Abstract
One of the most efficient ways to recycle elastomeric residues from industrial processes is to incorporate them into compositions. The study of these new compositions is interesting in terms of reducing cost, the consumption of raw materials, and the generation of new waste, working towards sustainable development. Thus, this research aimed to produce and characterize elastomeric blends containing one phase comprised of ethylene–propylene–diene monomer rubber (EPDM) industrial waste aged by the action of ultraviolet radiation (UV) in a UV chamber, and the other comprised of raw EPDM, containing different concentrations of residue. Therefore, the mechanical properties and the vulcanization characteristics of the blends containing different concentrations of EPDM residue—aged and un-aged—were analyzed and compared to the properties of a standard formulation (Control). The results showed that the aging of the waste for a period of 156 h did not trigger a severe degradation process. Additionally, its reuse into new compositions promoted improvements of the studied mechanical properties without compromising the vulcanization characteristics due to the higher molecular stiffness of the samples.
1. Introduction
The high production and consumption of polymeric materials in recent decades has raised questions about their final destination in the environment. Millions of tons of urban solid waste are inappropriately dumped every year in landfills and dumps, including polymeric materials. In addition, concerns about the disposal of these materials are further intensified in regions where there are low tax incentives for the development of the recycling industry and in regions with precarious solid waste management systems [1,2,3,4].
Elastomeric residues can also be responsible for the proliferation of mosquitoes and other disease vectors [5,6,7]. A fairly well-studied way to recycle vulcanized elastomeric residues is the production of polymeric blends, which involves first milling them into a powder (in order to increase the surface area, and consequently improve adhesion) [6,8,9,10]. In the case of industry-generated residues whose origin and formulation are known, their incorporation into raw elastomers is attractive in the development of compositions with technologically interesting properties, providing economic value to the company. This procedure can be used to lower costs, but only small amounts of residue can be incorporated into raw rubber without altering the material properties, due to the weak interaction of vulcanized rubber with raw rubber [1,2,5]. Some methods aim to improve this interaction by de-vulcanization. Among the most-studied methods, the ultrasound method uses ultrasound waves to produce cavitation in the rubber, which generates tensions that are able to break the chemical bonds [3,5,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Another de-vulcanization method based on the action of microwaves presents some advantages that make it one of the most promising for the recycling of rubber [2,3,4,13,15,18,19,20,21,22], including its physical nature, the volumetric heating of the material by the microwaves, and the possibility of high productivity [23].
The aging of elastomers can be defined as the degradation process produced by the interaction between a material and an environment, modifying their structure and properties (i.e., mechanical, electrical, chemical, and/or thermal). It is a complex chemical process that occurs under the influence of heat, oxygen, light, ozone, and mechanical tension, and it results in time-dependent modifications of the chemical and physical properties [24]. In elastomeric compositions, the term “aging” is related to molecular scission, which results in smaller chains, a larger number of chain terminals, and/or cross-link formation, which generates a strong linked network structure [16]. UV radiation is one of the most effective means for the degradation of organic materials through photo-oxidation. This radiation causes irreversible chemical modifications that affect the mechanical properties of materials. UV degradation can make materials brittle, lose resistance, and induce color change, affecting the lifetime of materials that are exposed to the weather [25]. In this work, a UV-aging process was used. It is a type of accelerated degradation that involves the exposure of materials to different environmental conditions (i.e., heat, humidity, and UV radiation), and it is an efficient aging method. This process, aiming to “de-vulcanize”, is innovative and very rarely explored, so the present work brings about a significant scientific contribution regarding the possibility of applying a recycling process to elastomers. In addition, the process of “de-vulcanization” during aging in the UV chamber results in lower levels of elastomer degradation compared to other de-vulcanization techniques (e.g., microwave de-vulcanization) [13,18].
This study aimed to analyze the influence of the exposure of vulcanized residues of ethylene–propylene–diene monomer rubber (EPDM), called EPDM-r, to accelerated aging by ultraviolet radiation (UV) in blends containing raw EPDM, in order to improve the compatibility between the phases. The mechanical properties and the vulcanization characteristics of the blends containing different concentrations of EPDM-r—both aged and un-aged—were analyzed and compared to the properties of a standard formulation (Control), and showed promising results.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
Vulcanized residues of EPDM from profile trims (from the automobile industry), called EPDM-r, were kindly supplied by NSO Borrachas Ltd. (Joinville—SC, Brazil). Both residue and raw elastomer compounds contained sulfur (Intercuf industry and trade Ltd., Campinas, Brazil); zinc oxide (ZnO) (Agro Zinco industry and trade Ltd., Ferrraz de Vasconcelos, Brazil); stearic acid (C18H36O2) (Proquiec chemical industry S/A, São Paulo, Brazil); and dibenzothiazole disulfide (MBTS) (Proquiec chemical industry S/A, São Paulo, Brazil).
2.2. Collection and Milling of EPDM Residues
The EPDM profile samples were collected by NSO Borrachas Ltd. (Joinville-SC/Brazil), according to NBR 10007-04, for a period of 21 days in interspersed weeks, with a total of 14 days of collection and a sampling of approximately 2 kg day−1. The total amount of collected profiles was 28 kg. The material was passed through an agglutinator (SEIBT, model AS 30/500, Petrópolis, Brazil). After this step, the obtained material was milled in a knives mill (Marconi, model MA 580, Piracicaba, Brazil), obtaining a fine powder to be used in the production of the blends.
2.3. UV-Accelerated Aging Process
After milling, the EPDM residue was subjected to UV-accelerated aging in a UV chamber (Comexin, São Paulo, Brazil) containing eight UVB lamps (UVBTL40W/12RS-PHILIPS) in interspersed exposure sessions to a condensing atmosphere and radiation (λ = 313 nm), both at 50 °C, for 156 h in total.
2.4. Characterization of the Granular Solids
The expression “granular solids” was adopted in this work since the particle size achieved in the process of milling was between 0.5 and 10 mm [5]. The characterization of granular solids obtained from the EPDM milling (EPDM before aging, called EPDM-r), as well as the EPDM-r after aging in the UV chamber (called EPDM-r UV), was performed through physical and thermal methods. Physical characterization of EPDM-r and EPDM-r UV was performed via particle size determination through granulometric analysis according to ASTM D 5644-01, by using sieves of 20, 25, 28, 35, 48, and 65 mesh. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was used to determine the composition of the EPDM-r and EPDM-r UV based on the mass reduction as a function of temperature. The analyses were performed on a thermogravimetric analyzer (Shimadzu, TGA-50, Kyoto, Japan), with a heating rate of 10 °C·min−1, under the following atmospheres: nitrogen, in the temperature range from 20 to 450 °C (flow of 50 mL·min−1); and synthetic air, from 450 to 800 °C (flow of 63 mL·min−1) in order to quantify the amount of carbon black present in the sample, according to ASTM D 6370-03.
