Green Mechanochemical Synthesis of Binary and Ternary Cadmium Chalcogenides with Tunable Band Gaps
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ball Milling
2.2. Characterization
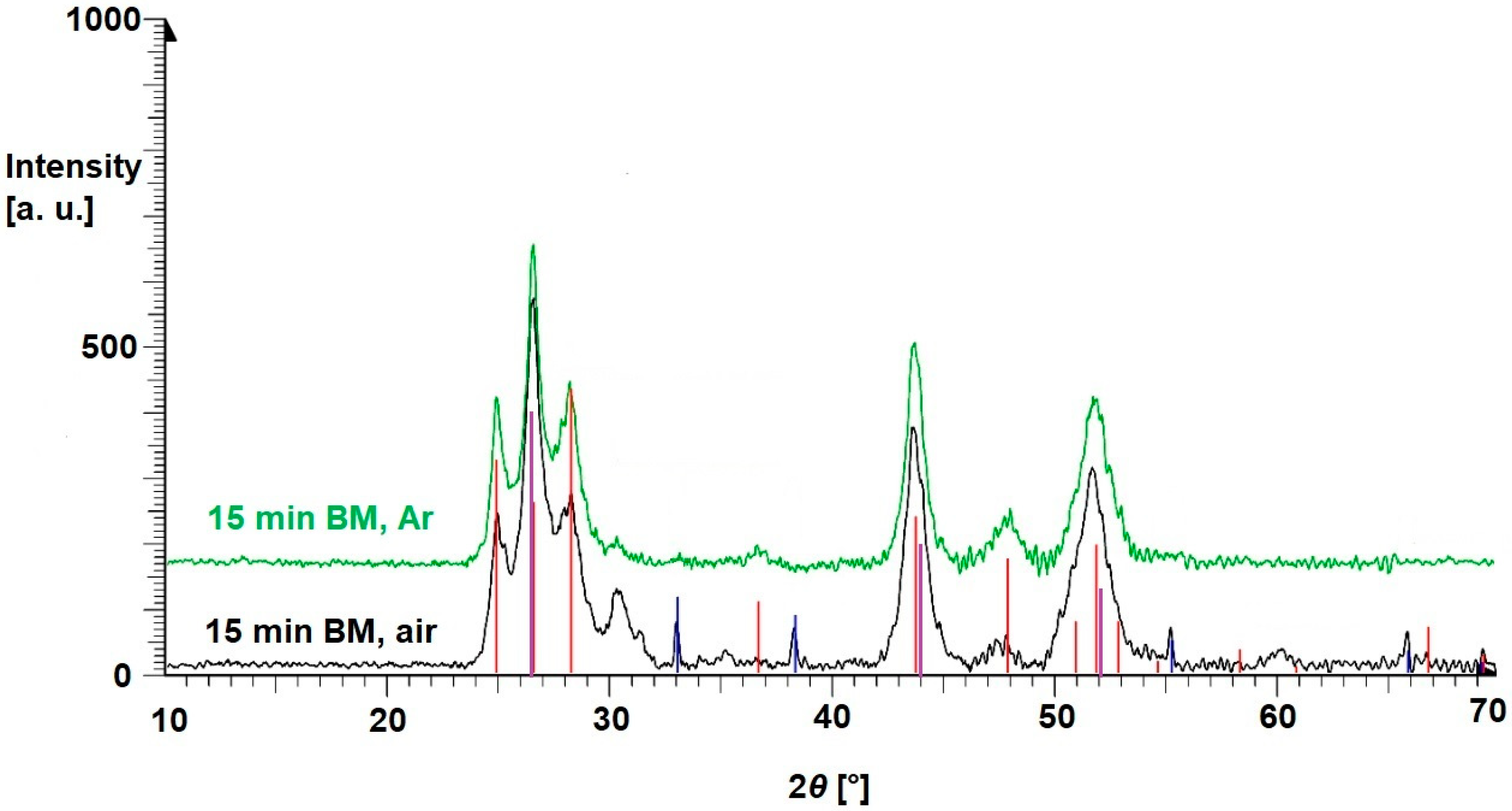
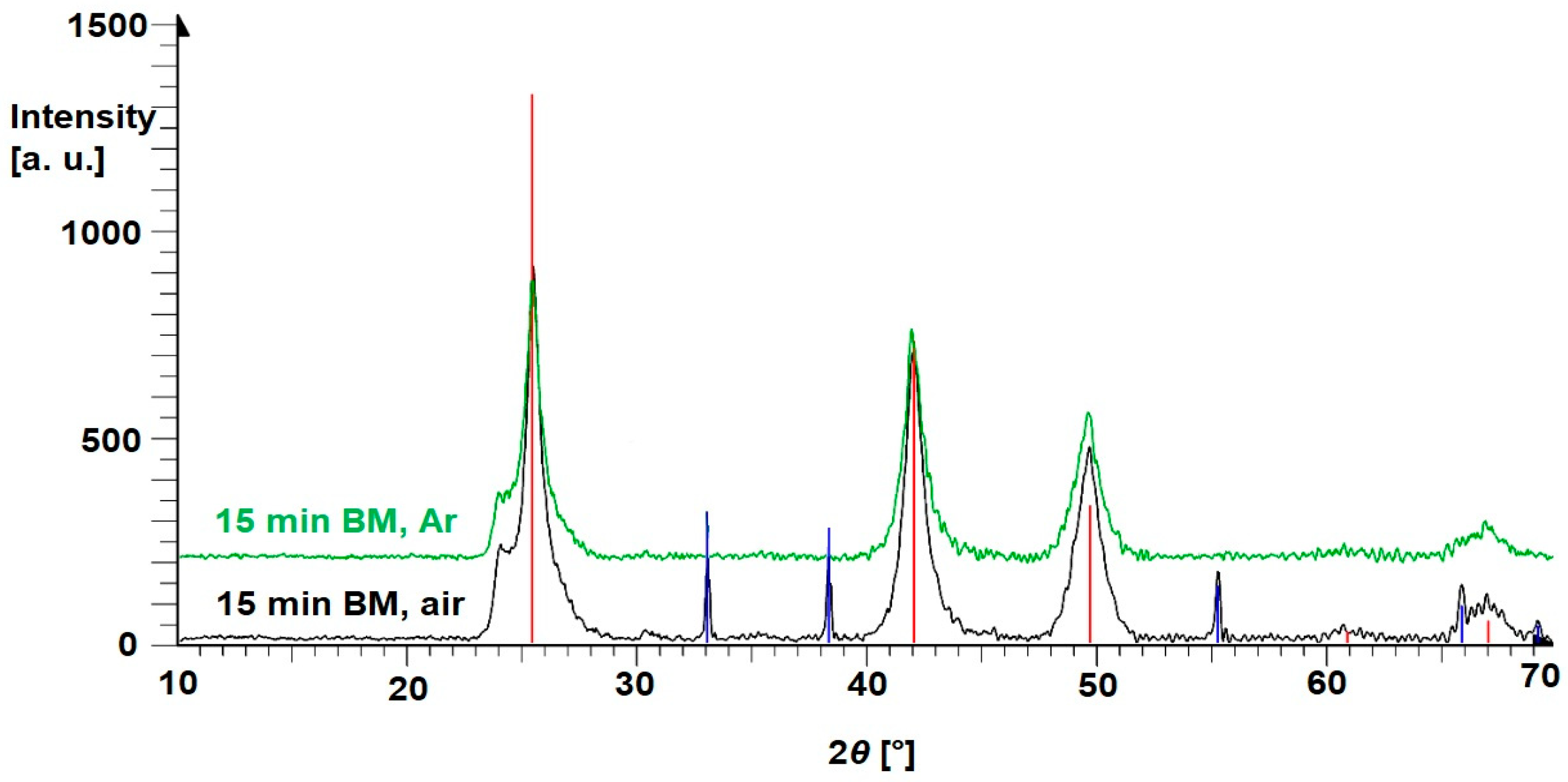
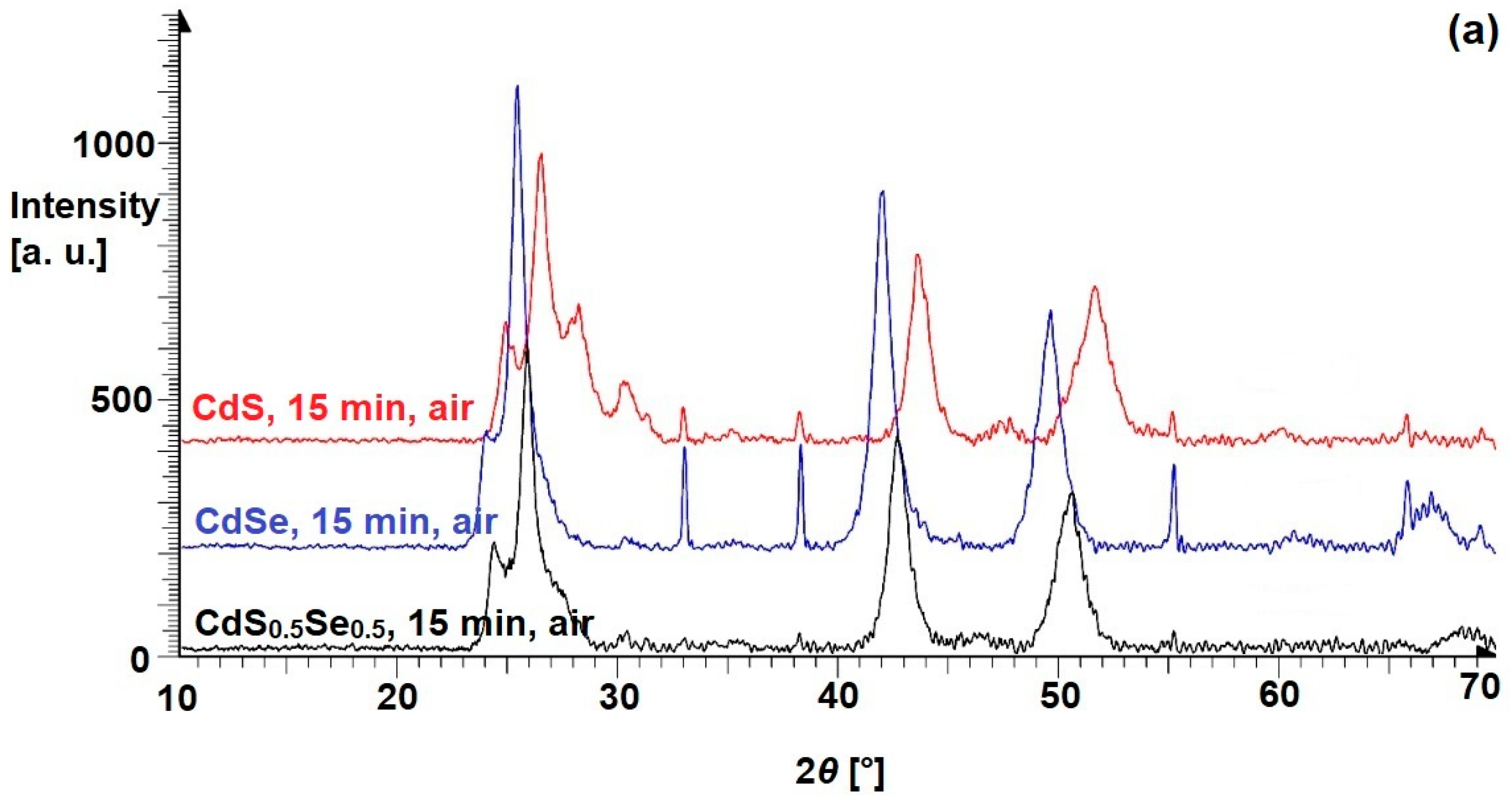
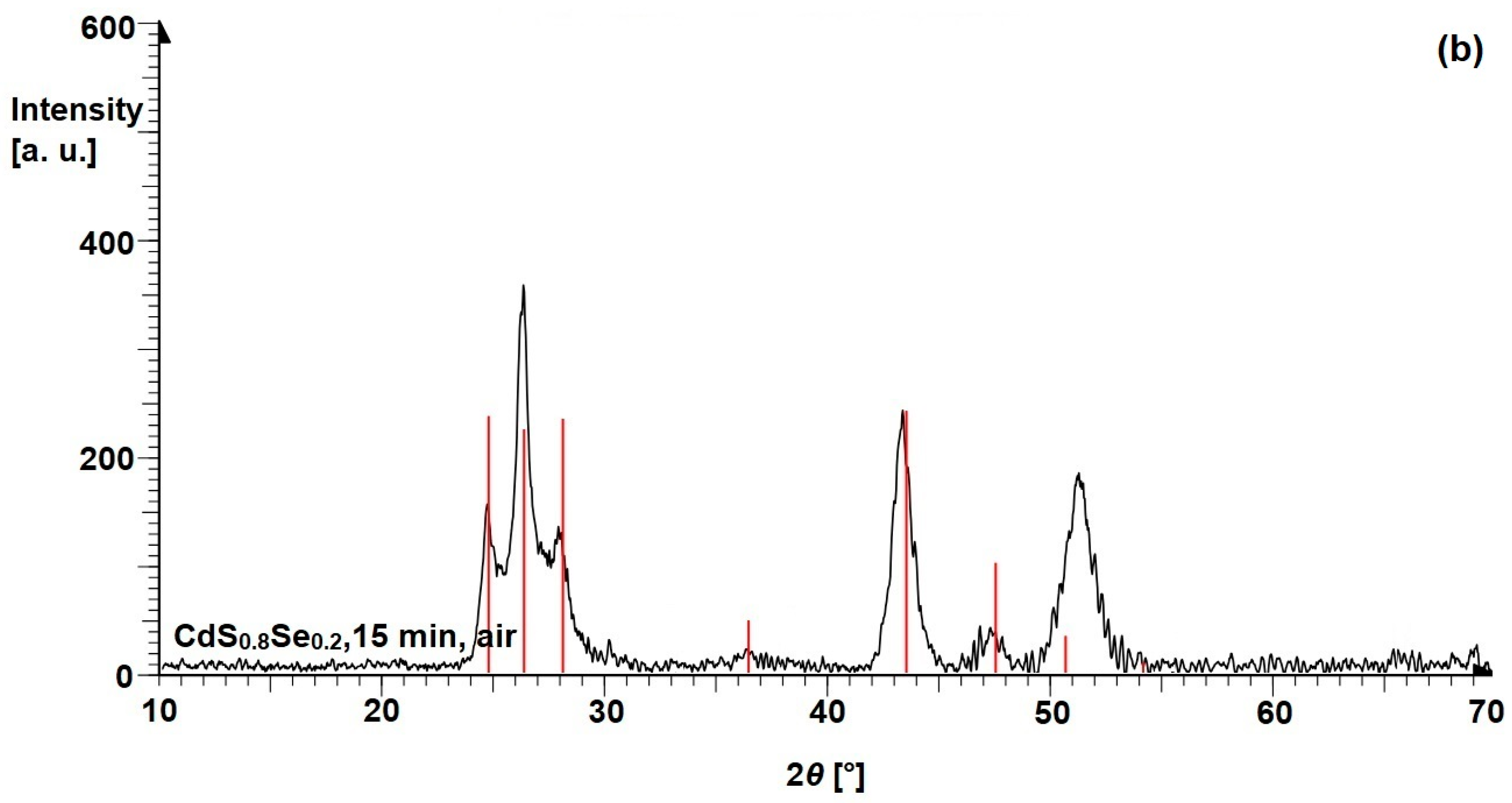
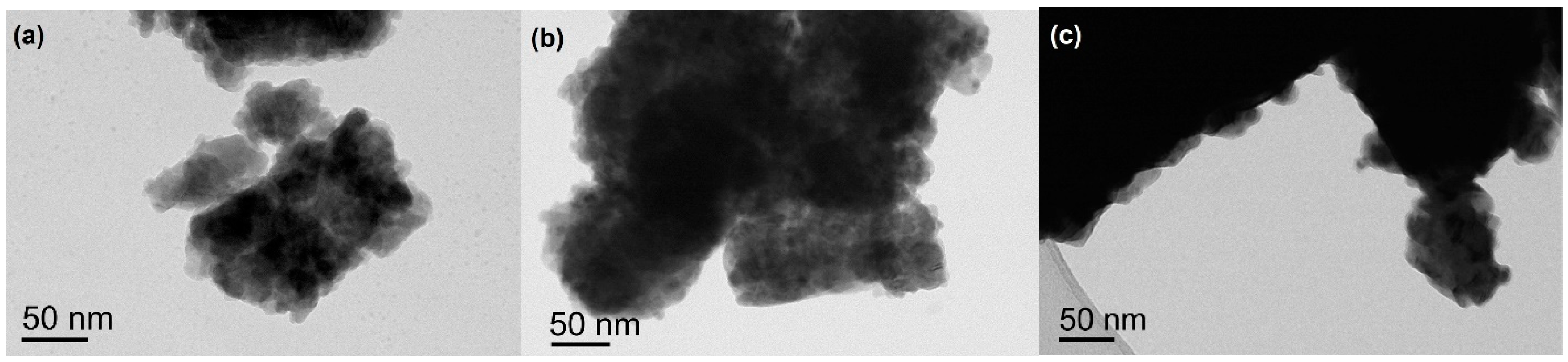
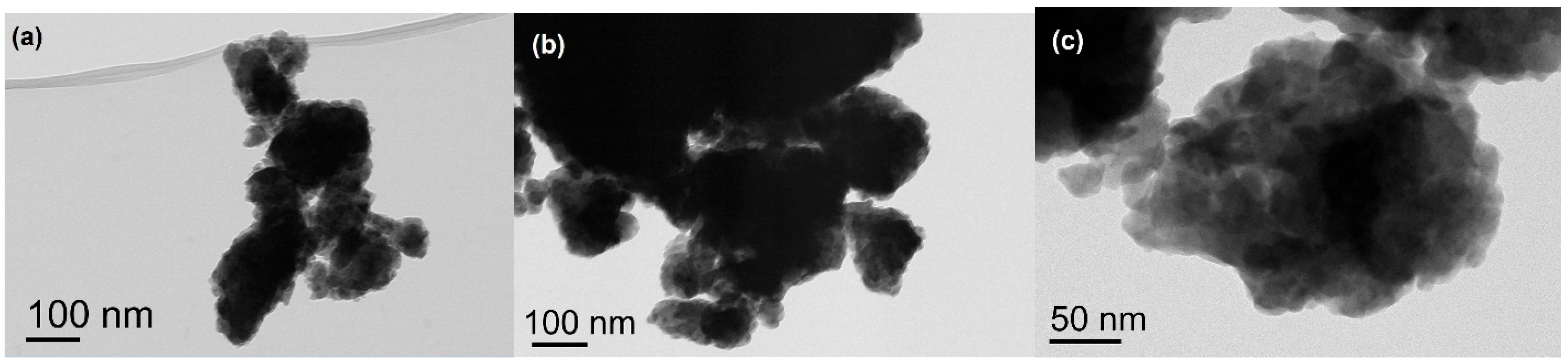
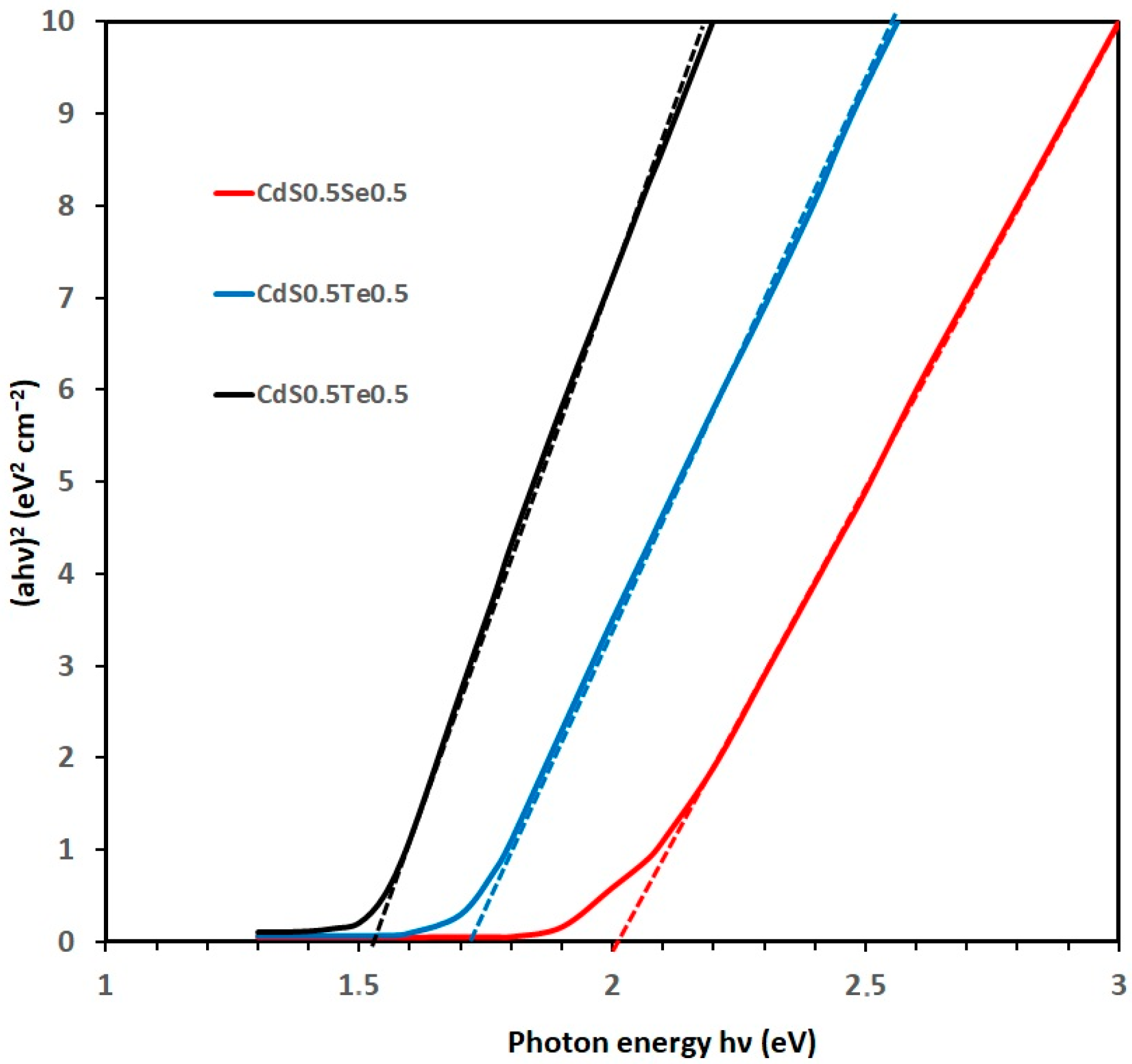
3. Results and Disussion
3.1. Binary Mixtures
3.2. Ternary Mixtures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| pXRD | Powder X-ray Diffraction |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| EDX | Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| AAS | Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy |
References
- Maity, R.; Kundoo, S.; Chattopadhyay, K.K. Synthesis and Optical Characterization of CdS Nanowires by Chemical Route. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2006, 21, 644–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isa, A.T.; Hafeez, H.Y.; Mohammed, J.; Kafadi, A.D.G.; Ndikilar, C.E.; Suleiman, A.B. A review on the progress and prospect of CdS-based photocatalysts for hydrogen generation via photocatalytic water splitting. J. Alloy. Comp. Comm. 2024, 4, 100043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaimi, N.H.S.; Syed, J.A.S.; Azhar, R.; Adzis, N.S.; Halim, O.M.A.; Chang, Y.H.R.; Taylor, S.H.; Bailey, L.A.; Ab Rahim, M.H.; Ramli, M.Z.; et al. Perspective on CdS-based S-scheme photocatalysts for efficient photocatalytic applications: Characterisation techniques and optimal semiconductor coupling. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 165, 150929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamiyev, Z.; Balayeva, N.O. Metal Sulfide Photocatalysts for Hydrogen Generation: A Review of Recent Advances. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, Z.; Rong, H.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, H. Synthesis of CdSe and CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots with Tunable Crystal Structure and Photoluminescent Properties. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Ali, A.; Ul Haq, I.; Abdul Aziz, S.; Ali, Z.; Ahmad, I. The effect of potassium insertion on optoelectronic properties of cadmium chalcogenides. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2021, 122, 105466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.A.; Oliva, A.I. A Double Energy Transition of Nanocrystalline CdxZn1-xS Films Deposited by Chemical Bath. