Effects of Bacillus cereus on Photosynthesis and Antioxidant Metabolism of Cucumber Seedlings under Salt Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Cultivation and Treatment
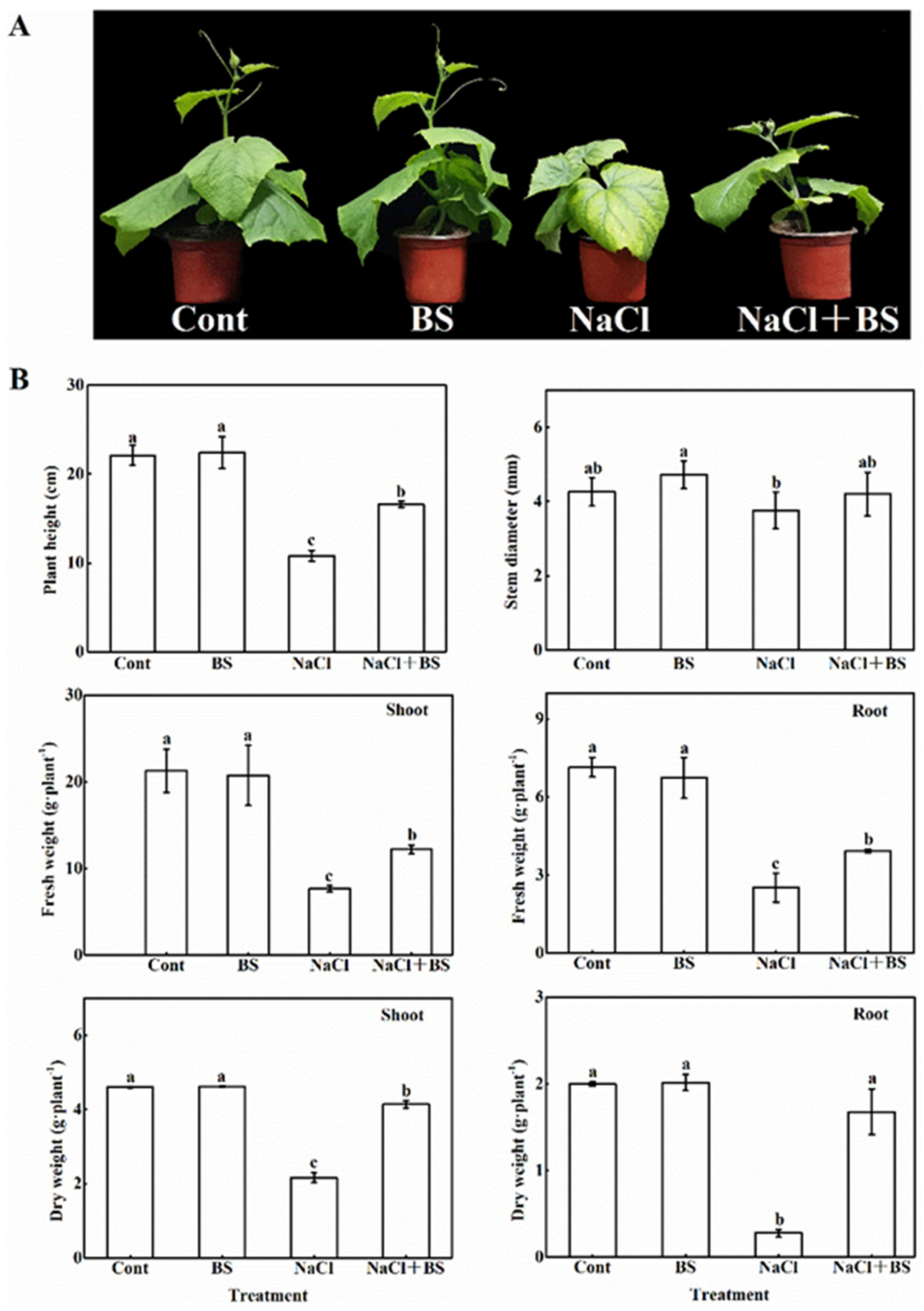
- Cont: Seedlings were grown in the solid substrate and treated with sterile distilled water;
- BS: Seedlings were grown in the solid substrate and treated with B. cereus suspension;
- NaCl: The seedlings grew in the solid substrate and were irrigated with 150 mM NaCl solution (EC: 9.17 mS·cm−1);
- NaCl+BS: Seedlings were grown in solid substrate containing NaCl (EC: 9.17 mS·cm−1) and treated with B. cereus suspension.
