Abstract
In recent years, industries have prioritized low-cost, biodegradable, long-lasting materials. Businesses are focusing on composite materials using the world’s abundant natural fibers. Researchers and academics are considering using plant and animal fibers as polymer composite reinforcement to enhance their sustainability. In this context, finding new plant fibers for polymer composite reinforcement is important. This study hybridizes jute and acacia fibers using compression molding and changing epoxy fiber weight percentages to create novel polymer composites. This article examines how fiber orientation affects mechanical and morphological analysis for manufactured jute–acacia hybrid composites. The composite had the highest tensile strength of 33.59 MPa, a flexural strength of 66.42 MPa, an impact strength of 3.22 J/m, and a hardness of 85 Shore D. The scanning electron microscope (SEM) showed that alkali treatment filled microscopic cracks, gaps, and pores in natural fiber composites, improving their tensile, flexural, and impact strength. Sandwich composites had better mechanical and morphological qualities than two-layer stack patterned composites. The research findings of jute–acacia fiber-based composites can be applied in various industrial applications.
1. Introduction
In light of environmental awareness and the need for more sustainable industrial practices, scientists and enterprises have focused on environmentally friendly and sustainable composite materials. Natural lingo-cellulosic fibers work well with thermoset and thermoplastic polymer matrices [1]. Lingo-cellulosic fibers can be used as reinforcement in polymer matrix composites because of their accessibility, comparatively low cost, ease of fabrication, lower tool aggressiveness, sustainability, and biodegradability. Lignocellulosic composites have better physical, thermal, acoustic, and electrical properties [2]. Lignocellulosic fibers are intriguing to researchers; therefore, they are used in reusable and hybrid composites. However, natural fibers have excessive moisture absorption (causing fiber swelling), weak wettability, poor fiber/matrix adherence, property unpredictability, and reduced lifespan [3]. Mixed reinforcement in hybrid composites allows one form to substitute for another’s constraints, enhancing the overall characteristics. Hybrid composites combine dissimilar bio-fibers or bio- and synthetic fibers in a matrix. Hybrid composites are cheaper than single-fiber composites and can suit a range of design objectives [4]. However, synthetic fibers are harmful and researchers have created natural fiber composites. Bio-composites are largely employed in transportation. Marichelvam et al. [5] offered a hybrid natural fiber composite containing epoxy resin to be a matrix with palm sheath and bagasse from sugarcane fiber reinforcements and generated a dashboard following tensile, impact, and flexural tests. Shahinur et al. [6] show that composites with better characteristics are usually made by chemically treating raw fibers.
Jute fiber is a biological fiber made from Corchorus jute plant bark. It is mostly grown in Bangladesh, India, and China. Compared to other advancements with similar materials like natural fibers, the results are competitive. Jute is mainly cellulose (60–70%), hemicellulose (12–14%), and lignin (5–10%) [7]. It is called “the golden fiber” for its smooth, shiny texture. Jute fiber is important since it is renewable, decomposes naturally, and benefits the environment. This marks an alternative to synthetic fibers. In spite of its cost, great strength-to-weight ratio, and superior insulation, it absorbs moisture and has issues with quality [8]. Jute fiber is replacing synthetic fibers, metals, and alloys due to its economical, ecological, and technical benefits. Jute fiber-reinforced composites (JFRCs) increase mechanical properties by adding jute fibers to a polymer matrix [9]. These composites leverage jute fibers’ strength and stiffness and the polymer matrix’s ability to appropriately distribute stresses and protect fibers from environmental damage. JFRC research is important because of the growing need for eco-friendly materials. Using natural fibers like jute in polymer matrix composites reduces the environmental impact of composite products by replacing glass or carbon fiber. Moreover, JFRCs are a cost-effective option with sufficient mechanical properties for many technical applications [10]. Jute fiber-based composites are appropriate for many industries due to their benefits and environmental impact. JFRCs make car components like door panels, dashboards, and seat backs. This application reduces weight and boosts fuel economy. Construction companies employ JFRCs to make lightweight, durable partition boards, panels, and sheets for roofing [11]. The furniture industry uses JFRCs to make eco-friendly, attractive products. JFRCs can replace plastics in packaging, reducing waste. JFRCs’ broad range for applications and rising usage demonstrate their importance and potential for advancement. Despite the wealth of research on natural fiber composites, jute fiber-based composite production procedures and their influence on mechanical properties are understudied [12].
Acacia bark fibers possess 51% crystallinity, 1385 kg/m3 density, and 68.09 weight percent cellulose. Acacia is considered for environmentally friendly composites. Green composites that are reinforced with fiber are environmentally friendly alternatives to non-biodegradable synthetic fibers [13]. Research on mechanical testing, characterization, and acacia fiber extraction has yielded promising results. Mechanical properties and the water absorption of acacia bark fiber composites have been examined. Alkali treatment on the fiber surface, variable fiber volume percentage, and fiber length have also been studied. Chemically treated fibers have better mechanical qualities and lower water absorption. The mechanical qualities of acacia fibers’ tear strength are better than its tensile strength. It has also been found that fiber–rubber adhesion improves results. They studied the physical, mechanical, and moisture absorption capabilities of Acacia concinna and Vachellia seed powder strengthened with short Turkish hemp and epoxy resin in numerous matrixes of various seed powder weight percentages [14]. The 7.5 weight percentage indicated better physical–mechanical properties. Filler increases composite bonding strength. Marine and automotive applications benefit from these fibers’ resistance to moisture. A study on acacia bark fiber characterization found that the fibers’ rapid splitting and extreme roughness could be employed when they were used as a filler to eliminate slack spots. Vadivel et al. [15] investigated untreated as well as treated acacia and pencil cactus fiber thermal behavior. The dashboard and door panel of the car were manufactured utilizing the best specimens of treated fibers since they have a better thermal stability. Marichelvam et al. [16] created a hybrid composite with epoxy as a matrix and acacia and Sida cordifolia fibers as reinforcement. In total, three of six specimens were chemically altered and three were not. The fibers were chemically treated with 5% NaoH. Each of the six samples was tested. The results showed that chemically treated samples are better than untreated ones.