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2015, 30, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldakov, D.; Lefrançois, A.; Reiss, P. Ternary and quaternary metal chalcogenide nanocrystals: Synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 3756–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, F.; Al-Hartomy, O.; Wageh, S. Cadmium-Based Quantum Dots Alloyed Structures: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Materials 2023, 16, 5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moger, S.N.; Mahesha, M.G. Colour tunable co-evaporated CdSxSe1-x (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) ternary chalcogenide thin films for photodetector applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 120, 105288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diker, H.; Unluturk, S.S.; Ozcelik, S.; Varlikli, C. Improving the Stability of Ink-Jet Printed Red QLEDs By Optimizing The Device Fabrication Process. Nanofabrication 2024, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Luan, C.; Chen, X.; Yu, K. Development of aqueous-phase CdSeS magic-size clusters at room temperature and quantum dots at elevated temperatures. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 10529–10535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Farsakh, H.; Gul, B.; Khan, M.S. Investigating the Optoelectronic and Thermoelectric Properties of CdTe Systems in Different Phases: A First-Principles Study. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 14742–14751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, A.; Artegiani, E. CdTe-Based Thin Film Solar Cells: Past, Present and Future. Energies 2021, 14, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosio, A.; Rosa, G.; Romeo, N. Past, present and future of the thin film CdTe/CdS solar cells. Sol. Energy 2018, 175, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpulla, M.A.; McCandless, B.; Phillips, A.B.; Yan, Y.; Heben, M.J.; Wolden, C.; Xiong, G.; Metzger, W.K.; Mao, D.; Krasikov, D.; et al. CdTe-based thin film photovoltaics: Recent advances, current challenges and future prospects. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2023, 255, 112289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankar, S.M.; Amorim, C.d.O.; Cunha, A.F.d. Progress in Thin-Film Photovoltaics: A Review of Key Strategies to Enhance the Efficiency of CIGS, CdTe, and CZTSSe Solar Cells. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaatisomarin, F.; Chen, R.; Hosseini-Zavareh, S.; Lei, S. Laser Scribing of Photovoltaic Solar Thin Films: A Review. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2023, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.H.; Cho, D.Y.; Oliynyk, A.O.; Silverman, J.R. Green Chemistry Applied to Transition Metal Chalcogenides through Synthesis, Design of Experiments, Life Cycle Assessment, and Machine Learning. In Green Chemistry—New Perspectives; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022; Volume 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasempour, A.; Dehghan, H.; Ataee, M.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Z.; Sedighi, M.; Guo, X.; Shahbazi, M.-A. Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2023, 28, 3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckingham, M.A.; Norton, K.; McNaughter, P.D.; Whitehead, G.; Vitorica-Yrezabal, I.; Alam, F.; Laws, K.; Lewis, D.J. Investigating the Effect of Steric Hindrance within CdS Single-Source Precursors on the Material Properties of AACVD and Spin-Coat-Deposited CdS Thin Films. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 8206–8216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmakar, G.; Tyagi, A.; Shah, A.Y. A comprehensive review on single source molecular precursors for nanometric group IV metal chalcogenides: Technologically important class of compound semiconductors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 504, 215665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dojer, B.; Pevec, A.; Breznik, K.; Jagličić, Z.; Gyergyek, S.; Kristl, M. Structural and thermal properties of new copper and nickel single-source precursors. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1194, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristl, M.; Ban, I.; Danč, A.; Danč, V.; Drofenik, M. A sonochemical method for the preparation of cadmium sulfide and cadmium selenide nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2010, 17, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, I.; Kristl, M.; Danč, V.; Danč, A.; Drofenik, M. Preparation of cadmium telluride nanoparticles from aqueous solutions by sonochemical method. Mater. Lett. 2012, 67, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, B.; Paul, B.; Chang, C.-H. The synthesis of cadmium sulfide nanoplatelets using a novel continuous flow sonochemical reactor. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 26, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denac, B.; Kristl, M.; Gyergyek, S.; Drofenik, M. Preparation and characterization of ternary cadmium chalcogenides. Chalcogenide Lett. 2013, 10, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Shalabayev, Z.; Baláž, M.; Khan, N.; Nurlan, Y.; Augustyniak, A.; Daneu, N.; Tatykayev, B.; Dutková, E.; Burashev, G.; Casas-Luna, M.; et al. Sustainable Synthesis of Cadmium Sulfide, with Applicability in Photocatalysis, Hydrogen Production, and as an Antibacterial Agent, Using Two Mechanochemical Protocols. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gancheva, M.; Iordanova, R.; Ivanov, P.; Yordanova, A. Effect of Ball Milling Speeds on the Phase Formation and Optical Properties of α-ZnMoO4 and ß-ZnMoO4 Nanoparticles. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagola, S. Outstanding Advantages, Current Drawbacks, and Significant Recent Developments in Mechanochemistry: A Perspective View. Crystals 2023, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantozzi, N.; Volle, J.-N.; Porcheddu, A.; Virieux, D.; Garcia, F.; Colacino, E. Green metrics in mechanochemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 6680–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, N. Mechanochemistry: A Resurgent Force in Chemical Synthesis. Synlett 2024, 35, 2331–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, V.; Stolar, T.; Karadeniz, B.; Brekalo, I.; Užarević, K. Advancing mechanochemical synthesis by combining milling with different energy sources. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2023, 7, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubadi, R.; Huang, S.D.; Jaroniec, M. Mechanochemical Synthesis of Nanoparticles for Potential Antimicrobial Applications. Materials 2023, 16, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschakarov, C.G.; Gospodinov, G.G.; Bontschev, Z. Über den Mechanismus der mechanochemischen Synthese anorganischer Verbindungen. J. Solid. State Chem. 1982, 41, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacs, L. Self-sustaining reactions as a tool to study mechanochemical activation. Faraday Dicuss. 2014, 170, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuzuki, T.; McCormick, P. Synthesis of CdS quantum dots by mechanochemical reaction. Appl. Phys. A 1997, 65, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.L.; Hömmerich, U.; Temple, D.; Wu, N.Q.; Zheng, J.G.; Loutts, G. Synthesis and optical characterization of CdTe nanocrystals prepared by ball milling process. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baláž, P.; Baláž, M.; Dutková, E.; Zorkovská, A.; Kováč, J.; Hronec, P.; Kováč, J., Jr.; Čaplovičová, M.; Mojžiš, J.; Mojžišová, G.; et al. CdS/ZnS nanocomposites: From mechanochemical synthesis to cytotoxicity issues. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baláž, P.; Baláž, M.; Achimovičová, M.; Bujňáková, Z.; Dutková, E. Chalcogenide mechanochemistry in materials science: Insight into synthesis and applications (a review). J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 11851–11890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.E.M. Solid State Synthesis and Characterization of NiTe Nanocrystals. J. Nano Res. 2014, 29, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baláž, M.; Džunda, R.; Bureš, R.; Sopčák, T.; Csanádi, T. Mechanically induced self-propagating reactions (MSRs) to instantly prepare binary metal chalcogenides: Assessing the influence of particle size, bulk modulus, reagents melting temperature difference and thermodynamic constants on the ignition time. RSC Mechanochem. 