Abstract
Citrus grandis “Tomentosa” (“Huajuhong”) is a famous traditional Chinese medicine. The aim of the present study is to provide a comprehensive characterization of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis, and examine their expression patterns in fruits of C. grandis “Tomentosa” during various developmental stages. A total of 26 N6-methyladenosine (m6A) regulatory proteins were identified from the genome of C. grandis, which were distributed across nine chromosomes in C. grandis. Phylogenetic relationships revealed that all m6A regulatory genes were divided into groups of m6A writers, erasers, and readers. The m6A writer groups included CgMTA, CgMTB, and CgMTC three MTs (methyltransferases), one CgVIR (virilizer), one CgHAKAI (E3 ubiquitin ligase HAKAI), and one CgFIP37 (FKBP interacting protein 37). Moreover, 10 CgALKBH (α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase homolog) members (numbered from CgALKBH1 to CgALKBH10) and 10 CgECT (C-terminal region) members (numbered from CgECT1 to CgECT10) in C. grandis were identified as m6A erasers and readers, respectively. The domain structures and motif architectures among the groups of m6A writers, erasers, and readers were diverse. Cis-acting elements in the promoters of the 26 m6A regulatory genes predicted that the abscisic acid-responsive (ABA) element (ABRE) was present on the promoters of 19 genes. In addition, the expression profiles of all m6A regulatory genes were examined in the fruits of two varieties of C. grandis “Tomentosa” during different growth stages to give basic hints for further investigation of the function of the N6-methyladenosine regulatory genes in C. grandis “Tomentosa”.
1. Introduction
Methylation is an epigenetic modification which can regulate the heritage information to affect its function without altering the DNA sequence [1,2,3]. In general, methylation is divided into DNA methylation, histone modification, and RNA methylation according to molecular biological processes [3]. The methylation of RNA usually occurs in the internal modification of RNA. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) plays an important role in eukaryotic RNA methylation in animals and plants [4,5]. According to the three pivotal proteins, a sophisticated regulatory network of m6A is composed of m6A writers (methyltransferases), m6A erasers (demethylases), and m6A reader proteins [5,6,7]. The m6A writers add methyl groups to the conserved sequence. Similarly, m6A erasers can remove methylation. In addition, m6A readers have a specific recognition function that decodes the specific proteins of m6A modifications in RNA levels [5,6].
Previous research has been conducted on the m6A modification in animals. However, to the best of our knowledge, m6A modification in plants has rarely been reported. Recently, regulatory complexes of m6A writers have been identified from Camellia sinensis and Arabidopsis thaliana [8]. The m6A writers are not only regulated by methyltransferases (MTs), but are also controlled by a series of m6A writer components, such as FKBP interacting protein 37 (FIP37), virilizer (VIR), and E3 ubiquitin ligase HAKAI [9]. The MT family is the first m6A writer component which contains three subfamilies of methyltransferase A (MTA), methyltransferase B (MTB), and methyltransferase C (MTC) [10]. MTA subfamilies contain the MT-A70 domain which can activate RNA modification. Subsequently, MTB is regarded as one of the second most-active proteins in regulating m6A level [10]. The MTC subfamily, which also belongs to the MT family, was recently discovered. Therefore, little information has been reported about the function of MTC in m6A modification [11]. Apart from the aforementioned, m6A writers contain other components, including FIP37, VIR, and HAKAI. Among them, FIP37 contains the Wilms’ tumor 1-associating protein (WTAP) domain [12]. Previous research has shown that the suppression of FIP37 could lead to a decrease of the m6A modification level [12]. It has shown that FIP37 also plays an indispensable role in regulating m6A modification. As the third component of the m6A writer, VIR could regulate the MTA–MTB heterodimer to affect the level of RNA modification [13]. Similarly, inhibition of HAKAI expression could reduce m6A methylation [13]. Additionally, previous studies have found that HAKAI can interact with other components and together can regulate RNA levels [13].