The current research gap identified in the literature assessment is that there has been limited examination of composites with acacia fiber. Hybrid composites made from acacia and jute fibers have not yet been studied. The above two fibers can be used to create hybrid composites. This paper attempts to construct a novel hybrid composite using acacia and jute fibers and performs tensile, flexural, impact, and hardness testing. Tensile fracture specimens are evaluated through a scanning electron microscope. Environmentally friendly acacia fiber is a sustainable substitute for natural fibers. Presenting composite materials’ eco-friendliness and promise in lessening environmental impacts is innovative.
2. Materials and Methods
Compression molding is a widely utilized manufacturing process, particularly in producing composite materials that require high strength and lightweight characteristics. In this context, epoxy-based composites reinforced with natural fibers such as jute and acacia offer an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic materials, benefiting from the unique properties of both the matrix and the reinforcement. Following this, each stage will be discussed more deeply and detailed with the following sections.
2.1. Materials
The current work used epoxy resin (Araldite LY651) as the matrix material. The reinforcement consists of a combination of jute and acacia fibers in different quantities. The epoxy resin is acquired from Excel Polymers, Delhi. The jute and acacia fibers are procured from Go-Green products, Chennai. It is essential to meticulously separate the jute and acacia fibers prior to washing them under running water until all visible impurities are removed. The grams per square meter (gsm) of jute fiber and acacia fiber is 320 and 280, respectively. Furthermore, the fibers undergo chemical treatments to induce surface modifications. A 5% NaOH (sodium hydroxide) solution is used as a chemical treatment for two hours in order to efficiently treat the fiber. Epoxy is composed of a mixture of resin and hardener, typically in a 10:1 ratio. Preliminary literature reviews and initial experiments suggest that the combination of resin LY556 and hardener HY951 produces the best results. Images of untreated jute and acacia fibers are shown in Figure 1a,b. The characteristics of acacia and jute are presented in Table 1 and Table 2.
Figure 1.
Untreated (a) jute fiber and (b) acacia fiber.

Table 1.
Properties of jute fiber.

Table 2.
Properties of acacia fiber.
2.2. Chemical Treatment
Both acacia and jute fiber undergo a process of cleansing using distilled water. After a 3–4 h drying phase, the fibers were treated with a 5% NaOH solution for 2 h at room temperature. To eliminate residual NaOH, the fibers were then rinsed with distilled water. Finally, the fibers underwent a 24 h drying period at room temperature. A key challenge in natural fiber composites lies in the contrasting properties of the fibers’ water-attracting nature and the water-repelling nature of the matrix. The reinforcement of fibers may undergo chemical treatment to diminish its hydrophilic propensity, thus enhancing its compatibility with the matrix. Nevertheless, such treatment is not consistently effective. A range of physical as well as chemical surface treatment procedures have been documented in prior literature investigations [17,18]. Treatment with a 5% NaOH solution for two hours significantly enhances the interfacial bonding between jute–acacia fibers and an epoxy matrix, resulting in a cellulosic crystalline structure. This alkaline treatment is key to improving adhesion between the natural fibers and the resin. This enhancement is especially important in applications where composite materials are subjected to varying environmental conditions [19,20]. The altered surface texture of the jute–acacia fiber, resulting from chemical reactions, facilitated improved mechanical interconnection. The findings revealed that the composite properties were enhanced due to the chemical modification of the fiber. In many cases, non-cellulosic components can interfere with the bonding and interaction of these elements [21]. These components may include lignin, hemicellulose, waxes, and other extractives that can negatively impact the performance of the composite. Figure 2a,b present the pictures of NaOH-treated jute and acacia fibers, respectively.
Figure 2.
NaOH-treated (a) jute fiber and (b) acacia fiber.
2.3. Fabrication of Jute–Acacia Composites
Composite materials were produced utilizing the compression molding method. Before the manufacturing process, the mold underwent scrubbing using sandpaper. A fragile and translucent glass paper was positioned on top of the mold, combined with a robust paper to improve dimensional stability. In the process of composite manufacturing, 300 g of epoxy and 30 g of hardener (10:1 ratio) was utilized. The compression molding (Fine Testing Instruments Pvt. Ltd., Kolkata, India) process was employed for composite manufacture. An illustration of composite preparation is shown in Figure 3. A 30 cm × 30 cm mold was utilized to compress the fibers and epoxy–hardener mixture. At first, hand-laid fibers were arranged in sequence and compression molding followed. After mixing epoxy resin and hardener at a 1:10 ratio, the mixture was applied to every side of the laid fibers using a painting roller. Each of the samples was squeezed and cured for 3 h in the mold. The fibers were placed in the sequences listed in Table 3. Table 3 presents the fiber–epoxy compositions. The orientations of samples Epoxy, J-A-Epoxy, and J-A-J-Epoxy are presented in Table 4 and Table 5, respectively. The fiber and epoxy mixture is thoroughly integrated into the layers and applied on the metallic mold, and the procedure lasts for 3 h. The composite produced is confined to a size of 20 × 20 × 6 mm. Water jet (SAME water jet-Australia) techniques were employed for cutting the test samples to the appropriate dimensions in accordance with the ASTM standards. Figure 4a–c illustrate the fabricated specimens Epoxy, J-A-Epoxy, and J-A-J-Epoxy, respectively. Figure 5a,b illustrate the cross-section of the specimens J-A-Epoxy and J-A-J-Epoxy.

