Abstract
Bauxite residue, known as red mud, is a by-product of alumina production using the Bayer process. Currently, its total global storage amounts to over 4.6 billion tons, including about 600 million tons in Russia. The total global storage of red mud occupies large areas, leading to environmental damage and increasing environmental risks. Moreover, it contains a significant amount of sodium, which is easily soluble in subsoil water; therefore, a sustainable approach for comprehensive recycling of red mud is necessary. The bauxite residue contains valuable elements, such as aluminum, titanium, and scandium, which can be recovered using liquid media. In recent years, many methods of recovery of these elements from this waste have been proposed. This paper provides a critical review of hydrometallurgical, solvometallurgical, and complex methods for the recovery of valuable components from red mud, namely, aluminum, titanium, sodium, and rare and rare-earth elements. These methods include leaching using alkaline or acid solutions, ionic liquids, and biological organisms, in addition to red mud leaching solutions by extraction and sorption methods. Advantages and disadvantages of these processes in terms of their environmental impact are discussed.
Keywords:
red mud; bauxite residue; hydrometallurgy; scandium; alumina; titanium; recycling; waste treatment; recovery 1. Introduction
The main industrial approach used for alumina production is the Bayer method, which is based on the selective dissolution of bauxite ore components by alkaline solution. This method generates a large amount of waste called red mud. Red mud is the insoluble portion of the ore that is dumped into landfills.
By various estimates, production of 1 ton of alumina generates from 0.9 to 1.5 tons of red mud [1,2]. Currently, red mud landfills occupy large areas, which leads to environmental damage and increases environmental risks.
According to [3], more than 4.6 billion tons of this waste had been accumulated globally by 2018, including about 600 million tons in Russia [4]. Moreover, global alumina production also generates more than 175.5 million tons of red mud annually [5]. Consequently, development of cost-effective technologies for red mud processing is a crucial environmental, scientific, and technical task.
At present, only about 15% of the annually generated red mud is recycled [6]. The storage of the main part of red mud in special sludge dumps results in misuse of large land areas, and necessitates special dump protection and maintenance. These areas could be used for other purposes, e.g., for agriculture. The maintenance of sludge dumps and the construction of new dumps require significant material, financial, and human resources. In addition, the storage of red mud is potentially dangerous due to the possibility of release to the environment of compounds containing sodium, chromium, arsenic, and other toxic components [7].
Numerous approaches for red mud processing are currently known. The Scopus search engine finds over 5800 documents for the queries of “red mud” and “bauxite residue”. Furthermore, many review articles reporting different red mud applications, have been published. Among these, a wide range of reviews considers recovery of valuable elements from red mud by pyrometallurgical, hydrometallurgical, and complex methods [6,8,9,10,11,12,13,14], including those focused on the chemistry of these processes [15], in addition to application in construction materials [16], road material [17], catalyst [18], coagulant and adsorbent [19], geotechnical engineering applications [20,21], etc.
Several articles describe a complex influence of red mud storage and recycling on environment and socio-technological development, in addition to methods of reducing their negative impact [3,22,23]. Other research papers aim to discuss all developed methods for red mud usage and storage management [24,25]. Articles have discussed storage and processing of red mud with a focus on different regions [2,26,27,28].
However, there are still no cost-effective integrated technologies for comprehensive recycling of red mud applied on a large industrial scale.
Red mud has a complex chemical and mineralogical composition and contains up to 60% Fe2O3, up to 25% Al2O3, and up to 12% TiO2. In addition, it can contain up to 1700 mg/kg of rare-earth elements (REEs), including up to 120 g/t Sc, 80 ppm Ga, 150 ppm Y, 350 ppm Zr, and about 60 ppm U and 30 ppm Th [29]. In our previous work [30], we reviewed the pyrometallurgical methods of red mud processing, mainly for iron recovery. In this work, we consider the hydrometallurgical, solvometallurgical, and complex methods of selective recovery of aluminum, titanium, and sodium, and rare and rare-earth elements from red mud, including the economic viability and environmental impact of these processes, with emphasis on using alkaline or acid solutions, in addition to ionic liquids, bacterial cultures, and microorganisms. Unlike most other review articles, which briefly review various methods for extraction of valuable elements from red mud, this paper concentrates only on the methods of extraction of valuable elements using liquid media. Additionally, the paper describes experimental details and results more carefully, which allows other researchers to assess more quickly the prospects for using various methods for the extraction of valuable elements from red mud, including material and energy costs depending on red mud composition and the need for final products. This is especially important for industrial utilization of red mud.
2. Red Mud Processing Using Alkaline Solutions
Red mud can contain a significant amount of unextracted alumina, which is partly alkali soluble and partly in the form of complex sodium aluminosilicates such as sodalite and cancrinite [31,32]. The treatment of red mud by alkaline solutions enables extraction of a part of such alumina, in addition to sodium, and can be comparatively easily integrated into the main technological cycle of aluminum plants. Table 1 demonstrates the main trends of red mud processing using leaching of aluminum and sodium by alkaline solutions.

Table 1.
Methods of red mud processing using alkaline solutions.
2.1. Hydro-Chemical Process
Baica et al. [33] studied the effect of leaching conditions on the solubility of the aluminum compounds contained in red mud using NaOH solutions at atmospheric pressure. Statistical processing using the Taguchi method showed that the most important parameters are solid-to-liquid (S/L) ratio in the leaching slurry and interaction temperature. The second important set of parameters that affects the aluminum recovery comprises NaOH concentration, time, and temperature. NaOH concentration of 10 M (400 g/L), temperature of 80 °C, duration of 4 h, and stirring speed of 800 rpm were the optimal leaching parameters for the recovery of 67.3% Al.
To convert aluminum from hardly soluble compounds into highly soluble ones, the Bayer process is used, namely, the autoclave leaching of red mud by alkaline solution with the addition of calcium oxide. The process can be described by the following reactions [34]:
Na2O·Al2O3·2SiO2·nH2O + Fe2O3 + NaOH + Ca(OH)2 + H2O = NaAl(OH)4 + H2O + NaCaHSiO4 + Ca3(Fe0.87Al0.13)2(SiO4)1.65(OH)5.4;
NaCaHSiO4 +NaOH + H2O = Na2SiO3 +2Ca(OH)2 + H2O = 2CaO·SiO2·nH2O + 2NaOH + H2O.
The experiments of red mud autoclave leaching by 40–60% NaOH solution in the temperature range of 170–210 °C with lime milk addition has shown the possibility of the recovery of 87.5% and 96.4% for Al2O3 and Na2O, respectively [34]. The best results were obtained by leaching for 3.5 h with a 100/25 ratio of red mud/calcium oxide in a 45% NaOH solution at temperature of 200 °C and pressure of 0.8 MPa. An increase in temperature up to 250 °C led to a decrease in the leaching time to 1 h with a dosage of CaO/SiO2 = 0.3, and resulted in over 70% Al2O3 recovery in the solution and <1% of remaining Na2O in the residue [35]. It was also shown [1] that an elevated content of iron oxides in red mud increases the dissolution degree of sodium.
The aluminum recovery degree and the filtration rate of the leached red mud slurry can be improved by adding fly ash from coal-fired power plants. Liu et al. [36] carried out high-temperature leaching at 260 °C using a strong alkaline solution containing 530 g/L Na2O with varying chemical composition of the ash and the ash:red mud ratio at molar ratios of Na2O/Al2O3 = 30, CaO/SiO2 = 1.05, and S/L = 1/8. The optimal ratio of the ash:red mud equal to 1:1 led to 91.7% alumina recovery, whereas recovery was 72.14% without additives. In addition, filtration time dropped from more than 240 s to 80 s using the optimal ash:red mud ratio. The chemical composition change of the ash by variation of Al2O3/SiO2 ratio had a minimal effect on the recovery degree of alumina. However, a decrease in the Al2O3/SiO2 ratio significantly increased filtration time.
2.2. Sintering Process
To improve aluminum recovery, many authors proposed sintering red mud with Na2CO3 and materials containing divalent earth alkali oxides (CaO, MgO, BaO) for conversion of aluminum from sodium aluminosilicates that are insoluble in alkaline solutions into water-soluble sodium aluminate NaAlO2, and for fixing silicon into barely soluble silicates (M2SiO4, where M is a divalent alkaline earth metal). The sintering process can be described according to the following reactions (3)–(8) [37]:
SiO2 + 2MO = M2SiO4
Al2O3 + Na2CO3 = 2NaAlO2 + CO2
Fe2O3 + Na2CO3 = 2NaFeO2 + CO2
TiO2 + Na2CO3 = Na2TiO3 + CO2
Na2TiO3 + MO = MTiO3 + Na2O
2NaFeO2 + 2MO = M2Fe2O5 + Na2O
This method can be combined simultaneously with carbothermic reduction of iron to obtain cast iron at the temperature range of 1300–1450 °C [38,39] or an iron-containing concentrate at the range of 1000–1200 °C [40,41].
Hodge et al. [42] studied the kinetics of sodium monoaluminate formation in the process of red mud sintering with soda and calcium carbonate at 1000 °C. Peak formation of sodium monoaluminate occurred after 5 min of sintering, and then its content in the sample decreased with an increase in sintering time. Leaching of the obtained sinter by a solution containing 5 g/L NaOH and 5 g/L Na2CO3 at 80 °C for 30 min dissolved 64% of sodium and 55% of aluminum.
Wai et al. [43] investigated the effect of CaO, MgO, and BaO addition on the aluminum and sodium recovery from red mud after sintering with Na2CO3. The mixtures of red mud, 25% of soda, and various additives in the amount of 20% were sintered at 900 °C for 2 h and then leached in 0.1 M NaOH solution. It was revealed that BaO has the greatest effect on dissolution of aluminum and sodium; their maximum recovery degree reached 75.2% and 94%, respectively. The rise of temperature and duration of soda sintering of red mud with BaO up to 1000 °C and up to 4 h, respectively, achieved 99.5% aluminum recovery in the solution [44].
Gao et al. [40] considered the reduction roasting process of red mud with the addition of MgO and Na2CO3 followed by magnetic separation of iron and subsequent leaching of aluminum by alkaline solution. It was shown that the optimal roasting conditions, which are a MgO/SiO2 ratio of 1.5, temperature of 1200 °C, and duration of 90 min, lead to an iron recovery degree of 92%. The leaching of the magnetic separation tailings by 3% NaOH solution at 90 °C for 20 min resulted in recovery of over 70% of aluminum.
In general, the application of the alkaline methods enables the selective recovery of alumina and sodium from red mud without significant iron dissolution. Despite using a higher temperature and pressure, direct alkaline leaching leads to incomplete dissolution of alumina phases in red mud, so the application of this method for aluminum extraction from red is unpromising. The use of the sintering method with simultaneous iron reduction allows two types of products to be obtained, but this method also has some disadvantages. In particular, the aluminum recovery degree is low due to incomplete conversion of aluminum into water-soluble aluminates with the application of CaO and MgO as additives, whereas the use of BaO considerably increases the processing cost.
3. Red Mud Processing Using Acid Solutions
In recent years, many authors [8,12] have made efforts to find an optimal technology for selective acid recovery of REEs from red mud. The processes of direct leaching of valuable elements from red mud by the most common acids, such as H2SO4, HCl, HNO3, and H3PO4, and their mixtures, have been widely studied. It has become apparent that sulfuric acid has a sufficiently high selectivity for scandium and titanium; the use of hydrochloric acid leaching leads to efficient recovery of aluminum, iron, and REEs.
3.1. Direct Acid Digestion
Karimi et al. [45] studied the efficiency of red mud dissolution in hydrochloric, nitric, sulfuric, and phosphoric acids, and in their mixtures, in the presence and in the absence of hydrofluoric acid. The experiments were carried out at 85 °C, stirring time of 120 min, and liquid-to-solid ratio of 20 mL/g. The dissolution efficiency of red mud in three N acid solutions was 79.35% for HCl, 46.21% for H2SO4, 79.70% for HNO3, and 41.33% for H3PO4. The highest dissolution degree of red mud was 80.37%, which was obtained by leaching using the mixture of HCl:HNO3 1:1 in the presence of 3 wt.% of HF. This research showed that a single acid alone cannot fully decompose red mud at atmospheric conditions. Accordingly, direct acid leaching only enables extraction of some elements from red mud.
Reid et al. [46] compared application of different acids for leaching of REEs from Canadian red mud at atmospheric pressure. HCl, HNO3, and H2SO4 were used at various leaching conditions in the ranges of acid concentration from 0.5 to 3 M and temperature from 25 to 90 °C for 30 min. Systematic experiments have indicated that nitric acid is the most effective for REE recovery. However, taking into account the cost, practical consideration of the process with application of volatile reagent, and its efficiency, 1.5 M H2SO4 at 90 °C was chosen as the best leaching condition. The maximum recovery of Ce, La, Nd, and Sc was at the S/L ratio of 1/15. Microwave pretreatment tests of red mud to increase the recovery of REEs showed that the pretreatment leads to the formation of cracks and pores in the particles, which enables the leaching agent to diffuse into the interior of the particle, and therefore facilitates the dissolution of REEs. As a result, the recovery degrees of Sc and Nd were increased from 40.0% to 64.2%, and from 54.3% to 78.7%, respectively.
Lim and Shon [47] investigated the influence of ultrasonic waves on the process of sulfuric acid leaching of titanium from red mud. The recovery degrees of iron, aluminum, and titanium increased with an increase in ultrasonic power output, leaching temperature, and acid concentration, but decreased with an increase in S/L ratio. The recovery rates of iron, aluminum, and titanium were 48.22%, 72.94%, and 88.95%, respectively, using the following optimal conditions: ultrasonic power of 150 W, H2SO4 concentration of 6 M, leaching at temperature of 70 °C for 2 h at an S/L ratio of 2/100. The significant S/L ratio was used to prevent silica gel formation. The REE behavior was outside the scope of the research.
Ochsenkuehn-Petropoulou et al. [48] also found that the application of sulfuric acid for selective recovery of scandium is more appropriate compared with hydrochloric and nitric acids, and with aqua regia. Experiments conducted under wide ranges of temperature and concentration showed that leaching by 2 M H2SO4 at 80 °C for 60 min with an S/L ratio of 1/20 was optimal, and resulted in Sc recovery of about 50%. High pressure acid leaching at 220 °C, in addition to acid concentration rise, led to a significant increase in iron dissolution. High-temperature conditions contributed to the optimal selectivity of scandium recovery with respect to iron and excluded the formation of silica gel, which substantially hinders the separation of the target solution from the residue.
Xie et al. [49] studied the effect of red mud particle size on the recovery of aluminum and iron by hydrochloric acid leaching at varying acid concentrations, S/L ratios, and durations. The optimal leaching conditions, which led to dissolution of 96.7% Al and 95.1% Fe, for red mud with a particle size of 150 microns were as follows: temperature of 80 °C, duration of 150 min, HCl concentration of 10 M, and S/L ratio of 1/8.
Zhao et al. [50] investigated leaching of bauxite reaction residue (BRR) by hydrochloric acid. It was found that direct acid leaching at optimal conditions, namely acid concentration of 8 M, L/S 5:1, leaching temperature of 85 °C, and leaching time of 3 h, can pass into solution only 44.15% Al, 38% Fe, 42%Ca, and 12% Ti. After removal of 81.21% Si from BRR by 3 M NaOH solution at 75 °C for 2 h and a 5:1 L/S ratio, the aluminum leaching rate only increased by 5.05%. Preliminary mechanical activation treatment for 10 h also led to only 46% Al being passed into solution. To increase aluminum dissolution efficiency, high-pressure acid leaching was used. After 10 h milling pretreatment and high-pressure red mud leaching at 210 °C, dissolution degrees of Al, Ca, Fe, and Ti were 84.23%, 73%, 43% and 15%, respectively. A study on kinetics of high-pressure aluminum dissolution determined that the apparent activation energy of the process was 20.82 kJ/mol, which corresponds to a liquid diffusion rate-controlling process. It showed that a liquid poly-aluminum chloride solution for water treatment can be prepared from the obtained solution. The developed process can be used for red mud treatment after the removal of iron.
