationwith discrete angular commands.
- Collision and Respawn: If a defender collides with a target, the target is removed and immediately respawned at a new random location.
3.3. Environmental Dynamics
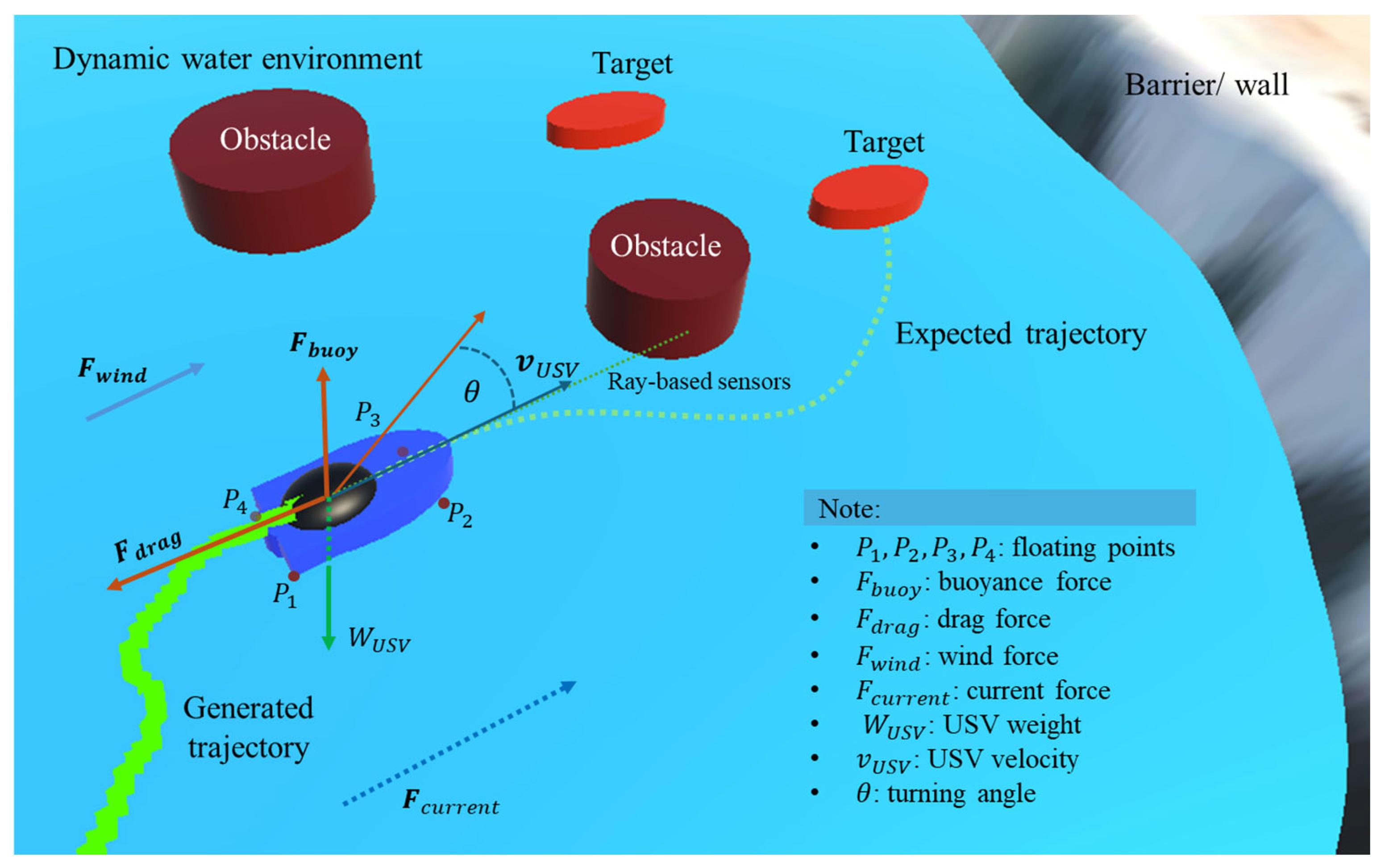
The experiments were conducted in both static and dynamic environments. In the dynamic environment, the swarm USVs and the target were subjected to real-world physical parameters such as wave-induced surface motion, water and air drag, buoyant force, water currents, wind effects, inertia, and thruster delays. In contrast, the static environment ignored these factors, providing an idealized and simplified setting. The dynamic water surface behavior is described as this equation [35]:
where denotes the wave height, is the amplitude, are wave constants, is angular frequency, and is the initial phase. The vessel’s flotation is simulated with four reference points () along the hull, each interacting with the wave height; the buoyant force is then computed as
ensuring stable floating behavior. Drag is applied depending on the vessel’s submersion, with air drag for and water drag for , formulated as . Environmental disturbances also include wind force, expressed as , and water current force, modeled as to capture natural variations. Inertia is introduced by exponential interpolation, given as with , where is the inertia smooth time. Finally, actuator dynamics are incorporated by applying a thruster delay through a queue mechanism: where is the simulation interval and is the delay frame count. Collectively, these formulations ensure that USV realistically responds to wave fluctuations, hydrodynamic resistance, and environmental disturbances in the simulation. Figure 2 illustrates the real-world dynamics implemented in this study.
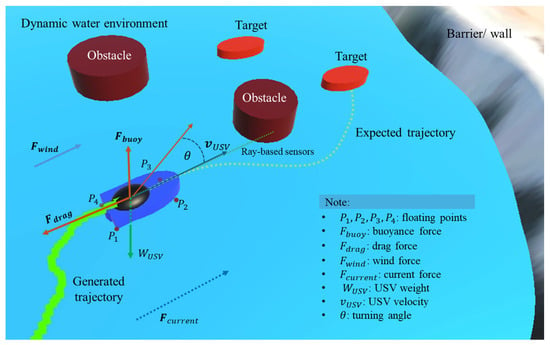
Figure 2.
Visualization of agent’s and environment dynamics of physics parameters.
3.4. Research Contributions
This study presents several key contributions to the field of multi-agent coordination and reinforcement learning for swarm USVs in maritime defense and security applications:
- a.
- Novel ETA-hysteresis assignment mechanism for continuous multi-target huntingThe study introduces a new hybrid framework that integrates estimated time of arrival (ETA)-based task allocation with a dual-threshold hysteresis mechanism into Multi-Agent Proximal Policy Optimization (MAPPO). This design stabilizes target assignment by preventing oscillatory switching between targets caused by marginal ETA differences, ensuring more consistent cooperation among multiple defenders in continuous multi-target hunting.
- b.
- First RL framework for continuous multi-target hunting scenario formulationA continuous-hunting problem is formulated where new targets respawn immediately after interception, maintaining a persistent multi-target environment. This formulation better represents real-world maritime surveillance and defense scenarios compared to episodic or single-target tasks, enabling agents to learn long-term pursuit and coordination strategies.
- c.
- Integration of static and dynamic maritime environment modelingThe simulation incorporates realistic hydrodynamic conditions (including wave-induced motion, wind, current, drag, inertia, and thruster delay), creating a dynamic and physically consistent testing environment. This enables evaluation of learning stability and adaptability under real-world disturbances, advancing the realism of USV reinforcement learning studies.
- d.
- Comprehensive multi-metric evaluation and comparative analysisThe proposed method is systematically compared with baseline MAPPO and MAPPO-LSTM models across static and dynamic conditions using multiple performance indicators (capture rate, mean time-to-capture, total distance, trajectory smoothness, and energy consumption). The results show significant improvement in convergence speed, interception efficiency, and energy optimization.
- e.
- Practical insights for real-world swarm USV deploymentBy demonstrating faster convergence, higher interception success, and stable task coordination, the ETA-hysteresis MAPPO framework provides a robust foundation for deploying autonomous USV swarms in maritime defense, rescue, and surveillance missions. The findings highlight the importance of integrating temporal assignment logic within multi-agent RL to achieve scalable, cooperative, and energy-efficient swarm operations.
Compared to existing control, heuristic, and reinforcement-learning-based multi-target hunting methods, the proposed ETA-hysteresis MAPPO framework offers three key advantages. Firstly, the proposed method is stable and efficient because the existing method (mentioned in the related works section) typically relies on distance-based heuristics or implicit coordination, which often lead to unstable or oscillatory target reassignment (especially in continuous multi-target scenarios). Secondly, the proposed method provides faster and more robust learning in dynamic environments. Prior studies mainly evaluate RL-based USV hunting in simplified or static environments. In contrast, our method is validated in both static and highly dynamic maritime settings. Lastly, the proposed method produces better results, especially in interception efficiency and pursuit time (as explained in Section 5: Result and Analysis).
4. Methodology
This section describes the experimental setup, baseline multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) algorithms, the proposed ETA-hysteresis-guided MAPPO framework, and performance evaluation metrics. All notations used are consistent with the definitions provided in the notation in Table 2.

Table 2.
Summary of notations used in methodology.
4.1. Experimental Setup
The experimental environment is developed in the Unity ML-Agents platform to simulate multi-target hunting scenarios. Three defender USVs are deployed against five targets. Targets are stationary in this stage (velocity = 0) and respawn at random positions immediately after interception, ensuring a continuous multi-target hunting task as illustrated in Figure 1. Defenders are controlled via reinforcement learning (RL). Action space is discrete commands (forward, left turn, right turn, idle, rotate in place). Observations include the following:
- Self-state (position, heading).
- Assigned attacker: relative position and ETA (distance or max speed).
- Top K nearest attackers (optional).
- Obstacle perception via ray-based sensors.
Interception occurs when a defender collides with an attacker. Defender receives a positive reward, and the attacker respawns at a new random location. This scenario allows training in a continuous stream of targets, simulating a persistent surveillance or defense mission.
