Abstract
Mangifera plants are tropical fruits that have high economic value and scientific utility. However, the chloroplast genome characteristics and phylogenetic relationships among Mangifera species remain unclear. In this work, we reconstructed maximum likelihood (ML) and Bayesian inference (BI) phylogenetic trees using 11 newly sequenced chloroplast genomes as well as six existing genomes obtained from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database. The chloroplast genomes all had a typical quadripartite structure, with lengths ranging from 157,368 to 158,942 bp. The GC-content in the genomes ranged from 37.8% to 37.9%. We found conserved boundaries comprised of two inverted repeats (IRs), large single-copy (LSC) regions, and small single-copy (SSC) regions. Nucleotide polymorphism analysis revealed three hypervariable regions (ycf4-cemA, rps18-rpl20, and rpl32-ndhF) in the LSC and SSC regions, which could potentially be used as DNA barcodes for Mangifera species. According to our phylogenetic analysis, Mangifera plants were clustered into three clades. Among them, all five samples of M. indica formed a monophyletic group in Clade Ⅰ. Clade Ⅱ included seven Mangifera species and could be further divided into five subclades with 100% branch support values. Clade Ⅲ included two M. persiciforma samples that formed a monophyletic group. Taken together, these results provide a theoretical basis for species determination, in addition to shedding light on the evolution of Mangifera.
1. Introduction
Mangifera (Anacardiaceae) is a group of evergreen trees containing 69 species that are mainly distributed in India, Bangladesh, the Indochina Peninsula, and Malaysia. India is the origin of Mangifera cultivars, which were first recorded as early as 2000 BCE [1]. Mangifera fruits are rich in vitamins, protein, carotene, and other beneficial phytochemicals. Their fruit is valued for its sweet taste and attractive colour [2]. Due to their long history of cultivation, diverse varieties, rapid growth, early fruit bearing, long lifespan, and high nutritional value, Mangifera species have become some of the most widely grown fruit trees in the world [3,4,5]. At present, there are at least 26 species of Mangifera that produce edible fruits, including M. indica, which is mainly grown in Southeast Asia [6]. There are only five species native to China, including M. indica (Linn.), M. longipes (Griff.), M. persiciformis (C. Y. Wu et T. L. Ming), M. siamensis (Warbg. ex Craib), and M. sylvatica (Roxb.), most of which are located in the subtropical regions of Guangxi, Hainan, and Yunnan. Among them, M. siamensis is not only sweet in fruit, but also hard in wood, resistant to seawater, and can be made into boats and furniture; the fruit of M. sylvatica is acidic, but the medicine made from leaves has an obvious inhibitory effect on influenza virus; M. longipes has a thin flesh and large core, and has not yet been cultivated by artificial introduction; M. persiciformis is mostly used as a garden shade tree, street tree, and other landscaping. Compared to M. indica, other edible Mangifera species have lower fruit quality, size and sugar content. However, better classification and conservation of diverse Mangifera germplasm is still needed for potential breeding improvement [7,8]. At present, morphological characteristics are generally used to identify species, which are usually reliable for distantly related species but often fail to distinguish closely related species or cultivars with atypical phenotypes [9]. In addition, morphological traits are sensitive to environmental changes, and convergent or parallel evolution can result in incorrect classification. Such challenges make it difficult to develop a classification scheme for Mangifera in China, and additional research is needed in this area [6]. Molecular techniques are therefore required to better understand the phylogenetic relationships between similar species within this genus [10,11].
To date, there have been few reports on the phylogenetic relationships of Mangifera species. Suparman [12] constructed a phylogenetic tree of 16 taxa of Mangifera based on rbcL sequences, including 13 from Indonesia and three from Thailand. This analysis further supported the idea that M. odorata is a hybrid of M. indica and M. foetida. Fitmawati et al. [13] analysed the relationship between Mangifera species and their related genera based on the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequences trnL-F and rbcL, and found that Mangifera species are monophyletic. Dinesh et al. [14] determined the phylogenetic relationships among five Mangifera species using the rps16 gene, petB-petD, trnL-trnF intergenic spacer region, and the nuclear ribosomal DNA external transcribed spacer (ETS), and found that M. indica, M. griffithii, and M. camptosperma were closely related. However, phylogenetic analyses based on some segments, such as petB-petD, could not resolve the relationships between species. Additionally, trnL-trnF and rbcL gave only weak support for species relationships. To date, the relationships between different Mangifera species have not been satisfactorily resolved using fragment analyses. However, the phylogenetic tree constructed by Niu et al. [15] using whole chloroplast genomes of five Mangifera species was able to resolve the relationships between species. This approach does require full chloroplast genome sequences, which thus far are only available for nine species. The current lack of chloroplast genome sequences for most Mangifera species makes elucidating their relationships difficult.
The chloroplast genomes of most plants are circular, with double-stranded structures (115–116 kb) that include large single-copy (LSC) regions, small single-copy (SSC) regions, and two inverted repeat (IR) regions [16,17,18]. In recent years, the chloroplast genome of plants has become a powerful tool for developing molecular markers and phylogenetic analysis [19,20,21,22]. Since the chloroplast genomes of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) [19] and liverwort (Marchantia polymorpha) [23] were first reported in 1986, there has been a dramatic increase in the availability of genomic data from diverse plant species, creating new opportunities to classify and understand species [24,25].
