Abstract
We present a novel controllable platform for engineering Majorana zero modes. The platform consists of a ferromagnetic metallic wire placed among conventional superconductors, which are in proximity to ferromagnetic insulators. We demonstrate that Majorana zero modes emerge localised at the edges of the ferromagnetic wire, due to the interplay of the applied supercurrents and the induced by proximity exchange fields with conventional superconductivity. Our mechanism does not rely on the pairing of helical fermions by combining conventional superconductivity with spin-orbit coupling, but rather exploits the misalignment between the magnetization of the ferromagnetic insulators and that of the ferromagnetic wire.
1. Introduction
The development of quantum computers promises a new technological revolution [1]. However, a fundamental obstacle hindering the development of quantum computation is quantum decoherence, the loss of quantum mechanical phase coherence and, therefore, of information encoded in qubits. Attempts to deal with this problem through quantum error correction algorithms lead to elaborate schemes consuming a highly disproportional amount of qubits. On the contrary, topological quantum computers suppress quantum decoherence at the hardware level. Qubits in these devices are realized from topologically protected entities, which are immune to environmental noise and, therefore, decoherence [2,3,4].
Such topological protected entities are Majorana zero modes—massless neutral particles that constitute their own antiparticles. Characterised by their particle–antiparticle symmetry, MZMs emerge as quasiparticles bound to defects or boundaries of topological superconductors [5]. The simplest topological superconductor is the effectively spinless superconducting phase of p-wave symmetry [6,7]. Although a topological p-wave state is proposed for the superconducting phase of Sr2RuO4 [8], experimental results are yet inconclusive [9].
Instead, several proposals have been put forward for engineering topological p-wave superconductivity out of more trivial materials. Among them, we distinguish conventional superconductor/topological insulator heterostructures [10], semiconductors in proximity to conventional superconductors [11], non-centrosymmetric superconductors [12] and planar Josephson junctions [13]. All these proposals effectuate the pairing of helical fermions by combining conventional superconductivity with spin orbit coupling in the presence of a spin-splitting field, in order to realize an effectively spinless superconducting state.
2. Majorana Zero Modes in Superconductor/Ferromagnet Heterostructures
As aforementioned, realising MZMs using conventional superconductors requires the presence of a spin-splitting field. The simplest way to satisfy this requirement is by applying an external magnetic field. However, magnetic fields are detrimental to conventional superconductivity; thereby, many proposals for realising MZMs are based on heterostructures among superconductors with ferromagnetic materials. Superconductor-ferromagnet heterostructures do not require the application of an external magnetic field and, therefore, are advantageous with respect to other platforms. Following this line of argument, topological superconductivity and MZMs have been demonstrated to emerge in half-metal/superconductor [14] or ferromagnet/unconventional superconductor [15] heterostructures, in ferromagnetic wires proximised to conventional superconductors [16,17,18] and in ferromagnetically aligned chains of magnetic impurities embedded in conventional superconductors [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Spin-orbit coupling is an essential component in all of these proposals.
2.1. A Novel Platform
Here, we put forward a novel platform for engineering topological superconductivity and Majorana zero modes, which does not require spin orbit coupling. The platform, as presented in Figure 1, consists of a ferromagnetic metallic wire, which is placed between two conventional superconducting layers where supercurrents flow in opposite directions. The superconducting layers are deposited on ferromagnetic insulators. The magnetisations of the two ferromagnetic insulators point in opposite directions and both are perpendicular to the magnetisation of the ferromagnetic metallic wire.
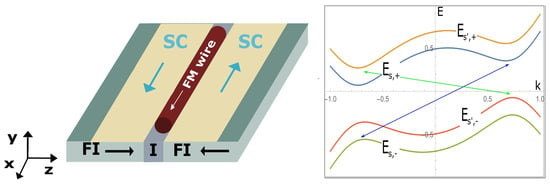
Figure 1.