4.2. Baseline Algorithm (MAPPO and MAPPO-LSTM)
This study applied the basic proximal policy optimization (PPO) algorithm, an RL method based on policy and actor–critic framework. Derived from the Trust Region Policy Optimization (TRPO) algorithm, this approach simplifies computation and enhances learning performance by refining the objective function. The Multi-Agent Proximal Policy Optimization (MAPPO) is a development of the PPO algorithm designed to address the dynamics of interactions between agents in a single environment. Essentially, PPO maintains the stability of policy updates through clipping so that policy changes are not too far from the previous one. In a multi-agent context, MAPPO adopts the centralized training–decentralized execution (CTDE) paradigm: training utilizes global information for stability and coordination, while execution is carried out autonomously by agents based on local observations.
For other comparison to the proposed method, this paper performed experiments using MAPPO-LSTM [36]. This approach extends the MAPPO algorithm by embedding an LSTM network within the policy structure. While MAPPO enhances stability in multi-agent training via the CTDE framework, the addition of LSTM equips agents with memory to handle partial observability and temporal correlations. This internal state tracking allows agents to recall past observations, enabling more consistent and context-aware decision-making, ultimately improving coordination and adaptability in dynamic and sequential environments. Table 3 shows the summary of reward systems in the algorithm (MAPPO, MAPPO-LSTM, and proposed method), and Table 4 provides the detailed summary of hyperparameter used in the experiment.

Table 3.
Summary of reward shaping system in the algorithm.

Table 4.
Summary of hyperparameter used in the experiments.
In multi-target hunting scenarios, increasing the number of defenders and targets naturally increases environmental complexity. In MAPPO and MAPPO-LSTM, scalability challenges are primarily associated with the centralized critic used during training, as it must process joint observations or global states. This increases computational cost as the number of agents grows. However, during execution, both MAPPO and MAPPO-LSTM operate in a decentralized manner, allowing each USV to act independently based on local observations, which preserves scalability in real deployments. Furthermore, the ETA-hysteresis assignment mechanism reduces coordination burden by stabilizing target allocation and preventing excessive switching, which mitigates combinatorial explosion in agent interactions. While large-scale swarms may still require further optimization or hierarchical coordination, the proposed framework remains computationally feasible for the defender–target ratios considered in this study.
4.3. Proposed Method (ETA-Hysteresis-Based MAPPO)
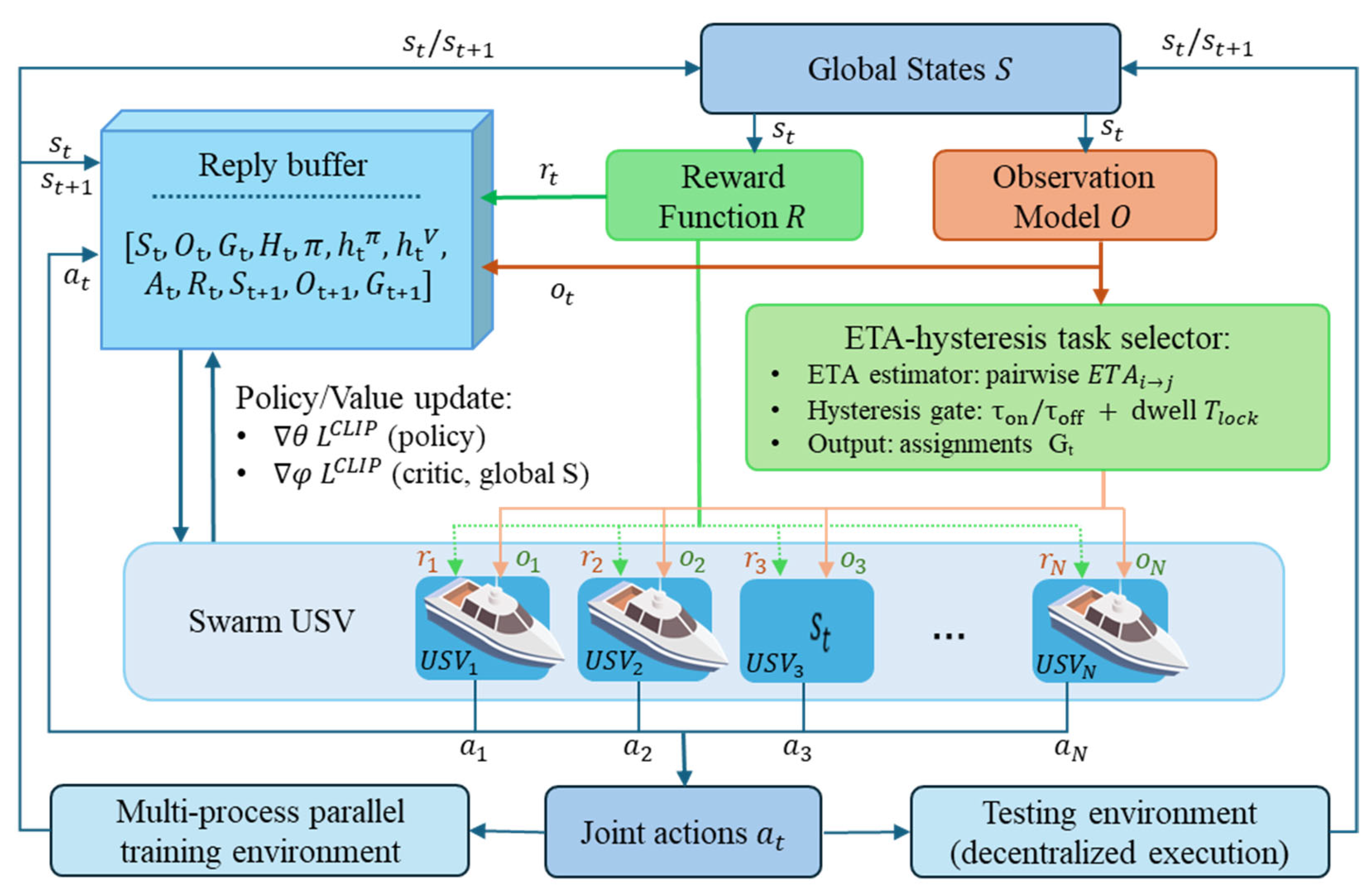
In the proposed framework, reinforcement learning serves as the core decision-making mechanism that enables each defender USV to learn how to move, pursue, and coordinate in a continuous multi-target environment. This work proposed an ETA-hysteresis-guided MAPPO framework for continuous multi-target hunting with swarm USVs under a centralized training and decentralized execution (CTDE) paradigm. Hysteresis-based RL is a method that combines RL with hysteresis logic in a hybrid system to improve the robustness of RL policies against noise in measurements [37]. At each timestep , the environment provides a global state and local observations for each agent , constructed by the observation model as detailed shown in diagram Figure 3. Moreover, Algorithm 1 shows the ETA-hysteresis MAPPO training algorithm (pseudocode). The estimated time of arrival (ETA) matrix between each defender and target is defined as follows:
where is the target position and is the defender’s velocity. More complex ETA models (e.g., considering currents, drag, or sea state) can be used without loss of generality.
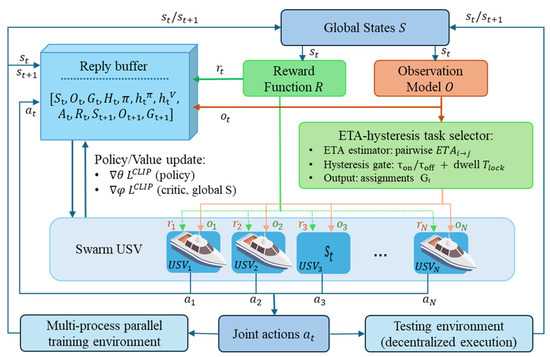
Figure 3.
Centralized training–decentralized execution framework of swarm USV.