The complex hydrochloric acid leaching process developed by Orbite aluminate Inc. [51] allows extraction of more than 90% of valuable elements from red mud, including REEs. The process consists of several stages. The initial stage is high-pressure acid leaching of red mud at 150–170 °C with dissolution of almost all elements except Si and Ti, followed by HCl gas treatment of leached solution for AlCl3·6H2O precipitation. The roasting of the obtained AlCl3·6H2O at 900–950 °C allows production of Al2O3; the off-gas can be returned to the precipitation stage. After Al removal, the solution heats up to 180 °C for Fe2O3 formation after Mg recovery by precipitation and calcination. To recover REEs from the solution, solvent extraction was proposed.
A statistical analysis of experimental data [52] indicated that concentration of the sulfuric acid solution used, in addition to the process temperature, have the greatest influence on titanium leaching efficiency from red mud. In addition, two-factor conditions—acid concentration and temperature, or acid concentration and S/L ratio—were also statistically significant; thus, the leaching efficiency can be considered to be dependent not only on one, but on several process parameters. The "best" model of the parameters with recovery of 64.5% Ti was obtained for the leaching by 6 N H2SO4 for 4 h at a temperature of 60 °C, S/L ratio of 5%, and fixed stirring speed of 700 rpm. The use of concentrated sulfuric acid solution resulted in dissolution of 46% Fe and 37% Al in addition to titanium. The main phases of the insoluble residue were anhydrite (CaSO4), bassanite (CaSO4∙0.5H2O), and various hydrated aluminum sulfates, whereas, taking into account experimental conditions, the existence of unreacted gibbsite (Al(OH)3) and diaspore (AlO(OH)) in the sulfate residue appears to be doubtful.
Lymperopoulou et al. [53] investigated leaching of iron and scandium from red mud by sulfuric acid using a statistical analysis of the obtained data using the Taguchi method. In the experiments the following ranges of the parameters were used: acid concentration of 1–6 M, S/L ratio of 10–30%, temperature of 25–85 °C, and leaching time of 1–7 h. The analysis indicated that the most important factors were S/L ratio and temperature for scandium recovery, and mainly temperature for iron recovery. The optimized leaching conditions for Sc recovery were as follows: 6M H2SO4, 85 °C, 30% S/L ratio, 4 h; the conditions for Fe recovery were as follows: 2M H2SO4, 25 °C, 10% S/L ratio, 1 h.
Alkan et al. [54] derived a more efficient application of sulfuric acid for leaching compared with hydrochloric acid or their mixture in terms of titanium recovery from red mud. After 2 h red mud treatment by 4 M H2SO4 solution at 70 °C and S/L ratio of 1/50, the recovery of titanium was 67.3%, which was the highest among all used lixiviants. The application of 4 M HCl and a combination of the two acids in the ratio of HCl to H2SO4 of 1:3 led to titanium recovery degrees of 59.8% and 56.4%, respectively, which were slightly lower.
Shoppert and Loginova [55] suggested a method of sequential processing of red mud by diluted solutions of hydrochloric and sulfuric acids to obtain a titanium-containing concentrate. In the first stage, Ca, Na, Al, Si and K were removed from red mud by the treatment using HCl solution of pH = 3 at 25 °C for 1 h. In the second stage, the residue enriched in titanium and iron was leached by H2SO4 solution. The optimal conditions for the separation of iron from titanium were determined by factorial design. Dissolution of iron with titanium recovery up to 6% was carried out using H2SO4 solution of 80 g/L at an S/L ratio of 1/20 and 50 °C for 90 min. The insoluble perovskite residue contained 46.7% titanium.
It is known that silicon dioxide polymerization with the formation of silica gel significantly impedes the filtration rate of the leachates, and this effect is particularly profound with the use of 1–3 M H2SO4 solutions [56]. Alkan et al. [57] studied a silicagel formation rate in the process of direct sulfuric acid leaching of red mud, in addition to slags obtained by its reduction smelting at 1500–1550 °C in the presence of the fluxes, silicon oxide, or lime. Acidic slag contained 1.4% Fe2O3, 15.3% CaO, and 38% SiO2; basic slag included 1.4% Fe2O3, 43.2% CaO, and 7.6% SiO2. In all cases, the leaching by 2.5 M H2SO4 solution at 75 °C and S/L ratio of 1/10 for 1 h formed a stable silica gel, and for acid slag at the highest rate. The preliminary sulfating of dry red mud or slags by 97% H2SO4 at 75 °C followed by water leaching contributed to a significant suppression of silica gel formation. The treatment of acidic slag by this method showed that it is possible to achieve the most efficient recovery of about 70% Sc with a simultaneous insignificant dissolution of Ti (<10%) and Si (<3%).
Alkan et al. [58] proposed an application of a mixture of sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide to increase the efficiency and selectivity of titanium and scandium recovery. A parametric study demonstrated that H2O2 addition suppresses silica gel formation, decreases iron dissolution, increases titanium recovery degree due to the formation of soluble titanium peroxosulfate, and negligibly affects solubility of other red mud components. The leaching by the mixture of 2.5 M H2O2 and 2.5 M H2SO4 at 90 °C and an S/L ratio of 1/10 for 30 min resulted in the recovery of 68% Sc and 91% Ti; the yield of Fe and Al in the sulfuric acid solution was 23% and 43%, respectively.
Some authors [59,60] have attempted to combine pyro- and hydrometallurgical methods aimed to reduce and remove iron in metallic form from the process, because, due to significant iron content compared to REEs both in red mud and in leached solutions, it is the main hindering factor for the separation and subsequent processing of the solutions. However, leaching of the slags from reduction smelting, which can be essentially considered REE preconcentrates, is complicated. To increase the solubility of the slags, their composition can be adjusted during the smelting process depending on the composition of red mud and the lixiviant used.
Yagmurlu et al. [59] tested six slag samples for selective recovery of REEs that were obtained by reduction smelting of red mud with fluxes, lime, or silica, at different rates of cooling rates, water quenching, or slow cooling. Table 2 demonstrates the chemical composition of red mud and the slags.

Table 2.
Chemical composition of red mud and the slag samples from reduction smelting analyzed by [59], wt.%. (reproduced from Ref. [59]).
A kinetic study of REE leaching from different slags using the mixture of 2.5 M H2SO4 and 2.5 M H2O2 was carried out at 75 °C and S/L ratio of 1/10. It showed that both slag composition and cooling rate affect REE recovery. The best results were found for the quenched basic slag with recovery of 97% Sc and 95% Ti in solution without the formation of silica gel. Scandium phosphate concentrate with 85% total scandium recovery from red mud was precipitated from the obtained solution by a three-stage treatment using a solution of ammonia and ammonium hydrogen phosphate (NH4)2HPO4.
Rivera et al. [60] studied high-pressure acid leaching of REEs by HCl and H2SO4 at elevated temperatures from the slags obtained by reduction smelting of red mud. Six types of slags were obtained using the different fluxes, lime or silica, and the cooling rate, water quenching, or slow cooling. Table 3 presents the chemical compositions of red mud and the slag samples.

Table 3.
Chemical composition of red mud and the slag samples * from reduction smelting analyzed by [60], where slag I was obtained by 20% CaO addition, and slags II and III were obtained by CaO and SiO2 addition, respectively, wt.%. (reproduced from Ref. [60]).
After leaching of the slowly cooled slag III by 3 N H2SO4 solution at 150 °C, selective recovery of above 95% Sc occurred due to the formation of double sulfates [40], whereas the recovery of other REEs was about 20%. In addition, leaching of the quenched slag II by 3 N HCl solution at 120 °C led to the recovery of over 90% Y, La, and Nd, and of 80% Sc. The dissolution degree of Ti and Si under the optimal conditions was up to 5%, and over 60% Fe and 90% Al passed into solution. A cost-benefit evaluation of the high-pressure acid leaching process is required.
Acid leaching can be used in combination with physical beneficiation methods of raw materials, such as hydrocyclone processing followed by drying [61]. This treatment increased the contents in the separated fraction of La by 19%, Ce by 23%, and Sc by 7%, and decreased Fe content by 22%. It also contributed to minimizing total recovery of iron and increased leaching degree of REEs. Leaching of fine hydrocyclone beneficiated fraction by 2 M H2SO4 solution at 95–100 °C, pH = 4 and S/L ratio of 1/10 for 2 h increased Sc recovery by 15%, La by 16%, and Ce by 9% compared with original red mud, whereas Fe content in the solution was decreased from 4.9% to 2.2%.
Guo et al. [62] proposed the preliminary calcination process of a mixture of red mud and fly ash from coal-fired power plants in the presence of sodium carbonate in the temperature range of 600–900 °C for 2 h followed by acid leaching. Leaching of the calcine, which was obtained by roasting at 850 °C the mixture of 100 g of the ash and 106.4 g of red mud, by 6 M HCl solution and boiling for 2 h led, to the dissolution of above 90% of alumina.
Kashcheev et al. [63] suggested an improved sulfuric acid method for red mud processing using ammonium sulfate as a leaching agent. A comparative assessment of leaching characteristics of ammonium sulfate and sulfuric acid showed that they are equal in terms of their efficiency of the dissolution of sodium, calcium, iron, and aluminum. In the first stage, the boiling treatment by 8.45% (NH4)2SO4 solution at S/L ratio of 1/14 for 30 min extracted 95% Na and no more than 13–17% Al and Fe, thereby decreasing red mud weight by 23%. In the second stage, when the reagent concentration was increased to 58.7% and the volume of the solution to the S/L ratio was 1/30, boiling for 60 min led to dissolution of 77.2% Al, 78.6% Ca, 60.25% Fe, 95.7% La, 71.0% Sc, and 86.5% Y. Then, hydroxides of aluminum, iron, and alkaline-earth metals with an admixture of REEs were precipitated by sequential neutralization to obtain a solution of ammonium and alkali metal sulfates. In the final residue, titanium and silicon compounds, in addition to calcium sulfate, were concentrated. It is the authors’ opinion that the advantage of this technology compared with sulfuric acid leaching is a lower cost of ammonium sulfate, which is used as a lixiviant. Other important advantages are the possibility of obtaining a neutralizing reagent, ammonia, during the regeneration of ammonium hydrosulfate, in addition to environmental compatibility, high productivity due to better filtration characteristics of the solutions, etc.
The extraction of valuable elements from red mud by direct acid leaching is a well-studied method. The use of sulfuric and hydrochloric acids as leaching agents is most promising for industrial application due to their wide application and low cost. Nevertheless, these methods have several disadvantages, such as high dissolution of iron, silica gel formation, the need for the use of a high temperature, leaching duration, acid concentration, and pressure or preliminary roasting to increase the recovery degree. A significant interest for industrial application exists in the Orbite process [51], which allows extraction of valuable elements from red mud with the acquisition of high-grade alumina. However, using high pressure avoids the formation of silica gel and leads to the high dissolution of iron, which is the main hindering factor for the subsequent extraction of REEs from the solutions. Although dissolution of iron can be decreased by the use of a mixture of sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide [58], its concentration in the solution remains too high, so the most promising means of decreasing iron content in the solution is preliminary extraction by pyrometallurgical methods. Using ammonium sulfate as a leaching agent for the extraction of valuable elements from red mud is a new and prospective but poorly studied method.
3.2. Scandium Recovery by Sulfation Method
Scandium is among the most important rare-earth elements in red mud because its price is about 90% of the total price of all REEs contained in this waste. Red mud contains scandium and other REEs in various mineral forms. Scandium is mainly present as an impurity of hematite or goethite that substitutes Fe3+ and Al3+ [64]. A portion of scandium is in silicon-rich minerals such as quartz or zeolite. Unlike other REEs, individual scandium mineral particles have not been detected. Particles containing REEs also consist of titanium and iron, therefore, they are called REE ferrotitanates [65]. The REE distribution varies significantly depending on the origin of red mud. For example, in Greek red mud, 65% of scandium is present in an easily extractable form on the surface of red mud particles, but Russian red mud from Ural aluminum plants contains a smaller amount of scandium in chamosite.
One of the most widely studied and simple acid methods for the recovery of REEs, particularly scandium, from red mud is the sulfation method, which is the roasting of red mud with concentrated sulfuric acid at an S/L ratio close to 1 to convert scandium minerals into water-soluble sulfates followed by water leaching [66]. This method makes it possible to recover scandium selectively without silica gel formation. The advantage of this method is the possibility to process and reuse some products that are formed during thermal decomposition of the acid and during the roasting, namely SO2, SO3, NaFe(SO4)2, and NaAl(SO4)2, as raw materials for regeneration of sulfuric acid [67].
Meng et al. [68] studied the process of red mud sulfation by the treatment of its aqueous emulsion using concentrated H2SO4 at an S/L ratio of 2/1 followed by heating in a muffle furnace up to the required temperature and holding for 30 min. As a result, metal oxides in red mud were converted into highly soluble sulfates, and silicon was polymerized and transformed into an insoluble macromolecular form of silicic acid. An increase in roasting temperature led to the decomposition of titanium, iron (III), and aluminum sulfates into corresponding oxides. The maximum recovery degree of scandium sulfate from red mud was 96.5%, which was obtained by the leaching of the sample roasted at 750 °C for 60 min. An increase in the roasting temperature up to 850 °C led to a decrease in the solubility of scandium sulfate to about 90% due to its partial decomposition to hardly soluble oxide. However, it contributed to significantly better scandium selective recovery due to lower dissolution of titanium, iron (III), and aluminum, which also dissociated during the roasting from sulfates into oxides, but at lower temperatures of 544 °C, 683 °C, and 716.6 °C, respectively.
Liu et al. [69] showed that sodium can have an inhibitory effect on the release of SO2 or SO3 from metal sulfates during the roasting of red mud with concentrated sulfuric acid, and an excess of the acid over 1 mL/g has no growth effect on Sc and Na leaching. The optimal treatment conditions were chosen as follows: roasting temperature of 750 °C, roasting duration of 40 min, liquid-to-solid ratio of 10 mL/g, leaching temperature of 65 °C, leaching time of 30 min, and stirring speed of 250 rpm. The roasting and leaching under these conditions extracted over 95% Na and about 60% Sc in the presence of the obtained solution of 7% Al, 29% Ca, and 3% Si, in addition to Fe, Ti4+, and Ga3+ in inconsequential amounts.
Roasting of the mixture of Chinese red mud and sulfuric acid with S/L ratio of 1 g/mL at 750 °C for 40 min and subsequent water leaching at 50 °C for 30 min contributed to the dissolution of about 53% Sc, 30.3%, Ca, and 8.9% Al, in addition to less than 1.0% Fe and 0.3% Si. A roasting temperature rise up to 760 °C led to a drop in recovery degree of Sc to 49.5%, Fe to 0.1%, Si to 0.2%, Ca to 27.0%, and Al to 1.6%. According to the authors [66], scandium after roasting was in the form of complex sulfate Na3Sc(SO4)3.
Narayanan et al. [70] indicated that scandium and other REEs can be easily separated by a precipitation from the sulfate leaching solution obtained by red mud processing. Sulfation was carried out by the treatment of red mud using 80% H2SO4 at 120 °C for 14 h, followed by calcination at 700 °C for 1 h. Mixtures of REE oxides were sequentially precipitated from the leached sulfate solution by the addition of sodium hydroxide at pH = 8; scandium was deposited as scandium oxalate by the addition of oxalic acid followed by calcination at 800 °C for 1 h to obtain a pure oxide. The recovery degree of scandium by this method was 75%.
Alkan et al. [57] extracted scandium from the slags that were obtained by reduction smelting of red mud with the addition of lime and silica. Slags with a weight of 13 g were mixed with 5, 10, and 15 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid (97% H2SO4) and 5 mL of deionized water, then the samples were held at 75 °C for 1 h in a furnace. After the treatment of the silicic slag, about 70% Sc, less than 10% Ti, and 3% Si passed into solution without silica gel formation.