In this study, the chloroplast genome sequences of 11 Mangifera species were obtained in order to understand their structural characteristics, identify highly variable regions, and construct phylogenetic trees. The results of this analysis have implications for species discrimination, phylogenies, and other molecular biology studies in Mangifera.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
Twelve leaf samples from ten Mangifera species were collected from Thailand, including Thailand’s variety M. indica Bao and Australia’s variety M. indica R2E2 (Table 1). After collection, the leaves were dried using silica gel. In addition, six chloroplast genome sequences from four Mangifera species (M. sylvatica, M. indica, M. persiciforma, and M. persiciforma) were downloaded from the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 25 March 2022). Combined, these data represented a total of 18 sequences from 11 species. Based on existing phylogenetic studies of Anacardiaceae [26], we chose Anacardium occidentalie (GenBank accession: KY635877), Pistacia weinmaniifolia (GenBank accession: NC037471), and Toxicodendron vernicifluum (GenBank accession: MK550621) as outgroups for phylogenetic tree construction.

Table 1.
The chloroplast genome characteristics of Mangifera spp.
2.2. DNA Extraction and Genome Sequencing
The cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) method was utilized to extract DNA from leaves dried with silica gel [27]. DNA purity and concentration were then examined via gel electrophoresis. Next, 150 bp paired-end Illumina libraries were constructed and sequenced on a NovaSeq sequencing platform at the Beijing Nuohe Zhiyuan Technology Company.
2.3. Genome Assembly and Annotation
The complete chloroplast genome was assembled from the GetOrganelle v1.7.5 pipeline [28]. The resulting graphical fragment assembly (GFA) file was visualized in Bandage v0.8.1 [29]. Assemblies which formed the typical quadripartite structure were considered successful. Those which failed to form this structure were reimported into GetOrganelle and reassembled manually using BioEdit v7.2.5 software (http://www.mbio.ncsu.edu/bioedit/bioedit.html, accessed on 28 March 2022) with the M. indica (GenBank accession: MN711724) reference sequence. The assembled chloroplast genomes were annotated with software Geneious R8.1 [30], using M. indica (GenBank accession: MN711724) as the reference sequence with 75% similarity.
2.4. Chloroplast Genome Structural Analysis
Geneious software [30] was used to determine the number of LSC, SSC, and IR regions of the 18 chloroplast genomes of Mangifera species. We also employed Geneious to determine gene content, including protein coding genes, ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes, and transfer RNA (tRNA) genes. IRscope software (https://irscope.shinyapps.io/irapp/, accessed on 30 March 2022) was used to visualize the four regional junction sites of the LSC, SSC, IRa, and IRb regions and to investigate the boundary contraction and expansion of IR regions of Mangifera chloroplast genomes.
2.5. Codon Usage Bias Analysis
We first filtered out all coding sequences (CDSs) with lengths below 300 bp. Then, CodonW v1.4.2 was employed to determine the number of codons (CN), number of effective codons (ENC), and relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) of each sequence (http://codonw.sourceforge.net, accessed on 3 April 2022).
2.6. Structural Analysis of Repeats
We used the MicroSatellite Identification Tool (MISA) website (https://webblast.ipk-gatersleben.de/misa/, accessed on 8 April 2022) to detect simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in the chloroplast genomes of the 11 Mangifera species [31] and compared their types, quantities, and distribution. The parameters were set as follows: repetition unit/minimum repetition times: 1/10, 2/5, 3/4, 4/3, 5/3, and 6/3. In addition, if the distance between two SSRs was less than 100 bp, the two SSRs were considered composite microsatellite SSRs.
2.7. Genome Comparison
To determine the differences among M. indica and other species, we used Ubuntu 18.04 LTS software to convert the annotation file of Mangifera sequences, which output the gene location information in TXT format, and then used the mVISTA tool for comparative genomics (https://genome.lbl.gov/vista/mvista/submit.shtml, accessed on 15 April 2022). We then analyzed the sequence differences among the other 10 species based on the Shuffle-LAGAN global comparison model [32] with M. indica (GenBank accession: MN711724) as a reference.
DnaSP 6 software was used for sliding window analysis, and the highly variable regions were extracted [33] by counting the nucleotide polymorphism (Pi) of the 18 Mangifera chloroplast genome sequences. We utilized a window length of 600 bp and a step size of 200 bp [34]. The results were imported into R software to draw a peak map of the nucleotide polymorphisms. DNA segments with a Pi value greater than 0.01 were considered highly variable regions and denoted as such in Geneious.
2.8. Phylogenetic Analyses
A phylogenetic analysis of 18 sequences of 11 Mangifera species was carried out to determine the genetic relationships among them. All chloroplast genomes used to construct phylogenetic trees retained an IR region. We used the MAFFT online tool (https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/server/, accessed on 25 April 2022) [35] to compare the 21 sequences, using the cashew species A. occidentale, P. weinmaniifolia, and T. vernicifluum as outgroups. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the CIPRES online computing platform (https://www.phylo.org/, accessed on 27 April 2022) [36], with both maximum likelihood (ML) and Bayesian inference (BI) approaches. The RAxML pipeline was used for maximum likelihood analysis, and GTRCAT (GTR, General time-reversible) was used for the nucleotide substitution model [37]. Simultaneous rapid bootstrapping (1000 replicates) was utilized to compute bootstrap support values for each node of the phylogenetic tree. Bayesian inference analysis was carried out in the Mrbayes 3.2.7a module of the CIPRES platform [38]. Firstly, jModeltest 22.1.6 [39] in the CIPRES platform was used to estimate the best nucleotide substitution model. This analysis identified the best model as TPM1uf+I, which is a 3-parameter model with invariable sites included [40]. The relevant parameters were then calculated and MCMC (Markov Chain Monte Carlo) was used to simulate 1,000,000 generations. Samples were taken every 100 generations, and the first 25% of the trees were discarded. Finally, we utilized the chloroplast genome nex file to construct a phylogenetic tree in Mrbayes 3.2.7a. The final results were visualized with the Figtree (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/, accessed on 30 April 2022) and TreeGraph (http://treegraph.bioinfweb.info, accessed on 31 April 2022) software.