2024, 1, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristl, M.; Ban, I.; Gyergyek, S. Preparation of Nanosized Copper and Cadmium Chalcogenides by Mechanochemical Synthesis. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2013, 28, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristl, M.; Gyergyek, S.; Srt, N.; Ban, I. Mechanochemical Route for the Preparation of Nanosized Aluminum and Gallium Sulfide and Selenide. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 1608–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristl, M.; Gyergyek, S.; Škapin, S.D.; Kristl, J. Solvent-Free Mechanochemical Synthesis and Characterization of Nickel Tellurides with Various Stoichiometries: NiTe, NiTe2 and Ni2Te3. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutková, E.; Sayagués, M.J.; Briančin, J.; Zorkovská, A.; Bujňáková, Z.; Kováč, J.; Kováč, J., Jr.; Baláž, P.; Ficeriová, J. Synthesis and characterization of CuInS2 nanocrystalline semiconductor prepared by high-energy milling. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 1978–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutková, E.; Sayagués, M.J.; Kováč, J.; Kováč, J., Jr.; Bujňáková, Z.; Briančin, J.; Zorkovská, A.; Baláž, P.; Ficeriová, J. Mechanochemically synthesized nanocrystalline ternary CuInSe2 chalcogenide semiconductor. Mater. Lett. 2016, 173, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Liu, Y.; Na, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, M.; Dai, S.; Guo, X.; Li, P.; Zhao, T.; Zheng, R. Mechanochemical preparation of Z-scheme CdIn2S4/Zn-Al LDH heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic performance for SIPX degradation. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, A.; Pascual-Martí, M.C.; Aragó, E.; Chisvert, A.; March, J.G. Determination of selenium, zinc and cadmium in antidandruff shampoos by atomic spectrometry after microwave assisted sample digestion. Talanta 2000, 51, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Bassam, A.A.I.; Al-Juffali, A.A.; Al-Dhafiri, A.M. Structure and lattice parameters of cadmium sulphide selenide (CdSxSe1−x) mixed crystals. J. Cryst. Growth 1994, 135, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, M.; Gullu, H.H.; Delice, S.; Parlak, M.; Gasanly, N.M. Structural and