(Left) Novel platform for engineering Majorana zero modes. A ferromagnetic metallic wire placed among two conventional superconductors where supercurrents flow in opposite directions (blue arrows). The superconducting layers are deposited upon ferromagnetic insulators with opposite magnetisations (black arrows), which are perpendicular to the magnetisation of the ferromagnetic wire (white arrow). (Right) The energy bands, where s refers to spin components and ± to hole and particles, respectively, of a conventional superconductor when a supercurrent and an exchange field are applied. Supercurrent breaks inversion symmetry (k, −k momenta are not equivalent) and the exchange field breaks spin symmetry (s and are not equivalent) leading to the emergence of p-wave superconducting correlations. Arrows indicate the pairing components of conventional superconductivity.
Majorana zero modes emerge localised at the edges of the FM, due to the synergy between the externally applied supercurrents with the emergent in the SCs exchange fields [27]. We remark that several works have demonstrated both theoretically [28,29] and experimentally [30,31,32] the emergence of exchange fields in conventional SCs proximised by FIs. Moreover, developments in the fabrication of SC-FI heterostructures [33] and ferromagnetic metallic nanonwires embedded in conventional SCs [34,35,36], enhance the experimental feasibility of the proposed platform.
2.2. The Underlying Mechanism
According to our mechanism, a topological superconducting state is stabilized over the FM wire, when charge supercurrents are applied in conventional SCs where finite exchange fields are present. The supercurrent and the exchange field break inversion and spin symmetries, respectively, and, therefore, partially convert conventional superconductivity to a p-wave superconducting field. This emergent p-wave superconducting field still pairs electrons of different energy bands of the superconductor, while MZMs require intraband superconductivity.
However, in an FM wire with magnetisation perpendicular to the magnetisation of the ferromagnetic insulators, the induced p-wave superconducting field pairs electrons of the same energy band of the FM. An intraband superconducting component emerges when the d-vector of p-wave superconductivity [37] is misaligned to the exchange field of the FM wire [38]. Thus, when this p-wave superconducting field mediates into the FM wire, due to the proximity effect, an effectively spinless superconducting state is stabilised, and MZMs emerge. In the next section, we present analytically how the triplet superconducting component emerges, due to the coexistence of the exchange field and the supercurrents with conventional superconductivity.
3. Induced p-Wave Superconductivity
In order to demonstrate how triplet p-wave superconductivity is induced, we consider a superconducting wire with order parameter , where a supercurrent J is applied in the presence of an exchange field . We consider the following Hamiltonian
where the extended Nambu spinor and and are the Pauli matrices acting on particle-hole and spin space, respectively, the operator destroying(creating) an electron with spin s at coordinate x, the exchange field and the singlet superconducting field. Under the gauge transformation
kinetic term transforms to where is a current term and can be absorbed in the chemical potential . Thus, Hamiltonian Equation (1) takes the form
Considering a translationally invariant wire Hamiltonian Equation (3) takes the following form upon the Fourier transformation
to momenta k space, where .
The energy bands of the wire
where corresponds to ↓ and ↑ bands respectively, derive from the transformation
and
diagonalising Hamiltonian matrix , where
and
The induced p-wave correlations derive from the equation
where the Fermi distribution and . For , we find
where
Therefore,
and apparently the correlations emerge from the imbalance between singlet pairing in the channel and in the channel . From Equation (14) it is straightforward that, for , since, in this case, and , and therefore . Moreover, for expression is even in momenta, and therefore , due to the multiplication with momenta k. Thus, p-wave correlations are induced only when both and .
For the other two components of the d vector, and , there are no p-wave correlations induced. Particularly, for we get
where
Therefore,
since matrix has no diagonal term. Similarly, for we obtain
where
Therefore,
since, again, matrix has no diagonal terms. Thus, we conclude that only p-wave correlations with emerge, due to the imbalance among the two spin configurations of interband conventional pairing.
4. Engineering Majorana Zero Modes without Spin-Orbit Coupling
4.1. Intraband p-Wave Superconductivity in the Ferromagnetic Wire
As demonstrated in the previous section, triplet p-wave correlations are induced in a conventional superconductor when a supercurrent and an exchange or Zeeman field are applied. However, topological superconductivity and Majorana zero modes cannot be engineered in a superconducting wire simply by applying a supercurrent and a magnetic field. The triplet p-wave correlations induced in this setup still connect different energy bands of the wire, while MZMs require intraband or effectively spinless superconductivity. Nevertheless, when these correlations mediate to a material with magnetisation perpendicular to the exchange field induced in the superconductors, an intraband superconducting state that hosts MZMs is realised.