Unlike m6A writers, m6A erasers can also regulate RNA methylation in plants. Previous studies have confirmed that the α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase homolog (ALKBH) could effectively remove the specific region of m6A [14]. A conserved clavaminate synthase-like domain was included in the ALKBH family which plays an important role in the demethylation of m6A-modified RNAs. Different from m6A methylation, the demethylations of m6A only include an ALKBH family [14]. The abundance of ALKBH in A. thaliana and Solanum lycopersicum is related to the decrement of m6A level [15,16]. Nevertheless, the m6A erasers in other plants need to be further confirmed. As the third component of regulatory m6A genes, the m6A readers have been divided into two types of CPSF30 (cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor 30) and ECT (C-terminal region) [17,18]. A highly conserved YTH domain is contained in ECT, which could specifically regulate m6A methylation. Moreover, CPSF30 contains a conserved C3H1-type zinc finger domain at the N-terminal region, which mainly contributes to sweeping away deleterious mRNA transcripts [19].
Citrus grandis (also annotated as Citrus maxima) is one of the three ancestors of the Citrus family [20]. In addition to the freshly consumed pummelo, the immature fruits of C. grandis “Tomentosa”, named as “Huajuhong”, are processed to be a famous traditional Chinese medicine for effectively curing chronic cough [21]. Nowadays, “ZhengMao” (ZM) is the main cultivated variety of “Huajuhong” whose fruits are covered with a thick layer of trichomes. There is also a local pummelo variety called “GuangQing” (GQ) whose fruits are smooth without trichome. Our previous study indicated that the terpenoid compositions and contents in the fruits of ZM and GQ were somehow different [22]. Whether the trichomes are related to the internal fruit quality is not yet known. It has been reported that m6A regulatory genes played important roles in the trichome branching [8]. Hence, it is necessary to study RNA methylation in C. grandis, which has not yet been reported.
In this research, the m6A regulatory genes family was comprehensively investigated in the genome from C. grandis. Firstly, all m6A regulatory genes were identified using HMMER and their chromosomal localization was investigated. The phylogenetic relationships of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis, S. lycopersicum, and A. thaliana combined with the conserved domains were analyzed. Gene structure and cis-element analysis of all the identified m6A regulatory genes were performed. Expression levels of m6A regulatory genes in the fruits of the two varieties of C. grandis “Tomentosa” were examined by RNA-seq and q-RT-PCR. The objective of this investigation is to give general information about the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis, and to lay a basis for the future research on the function of RNA methylation during the development of C. grandis “Tomentosa” fruits.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification and Chromosomal Localization of the m6A Regulatory Genes from C. grandis
To identify all the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis, the sequences of the m6A regulatory genes in A. thaliana and S. lycopersicum were downloaded from the Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) (https://www.arabidopsis.org/, (accessed on 10 January 2022)) [23] and the Sol Genomics Network (SGN) database (https://solgenomics.net/, (accessed on 10 January 2022)) [24], respectively. These sequences were queried against the genome sequences of C. grandis using BLAST with the parameter E-value < 1.0 × 10−5. Then, the hidden Markov model (HMM) profiles of the MT-A70 family (PF05063), VIR-N domain (PF15912) and WTAP family (PF17098), 2OG-FeII-Oxy-2 superfamily (PF13532), and YTH domain (PF04146) downloaded from the Pfam 35.0 database (http://pfam.xfam.org/, (accessed on 10 January 2022)) were used to identify the m6A regulatory genes of the C. grandis genome (https://www.citrusgenomedb.org/, (accessed on 10 January 2022)). Moreover, the obtained m6A regulatory genes of C. grandis were further confirmed through the online SMART database (http://smart.embl.de/smart/set_mode.cgi?GENOMIC=1#, (accessed on 10 January 2022)) [25], NCBI Conserved Domain Search databases (NCBI CDD) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi, (accessed on 10 January 2022)) [26] and Pfam 35.0 (http://pfam.xfam.org/, (accessed on 10 January 2022)) databases. The amino acids number (AAs), molecular weights (Mw), and isoelectric points (pI) of the identified m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis were examined using the ExPasy tool (http://web.expasy.org/protparam/, (accessed on 10 January 2022)) [27]. The subcellular location of the m6A regulatory genes was predicted using the online software WoLF PSORT II (https://www.genscript.com/wolf-psort.html, (accessed on 10 January 2022)) [28].