2.5. Processing of the Blends
The formulations were based on a premix (raw premix EPDM), generously donated by NSO Borrachas Ltd. (Joinville, Brazil), without accelerators, into which different levels of EPDM-r and EPDM-r UV were incorporated, according to the formulations presented in Table 1. The residue (EPDM-r) had the same composition of the raw premix, being that it was previously vulcanized. After the residue incorporation, all the formulations were vulcanized using the same acceleration system. The blends were prepared in a laboratory two-roll mill (MH, model MH-600, São Paulo, Brazil), according to ASTM D 3182-07, at 60 °C and a mixing time of 30 min (the total mass of the base formulation was 500 g).

Table 1.
Recipes of the analyzed samples. Blends contained different concentrations of the recycled ethylene–propylene–diene monomer rubber (EPDM) before (EPDM-r) and after aging by UV (EPDM-r UV).
The nomenclature adopted was “EPDM-r X” and “EPDM-r UV X”, where “X” denotes the amount of EPDM-r and EPDM-r UV residues contained in the blend, respectively. The residue amount varied in 10, 20, and 30 phr (Table 1). For comparison, a sample called Control was developed which did not contain EPDM-r in its formulation (i.e., standard formulation).
2.6. Characterization of the Blends
Vulcanization characteristics were determined by using an oscillating disk rheometer (Rheotech, Tech Pro Rheometer OD+, Middleboro, MA, USA), according to ASTM D 2084. Curves of torque versus time were obtained at 160 °C, providing the following parameters: maximum torque (MH); minimum torque (ML); ∆M = MH − ML; scorch time (ts1); and optimum vulcanization time (t90). Values of the CRA (cure rate average) were calculated by using Equation (1) [26]:
Plates with dimensions of 160 × 160 × 1.5 mm3 were vulcanized at 160 °C and at a pressure of 7.5 MPa, according to ASTM D 3182-89, in periods of time related to the t90 values corresponding to each formulation. The absolute density test was conducted by the hydrostatic method, according to ASTM D 297-93. The density of the samples was calculated using Equation (2):
where ρ is the density of the sample at 25 °C (g·cm−3), ma is the mass of the sample in air (g), and mb is the mass of the sample in water (g).
The mechanical properties of the blends were obtained by performing hardness, tensile, and tear strength tests. Hardness tests were carried out on a Shore A durometer (Teclock, GS709, Osaka, Japan), according to ASTM 2240-05. Tensile tests were performed on a universal testing machine (EMIC, DL-3000, São Paulo, Brazil), with a rate of grip separation of 500 mm·min−1 and with a 20 kN load cell, according to ASTM D 412-06. Tensile strength and elongation at break were obtained. The tear strength tests were carried out on a universal testing machine (EMIC, DL-3000, São Paulo, Brazil), with a rate of grip separation of 500 mm·min−1 and with a 20 kN load cell, according to ASTM D 624-00. The specimens were kept at a temperature of 23 ± 2 °C and at a relative humidity of 50% ± 5% for 48 h.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the EPDM-r and EPDM-r UV
3.1.1. Milling and Particle Size Distribution
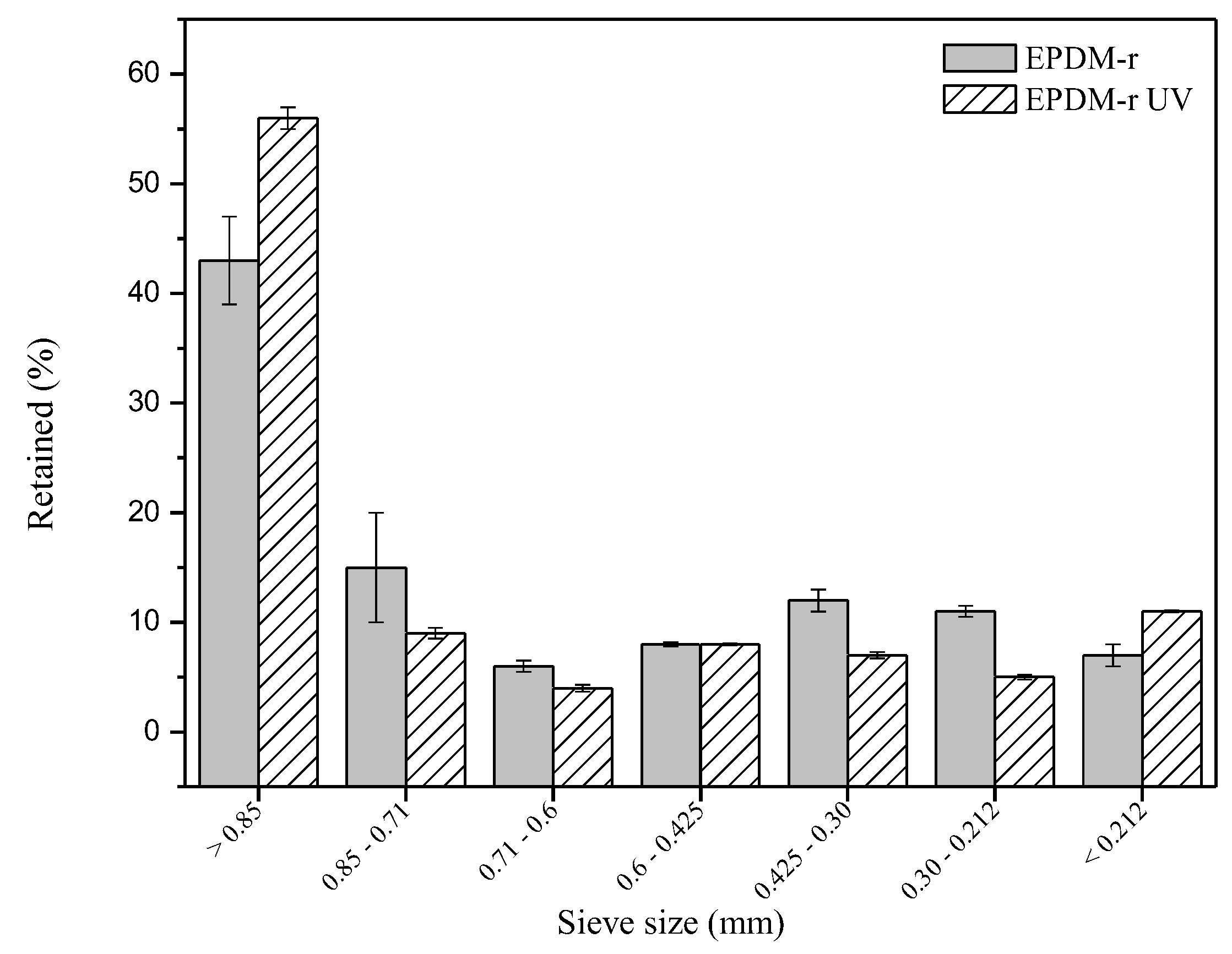
Results of the granulometric analysis of the EPDM-r and the EPDM-r UV are shown in Figure 1.