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Features of Various Chloroplast Genomes
The chloroplast genomes of the 11 Mangifera species all had quadripartite structures (Figure 1), with lengths ranging from 157,368 to 158,942 bp. The largest was M. macrocarpa, and the smallest was M. sylvatica. The different regions of the genome ring included an LSC region of 86,228 to 87,735 bp, with the largest being M. cochinchinensis and the smallest being M. sylvatica. There was also an SSC region that was 18,347 to 20,572 bp, with the largest being M. perseciforma and the smallest being M. sylvatica. Additionally, an IR region of 25,252 to 26,396 bp was found, with the largest being M. sylvatica and the smallest being M. perseciforma. The GC-content in the genomes ranged from 37.8% to 37.9%. The GC-content in the LSC regions was approximately 35.8% to 36.0%, whereas the GC-content in the SSC regions was approximately 32.3% to 32.8%, and the GC-content of the IR regions was approximately 43.0% to 43.3% (Table 1).
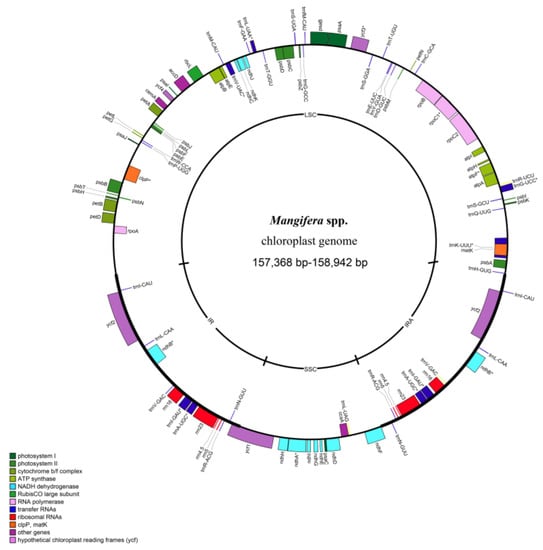
Figure 1.
Gene map of the chloroplast genome of 11 species of Mangifera. Genes inside and outside the circle are transcribed in a clockwise and counterclockwise direction, respectively. Genes are colour-coded based on their function. The grey area in the inner circle indicates the GC content of the chloroplast genome.
A total of 129 genes were found in the Mangifera chloroplast genome, including 84 protein-coding genes, eight rRNA genes, and 37 tRNA genes. Seventeen genes were duplicated in the IR regions, including six protein-coding genes, seven tRNA genes, and four rRNA genes. According to functional classification, there were 44 photosynthesis-related genes, 74 self-replicating genes, and 11 other genes. Moreover, because rps12 undergoes trans-splicing events, the 5’ end was located in the LSC region, while the 3’ end was located in the IR region. In addition, 15 genes (rpl16, rpl2, rpoC1, rps16, atpF, ndhB, ndhA, petb, petd, trnK-UUU, trnG-UCC, trnL-UAA, trnV-UAC, trnI-GAU, and trnA-UGC) contained one intron, and three genes (ycf3, clpP, and rps12) contained two introns (Table 2).

Table 2.
Genes of Mangifera, separated by categories.
3.2. Contraction and Expansion of the IR Regions
A comprehensive comparison of the boundaries of the four regions of the chloroplast genome of the 11 Mangifera species showed that the IR, LSC, and SSC regions were conserved. With the exception of the rps19 gene of M. caloneura, M. pentandra, and M. foetida, which did not cross the boundary of the LSC/IRb, the other rps19 genes crossed the LSC/IRb boundary at 104 bp to 106 bp. The ycf1 gene crossed the SSC/IRb boundary at 104 to 106 bp, whereas the ndhF gene was located in the SSC region and extended into the IRa region. The extension length was 33–39 bp (Figure 2).
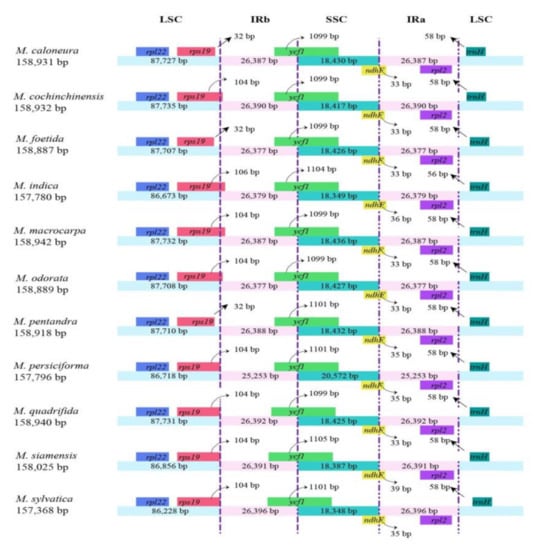

Figure 2.
Comparison of large single-copy (LSC), small single-copy (SSC), and inverted repeat (IR) borders among the 11 chloroplast genomes of Mangifera.
3.3. Codon Bias Analysis
There were 21,276 codons in the CDSs of the chloroplast genome of Mangifera, and the highest frequency was leucine (Leu), which appeared 2234 times, among which UUA occurred most frequently (696 times). The lowest frequency was the terminator (Ter), which occurred 53 times. In addition, the GC content of codons in Mangifera was 38.3%, and the range of ENC (effective number of codons) was between 35.38 and 56.29, with an average value of 50.09. The RSCU analysis indicated that the number of codons with relatively high frequency was 30 (codons with RSCU values greater than 1.00), of which 16 were U-terminated codons, and 13 were A-terminated codons (Figure 3). There was only one codon ending in G (UUG), indicating that the chloroplast genome of Mangifera prefers codons ending in U or A. No preference was seen when comparing UGG and AUG (RSCU 1.00).