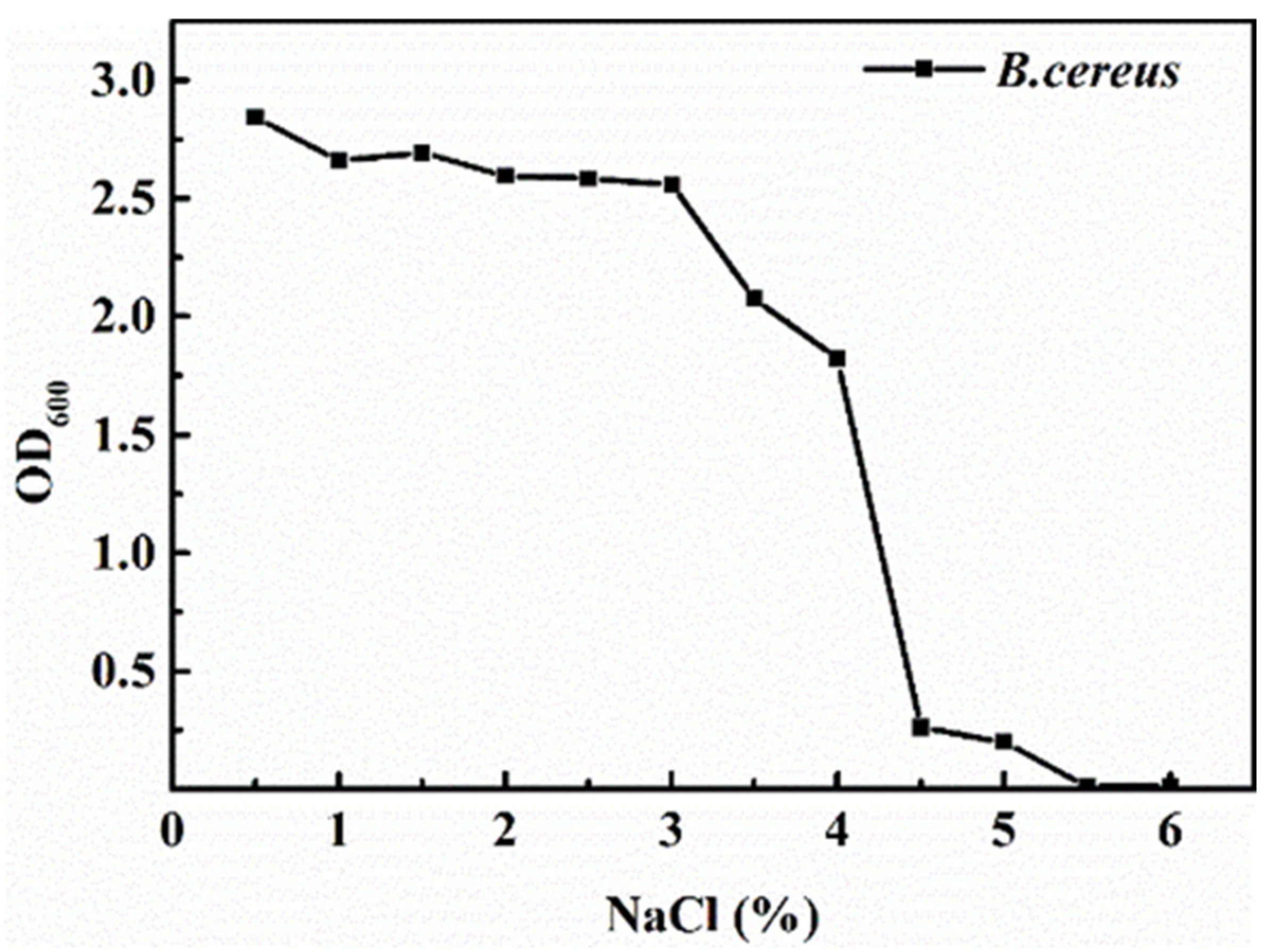
2.2. Salt Tolerance of B. cereus
2.3. Growth Parameters
2.4. Chlorophyll Content
2.5. Photosynthesis
2.6. H2O2 and MDA Contents
2.7. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
2.8. Proline Content
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Salt Tolerance of B. cereus
3.2. Effect of B. cereus on the Growth of Cucumber Seedlings under Salt Stress
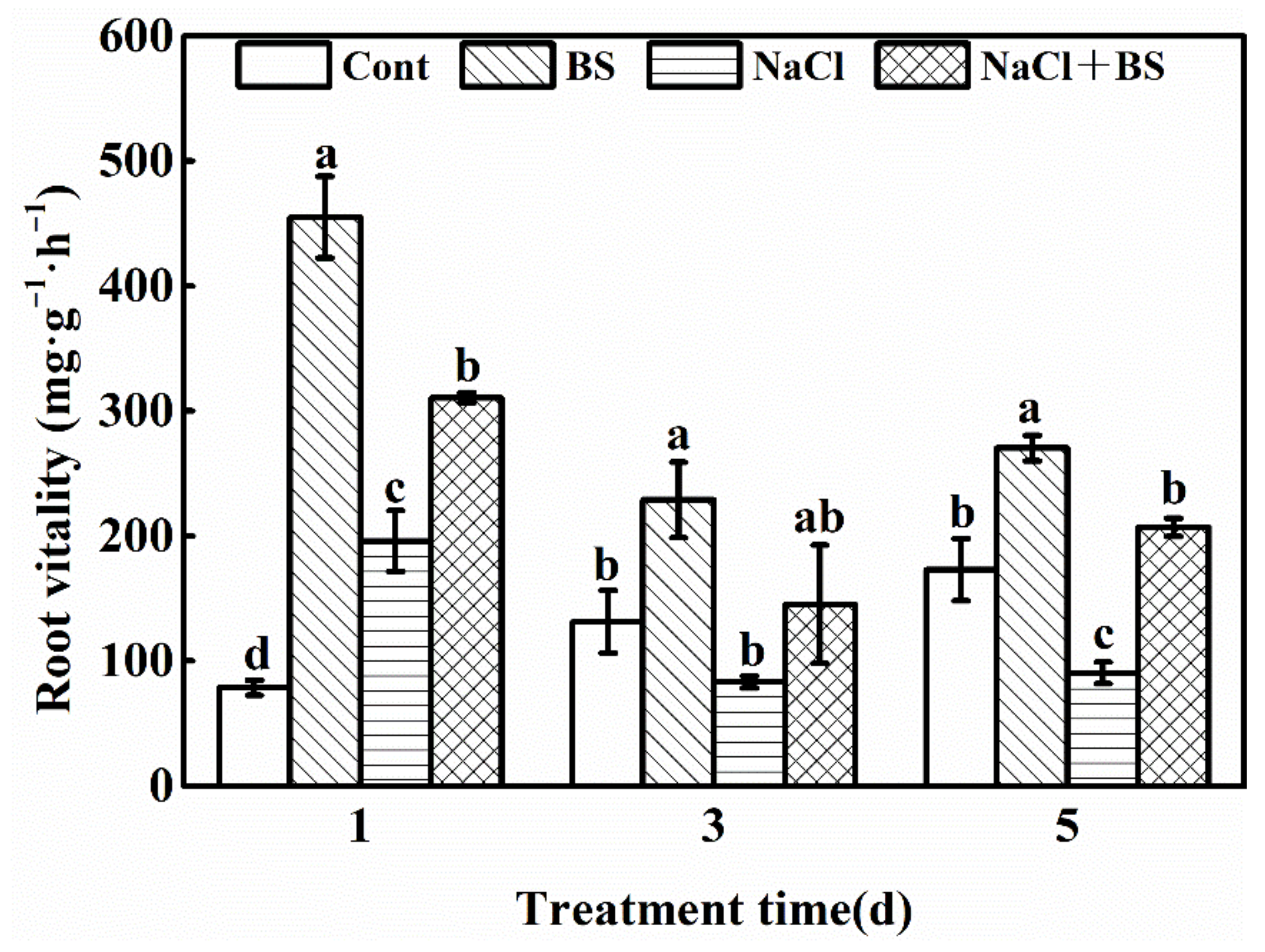
3.3. Effect of B. cereus on the Root Vitality of Cucumber Seedlings under Salt Stress
3.4. Effect of B. cereus on the Chlorophyll Content of Cucumber Seedlings under Salt Stress
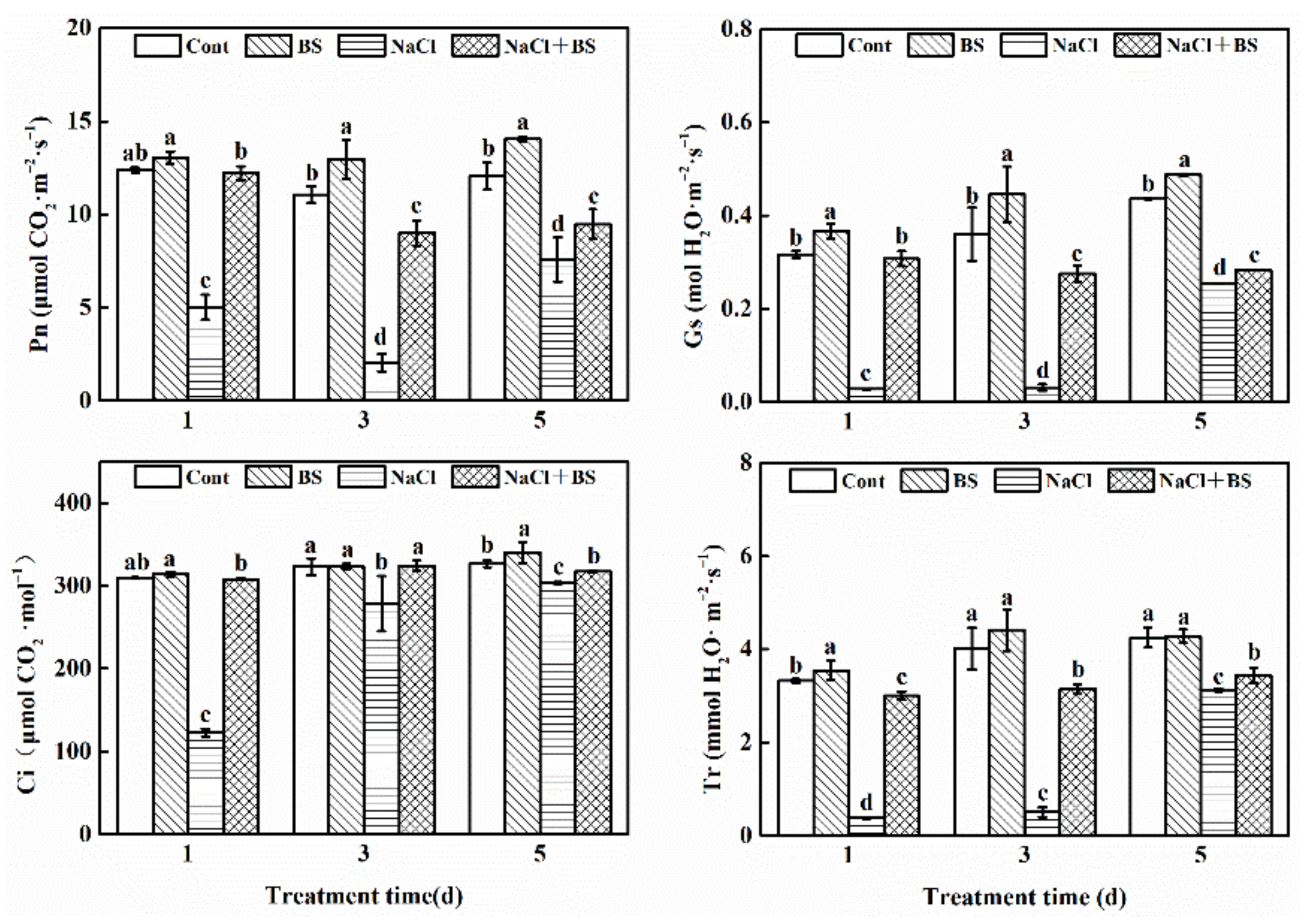
3.5. Effect of B. cereus on Gas Exchange Parameters of Cucumber Seedlings under Salt Stress
3.6. Effects of B. cereus on Chlorophyll Fluorescence of Seedlings under Salt Stress
3.7. Effects of B. cereus on the Contents of MDA and H2O2 in Cucumber Seedlings under Salt Stress
3.8. Effect of B. cereus on the Antioxidant Enzyme Activities of Cucumber Seedlings under Salt Stress
3.9. Effect of B. cereus on the Content of Proline in Cucumber Seedlings under Salt Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munns, R. Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, P. World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Song, C.; Zhu, J.K.; Shabala, S. Mechanisms of plant responses and adaptation to soil salinity. Innovation 2020, 1, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, H.; Meena, M.; Swapnil, P. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria as a green alternative for sustainable agriculture. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Q.; Lu, X.B.; Li, Z.H.; Tian, C.Y.; Song, J. The role of root-associated microbes in growth stimulation of plants under saline conditions. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 3471–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, Y.M.; Attia, K.A.; Kamel, S.; Alamery, S.F.; El-Gendy, S.; Al-Doss, A.A.; Mehiar, F.; Ghazy, A.I.; Ibrahim, E.I.; Abdelaal, K.A.A. Bacillus subtilis as a bio-agent combined with nano molecules can control powdery mildew disease through histochemical and physiobiochemical changes in cucumber plants. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 111, 101489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiao, Q.Q.; Wang, P.C. Phosphate-solubilizing Bacterium burkholderia sp. strain N3 facilitates the regulation of gene expression and improves tomato seedling growth under cadmium stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 217, 112268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, N.A.; Akram, W.; Khan, W.U.; Ahmad, S.R.; Ahmad, A.; Ali, A. Halotolerant plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria modulate gene expression and osmolyte production to improve salinity tolerance and growth in Capsicum annum L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 23236–23250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Y.N.; Jin, C.; Guan, C. A novel PGPR strain Kocuria rhizophila Y1 enhances salt stress tolerance in maize by regulating phytohormone levels, nutrient acquisition, redox potential, ion homeostasis, photosynthetic capacity and stress-responsive genes expression. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 174, 104023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, U.; Khizar, M.; Liaquat, F.; Ali, M.; Akbar, M.; Tahir, K.; Batool, S.S.; Kamal, A.; Chaudhary, H.J.; Munis, M.F.H. Halotolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria induce salinity tolerance in wheat by enhancing the expression of SOS genes. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noctor, G.; Foyer, C.H. Ascorbate and glutathione: Keeping active oxygen under control. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 49, 249–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, I.M.; Jensen, P.E.; Hansson, A. Oxidative modifications to cellular components in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 459–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ankati, S.; Srinivas, V.; Pratyusha, S.; Gopalakrishnan, S. Streptomyces consortia-mediated plant defense against Fusarium wilt and plant growth-promotion in chickpea. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 157, 104961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Ahmad, Y.N.; Kanwal, A.; Aqeel, A.; Ullah, K.W.; Waheed, A.; Muhammad, A. Ameliorative role of Bacillus subtilis FBL-10 and silicon against lead induced stress in Solanum melongena. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 158, 486–496. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.G.; Zhang, F.H.; Mickan, B.D.; Wang, D.; Wang, W. Physiological, proteomic, and metabolomic analysis provide insights into Bacillus sp.-mediated salt tolerance in wheat. Plant Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Qu, Y.; Li, H.; Wan, M.H.; Zhang, J.Y. Pseudomonas simiae augments the tolerance to alkaline bauxite residue in Atriplex canescens by modulating photosynthesis, antioxidant defense enzymes, and compatible osmolytes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 24370–24380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, C.; Cheow, Y.L.; Ting, A.S.Y. Comparative analysis on metal removal potential of exopolymeric substances with live and dead cells of bacteria. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2022, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.K.; Yan, X.J.; Wang, J.H.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Wen, S.; Kim, Y.M. Mechanism for biodegradation of sulfamethazine by Bacillus cereus H38. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 152237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, F.; Duraisamy, S.; Balakrishnan, S.; Ranjith, S.; Chidambaram, P.; Kumarasamy, A. Phenotypic assessment of safety and probiotic potential of native isolates from marine fish Moolgarda seheli towards sustainable aquaculture. Biologia 2022, 77, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.X.; Chen, C.; Zhong, K.; Wu, Y.; Gao, H. Purification, fermentation optimization, and antibacterial activity of pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid produced by an endophytic bacterium, Bacillus cereus ZBE, Isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Y.; Jiang, Y.D.; Gong, L.M.; Chen, X.; Xie, Q.; Jin, Y.; Du, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, G. Mechanism of beta-cypermethrin metabolism by Bacillus cereus GW-01. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, M.; James, C.; Pruinská, A.; Hrtensteiner, S.; Thomas, H.; Ougham, H. Analysis of the chlorophyll catabolism pathway in leaves of an introgression senescence mutant of Lolium temulentum. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.Y.; Shu, S.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, R.N.; Guo, S.R. Exogenous putrescine alleviates photoinhibition caused by salt stress through cooperation with cyclic electron flow in cucumber. Photosynth. Res. 2019, 141, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.Y.; He, M.W.; Jahan, M.S.; Wu, J.; Gu, Q.; Shu, S.; Sun, J.; Guo, S. CsCDPK6, a CsSAMS1-interacting protein, affects polyamine/ethylene biosynthesis in Cucumber and enhances salt tolerance by overexpression in tobacco. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Q.; Shu, S.; Li, C.C.; Sun, J.; Guo, S.R. Spermidine-mediated hydrogen peroxide signaling enhances the antioxidant capacity of salt-stressed cucumber roots. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 128, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; He, C.X.; Guo, S.R.; Xu, G.; Yu, X.; Sun, J. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on osmoregulation substance contents and antioxidant enzyme activities of cucumber seedlings under salt stress. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2011, 31, 2492–2497. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Xie, J.K.; Huang, W.X.; Chen, D.; Peng, X.; Fu, X. Effects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on physiological characteristics of rice under drought stress. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2018, 32, 485–492. [Google Scholar]