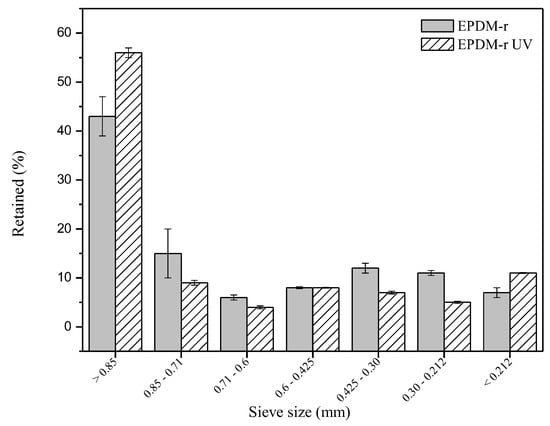
Figure 1.
Particle size distribution of the EPDM-r and the EPDM-r UV.
The first step of any rubber recycling process is milling the material, which is necessary to increase the surface area of the particles and to produce a more uniform product [8,9,10,27].
It is known that the size of the filler particle has a strong influence on the final properties of the polymeric blends—the smaller the particle size, the higher the surface area that is able to interact with the polymeric matrix, which improves the adhesion between the phases. According to reference [28], the powder to be used as a filler (or a second phase) in new rubber formulations, by compression molding processes, must have particles with size less than 0.60 mm and a rough surface. The irregular shape generated as a result of the mechanical milling contributes to an increase of the surface roughness, promoting a good particle–matrix adhesion when compared to cryogenic milling.
It was found that the particle size distribution generally did not present significant differences. The largest proportion of granular solids was found in the range of 20–25 mesh (0.85–0.71 mm) for both samples. However, a higher concentration of EPDM-r UV was retained in the 20-mesh sieve (particle size > 0.85 mm).
Several studies have been conducted on the incorporation of waste vulcanized rubber powder into formulations with raw elastomers and later vulcanization [6,10,29]. Through the analysis of micrographs of a sample of residual styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), Weber et al. [10] observed that the particles presented fairly irregular shapes and roughnesses due to the mechanical milling, favoring the filler–matrix adhesion. Zanchet et al. [6] produced elastomeric blends containing recycled EPDM (called EPDM-r) and analyzed the morphology of the residue, the vulcanization characteristics, and the mechanical properties of the blends. By milling the residue at room temperature, the authors observed that the obtained powder presented a particle size distribution in the ideal range for incorporation into compounds by compression molding processes. The authors proved the irregular shape and large particle surface roughness through scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of the EPDM-r, which were the results of the milling process.
3.1.2. Thermo-Oxidative Degradation
Table 2 presents the TGA results of the EPDM-r and the EPDM-r UV.

Table 2.
Partial composition of the EPDM-r and the EPDM-r UV determined by the thermogravimetric analysis (TGA).
Based on the results, a mass loss between 200–400 °C was observed, which was related to the processing oil. According to reference [16], the use of these oils facilitates the processing and the vulcanization process, ensuring a good surface finish. Another mass loss between 400 and 450 °C was related to the EPDM used in the elastomeric formulations. From 450 °C on, the mass loss was related to the combustion of carbon black due to the atmosphere change from N2 to synthetic air.
Regarding the EPDM-r UV, the mass loss related to the processing oil decreased to 20.5% when compared to the EPDM-r mass loss of the same component (25.3%). The release of the processing oil in the EPDM-r sample, by the action of the UV radiation, could be due to its low molar mass and localization between the polymeric chains. In this way, by the joint action of the UV and heat, the migration of the additive to the EPDM-r UV surface was observed. The partial “extraction” of the processing oil after aging resulted in a greater proximity among the polymer chains and a reduction of the free volume, promoting a shift to higher values of the degradation start temperature (T0), maximum degradation temperature (Tmax), and final degradation temperature (Tf) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Degradation start temperature (T0), maximum degradation temperature (Tmax), and final degradation temperature (Tf) related to the processing oil mass loss of the EPDM-r and the EPDM-r UV samples.
According to Zanchet et al. [3], during aging, scissions can occur in the main chains and in the cross-links, and new cross-links can form. The UV aging process is similar to the de-vulcanization process by microwaves, being that some authors [13] observed the breaking of the cross-links and the formation of new bonds as a result of the rearrangement of the sulfur free radicals from the de-vulcanization. According to Zhao et al. [30,31], the accelerated aging process of the EPDM by UV radiation (after 18 days of exposure) can promote the formation of carbonyl groups (C=O), which can combine and result in new cross-links, generating an increase in the cross-link density of the sample.
3.1.3. Characterization of the Blends
Vulcanization Characteristics
The vulcanization characteristics of the analyzed samples are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Vulcanization characteristics of the analyzed samples. CRA: cure rate average; MH: maximum torque; ML: minimum torque.
The ts1 is an important parameter from the point of view of the security process. Knowing that it sets the time limit for the beginning of the cross-links formation, its reduction may allow the artifacts to be obtained in shorter periods of time, resulting in a more economical process. In general, the ts1 results of all the blends indicated a tendency to a slight reduction with an increasing amount of residue compared to the Control sample. This behavior has already been reported in the literature [1,3,32,33,34,35], and is attributed to the residual acceleration system present in the elastomeric residue.
The optimum vulcanization time (t90) indicates the ideal time for the vulcanization of the samples without degradation. It was observed that the addition of the EPDM-r increased the t90 values in relation to the Control sample, probably due to the difficulty of the additives’ diffusion caused by the presence of the vulcanized phase. However, the opposite behavior was verified in the blends containing EPDM-r UV. It is known that such samples have low oil content, which tends to approximate the chains (TGA results), besides possibly presenting lower cross-link density, which provides greater freedom to the chains during the vulcanization reaction and does not hinder the additives’ diffusion.
The minimum torque (ML) is related to the initial viscosity of the samples, and the maximum torque (MH) to the molecular stiffness after the cross-link formation [3]. All the samples presented higher ML values compared to the Control sample, which was expected since a phase of the blends was composed of vulcanized residue, which had a greater viscosity [1]. The ML values of the EPDM-r UV blends showed a slight reduction compared to the values of the EPDM-r blends, which is possibly due to the cross-link breakage that occurred during the aging of the recycled phase. As the intention of the aging was to de-vulcanize the residue, this result shows that the goal was probably achieved. The same behavior was previously observed in the literature [4,11,17]. The MH results showed a slight reduction of the molecular stiffness of some samples containing EPDM-r when compared to the Control sample. This reduction was probably related to a greater difficulty of the additives’ diffusion due to the presence of the recycled phase, which influenced the cross-link density of these samples. The behavior was not observed in the EPDM-r UV blends since the recycled phase was de-vulcanized during aging, which probably increased the freedom of the chains during the vulcanization reaction.