To prevent thrashing when ETA values are close, this paper adopted a dual-threshold hysteresis mechanism with a dwell time . Let denote the target currently locked by agent , defined as follows:
The ETA-hysteresis assignment rule is as follows:
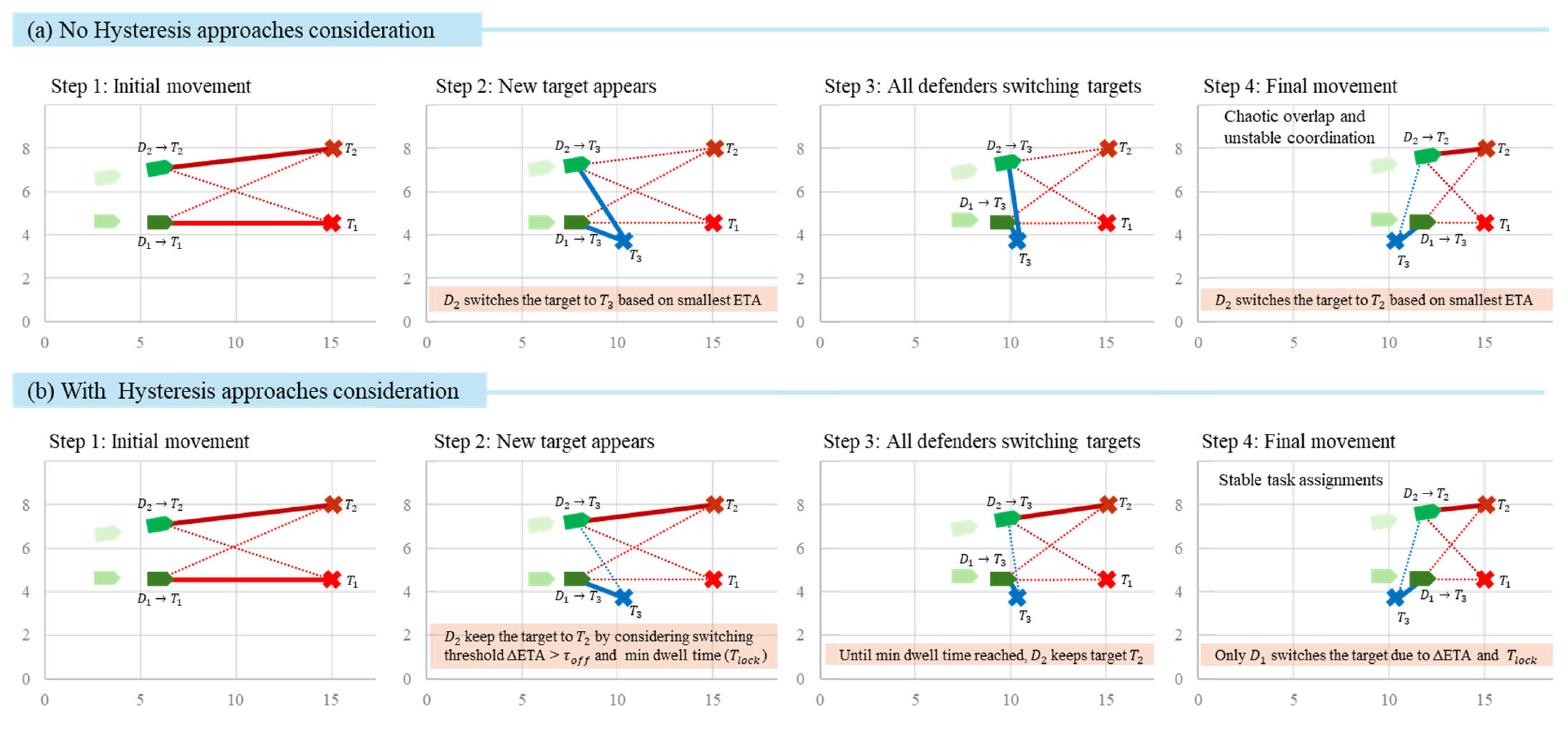
where is the locking time. The module outputs assignment vectors (or soft weights in encoding the locked target. Figure 4 visualized the comparison between no hysteresis and ETA-hysteresis in deciding target switching. In this visualization, method with ETA-hysteresis and task allocation provide more stable switching targets.
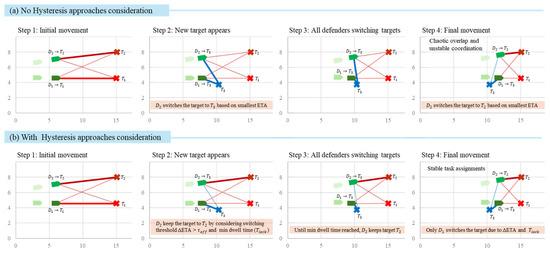
Figure 4.
Comparison between no hysteresis (top) and ETA-hysteresis with task allocation (bottom) oversteps 1 to 4 in continuous target hunting with new target () spawned.
During decentralized execution, each USV uses the shared actor with input and produces action . A centralized critic estimates state values from the global state: .
In centralized training, transitions are stored as follows:
where records lock states. We compute generalized advantage estimation (GAE):
The actor is optimized with PPO-Clip is as follows:
while the critic minimizes as follows:
Parameters are updated via Adam:
By integrating ETA-hysteresis, the framework stabilizes target assignments using thresholds and dwell time , which reduces oscillatory reassignments, improves capture rate, and accelerates convergence in multi-target dynamic scenarios.
| Algorithm 1. ETA-Hysteresis MAPPO for Continuous Multi-Target Hunting. | |
| 1. Initialize actor , critic , hysteresis parameters , 2. Initialize replay buffer 3. while training do 4. Reset environment and initialize locked targets L_i and dwell times δt_i 5. for t = 1 … T_steps do 6. # 1. ETA computation and hysteresis switching 7. for each defender i do 8. Compute for all targets 9. ← 10. if (+ ) and () then 11. 12. else 13. 14. end if 15. Build local observation 16. end for 17. # 2. Action selection and environment step 18. Sample actions 19. Step environment to obtain next states and rewards 20. Store transition in buffer 21. if episode ends then break 22. end for 23. # 3. PPO update 24. Compute advantages using GAE (γ, λ) 25. Update actor with PPO-clipped loss 26. Update critic with value loss 27. Clear buffer 23. end while | |
In Figure 4, each panel shows example of two defenders ( and ) and their assigned targets ( and newly spawned ). Colored solid lines indicate an active assignment, while dashed lines represent ETA estimates to other potential targets. In the no hysteresis condition (top row), both defenders instantly switch to the newly spawned target at Step 2 because it has the smallest ETA. This impulsive behavior causes both agents to pursue the same target simultaneously, leading to chaotic overlap and unstable coordination.
In contrast, under the ETA-hysteresis and task allocation scenario (bottom row), each defender updates its target only when two conditions are met: (1) the ETA improvement exceeds the switching threshold (), and (2) the defender has maintained its current lock for at least the minimum dwell time (). As a result, gradually switches to the new target once its ETA advantage becomes significant, while maintains its lock on , preventing conflict. This hysteresis-based mechanism stabilizes task assignments, avoids oscillatory switching, and ensures a balanced distribution of defenders across available targets.
The hypotheses of this study are formulated based on the expected behavioral differences among the tested reinforcement learning algorithms. It is hypothesized that the basic MAPPO algorithm will improve coverage and enable cooperative pursuit among defenders; however, it will suffer from frequent target switching and unstable task assignments due to its purely distance-based coordination. The MAPPO-LSTM, which incorporates temporal memory through recurrent layers, is expected to demonstrate better temporal consistency and smoother policy adaptation compared to basic MAPPO, yet it may still exhibit slower convergence and less stable coordination in continuous multi-target scenarios. In contrast, the proposed ETA-hysteresis MAPPO is hypothesized to achieve the highest capture rate, the lowest switching frequency, and the fastest convergence speed. By integrating ETA-based assignment with hysteresis filtering, this approach is expected to ensure more stable, cooperative, and energy-efficient multi-agent behavior, particularly in dynamic maritime environments where environmental disturbances can induce decision oscillations.
4.4. State Representation and Reward Function
Each defender USV interacts with the environment using local observation and obtains a scalar reward . The global state used only by centralized critic. Moreover, the local observation at the time for defender USV is defined as this equation:
where and denote the current position and heading of defender , and denotes the currently locked target index with its position . Then, the ETA to target is defined as . are indices for the top- nearest other potential targets. Moreover, defines the distance to obstacles or objects encoded from ray-based sensors. denotes the dwell time since the last target switch, and define the binary flag indicating whether both hysteresis conditions are satisfied.
The accumulative reward for defender USV is a weighted sum of reward shaping terms defined in Table 3. The reward shaping formulation is defined in this equation:
where:
- : main (biggest) positive reward when intercepts a target (with an additional bonus reward if the target is its locked target ),
- : team reward obtained if other USV defenders are near the interception area,
- : dense shaping reward proportional to the reduction in distance to the locked target,
- : commit-zone reward for staying near the target until interception stage,
- : small timestep penalty to encourage efficient completion,
- : penalty for idle actions,
- : penalties for collisions with obstacles, walls, or the base zone,
- : penalty when USV defenders are too close to each other, encouraging spatial dispersion.
The specific numerical values for these terms (e.g., for interception, per step, etc.) are listed in Table 3.
4.5. Parameter Selection and Sensitivity Considerations
To balance assignment stability and policy responsiveness, the hysteresis and learning parameters are chosen based on preliminary experiments. The ETA threshold for switching was selected to be large enough to force oscillatory target switching from marginal ETA fluctuations yet small enough to allow switching when a defender encounters a significantly better target. Moreover, the dwell-time threshold is set to prevent quick back-and-forth switching, with shorter values resulting in unstable coordination and longer values reducing the response. For learning hyperparameters such as the learning rate and clipping range of PPO, this study adopted common values applied for the multi-agent PPO literature and ensured that they yield stable training curves in both static and dynamic environments. Empirically, small deviations (±20–30%) from the chosen values do not significantly affect the convergence trend, while larger deviations can lead to slower learning or increased variance. These observations provide practical guidance for refining the proposed method in other maritime scenarios while ensuring a balance between learning stability and flexible task allocation.
4.6. Performance Evaluation
The performance of the proposed method is compared with basic MAPPO and MAPPO-LSTM. This study used the following evaluation metrics:
- Capture Rate. This is percentage of attackers intercepted during an episode.
- Mean Time-to-Capture. This evaluation is based on average number of steps per successful interception. Mean time-to-capture is following this equation:is the timestamp of the previous sample/reset.
- Total Distance. Let the samples be indexed by , taken every seconds. Position: . Forward (projection to the plane and normalized): . Path length or total distance of swarm USV is measured by this equation:
- Smoothness (deg/m). The total smoothness of swarm USV is measured by this equation:with a tiny to avoid divide-by-zero. Let be the signed yaw change from ) to (in degrees). Lower number of smoothness is better, indicating straighter for smoother path.