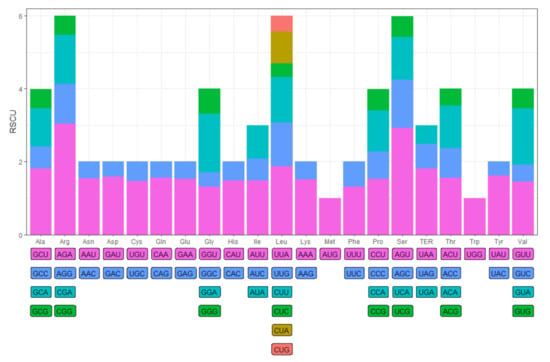
Figure 3.
Relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) of chloroplast genes in Mangifera species.
3.4. SSR Analyses
There were 778 SSR sites detected in the 11 Mangifera species (Figure 4), including six types of SSRs such as single-nucleotide repeats, dinucleotide repeats, and complex SSRs. According to base complementarity, these six types can be classified into 28 categories. Among them, the number of single-nucleotide repeats comprised of A/T was the largest at 517. There were also 47 dinucleotide AT/AT SSRs, 102 AAG/CCT trinucleotide SSRs, and 100 AAT/ATT tetranucleotide SSRs. The numbers of pentanucleotides and hexanucleotides were small, at two and 10, respectively (Figure 4).
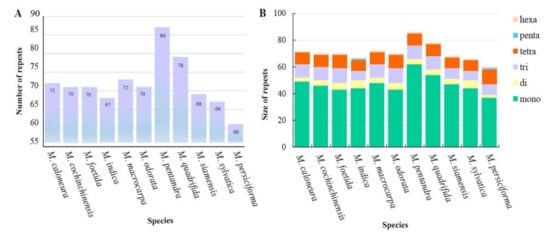
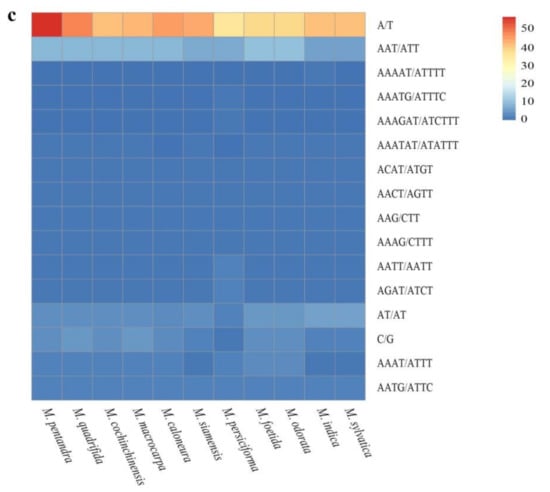
Figure 4.
(A) and (B) indicate the numbers of simple sequence repeats (SSRs) and SSR types detected in the 11 Mangifera chloroplast genomes. (C) indicate distribution of the 11 types of SSR repeat units among Mangifera sequence.
3.5. Comparative Analysis of Chloroplast Genomes
Using M. indica as a reference, the chloroplast genome sequence alignment of Mangifera species (Figure 5) showed that: (1) variation in noncoding regions (intergenic regions and some introns) was significantly higher than that in coding regions; (2) in the IR region where rRNA genes are located, the degree of variation was significantly lower than that in the LSC and SSC regions; and (3) the genes in the untranslated region (UTR) were highly conserved. Analysis of hypervariable regions in the chloroplast genomes of Mangifera species by DnaSP6 (Figure 6) showed Pi values ranging from 0 to 0.1399, with an average of 0.00243. The ycf4-cemA (63,712–65,340 bp), rps18-rpl20 (71,789–73,220 bp), and rpl32-ndhF (131,885–133,418 bp) genomic segments had high variation, which occurred in the LSC region and SSC region. However, nucleic acid variations in the IR region were rare.
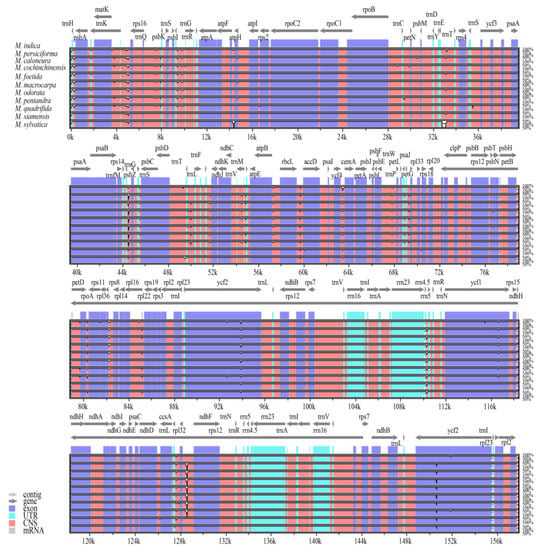
Figure 5.
Complete chloroplast genome comparison of the 11 species of Mangifera using the mVISTA alignment program. Coding and noncoding regions are coloured blue and red, respectively. The Y-scale represents the percentage of identity, ranging from 50% to 100%.
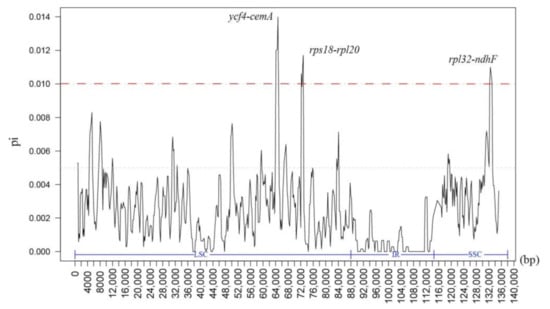
Figure 6.
Nucleotide diversity of the complete chloroplast genome sequences of Mangifera species.