The ∆M values, which were proportional to the cross-link density of the samples, generally had the tendency be slightly reduced in the blends compared to the Control sample. In the samples containing aged residue, the reduction in the ∆M value was not significant since the aged phase—which presented a higher level of freedom due to the cross-link breakage—possibly performed a greater number of effective shocks during the vulcanization reaction, which ultimately resulted in a greater cross-link density in these blends. For CRA values, which are related to the reaction rate, it was verified that the EPDM-r UV 10 and EPDM-r UV 20 samples presented higher values, which was probably due to the better interaction between the phases and a greater freedom of the polymeric chains caused by the breakage of cross-links during the aging of the residue phase.
Density and Hardness
Table 5 presents the hardnesses and densities of the samples containing different concentrations of EPDM-r and EPDM-r UV before and after the vulcanization process.

Table 5.
Hardness and density values of the analyzed samples.
According to the results, the densities of all the vulcanized samples were higher than the un-vulcanized ones. This increase was due to the formation of cross-links that approximated the chains in the vulcanized samples [6]. Complex reactions occur in sulfur vulcanization systems (one of the most common types in the industry), leading to cross-link formation of types C–S–C (monosulfidic), C–S2–C (disulfidic), and C–Sx–C (polysulfidic).
The density and cross-links type are very important parameters due to their dominant effects on the mechanical properties of the compounds [15]. A conventional vulcanization system was used in the present study, which resulted primarily in the formation of polysulfidic links. Formulations with higher contents of polysulfidic links have greater tensile strength and fatigue, due to the ability of S–S links to break up and to reorganize, relieving high tensions before the material failure begins.
The hardness was proportional to the number of cross-links formed during the vulcanization process. However, a slight reduction was observed in some blends compared to the Control sample, particularly in the EPDM-r UV samples. However, variations in the results are common when dealing with blends containing recycled polymers.
According to some studies [30,31], the modification of the hardness occurs because the aging is cyclical. The increase of the cross-link density was promoted by the aging of the residue, which can be said because tensile strength, elongation at break, and hardness were sharper after 18 days of exposure of raw EPDM to UV in the study of Zhao et al., and the exposure was 6.5 days in the present study. For the hardness results, it was observed that the higher the residue content incorporated, the lower the hardness, which was probably due to the reduced amount of raw matrix.
Mechanical Properties
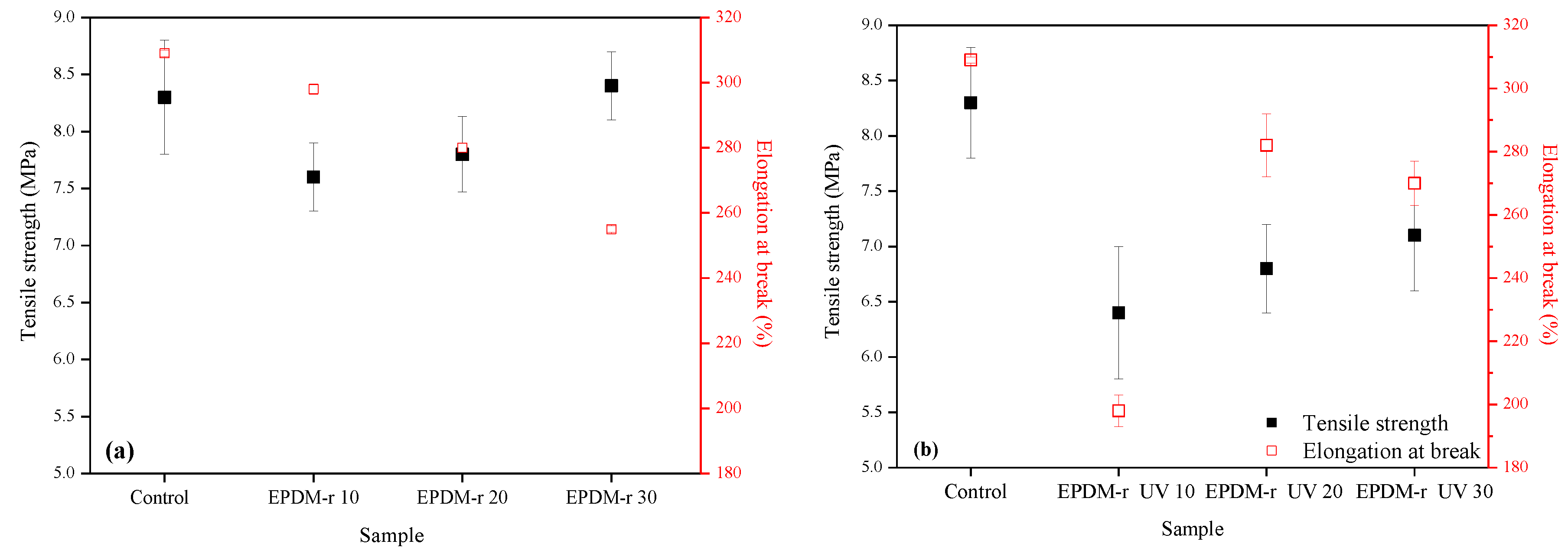
Tensile strength and elongation at break results of the samples are shown in Figure 2.
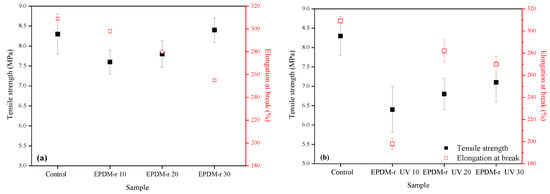
Figure 2.
Tensile strength and elongation at break results of the blends: (a) EPDM-r and (b) EPDM-r UV.
The tensile strength results of the EPDM-r samples (Figure 2a) were in accordance with the values observed in Table 4 for MH, indicating that the increase of the cross-link density led to the observed increase of the tensile strength [36]. The tensile strength of the sample EPDM-r 30 was higher than that of the Control sample, indicating that 30 phr of EPDM-r can be added to the formulation without compromising the mechanical behavior of the composition.
The elongation at break tended to reduce with the increase of the EPDM-r content, since a greater amount of the residue gave the blend a more rigid characteristic, and decreased the amount of raw EPDM in the blends. In other words, the elastic strength of the recycled rubber was lower than that of the raw rubber [37]. The higher the amount of cross-links of the EPDM-r 30 sample led to the low elongation at the observed break value [38]. According to the literature [3,39], the decrease of the elongation at break can be attributed to the continuous increase of the cross-link density. When the cross-link density is high, the mobility of the chain segments becomes limited, which causes an increase in the stiffness of the elastomeric compounds, and therefore, a reduction in the elongation at break values.