- Energy Consumption. Lower energy consumption is better. With cost coefficient , . Define idle indicator , else 0. Idle power rate . Energy consumption follows this formulation:
5. Result and Analysis
To provide a more comprehensive comparison, the analysis integrates multiple complementary perspectives including convergence behavior, interception effectiveness, coordination stability, motion efficiency, and energy consumption. Convergence behavior shows how rapidly each method stabilizes during training. The interception effectiveness compares total interceptions and mean time-to-capture. Moreover, coordination stability highlights the redundant clustering and target-switching frequency. Motion efficiency is evaluated through trajectory smoothness and total distance travel. Finally, energy consumption reflects operational efficiency in both static and dynamic water conditions. Together with the statistical significance tests, these diverse presentation angles offer a multi-faceted understanding of why the proposed ETA-hysteresis MAPPO consistently outperforms the baseline MAPPO and MAPPO-LSTM.
5.1. Convergence Speed Analysis
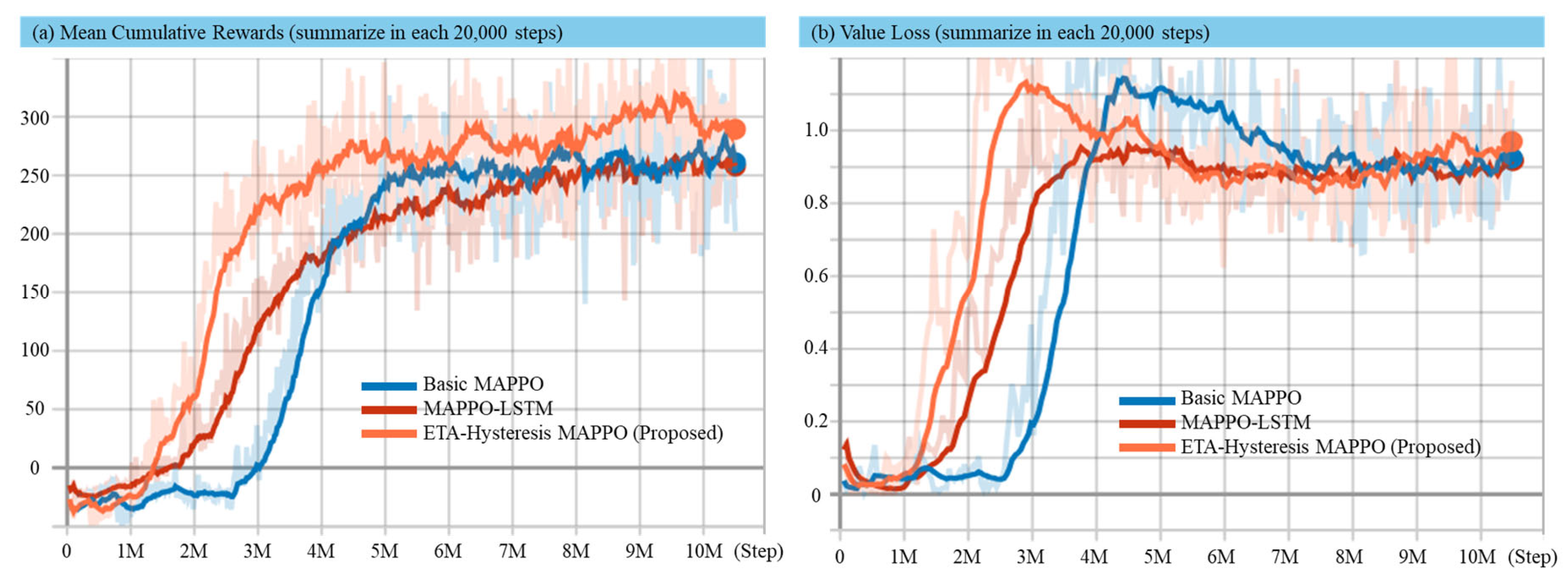
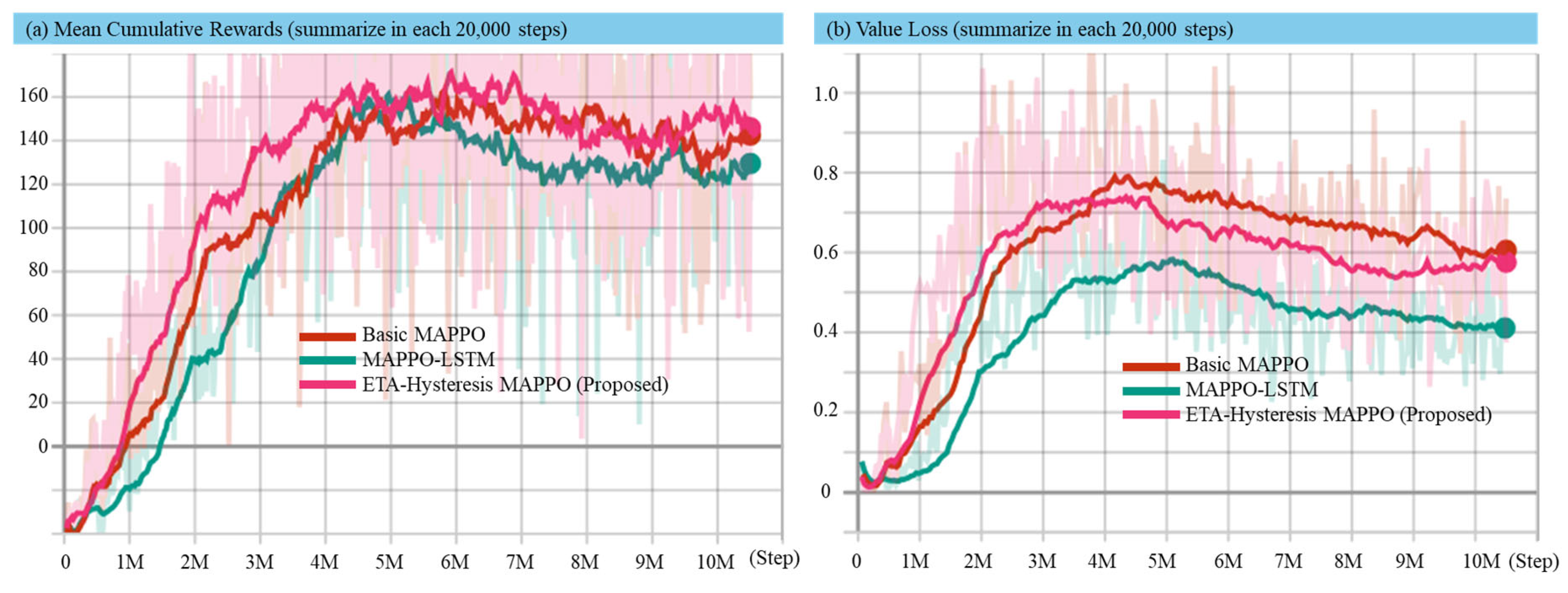
Convergence speed analysis measures how quickly the method used reaches a convergent solution (related to multi-target hunting task). In this analysis, the average reward is recorded at every 20,000 steps and is visualized from step 0 to step 1,050,000 in Figure 5 and Figure 6 for static and dynamic environment, respectively. For the static environment, one episode contains 7000 steps, while in the dynamic environment, one episode contains 8000 steps. This consideration is because in dynamic environment it is more challenging to earn cumulative rewards. Value loss visualization is shown to strengthen the convergence analysis.
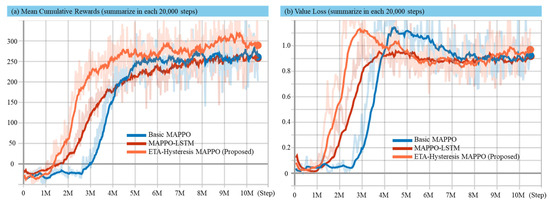
Figure 5.
Experimental results in static environment for mean cumulative reward (a) and value loss (b) using the basic MAPPO, MAPPO-LSTM, and proposed method.
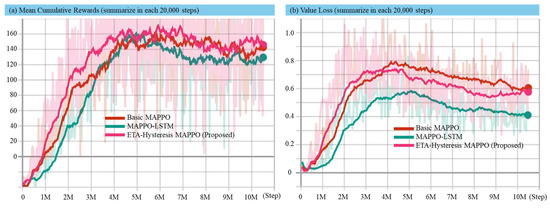
Figure 6.
Experimental results in dynamic environment for mean cumulative reward (a) and value loss (b) using the basic MAPPO, MAPPO-LSTM, and proposed method.
Figure 5 and Figure 6 present the comparative performance of the proposed ETA-hysteresis MAPPO, MAPPO-LSTM, and basic MAPPO algorithms in both static and dynamic maritime environments. In the static environment (Figure 5), the proposed ETA-hysteresis MAPPO demonstrates clear superiority in learning speed and stability. It surpasses the 200-reward threshold at approximately 2.5–3 million steps, achieving convergence around 270–280 reward units. By comparison, MAPPO-LSTM reaches the same threshold at 3.5–4 million steps, converging around 250–260, while basic MAPPO requires more than 4.5 million steps and stabilizes near 230–240. The value loss trends show that ETA-hysteresis achieves earlier and more stable convergence, maintaining a lower loss throughout training, while MAPPO-LSTM converges more slowly and basic MAPPO exhibits the largest fluctuations with delayed stabilization. These findings indicate that the ETA-hysteresis mechanism effectively reduces oscillatory reassignments of targets and improves critic estimation accuracy, leading to both faster convergence and higher final performance in stable conditions.
When the environment becomes dynamic, as shown in Figure 6 (incorporating wind disturbance, surface waves, ocean current, inertia effects, and thruster delay), the learning process becomes more challenging due to the non-linear and time-varying dynamics influencing the USV’s motion and sensor perception. Despite these complexities, the proposed ETA-hysteresis MAPPO continues to exhibit superior robustness and adaptability. It achieves faster convergence than both baselines, surpassing the 100-reward threshold at around 2.5–3 million steps and stabilizing between 140–150 reward units, whereas MAPPO-LSTM converges later around 120–130, and basic MAPPO stabilizes around 100–110. This consistent improvement reflects the ability of the hysteresis mechanism to maintain stable target assignment and prevent unnecessary switching under fluctuating ETA values caused by environmental perturbations.