Rivera et al. [52] investigated REE recovery from red mud by a multistage treatment using hydrochloric and sulfuric acids, followed by water leaching. The recovery of Si, Al, Fe, Sc, Y, La, and Nd into the solution was studied depending on the amount of acid and number of treatment cycles. Sulfating with 95–97% sulfuric acid for 24 h with H2SO4 consumption of 412 g/kg of red mud and subsequent water leaching of the roasted sample for 24 h at 25 °C and S/L ratio of 1/5 led to dissolution of 2.5% Si, 30% Al, 22% Ti, 3% Fe, 22% Sc, 12% Y, 11% La, and 11% Nd. Treatment by 37% HCl with following water leaching under the same conditions caused the dissolution of the main macrocomponents to decrease slightly, but dissolution of REE increased; thus, 28% Al, 2% Ti, 3% Fe, 29% Sc, 44% Y, 25% La, and 28% Nd passed into solution at HCl consumption of 788 g/kg. A 4–9-fold increase in recovery degree of the components following a decrease in water consumption by 50–60% was achieved by five treatment cycles. Taking into account the price of scandium oxide for December 2017, the preliminary evaluation showed that the estimated profit margin of the technology with multistage leaching by HCl is 531 USD per tonne of red mud, whereas for leaching by H2SO4, profit is 563 USD per tonne of red mud.
The use of sulfation roasting and water leaching leads to selective extraction of more than 60% Sc from red mud without a significant dissolution of iron, titanium, and silica gel formation [69]. This method can be applied only for the extraction of Sc and has industrial potential due to high scandium prices. However, due to the large amount of accumulated red mud and low Sc content in it, this method can be used only as a part of a complex treatment of red mud with extraction of major valuable elements such as Fe, Al, and Ti.
Generally, it should be noted that an application of acid methods is a promising approach for red mud processing, and enables extraction of almost all elements, including small amounts of scandium and other REEs. The main disadvantages of these methods are the need for acid-resistant equipment and low selectivity. This necessitates development of multistage technologies that are difficult to practically implement.
4. Red Mud Processing by Organic Solvents
The application of organic media for the treatment of raw materials and the recovery of valuable components can avoid the formation of a significant amount of processing solutions and spent liquor, which also need to be utilized for the mitigation of environmental impacts. Recently, non-aggressive hydrocarbons with low toxicity, and their mixtures, have been synthesized and introduced into industry. These hydrocarbons are attractive due to their use as promising extraction media and sorption materials. The application of such leaching agents makes it possible to use cheaper equipment, thereby reducing the loss of the extractant by evaporation or hydrolysis in contact with aqueous solutions.
4.1. Organic Acid Leaching
Yang et al. [71] proposed applying a mixture of oxalic and sulfuric acids for selective recovery of iron from red mud. To reduce the loss of more expensive oxalic acid before leaching, red mud was neutralized by diluted hydrochloric acid of 3 mol/L at a liquid-to-solid ratio of 2 mL/g for 1 h at room temperature. As a result of pretreatment, the loss of H2C2O4 with leached residue decreased from about 17% to less than 1%. Leaching of iron was carried out using the mixture of pretreated mud/H2C2O4·2H2O/H2SO4 at the mass ratio of 3/3/2 and S/L ratio of 1/16 g/mL. The treatment at 95 °C for 1.5 h led to the recovery of 94.15% Fe and 21.12% Al, and no more than 0.69% Fe remained in the residue. The treatment of the leached solution with the addition of iron scrap as a reducing agent at 50 °C for 60 min led to the precipitation of FeC2O4∙2H2O. The precipitated iron oxalate was treated by 9 M H2SO4 solution at S/L ratio of 1/5 g/mL at 50 °C for 20 min to obtain FeSO4·H2O and for H2C2O4 regeneration. In another paper [72], after oxalic acid leaching, the same authors carried out the precipitation of iron as iron hydroxide by neutralization of the solution to pH = 3.5 using CaCO3 addition. To selectively dissolve iron from the precipitate, leaching by the aqueous solution containing 1 M HCl and 200 g/L of CaCl2 at S/L ratio of 1/4 g/mL was used. The following reprecipitation of Fe(OH)3 at pH = 3.52 and the calcination at 750 °C for 3 h resulted in the acquisition of Fe2O3 of 98.44% purity. Oxalic acid and, in part, the solution of HCl–CaCl2 were regenerated, and the remaining part of calcium was precipitated as CaSO4·2H2O of 99.31% purity.
Yu et al. [73] precipitated iron in the form of poorly soluble β-FeC2O4·2H2O by ultraviolet irradiation without any reagent addition from iron (III) oxalate solution obtained by the leaching of red mud by 1 M C2H2O4 at 75 °C for 2 h. As a result, the residual iron content in the solution decreased to 1 g/L, and the oxalate solution after filtration was regenerated for the leaching of red mud.
Ujaczki et al. [74] studied selective recovery of gallium by the leaching of red mud using 1–2 M solutions of HCl, HNO3 and H2SO4, in addition to 1 M C2H2O4. The degree of gallium recovery from the suspension of 100 g of red mud in 1 L of the solution after the treatment at 60 °C for 24 h varied depending on the type of acid, and was 34.8% for HCl, 27.9% for HNO3, 28.6% for H2SO4, and 42.0%, the highest value, for C2H2O4. Oxalic acid leaching was investigated by varying the concentration of the acid from 0.05 to 3 M, treatment duration from 1 to 24 h, temperature from 22 to 80 °C, and concentration of the suspension from 10 to 200 g/L. The best results with the recovery of about 80% Ga was obtained using 2.5 M oxalic acid at 80 °C and an S/L ratio of 10 g/L for 21.7 h.
In the method [75], solutions of formic and acetic acids, and their mixtures, were used to extract aluminum and REEs from red mud. Leaching was carried out in a reactor with a stirrer at 80 °C using gradual addition of raw materials and continuous pH monitoring. The red mud addition was terminated upon reaching the specified acidity of the suspension in the range of pH = 1.6–4.0, but the leaching was continued for 1 h thereafter, and then held at a fixed temperature for an additional 1 h. Analysis of the acid leachates obtained after separation and extraction showed that an increase in pH from 1.6 to 3.8 led to a decrease in the aluminum recovery from 71.5% to 67.5% and scandium recovery from 74.4% to 70.2%, whereas the application of acetic acid resulted in a decrease in the recovery from 65% to 61.4% for Al, and from 67.7% to 63.9% for Sc. For the mixture of the acids of 1:1 ratio, the recovery degree of aluminum and scandium dropped from 67.6% to 63.8% and from 70.3% to 66.4%, respectively.
Atalay Kalsen et al. [76] compared the solubility of red mud components, namely Fe, Al, Ca, Si, Na, and Ti, in hydrochloric and citric acids depending on acid concentration, temperature, and leaching time. It was shown that the temperature was the most significant factor of the leaching process by hydrochloric acid, whereas the leaching process by citric acid depended on the temperature to a lesser degree. Leaching by 8 M HCl solution for 5 h at 100 °C caused almost full recovery of calcium and iron, in addition to the dissolution of over 60% Ti and 80% Al. The use of citric acid under the same conditions enabled recovery of 50% Ca and 60% Al with a simultaneous low dissolution of the remaining elements without any studies of the REEs’ behavior.
Gu et al. [77] leached over 46% of lithium from red mud, which was previously neutralized by 0,5 mol/L oxalic acid, using 25% solution of acetic acid at 85 °C for 60 min. The increase in acetic acid concentration above 25% and temperature led to the decrease in the percentage of metals dissolved, such as Al and Fe, and precipitation of a part of the released metal including lithium. Nevertheless, the leaching efficiencies of lithium were developed up to 60.27%, which is higher than those of sodium under neutralizing red mud using 0.01 mol/L hydrochloric acid.
The most important lixiviant among the investigated organic acids is oxalic acid, which enables selective dissolution of Fe [71,72,73] and Ga [74] from red mud. This method can be used as an alternative approach to iron recovery instead of pyrometallurgical methods.
4.2. Leaching by Ionic Liquids
Ionic liquids are salts that consist of an organic cation and an inorganic anion, the melting point of which is lower than the boiling point of water. They also have been used as alternative solvents for the recovery of valuable components from mineral raw materials [78,79].
Davris et al. [80] considered leaching of REEs from red mud by betainium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide [HBet][Tf2N], which is hydrophobic ionic liquid. The leaching was carried out at atmospheric pressure with the addition of water, and under autoclave conditions. After the leaching, the dissolved elements were desorbed by hydrochloric acid solution using stirring at room temperature for 30 min. Then, the purified organic media was reused. The studied factors influencing the recovery of elements were the amount of water, temperature, rate and duration of mixing, and pulp density. The optimal leaching conditions, namely aqueous solution of 40% at 150 °C with stirring at 400 rpm for 4 h, resulted in the recovery of 45% Sc, 30% Al, and below 3% Fe, and negligible dissolution of Ti and Si. Temperature had the greatest impact on Sc recovery.
Bonomi et al. [81] investigated direct leaching of red mud by 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulfate [Emim][HSO4]. The experiments were carried out in a 50 mL mini-reactor with a stirrer and a steam condenser at the temperatures of 150, 175, and 200 °C. To reduce the viscosity and facilitate the process, dimethyl sulfoxide was added during vacuum filtration, and the obtained solutions were treated by 65% HNO3. The experiments showed that the temperature and duration of the leaching had the greatest influence on the recovery of Sc and Ti in the solution. A stirring speed of 200 rpm and temperature of 200 °C for 12 h at an S/L ratio of 1/20 led to the recovery of 80% Sc, 90% Ti, 98% Fe, 38% Al, and 42% Na. The analyses of the leach residue using scanning and transmission electron microscopes indicated that undissolved scandium is mainly associated with ZrSiO4.
Thus, the use of hydrophilic ionic liquids, especially [Emim][HSO4], as the solvents for the recovery of valuable components from red mud, is more favorable than the use of hydrophobic ionic liquids, due to their low cost and high degree of scandium and titanium recovery [82]. However, due to the high solubility of iron in hydrophilic ionic liquids, preliminary recovery of iron is necessary.
5. Combined Methods
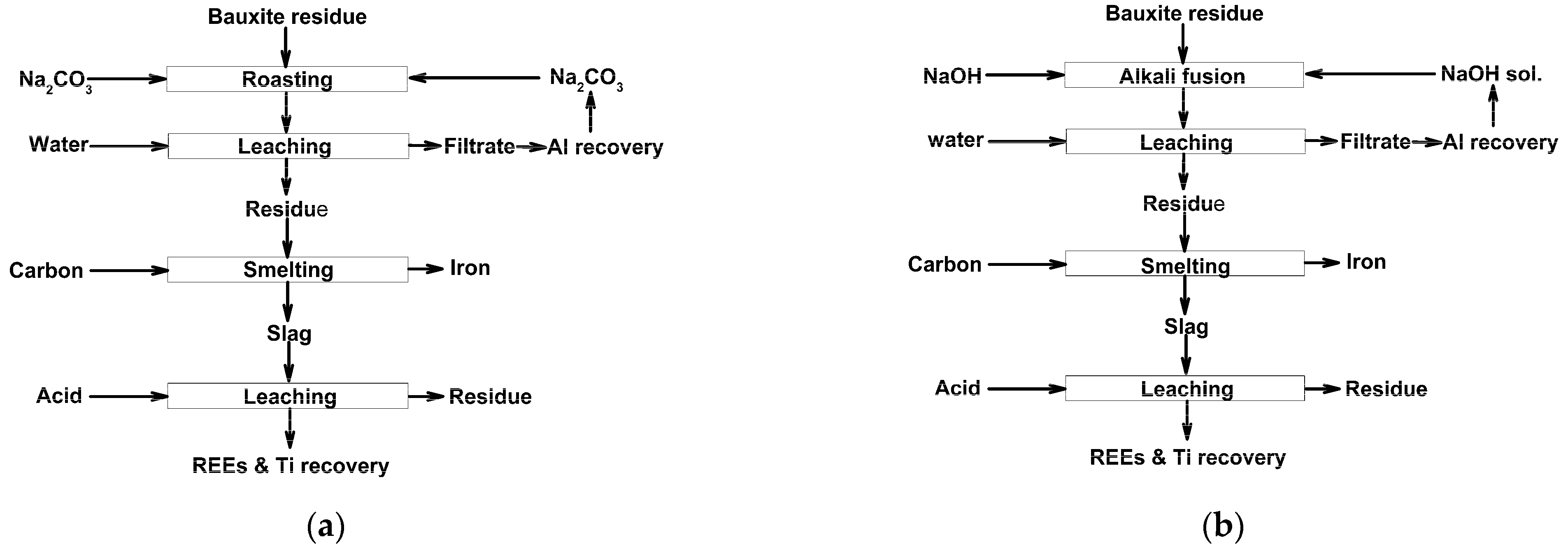
Due to the complex mineralogical and multicomponent chemical composition of red mud, its comprehensive utilization using any one solvent is often inefficient; thus, combined pyro- and hydrometallurgical processes with sequential leaching of elements by different solvents were developed, as mentioned above, and summarized in [83]. Such technological flowsheets before leaching can typically include different previous treatments, such as high-temperature sintering with alkaline compounds to obtain soluble aluminum compounds, reduction roasting followed by magnetic separation of iron, or smelting for almost full iron segregation. The use of different acids at various conditions in a different order, and more selective recovery methods, have been proposed for the extraction from tailings or slags of the most valuable components—REEs and titanium. Figure 1 illustrates the flowsheets of red mud processing using alkaline roasting, water leaching, reduction smelting, and acid leaching.
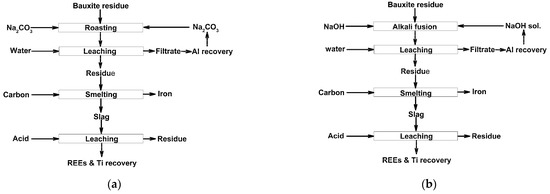
Figure 1.
The schematic diagrams of metals recovery from red mud via alkaline roasting–water leaching–reduction withNa2CO3 (a) or NaOH (b) as an alkaline agent. Adopted from [83].
The main advantage of these flowsheets is the preliminary extraction of iron, which can avoid its dissolution and decreases reagent consumption. The removal of alumina by alkaline roasting before smelting causes a decrease in the consumption of fluxes during smelting, but two-stage high-temperature roasting leads to high energy consumption and increases the total cost of these processes. The more promising approach is direct carbothermic roasting followed by magnetic separation for preliminary extraction of iron.