Regarding the results of the EPDM-r UV blends, there was an increase in the tensile strength and elongation at break with the increase of the EPDM-r UV content. However, the obtained values for all the compositions were inferior to the blends containing EPDM-r and to the Control sample, indicating that the aging of the residue did not promote improvements in these properties. The release of the processing oil from the EPDM-r UV may have restricted the mobility of the elastomeric chains, decreasing the elongation at the break of these compositions.
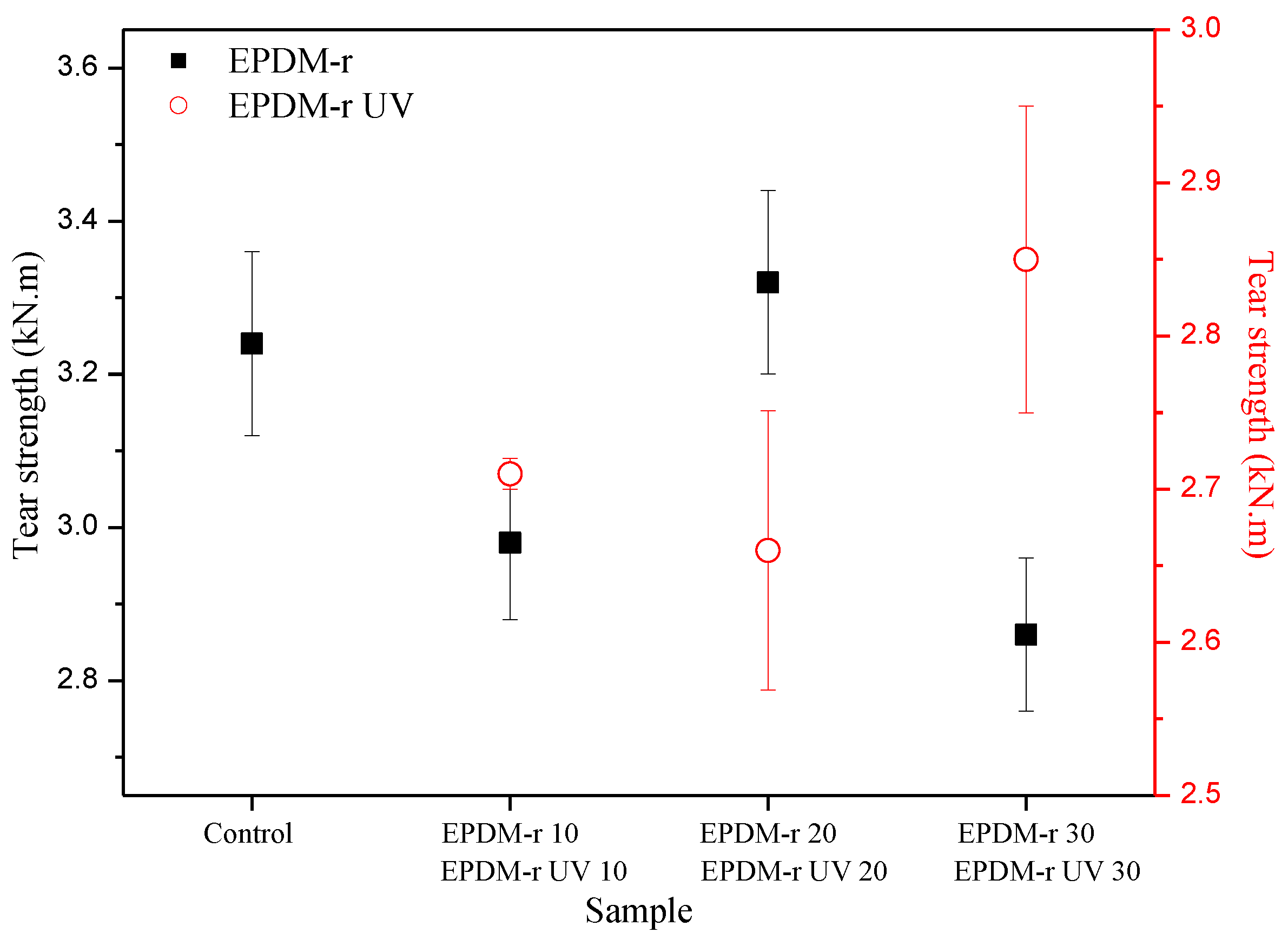
The tear strength of the samples is shown in Figure 3.
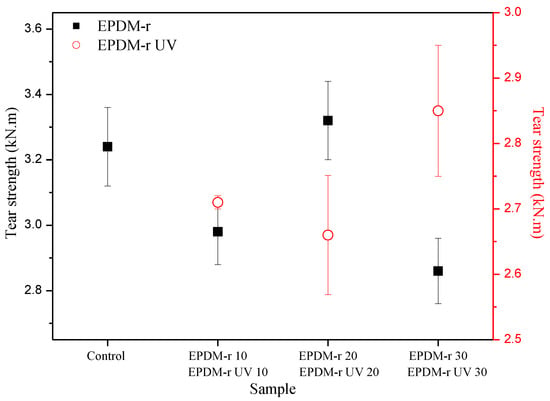
Figure 3.
Tear strength of the analyzed samples.