All m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis were mapped on the chromosomes according to their positions in the database. The database was obtained from annotated gff3 files. The chromosomal distribution was graphically visualized using Mapchart 2.32 software created by Roeland E. Voorrips which could be download and freely licensed in Guangzhou, China [29].
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the m6A Regulatory Genes from C. grandis, S. lycopersicum, and A. thaliana
The phylogenetic tree of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis, S. lycopersicum, and A. thaliana was generated by MEGA X64 with 1000 bootstrap replicates. The phylogenetic tree was employed by using the neighbor-joining (NJ) algorithm and the pairwise gap deletion mode [30]. The conserved domain information of m6A writers, erasers, and readers was obtained from the SMART database (http://smart.embl.de/smart/set_mode.cgi?GENOMIC=1#, (accessed on 11 January 2022)) and NCBI CDD (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi, (accessed on 11 January 2022)), and was graphically visualized using DOG 2.0 software [31].
2.3. Gene Structure Analysis, Cis-Element Analysis, and Heat Map Construction of the m6A Regulatory Genes from C. grandis
The phylogenetic tree of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis was generated by MEGA X64. The gene structures of the m6A regulatory genes in C. grandis were graphically visualized using the TBtools software [32]. Furthermore, for cis-acting element analysis, the promoter sequences of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis which were in the 1500 bp upstream region were collected. Moreover, the promoter sequences were obtained using the PlantCARE database (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/, (accessed on 11 January 2022)) [33]. The expression profiles of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis were visualized with heat maps using TBtools [32]. FPKM-normalized counts were regarded as thresholds.
2.4. Plant Materials and Treatments
“Huajuhong” (C. grandis “Tomentosa”) fruits, which were regarded as samples, were collected from an orchard of Huazhou Traditional Chinese Medicine Company located in Hexi District, Huazhou, Guangdong province. The fruits of 2, 4, 6, and 8 cm in diameters were harvested in the year 2019. The fruits were cut and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80 °C before usage.
2.5. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR Analysis
The total RNA from each abovementioned sample was isolated and treated to eliminate any potential contamination with DNA using the PrimeScript™ RT Reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (TaKaRa, Dalian, China), following the manufacturer’s instructions. Then, the real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis was conducted as described previously (2019) [34]. Primer pairs of each m6A regulatory gene from C. grandis were designed using the online software program Primer 3 (http://primer3.ut.ee/, (accessed on 12 January 2022)), and they are listed in Table 1. Actin was used as a reference gene which normalized the gene expression. The relative gene expression of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis was calculated by the comparative 2−ΔΔCt method [35], and the values are shown as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent biological replicates.

Table 1.
The primers used for qRT-PCR.
3. Results
3.1. Identification of the m6A Regulatory Genes from C. grandis
In this paper, a total of 6 m6A writers, 10 m6A erasers, and 10 m6A readers of m6A regulatory genes were identified from the genome of C. grandis according to the characteristics of m6A regulatory gene domain-containing proteins. The m6A regulatory genes family were divided into the MT-A70 family (PF05063), VIR-N domain (PF15912), WTAP family (PF17098), 2OG-FeII-Oxy-2 superfamily (PF13532), and YTH domain (PF04146)). All 26 m6A regulatory genes were identified based on the genome of C. grandis. The 26 m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis were named according to the homologs of m6A regulatory genes identified from S. lycopersicum [24] and A. thaliana [23]. As illustrated in Table 2, the number of amino acids (AAs) in the m6A regulatory proteins ranged from 195 (CgALKBH6) to 2199 (CgVIR) amino acids. The molecular weight (MW) of the m6A regulatory proteins varied from 22.14 (CgALKBH6) to 241.16 (CgVIR) kDa. Similarly, the isoelectric point (pI) of the 26 identified m6A regulatory proteins were quite different. For instance, the highest pI was observed in CgALKBH3 (9.50), while CgALKBH8 had the lowest pI (4.50). As shown in Table 2, the subcellular localization of 19 m6A regulatory proteins were in the nucleus (nucl), while a total of 7 m6A regulatory proteins targeted to the cytoplasm (cyto).