3.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
The phylogenetic relationships of the 18 complete chloroplast genome sequences from the 11 Mangifera species were determined using both ML and BI. Trees constructed via the two pipelines were highly consistent. In both cases, Mangifera contained three groups, termed Clade I, Clade II, and Clade Ⅲ. Clade I was composed of three Mangifera species, including M. indica, M. sylvatica, and M. siamensia. In this clade, M. siamensia was the first to diverge, while M. sylvatica was the second (bootstrap support, BS = 100%, posterior probability, PP = 1.00). The samples from our study did not form a monophyletic group with the NCBI database samples. Five samples of M. indica formed a monophyletic group, which was sister to one sample of M. sylvatica, although the grouping had poor support (BS = 82%, PP = 1.00). Clade II was composed of seven Mangifera species, including M. macrocarpa, M. caloneura, M. pentandra, M. quadrifida, M. cochinchinensis, M. foetida, and M. odorata, and was divided into five sub-branches that were highly supported. Among them, M. foetida and M. odorata were the first to diverge, while the second sub-branch was M. cochinchinensis. The subclade formed by M. quadrifida was supported as the sister group to M. macrocarpa, M. pentandra, and M. caloneura (BS = 100%, PP = 1.00). Clade Ⅲ included two M. persiciforma samples and formed a monophyletic group (Figure 7).
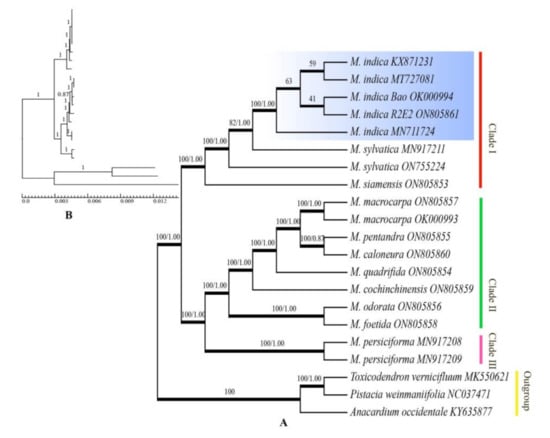
Figure 7.
Phylogenetic relationship of Mangifera species inferred by maximum likelihood (ML) and Bayesian inference (BI) methods using whole chloroplast genomes. Note: (A): Phylogram of Mangifera species; (B): BI tree with branch lengths.
4. Discussion
4.1. Chloroplast Genome of Mangifera
The chloroplast genome of Mangifera had the typical angiosperm circular tetrad structure, with genome lengths ranging from 157,368 to 158,942 bp. Chloroplasts of Mangifera species had 129 genes, including 84 protein-coding genes, eight rRNA genes, and 37 tRNA genes. There was no obvious difference in the average GC content across any of the species. In addition, the genotype, quantity, and GC content of the chloroplast genome of Mangifera species were highly consistent with those of other reported chloroplast genomes, such as Pyrus betulifolia and Pinus armandii [41,42].
The IR regions of the chloroplast genomes have been shown to be important during evolution, and their boundaries can expand or contract in angiosperms [43,44]. In this study, the rps19 gene was found to span the boundary of LSC and IRa, while ndhF spanned the boundary of SSC and IRb. The rps19 gene overhung the boundary by 104 to 106 bp, the ycf1 gene overhung the boundary by 1099 to 1105 bp, and the ndhF gene overhung the boundary by 33 to 39 bp. There was no obvious contraction or expansion of the IR regions found between species or within species, which is consistent with the research results of Niu et al. [15], who examined the IR boundaries of M. hiemalis, M. longipes, M. occidentale, and other Mangifera species. In addition, the ψycf1 pseudogene exists in the IRa/SSC border region, but was not annotated in this study. The emergence of the ψycf1 pseudogene may be due to its location at the border of the chloroplast gene region, resulting in a border effect [45].
4.2. Codon Usage and SSR Analysis
Codon bias is ubiquitous and can be affected by mutation or selection [46,47]. Several studies have pointed out that codons cannot be used in a perfectly balanced manner. This phenomenon results from the long-term evolution of the species’ own genes and long-term adaptation to external environmental pressures [48]. We analyzed the codon usage of the 53 CDSs found in the Mangifera chloroplast genomes and found that the ENC value was high, indicating that the preference of codons in the plastid genome of Mangifera was weak. Additionally, GC content was relatively conserved, indicating that codon preference is greatly affected by selection pressure. These findings are consistent with the codon preference found in plants such as Keteleeria evelyniana, Capsicum annuum, and Urtica fissa [49,50,51]. Xin et al. [2] obtained similar results in a study investigating the codon bias of Mangifera indica, indicating that many Mangifera species may share codon biases, likely due to their relatively conserved chloroplast genome structure. In addition, examination of codons with high usage frequency revealed that in Mangifera, codons preferentially end in U or A, which is consistent with findings in Saussurea involucrate, Cinnamomum glanduliferum, and Michelia species [52,53].
SSRs in chloroplast genomes have been widely used to develop molecular markers that can be deployed in studies focused on population genetics and variety identification. Such markers are particularly useful due to their high rate of polymorphism and unique maternal inheritance pattern [54,55,56]. A total of 778 SSRs were detected from the chloroplast genome sequences of Mangifera, most of which were single-nucleotide A/T repeats. Yan et al. [57] also obtained similar results when they analyzed Mangifera EST-SSR loci to develop markers. These findings further demonstrate that chloroplast genome SSRs are dominated by polyA and polyT repeats [58]. Mangifera GC content typically ranged from 37.8% to 37.9%, which may be the underlying reason for the bias towards A/T repeats. Nevertheless, different Mangifera species did have variations in the number and location of SSRs, which could be utilized for linkage mapping and genetic diversity research.