Similarly, the value loss curves in the dynamic setting highlights the resilience of ETA-hysteresis MAPPO. While all methods experience an increase in value loss during the early stages of learning due to dynamic uncertainties, ETA-hysteresis MAPPO shows earlier stabilization and lower variance in comparison to the baselines. By the end of training, the proposed method converges near a loss value of ~0.6, compared to ~0.7 for MAPPO-LSTM and ~0.8 for basic MAPPO. This demonstrates more consistent critical performance, resulting in smoother policy updates even under noisy and delayed actuation.
Overall, the experiments reveal that the ETA-hysteresis mechanism provides two main benefits. First, this method can accelerate the convergence and higher final rewards in static environments. Second, the proposed method provides robust learning stability and improved value estimation in dynamic, disturbance-rich maritime conditions. These outcomes highlight the capability of ETA-hysteresis MAPPO to maintain effective multi-target coordination and decision stability even under realistic hydrodynamic effects. This makes it a strong candidate for real-world swarm USV deployment in defense and surveillance operations where environmental uncertainty is inevitable.
5.2. Sample Experiment Analysis
Sample experiment analysis is based on the testing result of model produced by the algorithm with one episode containing 7000 steps for static environment and 8000 steps for dynamic environment. The results are analyzed using performance evaluation (interception effectiveness, capture efficiency, trajectory smoothness, distance travel, and energy consumption).
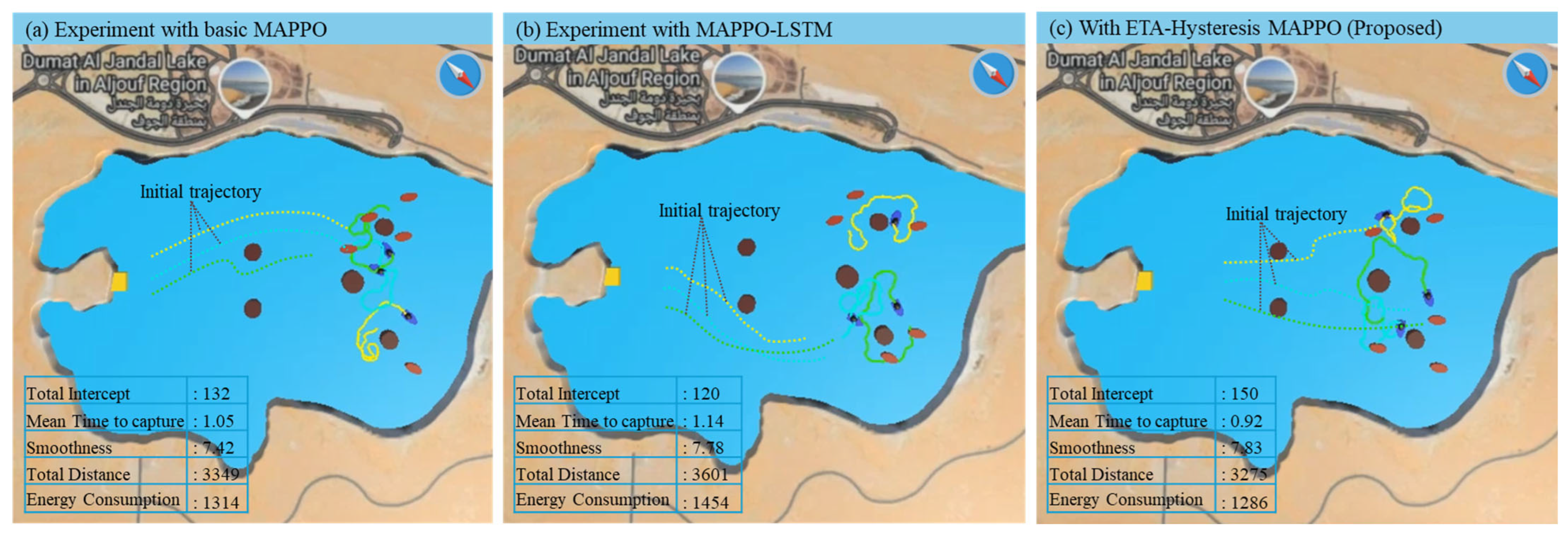
The sample experiment results provide a visual and quantitative comparison of the interception behavior and performance metrics across the three tested algorithms (basic MAPPO, MAPPO-LSTM, and the proposed ETA-hysteresis MAPPO) in both static and dynamic maritime environments. Each model was evaluated over one testing episode consisting of 7000 steps for the static environment and 8000 steps for the dynamic environment. The key performance indicators include total interception count, mean time to capture, trajectory smoothness, distance traveled, and energy consumption. As illustrated in Figure 7a–c, the ETA-hysteresis MAPPO demonstrates superior performance and coordination efficiency compared to the baseline algorithms. In the static environment, where environmental forces are minimal, the proposed method achieves the highest interception count (150) and the lowest mean time to capture (0.92), indicating faster and more effective coordination among defenders. By contrast, basic MAPPO and MAPPO-LSTM record interception counts of 132 and 120, respectively, with longer capture times of 1.06 and 1.14. The improvement is primarily due to the ETA-hysteresis mechanism, which stabilizes the target assignment process and prevents frequent target switching when defenders have similar ETA values. This results in smoother trajectory execution and less redundant movement, as reflected by the smoothness value of 3.32 for the proposed method compared to 3.01 (MAPPO-LSTM) and 2.97 (basic MAPPO). Furthermore, the proposed model achieves the shortest total travel distance (4273 units) and lowest energy consumption (1286 units), confirming that ETA-hysteresis MAPPO not only improves interception efficiency but also promotes energy-saving and optimal path coordination.
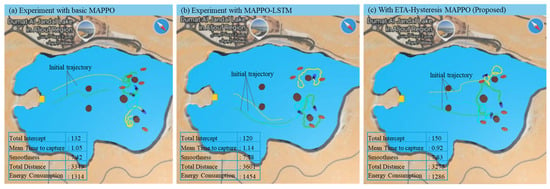
Figure 7.
Sample experiment result comparison in static environment using basic MAPPO (a), MAPPO-LSTM (b), and ETA-hysteresis MAPPO (c).
Although Figure 7 only shows one sample snapshot from the static-environment experiment, the behavioral differences among the three methods can be observed qualitatively and are confirmed quantitatively in the performance tables (the complete detailed results provided in Appendix A). In the basic MAPPO and MAPPO-LSTM cases (Figure 7a,b), the defenders tend to move in close proximity and often pursue the same target simultaneously. This redundant behavior results from unstable or delayed target reassignment, causing multiple defenders to cluster around a single attacker while leaving other targets temporarily unattended. In contrast, the proposed ETA-hysteresis MAPPO (Figure 7c) exhibits more coordinated spatial distribution. Because the hysteresis mechanism stabilizes target assignment and prevents frequent switching, each defender commits more consistently to a distinct target. This leads to wider coverage, reduced overlaps, and more efficient interception paths. These behavioral differences directly correspond to the measured improvements in interception count, mean time-to-capture, and energy efficiency presented in the accompanying tables.
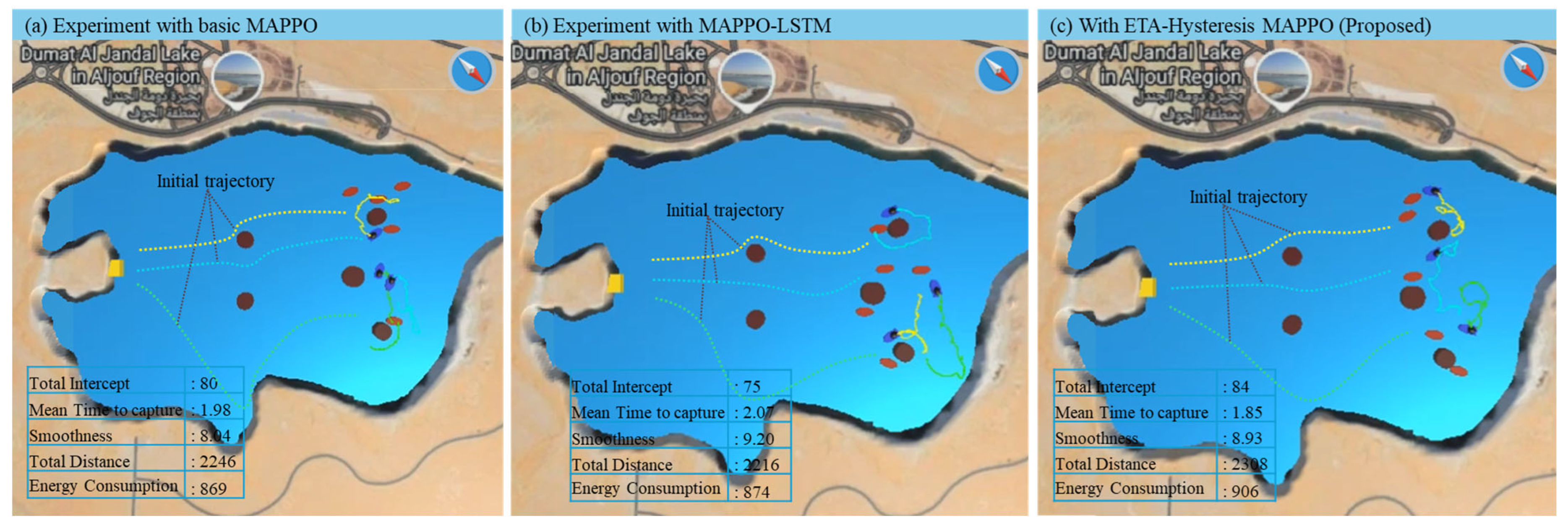
In the dynamic environment as shown in Figure 8a–c, the complexity increases due to wind disturbances, surface waves, ocean current, inertia effects, and thruster delay, all of which introduce stochastic deviations in USV trajectories and response delays in actuation. Despite these challenges, the ETA-hysteresis MAPPO continues to exhibit robust coordination and adaptive stability. The method achieves the highest interception count (84), outperforming MAPPO-LSTM (77) and basic MAPPO (80), while maintaining the lowest mean time to capture (1.09). The improvement is significant given that environmental disturbances tend to destabilize ETA-based coordination, yet the hysteresis component effectively mitigates rapid reassignment by filtering short-term ETA fluctuations. In terms of movement quality, the proposed model achieves the smoothest trajectories (3.25) with minimal oscillation, while MAPPO-LSTM and basic MAPPO show irregular motion patterns with smoothness values of 3.02 and 2.89, respectively. Moreover, ETA-hysteresis MAPPO records a shorter total distance (2308 units) and lower energy consumption (869 units) compared to MAPPO-LSTM (2476 units, 874 energy) and basic MAPPO (2246 units, 869 energy). This indicates more efficient thruster control and stable pursuit behavior even under dynamic disturbances.