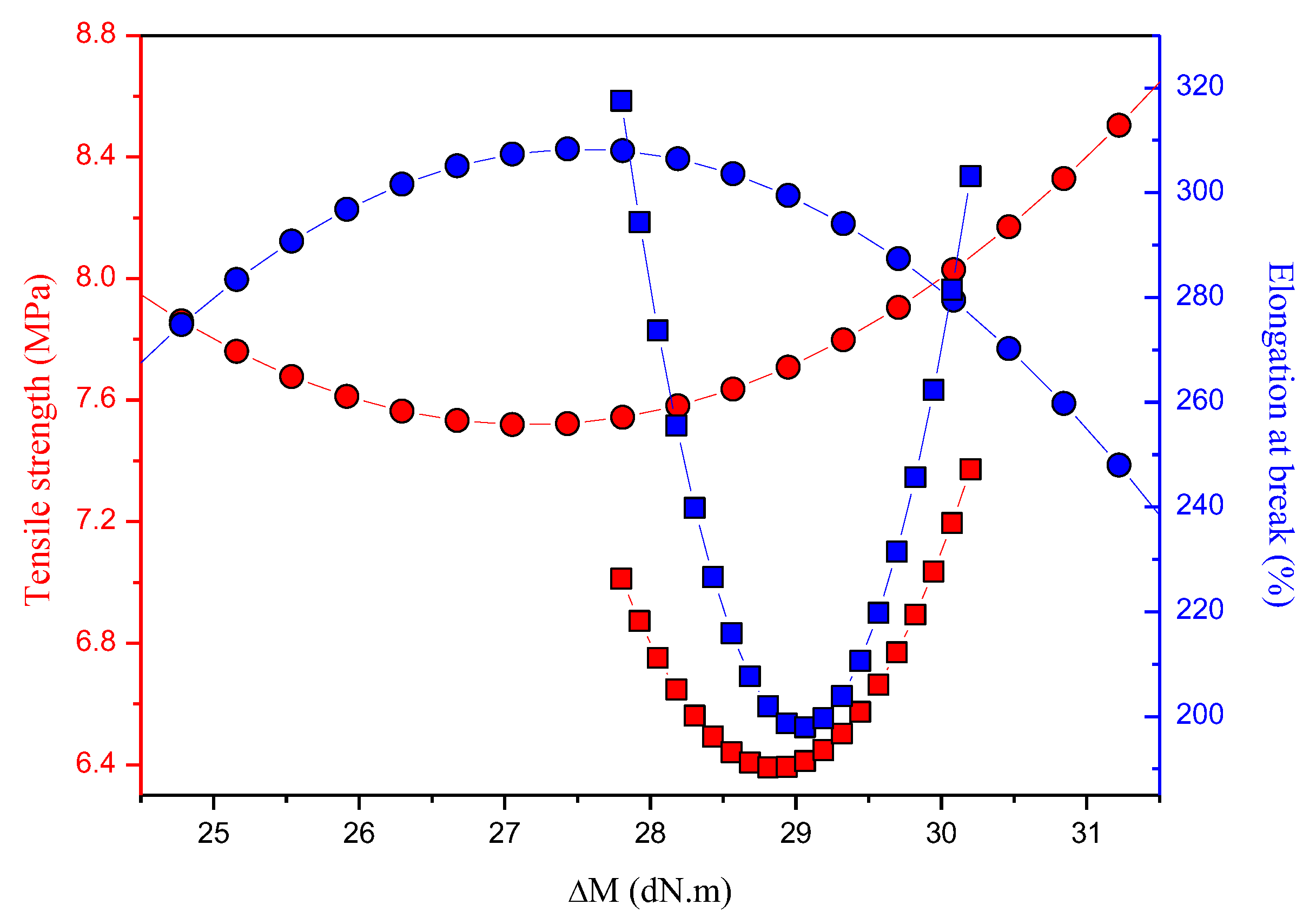
In general, the results of the tear strength of all the samples were inferior to the value of the Control sample, with the exception of the EPDM-r 20 sample. These results corroborated the previously discussed MH (Table 4) and density (Table 5) results. The tear strengths of the EPDM-r UV samples were lower than those of the EPDM-r samples. According to Coran et al. [38], the tear strength property is higher for smaller cross-link density, and the de-vulcanization which took place during the aging process favored the later vulcanization of the blends by promoting an increase of the cross-link density. The influence of the ∆M on the tensile strength and elongation at break behavior of the EPDM-r and EPDM-r UV blends is shown in Figure 4. The curves represent the trends observed during the analysis of the results.
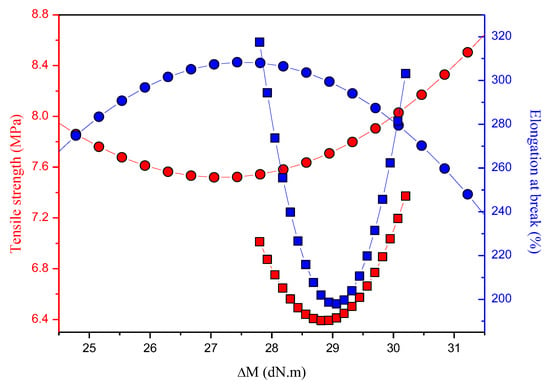
Figure 4.
Influence of the ∆M on the tensile strength and elongation at break behavior of the blends. The circles are the EPDM-r samples and the squares are the EPDM-r UV samples.
According to de Sousa [7], the addition of new factors (e.g., the introduction of a recycled phase into another raw one) and the formulation used can directly influence the vulcanization reaction of the polymeric blend containing a recycled phase, as was verified in this work. The change in the vulcanization reaction directly results in changes to the final properties of the elastomeric compounds—mainly in the mechanical properties, which was clearly observed through our obtained results. Factors such as the formulation used, the type and density of cross-links, the type and amount of filler, and the interaction between the phases (in the case of polymeric blends) influence the final properties of the compounds as a whole.
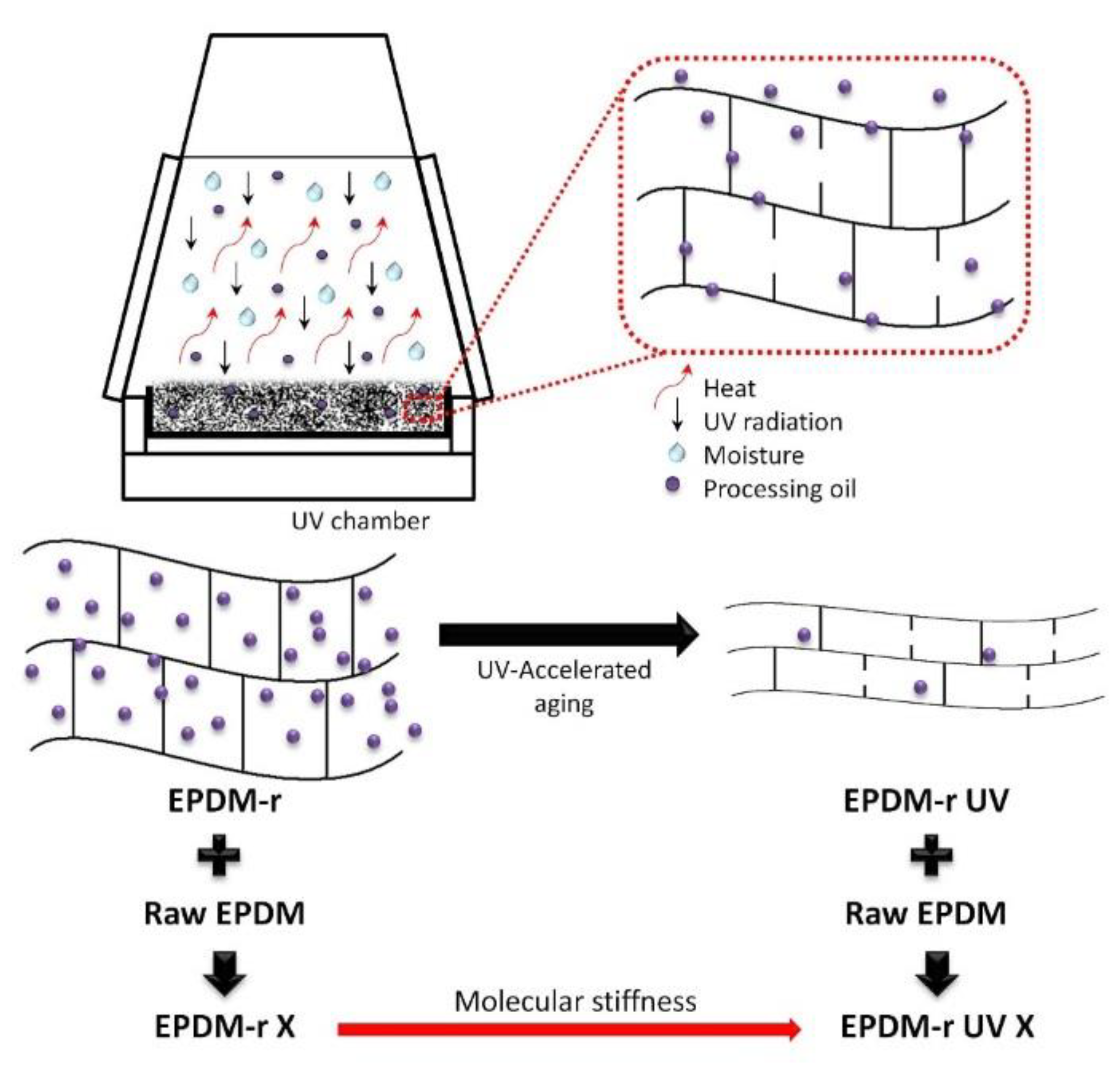
In the case of the present work, the UV-accelerated aging of the residue resulted in the release of the processing oil, which brought the polymer chains closer together and reduced the free volume among them, and also de-vulcanized the residue, according to the schema shown in Figure 5. In this form, the structure of the recycled phase was modified, resulting in greater molecular stiffness, even after the incorporation of the recycled material into another raw phase to form polymeric blends. The behavior of the mechanical properties of the EPDM-r and EPDM-r UV blends were quite distinct, due to the cited factors.
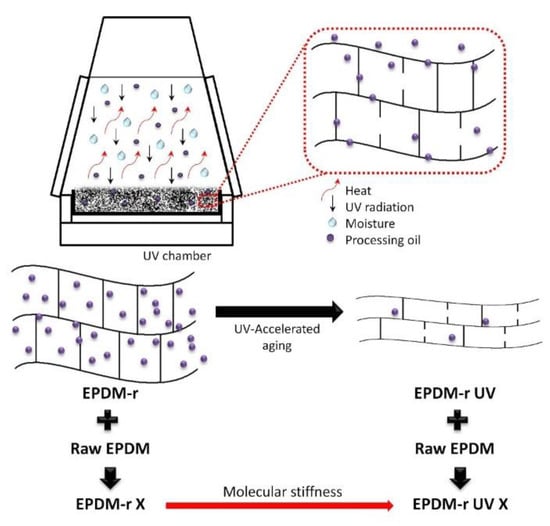
Figure 5.
Schema showing the UV-accelerated aging process of the EPDM residue and its influence on the properties of the EPDM-r UV blends.