4.3. Structural Variation
The variation in chloroplast IR sequences in the 11 Mangifera species was significantly smaller than that in LSC and SSC regions, and variation in noncoding regions (intergenic and intronic) was significantly higher than that in coding regions, which was consistent with the pattern of genomic sequence variation in Schisandra chinensis and other angiosperms [59,60]. These findings indicate that noncoding regions have much higher rates of change than coding regions. Furthermore, nucleotide polymorphism analysis showed that the Mangifera species had three regions of high variation at ycf4-cemA (63,712–65,340 bp), rps18-rpl20 (71,789–73,220 bp), and rpl32-ndhF (131,885–133,418 bp). Niu et al. [15] have previously noted that the ycf4-cemA region has a high rate of polymorphism. However, the three hypervariable regions identified by Niu et al. [15] were located in the LSC region, while the mutation hotspots in this study were located in the LSC region and the SSC region. This inconsistency may be due to the selection of different Mangifera species in the two studies. In addition, IR region sequences are highly conserved, which is consistent with the results of our mVISTA analysis. This may be because the structural characteristics of the inverted repeats in the IR regions make the IR region sequence less likely than the LSC region to accrue mutations [61]. Regardless, the three mutation hotspots identified in this study can be considered candidates for the development of DNA barcoding for Mangifera plants.
4.4. Phylogenetic Relationships
In this study, we used 18 chloroplast genomes from 11 Mangifera species for phylogenetic analysis, with A. occidentale, P. weinmaniifolia, and T. vernicifluum as outgroups. Our results differed from the phylogenetic trees constructed by Fitmawati et al. [3] based on ITS sequences, but both analyses indicated that M. odorata and M. foetida are more closely related than most other Mangifera species. In Fitmawati’s study, the three samples of M. foetida were not clustered into a clade, which may be due to different sampling sites and different species used in constructing the phylogenetic tree. Overall, ITS-based phylogenetic trees had weak support values and could only resolve species relationships to a limited extent, which was further confirmed by ITS samples of Mangifera from Sumatra, Indonesia [13]. In this analysis, 23 species were divided into two subgenera, Limus and Mangifera. Additionally, multiple samples of M. odorata and M. foetida were not separated by species, but rather formed a mixed monophyly. This is likely because ITS is a segment of the ribosomal RNA precursor gene, which is located in the nucleus, and therefore jointly determined by both parents. The level of homology of these two genes may therefore prevent accurate assessment of the phylogenetic relationship between M. odorata and M. foetida. This may be because M. odorata is a natural hybrid of M. foetida and M. indica [62,63]. Teo et al. [64] demonstrated this relationship earlier using AFLP (amplified fragment length polymorphism). Their analysis not only verified the hybrid status of M. odorata, but also found that M. odorata was closer to M. foetida than to M. indica, indicating that backcrossing with M. foetida might have taken place. More recently, studies using ITS [65] and rbcL [12] sequences have also indicated that M. odorata could be a hybrid. ITS markers also indicated that M. casturi was generated from cross-hybridization of multiple species [65]. Compared to the ITS sequence, the chloroplast genome is maternally inherited, its genome is relatively stable and therefore generates more reliable phylogenetic trees for Mangifera species. This trend was confirmed by Fitmawati et al. [66] when they utilized the chloroplast fragment trnL-F. Although some of their branches had weak support values, they were able to separate M. odorata and M. foetida.
Complete chloroplast genomes can provide sufficient informative loci to help determine elusive relationships at low taxonomic levels [67,68]. In this study, Clade I, Clade II, and Clade Ⅲ were further divided into 10 sub-branches, with good resolution between nearly all species. However, subclades formed by M. indica had five samples with weak support. After examining the sequence matrix, it was found that the weak support of the internal subclades of M. indica may be due to high sequence similarity. It is worth noting that the two samples of M. sylvatica in Clade I were not monophyletic. The sample collected from Thailand and the sample from the NCBI database formed separate subbranches, possibly due to evolutionary differences caused by regional separation. In future analyses, increasing the number of M. sylvatica samples could enable more accurate clarification of the phylogenetic position of M. sylvatica species in the genus Mangifera. In addition, our results indicate that M. indica and M. sylvatica are closely related. Niu et al. [15] also had similar findings when they carried out a comparative analysis of the ML phylogenetic trees of five species of Pistacia spp. and 21 related species based on their chloroplast genomes.
It is worth noting that this study only included 11 different species, and integrating the cpDNA sequences of other Mangifera species would be required to more accurately classify all Mangifera species. Despite these limitations, our analysis of Mangifera chloroplast sequences lays a foundation for molecular breeding and genetic engineering of these species.
5. Conclusions
The chloroplast genome structures of Mangifera species were similar to those of most angiosperms, with relatively conserved gene structures and gene contents. Sequence variations were primarily concentrated in the LSC and SSC regions. Among them, three highly variable regions, ycf4-cemA, rps18-rpl20, and rpl32-ndhF, could be used as potential DNA barcoding regions for Mangifera plants. In addition, the topological structures of the phylogenetic trees constructed using ML and BI were consistent, and the species of Mangifera were divided into two branches. These results can serve as a guide for subsequent analyses focused on species classification, phylogenetic evolution, and population genetics of Mangifera species.
Author Contributions
Sampling, W.E.; DNA sequencing, W.Y.; data analysis, Y.X., Z.Y., Q.L., Z.C. and W.Z.; thesis writing, Y.X.; project fund support provider, P.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Yunnan Province Science and Technology Talents and Platform Project (No. 202205AF150022).