Figure 3.
Illustration of Composite preparation. (a) Epoxy resin applied over the mold. (b) Jute fiber laid over the epoxy resin. (c) Acacia fiber laid. (d) Compression molding process.

Table 3.
List of composite laminates prepared.

Table 4.
J-A-Epoxy fiber orientation (double-layer composite).

Table 5.
Specimen J-A-J-Epoxy fiber orientation (sandwich composite with 3 layers).

Figure 4.
(a) Epoxy specimen. (b) J-A-Epoxy. (c) J-A-J-Epoxy.

Figure 5.
Cross-section of (a) J-A-Epoxy; (b) J-A-J-Epoxy.
2.4. Mechanical Testing of Specimens
Natural fiber composite materials should be mechanically tested to determine their behavior and performance under various loads. The following sections provide specific information regarding the tensile, flexural, impact, and hardness tests performed in this research. An error analysis is conducted for every experiment.
2.4.1. Tensile Tests
For the tensile test, the specimen was manufactured in accordance with the standard that is provided by ASTM D638. When it came to carrying out the tensile test, a Universal Testing Machine (UTM) instrument was employed. Five samples are produced in accordance with standards that have been defined by the ASTM.
2.4.2. Flexural Tests
UTM was used to conduct the test, and flexural specimens were developed in line with ASTM D790 (American Society for Testing and Materials). The three-point flexural method, which tends to be the most frequent flexural test method, was used to determine the bending resistance of the composite material.
2.4.3. Impact Tests
The Izod impact test helps in determining the energy required to fracture a specimen, which is crucial for applications where materials are subjected to sudden forces. The samples that are going to be utilized in the impact assessment are manufactured in line with the measurements that have been specified, as required by the ASTM D256 standard. A downward cut of 2.5 mm was performed on each specimen so that the experiment could be carried out and the results could be analyzed.
2.4.4. Hardness Tests
For the purpose of obtaining the findings from the hardness test, the Shore D testing device was employed. The degree of penetration that takes place during the process of inserting the durometer indenter to the specimen, in accordance with ASTM D2240, is what determines the numerical value associated with hardness. The amount of hardness was assessed by taking readings at five different spots, and the average results were recorded.
2.5. Surface Morphology Analysis
SEM (Zeiss Sigma VP, Dublin, CA, USA) was employed to examine the topographic morphology associated with the composites. The sample’s surface is coated with a tiny amount of gold (sputtering) to ensure uniform conductivity. SEM images were obtained using extremely energetic electron beams reaching vacuum rates of 5 kilovolts and 1.5 × 10−3 Pa.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Tensile Properties
As shown in Figure 6, the epoxy composite reinforced with acacia and jute exhibited superior tensile properties compared to the neat epoxy specimen, which recorded the lowest tensile strength at 20.3 MPa. The other two specimens, J-A-Epoxy and J-A-J-Epoxy, have tensile strengths of 21.98 MPa and 33.59 MPa, respectively. This makes it abundantly clear that the epoxy-based composites’ increased tensile strength was due to the fiber reinforcement’s composition and stacking. The jute fibers on the outer skin of the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy exhibit an exceptionally high level of tensile strength, indicating that they can withstand tensile stress. Furthermore, the acacia maintains the jute fibers evenly distributed throughout the composites. According to the findings of a previous research study [22], jute’s inherent fiber structure offers a number of advantages. The specific combination of reinforcing fibers and the surrounding matrix is a key determinant of the mechanical behavior observed in hybrid composite materials. For example, a sandwich structure using jute and acacia fibers (J-A-J-Epoxy) leads to higher tensile strength in the resulting composite. Furthermore, on the basis of the tensile properties of acacia and jute fibers, this gain in tensile strength may be related to the solid bonding between the outermost layer of jute fibers and epoxy, as evidenced in images taken by the scanning electron microscope (SEM). The sandwich pattern of fiber-based epoxy composites was the focus of this inquiry, which was carried out with the purpose of determining its characteristics. The findings indicated that sandwich composites have an excellent bond due to improved fiber–matrix linking and display fewer fractures at break than other composites. The mechanical properties of materials made from natural fibers are often superior to those of synthetic alternatives. This advantage arises from the ability of natural fibers to stretch and adhere within the structure, leading to varying degrees of damage during different stages of use. Furthermore, each fiber is capable of stretching out on its own and resisting deformation on its own until it reaches the point where it is capable of breaking. The mechanical properties of fiber-reinforced composites are improved by several factors, most notably the fiber type, the matrix material, and the order in which the fibers are arranged (stacking sequence). Recent research highlights the significant role of stacking patterns in defining the tensile properties of natural fiber hybrid composites. Previous studies have found that various fiber-reinforced composites exhibit similar trends in tensile property responses when assessed against their stacking patterns. This suggests that certain configurations may enhance specific mechanical properties universally across different composite systems [23]. This specimen demonstrates the many ways these specific fibers can be oriented. The purpose of this is to increase the area of contact between the acacia and jute fibers, which will ultimately lead to an increase in the tensile strength. Therefore, it is possible to determine that the hybrid composite has a more ductile look than the neat composite does. This is a possible conclusion that may be reached. Therefore, it is clear that the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy performs extremely well in contrast with different types of composites in combination.