Considering the particular setup presented in Figure 1, the induced correlations in the SCs correspond to Cooper pairs of electrons with opposite spin, i.e., correlations. These correlations, for which , mediate in the ferromagnet with polarisation along the x-axis, i.e., perpendicular to the vector of the induced correlations, described by the following Hamiltonian
The energy bands of the FM wire derive from the following transformation
where U is the matrix that diagonalises the Hamiltonian . In this eigenbasis, the induced triplet correlations are expressed as
From Equation (23), it becomes apparent that, in the eigenbasis of the FM, the induced by proximity p-wave field pairs electrons from the same energy band, i.e., we obtain intraband pairing. The Hamiltonian Equation (21) upon the U transformation acquires the form
which can be reduced into two copies of the Kitaev’s Hamiltonian
where , the band index and .
Based on the above analysis, it becomes clear that the optimal configuration for the emergence of MZMs in the particular platform, is that of anti-parallel supercurrents in the SCs and anti-parallel magnetisations in the FIs. This configuration guarantees that no supercurrent or exchange fields parallel to the magnetisation of the FIs are induced in the FM wire. Thus, the d-vector of the induced p-wave superconducting correlations remains perpendicular to the magnetisation of the FM wire and an intraband superconducting state is realised. However, as we will elaborate in a future work, MZMs are robust against significant deviations from this optimal configuration for the supercurrents and the FIs magnetisations.
4.2. Topological Criteria for the Ferromagnetic Wire
Based on Hamiltonian Equation (24) describing the FM wire, we derive, in this section, the criteria regarding the exchange field and the chemical potential for which MZMs emerge localised at the edges of the FM. To this aim, we consider periodic boundary conditions and transform Hamiltonian Equation (24) in momenta k space. Introducing the spin-dependent Nambu spinor , where are the operators destroying (creating) an electron with momenta k and spin s and the Pauli matrices for the particle-hole and for the spin space, the Hamiltonian of the FM acquires the form
where we also considered an induced by proximity conventional superconducting field . We remark that Hamiltonian Equation (26) is expressed in lattice instead of continuum space, in order to connect with the numerical results presented in the next section. In the particular case, the reality conditions, and where and anti-unitary operators [39], are satisfied for with and with . In addition, a unitary chiral symmetry operator anticommutes with the Hamiltonian.
Thus, the system belongs to the BDI symmetry class, characterised by an integer topological invariant, and Hamiltonian Equation (26) acquires a block off-diagonal form in the eigenbasis of the chiral operator . Therefore, by applying the transformation , we obtain . The topological invariant of the Hamiltonian is defined as the winding number [40], where the unimodular complex number defined as . For the particular system, we find
Since within each topological phase, the is a continuous function of momentum k, the maximum possible value of the winding number relates to the number n of roots within the interval , . Notice that because , number n is always even. Next, we distinguish the two following cases.
The first case holds for . In this case, only for , and therefore the maximum absolute value of the winding number is . The topological phase is realised when
, which results in the following condition for the chemical potential
or equivalently for the exchange field
The second case holds for . When this condition holds, is realised also for another pair of momenta . However, since for , , it is straightforward that within these limits, even in this case. In general, considering , a topological phase can be realised for
for which and .
4.3. Numerical Calculations for the FI-SC-FM-SC-FI Heterostructure
In order to verify the above arguments, we employ the following lattice Bogoliubov de Gennes equation,
which describes the FI-SC-FM-SC-FI heterostructure presented in Figure 1, with
the Hamiltonian of the superconductor, where stand for left and right SC with , and
the Hamiltonian of the FM, where and with and the operators destroying (creating) an electron with spin s of the SC and FM, respectively, at lattice site , and the Pauli matrices acting on particle-hole and spin space respectively, and the even and odd in spatial inversion, respectively, functions connecting nearest neighbours lattice points. Moreover, t is the hopping integral and J the supercurrent term. The proximity of the SCs to the FIs is modelled by the introduction of an exchange field term in the Equation (32). The SCs are connected with the FM wire through the following Hamiltonian
In general, we consider for simplicity. MZMs are anticipated to emerge localised at the edges of the wire for where is the induced by proximity conventional superconducting field over the FM. In Figure 2a we present the phase diagram for the setup of Figure 1 considering , , and . Based on this diagram, we observe that for , the induced singlet superconducting field over the FM is while the hopping term along the wire is normalised to , due to the coupling of the wire to the SCs [41].
