Experimental Study of the Combined Use of Silver Nanoparticles and Graphene Oxide to Predict the Operational Properties of New Bactericidal Composite Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Bactericidal: This process involves releasing an antibacterial substance, also known as “drug release” (DR). The drug is loaded into a carrier and typically released through diffusion.
- “Contact-killing” (CK): This method uses surfactants to directly destroy bacterial biofilms.
- “Anti-adhesion” (AA): This strategy aims to prevent the early stages of colonization and the formation of bacterial biofilms by inhibiting their adhesion to surfaces.
2. Materials and Methods
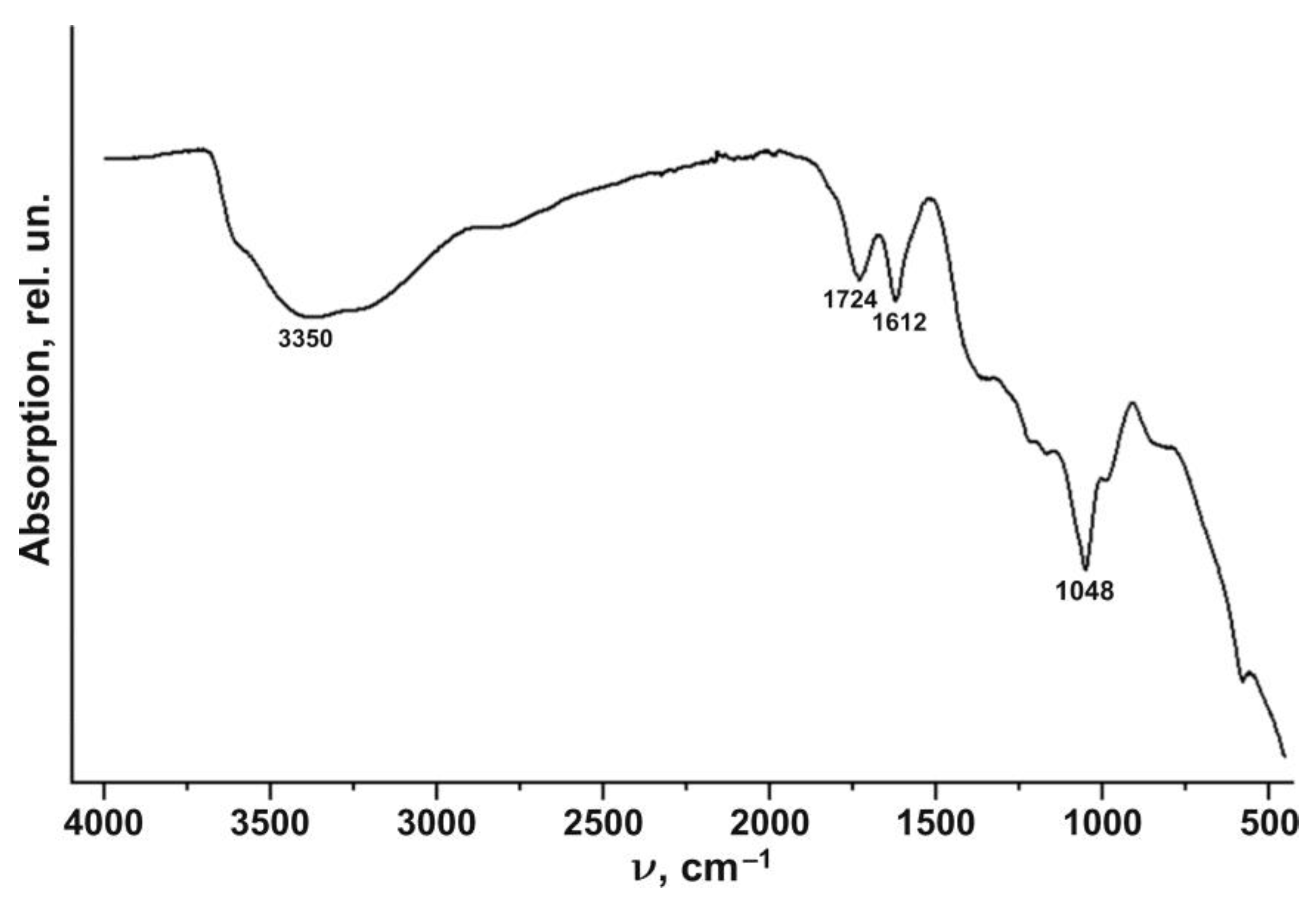
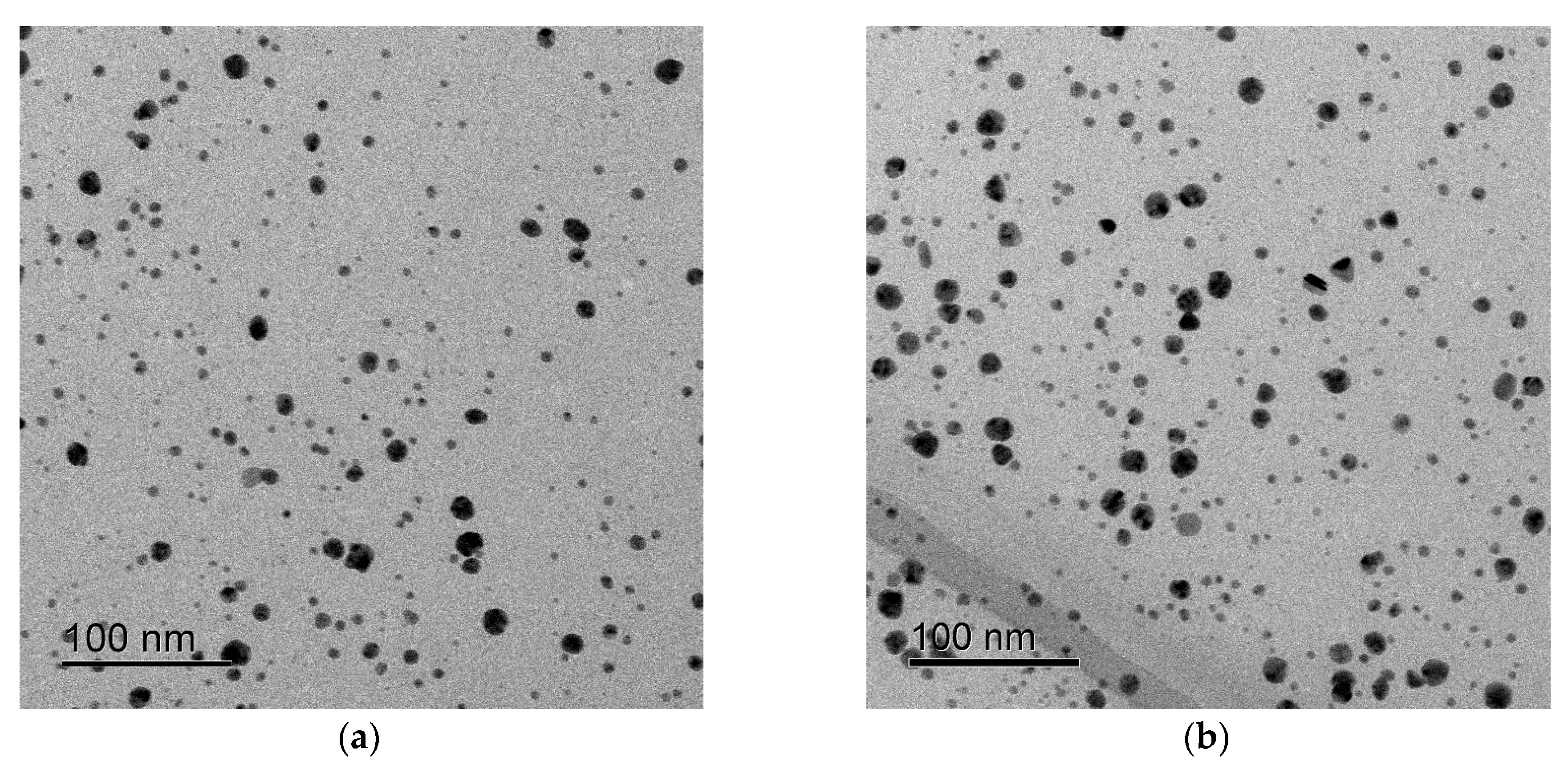
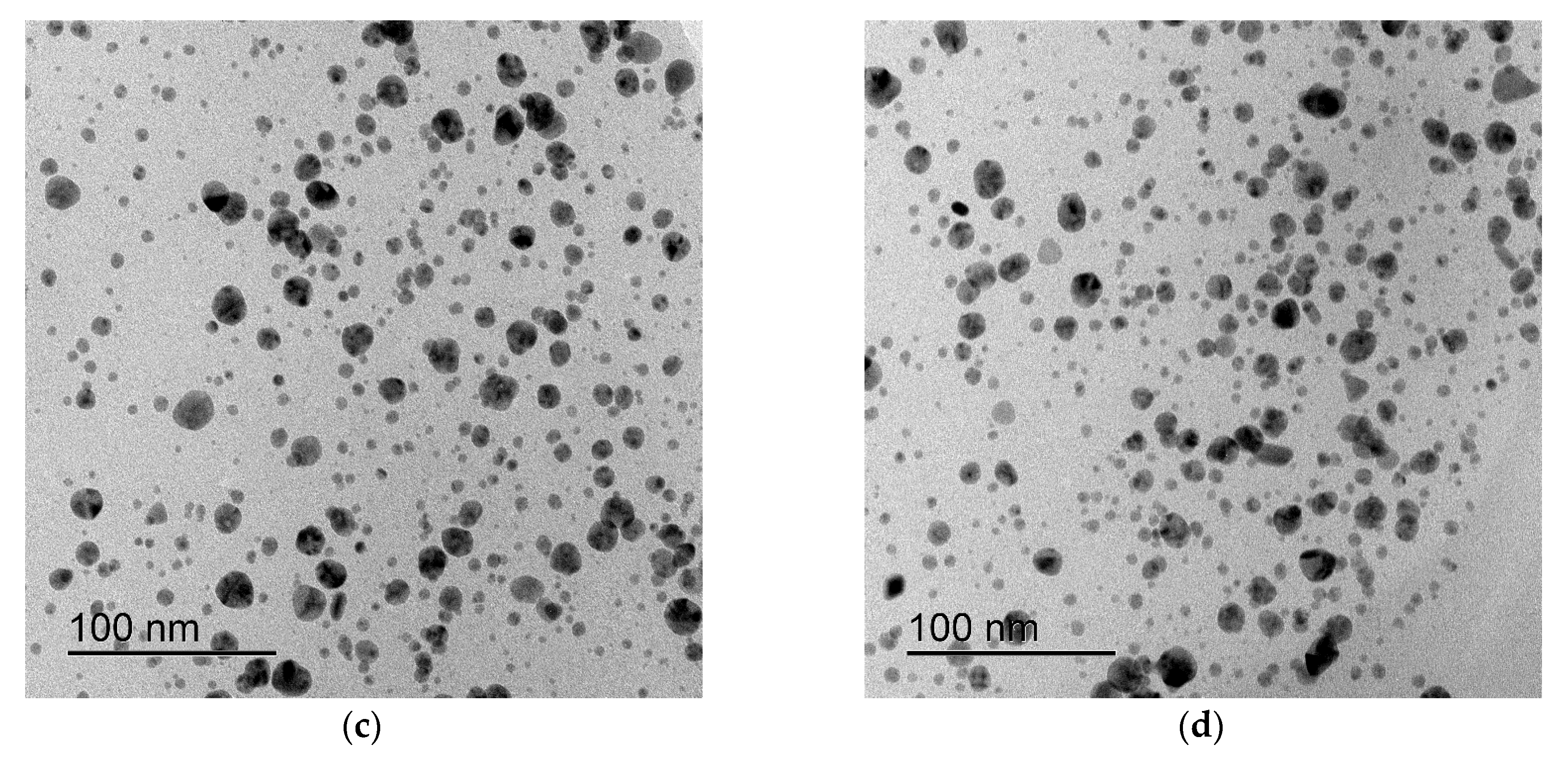