temperature-dependent optical properties of thermally evaporated CdS thin films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2019, 93, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, K.; Xu, X.; Yu, J.; Li, X.; Tian, J. In situ synthesis of spherical CdS1-xSex red pigment used for ceramic ink-jet printing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 203, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbassi, A.; Zarhri, Z.; Azahaf, C.; Ez-Zahaouy, H.; Benyoussef, A. Boltzmann equations and ab initio calculations: Comparative study of cubic and wurtzite CdSe. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.F.; Lam, Y.M. Synthesis and characterization of CdSe nanorods using a novel microemulsion method at moderate temperature. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 316, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freik, D.; Parashchuk, T.; Volochanska, B. Thermodynamic parameters of CdTe crystals in the cubic phase. J. Cryst. Growth 2014, 402, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.L.; Liu, R.H. Preparation of pure CdSe nanocrystals through mechanical alloying. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.E.M.; Ersching, K.; De Lima, J.C.; Grandi, T.A.; Höhn, H.; Pizani, P.S. Influence of minor oxidation of the precursor powders to form nanocrystalline CdTe by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 466, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souaya, E.R.; Elkholy, S.A.; Abd El-Rahman, A.M.M.; El-Shafie, M.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Abo-Shanab, Z.L. Partial substitution of asphalt pavement with modified sulfur. Egypt. J. Pet. 2015, 24, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triboulet, R. Fundamentals of the CdTe synthesis. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 371, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibiano-Salas, L.A.; Martínez-Ara, L.A.; Maldonado-Altamirano, P.; Hernández-Pérez, M.A.; Sastré-Hernández, J.; Santoyo-Salazar, J. High-quality CdSxSe1−x thin films with tunable bandgap for optoelectronic applications: Growth by pulsed laser deposition and characterization. Mater. Res. Express 2025, 12, 055902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouendadji, S.; Ghemid, S.; Meradji, H.; El Haj Hassan, F. Density functional study of CdS1−xSex and CdS1−xTex alloys. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2010, 48, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, I.; Markuš, S.; Gyergyek, S.; Drofenik, M.; Korenak, J.; Helix-Nielsen, C.; Petrinić, I. Synthesis of Poly-Sodium-Acrylate (PSA)-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Use in Forward Osmosis Draw Solutions. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larichev, Y.V. Application of DLS for metal nanoparticle size determination in supported catalysts. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 2059–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praus, P.; Kozák, O.; Kočí, K.; Panáček, A.; Dvorský, R. CdS nanoparticles deposited on montmorillonite: Preparation, characterization and application for photoreduction of carbon dioxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 360, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, T.; Verma, L.; Khare, A. Variations in photovoltaic parameters of CdTe/CdS thin film solar cells by changing the substrate for the deposition of CdS window layer. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, A. Controllable Vapor Growth of Large-Area Aligned CdSxSe1−x Nanowires for Visible Range Integratable Photodetectors. Nano-Micro Lett. 2018, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, J.; Gupta, H.; Purohit, L.P. Ternary alloyed CdS1−xSex quantum dots on TiO2/ZnS electrodes for quantum dots-sensitized solar cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 880, 160480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezrag, F.; Bouarissa, N.; El-Houda Fares, N. The band gap bowing of CdSxTe1−x alloys beyond the virtual crystal approximation. Emerg. Mater. Res. 2020, 9, 1056–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.W. A review of the optical band gap of thin film CdSxTe1−x. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2006, 90, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baines, T.; Zoppi, G.; Bowen, L.; Shalvey, T.P.; Mariotti, S.; Durose, K.; Major, J.D. Incorporation of CdSe layers into CdTe thin film solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 180, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Ma, Z.; Li, L.; Tian, T.; Yan, Y.; Su, J.; Deng, J.; Xia, C. Aqueous synthesis of alloyed CdSexTe1-x colloidal quantum dots and their In-situ assembly within mesoporous TiO2 for solar cells. Sol. Energy 2020, 196, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wei, S.-H. First-principles study of the band gap tuning and doping control in CdSexTe1−x alloy for high efficiency solar cell. Chin. Phys. B 2019, 28, 086106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, N.M.; Thi, L.A.; Hung, L.X.; Toan, L.D. Tunable excitonic dynamics and photoluminescence modulation in graded CdSe/CdSeS quantum dots for optoelectronic applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2025, 36, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashuba, A.I.; Andriyevsky, B. Growth and crystal structure of CdTe1−xSex (x ≥ 0.75) thin films prepared by the method of high-frequency magnetron sputtering. Low Temp. Phys. 2024, 50, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