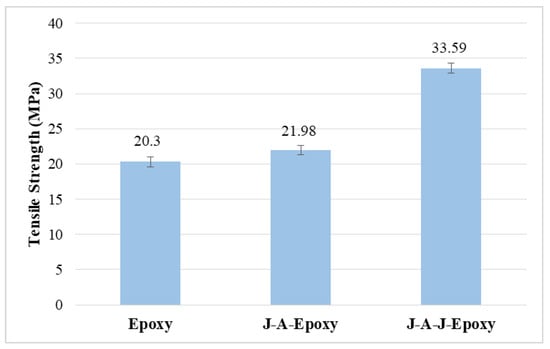
Figure 6.
Tensile strength of composites.
3.2. Flexural Properties
Flexural strength is displayed in Figure 7. The epoxy specimen of neat epoxy composite has a very low flexural strength, measuring in at 31.15 MPa. This constitutes the lowest value. The specimen J-A-Epoxy has a flexural strength of 51.77 MPa, whereas the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy has a flexural strength of 66.42 MPa. Compared to the specimens Epoxy and J-A-Epoxy, respectively, the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy’s flexural strength is considerably higher. By layering acacia for the middle layer and jute as the outermost one, the flexural strength of the sandwich composite sample J-A-J-Epoxy was increased to 66.42 MPa. This layered sandwich combination resulted in significant improvements in the scenario. The layered structure, with acacia fiber forming the core and jute fiber as the outer layer, contributed to improved results in this study. This improvement was a result of the combined use of both types of fiber. Ultimately, the material’s flexural strength was significantly increased by changing the order of how jute fibers were arranged. In composites constructed of polymers, the flexural strength will be affected by a wide variety of parameters. These effects can be broken down into many categories. There is a possibility that these elements are distinct from one another. Based on the data, we can reasonably determine that the flexural strength was influenced by the strength provided by the reinforcing composites which had been layered on top of each other. A previous research study [24] came to the conclusion that inadequate interfacial contact between natural fibers and the matrix was the cause of poor flexural properties. Comparing the specimens Epoxy and J-A-Epoxy, it was discovered that the sample J-A-J-Epoxy’s composite compositions had better interfacial bonding properties. Over the whole duration of the present research, the order of the fiber stacking was the factor that was accountable for the improvement in the flexural characteristics. When flexural applied forces are introduced to hybrid composites, they experience structural changes that ultimately lead to an increase in toughness. The enhanced toughness results from the interaction between the fibers and the matrix, which helps to distribute stress more effectively. Changes in the fiber configuration within the composite significantly enhance its flexural properties. As the properties of the fibers change, so do the mechanical performance characteristics of the composite. This adaptation can lead to better load-bearing capabilities and improved resistance to deformation [25,26]. Jute fiber mats feature a woven design incorporating continuous log fibers, resulting in significant mechanical strength. There is a correlation between the weight-bearing capabilities of these log fibers and those of single and short fibers. The inherent alignment of the fibers and the specific areas rich in resin play crucial roles in influencing the material’s flexural properties. It is widely recognized that the woven configuration of the hybrid composite, which incorporates natural fibers, contributes to its modest enhancement in flexural strength. The natural composite will experience deformation as the outcome of bending, and its flexural modulus acts as a measurement that determines the extent to which the deformity is compensated for. It can be concluded that the layering pattern is a key factor that enhances the mechanical characteristics of natural hybrid composites. Interfacial connections pertain to the interactions at the interface between various materials, including fibers and matrices in composite structures. The strength of these connections can significantly affect the overall mechanical properties of the composite, especially flexural strength, which is crucial for applications requiring bending resistance.
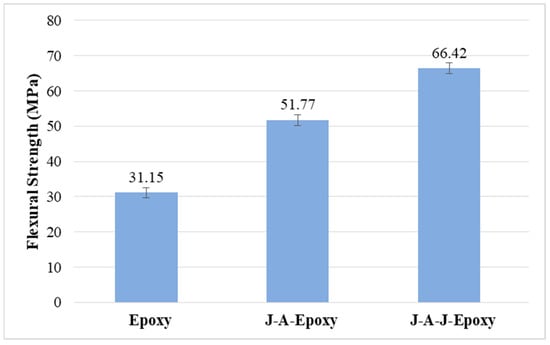
Figure 7.
Flexural strength of composites.