Concerning the EPDM-r blends, tensile strength and elongation at break showed the behavior of a typical elastomeric compound. Elongation at break is usually reduced as cross-link density increases, since the cross-links require more energy to be broken, which consequently increases the tensile strength [6]. In addition, a greater variation in the ∆M values of these samples was observed, since the processing oil facilitated the movement of the polymeric chains during the vulcanization reaction. On the other hand, the opposite performance was clearly observed for the EPDM-r UV blends since, as depicted above, the release of the processing oil restricted the mobility of the elastomeric chains, which increased the cross-link density of the samples after the vulcanization of the blends, resulting in blends with higher molecular stiffness.
As a conclusion, the aging process of the residue was able to de-vulcanize it, which reduced the initial viscosity of the EPDM-r UV blends observed by ML values, and consequently facilitated the processing of the blends. As a consequence of the release of the processing oil, the samples presented higher molecular stiffness. Thus, the aging process was able to produce blends with easier processing and a higher stiffness.
In addition to all the advantages observed, it is known that the use of recycled materials in new applications is a sustainable action, as it saves the use of raw materials, often polymers derived from petroleum, which is a finite resource, in addition to being a possible solution for the major global problem of the final disposal of solid residues [6]. Moreover, recycling is considered to be a category of green chemistry (i.e., the use of renewable or recycled sources of raw material), while also being a source of income for many families around the world [4,40].
4. Conclusions
In this work, blends containing one phase comprising industrial EPDM waste aged by the action of UV radiation in a UV chamber, and another phase comprising raw EPDM (containing different concentrations of elastomeric residue), were produced and characterized in terms of mechanical properties and vulcanization characteristics.
In general, the aging process of the residue was able to de-vulcanize it, which reduced the initial viscosity of the EPDM-r UV blends observed by ML values, and consequently facilitated the processing of the blends, and also presented higher molecular stiffness as a consequence of the release of the processing oil. Thus, the aging process was able to produce blends with a facilitated processing and a higher stiffness. The aging process in the UV chamber resulted in an elastomer with similar properties to de-vulcanized elastomer obtained using other techniques such as microwave irradiation, with the advantage of a lesser degradation level of the recycled material. The results pointed to a potential use of the recycled material in new formulations and applications, which is a possible solution for the major global problem of the final disposal of solid residues, working towards sustainable development.