Table 2.
The m6A regulatory genes identified in C. grandis.
3.2. Chromosomal Localization of the m6A Regulatory Genes from C. grandis
The genome location information shown in Figure 1 demonstrated that a total of 26 m6A regulatory genes were unevenly anchored to the chromosomes of C. grandis. The results revealed that the 26 m6A regulatory genes in C. grandis were distributed across nine chromosomes, including in chr1, chr2, chr3, chr4, chr5, chr6, chr7, chr8, and chr9. Seven of the m6A regulatory genes were distributed on chromosome 5 (chr5). In contrast, only one gene was distributed on chr4 and chr8.
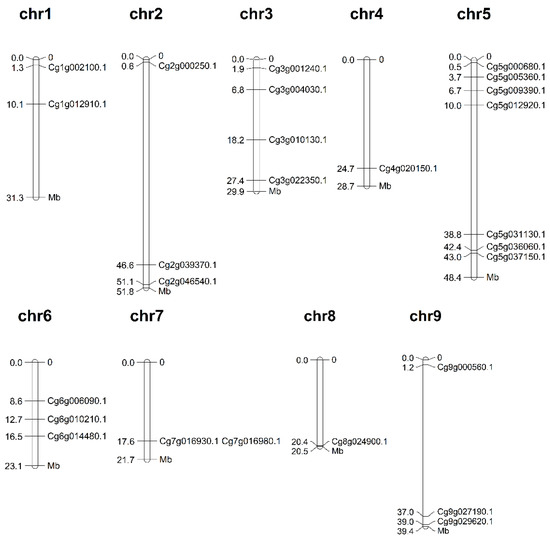
Figure 1.
Chromosomal locations of m6A regulatory genes in C. grandis. The chromosomal position of each m6A regulatory gene was mapped according to the genome of C. grandis. The chromosome number is marked at the top of each chromosome and the unit for the scale is megabases (Mb).
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of the m6A Regulatory Genes from C. grandis, S. lycopersicum, and A. thaliana
To study the phylogenetic relationships of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis, S. lycopersicum, and A. thaliana, a phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA X64 with the m6A regulatory protein sequences (Figure 2A). According to previously reported conserved domains from S. lycopersicum and A. thaliana, all m6A regulatory members were divided into three groups classified as m6A writers, erasers, and readers [5,6]. As illustrated in Figure 2A, three groups of m6A writers, erasers, and readers included three MT genes (CgMTA, CgMTB, and CgMTC), one CgVIR, one CgHAKAI, one CgFIP37, 10 CgALKBH genes (CgALKBH1 to CgALKBH10), and 10 CgECT members (CgECT1 to CgECT10) in C. grandis, respectively. It is obvious that CgALKBH and CgECT were the two largest groups, including 10 family members, respectively. Different categories contained different domain structures. In the m6A writer groups, the domain architectures were diverse. In the m6A writer groups, MT, VIR, HAKAI, and FIP37 subfamilies were identified. According to the phylogenetic analysis, the MT gene family can be classified into three categories, namely, MTA, MTB, and MTC (Figure 2A). One CgMTA, one CgMTB, and one CgMTC were identified as illustrated in Figure 2A. The MTA, MTB, and MTC were present in C. grandis, S. lycopersicum, and A. thaliana. Similarly, only one gene was identified in the components of VIR, HAKAI, and FIP37 from C. grandis, respectively (Figure 2A). Additionally, in the m6A eraser groups, all of the CgALKBH proteins contained only one highly conserved 2OG-FeII-Oxy-2 domain. Similarly, all 10 m6A eraser proteins from C. grandis were closely clustered with their homologs in S. lycopersicum and A. thaliana. Nevertheless, m6A reader components of ECT and CPSF30 were identified through phylogenetic relationship analysis. A total of 10 CgECT family genes which had one conserved YTH domain were found in C. grandis. However, another key component of the m6A readers, CPSF30, with a ZnF-C3H1 domain previously identified from A. thaliana, was not identified from C. grandis.