3.3. Impact Properties
Figure 8 illustrates the energy absorbed for each sample after the impact test. The samples’ impact strength showed similarities with their tensile and flexural strength, with the incorporation of fiber layers augmenting their properties. The figure suggests that the way fibers are stacked significantly enhances the overall impact resistance of the composite material. The specimen J-A-J-Epoxy, having a direct impact absorption of 37.22 J/m, is higher than the specimens Epoxy and J-A-Epoxy in impact absorption efficacy. The specimens Epoxy and J-A-Epoxy exhibit impact strengths of 19.36 J/m and 28.11 J/m, correspondingly. The energy absorption capacity of composites correlates directly with the fiber content and the order of stacking of the material employed. Furthermore, the fibers inside the composites function as a load transmission medium and are capable of inhibiting fracture propagation. The addition of fiber layers to composite materials significantly enhances their impact strength due to the strong interfacial connections between the matrix and the fibers [27]. This phenomenon can be credited to numerous aspects related to the arrangement and distribution of the fibers within the composite. The quality of the bond between the fiber and the matrix is crucial. A robust interfacial connection ensures effective stress transfer during impact, leading to improved energy absorption and distribution throughout the material [28,29].
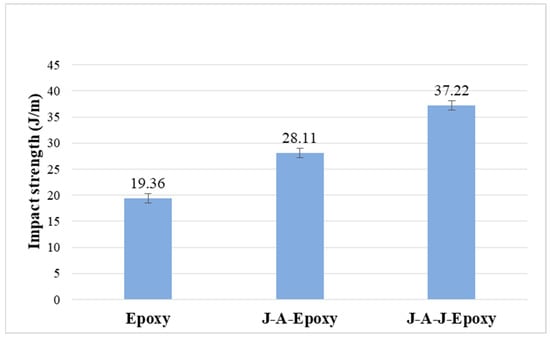
Figure 8.
Impact strength of composites.
3.4. Hardness Properties
Figure 9 presents the findings that were obtained from the hardness test. It is over the objective of determining the level of hardness that the Shore D hardness apparatus is employed throughout the process. Due to the presence of fibers and fiber layers, the hardness properties of the composites increased and were comparable to tensile, flexural, and hardness values. The hardness properties of the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy, measuring 85 Shore D, are significantly different from those of the specimens Epoxy and J-A-Epoxy, due to the fact that the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy is a significantly harder material. A hardness of 79 Shore D is found in the Epoxy specimen, whereas a hardness of 83 Shore D is found in the specimen J-A-Epoxy. Experimental evidence indicates that adding more fiber layers correlates with increased hardness in the composite samples. This improvement can be attributed to the greater structural integrity provided by the additional fibers. The specimen J-A-J-Epoxy exhibits a particularly noteworthy increase in hardness, suggesting that its specific stacking order is optimized for strength and rigidity. SEM image (Figure 10C) reveals that the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy displays minimal void formation. Voids can compromise material strength; therefore, their reduction is a significant advantage. The absence of severe voids indicates that the material’s density and uniformity are enhanced, which is crucial for achieving the desired mechanical properties. Strong interfacial bonds facilitate better load transfer between components, contributing to overall material performance [30].
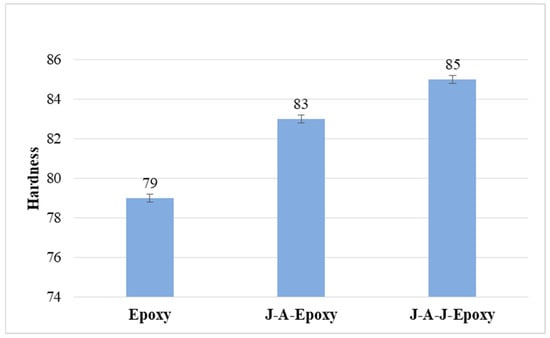
Figure 9.
Hardness of composites.
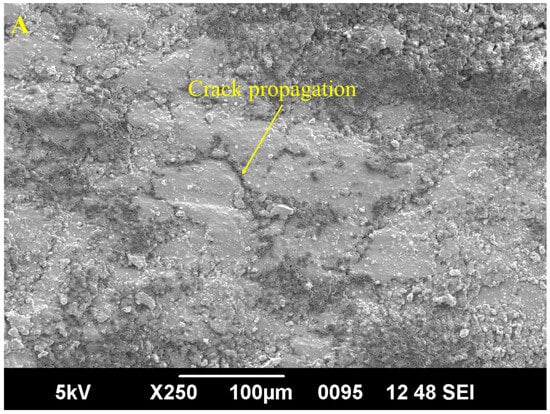
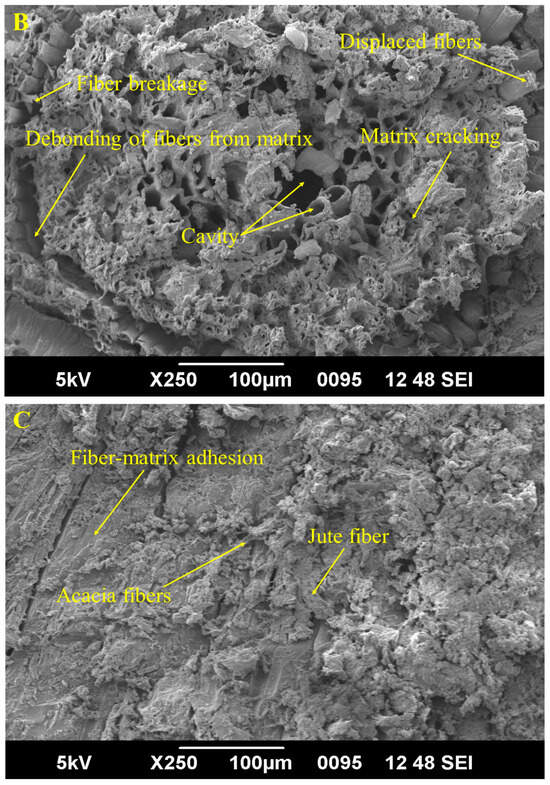


Figure 10.