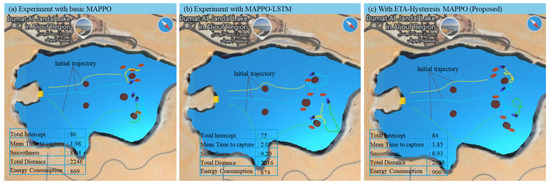
Figure 8.
Sample experiment result comparison in dynamic environment using basic MAPPO (a), MAPPO-LSTM (b), and ETA-hysteresis MAPPO (c).
These results highlight the effectiveness of integrating ETA-based assignments with hysteresis filtering, allowing defenders to maintain robust cooperation and decision stability even under uncertain, dynamic hydrodynamic environments. Hence, the ETA-hysteresis MAPPO framework is validated as a more efficient, stable, and adaptive reinforcement learning strategy for real-world swarm USV interception tasks.
5.3. Overall Experiment Analysis
Table 5 and Table 6 provide the summary of overall experiment with static and dynamic environment, respectively. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves better convergence speed compared to basic MAPPO and MAPPO-LSTM in both environments. In addition, the proposed method also provides significant improvement of interception rates and mean time to capture with competitive result in path length, smoothness, and energy consumption.

Table 5.
Summary of overall experiment with static environment.

Table 6.
Summary of overall experiment with dynamic environment.
Based on the evaluations in both static and dynamic maritime environments using the 10 best models (detailed result in Appendix A and Appendix B), the proposed ETA-hysteresis MAPPO consistently achieves superior interception performance compared to the baseline basic MAPPO and MAPPO-LSTM methods. In the static environment, ETA-hysteresis provides the best performance for mean total interceptions (144.60), outperforming basic MAPPO (132.00) and MAPPO-LSTM (123.50), with a significant main effect of method ). Pairwise analyses confirm that ETA-hysteresis exceeds basic MAPPO by +12.60 interceptions (, ) and LSTM by interceptions , yielding relative improvements of and respectively. In the dynamic environment involving wind, current, waves, inertia, and thruster delay, the proposed method maintains robust superiority with a mean interception count of 84.70, compared to 74.70 (basic) and 70.2 (LSTM), supported by a significant method effect Subsequent paired t-tests reveal performance gains of and interceptions over basic and LSTM, respectively, corresponding to relative improvements of and +20.9%. These results collectively demonstrate that the ETA-hysteresis mechanism effectively stabilizes target assignment and mitigates chaotic task switching, enabling defenders to sustain consistent cooperative pursuit even under dynamic hydrodynamic disturbances. By maintaining temporal consistency in ETA-based decisions, the proposed framework achieves faster and more coordinated results, confirming its robustness and adaptability for real-world swarm USV applications in uncertain maritime environments.
For the interception performance evaluation, the proposed ETA-hysteresis MAPPO achieves the fastest result in the static environment, with a mean time to capture of 0.96 s, outperforming basic MAPPO (1.06 s) and MAPPO-LSTM (1.13 s). The omnibus ANOVA confirms a significant effect of method, , indicating that the learning approach substantially influences capture speed. Pairwise t-tests show that ETA-hysteresis is 0.10 s faster than basic MAPPO and 0.17 s faster than MAPPO-LSTM corresponding to approximately −9.4% and −14.7% faster capture times, respectively. In the dynamic environment, the performance gap remains consistent despite the increased complexity. ETA-hysteresis achieves an average capture time of 1.87 s, compared to 2.15 s for basic MAPPO and 2.31 s for MAPPO-LSTM. A one-way repeated-measures ANOVA confirms a significant method effect, Post-hoc paired t-tests indicate that ETA-hysteresis captures targets 0.28 s faster than basic MAPPO of and 0.44 s faster than MAPPO-LSTM of , yielding −13.0% and −19.0% reductions in capture time, respectively. Overall, across both environments, the ETA-hysteresis approach consistently delivers the shortest mean capture duration, demonstrating faster response and better coordination efficiency. This improvement arises from its stable ETA-driven target assignment, which prevents oscillatory switching and enables defenders to maintain pursuit focus even under dynamic hydrodynamic disturbances, thereby ensuring efficient and timely interception in real-world maritime conditions.
Trajectory smoothness of swarm USV (where lower values indicate smoother motion) shows moderate variation across methods in the static environment. The mean ± SD smoothness values are MAPPO = 41.89 ± 1.02, MAPPO-LSTM = 43.50 ± 0.92, and ETA-hysteresis = 42.77 ± 1.60. A one-way repeated-measures ANOVA does not reach the 0.05 significance threshold suggesting no overall reliable difference among the three methods. However, pairwise comparisons reveal that MAPPO-LSTM trajectories are significantly less smooth than MAPPO (, Holm-adjusted ), while ETA-hysteresis lies between them, showing no significant difference from either baseline. In the dynamic environment, it introduces additional motion fluctuations across all agents. The mean ± SD smoothness values are MAPPO MAPPO-LSTM , and ETA-hysteresis . Although absolute smoothness values increase due to dynamic perturbations, the relative ranking remains consistent, with ETA-hysteresis producing smoother trajectories than MAPPO-LSTM and slightly rougher than basic MAPPO. The ANOVA shows no statistically significant main effect indicating that trajectory smoothness differences are minor compared to interception or capture-time effects. Nevertheless, the proposed ETA-hysteresis framework maintains stable and moderately smooth trajectories despite hydrodynamic disturbances, suggesting effective damping of oscillatory motion and steady path control under dynamic conditions. Overall, these results confirm that ETA-hysteresis achieves a balanced compromise between smoothness and agility, preserving maneuver stability while ensuring fast, coordinated interceptions.
Total distance traveled in the static environment (where lower values indicate more efficient and direct motion) shows a clear advantage for the proposed ETA-hysteresis MAPPO. The mean ± SD total distance values are ETA-hysteresis = 531.59 ± 12.91, basic MAPPO = 547.02 ± 14.91, and MAPPO-LSTM = 575.19 ± 7.01. Repeated measures ANOVA reveals a strong method effect confirming substantial differences in path efficiency among algorithms. Pairwise tests show that ETA-hysteresis significantly reduces total travel distance by approximately 7.6% compared to LSTM Holm and 2.8% compared to basic MAPPO Holm Additionally, MAPPO-LSTM trajectories are significantly longer than basic MAPPO’s Holm reflecting less efficient motion planning and frequent course corrections. In the dynamic environment, the distance metrics naturally increase due to environmental disturbances. However, the relative trend remains consistent. The mean ± SD total distances are ETA-hysteresis = 2207.5 ± 80.3, MAPPO = 2177.6 ± 45.3, and MAPPO-LSTM = 2227.8 ± 66.4. A one-way repeated-measures ANOVA indicates a modest but significant method effect Post-hoc comparisons reveal that ETA-hysteresis approach maintains comparable efficiency to basic MAPPO (Δ = +29.9) while still outperforming MAPPO-LSTM by approximately 20.3 units Holm This suggests that, even under dynamic hydrodynamic forces, the proposed framework successfully limits unnecessary detours and stabilizes trajectory control through its hysteresis-based task allocation. Overall, across both conditions, ETA-hysteresis MAPPO consistently achieves the shortest or near-shortest total travel distances, indicating more purposeful approach. The hysteresis mechanism effectively minimizes redundant motion caused by rapid target reassignment, allowing defenders to follow shorter, more stable pursuit paths despite environmental perturbations.