- Ateş, Ö; Kivanç, M. Isolation of ACC deaminase producing rhizobacteria from wheat rhizosphere and determinating of plant growth activities under salt stress conditions. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Smith, D.; Sultan, T.; Seleiman, M.F.; Alsadon, A.A.; Amna; Ali, S.; Chaudhary, H.J.; Solieman, T.H.I.; et al. Mitigation of heat stress in Solanum lycopersicum L. by ACC-deaminase and exopolysaccharide producing Bacillus cereus: Effects on biochemical profiling. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajilogba, C.F.; Babalola, O.O. RAPD profiling of Bacillus spp with PGPR potential and their effects on mineral composition of tomatoes. J. Hum. Ecol. 2016, 56, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishal, V.K.; Manuel, V.B.R. Effect of ACC-deaminase producing Bacillus cereus brm on the growth of Vigna radiata (Mung beans) under salinity stress. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 10, 122–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.G.; Long, S.P.; Ort, D.R. Improving photosynthetic efficiency for greater yield. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 235–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardoso, A.F.; Alves, E.C.; Costa, S.D.A.; Moraes, A.J.G.; Silva Júnior, D.D.; Lins, P.M.P.; Silva, G.B. Bacillus cereus improves performance of Brazilian green dwarf coconut palms seedlings with reduced chemical fertilization. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 649487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahtani, M.D.F.; Attia, K.A.; Hafez, Y.M.; Khan, N.; Eid, A.M.; Ali, M.A.M.; Abdelaal, K.A.A. Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and antioxidant defense system can display salt tolerance of salt acclimated sweet pepper plants treated with chitosan and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeseman, J.M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance in plants. Plant Physiol. 1988, 87, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, A.; Niu, S.; Yang, D.; Ren, W.; Zhang, J. Two PGPR strains from the rhizosphere of Haloxylon ammodendron promoted growth and enhanced drought tolerance of ryegrass. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 161, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Yasmeen, T.; Arif, M.S.; Ali, S.; Ali, B.; Hameed, S.; Zhou, W. Plant growth promoting bacteria confer salt tolerance in Vigna radiata by up-regulating antioxidant defense and biological soil fertility. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 80, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, K.; AlKahtani, M.; Attia, K.; Hafez, Y.; Király, L.; Künstler, A. The role of plant growth-promoting bacteria in alleviating the adverse effects of drought on plants. Biology 2021, 10, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.; Redman, R. Balancing the generation and elimination of reactive oxygen species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3175–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.J.; Huang, L.; Lin, X.Y.; Sun, C.L. Hydrogen peroxide alleviates salinity-induced damage through enhancing proline accumulation in wheat seedlings. Plant Cell Rep. 2020, 39, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Esawi, M.A.; Alaraidh, I.A.; Alsahli, A.A.; Alamri, S.A.; Ali, H.M.; Alayafi, A.A. Bacillus firmus (SW5) augments salt tolerance in soybean (Glycine max L.) by modulating root system architecture, antioxidant defense systems and stress-responsive genes expression. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 132, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar-ul-Hye, M.; Akbar, M.N.; Iftikhar, Y.; Abbas, M.; Zahid, A.; Fahad, S.; Datta, R.; Ali, M.; Elgorban, A.M.; Ansari, M.J.; et al. Rhizobacteria inoculation and caffeic acid alleviated drought stress in lentil plants. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
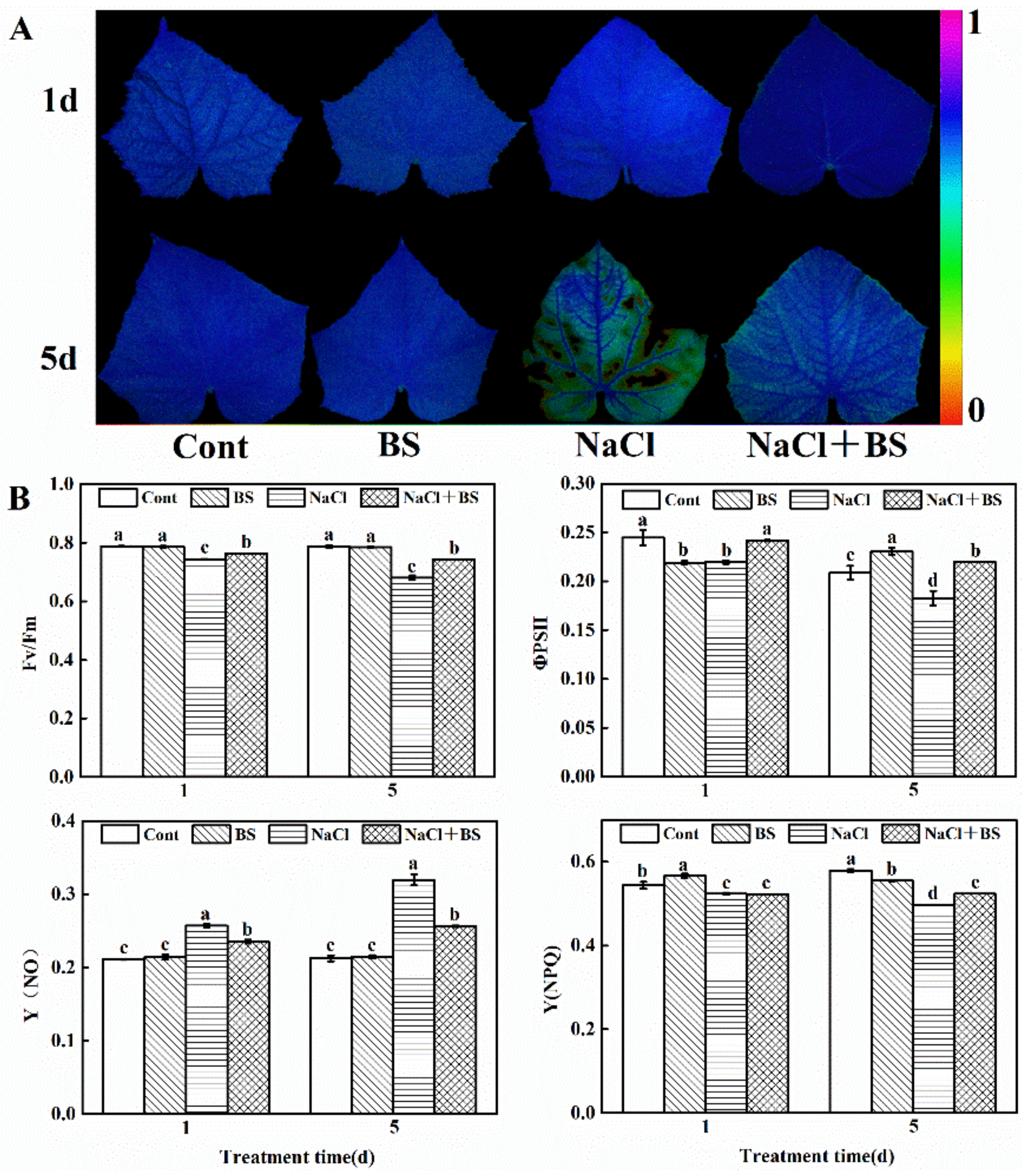
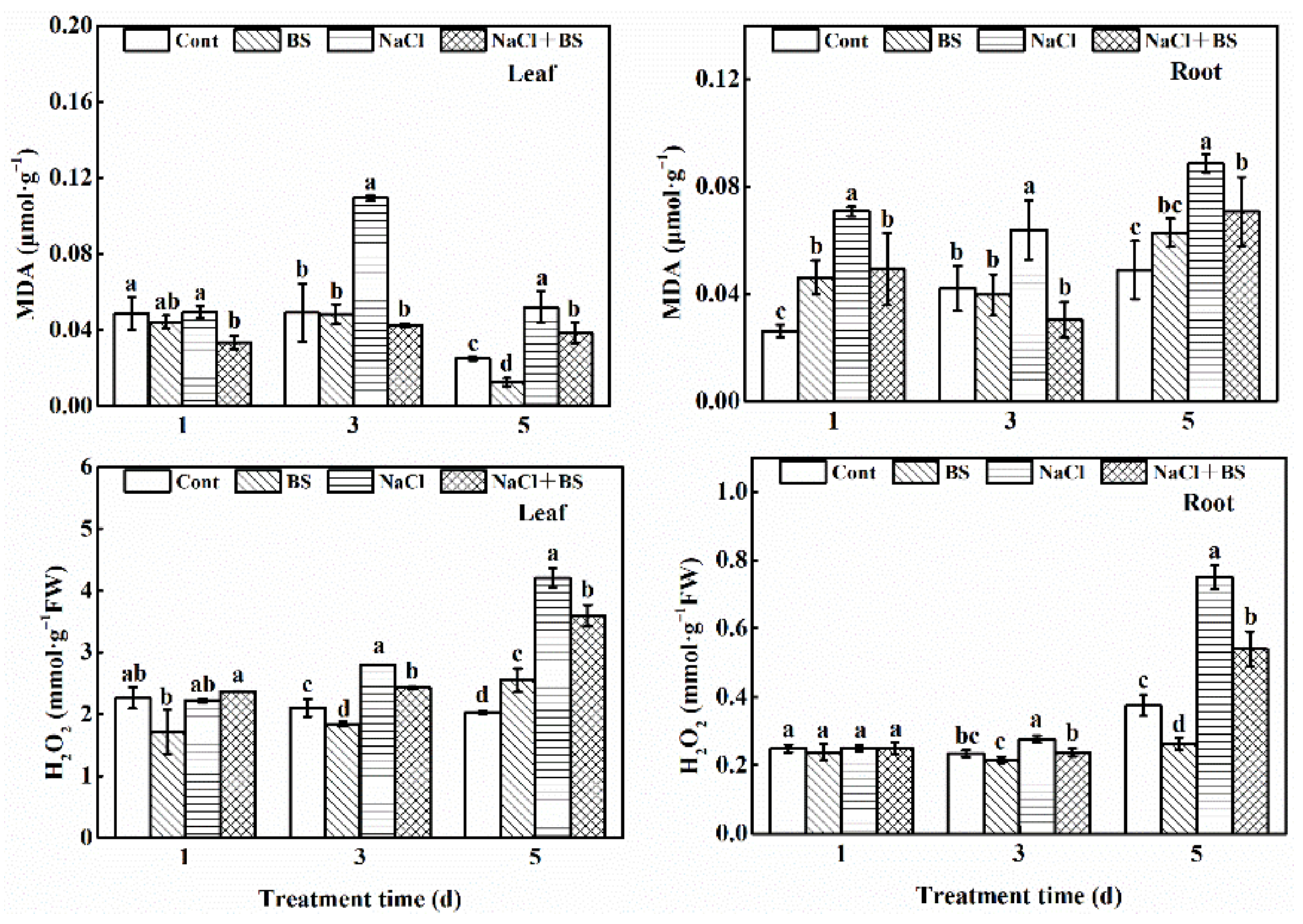
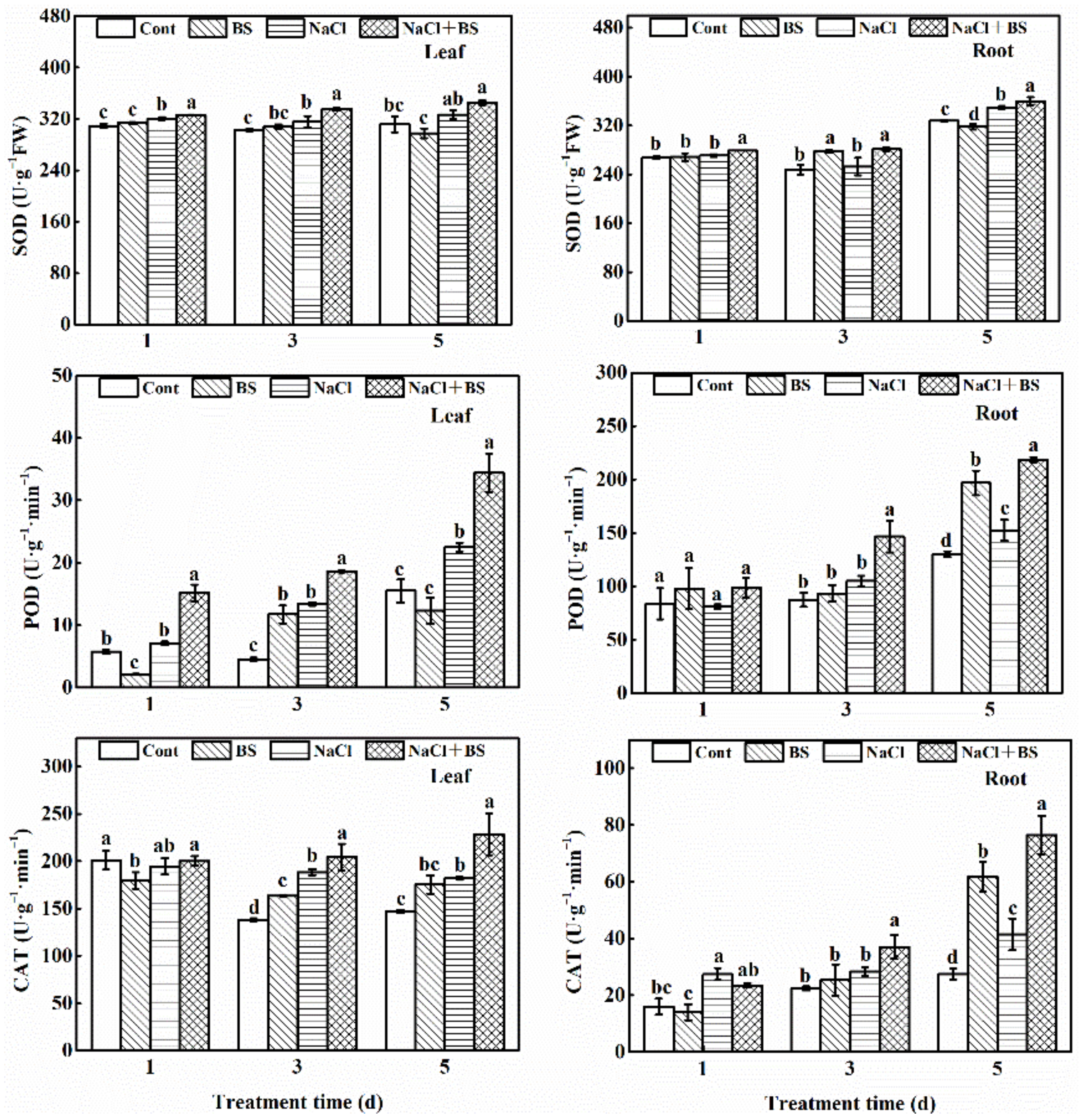
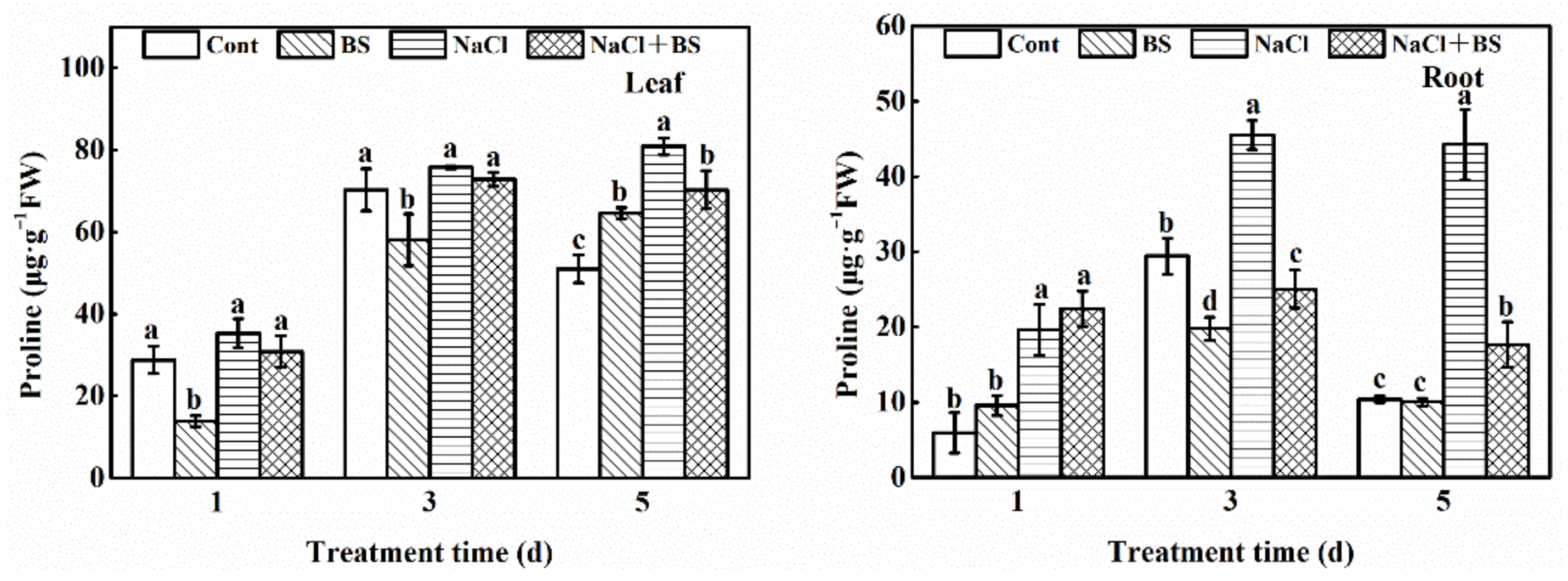
| Time | Treatments | Chl a (mg·g−1) | Chl b (mg·g−1) | Total Chl (mg·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | Cont | 23.95 ± 1.55 a | 7.37 ± 0.46 a | 31.32 ± 2.01 a |