SEM images of tensile analysis of the specimens (A) Epoxy, (B) J-A-Epoxy, and (C) J-A-J-Epoxy.
3.5. Morphological Analysis
Figure 10A–C show scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images that highlight the surface characteristics of broken tensile composite samples of J-A-Epoxy and J-A-J-Epoxy. A number of factors can cause failure in polymer composites, with problems at the interface between the polymer matrix and the natural reinforcing fibers being particularly important. These problems can take the form of fiber fracture, interfacial de-bonding, matrix cracking, delamination, and fiber pull-out. During failure, significant evidence of fiber separation is seen, indicating that the individual fibers within the composite had fractured, and delamination occurred along the composite’s edge.
Figure 10A’s neat Epoxy specimen shows a flat surface, indicating a brittle fracture. This implies that the sample has a low crack propagation resistance and can readily break under load. However, the fracture surfaces of the J-A-Epoxy and J-A-J-Epoxy specimens are rougher and wavier than the Epoxy specimen, indicating that fiber-reinforced epoxy composites require more energy for crack propagation. Figure 10B shows the phenomenon of fiber pull-out, with a particular focus on the mechanics of the separation process. Furthermore, it highlights the complex interconnection between fiber, micro-cracks, vacancies, and the matrix. Furthermore, the presence of voids enhances our perception of fracture behavior. Cavity formation due to fiber pull-out is seen in Figure 10B.
The void fraction impacts the composite’s mechanical, thermal, and durability. Voids concentrate stress and cause cracks, reducing matrix-dominated interlaminar shear, flexural, compressive, and tensile strength. Voids weaken composite fatigue and durability. For optimal mechanical strength, thermal characteristics, and durability, the manufacturing of the composites required void fraction reductions. Mechanical and morphological data demonstrate that J-A-J-Epoxy has a lower void % than the other specimens. Consequently, the mechanical characteristic analysis of the specimen J-A-Epoxy composites yielded poor results. Figure 10B illustrates the damage mechanisms observed in the fractured composite matrix, including fiber pull-out, broken fibers, and cracks within the matrix itself. Additionally, the image reveals fiber de-bonding and the presence of fiber splitting and matrix debris at the fiber–matrix interface. Evidence of matrix detritus was present on the fiber surfaces, indicating that matrix material had separated from the fibers in the failure phase. Figure 10C effectively illustrates the enhanced bonding that exists among the jute–acacia fibers and the epoxy matrix, as well as the fractured fibers resulting from tensile stress. Despite minimal fiber delamination, the sample exhibited superior fiber-to-matrix adherence. The mechanical properties of epoxy are enhanced when it has a stronger bond among the jute–acacia fibers with epoxy. Cracks within the matrix signify brittle failure, which is the primary mechanism of failure [31]. Even so, significant fractures are absent in the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy because of excellent fiber–matrix adhesion. Conversely, significant fractures are improbable in this region because of the excellent fiber–matrix adhesion. Due to the existence of fiber sandwich structures and the lack of significant cavities and cracks, the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy demonstrates enhanced bonding relative to the specimen J-A-Epoxy composite. Because of the amount of fibers in the inner layers, which take up more load before breaking and undergo greater amounts of bending, Figure 10C indicates that the existence of fibers results in jute–acacia–epoxy bonding and a reduced degree of matrix fracture [32]. This is because the fibers absorb more weight before breaking. The sandwich structure led to a reduction in the percentage of broken fibers and fiber breakage, which significantly influenced the flexibility and tensile strength [33]. The tensile and flexural characteristics of hybrid composites have been examined, revealing that sandwich composites exhibited the most optimal results, demonstrating substantial tensile and flexural strengths. According to the investigation, the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy exhibits low voids and favorable fiber–resin adhesion properties. It has been shown, therefore, that multidimensional composites are stronger when compared to their mono-layered counterparts [34]. The SEM details indicated that Figure 10C demonstrated superior interfacial interactions. A more even fiber distribution and lessened clumping result from this process. The enhanced tensile strength may be attributed to the consistent dispersion of jute–acacia throughout the matrix. The inclusion of layers enhances the connection between the fibers and that helps to prevent the formation of micro-voids. Moreover, an increase in the layers enhances reinforced stiffness and uniformly increases load distribution. The mechanical, physical, and durability qualities of natural fiber-reinforced epoxy composites depend on their chemical affinity. The effectiveness of natural fiber-reinforced epoxy composites depends on it. The chemical and physical processes of fibers strengthen interfacial bonding, improving mechanical characteristics, durability, and environmental resistance. Thus, developing sustainable, high-performance bio-composites requires optimizing fiber–matrix chemical compatibility. Mechanisms of interfacial bonding include mechanical, chemical, and physical interactions. Fiber surface roughness allows matrix–fiber physical interlocking. Covalent or hydrogen bonding between fiber surface functional groups and the epoxy matrix improve adhesion. Van der Waals and electrostatic forces contribute but are weaker than chemical bonds. The impact on composite features includes stress transfer, moisture resistance, and durability. Strong chemical affinity improves the tensile, flexural, and impact strengths by efficiently transferring load from the matrix to the fibers. Water infiltration can impair the interface and mechanical qualities, but good chemical bonding prevents it. Improved interfacial adhesion resists fracture development, delamination, and environmental degradation.