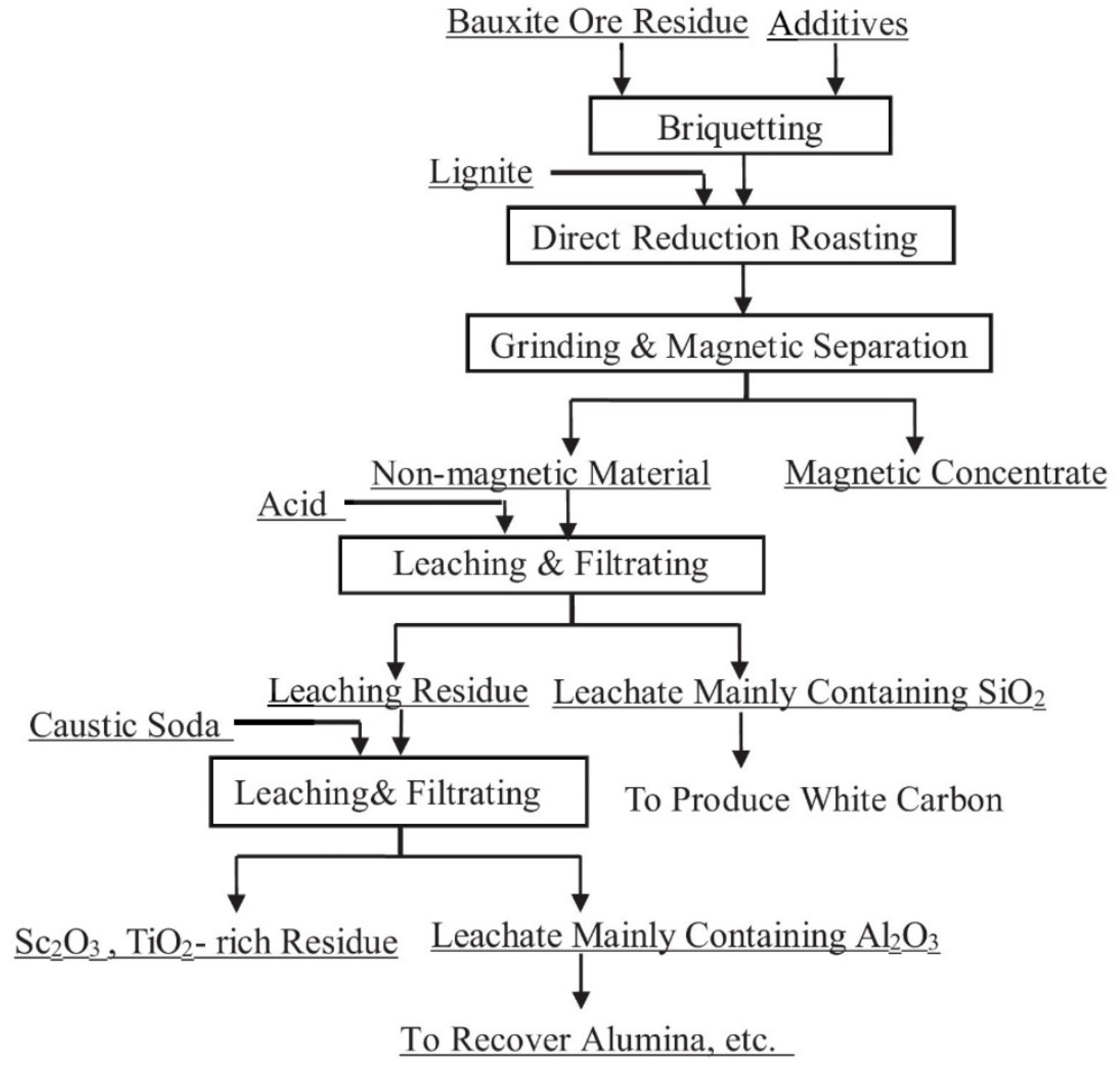
Deng et al. [41,84] suggest a multistage method of red mud treatment including the recovery of iron by solid-phase reduction with the addition of alkali metal salts followed by magnetic separation, leaching of the tailings by phosphoric acid, and pressure leaching of the residue by alkaline solution to extract Ti, Al, and Sc. Figure 2 shows the flowsheet of the proposed method.
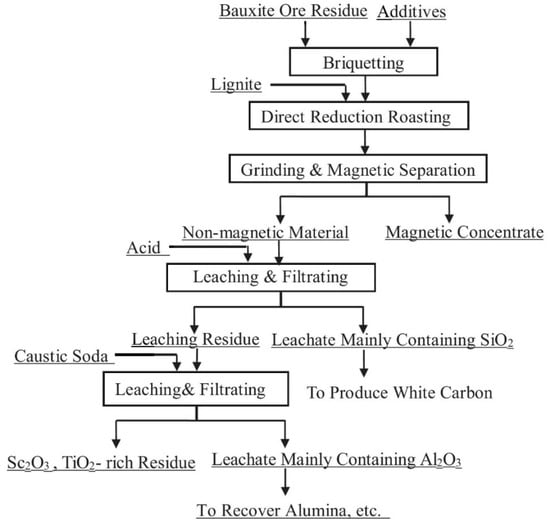
Figure 2.
The schematic diagram of comprehensive processing of red mud via reduction-alkaline roasting–magnetic separation–acid leaching–pressure alkaline leaching. Reproduced from [84].
The optimal conditions for the phosphoric acid leaching of the tailings with the dissolution of 78.06% SiO2, 44.63% Fe2O3, 29.23% Al2O3, and 42.03% CaO were temperature of 30–40 °C, acid concentration of 1–1.5 mol/L, duration of 40–60 min, and S/L ratio of 10–15 mg/L. Autoclave leaching of the acid residue, which contained the main part of Sc2O3 and TiO2, by 35–40% NaOH solution at 230–260 °C and S/L ratio of 8–10 mg/L for 90–120 min, dissolved above 95% of Al2O3, SiO2, and P2O5. The treatment of the obtained alkaline residue after the removal of Fe, Si, and Al by 8M H3PO4 solution at 150 °C led to the recovery of about 90% REEs, and no more than 2% Ti, which is negligible [85].
In the next study, Deng et al. [86] used phosphoric acid leaching to separate La2O3, Ce2O3, Sc2O3, and Y2O3 from the macrocomponents of red mud. After removal of 90% Fe from the red mud by reduction roasting at 1100 °C and magnetic separation, the obtained tailings were leached by 1.2 M H3PO4 solution at a liquid-to-solid ratio of 11 mL/g at 40 °C to separate REEs from silicon. It was found that during the reduction roasting of red mud, La2O3 and Ce2O3 enter the lattice of perovskite, which is highly resistant to acids at atmospheric pressure, and remain undissolved. Sc2O3 and Y2O3 were also partially entered into the perovskite lattice by 30% and 70%, respectively. The remainder of scandium and yttrium oxides with calcium and aluminum atoms remained in aluminosilicates that are almost insoluble at low concentrations of phosphoric acid, so they were almost fully in the residue. The authors noted that the advantages of this method are low energy consumption and low process cost.
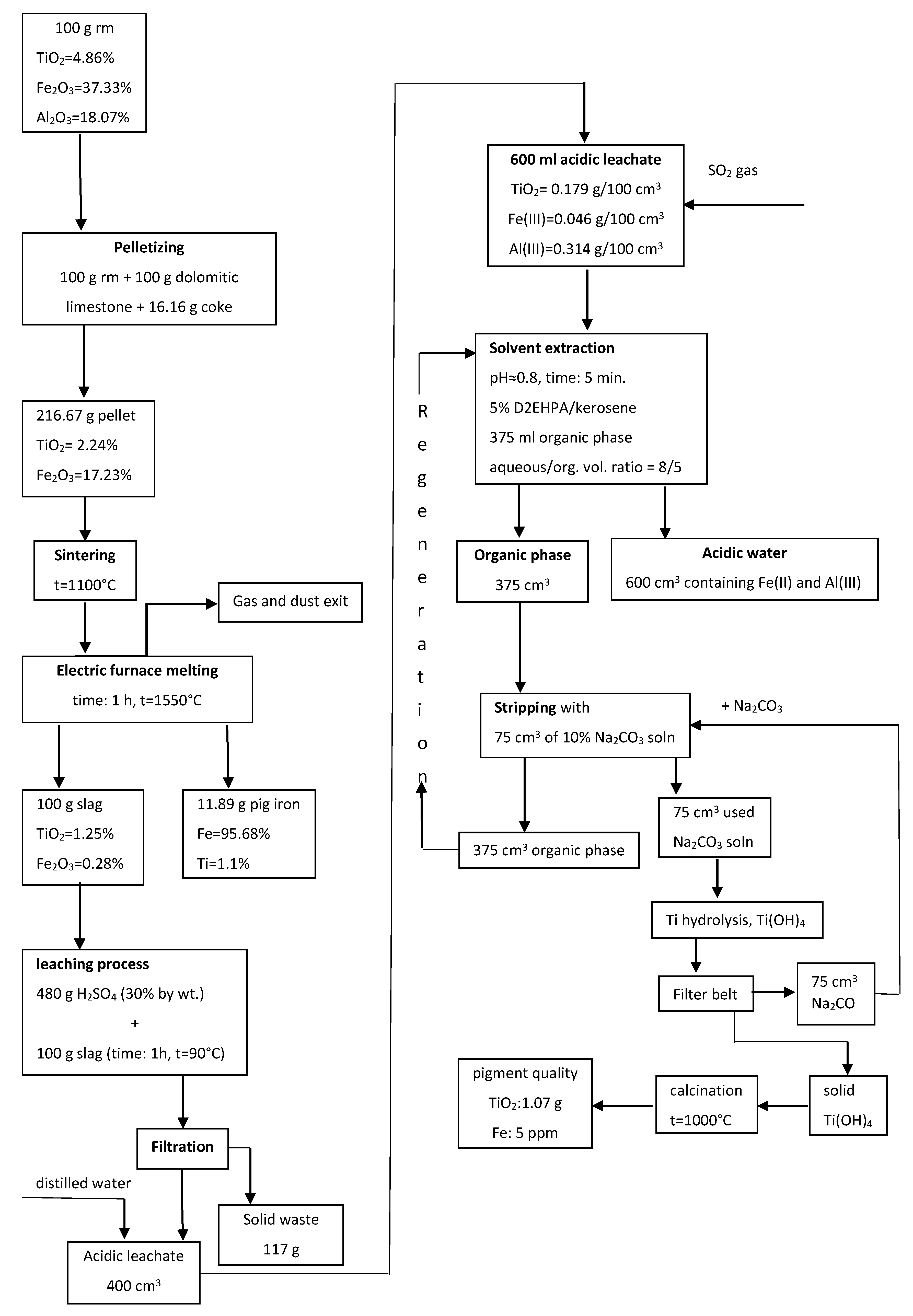
The application of phosphoric acid leaching to remove silicon from tailings is an alternative means of avoiding Si dissolution in conjunction with the sintering process in flowsheets based on alumina leaching using alkaline solutions. The disadvantage of this method is the loss of a portion of alumina during phosphoric acid leaching. A rather abrupt change of the reaction media from alkaline to acidic and vice versa casts doubt upon the prospects for the practical application of the suggested process due to neutralization of not only the soluble portion, but also the conversion of acidic compounds into the insoluble residue containing Sc and Ti. A more promising approach may be the use of a high-pressure acid leaching of the tailings after iron removal to extract Al and REEs into solution and concentrate Ti and Si in the leached residue [60]. Ercag et al. [87] developed a complex route for red mud processing, including its roasting with carbon, dolomite, and limestone; smelting of the roasted sample in an electric arc furnace with acquisition of pig iron and slag; leaching of the slag by sulfuric acid; and treatment of the leached solution by solvent extraction. After the leaching of the slag, the main portion of Ti and Fe passed into solution. Then solvent extraction of Ti by 5% D2EHPA in kerosene treatment of organic phase by Na2CO3 solution, titanium hydrolysis, and calcination of precipitate to obtain a high-quality TiO2 pigment were carried out. Figure 3 presents the flowsheet of this process.
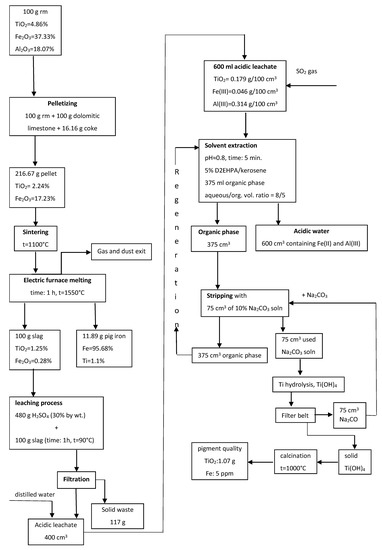
Figure 3.
The schematic diagram of comprehensive processing of red mud via reduction roasting–smelting–sulfuric acid leaching–solvent extraction. Reproduced from [13].
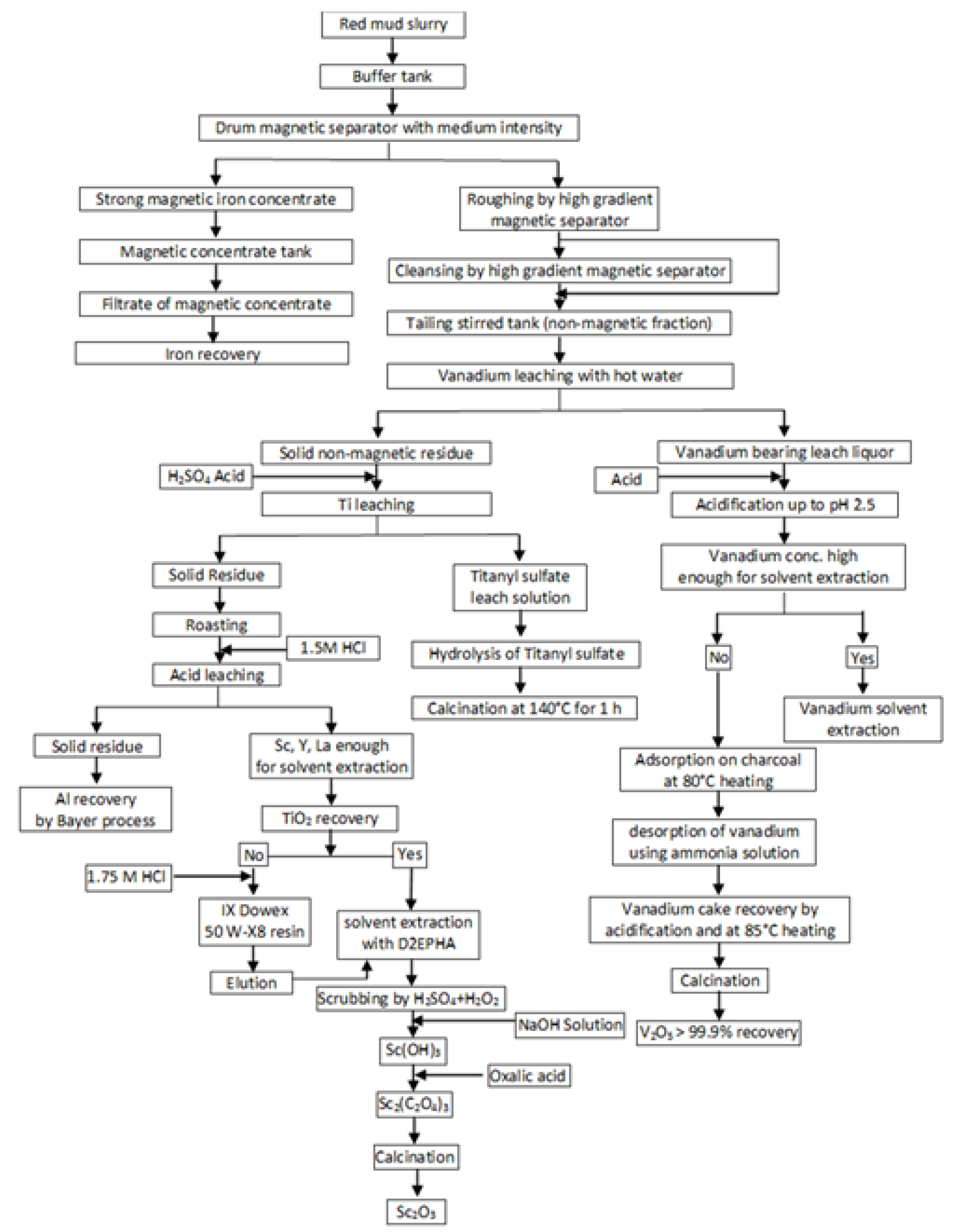
This process was one of the first developed complex methods for red mud processing. The main benefit is the acquisition of two products, namely, pig iron and pigment quality TiO2. It should be noted that the main distinction of pigment titanium dioxide obtained using the sulfuric acid scheme is its increased whiteness compared to that obtained by hydrochloric acid technology, which significantly improves physicochemical properties of TiO2 dioxide. The disadvantages are high consumption of fluxes, which leads to an increase in acid consumption, loss of part Ti due to its passing into pig iron during reduction smelting, and silica gel formation during sulfuric acid leaching. The application of aryl phosphoric acid, which is widely used in nonferrous metallurgy for the extraction of metals with high distribution coefficients, requires selectivity of the extraction-stripping conditions and the use of strong acids as stripping agents. A disadvantage in such extraction system is increased emulsification without a preliminary preparation of the initial solution with a demulsifying liquid. The authors also note that after titanium re-extraction with a carbonate solution, it is necessary to regenerate the extractant before reuse by treatment with a sulfuric acid solution. Information on the behavior of REEs is absent. Swain et al. [15] analyzed a large number of publications and proposed a flowsheet based on physical separation and hydrometallurgical approaches for the recovery of valuable elements from red mud. Figure 4 shows the flowsheet of the developed process. The first stage is iron recovery by several sequential stages of magnetic separations. After the magnetic separation, a non-magnetic fraction treatment by leaching using hot water with the extraction of vanadium into solution is used. Vanadium can be extracted from the solution by different methods depending on its concentration. Titanium can be extracted from the non-magnetic fractions by sulfuric acid with acquisition of TiO2 after hydrolysis and calcination. The residue after sulfuric leaching was treated by roasting and hydrochloric acid leaching. The obtained solid residue recycles in the Bayer process for Al recovery. Solvent extraction of the solution using D2EHPA, scrubbing by H2SO4 + H2O2 solution, sequential NaOH solution and oxalic acid treatment, and calcination led to the acquisition of Sc2O3. The main new proposals in this flowsheet are the use of physical separation for iron extraction and the inclusion of leaching of vanadium by hot water in the scheme. An application of physical separation for the extraction of iron is an alternative route for iron recovery compared with pyrometallurgical methods and oxalic acid leaching with lower costs, but the effectiveness of this method may be low. The authors consider that the proposed route can be cost effective, but experimental verification, economic estimation, and optimization are required.