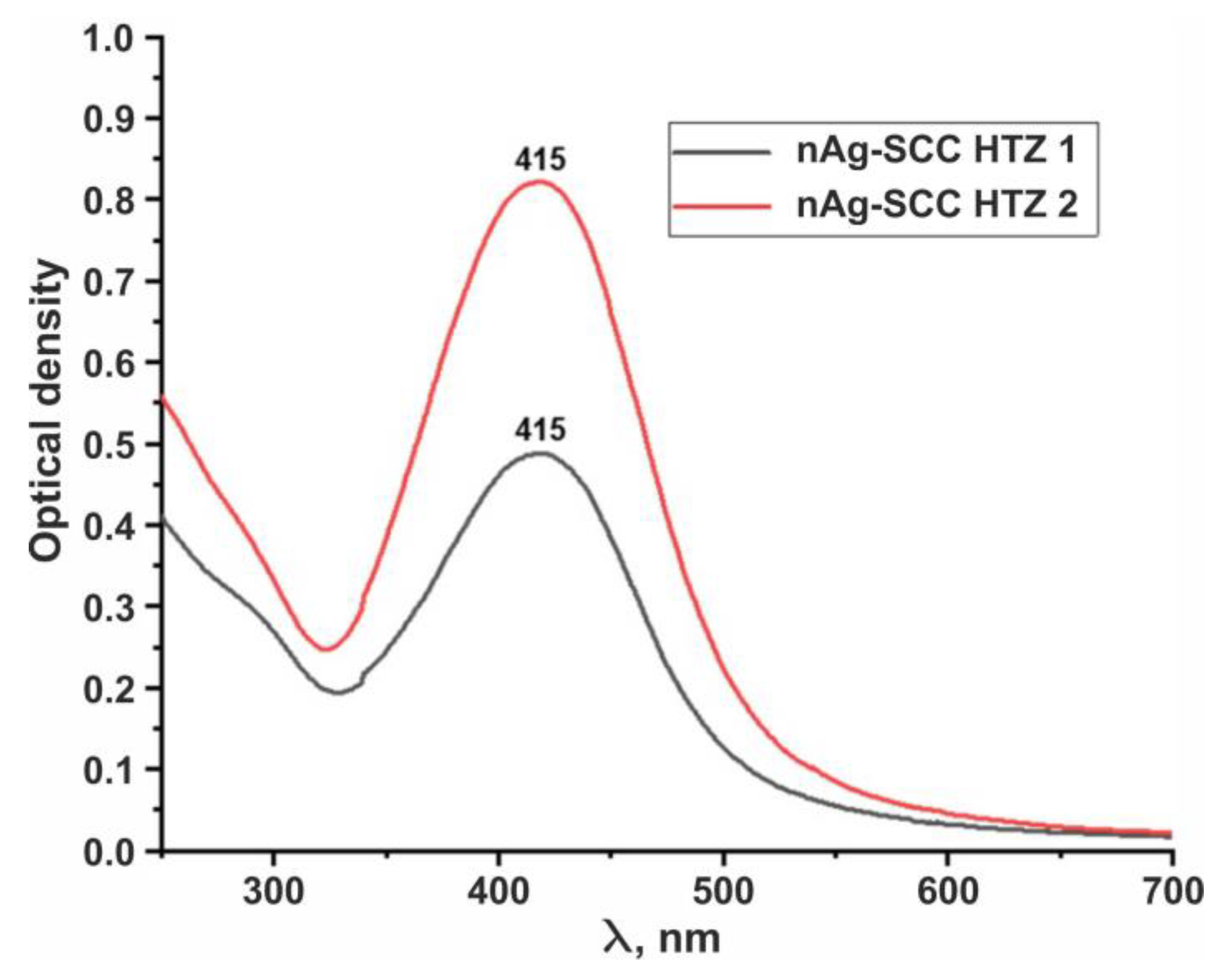
3. Results
4. Discussion
- A supernatant-colored transparent dye solution and a densely colored precipitate at the bottom of the container.
- The supernatant was removed and an equal volume of water was added to the remaining sediment. This mixture was then shaken until a colored solution formed. The process was repeated three times. As a result, a solution containing bacterial elements, colored with crystal violet, was obtained in both the case without the inhibitor and with the inhibitor at a known dosage.
- The optical density was measured at the maximum absorption of the two solutions. The inhibitory activity (IA) was believed to be the ratio of the optical density of a calibrator sample to the optical density of an inhibitor sample.