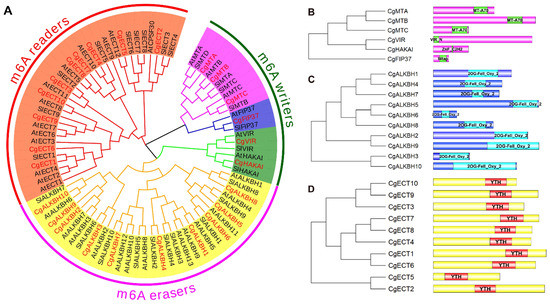
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic relationship of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis, S. lycopersicum, and A. thaliana. (A) Phylogenetic relationship of m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis, S. lycopersicum, and A. thaliana. (B) MT-A70, VIR-N, ZnF-C2H2, and WTAP conserved domains of m6A writer groups (Pink represents’ MTs; Blue represents’ FIP37s; Green represents’ VIRs and HAKAIs). (C) One highly conserved 2OG-Fell-Oxy-2 domain of m6A eraser groups (Yellow represents’ ALKBHs). (D) YTH conserved domain of m6A reader groups (Orange represents’ ECTs).
As illustrated in Figure 2B–D, the structure characteristics of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis were examined. In Figure 2B, CgMTA, CgMTB, and CgMTC possessed a typical MT-A70 conserved domain. Among other m6A writer components, the structures of CgVIR, CgHAKAI, and CgFIP37 proteins are conserved with a VIR-N, a ZnF-C2H2, and one WTAP domain, respectively. As shown in Figure 2C, compared with the m6A writer components, all members of the CgALKBH family contain a highly conserved 2OG-Fell-Oxy-2 domain in the m6A eraser groups. Similarly, in the m6A readers, all ECT family members with a conserved YTH domain were identified (Figure 2D).
3.4. Gene Structure Analysis of the m6A Regulatory Genes from C. grandis
The gene structures and conserved motif characters of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis were analyzed and are illustrated in Figure 3. As shown in Figure 3B, motif 1 and motif 2 were observed in almost all 10 CgETC subgroup members of the m6A eraser groups. Intriguingly, in the m6A reader groups, motif 4 and motif 7 were observed in CgALKBH1, CgALKBH4, and CgALKBH7. Nevertheless, any conserved motif characters were not detected from three CgMT members, one CgVIR, one CgHAKAI, and one CgFIP37 member in the m6A writer groups. The structural diversity of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis was investigated by the analysis of the exon/intron structures’ architectures. The exon number of the m6A regulatory genes caused a huge change, as shown in Figure 3C. Moreover, no introns were contained in CgMTB and CgHAKAI (Figure 3C).
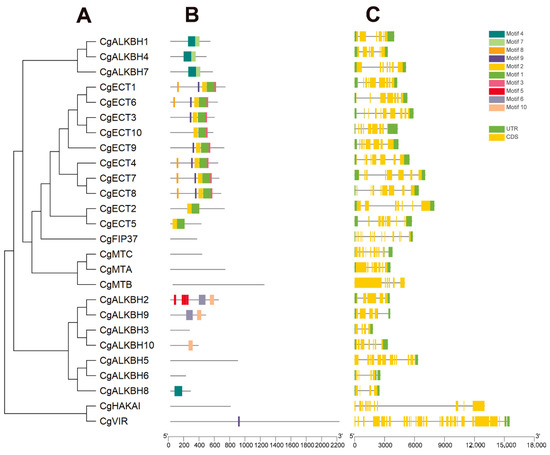
Figure 3.
The gene structure analysis of m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis. (A) Phylogenetic relationship of m6A regulatory genes. (B) Conserved motifs analysis of m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis. All motifs were identified by the MEME database with the complete amino acid sequences of m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis. The detailed information for each motif is provided in Figure S1. (C) The exon and intron structures of m6A regulatory genes. Yellow represents exons.