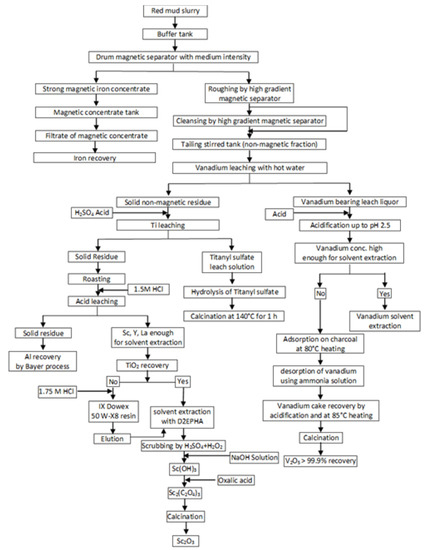
Figure 4.
A conceptual route for recovery of valuable elements from red mud. Adopted from [15].
Kounalakis et al. [88] considered a method of red mud processing that potentially allows the acquisition of compounds of sufficiently high purity, namely 95–99% Fe2O3, 85–94% Al2O3, 90–100% CaCO3, 100% Na2O3, and 82–85% TiO2. Authors proposed a method consisting of hydrochloric acid leaching of red mud with the acquisition of iron, aluminum, sodium, and calcium chlorides, and sequential leaching of the solid residue enriched by titanium and silicon. According to this method, to obtain hematite, the salt solution is sequentially treated by hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid with the addition of metallic scrap, and sodium hydroxide. Hydrogen peroxide is used for the solid residue treatment to remove silicon, and is then leached by sulfuric acid. Titanium and aluminum compounds are precipitated from the obtained solution, then calcium sulfate is also precipitated by the addition of the solution of ammonia with calcium chloride. Preliminary economic estimation has shown that the processing of 32 tons of red mud per day can result in the income of EUR 2,615,883 after the 3rd year. The estimated net private value was EUR 21,364,732. However, it should be noted that this method has not been experimentally tested.
6. Recovery of Elements from Red Mud Leaching Solutions
Leaching of red mud, tailings, and slag after iron removal represents a solution that comprises multiple components. Recovery of solution components is a difficult task, so selective precipitation methods are often infeasible or economically ineffective. Therefore, many studies focus on the use of sorption and extraction methods for the recovery of valuable components from the solutions obtained during leaching of red mud or slags, and tailings after iron is removed.
6.1. Extraction Methods
Extraction systems of water-immiscible organic solvents containing complexing reagents are mainly suitable for selective extraction and separation of metals from the solutions of red mud acid leaching. Currently, the studied and available extractants are tributyl phosphate (TBP), tri-n-octylphosphine oxide (TOPO), di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (D2EHPA or DEHPA), amyl phosphonates, and quaternary ammonium salts with aliphatic substituents, in addition to alcohol esters, alcohols, and kethones dissolved in kerosene, toluene, octanol, trichloromethane, and other hydrocarbons.
Boudreault et al. [89] proposed the method of separation of iron (III) and aluminum from the hydrochloric acid solutions, which were obtained by leaching of aluminum-containing materials including red mud. The first stage is the treatment at pH = 1–2.5 by the mixtures of heptane and derivatives of phosphoric or phosphinic acids, namely D2EHPA, bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl) phosphinic acid, and 2-ethylhexyl phosphonic acid mono-2-ethylhexyl ester, at a volumic ratio organic phase/aqueous phase (O/A) of about 1/1 with extraction up to 98% Fe. To recover iron, the reverse extraction at O/A ratio of about 1/0.5 by 2–6 M HCl was carried out. The second stage is the treatment at pH = 2.5–3.5 by 20% heptane solution of bis (2,4,4-trimethylpentyl) phosphinic acid (Cyanex 272) at O/A ratio of 1/3 with extraction up to 90% Al. Wang et al. [90] used the mixture of 5–7% TBP, 20–28% secondary octanol, 15–25% sulfonated kerosene in weight for recovery of iron from hydrochloric acid red mud leaching liquor. The stripping by 0.5 M NaOH solution at O/A of 2–3/1 followed by iron hydroxide precipitation and drying led to the acquisition of high-purity iron oxide.
Zhang et al. [91] suggested 30% methyltrioctylammonium chloride solution in octanol, which is known as Aliquat 336, for iron extraction in the form of anionic complex FeCl4− in a strongly acidic medium. Accompanying metals, namely Al, Zn, Cu, Mg, Ca, Na, Ti, Sc, Y, Nd, Ce, and La, fully remained in the raffinate, which was further treated for scandium extraction by 5 vol. % D2EHPA; increase in D2EHPA concentration to 25 vol. % resulted in Ti and Y separation from Al and other REEs. The organic phase Aliquat 336 with up to 100 g/L Fe content was treated by 1.5 M NaH2PO4 solution to re-extract iron in the form of a phosphate complex [92]. Aliquat 336 was efficiently able to re-extract iron for six cycles.
The optimal parameters for the extraction of REEs and retention of aluminum in the raffinate from the hydrochloric acid red mud liquor after precipitation of the main part of iron at pH = 3 were calculated using mathematical modeling. The best REE extraction and stripping degrees were obtained at O/A ratios of 0.1 and 0.67 using 0.78 M D2EHPA solution in kerosene and 4–3.8 M HCl solution, respectively. As a result, 87% Fe was separated in the first stage, 33% Al remained in the raffinate, and 79% REEs from 58% of the previously leached red mud was recovered for further processing. Even this degree of red mud processing with incomplete recovery of the valuable components has been found to be cost effective [93]. Zhou et al. [94] showed that co-use of hydrochloric acid and EDTA solutions in optimal ratios is thermodynamically favorable for the selective extraction of scandium. The leaching tests led to recovery of 79.6% Sc and 6.12% Fe.
The red mud treatment using a controlled HCl concentration at this stage can lead to selective leaching of yttrium and calcium with significantly less dissolution degree of other components [95]. Yttrium was selectively recovered from the leachate by the extraction using 25% D2EHPA in kerosene at an O/A ratio of 1/3 in the presence of iron turnings, which promoted the reduction of Fe(III) to Fe(II) without reducing the extraction capacity of the extractant with respect to yttrium. Stripping was carried out by 200 g/L H2SO4 solution containing 10 g/L NaCl in 4–6 steps followed by the precipitation of oxalates and their calcination to yttrium oxide. In another paper [96], stripping was carried out by a dilute solution of hydrofluoric acid or solutions of fluoride salts, e.g., NH4F and KF, in one stage to obtain a suspension of yttrium fluoride followed by its separation and washing.
Zhu et al. [97] suggested the addition of 2.5–7.5% CaF2 during sulfuric acid leaching of red mud to increase scandium recovery up to 92%. Wang et al. [98] almost fully extracted Sc and partially extracted Al and Fe from a leached solution using a mixture of 10% D2EHPA and 5% TBP in sulfonated kerosene at pH = 0.1 for 4 min. Solid-phase stripping using 2 M NaOH solution resulted in scandium separation as hydroxide from Al and Fe impurities in the raffinate. Sc2O3 of 99% purity was obtained by calcination of the oxalate, which was re-precipitated from 2M H2SO4 solution.
Liu et al. [99] found that the addition of 15 vol.% isooctyl alcohol during the D2EHPA extraction reduces the efficiency of scandium extraction from 1 M H2SO4 solution, but promotes its separation from titanium and zirconium with separation factors of 34 and 494 for Sc/Zr and Sc/Ti, respectively. Ochsenkühn-Petropulu et al. [100] selectively separated scandium from yttrium and heavy lanthanides at pH = 0 by 0.05 M D2EHPA in hexane, and in the second stage extracted La and Ce by an increase in D2EHPA concentration to 1 M at pH = 1.5. Phosphine extractants Cyanex 923 and Cyanex 301 in hexane under certain conditions showed a high selectivity for cerium and lanthanum with respect to iron from 1 M HCl solution [101].
Li et al. [102] studied autoclave leaching at 120–140 °C by 6–8 M H3PO4 solution for 60–90 min and achieved the dissolution of 94% Sc, 50% Ca, 42% Ti, and over 90% Al and Fe. The extraction by 2% EDTA at an O/A ratio of 1/3 led to a better separation degree of Sc from Fe and Al from the obtained phosphate solutions compared with hydrochloric, sulfuric, and nitric acid solutions. At pH = 1.8, the scandium extraction degree was 98.64% with the Sc/Fe and Sc/Al separation factors of 2703 and 230, respectively.
Zhu et al. [103] extracted more than 96% of scandium, vanadium, aluminum, and iron at pH = 1.9 from a hydrochloric acid solution using a mixture of 15% mono(2-ethylhexyl)2-ethylhexylphosphonate (P507) and 5% TBP in sulfonated kerosene. Vanadium was re-extracted using 2 M H2SO4 with its precipitation from the solution as vanadium oxide. Scandium hydroxide suspension was obtained from the organic phase by the treatment using 2 M NaOH. The next stage was the addition of 20 g/l of Na2SO4 in the organic raffinate and stirring for 5 min. The aging of the pulp at pH = 5.0 for 4 h with vigorous stirring and heating to 50 °C resulted in precipitation of a mixture of aluminum and iron chlorides, which were separated by filtration. The aluminum and iron recovery degrees from red mud were 83% and 52%, respectively.
To extract scandium from leaching liquors, Onghena and Binnemans [104] suggested the application of ionic liquid–betainium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide [HBet][Tf2N], which forms a homogeneous system in aqueous solutions above 55–65 °C and stratifies with a decrease in temperature. The conditions for the extraction of above 95% Sc and up to 80% Fe from hydrochloric acidic and nitrate media of pH = 1.5–4 with their separation from non-ferrous metals and REEs (Y, La, Ce, Nd, Dy) were determined both with and without heating. Scandium stripping was carried out by the treatment using 1.5–2 M HCl solution or by precipitation of the oxalate. To separate scandium and iron (III) during the extraction by [Hbet][Tf2N] at pH = 2.5 from a sulfate solution, reduction by ascorbic acid to iron (II) was carried out [105]. To remove impurities, such as calcium and aluminum, a three-stage treatment by hydrochloric acid solution was used until reaching a pH of 1.7, and then stripping by 6 N H2SO4 solution was performed. However, due to significant contents of the main red mud components—Al, Fe, Ti, Ca, and Si—there was no selective extraction of scandium and other REEs.
Zhang et al. [106] increased content ratios of Sc/Fe and Sc/Al by 8.8 and 265 times, respectively, in nitric acid solution, thus obtaining 91.1% Sc recovery by a single treatment using hydrated titanium phosphates. The application of sodium sulfite as a reducing agent considerably decreased simultaneous recovery of Fe3+ with scandium.
Despite the search for new extractants, the majority of authors have used the most common extractants and solvents, which often have toxic properties [10]. In addition, the processing of large volumes of red mud or acidic leaching liquors leads to irrevocable consumption of expensive reagents and technological problems associated with the formation of the third phase—emulsion or suspension—which hinders the separation of the organic and aqueous phases and results in losses of the extracted component.
6.2. Sorption Methods
The application of sorption processes for the red mud treatment provides a selective recovery of target elements by the materials based on an inert polymer matrix or inorganic hydroxy-hydroxide compounds, either from leached solutions, mainly acidic (H2SO4, HCl, HNO3, and their mixtures), or from leaching slurries containing both sludge and sorbent in a dispersive aqueous medium. Currently, various cation and anion exchangers, in addition to ampholytic resins, have been developed containing organophosphoric, phosphonic, phosphine, carboxylic, sulfonic, nitro, amine, and other functional groups and their combinations (−POOH, −COOH, −SO3H, −NH2, etc.), which are selective to one or a group of ions. The type of ion exchanger chosen depends on the recovered metal, the composition of the medium and impurities, and the need for selective or group separation, which ultimately determines the total recycling degree of red mud. Therefore, a wide variety of sorption processes and materials has been developed to date that can be successfully used for the treatment of different raw materials, mainly for the recovery of the most valuable rare metals.
For example, Deep et al. [107] investigated sorption of Ti4+ in the presence of Fe3+, Zr4+, and Th4+ from 1 M HCl solution with its separation from V5+, Ce4+, Al3+, Ga3+, Mg2+, and Mn2+ ions by bis-(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)mono- or dithiophosphinic acids (Cyanex 301, Cyanex 302) impregnated on silica gel. Subsequent elution by the mixture of 3% H2O2 in 0.5 M H2SO4 enabled separation of Ti4+ from the cations Fe3+, Zr4+, and Th4+, which are washed out by oxalic acid solution followed by regeneration of the sorbent. This process can be combined with hydrochloric acid leaching of red mud or ilmenite.
The recovery of scandium by nitrogen- and phosphorus-containing ampholytes (AFI-21 and AFI-22) after direct leaching of red mud using sulfuric acid was developed similarly to the processing of poor uranium ores with subsequent separation of radioactive and valuable components [29]. The capacity of the resin was 0.04–0.15 g/dm3 of scandium with simultaneous uranium recovery, and the yield after desorption by 150 g/dm3 Na2CO3 solution for scandium was up to 80%. The capacity of the used resins was significantly reduced at high concentrations of Al, Fe, Ti, and Si. Smirnov et al. [108] increased the recovery degree of scandium to 28.6% by a sorption process from pulp with direct contact with slurry using a KU-2 gel cation exchanger with direct contact with slurry at pH = 1.3–1.7 and sorbent/red mud slurry ratio of 1/20–50. Scandium, yttrium, and aluminum recovery degrees from the slurry were 48%, 42%, and 29%, respectively, with application of multiple desorption by the same solution containing 100 g/L Na2SO4 and 30 g/L H2SO4. Removal of aluminum from the collective Al-REE concentrate by an alkaline solution enabled acquisition of a concentrate 15–20-fold richer in REEs, including yttrium, and to recycle the aluminate solution to alumina production.
Dostova and Salnikova [109] achieved 100% of REE recovery in HCl solution with total dissolution degree of 60% after preliminary treatment of red mud by ammonium chloride to dissolve calcite. A KB-4 carboxyl cation exchanger in the form of NH4+ was used for REE sorption. KB-4 has a higher capacity than the KU-2 sulfonic cation exchanger due to not only electrostatic interaction with sulfogroup, but the formation of strong bonds with carboxyl groups. To increase the selectivity, Fe(III) and Al impurities were converted into the hydroxide form by neutralization with ammonia to pH = 6.2–6.5. Divalent metals have no effect on the REE recovery. The disadvantage is the fact that three days of contact of the phases led to losses up to 25% of REEs due to their coprecipitation with iron and aluminum hydroxides.