Data Availability Statement
The dataset provided in this study has been uploaded to the NCBI database, and the sequence information and NCBI number have been stated in the article.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ru-Li Zhang for helping upload partial data, Fu-Yan Chen for checking grammar problems. We thank TopEdit (www.topeditsci.com, accessed on 8 November 2022) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, Y.Y.; Dang, Z.G.; Lin, D.; Hu, M.J.; Huang, J.F.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, H.; Han, D.; Gao, A.; Gao, Z.Y.; et al. Mango scientific research in China in the past 70 years. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2020, 41, 2034–2044. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Y.X.; Li, R.Z.; Li, X.; Chen, L.Q.; Tang, J.R.; Qu, Y.Y.; Yang, L.Y.; Xin, P.Y.; Li, Y.F. Analysis of codon usage bias of chloroplast genome in Mangifera indica. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2021, 41, 148-156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitmawati, F.; Ningrum, M.R.; Mahatma, R.; Suzanti, F. Phylogenetic study of genus Mangifera in southern Sumatera based on DNA Sequences of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 197, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.M.; Huang, H.; Li, X.Y.; He, F.P.; Fan, J.X.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, D.Y.; Liu, Q.G.; Li, T.Y.; Huang, J.F.; et al. Quality analysis of Mango suitable for planting in Guizhou. Non-Wood For. Res. 2020, 38, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Fang, J.; Ye, J.M.; Yao, Q. Effect of Heat Treatment Composite Chitosan Coating on ‘Tainong No.1’ Mango Storage Quality at Room Temperature. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 47, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.T.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Jin, Z.Q. Advances in molecular markers of Mango germplasm resources. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2009, 37, 15722–15724+15850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, K.; Choi, Y.A.; Honsho, C.; Eiadthong, W.; Yonemori, K. Application of genomic in situ hybridization for phylogenetic study between Mangifera indica L. and eight wild species of Mangifera. Sci. Hortic. 2006, 110, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, M.; Dinesh, M.R.; Chaitra, N.; Ravishankar, K.V. Morphological, cytological, palynological and molecular characterization of certain Mangifera species. Curr. Sci. 2018, 115, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.H.; Li, Y.R.; Guo, Y.Z.; Ou, S.J.; Li, R.B. Identification of closely related Mango cultivars by ISSR. Guihaia 2007, 27, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, W.R.; Hou, B.W.; Guan, J.J.; Luo, J.; Ding, X.Y. Sequence analysis of LEAFY homologous gene from Dendrobium moniliforme and application for identification of medicinal Dendrobium. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2013, 48, 597–603. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Nie, L.; Xu, Z.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; He, C.; Song, J.Y.; Yao, H. Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of three Paeonia section Moutan species (Paeoniaceae). Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suparman, P.A.; Hidayat, T. Phylogenetic analysis of Mangifera based on rbcL sequences, chloroplast DNA. Sci. Papers Ser. B Hortic. 2013, 57, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Fitmawati, F.; Hayati, I.; Mahatma, R.; Suzanti, F. Phylogenetic study of Mangifera from Sumatra,Indonesia using nuclear and chloroplast DNA sequences. SABRAO J. Breed. Genet. 2018, 50, 295–312. [Google Scholar]
- Dinesh, M.R.; Ravishankar, K.V.; Nischita, P.; Sandya, B.S.; Padmakar, B.; Ganeshan, S.; Chithiraichelvan, R.; Sharma, T.V.R.S. Exploration, characterization and phylogenetic studies in wild Mangifera indica relatives. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 2151–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Gao, C.; Liu, J. Comparative analysis of the complete plastid genomes of Mangifera species and gene transfer between plastid and mitochondrial genomes. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, R.K.; Raubeson, L.A.; Boore, J.L.; DePamphilis, C.W.; Chumley, T.W.; Haberle, R.C.; Wyman, S.K.; Alverson, A.J.; Peery, R.; Herman, S.J.; et al. Methods for obtaining and analyzing whole chloroplast genome sequences. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 395, 348–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.C. Process in chloroplast genome analysis. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 35, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Dong, W.P.; Zhou, S.L. Structural mutations and reorganizations in chloroplast genomes of flowering plants. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident Sin. 2012, 32, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, K.; Ohme, M.; Tanaka, M.; Wakasugi, T.; Hayashida, N.; Matsubayashi, T.; Zaita, N.; Chunwongse, J.; Obokata, J.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; et al. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: Its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 2043–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.J.; Guo, M.Y.; Pang, X.H. Application of chloroplast genome in identification and phylogenetic analysis of medicinal plants. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 702-708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.P.; Zhu, Z.L.; Fan, Y.J.; Zhu, F.; Chen, Y.J.; Niu, Z.T.; Ding, X.Y. Comparative plastomic analysis of three Bulbophyllum medicinal plants and its significance in species identification. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2020, 55, 2736–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, X.F.; Gao, J.; Liu, A.P.; Yan, Y.G.; Yang, X.J.; Zhang, G. Complete chloroplast genome of Paeonia mairei H. Lév.: Characterization and phylogeny. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2020, 55, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, K.; Fukuzawa, H.; Kohchi, T.; Shirai, H.; Sano, T.; Sano, S.; Umesono, K.; Shiki, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Chang, Z.; et al. Chloroplast gene organization deduced from complete sequence of liverwort Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast DNA. Nature 1986, 322, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Yan, N.; Song, Q.; Guo, J. Complete chloroplast genome sequence and characteristics analysis of Morus multicaulis. Bull. Bot. 2018, 53, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.L.; Liu, Y.; Kang, H.M.; Chen, Z.H. Analysis of codon usage bias in chloroplast genome of Malania oleifera. J. Southwest For. Univ. 2021, 41, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.F.; Ren, Z.M. Complete chloroplast genome of Pistacia chinensis Bunge (Anacardiaceae: Rhoideae), an important economical and ornamental plant. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2020, 5, 1931–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochemistry. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.J.; Yu, W.B.; Yang, J.B.; Song, Y.; de Pamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.S.; Li, D.Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Schultz, M.B.