4. Conclusions
This research focused on evaluating the impact of the distribution of jute and acacia fibers on the mechanical properties and morphological features of hybrid composites. The findings from the experiments point to the subsequent conclusions.
- Compression molding was used to create the innovative sandwich composites of jute and acacia. The specimen J-A-J-Epoxy (sandwich composite) exhibits significant improvement in its tensile, flexural impact, hardness, and morphological characteristics, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
- According to the results of the tensile strength investigation, the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy has exceptional strength.
- The statistics make it very clear that the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy possesses a flexural strength which is greater than that of the others.
- The outcomes of the impact test demonstrate that the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy had a much greater impact strength.
- The hardness of the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy exceeds the value of the specimens Epoxy and J-A-Epoxy. The increased quantity of fiber layers and layering sequence points to a rise in the hardness of the sample J-A-J-Epoxy. SEM images indicate the absence of significant voids in the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy in contrast to the specimen J-A-Epoxy.
- The SEM analysis demonstrated that the specimen exhibited enhanced structural properties, marked by reduced fiber breakage as well as fiber pull-out, relative to the specimen J-A-J-Epoxy.
- In summary, the research reinforces the potential of jute–acacia–epoxy composites as a sustainable composite. Treatment with NaOH significantly improved the bonding between the jute and acacia fibers, resulting in composites with superior mechanical properties. The excellent characteristics of these composites suggest they are viable alternatives in various engineering applications, especially in structural contexts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.A.K. and M.B.; Data curation, N.D.M., M.P., S.V.R. and P.P.; Formal analysis, R.A.K. and M.B.; Investigation, R.A.K. and M.B.; Methodology, R.A.K. and M.B.; Supervision, R.A.K. and M.B.; Writing—original draft, N.D.M., M.P., S.V.R. and P.P.; Writing—review and editing, R.A.K. and M.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
There was no external funding for this project.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Saintgits College of Engi-neering (Autonomous), Kottayam, Kerala, India, for providing a platform for this research.
Conflicts of Interest
I would like to declare on behalf of my co-authors that the submission is an original work and is not currently under review by other publications elsewhere.
References
- Dev, B.; Rahman, A.; Alam, R.; Repon, R.; Nawab, Y. Mapping the Progress in Natural Fiber Reinforced Composites: Preparation, Mechanical Properties, and Applications. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 3748–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, B.; Rahman, M.A.; Tazrin, T.; Islam, M.S.; Datta, A.; Rahman, M.Z. Investigation of Mechanical Properties of Nonwoven Recycled Cotton/PET Fiber-Reinforced Polyester Hybrid Composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2024, 309, 2400020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, H.; Saha, A.; Hasan, M.; Haider, J. Effects of Alkaline and Carboxylated Graphene Oxide (CGO) Treatment on Mechanical, Thermal, and Electrical Properties of Jute Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaguru, S.; Thiagamani, S.M.K.; Siengchin, S.; Subramanian, J.; Ebrahimnezhad-Khaljiri, H.; Sanjay, M.R.; Khan, A.; Abuthakeer, S.S.; Rajesh, S.; Alromaizan, A.N. Effect of Various Weaving Architectures on Mechanical, Vibration and Acoustic Behavior of Kevlar-Hemp Intra-Ply Hybrid Composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 176, 107845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marichelvam, M.K.; Kumar, C.L.; Kandakodeeswaran, K.; Thangagiri, B.; Saxena, K.K.; Kishore, K.; Kumar, S. Investigation on Mechanical Properties of Novel Natural Fiber-Epoxy Resin Hybrid Composites for Engineering Structural Applications. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinur, S.; Hasan, M.; Ahsan, Q.; Haider, J. Effect of Chemical Treatment on Thermal Properties of Jute Fiber Used in Polymer Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, B.; Khan, A.N.; Rahman, M.A.; Siddique, A.B.; Nag, R.K.; Amit, J.A.; Nahid, I.A.; Rahman, Z. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Unidirectional Jute/Snake Plant Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Hybrid Composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 218, 118903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix Sahayaraj, A.; Muthukrishnan, M.; Ramesh, M. Experimental Investigation on Physical, Mechanical, and Thermal Properties of Jute and Hemp Fibers Reinforced Hybrid Polylactic Acid Composites. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 2854–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaguru, S.; Thiagamani, S.M.K.; Muthu Kumar, C.; Krishnasamy, S.; Arpitha, G.R.; Mayakannan, S. Erosion Characteristics of Epoxy-Based Jute, Kenaf and Banana Fiber Reinforced Hybrid Composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 64, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, T.S.; Kumar, S.S.; Kumar, L.R. Jute Fibers, Their Composites and Applications. In Plant Fibers, Their Composites, and Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2022; pp. 253–282. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Du, T.; Song, P.; Chen, Y. Research on Mechanics and Acoustic Properties of Jute Fiber Composite Material. Heliyon 2024, 10, e16813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natrayan, L.; Kaliappan, S.; Balaji, N.; Mahesh, V. Dynamic Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Polymer-Coated Jute Fibers for Enhanced Automotive Parts; SAE Technical Papers; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dawit, J.B.; Regassa, Y.; Lemu, H.G. Property Characterization of Acacia Tortilis for Natural Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composite. Results Mater. 