Author Contributions
Methodology, A.Z.; A.M., F.D.B.d.S., and R.N.B.; Investigation, A.Z., A.M., F.D.B.d.S., and R.N.B.; Data Curation, A.Z., A.M., F.D.B.d.S., and R.N.B.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, A.Z., A.M., F.D.B.d.S., and R.N.B.; Writing—Review & Editing, A.Z., A.M., F.D.B.d.S., and R.N.B.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zanchet, A.; Dal’Acqua, N.; Weber, T.; Crespo, J.S.; Brandelise, R.N.; Nunes, R.C.R. Propriedades reométricas e mecânicas e morfologia de compósitos desenvolvidos com resíduos elastoméricos vulcanizados. Polím. Ciênc. Tecnol. 2007, 17, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Zanchet, A.; Crespo, J.S.; Oliveira, M.G.; Suarez, J.C.M.; Nunes, R.C.R. Caracterização de artefatos elastoméricos obtidos por revulcanização de resíduo industrial de SBR (copolímero de butadieno e estireno). Polím. Ciênc. Tecnol. 2011, 21, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchet, A.; Carli, L.N.; Giovanela, M.; Brandelise, R.M.; Crespo, J.S. Use of styrene butadiene rubber industrial waste devulcanized by microwave in rubber composites for automotive application. Mater. Des. 2012, 39, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Zanchet, A.; Scuracchio, C.H. Influence of reversion in compounds containing recycled natural rubber: In search of sustainable processing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.S.; De Sousa, F.D.B.; De Lima, J.A.; Cruz, S.A.; Scuracchio, C.H. Devulcanization of ground tire rubber: Physical and chemical changes after different microwave exposure times. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchet, A.; Dotta, A.L.B.; De Sousa, F.D.B. Relationship among vulcanization, mechanical properties and morphology of blends containing recycled EPDM. Recycling 2017, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B. Vulcanization of natural rubber: Past, present and future perspectives. In Natural Rubber: Properties, Behavior and Applications; Hamilton, J.L., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 47–88. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Zhan, M.; Wang, Y. The status of recycling of waste rubber. Mater. Des. 2001, 22, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; De, D.; Maiti, S. Reclamation and recycling of waste rubber. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000, 25, 909–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Zanchet, A.; Brandalise, R.N.; Crespo, J.S.; Nunes, R.C.R. Grinding and characterization of scrap rubbers powders. J. Elastom. Plast. 2008, 40, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Gouveia, J.R.; De Camargo Filho, P.M.F.; Vidotti, S.E.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Amurin, L.G.; Valera, T.S. Blends of ground tire rubber devulcanized by microwaves/HDPE—Part A: Influence of devulcanization process. Polím. Ciênc. Tecnol. 2015, 25, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchet, A.; Carli, L.N.; Giovanela, M.; Crespo, J.S.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Nunes, R.C.R. Characterization of microwave-devulcanized composites of ground SBR scraps. J. Elastom. Plast. 2009, 41, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Hu, G.H.; Hoppe, S. Devulcanization of waste tire rubber by microwaves. Polym. Degrad. STable 2017, 138, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, D.; Saron, C. Chemical modifications in styrene-butadiene rubber after microwave devulcanization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 3975–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Hu, G.H.; Hoppe, S. Effects of processing parameters on the properties of microwave-devulcanized ground tire rubber/polyethylene dynamically revulcanized blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistor, V.; Ornaghi, F.G.; Fiorio, R.; Zattera, A.J.; Oliveira, P.J.; Scuracchio, C.H. Desvulcanização do resíduo de terpolímero de etileno-propileno-dieno (EPDM-r) por micro-ondas. Polím. Ciênc. Tecnol. 2010, 20, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Gouveia, J.R.; De Camargo Filho, P.M.F.; Vidotti, S.E.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Amurin, L.G.; Valera, T.S. Blends ground tire rubber devulcanized by microwaves/HDPE—Part B: Influence of clay addition. Polím. Ciênc. Tecnol. 2015, 25, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B. Devulcanization of elastomers and applications. In Elastomers; Çankaya, N., Ed.; Intech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; Chapter 10; pp. 209–230. [Google Scholar]
- Ramarad, S.; Khalid, M.; Ratnam, C.T.; Chuah, A.L.; Rashmi, W. Waste tire rubber in polymer blends: A review on the evolution, properties and future. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 72, 100–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.A.; Halász, I.Z.; Karger-Kocsis, J.; Bárány, T. Microwave devulcanized crumb rubbers in polypropylene based thermoplastic dynamic vulcanizates. Polymers 2018, 10, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colom, X.; Marín-Genescà, M.; Mujal, R.; Formela, K.; Cañavate, J. Structural and physico-mechanical properties of natural rubber/GTR composites devulcanized by microwaves: Influence of GTR source and irradiation time. J. Compos. Mater. 2018, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaro, L.; Gratton, M.; Seghar, S.; Aït Hocine, N. Recycling of rubber wastes by devulcanization. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 133, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuracchio, C.H.; Waki, D.A.; Bretas, R.E.S. Caracterização térmica e reológica de borracha de pneu desvulcanizada por microondas. Polím. Ciênc. Tecnol. 2006, 16, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escócio, V.A.; Martins, A.F.; Visconte, L.L.Y.; Nunes, R.C.R. Efeito do envelhecimento nas propriedades mecânicas e dinâmico-mecânicas de composições de borracha natural com mica. Polím. Ciênc. Tecnol. 2004, 14, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rånby, B. Photodegradation and photo-oxidation of synthetic polymers. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 1989, 15, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Scuracchio, C.H. Vulcanization behavior of NBR with organically modified clay. J. Elastom. Plast. 2012, 44, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leib, R.I.; Sullivan, A.B.; Trivette, C.D., Jr. Prevulcanization inhibitor the chemistry of scorch delay. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1970, 43, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, E.; Arastoopour, H.; Bernstein, B. Pulverization of rubber granulates using the solid state shear extrusion process Part II. Powder characterization. Powder Technol. 2001, 115, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Zanchet, A. In the search for sustainable processing in compounds containing recycled natural rubber: The role of the reversion process. Recycling 2018, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Gao, J. Aging of ethylene–propylene–diene monomer (EPDM) in artificial weathering environment. Polym. Degrad. STable 2007, 92, 1841–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Gao, J. Aging behavior and mechanism of ethylene-propylene-diene monomer (EPDM) rubber in fluorescent UV/condensation weathering environment. Polym. Degrad. STable 2009, 94, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Leonov, A.I. A kinetic model for sulfur accelerated vulcanization of a natural rubber compound. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 61, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirqueira, A.S.; Soares, B.G. O efeito de EPDM modificado com grupos mercapto ou tioacetato na cinética de vulcanização de misturas NR/EPDM. Polím. Ciênc. Tecnol. 2006, 16, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiaku, U.S.; Chong, C.S.; Ismail, H. Determination of optimum De-Link R concentration in a recycled rubber compound. Polym. Test. 1999, 18, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isayev, A.I.; Yushanov, S.P.; Kim, S.H.; Levin, V.Y. Ultrasonic devulcanization of waste rubbers: Experimentation and modeling. Rheol. Acta 1996, 35, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.A.S.; Cassu, S.N.; de Mello, S.A.C.; Dutra, J.C.N. Influência do método de vulcanização nas propriedades mecânicas e na densidade de ligações cruzadas da borracha natural. Polím. Ciênc. Tecnol. 2016, 26, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanasom, N.; Poonsuk, A.; Makmoon, T. Effect of curing system on the mechanical properties and heat aging resistance of natural rubber/tire tread reclaimed rubber blends. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, J.E.; Erman, B.; Eirich, F.R. Science and Technology of Rubber; Elsevier: Atlanta, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Carli, L.N.; Boniatti, R.; Teixeira, C.E.; Nunes, R.C.R.; Crespo, J.S. Development and characterization of composites with ground elastomeric vulcanized scraps as filler. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbernon, L.; Norvez, S. From landfilling to vitrimer chemistry in rubber life cycle. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 82, 347–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).