Mechanical activation of red mud slurry in the sulfuric acid solution of pH = 1 and S/L ratio of 1/3 in a bead mill for 10 min, and the processing of the sorbent with impregnated phosphoric acid ester inside the pores by a mixture of hydrofluoric and sulfuric acid solutions before desorption, makes it possible to more efficiently recover and separate scandium from most of accompanying macrocomponents [110]. To obtain a scandium concentrate, desorption after previous treatment was carried out by suspension of 1–10 g/L calcium fluoride in 10 g/L hydrofluoric acid due to a more complete coprecipitation with CaF2. The REE recovery from the scandium-depleted pulp was performed by the same macroporous sulfo cation resin after scandium desorbtion. Elution of REEs by an ammonium sulfate solution was proposed after a treatment by 50 g/L sulfuric acid. The recovery degrees of scandium and other REEs were 62–64% and 66%. The selectivity of scandium and REE recovery from multicomponent sulfuric acid solutions of red mud leaching is likely due to careful observance of the selected technological parameters and choice of the appropriate sorbent type. The technological difficulties of sorption from the pulp are possible resin losses at the stages of solid phase separation, in addition to contamination of the pore space due to physical adsorption of poorly soluble compounds, which leads to a decrease in capacity. In this case, the stages of preliminary washing of the resin before desorption of the target component allow satisfactory separation and selective recovery of metals, but significantly increase the material flows of solutions of various compositions.
The stepwise leaching of carbonate–hydrocarbonate slurry in a countercurrent mode led to an increase in scandium recovery up to 47.8–50.1% compared with carbonization no more than 30–40%. At a slurry/resin ratio of 10–80/1 and S/L ratio of ¼, the capacity of phosphorus-containing Na+ form of the Lewatit TP-260 ion exchanger for Sc was 0.33% [111]. The possibility of scandium recovery from model red mud leaching liquors allowed determination of its predominant interaction with phosphorus-containing functional groups of other ampholytes based on a styrene-polyacrylate copolymer [112]. The application of a saturated solution of 450 g/dm3 Na2CO3 with a yield of 96% resulted in a concentration of 275 mg/dm3 Sc2O3 in the desorbate. To extract scandium from sulfate pulp with pH = 1.8–2.0, several types of phosphorus-containing ion exchangers of gel and macroporous structures were tested. The scandium content in the most promising sorbent Purolite S957 was increased to 9%. Among the resins tested during the recovery from phosphate solutions—Tulsion CH-93, Purolite S940, Amberlite IRC-747, Lewatit TP-260, Lewatit VP OC 1026, Monophos, and Diphonix—aminophosphonic IRC-747 and aminomethylphosphonic TP-260 were identified as the most promising [113].
Polymeric materials based on polystyrene divinylbenzene (PS-DVB) have shown resistance to extreme pH conditions and high mechanical strength, which makes them suitable for use in highly acidic media. Nonetheless, a significant disadvantage of the reagent-impregnated resins is their washing out by acid solutions, which leads to a decrease in the total process efficiency. Microencapsulated extractants, also named solid extractants (SE), can be more stable in this regard; the synthesis of the styrene-divilylbenzene polymer in SE is performed simultaneously in the presence of D2EHPA, TBP, crown ethers, or other reagents [114]. However, for selective recovery and separation of REEs using SE, a strongly acidic medium up to 8M HCl or 6M H2SO4 is recommended, which significantly limits the technical feasibility of this approach [115,116].
Avdibegovic et al. [117] showed via a simulation of scandium sorption from hydrochloric acid and nitrate solutions that the highest efficiency only occurs in the presence of equimolar amounts of ions, namely Fe3+, Al3+, and Ca2+. The sorption materials were prepared by impregnating ionic liquid–betainium sulfonyl(trifluoromethanesulfonylimide) on Amberlite XAD-16 resin or silicon dioxide; the reagent [Hbet-STFSI-PS-DVB] was synthesized from the initial materials by swelling a sulfonyl chloride resin in an organic solvent to promote the formation of chemical bonds between the functional groups and the polymer. The studied metal phosphate ion exchangers proved to be as non-selective for Sc3+ from HCl and HNO3 solutions as REEs such as Dy, Nd, and Y. Due to the formation of stable sulfate complexes, scandium was desorbed with a high efficiency by 1 M H2SO4 solution with a four-fold concentration at an initial content from 0.2 to 5.6 mmol/L Sc. Selective separation of scandium and other REEs (Dy, Nd, Y) over base metals, namely Fe, Al, and Ca, from the leached red mud nitrate and sulphate solutions was proposed using [Hbet-STFSI-PS-DVB] by column chromatography [118]. Scandium was desorbed from all media during competitive complexation by the phosphoric acid solution at pH = 2.0–2.5. Stepwise elution through sorption columns of nitric and phosphoric acid solutions with pH control enabled separation of almost all metals contained in red mud with the sequence of elution: Sc(III) > Fe(III) > Ca(II) > Al(III) > Dy(III) ≈ Y(III) > Nd(III).
Zhang et al. [119] suggested the use of anionite D201 containing quaternary ammonium groups (–N (CH3)3+) for the anion-exchange separation of microquantities of scandium and an almost 2000–3000-fold excess of iron from a strongly acidic medium with the separation coefficient of β = 1348. The maximum adsorption capacity for iron was 147.06 mg/g, and it was only 0.95 mg/g for scandium. More than 96% Fe was sorbed in the form of the anionic complex FeCl4− from 9 M HCl solution in the presence of 3 M CaCl2 for 4 h with no more than 2% of scandium recovery. An increase in the amount of ion exchanger of more than 10 g per 100 mL of the solution led to losses of scandium with the organic phase and a ten-fold decrease in the capacity of the resin for iron to 14.54 mg/g. Iron was desorbed to a concentration of 35 g/L by dilute HCl solution of pH = 2. The resin could be reused without additional treatment. Calcium, sodium, aluminum, and titanium remained with scandium in the aqueous phase; further separation of Sc, Ca, Na, Al and Ti was not studied.
As a result of red mud leaching by 3 M HCl in the presence of 0.5 wt.% NaClO3 at 50 °C for 12 h, Zhu et al. [120] obtained a solution with pH = 1.47 containing (mg/L): 120 V, 15 Sc, 464 Fe, 1376 Al, 2645 Ca, 3324 Na, and 664 Mg. The recovery of vanadium anions by anion exchangers D201 (–N–(CH3)2C2H4OH), 201 × 7 (–N(CH3)2), and D452 (–N–(CH3)-H2O) with pH increasing to 1.8–2.4 was 99.5%, 82.6%, and 76.4%, respectively. These conditions can contaminate the ion exchanger due to physical sorption of iron hydroxide particles that form in small quantities. After washing the ion exchanger with distilled water to remove iron compounds, vanadium was desorbed using the mixture of 3% NaOH and 8% NaCl followed by crystallization of ammonium vanadate. After vanadium recovery, the extraction was carried out at pH = 0.2 and O/A ratio of 1/10 for 6 min using the mixture of 15% P507 and 5% TBP in kerosene, which is widely used for REE recovery. Almost 100% of scandium was selectively separated with a minimum amount of iron and aluminum impurities.
Zhou et al. [121] found that activated carbon modified by TBP is a satisfactory sorbent for scandium from hydrochloric acid red mud liquors with a dosage of 6.25 g/L and 40 min of adsorption time. An increase in the amount of sorbent leads to a decrease in selectivity and recovery of all red mud components, especially titanium. A strong acid 732-type sulfonic cation exchanger based on polystyrene matrix showed selectivity to scandium at pH 1–3 according to the sequence: Sc > Fe3+ > Al > Ca > Zr > Ti > Si [104]. As a result of the two-stage ion-exchange separation, 95–100% of Fe3+, Ti, Al, Ca, Zr, and Si can be removed from the hydrochloric acid red mud liquor.
Authors such as [122,123] studied the effect of electrodialysis on the sorption process using sulfonic cation resin Neospeta CMX and Neosepta CMB from hydrochloric acid red mud liquors in the presence of complexones, namely, nitriloacetic, ethylenediaminetetraacetic, and citric acids, which led to a considerable change in the cation mobility of metals such as Al, Fe, Ti, and Na. A significant decrease in the permeability of the formed complex compounds was used to separate metals. A significant decrease in flux of the formed complex compounds was used for the recovery of metals. A problem with this approach is the regeneration and reuse of costly complexonates.
It should be noted that improvement of the selectivity of the main part of the extraction and sorption methods requires a significant increase in the concentration of the acids used for the dissolution of the metals of red mud. This change in the medium is used to control the specific behavior and properties of one or a group of extractable ions. The variation of the phase ratio enables a significant increase in the concentration of metals in the solutions. Nevertheless, active reagents such as phosphorus, nitrogen, and sulfur-containing aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons remain relatively stable in both methods for a long time, which requires almost individual selection of extraction parameters depending on the ratio of target metals. Hence, it can be inferred that the composition of solutions and liquids of red mud, the kind of acid, and the acid concentration play a significant role in effective leaching of elements from red mud. In the review [9], it was opined that the solvent extraction and sorption could be a suitable option for the purification and recovery of metals from leach liquor, but the approach needed to be developed to reach its feasibility.
7. Bioleaching
There are several papers devoted to the research of leaching of various elements from red mud using biological organisms [124,125]. The main advantages of these methods are low cost, low energy consumption, and environmental friendliness [126].
Qu et al. [127] investigated the process of bioleaching of heavy metals from red mud using the fungus Aspergillus niger. The highest leaching ratio of valuable components was observed at an S/L ratio of 1/100 g/mL. The main active substance in this case was citric acid. The leaching degree of heavy metals was as follows: 80% Pb, 80% Zn, 67% Cu, 50% Ni, 44% As, 31% Ba, 26% Cr, 11% Fe, and 11% Zr. Vakilchap et al. [128] showed that treatment by Aspergillus niger fungus leads to recovery of 69.8% Al, 60% Ti, and 25.4% Fe at an initial red mud concentration of 1% and holding time with the fungus of 30 days. A strong negative relation was revealed between the biomass of Aspergillus niger fungus and pH value [129]. At continuous leaching the system can reach a steady state with the red mud concentration in the pulp of 10% and pH < 3. Compared to leaching by organic and inorganic acids, this method proved to be cost effective at a laboratory scale. At a temperature of 30 °C and holding time of 96 h, 31% Ga, 33% Ge, 19% V, 30% Sc, 16% La, 23% Eu, and 44% Yb were recovered. The use of Penicillium tricolor fungus for REE recovery showed a good survival level of microorganisms mixed with red mud [125]. The main active substances were oxalic and citric acids. The maximum recovery degrees of REEs were achieved in a one-stage biological leaching process with 2% of red mud in suspension. However, the highest recovery degrees were obtained in a two-stage process with 10% of red mud.
Čížková et al. [130] used green algae, Desmodesmus quadricauda, Parachlorella kessleri, and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, for the intracellular accumulation of lanthanides from red mud. The rate of lanthanide accumulation was 27.3 mg/kg per day at a red mud content of 0.1%. Increasing the red mud content led to a decrease in the accumulation rate. The concentration of Ce, La, and Nd in Desmodesmus quadricauda alga reached 22.5%, 11.9% and 10.1%, respectively; the other algae were less effective. Lanthanides are mainly distributed in chloroplasts and in the cytoplasm of algal cells. The biomass of algae enriched in lanthanides can be used as a fertilizer or for the recovery of absorbed elements by chemical methods.
Qu et al. [131] studied the recovery of major, rare-earth, and radioactive elements from red mud using Acetobacter bacteria. The advantage of bacteria compared to fungi is the lower risk of environmental pollution and less required content of biomass for an efficient leaching process. The total amount of organic acids (acetic, succinic, fumaric, lactic, malic, oxalatic, tartaric, and citric) excreted by Acetobacter increases with an increase in the density of the red mud pulp. After biological leaching, the contents of hematite and gibbsite in red mud were decreased, but a new phase of weddellite Ca(C2O4)·2H2O was detected. The results showed that in the one-step process and with pulp density of 2%, the leaching ratios of Al, Lu, Y, Sc, and Th were 55%, 53%, 61%, 52%, and 53%, respectively.
The disadvantage of bioleaching methods is the long duration, both of the cultivation process of microorganisms and the leaching process. In addition, bioleaching processes have a low selectivity [132]. The conducted research has shown that a red mud content of about 0.1–1% is favorable for the bioleaching process, and the process duration varies from several days to several weeks. These conditions limit the large-scale application of bioleaching technologies.
8. Discussion
To date, numerous studies have shown the technological possibility of the recovery of almost all elements from red mud using only hydrometallurgical methods, or their combination with pyrometallurgical and physical methods. However, the proposed approaches have yet to be applied in industry. This is mainly due to an insufficient study of the cost effectiveness of the proposed processes, and testing of most of the approaches only at a laboratory scale, which complicates the choice of technology. Moreover, it should be noted that the effective means to increase the utilization degree of red mud involves a significant increase in its storage cost. According to estimations, the cost is 9–20 USD per ton [23], which prohibits alumina producers from investing in red mud recycling. Considering the negative effects related to red mud storage on the environment and society [133], additional stimulation of alumina producers via an environmental charge for damage is required.
It should be noted that the processes proposed for red mud processing should not only be cost effective, but also comply with ever-increasing environmental requirements, meeting the general principles of green chemistry and sustainable development. These requirements can be described as follows:
- Atmospheric pressure and minimal practicable temperatures should be used for the recovery of valuable components.
- Process flowsheet should include a minimum number of stages.
- CO2 emission in all stages should be minimized
- The application of the most available and cheapest reagents.
- The concentration of reagents for leaching should be minimal.
- If possible, reagents should be replaced with waste from other industries
- All reagents should be regenerated as much as possible and recycled.
- The alkali contained in dump red mud should be recycled to the main process of alumina production.
- Obtained by-products and wastes must be recycled.
- Easy variability of products and technology stages.
- Required recovery of the most valuable and high-margin components, especially scandium and titanium.
- Low capital costs of the process.
- The acquisition of high-demand goods.
Currently, none of the emerging processes fully comply with the above listed requirements. Almost full dissolution of red mud components during leaching by inorganic solvents necessitates undertaking processes at high temperatures, pressures, and concentrations of lixiviants, which, in addition to a high recovery degree, lead to low selectivity. This circumstance has led to the need for development of comprehensive methods, which combine pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical stages.
Borra et al. [134] describes certain economic assessments of the application of various methods for red mud processing. The cost analysis of the processes of recovery of valuable components from red mud by various methods has shown that direct leaching of elements generates the lowest margin, in addition to a large amount of secondary wastes. It is more promising to reduce the cost of obtained products by iron recovery using smelting, followed by leaching of the slag. The favorable factor in this case is the supplementary possibility to influence the composition and solubility of the obtained slags by changing their cooling rate and addition of fluxes. Calcination before slag leaching, which enables dissolution of expensive titanium and REEs, can provide the cost reduction to an even greater degree. At the present time, scandium recovery has the largest impact on margins compared with other REEs. The use of the combination of methods of sulfating, roasting, and selective leaching [135] has shown approximately the same effect on the increase in the profit margin with recovery of scandium and other REEs separately, compared with the combined recovery of REEs and major metals. The best option for increasing the profit margin is the coupled recovery of major metals and scandium using a combination of calcination, carbonation, and subsequent leaching methods.
Hatzilyberis et al. [136] considered economic aspects of scandium recovery in the case of its leaching from Greek red mud by 96–98% H2SO4. The specific recovery of scandium was proven to be a key variable for cost-benefit evaluation of the leaching process. This value is directly proportional to the leaching yield, and scandium content in red mud and in leached solution, and is inversely proportional to the S/L ratio and the total acid consumption. Despite the high price of scandium, a process focused on its recovery can be considered as ineffective due to both economic and environmental reasons because, in this case, the amount of dumped red mud remained almost the same. Moreover, the generated waste is no less hazardous to the environment than the original red mud.
Agrawal et al. [137] performed a comparative study with a cost analysis of different red mud treatment routes, such as direct hydrochloric acid leaching, leaching with milling pre-treatment, HCl leaching after alkaline microwave roasting, or after carbothermic microwave roasting followed by magnetic separation. It was found that the maximal net cash flow was the direct acid leaching approach, whereas leaching after alkaline microwave roasting resulted in a negative net cash flow. A preliminary mechanical activation leads to a significant increase in processing cost due to the increase in energy consumption.