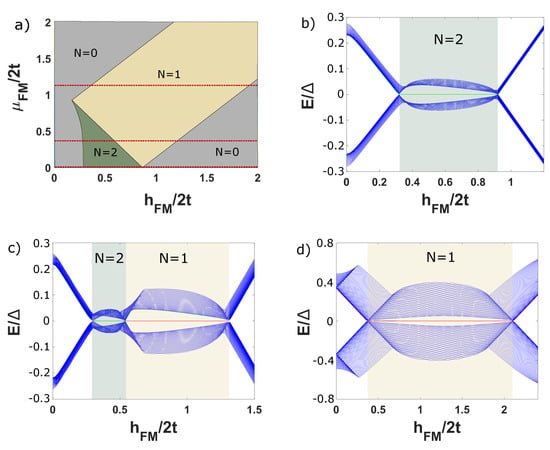
Figure 2.
For , , and , (a) topological phase diagram with respect to the chemical potential and the exchange field of the ferromagnet. The low energy spectra with respect to for (b) , (c) and (d) for denoted by red dashed lines in figure (a). The numerical results verify the topological criteria presented in the previous section.
For , again, the hopping term along the wire is normalised to and the black lines and define the region of parameters for which and a pair of MZMs emerge at the edges of the FM wire. Notice that the particular phase diagram is in accordance with the topological criteria for the and topological phases presented in the previous section. However, we remark that the particular results correspond to a fixed conventional order parameter, which has not been self-consistently determined over the SC regions.
Therefore, the effect of finite momentum Cooper pairs, which, in principle, can emerge due to the presence of the supercurrent and the exchange field in the conventional superconductor, on the phase diagram (Figure 2), has not been investigated and will be examined in a future work.
4.4. Local Density of States
The pursuit of functional platforms for topological quantum computation, requires the experimental verification of the theoretical proposals for engineering topological superconductivity, by detecting the emergent MZMs. A characteristic signature of MZMs in conductance spectroscopy measurements is the quantized zero-bias tunnelling conductance. Emanating from an Andreev reflection resonant at zero energy, the zero bias conductance in the presence of a single MZMs pair equals , i.e., double the conductance quantum, irrespective of the tunnelling barrier [42,43].
Several tunnelling experiments have demonstrated such zero bias conductance peaks and therefore provided supporting evidence for the emergence of MZMs in the semiconductor nanowires [44], the topological insulator/conventional superconductor heterostructures [45,46], the magnetic adatoms embedded in conventional superconductor [47], the heavy metal surfaces [48], the quantum anomalous Hall insulator [49], the iron-based superconductors [50] and the planar Josephson junctions [51] platforms. However, the results are far from being conclusive, since in each case several deviations from the corresponding theoretical predictions are observed.
Since differential conductance measurements in scanning tunnelling spectroscopy experiments are proportional to the local density of states of the sample, when the scanning tunnelling junction can be approximated by a point contact and the tunnelling amplitude is small, we calculate the local density of states at characteristic positions in the FM wire in order to link our results with relevant experiments. To this end, we solve the following eigenvalue equation
where the Hamiltonian matrix of the FI-SC-FM-SC-FI heterostructure (Equation (31)) and the eigenstate corresponding to eigenenergy . Based on the eigenstates and eigenvalues of the Hamiltonian we calculate the local density of states for spin up and down components according to the following equations
where the retarded Green’s function. In order to account for the presence of impurities in the system, we consider a scattering time , which corresponds to a mean free path , where the Fermi velocity. Including the scattering from impurities, the density of states derives from equation
where the Dirac function has been substituted by a Cauchy–Lorentz function , with . Taking the clean superconductor limit, we assume that , where the superconducting coherence length, and therefore .