- Paired regression modeling was performed. The independent variable was the inhibitor dosage and the dependent variable was IA.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prihandana, G.S.; Sriani, T.; Muthi’ah, A.D.; Machmudah, A.; Mahardika, M.; Miki, N. Study Effect of nAg Particle Size on the Properties and Antibacterial Characteristics of Polysulfone Membranes. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, S.I.; Vivian, L.; Zalati, C.W.S.C.W.; Sani, N.I.M.; Aklilu, E.; Mohamad, M.; Noor, A.A.M.; Muthoosamy, K.; Kamaruzzaman, N.F. Antimicrobial activities of graphene oxide against biofilm and intracellular Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhazouani, A.; Gamrani, H.; El Achaby, M.; Aziz, K.; Gebrati, L.; Uddin, M.S.; Aziz, F. Synthesis and Toxicity of Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles: A Literature Review of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5518999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljaafari, A.; Ahmed, F.; Husain, F.M. Bio-inspired facile synthesis of graphene-based nanocomposites: Elucidation of anti-microbial and biofilm inhibitory potential against foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Coatings 2020, 10, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Peng, H.; Wang, X.; Shao, F.; Yuan, Z.; Han, H. Graphene oxide exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against bacterial phytopathogens and fungal conidia by intertwining and membrane perturbation. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciancico, C.; Braidotti, M.C.; Gentilini, S.; Prizia, R.; Ghofraniha, N.; Angelani, L.; Palmieri, V.; Bugli, F.; De Spirito, M.; Sanguinetti, M. Nonlinear optics, optomechanics, and antibacterial coating by graphene oxide. In Proceedings of the Quantum Sensing and Nano Electronics and Photonics XIV, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2 February 2017; pp. 304–312. [Google Scholar]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial Biofilms: A Common Cause of Persistent Infections. Science 1999, 284, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, V.; Papi, M.; Conti, C.; Ciasca, G.; Maulucci, G.; De Spirito, M. The future development of bacteria fighting medical devices: The role of graphene oxide. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2016, 13, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y. Mechanisms of the Antimicrobial Activities of Graphene Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2064–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Dubey, A.; Shukla, S.; Saini, C.P.; Gupta, G.; Priyadarshini, R.; Lochab, B. Graphene oxide-coated surface: Inhibition of bacterial biofilm formation due to specific surface–interface interactions. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3070–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Mahmood, Z.; Zhang, W.; Akram, M.W.; Ainur, D.; Ma, H. In situ investigation of acute exposure of graphene oxide on activated sludge: Biofilm characteristics, microbial activity and cytotoxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 199, 110639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E.; Esfandiar, A. Wrapping Bacteria by Graphene Nanosheets for Isolation from Environment, Reactivation by Sonication, and Inactivation by Near-Infrared Irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Toxicity of Graphene and Graphene Oxide Nanowalls Against Bacteria. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Yang, C.-M.; Sun, X.-F.; Xia, P.-F.; Qin, J.; Guo, B.-B.; Wang, S.-G. Influences of graphene oxide on biofilm formation of gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 2853–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, L.; Peltier, R.; Hui, W.; Yao, X.; Cui, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z. Interfacial engineering of bi-metallic Ag/Pt nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide matrix for enhanced antimicrobial activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8834–8840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, F.M.; Khan, M.S.; Siddiqui, S.; Khan, A.; Arshad, M.; Alyousef, A.A.; Rahman, M.; Al-Shabib, N.A.; Ahmad, I. Nanoparticles as New Emerging Antibacterials: Potentials and Limitations. In Antibacterial Drug Discovery to Combat MDR; Ahmad, I., Ahmad, S., Rumbaugh, K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 561–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, F.; de Faria, A.F.; Nejati, S.; Elimelech, M. Antimicrobial Properties of Graphene Oxide Nanosheets: Why Size Matters. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.U.; Guo, J.; An, A.K. Bacterial inactivation and in situ monitoring of biofilm development on graphene oxide membrane using optical coherence tomography. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 564, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieerad, A.R.; Bushroa, A.R.; Amiri, A.; Gopinath, V.; Sookhakian, M.; Baradaran, S.; Rafieerad, M.; Saber-Samandari, S.; Vadivelu, J. Large-scale hybrid silver nanowall-reduced graphene oxide biofilm: A novel morphology by facile electro-chemical deposition. Surf. Coat. Int. 2018, 347, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, S.; Wierzbicki, M.; Sawosz, E.; Jung, A.; Gielerak, G.; Biernat, J.; Jaremek, H.; Łojkowski, W.; Woźniak, B.; Wojnarowicz, J.; et al. Graphene Oxide-Based Nanocomposites Decorated with Silver Nanoparticles as an Antibacterial Agent. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozovskis, P.; Jankauskaitė, V.; Guobienė, A.; Kareivienė, V.; Vitkauskienė, A. Effect of Graphene Oxide and Silver Nanoparticles Hybrid Composite on P. aeruginosa Strains with Acquired Resistance Genes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 5147–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskakov, S.A.; Baskakova, Y.V.; Dvoretskaya, E.V.; Krasnikova, S.S.; Lesnichaya, V.A.; Shulga, Y.M.; Gutsev, G.L. Mechanical and Water Absorption Properties of Waterborne Polyurethane/Graphene Oxide Composites. Materials 2022, 16, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhoyan, K.A.; Contryman, A.W.; Silcox, J.; Stewart, D.A.; Eda, G.; Mattevi, C.; Miller, S.; Chhowalla, M. Atomic and electronic structure of graphene-oxide. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, D.; Seah, M.P. Practical Surface Analysis, Auger and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1990; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Voylov, D.N.; Agapov, A.L.; Shulga, Y.M.; Sokolov, A.P.; Arbuzov, A.A. Room temperature reduction of multilayer graphene oxide film on a copper substrate: Penetration and participation of copper phase in redox reactions. Carbon 2014, 69, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulga, Y.M.; Tien, T.C.; Huang, C.C.; Lo, S.C.; Muradyan, V.E.; Polyakova, N.V.; Ling, Y.C.; Loutfy, R.O.; Moravsky, A.P. XPS study of fluorinated carbon multi-walled nanotubes. J. Electron. Spectros. Relat. Phenom. 2007, 160, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.; Rana, D.; Salave, S.; Gupta, R.; Patel, P.; Karunakaran, B.; Sharma, A.; Giri, J.; Benival, D.; Kommineni, N. Chitosan: A Potential Biopolymer in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardanova, A.M.; Kabanov, D.A.; Rudakova, N.L.; Sharipova, M.R. Biofilms: Basic Research Methods: Teaching Aid; Kazan Federal University: Kazan, Russia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Menshikova, E.A.; Kurbatova, E.M.; Vodopyanov, S.O.; Pisanov, R.V.; Titova, S.V. Evaluation of the ability of cholera vibrios to form a biofilm on the surface of the chitinous shell of a crayfish by real-time PCR. J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol. 2021, 98, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toc, D.A.; Csapai, A.; Popa, F.; Popa, C.; Pascalau, V.; Tosa, N.; Botan, A.; Mihaila, R.M.; Costache, C.A.; Colosi, I.A.; et al. Easy and Affordable: A New Method for the Studying of Bacterial Biofilm Formation. Cells 2022, 11, 4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tel’pukhov, V.I.; Shepelev, V.A.; Lisenkov, A.N. Use of mathematical methods of experimental planning to choose optimal conditions for preservation of the heart by weak aldehyde solutions. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 1982, 93, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Erythromycin/OG | ||
|---|---|---|
| −9.61 | −0.51 | |
| 15.03 | 24.13 | |
| −9.87 | −0.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimitrieva, S.E.; Timonin, A.N.; Baskakov, S.A.; Kuznetsova, O.A.; Shkirin, A.V. Experimental Study of the Combined Use of Silver Nanoparticles and Graphene Oxide to Predict the Operational Properties of New Bactericidal Composite Materials. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070315
Dimitrieva SE, Timonin AN, Baskakov SA, Kuznetsova OA, Shkirin AV. Experimental Study of the Combined Use of Silver Nanoparticles and Graphene Oxide to Predict the Operational Properties of New Bactericidal Composite Materials. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(7):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070315
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimitrieva, Svetlana E., Andrey N. Timonin, Sergey A. Baskakov, Oksana A. Kuznetsova, and Alexey V. Shkirin. 2025. "Experimental Study of the Combined Use of Silver Nanoparticles and Graphene Oxide to Predict the Operational Properties of New Bactericidal Composite Materials" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 7: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070315
APA StyleDimitrieva, S. E., Timonin, A. N., Baskakov, S. A., Kuznetsova, O. A., & Shkirin, A. V. (2025). Experimental Study of the Combined Use of Silver Nanoparticles and Graphene Oxide to Predict the Operational Properties of New Bactericidal Composite Materials. Journal of Composites Science, 9(7), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9070315