Joyce et al. [138] used a life cycle assessment (LCA) approach to estimate the environmental impact of different red mud processing methods. Analysis of several proposed processes has shown that it is necessary to consider the influence of these processes on other industries. For example, the use of a residue after metal extraction from red mud for production of construction materials leads to a significant decrease in the climate change impact due to a partial substitution of conventional charge. It is necessary to use this method more widely for the development of more eco-friendly processes for red mud recycling, considering not only economic viability, but also the environmental balance of a process and its influence on other industries [23,139].
The main component of red mud is iron, so it is expedient to extract it to obtain a high-demand product—cast iron or iron concentrate. To minimize CO2 emission, iron reduction by hydrogen is preferable [140]. It is also reasonable to use carbon-containing wastes [141] for iron reduction to minimize raw material consumption. Slag or tailings from magnetic separation enriched in aluminum, titanium, and scandium can be further processed using acid or alkaline leaching technology. In this case, effective dissolution of aluminum can be achieved by acid leaching, and scandium recovery can be achieved by sorption methods; acid wastes can be used to reduce acid consumption [142]. To minimize the formation of silica gel during red mud leaching by sulfuric acid, it is preferable to use the sulfatization method, the addition of hydrogen peroxide, leaching by ammonium sulfate with recovery of scandium from the solution both by sorption or extraction methods, or precipitation of hardly soluble hydroxide, phosphates, or oxalates. A promising, but insufficiently studied, method is the recovery of valuable components from leached red mud solutions using ionic liquids. The residues obtained after the extraction of valuable components are most advisable to be used for production of construction materials.
9. Conclusions
A review of methods using liquid media for recycling of red mud, which is a toxic waste product of the alumina industry, has shown that it is a valuable raw material for the recovery of REEs, particularly scandium, in addition to iron, aluminum, and titanium. The review highlighted that despite the numerous studies undertaken, an economically successful and environmentally sustainable method for red mud recycling is still absent. This is primarily due to the difficulties associated with the selective recovery of components via hydrometallurgical methods, particularly due to the high content of iron. Leaching by alkaline solutions is unsuitable for recovery of titanium and REEs; acidic leaching leads to dissolution of iron with the valuable components, which hinders the subsequent recovery of valuable components from the solution. In addition, direct leaching of valuable components from red mud generates a large amount of wastewater, which must be utilized and is therefore unacceptable for the environment.
Thus, at the present time, the optimal solution is the development of an integrated technology using pyrometallurgical methods for iron reduction, involving the application of hydrogen- or carbon-containing wastes, which leads to enrichment of non-metallic reduction products with valuable components. Then, aluminum can be extracted by alkaline solutions, and titanium and REEs can be recovered by acid leaching. The approaches aimed at selective REE recovery, particularly the application of ionic liquids and bioleaching, may be economically feasible, but they require further research and are unable to solve the problem of the utilization of the total amount of generated and accumulated red mud.
To develop new economically successful and environmentally sustainable processes for red mud recycling, different approaches, such as LCA, for the estimation of the influence of the process on the environment and industries, should be used more widely.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.Z. and V.D.; validation, V.D. and P.G.; formal analysis, D.Z.; investigation, D.Z., L.P. and M.F.; resources, V.D. and A.A.; data curation, D.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, D.Z., L.P. and M.F.; writing—review and editing, P.G.; visualization, D.Z. and P.G.; supervision, V.D. and A.A.; project administration, V.D. and A.A.; funding acquisition, A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was carried out according to the state order of Russia 075-00328-21-00. L.P.is grateful for the support under government assignment N AAAA-A19-119031890028-0 for the ISSC UB RAS.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data from [13] was reprinted from Waste Management, 34, Y. Liu, R. Naidu. Hidden values in bauxite residue (red mud): Recovery of metals, 2662–2673, 2014, with permission from Elsevier. Data from [15] was reprinted from Waste Management, 34, Yanju Liu, Ravi Naidu, Hidden values in bauxite residue (red mud): Recovery of metals, 2662–2673, 2014, with permission from Elsevier. Data from [60] was reprinted from Hydrometallurgy, 184, R.M. Rivera, B. Xakalashe, G. Ounoughene, K. Binnemans, B. Friedrich, T. Van Gerven. Selective rare earth element ex-traction using high-pressure acid leaching of slags arising from the smelting of bauxite residue, 162–174, 2019, with permission from Elsevier. Data from [83] was reprinted by permission from Springer Nature Customer Service Centre GmbH: Springer Nature, JOURNAL OF SUSTAINABLE METALLURGY, Recovery of Rare Earths and Major Metals from Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) by Alkali Roasting, Smelting, and Leaching, Borra C.R., Blanpain B., Pontikes Y., Binnemans K., Van Gerven T., 2016, 18 November 2016 (doi:10.1007/s40831-016-0103-3). Data from [84] was reprinted from Journal of Hazardous Materials, 331, Bona Deng, Guanghui Li, Jun Luo, Qing Ye, Mingxia Liu, Zhiwei Peng, Tao Jiang, Enrichment of Sc2O3 and TiO2 from bauxite ore residues, 71–80, 2017, with permission from Elsevier.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to appreciate A.V. Dyubanova for editing of English language.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, R.; Zheng, S.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y. Recovery of alumina and alkali in Bayer red mud by the formation of andradite-grossular hydrogarnet in hydrothermal process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K. The History, Challenges, and New Developments in the Management and Use of Bauxite Residue. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Kong, X.; Zhu, F.; William, H.; Li, X.; Ye, Y. Industrial wastes applications for alkalinity regulation in bauxite residue: A comprehensive review. J. Cent. South Univ. 2019, 26, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, A. The Comprehensive Utilisation of Red Mud Utilisation in Blast Furnace. In Recovery and Utilization of Metallurgical Solid Waste; Zhang, Y., Ed.; IntechOpen Ltd.: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archambo, M.; Kawatra, S.K. Red Mud: Fundamentals and New Avenues for Utilization. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2020, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.A.; Wang, Y.; Lu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Q. Comprehensive utilization of red mud: Current research status and a possible way forward for non-hazardous treatment. In Light Metals; Olivier, M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 135–141. ISBN 9783319722832. [Google Scholar]
- Dauvin, J.C. Towards an impact assessment of bauxite red mud waste on the knowledge of the structure and functions of bathyal ecosystems: The example of the Cassidaigne canyon (north-western Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Pontikes, Y. Towards zero-waste valorisation of rare-earth-containing industrial process residues: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 99, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, C.R.; Blanpain, B.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Recovery of Rare Earths and Other Valuable Metals from Bauxite Residue (Red Mud): A Review. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H. Metallurgical process for valuable elements recovery from red mud—A review. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 155, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Li, J. Aluminum Mineral Processing and Metallurgy: Iron-Rich Bauxite and Bayer Red Muds. In Aluminium Alloys and Composites; Cooke, K.O., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Akcil, A.; Akhmadiyeva, N.; Abdulvaliyev, R.; Meshram, A.; Meshram, P. Overview on Extraction and Separation of Rare Earth Elements from Red Mud: Focus on Scandium. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2017, 39, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Naidu, R. Hidden values in bauxite residue (red mud): Recovery of metals. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2662–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Hu, Z.; Cao, D.; Zeng, J.; Wu, B.; Wang, L. Extraction of valuable metals from red mud. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 881–883, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, B.; Akcil, A.; Lee, J. Chun Red mud valorization an industrial waste circular economy challenge; review over processes and their chemistry. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, T.; Pontikes, Y. Geopolymers, inorganic polymers, alkali-activated materials and hybrid binders from bauxite residue (red mud)—Putting things in perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukiza, E.; Zhang, L.L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, N. Utilization of red mud in road base and subgrade materials: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushil, S.; Batra, V.S. Catalytic applications of red mud, an aluminium industry waste: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 81, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, C.G.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Krishnan, V.; Li Puma, G. Application of modified red mud in environmentally-benign applications: A review paper. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.S.; Reddy, N.G.; Serjun, V.Z.; Mohanty, B.; Das, S.K.; Reddy, K.R.; Rao, B.H. Properties and Assessment of Applications of Red Mud (Bauxite Residue): Current Status and Research Needs. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 1185–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneez, M.; Hurel, C. A review on the potential uses of red mud as amendment for pollution control in environmental media. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 22106–22125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, H.I.; Mayes, W.M.; Rogerson, M.; Stewart, D.I.; Burked, I.T. Alkaline residues and the environment: A review of impacts, management practices and opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 3571–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujaczki, É.; Feigl, V.; Molnár, M.; Cusack, P.; Curtin, T.; Courtney, R.; O’Donoghue, L.; Davris, P.; Hugi, C.; Evangelou, M.W.H.; et al. Re-using bauxite residues: Benefits beyond (critical raw) material recovery. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 2498–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairul, M.A.; Zanganeh, J.; Moghtaderi, B. The composition, recycling and utilisation of Bayer red mud. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauber, C.; Gräfe, M.; Power, G. Bauxite residue issues: II. options for residue utilization. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.; Bahadure, S.; Chaddha, M.J.; Agnihotri, A. Disposal Practices and Utilization of Red Mud (Bauxite Residue): A Review in Indian Context and Abroad. J. Sustain. Metall. 2020, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, H.; Deng, Y.; Xiao, Y. Comprehensive utilization status of red mud in China: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 289, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Lyu, F.; Sun, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Progress on the industrial applications of red mud with a focus on China. Minerals 2020, 10, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, D.I.; Molchanova, T.V. The investigation of sulphuric acid sorption recovery of scandium and uranium from the red mud of alumina production. Hydrometallurgy 1997, 45, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinoveev, D.V.; Grudinskii, P.I.; Dyubanov, V.G.; Kovalenko, L.V.; Leont’ev, L.I. Global recycling experience of red mud—A review. Part I: Pyrometallurgical methods. Izv. Ferr. Metall. 2018, 61, 843–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Smart, R.S.C.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Gerson, A. Solubility of sodium aluminosilicates in synthetic Bayer liquor. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1998, 43, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaußen, F.M.; Friedrich, B. Methods for Alkaline Recovery of Aluminum from Bauxite Residue. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayca, S.U.; Kisik, H. Optimization of leaching parameters of aluminum hydroxide extraction from bauxite waste using the Taguchi method. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2018, 37, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Extraction of alumina and sodium oxide from red mud by a mild hydro-chemical process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasechnik, L.A.; Skachkov, V.M.; Bogdanova, E.A.; Chufarov, A.Y.; Kellerman, D.G.; Medyankina, I.S.; Yatsenko, S.P. A promising process for transformation of hematite to magnetite with simultaneous dissolution of alumina from red mud in alkaline mediumAutoclave hydrometallurgical processing of alumina production red mud. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 196, 105438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ma, S.; Zheng, S.; Luo, Y.; Ding, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Combined treatment of red mud and coal fly ash by a hydro-chemical process. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 175, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, S.N.; Rout, A.; Padhi, B.K. Extraction of Alumina from Red Mud by Divalent Alkaline Earth Metal Soda Ash Sinter Process. In Light Metals 2011; Lindsay, S.J., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisonyan, K.G.; Kopyev, D.Y.; Goncharov, K.V.; Sadykhov, G.B. An investigation of a single-stage red mud reducing roasting process with the cast iron and aluminate slag production. Non-Ferrous Met. 2018, 44, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisonyan, K.G.; Kopyev, D.Y.; Olyunina, T.V.; Sadykhov, G.B. Influence of Na2CO3 and CaCO3 additions on the aluminate slag formation during a single-stage reducing roasting of red mud. Non Ferrous Met. 2019, 46, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhang, J.; Deng, X.; Wang, K.; He, C.; Li, X.; Wei, Y. Comprehensive Recovery of Iron and Aluminum from Ordinary Bayer Red Mud by Reductive Sintering–Magnetic Separation–Digesting Process. JOM 2019, 71, 2936–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Jiang, T.; Li, G.; Ye, Q.; Gu, F.; Rao, M.; Peng, Z. Effects of reductive roasting with sodium salts on leaching behavior of non-ferrous elements in bauxite ore residue. In Light Metals 2018; Martin, O., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, H.; Rowles, M.R.; Hayes, P.C.; Hawker, W.; Vaughan, J. Bauxite residue sinter leach process—phases formation, reaction pathways and kinetics. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, P.W.Y.; Panias, D.; Vassiliadou, V. Sintering optimisation and recovery of aluminum and sodium from Greek bauxite residue. Minerals 2019, 9, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, S.N.; Padhi, B. A novel method for extraction of alumina from red mud by divalent alkaline earth metal oxide and soda ash sinter process. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2014, 13, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, Z.; Allahverdi, A.; Mahinroosta, M. Treatment of Red Mud Using Mineral Acids for Metals Recovery. In Proceedings of the Iran International Aluminium Conference (IIAC2018), Tehran, Iran, 24–25 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, S.; Tam, J.; Yang, M.; Azimi, G. Technospheric Mining of Rare Earth Elements from Bauxite Residue (Red Mud): Process Optimization, Kinetic Investigation, and Microwave Pretreatment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.; Shon, B. Metal Components (Fe, Al, and Ti) Recovery from Red Mud by Sulfuric Acid Leaching Assisted with Ultrasonic Waves. Int. J. Emerg. Adv. Eng. 2015, 5, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ochsenkuehn-Petropoulou, M.; Tsakanika, L.-A.; Lymperopoulou, T.; Ochsenkuehn, K.-M.; Hatzilyberis, K.; Georgiou, P.; Stergiopoulos, C.; Serifi, O.; Tsopelas, F. Efficiency of Sulfuric Acid on Selective Scandium Leachability from Bauxite Residue. Metals 2018, 8, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Zhou, F.; Ma, X.; Gu, G.; Zhang, W. Optimization of condition for extraction of aluminum and iron from red mud by hydrochloric acid leaching. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 11, 5677–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; He, H.; Sun, Z.; Li, A. Effective aluminum extraction using pressure leaching of bauxite reaction residue from coagulant industry and leaching kinetics study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreault, R.; Fournier, J.; Primeau, D.; Labrecque-Gilbert, M.-M. Processes for Treating red Mud. U.S. Patent US20150275330, 1 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Agatzini-Leonardou, S.; Oustadakis, P.; Tsakiridis, P.E.; Markopoulos, C. Titanium leaching from red mud by diluted sulfuric acid at atmospheric pressure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lymperopoulou, T.; Paraskevas, G.; Lamprini-areti, T.; Hatzilyberis, K.; Ochsenkuehn-Petropoulou, M. Optimizing Conditions for Scandium Extraction from Bauxite Residue Using Taguchi Methodology. Minerals 2019, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, G.; Schier, C.; Gronen, L.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B. A Mineralogical Assessment on Residues after Acidic Leaching of Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) for Titanium Recovery. Metals 2017, 7, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoppert, A.A.; Loginova, I.V. Red Mud as an Additional Source of Titanium Raw Materials. KnE Mater. Sci. 2017, 2, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, R.M.; Ulenaers, B.; Ounoughene, G.; Binnemans, K. Behaviour of Silica during Metal Recovery from Bauxite Residue by Acidic Leaching. In Proceedings of the 35th International ICSOBA Conference, Hamburg, Germany, 2–5 October 2017; pp. 547–556. [Google Scholar]