In Figure 3, we present the local density of states for three values of the exchange field of the wire considering , which corresponds to diagram (c) of Figure 2. From Figure 3a we deduce that the singlet pairing field induced in the wire, due to proximity with the conventional SC, is . Since in this case the FM is in a non-topological phase with . When the wire is in a topological (Figure 3b) or (Figure 3c) phase, and a peak for emerges at the local density of states spectrum only at the edges of the wire, signifying the presence of localised zero energy states, the MZMs.
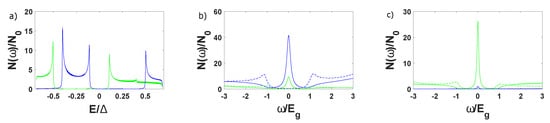
Figure 3.
The local density of states at the edge and the middle of the FM wire for (a) for which the wire is in a non-topological phase where the induced singlet pairing prevails, (b) for for which a topological phase is realised and (c) for for which the wire is in a topological phase. Solid and dashed lines correspond to the edge, mean value of the density at the first five lattice sites of the wire, and the middle of the wire, respectively. The blue line corresponds to the spin up, while the green line corresponds to the spin down component of the local density of states. The particular diagrams are relevant to spin-polarised scanning tunnelling microscopy (SP−STM) measurements tips polarised (anti−) parallel to the magnetisation of the FM wire. In (b,c) diagramms energy is normalised with respect to the triplet superconducting energy gap induced in the wire. is the density of states in the normal phase.
For where the two MZMs localised at the beginning of the wire, acquire opposite spin polarisation. The difference in the two zero energy peaks in Figure 3b indicates the different localization of the two MZMs, due to the difference in the Fermi velocity, , among the two spin bands. The localization length of the MZMs equals . For , a single pair of MZMs with particular spin polarisation emerges localised at the FM wire as indicated from the zero energy peak, which is significant for the spin down component. However, the zero energy density of states is also finite for the other spin component, due to the finite .
4.5. Robustness of Emergent Majorana Zero Modes against Disorder
In realistic experimental setups, the presence of disorder is unavoidable. On this account, we demonstrate, in this section, the robustness of the emergent MZMs against disorder in the FM wire. In particular, we consider a random on-site potential that derives from a normal distribution with mean value 0 and variance corresponding to correlator , i.e., .
The mean free path l along the wire is related to the variance through the following relation where the Fermi velocity and the density of states at the Fermi level. In the lattice model described by Hamiltonian Equation (33), in the FM wire equals considering a common Fermi velocity for the two spin components. We define the dimensionless parameter , where is the coherence length of the p-wave superconductivity induced in the FM wire. In Figure 4, we present the low energy spectrum of the wire for and for which and for which .
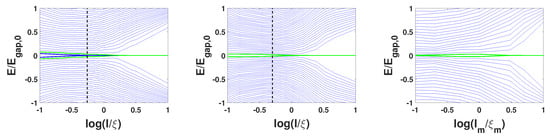
Figure 4.
Low energy spectrum of the FM wire with respect to the chemical potential disorder strength for and (left) , (middle) . The dashed black line denotes critical disorder , for which a topological phase transition occurs in p-wave superconducting wires. In both cases, the energy gap is reduced by with respect to that of a pristine wire, for . (right) For the low energy spectrum with respect to magnetic disorder . Although the energy gap is again reduced by approximately for , the MZMs appear to acquire finite energy only for . Green and blue colours for the zero energy modes correspond to spin components as in Figure 3. is the energy gap in the pristine ferromagnetic wire.
For , we observe that the energy gap essentially closes for , however, the spin up MZM remains at zero energy until , which is the critical value of disorder for p-wave superconducting wires [52]. We attribute the difference in the critical mean free path for the two MZMs pairs in their different localization. For the energy gap closes at . We remark that in both cases, the energy gap is reduced by with respect to that of a pristine wire when , signifying the robustness of the emergent MZMs against disorder of the chemical potential of the FM wire.
Finally, we investigate the robustness of the emergent MZMs against disorder in the exchange field of the FM wire. We remark that our mechanism does not depend on the structural characteristics of the FM wire, which can therefore also be considered as an array of ferromagnetically aligned magnetic impurities. Magnetic impurities induce in the superconductor subgap bound states, the Yu–Shiba–Rusinov states [53,54,55]. Depending on the hopping integral among the impurities, these subgap states form an energy band, which may lie within the superconducting gap (Shiba limit), or extent above the superconducting energy gap (wire limit) [18]. Our mechanism is valid in both limits.