2020, 5, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthanarieswaran, V.P.; Kumaravel, A.; Saravanakumar, S.S. Characterization of New Natural Cellulosic Fiber from Acacia Leucophloea Bark. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2015, 20, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadivel, K.S.; Govindasamy, P. Characterization of Natural Cellulosic Fiber from Treated Acacia Arabica and Pencil Cactus Fiber. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 3392–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marichelvam, M.K.; Manimaran, P.; Verma, A.; Sanjay, M.R.; Siengchin, S.; Kandakodeeswaran, K.; Geetha, M. A Novel Palm Sheath and Sugarcane Bagasse Fiber-Based Hybrid Composites for Automotive Applications: An Experimental Approach. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Busu, W.N.; Anuar, H.; Ahmad, S.H.; Rasid, R.; Jamal, N.A. The Mechanical and Physical Properties of Thermoplastic Natural Rubber Hybrid Composites Reinforced with Hibiscus cannabinus L. and Short Glass Fiber. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2010, 49, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrekirstos, A.; Teketay, D.; Fetene, M.; Mitlöhner, R. Adaptation of Five Co-Occurring Tree and Shrub Species to Water Stress and Its Implication in Restoration of Degraded Lands. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 229, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodi, M.M.; Sapuan, S.M.; Ahmad, D.; Ali, A.; Khalina, A.; Jonoobi, M. Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Kenaf/Glass Reinforced Epoxy Composite for Passenger Car Bumper Beam. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4927–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawit, J.B.; Lemu, H.G.; Regassa, Y.; Akessa, A.D. Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Acacia Tortilis Fiber Reinforced Natural Composite. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 2953–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Islam, R.; Uddin, M.A.; Afroj, S.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Karim, N. Sustainable Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A Review. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2022, 6, 2200258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, M.R.; Madhu, P.; Jawaid, M.; Senthamaraikannan, P.; Senthil, S.; Pradeep, S. Characterization and Properties of Natural Fiber Polymer Composites: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 566–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocharla, R.P.B.; Bandlamudi, R.K.; Mirza, A.A.; Kolli, M.; Shanmugam, R.; Cheepu, M. Investigation on the Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Jute/Carbon Fiber Hybrid Composites with the Inclusion of Crab Shell Powder. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athith, D.; Sanjay, M.R.; Gowda, T.G.Y.; Madhu, P.; Arpitha, G.R.; Yogesha, B.; Omri, M.A. Effect of Tungsten Carbide on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Jute/Sisal/E-Glass Fabrics Reinforced Natural Rubber/Epoxy Composites. J. Ind. Text. 2018, 48, 713–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, B.R.N.; Harisha, S.R.; Deepak, G.D.; Hiremath, P. Experimental Design and Optimization of Machining-Induced Cutting Force and Its Effect on Surface Roughness during Milling of Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, M.R.; Siengchin, S.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Jawaid, M.; Pruncu, C.I.; Khan, A. A Comprehensive Review of Techniques for Natural Fibers as Reinforcement in Composites: Preparation, Processing and Characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 108–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Nasir, M.A.; Khalid, M.Y.; Nauman, S.; Shaker, K.; Khushnood, S.; Altaf, K.; Zeeshan, M.; Hussain, A. Experimental and Numerical Characterization of Mechanical Properties of Carbon/Jute Fabric Reinforced Epoxy Hybrid Composites. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2019, 33, 4217–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beedu, R.N.M.; Beedu, R.; P K, J.; Potti, S.R. Study on Machining Quality in Abrasive Water Jet Machining of Jute-Polymer Composite and Optimization of Process Parameters through Grey Relational Analysis. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Kurien, R.A.; Kannan, G.; Kurup, G.B.; Reji, G.S.; Santhosh, A.; Paul, D.; Siengchin, S. Comparative Mechanical and Morphological Characteristics of an Innovative Hybrid Composite of Vetiver and Jute. J. Polym. Res. 2024, 31, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanthi, P.; Kondapalli, S.B.; Morampudi, N.K.S.R.; Vallabhaneni, V.V.M.; Saxena, K.K.; Mohammed, K.A.; Linul, E.; Prakash, C.; Buddhi, D. Elastic Properties of Jute Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites with Different Hierarchical Structures. Materials 2022, 15, 7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, B.R.N.; Makki, E.; Potti, S.R.; Hiremath, A.; Bolar, G.; Giri, J.; Sathish, T. Optimization of Process Parameters to Minimize the Surface Roughness of Abrasive Water Jet Machined Jute/Epoxy Composites for Different Fiber Inclinations. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, C.K.; Venkatachalam, G.; Bhuvaneshwari, M. Investigation of Thermal Conductivity of Prosopis juliflora/Acacia leucophloea/Acacia nilotica Fibers/Ceramic Fillers/Epoxy Composites. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 104225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachappareddy, C.; Padhy, C.P.; Pendyala, S. An Experimental Investigation on Delamination Factor and Thrust Force Evaluation of Kenaf Fiber and Acacia Concinna Filler Reinforced Epoxy Hybrid Composites. Green Technol. Sustain. 2025, 3, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheeba, K.J.; Priya, R.K.; Arunachalam, K.P.; Avudaiappan, S.; Flores, E.S.; Kozlov, P. Enhancing Structural, Thermal, and Mechanical Properties of Acacia pennata Natural Fibers through Benzoyl Chloride Treatment for Construction Applications. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).