- Alkan, G.; Yagmurlu, B.; Gronen, L.; Dittrich, C.; Ma, Y.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B. Selective silica gel free scandium extraction from Iron-depleted red mud slags by dry digestion. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 185, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, G.; Yagmurlu, B.; Cakmakoglu, S.; Hertel, T.; Kaya, Ş.; Gronen, L.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B. Novel Approach for Enhanced Scandium and Titanium Leaching Efficiency from Bauxite Residue with Suppressed Silica Gel Formation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagmurlu, B.; Alkan, G.; Xakalashe, B.; Schier, C.; Gronen, L. Synthesis of Scandium Phosphate after Peroxide Assisted Leaching of Iron Depleted Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) Slags. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, R.M.; Xakalashe, B.; Ounoughene, G.; Binnemans, K.; Friedrich, B.; Van Gerven, T. Selective rare earth element extraction using high-pressure acid leaching of slags arising from the smelting of bauxite residue. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 184, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.; Thawrani, S.A.; Ansari, M.S.; Puttewar, S.P.; Agnihotri, A. Studies on Beneficiation and Leaching Characteristics of Rare Earth Elements in Indian Red Mud. Russ. J. Non Ferrous Met. 2019, 60, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, K.; Cao, L.; Cheng, F. A prospective process for alumina extraction via the co-treatment of coal fly ash and bauxite red mud: Investigation of the process. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 186, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashcheev, I.D.; Zemlyanoi, K.G.; Doronin, A.V.; Kozlovskikh, E.Y. New Possibilities for an Acid Method of Preparing Aluminum Oxide. Refract. Ind. Ceram. 2014, 55, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zong, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, Z. Characterization of scandium and gallium in red mud with Time of Flight-Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) and Electron Probe Micro-Analysis (EPMA). Miner. Eng. 2018, 119, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vind, J.; Vassiliadou, V.; Panias, D. Rare earth elements and scandium mineralogy in bauxite residue. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Bauxite Residue Valorisation and Best Practices Conference, Athens, Greece, 7–10 May 2018; pp. 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhao, Z. Selective recovery of scandium from sulfating roasting red mud by water leaching. In Rare Metal Technology; Kim, H., Alam, S., Neelameggham, N., Oosterhof, H., Ouchi, T., Guan, X., Eds.; Springer Ltd.: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasechnik, L.A.; Skachkov, V.M.; Chufarov, A.Y.; Suntsov, A.Y.; Yatsenko, S.P. High purity scandium extraction from red mud by novel simple technology. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 202, 105597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Li, X.; Wang, P.; He, C.; Wei, Y. Recovery of Scandium from Bauxite Residue by Selective Sulfation Roasting with Concentrated Sulfuric Acid and Leaching. JOM 2019, 72, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zong, Y.; Li, H.; Jia, D.; Zhao, Z. Selectively recovering scandium from high alkali Bayer red mud without impurities of iron, titanium and gallium. J. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, R.P.; Kazantzis, N.K.; Emmert, M.H. Selective Process Steps for the Recovery of Scandium from Jamaican Bauxite Residue (Red Mud). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Xian, P. Recovery of iron from red mud by selective leach with oxalic acid. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 157, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Xian, P. Iron recovery from the leached solution of red mud through the application of oxalic acid. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 157, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Shi, Z.; Chen, Y.; Niu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wan, P. Red-mud treatment using oxalic acid by UV irradiation assistance. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujaczki, É.; Courtney, R.; Cusack, P.; Krishna Chinnam, R.; Clifford, S.; Curtin, T.; O’Donoghue, L. Recovery of Gallium from Bauxite Residue Using Combined Oxalic Acid Leaching with Adsorption onto Zeolite HY. J. Sustain. Metall. 2019, 5, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogomazov, A.V.; Senyuta, A.S. Method for the Acid Treatment of Red Mud. Russian Patent RU0002544725, 20 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Atalay Kalsen, T.S.; Karadağ, H.B.; Eker, Y.R.; Kerti, I. Chemical Composition Simplification of the Seydişehir (Konya, Turkey) Alumina Plant Waste. J. Sustain. Metall. 2019, 5, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Guo, T.; Wen, H.; Wang, N. Leaching Behavior of Lithium from Bauxite Residue Using Acetic Acid. Mining, Metall. Explor. 2020, 37, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Frisch, G.; Hartley, J.; Ryder, K.S. Processing of metals and metal oxides using ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Li, J.; Hua, Y. Application of ionic liquids in hydrometallurgy of nonferrous metals. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davris, P.; Balomenos, E.; Panias, D.; Paspaliaris, I. Selective leaching of rare earth elements from bauxite residue (red mud), using a functionalized hydrophobic ionic liquid. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 164, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi, C.; Alexandri, A.; Vind, J.; Panagiotopoulou, A.; Tsakiridis, P.; Panias, D. Scandium and titanium recovery from bauxite residue by direct leaching with a Brønsted acidic ionic liquid. Metals 2018, 8, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi, C.; Davris, P.; Balomenos, E.; Giannopoulou, I. Ionometallurgical Leaching Process of Bauxite Residue: A Comparison between Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Ionic Liquids. In Proceedings of the 35th International ICSOBA Conference, Hamburg, Germany, 2–5 October 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Borra, C.R.; Blanpain, B.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Recovery of Rare Earths and Major Metals from Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) by Alkali Roasting, Smelting, and Leaching. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 3, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Li, G.; Luo, J.; Ye, Q.; Liu, M.; Peng, Z.; Jiang, T. Enrichment of Sc2O3 and TiO2 from bauxite ore residues. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 331, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, B.; Li, G.; Luo, J.; Ye, Q.; Liu, M.; Rao, M.; Peng, Z.; Jiang, T. Selective Extraction of Rare Earth Elements Over TiO2 From Bauxite Residues After Removal of Their Fe-, Si-, and Al-Bearing Constituents. JOM 2018, 70, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Li, G.; Luo, J.; Ye, Q.; Liu, M.; Rao, M.; Jiang, T.; Bauman, L.; Zhao, B. Selectively leaching the iron-removed bauxite residues with phosphoric acid for enrichment of rare earth elements. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227, 115714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apak, R.; Ercag, E. Furnace Smelting and Extractive Metallurgy of Red Mud: Recovery of TiO2, Al2O3 and Pig Iron. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1997, 70, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounalakis, P.; Aravossis, K.; Karayianni, C.H.S. Feasibility study for an innovative industrial red mud utilisation method. Waste Manag. Res. 2016, 34, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreault, R.; Alex, S.; Biasotto, F. Processes for Extracting Aluminum from Aluminous Ores. U.S. Patent US8337789B2, 25 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Huang, G.; Wang, N.; Ma, G.; Xie, Y.; Li, B. Method for Preparing High-Purity Ferric Oxide by Using Aluminum Oxide Red Mud. Chinese Patent CN102390869B, 14 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, K.; Chen, W.; Lei, Q.; Huang, Y.; Peng, C. Recovery of iron and rare earth elements from red mud through an acid leaching-stepwise extraction approach. J. Cent. S. Univ. 2019, 26, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, K.; Lei, Q.; Xing, Y.; Peng, C.; Chen, W. Stripping of Fe(III) from Aliquat 336 by NaH2PO4: Implication for rare-earth elements recovery from red mud. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujaczki, É.; Zimmermann, Y.; Gasser, C.; Molnár, M.; Feigl, V.; Lenz, M. Red mud as secondary source for critical raw materials—purification of rare earth elements by liquid/liquid extraction. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 2683–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Teng, C.; Zhang, X.; Peng, C.; Chen, W. Enhanced selective leaching of scandium from red mud. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 182, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasechnik, L.A.; Yatsenko, S.P.; Yatsenko, S.P.; Skryabneva, L.M. Selective extraction of yttrium from alumina industry slimes. Non-Ferrous Met. 2014, 1, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Pyagai, I.N.; Medyankina, I.S.; Skachkova, O.V.; Yatsenko, S.P.; Pasechnik, L.A.; Skachkov, V.M.; Sabirzynov, N.A. Extraction recovery of yttrium from acidic solutions. Khimicheskaya Tekhnologiya 2016, 9, 403–407. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Li, W.; Xing, B.; Zhang, Y. Extraction of scandium from red mud by acid leaching with CaF2 and solvent extraction with P507. J. Rare Earths 2020, 38, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Pranolo, Y.; Cheng, C.Y. Recovery of scandium from synthetic red mud leach solutions by solvent extraction with D2EHPA. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 108, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Zou, D.; Deng, Y.; Li, D. Application of P507 and isooctanol extraction system in recovery of scandium from simulated red mud leach solution. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsenkuehn-Petropoulou, M.; Lyberopulu, T.; Parissakis, G. Selective separation and determination of scandium from yttrium and lanthanides in red mud by a combined ion exchange/solvent extraction method. Anal. Chim. Acta 1995, 315, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Pandey, B.D.; Meshram, P.; Kar, S.; Kumari, V.K. Abhilash Chloride leaching of lanthanum and cerium from Indian red mud and metal separation studies. Metall. Res. Technol. 2019, 116, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ye, Q.; Deng, B.; Luo, J.; Rao, M.; Peng, Z.; Jiang, T. Extraction of scandium from scandium-rich material derived from bauxite ore residues. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 176, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Niu, Z.; Li, W.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Q. A novel process for recovery of aluminum, iron, vanadium, scandium, titanium and silicon from red mud. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 8, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onghena, B.; Binnemans, K. Recovery of Scandium (III) from aqueous solutions by solvent extraction with the functionalized ionic liquid betainium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onghena, B.; Borra, C.R.; Van Gerven, T.; Binnemans, K. Recovery of scandium from sulfation-roasted leachates of bauxite residue by solvent extraction with the ionic liquid betainium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 176, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Koivula, R.; Wiikinkoski, E.; Xu, J.; Hietala, S.; Lehto, J.; Harjula, R. Efficient and Selective Recovery of Trace Scandium by Inorganic Titanium Phosphate Ion-Exchangers from Leachates of Waste Bauxite Residue. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3103–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, A.; Malik, P.; Gupta, B. Extraction and separation of Ti(IV) using thiophosphinic acids and its recovery from ilmenite and red mud. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2001, 36, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, D.I.; Molchanova, T.V.; Vodolazov, L.I.; Peganov, V.A. Sorption recovery of rare-earth elements, yttrium and aluminum from red mud. Tsvetnye Met. 2002, 8, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Dostova, T.M.; Salnikova, E.V. Removing the amount of rare earth elements by integrated waste processing industry alumina Ural Aluminum Plant. Vestnik Orenbg. State Univ. 2011, 12, 390–392. [Google Scholar]
- Rychkov, V.N.; Kirillov, S.V.; Kirillov, E.V.; Bunkov, G.M.; Botalov, M.S.; Gorbachev, S.N.; Petrakova, O.V.; Panov, A.V.; Suss, A.G.; Kozyrev, A.B. Method of Extracting Scandium and Rare-Earth Elements from Red Mud. Russian Patent RU2603418C1, 24 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kozyrev, A.B.; Petrakova, O.V.; Suss, A.G.; Gorbachev, S.N.; Panov, A.V. Method of Extracting Scandium from Red Mud from Alumina Production. Russian Patent RU2692709C2, 21 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rychkov, V.N.; Kirillov, E.V.; Kirillov, S.V.; Bunkov, G.M.; Titova, S.M. Scandium Recovery from Red Mud by Carbonate Assist. KnE Mater. Sci. 2017, 2, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hérès, X.; Blet, V.; Di Natale, P.; Ouaattou, A.; Mazouz, H.; Dhiba, D.; Cuer, F. Selective extraction of rare earth elements from phosphoric acid by ion exchange resins. Metals 2018, 8, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirokova, A.G.; Pasechnik, L.A.; Yatsenko, S.P. Prospects of application of microencapsulated extractants for extraction of scandium and rare-earth elements. Non Ferrous Met. 2014, 1, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Korovin, V.; Shestak, Y.; Pogorelov, Y. Scandium extraction by neutral organo-phosphorus compounds supported on a porous carrier. Hydrometallurgy 1999, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korovin, V.; Shestak, Y. Scandium extraction from hydrochloric acid media by Levextrel-type resins containing di-isooctyl methyl phosphonate. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 95, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdibegović, D.; Regadío, M.; Binnemans, K. Recovery of scandium(III) from diluted aqueous solutions by a supported ionic liquid phase (SILP). RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 49664–49674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdibegović, D.; Regadío, M.; Binnemans, K. Efficient separation of rare earths recovered by a supported ionic liquid from bauxite residue leachate. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 11886–11893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, K.; Wu, Y.; Lei, Q.; Peng, C.; Chen, W. Separation and recovery of iron and scandium from acid leaching solution of red mud using D201 resin. J. Rare Earths 2020, 38, 1322–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, W.; Tang, S.; Zeng, M.; Bai, P.; Chen, L. Selective recovery of vanadium and scandium by ion exchange with D201 and solvent extraction using P507 from hydrochloric acid leaching solution of red mud. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Li, D.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y. Extraction of scandium from red mud by modified activated carbon and kinetics study. Rare Met. 2008, 27, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kir, E.; Cengeloglu, Y.; Ersoz, M. Influence of Chelating Agents on the Recovery of Al(III), Fe(III), Ti(IV) and Na(I) from Red Mud by Cation Exchange Membranes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 961–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengeloglu, Y.; Kir, E.; Ersoz, M.; Buyukerkek, T.; Gezgin, S. Recovery and concentration of metals from red mud by Donnan dialysis. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 223, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoulnia, P.; Barthen, R.; Lakaniemi, A.-M. A critical review of bioleaching of rare earth elements: The mechanisms and effect of process parameters. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Lian, B. Bioleaching of rare earth and radioactive elements from red mud using Penicillium tricolor RM-10. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethurajan, M.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Nancharaiah, Y.V. Biotechnology in the management and resource recovery from metal bearing solid wastes: Recent advances. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 211, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Lian, B.; Mo, B.; Liu, C. Bioleaching of heavy metals from red mud using Aspergillus niger. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 136, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakilchap, F.; Mousavi, S.M.; Shojaosadati, S.A. Role of Aspergillus niger in recovery enhancement of valuable metals from produced red mud in Bayer process. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Li, H.; Tian, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, X.; Shi, B.; Song, G.; Tang, Y. Leaching of valuable metals from red mud via batch and continuous processes by using fungi. Miner. Eng. 2015, 81, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čížková, M.; Mezricky, D.; Rucki, M.; Tóth, T.M.; Náhlík, V.; Lanta, V.; Bišová, K.; Zachleder, V.; Vítová, M. Bio-mining of Lanthanides from Red Mud by Green Microalgae. Molecules 2019, 24, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Tian, W.; Shi, B.; Yao, M.; Zhang, Y. Bioleaching of major, rare earth, and radioactive elements from red mud by using indigenous chemoheterotrophic bacterium Acetobacter sp. Minerals 2019, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollmann, K.; Kutschke, S.; Matys, S.; Raff, J.; Hlawacek, G.; Lederer, F.L. Bio-recycling of metals: Recycling of technical products using biological applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1048–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayes, W.M.; Burke, I.T.; Gomes, H.I.; Anton, D.; Molnár, M.; Feigl, V.; Ujaczki, E. Advances in Understanding Environmental Risks of Red Mud After the Ajka Spill, Hungary. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, C.R.; Blanpain, B.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Comparative Analysis of Processes for Recovery of Rare Earths from Bauxite Residue. JOM 2016, 68, 2958–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, C.R.; Mermans, J.; Blanpain, B.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Selective recovery of rare earths from bauxite residue by combination of sulfation, roasting and leaching. Miner. Eng. 2016, 92, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzilyberis, K.; Lymperopoulou, T.; Tsakanika, L.A.; Ochsenkühn, K.M.; Georgiou, P.; Defteraios, N.; Tsopelas, F.; Ochsenkühn-Petropoulou, M. Process design aspects for scandium-selective leaching of bauxite residue with sulfuric acid. Minerals 2018, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Dhawan, N. Investigation of mechanical and thermal activation on metal extraction from red mud. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2021, 27, e00246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, P.J.; Björklund, A. Using Life Cycle Thinking to Assess the Sustainability Benefits of Complex Valorization Pathways for Bauxite Residue. J. Sustain. Metall. 2019, 5, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balomenos, E.; Davris, P.; Pontikes, Y.; Panias, D. Mud2Metal: Lessons Learned on the Path for Complete Utilization of Bauxite Residue Through Industrial Symbiosis. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samouhos, M.; Taxiarchou, M.; Pilatos, G.; Tsakiridis, P.E.; Devlin, E.; Pissas, M. Controlled reduction of red mud by H2 followed by magnetic separation. Miner. Eng. 2017, 105, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombelli, D.; Barella, S.; Gruttadauria, A.; Mapelli, C. Iron recovery from Bauxite Tailings Red Mud by thermal reduction with blast furnace sludge. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Huangfu, L.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Yu, J.; Li, W.; Gao, S. Recovery of Fe and Al from red mud by a novel fractional precipitation process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 14642–14653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).