Considering this possible formation of the FM wire, it is worth examining the robustness of the emergent MZMs against disorder in the ferromagnetic alignment of the magnetic impurities and, therefore, in the corresponding orientation of the local exchange field, which otherwise is considered to have a fixed magnitude. In complete analogy to the previous case, we consider two normal distributions and for the angle of the local magnetisation with respect to the x-axis and for the angle in the y-z plane.
We define a magnetic mean free path as a measure of disorder of the local exchange field and the magnetic coherence length . In Figure 4, we present the low energy spectrum of the FM wire with respect to disorder strength only for . We note that for the two pairs of MZMs interact with each other and acquire finite energy even for infinitesimal magnetic disorder, since magnetic disorder breaks the spin symmetry that prevents the two MZMs from interacting with each other.
5. Conclusions
We present a novel platform for realising Majorana zero modes based on superconductor–ferromagnet heterostructures. The platform consists of a ferromagnetic wire placed among conventional superconductors, which are proximised by ferromagnetic insulators. Instead of spin-orbit coupling, the essential element of the physical mechanism underlying the proposed platform is the misalignment between the magnetisation of the ferromagnetic wire and that of the ferromagnetic insulators.
The robustness of the emergent MZMs against impurities disorder resembles that of a p superconducting wire, although the emergence of two pairs of MZMs and the observation of a zero bias conductance peak in the corresponding phase is hindered even for infinitesimal disorder in the magnetisation of the FM wire. We assert that recent developments in heterostructures fabrication renders our platform experimentally feasible, while the controllable application of the supercurrents in the superconductors provides an additional advantage with respect to other relevant proposals.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.L. and G.V.; methodology, G.L.; software, G.L.; validation, G.L., N.V. and G.V.; formal analysis, G.L.; investigation, G.L.; resources, G.V.; data curation, N.V.; writing—original draft preparation, G.L.; writing—review and editing, G.V.; visualization, N.V.; supervision, G.L.; project administration, G.V.; funding acquisition, G.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is carried out in the context of the project “Majorana fermions from induced quartet states” (MIS 5049433) under the call for proposals “Researchers’ support with an emphasis on young researchers-2nd Cycle”. The project is co-financed by Greece and the European Union (European Social Fund- ESF) by the Operational Programme Human Resources Development, Education and Lifelong Learning 2014–2020.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| FM | ferromagnetic wire |
| SC | superconductor |
| FI | ferromagnetic insulator |
| MZMs | Majorana zero modes |
| TSC | topological superconductivity |
References
- Ladd, T.D.; Jelezko, F.; Laflamme, R.; Nakamura, Y.; Monroe, C.; O’Brien, J.L. Quantum computers. Nature 2010, 464, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, A.; Lindner, H.N. Topological Quantum Computation—From Basic Concepts to First Experiments. Science 2013, 339, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahtinen, V.; Pachos, J. A short introduction to topological quantum computation. SciPost Phys. 2017, 3, 021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, C.; Simon, S.; Stern, A.; Freedman, M.; Sarma, D.S. Non-Abelian anyons and topological quantum computation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Yoichi, A. Topological superconductors: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2017, 80, 076501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaev, A.Y. Unpaired Majorana fermions in quantum wires. Physics-Uspekhi 2001, 44, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.A. Non-Abelian Statistics of Half-Quantum Vortices in p-wave Superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, T.M.; Sigrist, M. Sr2RuO4: An electronic analogue of 3He? J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1995, 7, L643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeno, Y.; Kittaka, S.; Nomura, T.; Yonezawa, S.; Ishida, K. Evaluation of spin-triplet superconductivity in Sr2RuO4. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 81, 011009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Kane, C.L. Superconducting Proximity Effect and Majorana Fermions at the Surface of a Topological Insulator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 096407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sau, J.D.; Lutchyn, R.M.; Tewari, S.; Sarma, S.D. Generic New Platform for Topological Quantum Computation Using Semiconductor Heterostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 040502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Fujimioto, S. Topological phases of noncentrosymmetric superconductors: Edge states, Majorana fermions, and non-Abelian statistics. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 094504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pientka, F.; Keselman, A.; Berg, E.; Yacoby, A.; Stern, A.; Halperin, B.I. Topological Superconductivity in a Planar Josephson Junction. Phys. Rev. X 2017, 7, 021032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.B.; Zhang, H.J.; Qi, X.L.; Zhang, S.C. Topological superconducting phase and Majorana fermions in half-metal/superconductor heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 060510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, S.; Fregoso, B.M.; Galitski, V.; Sarma, S.D. Topological superconductivity and Majorana fermions in hybrid structures involving cuprate high-Tc superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 014504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, S.; Galitski, V. Microscopic theory for a ferromagnetic nanowire/superconductor heterostructure: Transport, fluctuations, and topological superconductivity. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 054521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sau, J.D.; Brydon, P.M.R. Bound States of a Ferromagnetic Wire in a Superconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 127003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, E.; Roberts, B.; Tewari, S.; Sau, J.D.; Sarma, S.D. Majorana fermions in chiral topological ferromagnetic nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 91, 094505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydon, P.M.R.; Sarma, S.D.; Hui, H.Y.; Sau, J.D. Topological Yu–Shiba–Rusinov chain from spin-orbit coupling. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 91, 064505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadj-Perge, S.; Drozdov, I.K.; Bernevig, B.A.; Yazdani, A. Proposal for realizing Majorana fermions in chains of magnetic atoms on a superconductor. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 020407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, H.; Drozdov, I.K.; Yazdani, A.; Bernevig, A.; MacDonald, A.H. Topological superconductivity induced by ferromagnetic metal chains. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 235433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rontynen, J.; Ojanen, T. Chern mosaic: Topology of chiral superconductivity on ferromagnetic adatom lattices. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 094521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyhonen, K.; Weststrom, A.; Ojanen, T. Topological superconductivity in ferromagnetic atom chains beyond the deep-impurity regime. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 014517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čadež, T.; Sacramento, P.D. Zero energy modes in a superconductor with ferromagnetic adatom chains and quantum phase transitions. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2016, 28, 495703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sticlet, D.; Morari, C. Topological superconductivity from magnetic impurities on monolayer NbSe2. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 100, 075420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.; Beck, P.; Posske, T.; Crawford, D.; Mascot, E.; Rachel, S.; Wiesendanger, R.; Wiebe, J. Topological Shiba bands in artificial spin chains on superconductors. Nat. Phys. 2021, 17, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livanas, G.; Sigrist, M.; Varelogiannis, G. Alternative paths to realize Majorana Fermions in Superconductor-Ferromagnet Heterostructures. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6259. [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu, T.; Sauls, J.A.; Rainer, D. Proximity effect of a ferromagnetic insulator in contact with a superconductor. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 38, 8823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijano, A.; Ilić, S.; Rouco, M.; González-Orellana, C.; Ilyn, M.; Rogero, C.; Virtanen, P.; Heikkilä, T.T.; Khorshidian, S.; Spies, M.; et al. Coexistence of superconductivity and spin-splitting fields in superconductor/ferromagnetic insulator bilayers of arbitrary thickness. Phys. Rev. Res. 2021, 3, 023131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedrow, P.M.; Tkaczyk, J.E.; Kumar, A. Spin-Polarized Electron Tunneling Study of an Artificially Layered Superconductor with Internal Magnetic Field: EuO-Al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 56, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Moodera, J.S.; Meservey, R. Spin-filter effect of ferromagnetic europium sulfide tunnel barriers. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 42, 8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strambini, E.; Golovach, V.N.; Simoni, G.D.; Moodera, J.S.; Bergeret, F.S.; Giazotto, F. Revealing the magnetic proximity effect in EuS/Al bilayers through superconducting tunneling spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2017, 1, 054402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Vaitiekėnas, S.; Martí-Sánchez, S.; Koch, C.; Hart, S.; Cui, Z.; Kanne, T.; Khan, S.A.; Tanta, R.; Upadhyay, S.; et al. Semiconductor–Ferromagnetic Insulator–Superconductor Nanowires: Stray Field and Exchange Field. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giroud, M.; Courtois, H.; Hasselbach, K.; Mailly, D.; Pannetier, B. Superconducting proximity effect in a mesoscopic ferromagnetic wire. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, R11872(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Singh, M.; Tian, M.; Kumar, N.; Liu, B.; Shi, C.; Jain, J.K.; Samarth, N.; Mallouk, T.; Chan, M.H.W. Interplay between superconductivity and ferromagnetism in crystalline nanowires. Nat. Phys. 2010, 6, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäck, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.; Jeon, S.; Bernevig, B.A.; Yazdani, A. Observation of a Majorana zero mode in a topologically protected edge channel. Science 2019, 364, 6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigrist, M.; Ueda, K. Phenomenological theory of unconventional superconductivity. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1991, 63, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, E.; Tewari, S. Topological properties of the time-reversal-symmetric Kitaev chain and applications to organic superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 220505(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnyder, A.P.; Ryu, S.; Furusaki, A.; Ludwig, A.W.W. Classification of topological insulators and superconductors in three spatial dimensions. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 195125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, S.; Sau, J.D. Topological Invariants for Spin-Orbit Coupled Superconductor Nanowires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 150408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Pientka, F.; Glazman, L.I.; von Oppen, F. Strong Localization of Majorana End States in Chains of Magnetic Adatoms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 106801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, K.T.; Lee, P.A.; Ng, T.K. Majorana Fermion Induced Resonant Andreev Reflection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 237001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.J.; Ng, T.K.; Lee, P.A.; Law, K.T. Selective Equal-Spin Andreev Reflections Induced by Majorana Fermions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 037001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourik, V.; Zuo, K.; Frolov, S.M.; Plissard, S.R.; Bakkers, E.P.A.M.; Kouwenhoven, L.P. Signatures of Majorana Fermions in Hybrid Superconductor-Semiconductor Nanowire Devices. Science 2012, 336, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.H.; Zhang, K.W.; Hu, L.H.; Li, C.; Wang, G.Y.; Ma, H.Y.; Xu, Z.A.; Gao, C.L.; Guan, D.D.; Li, Y.Y.; et al. Majorana Zero Mode Detected with Spin Selective Andreev Reflection in the Vortexof a Topological Superconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 257003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.H.; Li, C.; Xu, D.H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, F.Z. Theory of spin-selective Andreev reflection in the vortex core of a topological superconductor. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 224501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadj-Perge, S.; Drozdov, I.K.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Jeon, S.; Seo, J.; MacDonald, A.H.; Bernevig, B.A.; Yazdani, A. Observation of Majorana fermions in ferromagnetic atomic chains on a superconductor. Science 2014, 346, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Manna, S.; Eich, M.; Lee, P.; Moodera, J. Superconductivity in the Surface State of Noble Metal Gold and its Fermi Level Tuning by EuS Dielectric. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 247002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.L.; Pan, L.; Stern, A.L.; Burks, E.C.; Che, X.; Yin, G.; Wang, J.; Lian, B.; Zhou, Q.; Choi, E.S.; et al. Chiral Majorana fermion modes in a quantum anomalous Hall insulator–superconductor structure. Science 2017, 357, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Kong, L.; Fan, P.; Chen, H.; Zhu, S.; Liu, W.; Cao, L.; Sun, Y.; Du, S.; Schneeloch, J.; et al. Evidence for Majorana bound states in an iron-based superconductor. Science 2018, 362, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornieri, A.; Whiticar, A.; Setiawan, F.; Portolés, E.; Drachmann, A.; Keselman, A.; Gronin, S.; Thomas, C.; Wang, T.; Kallaher, R.; et al. Evidence of topological superconductivity in planar Josephson junctions. Nature 2019, 569, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, P.W.; Duckheim, M.; Romito, A.; von Oppen, F. Probability Distribution of Majorana End-State Energies in Disordered Wires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 196804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L. Bound state in superconductors with paramagnetic impurities. Acta Phys. Sin. 1965, 21, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Shiba, H. Classical spins in superconductors. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1968, 40, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinov, A.I. Superconductivity near a paramagnetic impurity. JETP Lett. 1969, 9, 146. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).