3.5. Cis-Element Analysis of the m6A Regulatory Genes from C. grandis
To further elucidate the potential biological functions and expression mechanisms of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis, the 1500 bp upstream sequences were firstly obtained. Then, PlantCARE was used to predict the cis-elements in the 1500 bp upstream sequences which are usually regarded as the promoters. The frequently appearing cis-elements are illustrated in Figure 4, and detailed information is also provided in Table S1. Defense and stress responsiveness, light responsiveness, and hormones responsiveness related elements were predicted from the promoters of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis. In Figure 4, 12 cis-elements were presented on the promoters of 26 m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis. Cis-elements TGA-element (auxin), ABRE (ABA), CGTCA-motif (MeJA), TCA-element (SA), and GARE-motif (GA) are involved in hormones in Figure 4. Among these elements, most of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis promoters include ABRE (ABA). According to the cis-elements analysis, TATC-box, P-box, and GARE-motif were involved in response to gibberellic acid (GA). In the defense and stress responses category, several types of stress-responsive elements were identified in the promoter regions of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis. TC-rich, LTR, and MBS were discovered, related with the defense and stress response, low-temperature response, and drought-inducibility, respectively. Moreover, light response elements were present in the promoter regions of 19 m6A regulatory genes, which indicated that the expression levels of the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis might relate to light signaling.
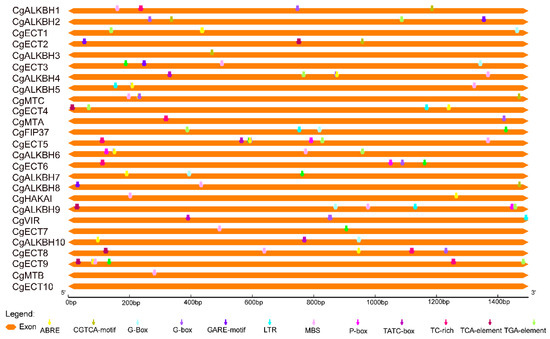
Figure 4.
Cis-element analysis of 26 identified m6A regulatory genes in C. grandis from the upstream 1500 bp sequences to the transcription start site.
3.6. Expression Patterns in the Fruits of C. grandis “Tomentosa” at Four Growth Points
To illustrate the expression patterns of the m6A regulatory genes in C. grandis, the transcriptional profiles of the ZM and GQ fruits of various developmental points were investigated by RNA-seq and qRT-PCR, respectively. The heatmap showing the expression profiles of the genes was plotted based on the FPKM-normalized log2 transformed values. As illustrated in Figure 5 and Table S2, in the m6A reader groups, the expression levels of CgECT1 and CgECT2 in ZM and GQ were higher compared with that of other m6A regulatory genes. However, in the m6A eraser groups, the FPKM values of CgALKBH7, CgALKBH9, and CgALKBH10 were close to 0, indicating that almost no expression of the three genes was observed in these samples. Furthermore, the qRT-PCR analysis shown in Figure 6 and Figure S2 indicated that the gene expression patterns of most of the m6A regulatory genes were consistent with the RNA-Seq data. Nevertheless, the expression levels of CgMTA and CgMTC were not consistent with the RNA-Seq values (Figure 6 and Figure S2).
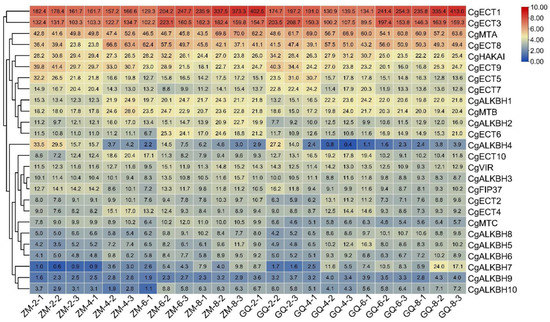
Figure 5.
Expression patterns of m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis in the fruits of 2, 4, 6, and 8 cm diameters of two varieties. The bar at the right of the heat map represents relative expression values. FPKM-normalized log2 transformed counts. (ZM and GQ are the names of the two varieties, the first number followed with ZM or GQ stands for the diameter of the fruits and the last number represents the biological replicate).