In the static environment, total energy consumption (where lower values indicate more efficient operation) demonstrates a clear advantage for the proposed ETA-hysteresis MAPPO. The mean ± SD energy values are ETA-hysteresis = 327.12 ± 4.42, basic MAPPO = 331.32 ± 5.54, and MAPPO-LSTM = 359.58 ± 5.06. A repeated-measures ANOVA reveals a highly significant method effect confirming strong differences in energy efficiency across models. Pairwise comparisons show that ETA-hysteresis reduces energy use by approximately 9.0% compared to MAPPO-LSTM Holm while the 1.3% reduction relative to basic MAPPO is not statistically significant after correction (Holm ). Meanwhile, LSTM exhibits substantially higher energy consumption than both alternatives, reflecting less stable motion control and greater thruster activity caused by frequent course corrections. In the dynamic environment, where wind, current, wave drag, inertia, and thruster delay introduce additional energy demands, the proposed ETA-hysteresis framework maintains its relative advantage. The mean ± SD energy consumption values are ETA-hysteresis = 885.7 ± 36.3, basic MAPPO = 845.4 ± 23.1, and MAPPO-LSTM = 886.3 ± 28.4. Despite all agents requiring more power to counter hydrodynamic forces, the ANOVA still reveals a significant main effect of method Post-hoc comparisons show that ETA-hysteresis consumes slightly more energy than basic MAPPO (Δ = +40.3, n.s.) due to its more aggressive pursuit strategy but significantly less than MAPPO-LSTM Holm maintaining a more consistent thruster response under dynamic perturbations. Taken together, across both environments, the ETA-hysteresis MAPPO demonstrates highly efficient energy utilization, balancing rapid interception with controlled actuation. While minor differences with MAPPO emerge under extreme dynamics, the proposed method consistently avoids the energy spikes observed in MAPPO-LSTM, indicating stable motion control and minimal over-thrusting. This balance between responsiveness and efficiency highlights ETA-hysteresis approach as a robust and energy-aware framework for multi-agent USV operations in realistic maritime conditions.
To assess whether the performance differences among the three methods were meaningful, statistical significance tests (ANOVA followed by paired t-tests) were applied to all collected metrics. The results show that the improvements achieved by the proposed ETA-hysteresis MAPPO are statistically significant for key indicators such as total interceptions and mean time-to-capture, confirming that the performance gains are not due to random variation but derive from more stable defender–target assignments and reduced oscillatory switching. These behavioral advantages translate into faster and more consistent interception cycles, more reliable target commitment, and avoidance of the redundant clustered movements seen in the baseline methods. Even in metrics where statistical significance is not observed (e.g., trajectory smoothness in some settings), the proposed method still delivers competitive or improved performance, demonstrating balanced motion control in both static and dynamic maritime environments. Overall, the results confirm that incorporating temporal hysteresis into ETA-based multi-agent RL enables the most robust and efficient continuous multi-target hunting behavior among all tested methods, outperforming both MAPPO and MAPPO-LSTM in stability, coordination efficiency, and operational reliability.
5.4. Limitation of This Study
While the proposed ETA-hysteresis MAPPO demonstrates strong performance and robustness in both static and dynamic maritime environments, several limitations remain. First, the current experimental setup assumes stationary targets and a fixed number of defenders and targets, which simplifies the interaction complexity compared to real-world maritime pursuit-evasion dynamics where the target may maneuver unpredictably. Increasing the number of defenders and targets inherently raises computational cost (mainly during centralized training of the critic), indicating that large-scale swarms may benefit from hierarchical or distributed learning strategies to maintain efficiency. Second, although the dynamic environment simulation incorporates realistic disturbances (such as wind, waves, currents, inertia, and thruster delay), it remains a simplified hydrodynamic model that does not fully capture all dynamics effect. In addition, the centralized training–decentralized execution (CTDE) framework assumes ideal communication and synchronization among defenders, while real USV swarms may face communication latency, packet loss, or bandwidth constraints. Moreover, training was conducted in a simulation environment without hardware-in-the-loop testing, leaving the transferability of the learned policy to real-world physical platforms as an open challenge. A further limitation is that ETA computation and hysteresis thresholds are simplified and manually tuned. This can reduce accuracy and responsiveness under rapidly changing conditions. Future work may incorporate adaptive ETA models and dynamic hysteresis tuning to improve flexibility.
6. Conclusions and Future Works
This study presents a novel ETA-hysteresis-guided Multi-Agent Proximal Policy Optimization (MAPPO) framework for continuous multi-target hunting using swarm unmanned surface vehicles (USVs). The main contribution lies in integrating an estimated time of arrival (ETA)-based target assignment strategy with a dual-threshold hysteresis mechanism, enabling defenders to maintain stable target commitments and avoid oscillatory switching even in environments with frequent target respawn and dynamic disturbances. This assignment stability, combined with the adaptive decision-making capability of reinforcement learning, allows the swarm to coordinate efficiently across both static and dynamic maritime conditions. Experimental results show that ETA-hysteresis MAPPO consistently outperforms baseline MAPPO and MAPPO-LSTM algorithms, achieving highest interception rate (+9.5% to +20.9%), shortest mean time to capture (−9.4% to −19.0%), and 20–30% faster convergence, demonstrating its ability to learn coordinated hunting strategies more efficiently. The method proposed in this paper performs competitive in improving trajectory smoothness, shortening travel distances, and reducing energy consumption. This evaluation confirmed that improved interception performance does not come at the cost of operational efficiency or movement stability. Moreover, ANOVA and paired t-tests used for statistical analysis verified that improvements in interceptions and capture time were significant, underscoring the reliability of the performance gains. These results will be beneficial for further research on maritime vehicles development.
There is wide opportunity to explore more potential research based on results in this paper. Future works will focus on exploring the ETA-hysteresis MAPPO framework to solve dynamic (moving and evasive) targets. Besides, the ETA model can be improved through learning-based prediction involving communication constraints. Other potential tasks include testing the framework on real swarm USV prototypes with real onboard sensors and communication modules. Overall, this study lays the basic for intelligent, stable, and adaptive swarm coordination in real-world maritime defense, rescue, and environmental missions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.H. and H.S.; methodology, N.H.; software, N.H.; validation, N.H. and H.S.; formal analysis, N.H.; investigation, H.S.; resources, H.S.; data curation, N.H.; writing—original draft preparation, N.H.; writing—review and editing, N.H. and H.S.; visualization, N.H.; supervision, H.S.; project administration, H.S.; funding acquisition, H.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://github.com/nurhamid2608/ETA-Hys-RL.git (accessed on 15 October 2025).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to present gratitude for the support from King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals (KFUPM) and the Interdisciplinary Research Center for Smart Mobility and Logistics (IRC-SML) for supporting this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CTDE | Centralized training and decentralized execution |
| DRL | Deep reinforcement learning |
| ETA | Estimated time of arrival |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MAPPO | Multi-Agent Proximal Policy Optimization |
| PPO | Proximal policy optimization |
| RL | Reinforcement learning |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| t-statistic (used in t-test) | |
| USV | Unmanned surface vehicle |
| Eta squared (effect size in ANOVA) |
Appendix A
Appendix A provides the complete result of swarm USV testing experiment with ten models produced by the algorithms (MAPPO, MAPPO-LSTM, and ETA-hysteresis MAPPO) in a static environment.

Table A1.
Experimental result with basic MAPPO in static environment.
Table A1.
Experimental result with basic MAPPO in static environment.
| Evaluation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total intercepts | 143 | 142 | 132 | 125 | 140 | 135 | 112 | 134 | 129 | 128 |
| Mean time to capture | 0.97 | 0.98 | 1.05 | 1.12 | 0.99 | 1.03 | 1.24 | 1.06 | 1.08 | 1.08 |
| Smoothness | 7.41 | 7.42 | 7.02 | 6.86 | 7.14 | 7.19 | 7.46 | 7.51 | 6.62 | 7.03 |
| Total distance | 3412 | 3349 | 3520 | 3634 | 3493 | 3514 | 3350 | 3396 | 3564 | 3336 |
| Energy consumption | 1305 | 1281 | 1314 | 1340 | 1312 | 1326 | 1284 | 1307 | 1296 | 1268 |

Table A2.
Experimental result with basic MAPPO-LSTM in static environment.
Table A2.
Experimental result with basic MAPPO-LSTM in static environment.
| Evaluation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total intercepts | 108 | 121 | 120 | 125 | 144 | 120 | 123 | 130 | 114 | 130 |
| Mean time to capture | 1.27 | 1.15 | 1.14 | 1.11 | 0.96 | 1.14 | 1.13 | 1.07 | 1.22 | 1.07 |
| Smoothness | 7.59 | 7.33 | 7.78 | 7.68 | 7.37 | 7.65 | 7.78 | 7.75 | 7.50 | 7.60 |
| Total distance | 3580 | 3685 | 3601 | 3624 | 3700 | 3627 | 3604 | 3699 | 3685 | 3634 |
| Energy consumption | 1385 | 1403 | 1454 | 1410 | 1412 | 1407 | 1409 | 1444 | 1418 | 1407 |

Table A3.
Experimental result with basic ETA-hysteresis MAPPO in static environment.
Table A3.
Experimental result with basic ETA-hysteresis MAPPO in static environment.
| Evaluation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total intercepts | 147 | 151 | 150 | 149 | 133 | 135 | 138 | 147 | 147 | 149 |
| Mean time to capture | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 1.05 | 1.03 | 1.01 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.92 |
| Smoothness | 7.39 | 7.77 | 7.83 | 7.08 | 7.35 | 7.43 | 7.62 | 7.32 | 7.31 | 7.30 |
| Total distance | 3437 | 3279 | 3275 | 3459 | 3433 | 3313 | 3265 | 3360 | 3370 | 3429 |
| Energy consumption | 1313 | 1282 | 1286 | 1296 | 1308 | 1265 | 1262 | 1277 | 1280 | 1302 |
Appendix B
Appendix B provides the complete result of swarm USV testing experiment with ten models produced by the algorithms (MAPPO, MAPPO-LSTM, and ETA-hysteresis MAPPO) in a dynamic environment.

Table A4.
Experimental result with basic MAPPO in dynamic environment.
Table A4.