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K.E. Bandage: Interactive visualization of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3350–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2007, 15, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DNASP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.T.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. IEEE Comput. Soc. Bioinf. Conf. 2010, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, A. Using Raxml to infer phylogenies. Curr. Protoc. Bioinf. 2015, 51, 6141–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P. Mebayes: Bayesian inference of phylogeney. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D. jModelTest: Phylogenetic model averaging. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. Estimation of evolutionary distances between homologous nucleotide sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, L. Analysis of chloroplast genome of Pyrus betulaefolia. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2020, 47, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Dong, Z.H.; Qu, S.H.; Xia, M.T.; Wang, Z.D.; Shen, W.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Yu, Q.F.; Xin, P.Y. Sequencing and characteristics analysis of chloroplast genome of Pinus armandii. Mol. Plant Breed. 2021, 19, 3223–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Tang, P.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H. The first complete chloroplast genome sequences in Actinidiaceae: Genome structure and comparative analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.F.; Zang, M.Y.; Li, M.; Fang, Y. Complete chloroplast genome sequence and phylogentic analysis of Quercus acutissima. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.R.; Zhao, Z.L.; Ni, L.H.; Wu, J.R.; Dan, Z.Z.G. Comparative analysis of complete chloroplast genome sequences within Gentianaceae and significance of identifying species. Chin. Tradit. Herbal Drugs. 2020, 51, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.P.; Dong, Y.Y.; Dang, Y.K. Codon codes: Codon usage bias influences many levels of gene expression. Sci. Sin. 2019, 49, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.M.; Wu, S.F.; Ren, D.M.; Zhu, Y.P.; He, F.C. The analysis method and progress in the study of codon bias. Hereditas 2007, 29, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.H.; Dai, D.Q.; Zhao, M.Y. Codon usage bias analysis of the genome-wide genes encoded in Agaricus bisporus. Mycosystema 2021, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Wang, Y.; Yan, T.Y.; Wang, Q.B.; Chen, S.; Cai, N.H.; Xu, Y.L.; Tang, H.Y. Analysis on codon usage bias of Keteleeria evelyniana chloroplast genome. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2022, 42, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Han, L.H.; Wu, L.F.; Dai, X.B.; Liu, j. Genome-wide codon usage bias analysis of Capsicum annuum. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2022, 50, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, H.; Cong, C.L.; Song, X.H.; Chen, W.W.; Pang, L.; Chang, X.C.; Tian, S.J. Codon Preference Analysis of the Chloroplast Genome of Urtica fissa. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 41, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.L.; Peng, Y.J.; Li, M.; Feng, B.; Qing, Y.J.; Wang, A.Y.; Zhu, J.B. Preference analysis of codon usage in the chloroplast genome of Saussurea involucrate. J. Shihezi Univ. Nat. Sci. 2022, 40, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.K.; Yan, W.; Xiong, X.K.; Shen, S.B.; Song, J.M.; Yi, H.F.; Zhang, L.H. Analysis of codon usage bias in the chloroplast genome of Cinnamomum glanduliferum. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2022, 42, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Wang, B.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, B. Genetic diversity and population structure of Chinese white poplar (Populus tomentosa) revealed by SSR markers. J. Hered. 2012, 103, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, H.; Petrino, M.G.; Kakunaga, T. A novel repeated element with Z-DNA-forming potential is widely found in evolutionarily diverse eukaryotic genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 6465–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Niu, N.; Li, Y.Y. Application of SSR marker in plant genome research. J. Shenyang Norm. Univ. 2010, 1, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.Q.; Liu, Z.B.; Ji, H.W.; Zhang, Y.M.; Sun, G.L.; Zhou, Q.; Luo, Q.H. Analysis of EST-SSR Loci and Primers Development in Mango (Mangifera indica). Mol. Plant Breeding 2020, 18, 6077–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Song, J.Y.; Gao, H.H.; Zhu, Y.J.; Xu, J.; Pang, X.H.; Yao, H.; Sun, C.; Li, X.E.; Li, C.Y.; et al. The Complete chloroplast genome sequence of the medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza. PLoS ONE 2013, 6, e57607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, J.; Luo, L.; Wei, X.; Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, B.G.; Liu, H.T.; Xiao, P. Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Schisandra chinensis: Genome structure, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic relationship of basal angiosperms. Sci. China Life Sci. 2017, 60, 1286–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Cui, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.Y.; Yao, H. Molecular structure and phylogenetic analyses of complete chloroplast genomes of two Aristolochia medicinal species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yi, X.; Yang, Y.X.; Su, Y.J.; Wang, T. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of a tree fern Alsophila spinulosa: Insights into evolutionary changes in fern chloroplast genomes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H. Mangifera . Flora Males. 1978, 1, 423–440. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.A. Mangifera indica germplasm resources and breeding in Thailand. South China Fruits 2018, 47, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, L.L.; Kiew, R.; Set, O.; Lee, S.K.; Gan, Y.Y. Hybrid status of kuwini, Mangifera odorata Griff. (Anacardiaceae) verified by amplified fragment length polymorphism. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matra, D.D.; Fathoni, M.; Majiidu, M.; Wicaksono, H.; Sriyono, A.; Gunawan, G.; Susanti, H.; Sari, R.; Fitmawati, F.; Siregar, I.Z.; et al. The genetic variation and relationship among the natural hybrids of Mangifera casturi Kosterm. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitmawati, F.; Harahap, S.P.; Sofiyanti, N. Short Communication: Phylogenetic analysis of mango (Mangifera) in Northern Sumatra based on gene sequences of cpDNA trnL-F intergenic spacer. Biodiversitas 2017, 18, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.B.; Tang, M.; Li, H.T.; Zhang, Z.R.; Li, D.Z. Complete chloroplast genome of the genus Cymbidium: Lights into the species identification, phylogenetic implications and population genetic analyses. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, R.; Bonnema, G.; Borm, T.J.A. A phylogenetic analysis of chloroplast genomes elucidates the relationships of the six economically important Brassica species comprising the triangle of U. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).