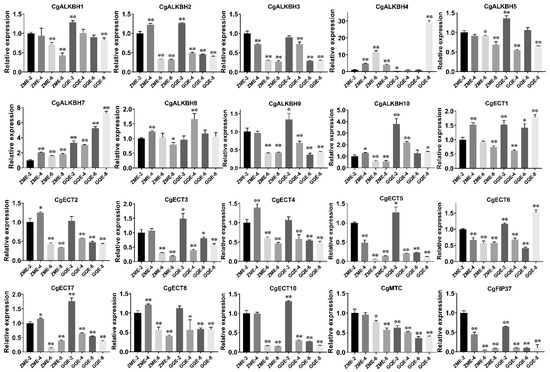
Figure 6.
Relative expression of 20 m6A regulatory genes in the fruits of ZM and GQ during various growth points. Actin was used for the qRT-PCR data normalization. The name of the genes is indicated above each bar diagram. Error bars indicate the standard deviation, Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. (ZM and GQ are the names of the two varieties, the first number followed with ZM or GQ stands for the diameter of the fruits and the last number represents the biological replicate).
4. Discussion
In general, according to molecular biological processes, methylation is divided into DNA methylation [36], histone modifications [37], and RNA methylation [38]. Previous studies demonstrated that N6-methyladenosine (m6A) plays an important role in the formation of eukaryotic RNA methylation in animals and plants [5,6]. To date, the research has shown that RNA methylation plays a prominent role in the defense and stress response, including for drought [39,40] and cold [41]. Meanwhile, m6A can reduce the damage of abiotic stress [42,43,44,45]. Furthermore, the regulatory mechanism of m6A is related to growth and development in A. thaliana [13]. Nevertheless, there is limited knowledge about the m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis. In the current study, a total of 26 m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis were ultimately identified, while 32, 26, and 34 of them were reported in A. thaliana, S. lycopersicum, and C. sinensis, respectively [5,46]. Compared with other species, the number of m6A regulatory genes in C. grandis is less than that in A. thaliana (32) and C. sinensis (34). Moreover, gene duplication and expansion events of m6A regulatory genes were not observed in C. grandis. Hence, during the evolutionary process of C. grandis, the m6A regulatory genes underwent a shrink and some redundant genes might have been deleted from the genome with certain unknown events.
Previous studies have shown that m6A is composed of m6A readers, writers, and erasers [5,6]. The effects of m6A on mRNA are mediated by an expanding list of m6A readers and m6A writer-complex components, as well as potential erasers that currently have an unclear relevance to m6A prevalence in the transcriptome [47]. The m6A writers include the components of MTs, FIP37, VIR, and HAKAI [9]. The conserved domain in m6A genes include MT-A70, WTAP, VIR-N, and ZnF-C2H2, respectively [5,6]. The MT family was further classified as MTA, MTB, and MTC subfamilies [5]. The ALKBH family has one highly conserved 2OG-Fell-Oxy-2 domain in m6A erasers and the ECT family and CPSF30 possess the conserved YTH domain and ZnF-C3H1 domain in m6A reader groups, respectively [5,6,8]. In this study, MTs, FIP37, VIR, and HAKAI components were detected in the m6A writers from C. grandis. However, only one highly conserved 2OG-Fell-Oxy-2 domain and another conserved YTH domain were discovered in the m6A erasers and readers of C. grandis, respectively. Additionally, the phylogenetic relationship and gene structure investigations identified three MT genes (CgMTA, CgMTB, and CgMTC), 10 CgALKBH genes, and 10 CgECT genes for reading, writing, and erasing mRNA methylation, respectively. However, compared with A. thaliana, S. lycopersicum, and C. sinensis, members from the CPSF30 family were not identified from C. grandis. The results further support the point of view of the shrinking of m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis during the long-term evolutionary course. Furthermore, it was reported that 30 m6A regulatory genes were randomly distributed on 13 chromosomes in C. sinensis, which is a descendant of C. grandis [5]. In the present study, m6A regulatory genes were distributed at nine chromosomes, including in chr1, chr2, chr3, chr4, chr5, chr6, chr7, chr8, and chr9. In addition, the evolution of gene functional differentiation was associated with the variation of structure and the expression profile [48]. The exon/intron structures of m6A regulatory genes obviously change, which may be related to the mutation during the process of post-transcriptional regulation [49]. Cis-acting elements are important for the down-stream gene transcriptional expression (activated or repressed) due to its potential binding ability with transcription factors (TFs) [50]. In the paper, the abscisic acid-responsive (ABA) element (ABRE) was presented on 19 m6A regulatory genes from C. grandis. Moreover, elements related with defense and stress responsiveness, light responsiveness, and hormones responsiveness were discovered from the promoters of the m6A regulatory genes of C. grandis. These results suggest that the transcriptional expressions of m6A regulatory genes might be affected by hormones (could be internal or external) and stress (could be abiotic or biotic).