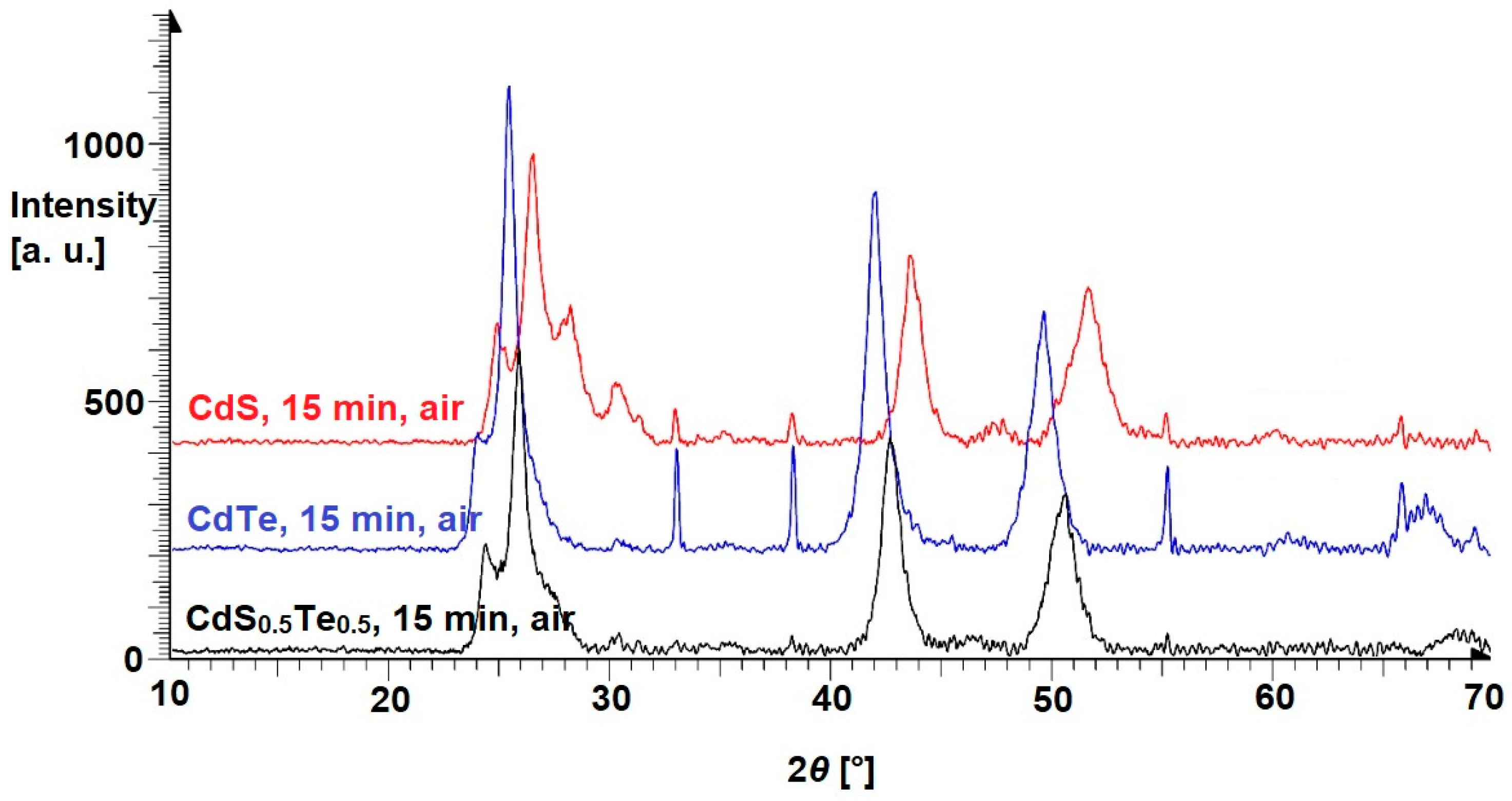
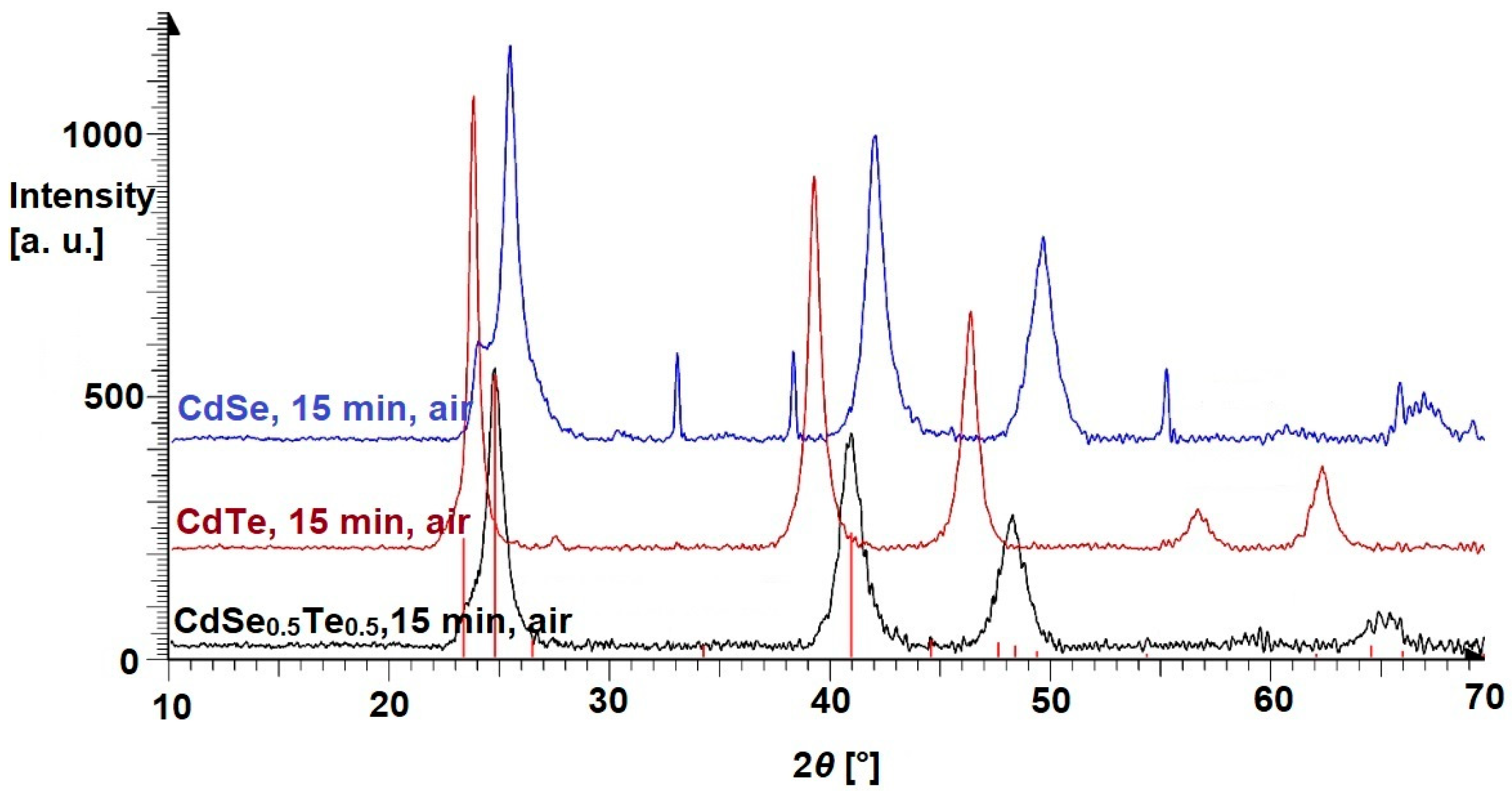
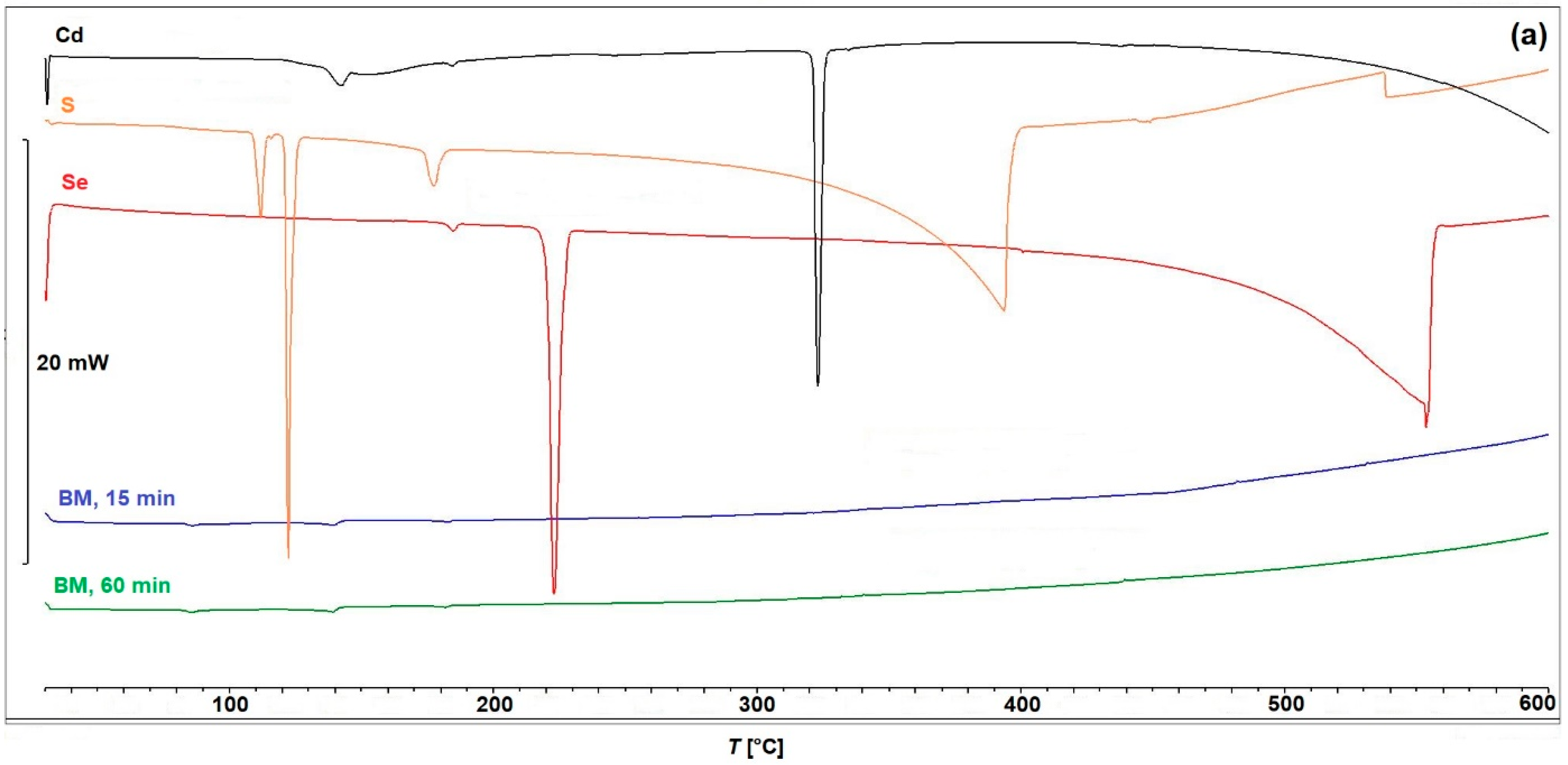
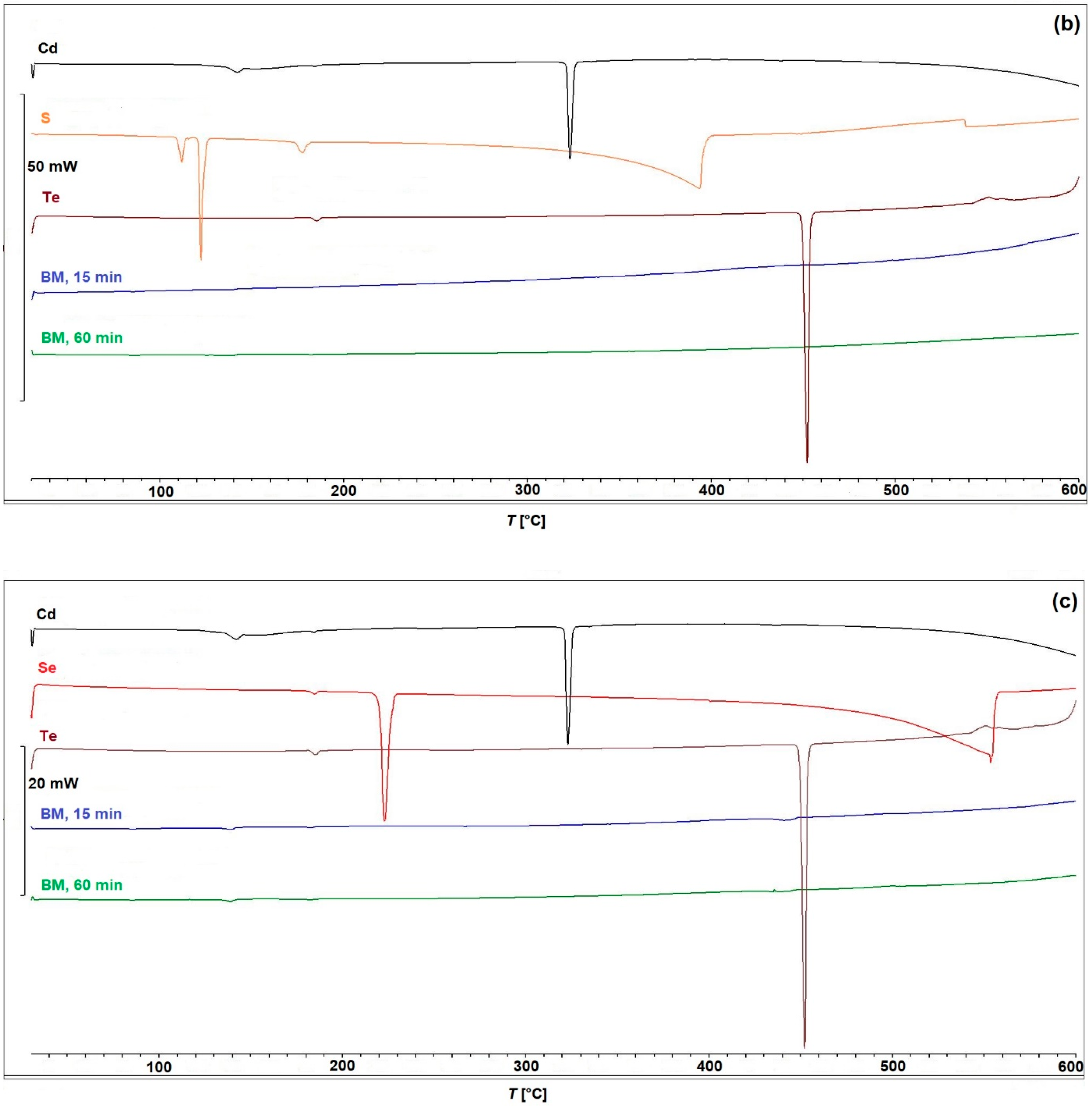

| Cubic (Zincblende) Structure | Hexagonal (Wurtzite) Structure | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CdS | a = 5.81 Å | a = 4.14 Å; c = 6.71 Å | [50,51,52] |
| CdSe | a = 6.05 Å | a = 4.30 Å; c = 7.01 Å | [53,54] |
| CdTe | a = 6.48 Å | a = 4.57 Å; c = 7.48 Å | [55] |
| Sample | CdS | CdSe | CdTe | CdS0.8Se0.2 | CdS0.5Se0.5 | CdS0.5Te0.5 | CdSe0.5Te0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d [nm] | 11.1 | 11.2 | 16.9 | 13.7 | 11.6 | 10.4 | 10.3 |
| Sample | Measured by EDX | Measured by AAS | Calculated | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd (at %) | S (at %) | Se (at %) | Te (at %) | Cd (wt. %) | Cd (wt. %) | |
| CdS | 49 | 51 | − | − | 77.4 | 77.8 |
| CdSe | 48 | − | 51 | − | 58.5 | 58.7 |
| CdTe | 47 | − | − | 52 | 46.3 | 46.8 |
| CdS0.5Se0.5 | 49 | 26 | 24 | − | 66.5 | 66.9 |
| CdS0.5Te0.5 | 48 | 27 | − | 25 | 58.5 | 58.5 |
| CdSe0.5Te0.5 | 49 | − | 23 | 27 | 51.9 | 52.1 |
| Sample | CdS | CdSe | CdTe | CdS0.8Se0.2 | CdS0.5Se0.5 | CdS0.5Te0.5 | CdSe0.5Te0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d(H) [nm] | 325.8 | 202.7 | 124.4 | 271.0 | 207.7 | 347.1 | 126.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kristl, M.; Zanjkovič, N.; Kunej, J.; Gyergyek, S.; Stergar, J. Green Mechanochemical Synthesis of Binary and Ternary Cadmium Chalcogenides with Tunable Band Gaps. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9110375
Kristl M, Zanjkovič N, Kunej J, Gyergyek S, Stergar J. Green Mechanochemical Synthesis of Binary and Ternary Cadmium Chalcogenides with Tunable Band Gaps. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2025; 9(11):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9110375
Chicago/Turabian StyleKristl, Matjaž, Neža Zanjkovič, Jona Kunej, Sašo Gyergyek, and Janja Stergar. 2025. "Green Mechanochemical Synthesis of Binary and Ternary Cadmium Chalcogenides with Tunable Band Gaps" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 9, no. 11: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9110375
APA StyleKristl, M., Zanjkovič, N., Kunej, J., Gyergyek, S., & Stergar, J. (2025). Green Mechanochemical Synthesis of Binary and Ternary Cadmium Chalcogenides with Tunable Band Gaps. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 9(11), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9110375