| BS | 23.33 ± 1.44 a | 7.19 ± 0.48 a | 30.51 ± 1.92 a | |
| NaCl | 22.94 ± 1.63 a | 7.12 ± 0.51 a | 30.05 ± 2.14 a | |
| NaCl + BS | 21.13 ± 1.59 a | 6.48 ± 0.53 a | 27.62 ± 2.12 a | |
| 3 d | Cont | 23.69 ± 1.21 a | 7.12 ± 0.34 a | 30.81 ± 1.54 a |
| BS | 21.84 ± 0.98 ab | 6.60 ± 0.33 ab | 28.44 ± 1.30 ab | |
| NaCl | 16.22 ± 1.88 c | 4.74 ± 0.68 c | 20.96 ± 2.56 c | |
| NaCl + BS | 19.59 ± 2.03 b | 5.72 ± 0.57 b | 25.31 ± 2.59 b | |
| 5 d | Cont | 22.29 ± 1.63 a | 6.73 ± 0.53 a | 29.01 ± 2.16 a |
| BS | 21.02 ± 1.24 a | 6.73 ± 0.69 a | 27.75 ± 1.04 a | |
| NaCl | 10.09 ± 0.75 c | 3.04 ± 0.23 c | 13.14 ± 0.97 c | |
| NaCl + BS | 15.95 ± 0.21 b | 4.57 ± 0.08 b | 20.52 ± 0.29 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Sang, T.; Tian, M.; Jahan, M.S.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Guo, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Shu, S. Effects of Bacillus cereus on Photosynthesis and Antioxidant Metabolism of Cucumber Seedlings under Salt Stress. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050463
Zhou Y, Sang T, Tian M, Jahan MS, Wang J, Li X, Guo S, Liu H, Wang Y, Shu S. Effects of Bacillus cereus on Photosynthesis and Antioxidant Metabolism of Cucumber Seedlings under Salt Stress. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(5):463. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050463
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yaguang, Ting Sang, Mimi Tian, Mohammad Shah Jahan, Jian Wang, Xiangyu Li, Shirong Guo, Hongyun Liu, Yu Wang, and Sheng Shu. 2022. "Effects of Bacillus cereus on Photosynthesis and Antioxidant Metabolism of Cucumber Seedlings under Salt Stress" Horticulturae 8, no. 5: 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050463
APA StyleZhou, Y., Sang, T., Tian, M., Jahan, M. S., Wang, J., Li, X., Guo, S., Liu, H., Wang, Y., & Shu, S. (2022). Effects of Bacillus cereus on Photosynthesis and Antioxidant Metabolism of Cucumber Seedlings under Salt Stress. Horticulturae, 8(5), 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050463