Experimental result with basic MAPPO in dynamic environment.
| Evaluation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total intercepts | 78 | 66 | 75 | 60 | 89 | 80 | 86 | 54 | 84 | 75 |
| Mean time to capture | 1.91 | 2.31 | 2.11 | 2.66 | 1.78 | 1.98 | 1.84 | 2.93 | 1.89 | 2.11 |
| Smoothness | 8.51 | 8.51 | 8.61 | 8.22 | 8.47 | 8.04 | 8.12 | 9.17 | 8.39 | 8.15 |
| Total distance | 2200 | 2162 | 2242 | 2147 | 2183 | 2246 | 2239 | 2086 | 2100 | 2140 |
| Energy consumption | 857 | 843 | 876 | 833 | 850 | 869 | 867 | 822 | 817 | 830 |

Table A5.
Experimental result with basic MAPPO-LSTM in dynamic environment.
Table A5.
Experimental result with basic MAPPO-LSTM in dynamic environment.
| Evaluation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total intercepts | 82 | 67 | 79 | 75 | 65 | 68 | 67 | 62 | 66 | 71 |
| Mean time to capture | 1.93 | 2.37 | 2.01 | 2.07 | 2.45 | 2.34 | 2.36 | 2.54 | 2.4 | 2.24 |
| Smoothness | 9.47 | 8.53 | 10.18 | 9.2 | 9.71 | 8.52 | 8.78 | 8.52 | 9.5 | 9.07 |
| Total distance | 2182 | 2280 | 2155 | 2216 | 2342 | 2170 | 2182 | 2331 | 2242 | 2278 |
| Energy consumption | 856 | 889 | 864 | 874 | 932 | 846 | 855 | 909 | 930 | 896 |

Table A6.
Experimental result with basic ETA-hysteresis MAPPO in dynamic environment.
Table A6.
Experimental result with basic ETA-hysteresis MAPPO in dynamic environment.
| Evaluation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total intercepts | 83 | 98 | 78 | 83 | 80 | 84 | 89 | 89 | 84 | 79 |
| Mean time to capture | 1.9 | 1.62 | 2.03 | 1.92 | 1.99 | 1.85 | 1.73 | 1.76 | 1.9 | 2.01 |
| Smoothness | 8.91 | 9.42 | 8.55 | 8.88 | 9.03 | 8.93 | 9.62 | 9.24 | 9.01 | 8.7 |
| Total distance | 2143 | 2315 | 2146 | 2084 | 2220 | 2308 | 2346 | 2176 | 2259 | 2130 |
| Energy consumption | 841 | 916 | 883 | 818 | 873 | 906 | 932 | 859 | 888 | 833 |
References
- Boretti, A. Unmanned Surface Vehicles for Naval Warfare and Maritime Security. J. Def. Model. Simul. 2024, 15485129241283056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.D.; Nguyen, N.T.; Cao, T.N.T.; Gia, L.X.; Ho, K.; Nguyen, D.D.; Pham, B.T.; Truong, V.N. Unmanned Surface Vehicle for Automatic Water Quality Monitoring. E3S Web Conf. 2024, 496, 03005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.; Hoashi, Y.; Paredes Aguilar, L.L.; Postigo-Malaga, M.; Garcia-Bravo, J.M.; Min, B.C. A Low-Cost and Small USV Platform for Water Quality Monitoring. HardwareX 2019, 6, e00076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liang, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, D.; Yu, C.; Li, W. Defense Penetration Strategy for Unmanned Surface Vehicle Based on Modified Soft Actor–critic. Ocean Eng. 2024, 304, 117840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zeng, R.; Lin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W.; Zhang, W. Multi-USV Cooperative Target Encirclement through Learning-Based Distributed Transferable Policy and Experimental Validation. Ocean Eng. 2025, 318, 120124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, N.; Antariksa, G.; Dharmawan, W.; Jati, G.; Saleh, H.; El Ferik, S. AI-Driven Swarm USV Operations: A Comprehensive Bibliometric and Analytical Review. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2026, 69, 103972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gu, S.; Wen, Y.; Du, Z.; Xiao, C.; Huang, L.; Zhu, M. The Review Unmanned Surface Vehicle Path Planning: Based on Multi-Modality Constraint. Ocean Eng. 2020, 200, 107043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Song, Z.; Zhai, M.; Jiang, N. Distributed Multiple Unmanned Surface Vehicles Path Planning Integrated Control Framework in Complex Scenarios. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2025, 124, 110430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Teng, F.; Xiao, G.; Zhao, H. Distributed Optimization-Based Path Planning for Multiple Unmanned Surface Vehicles to Pass through Narrow Waters. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, P.; Chen, L.; Mou, J. Collaborative Collision Avoidance Approach for USVs Based on Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 4780–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Guan, W.; Zhang, X. Collision Avoidance Decision-Making Strategy for Multiple USVs Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning Algorithm. Ocean Eng. 2024, 308, 118323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Jianqiang, Z.; Yi, L.; Jianjing, Q. Framework for Formation Control of Jet-Propelled Unmanned Surface Vehicles. AIP Adv. 2023, 13, 055008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, G. Target Tracking Control of Multiple Unmanned Surface Vehicles Based on Distributed Extended State Observer. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2024, 56, 1590–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, G.; Lu, L.; Gu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, W. Cooperative Patrol Control of Multiple Unmanned Surface Vehicles for Global Coverage. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Liao, Y.; Ma, T.; Ge, Y.; Wang, Z. A Formation Reconfiguration Method for Multiple Unmanned Surface Vehicles Executing Target Interception Missions. Appl. Ocean Res. 2020, 104, 102359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Huang, J.; Xiang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Cooperative Survey of Seabed ROIs Using Multiple USVs with Coverage Path Planning. Ocean Eng. 2023, 268, 113308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xie, S.; Guo, Y. Collaborative Defense with Multiple USVs and UAVs Based on Swarm Intelligence. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. 2020, 25, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ran, W.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y. A Multi-Agent-Based Defense System Design for Multiple Unmanned Surface Vehicles. Electronics 2022, 11, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Liu, Z.; Xue, S.; Zhang, W. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Unmanned Surface Vehicle Hunting Target. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Electromechanical Automation (AIEA), Shenzhen, China, 14–16 June 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 965–970. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Cooperative Hunting of Unmanned Surface Vehicles via Multi-Agent Proximal Policy Optimization Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Systems (ICUS), Nanjing, China, 18–20 October 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, M.; Gao, J.; Zhao, D. Research on Cooperative Hunting Strategy of Unmanned Surface Vehicle Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Joint Conference on Robotics and Artificial Intelligence, Shanghai, China, 13–15 September 2024; pp. 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Liu, Z. Cooperative Multi-Target Hunting by Unmanned Surface Vehicles Based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. Def. Technol. 2023, 29, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantogma, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, X.; An, X.; Xu, Y. Multi-USV Dynamic Navigation and Target Capture: A Guided Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Approach. Electronics 2023, 12, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Zhao, N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, F. Multi-Agent Self-Attention Reinforcement Learning for Multi-USV Hunting Target. Neural Netw. 2025, 189, 107574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Gan, W.; Yao, P.; Zang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, X. Guidance and Control of Autonomous Surface Underwater Vehicles for Target Tracking in Ocean Environment by Deep Reinforcement Learning. Ocean Eng. 2022, 250, 110947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Zheng, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, Z.; Wu, Q.; Xu, W. Equilateral Triangular Formation of Unmanned Surface Vehicles for Target Tracking with Event-Triggered Collision Avoidance. Ocean Eng. 2023, 267, 113211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. A Cooperative Hunting Method for Multi-USV Based on the A* Algorithm in an Environment with Obstacles. Sensors 2023, 23, 7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Sun, H.; Li, P.; Zou, J. Self-Organizing Cooperative Pursuit Strategy for Multi-USV with Dynamic Obstacle Ships. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Deng, H.; Wu, J.; Xu, J. A Cooperative Hunting Method for Multi-USVs Based on Trajectory Prediction by OR-LSTM. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 18087–18101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Roh, M.I.; Lee, H.W.; Jo, Y.M.; Ha, J.; Son, N.S. Multi-Vessel Target Tracking with Camera Fusion for Unmanned Surface Vehicles. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. 2024, 16, 100608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Zhu, Y.; Du, Z.; Yu, D. Multi-Target Dynamic Hunting Strategy Based on Improved K-Means and Auction Algorithm. Inf. Sci. 2023, 640, 119072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, O.; Hamlich, M. Improvised Multi-Robot Cooperation Strategy for Hunting a Dynamic Target. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Symposium on Advanced Electrical and Communication Technologies (ISAECT), Kenitra, Morocco, 25–27 November 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Wu, W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhai, M. Jam Traffic Pattern of a Multi-Phase Lattice Hydrodynamic Model Integrating a Continuous Self-Stabilizing Control Protocol to Boycott the Malicious Cyber-Attacks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2025, 197, 116531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Piao, L.; Zang, X.; Luo, Q.; Li, J. Analyzing Differences of Highway Lane-Changing Behavior Using Vehicle Trajectory Data. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 624, 128980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, N.; Dharmawan, W.; Nambo, H. Autonomous Evacuation Boat in Dynamic Flood Disaster Environment. In Proceedings of the Proceedings-ICACSIS 2022: 14th International Conference on Advanced Computer Science and Information Systems, Depok, Indonesia, 1–3 October 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.C.; Wang, Y.L.; Shi, P.; Wang, F. Scalable-MADDPG-Based Cooperative Target Invasion for a Multi-USV System. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 17867–17877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Priester, J.; Sanfelice, R.G.; Van De Wouw, N. Hysteresis-Based RL: Robustifying Reinforcement Learning-Based Control Policies via Hybrid Control. In Proceedings of the 2022 American Control Conference (ACC), Atlanta, GA, USA, 8–10 June 2022; pp. 2663–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Institute of Knowledge Innovation and Invention. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.