The expression levels of all m6A regulatory genes in the fruits of ZM and GQ, which are two local varieties of C. grandis, during four growth stage points were examined by both RNA-seq and qRT-PCR. The varieties of ZM and GQ are different in both the internal quality and morphology of fruits; the immature fruits of ZM are usually used for the production of a famous traditional Chinese medicine named “Huajuhong” with the medical effect of curing chronic cough [51,52]. The variety of GQ is a local pumelo (C. grandis). The results demonstrated that the expression patterns of CgECT1 and CgECT3 increased, while the expression amount of CgALKBH4, CgALKBH7, CgALKBH9, and CgALKBH10 decreased during the fruit development of the two varieties. Moreover, among all the identified m6A regulatory genes, the expression levels of CgECT1 and CgECT3 were notably high in the fruits of two varieties of C. grandis during four development points (Figure 5). It was reported that ECT2/3/4 proteins played important roles in the timing and regulation of leaf formation and normal leaf morphology in Arabidopsis [8]. CgECT3 identified from this study might play a vital role in the development of fruits of C. grandis, which could be investigated in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae8050462/s1, Figure S1. Sequence logos for the conserved motifs of m6A regulatory genes domain proteins from Citrus grandis. Conserved motifs and the sequence logos were generated using the MEME search tool. Numbers on the horizontal axis represent the sequence positions in the motifs and the vertical axis represents the information content measured in bits, Figure S2: Relative expression of 6 m6A regulatory genes in the fruits of ZM and GQ during various growth points, Table S1: The detailed information of cis-elements, Table S2: The FPKM values of 26 m6A regulatory genes in C. grandis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.F. and J.Z.; methodology, R.F.; software, Y.T.; validation, Y.T. and R.F.; investigation, R.F. and J.Z.; resources, J.Z.; data curation, Y.T.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.T.; writing—review and editing, R.F. and J.Z.; visualization, Y.T.; supervision, R.F.; project administration, J.Z.; funding acquisition, R.F. and J.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2019A1818011378), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32001999), the Fundamental and Applied Fundamental Research Fund of Guangzhou City (2021020493), the Special fund for scientific innovation strategy-construction of high level Academy of Agriculture Science (No: R2021PY-QF004; R2020PY-JG001), the Guangdong Province Science and Technology Plan Project (2019B090905002) and the China Scholarship Council (202108440301).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Matouk, C.C.; Marsden, P.A. Epigenetic regulation of vascular endothelial gene expression. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luger, K.; Richmond, T.J. The histone tails of the nucleosome. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1998, 8, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. The epigenetic landscape of plants. Science 2008, 320, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Dominissini, D.; Rechavi, G.; He, C. Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible m(6)A RNA methylation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, C.; Xie, S.; Chen, G.; Tian, C.; Xu, K.; Lin, Y.; Lai, Z.; Guo, Y. Genome-Wide Investigation of N6-Methyladenosine Regulatory Genes and Their Roles in Tea (Camellia sinensis) Leaves during Withering Process. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 702303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hsu, P.J.; Chen, Y.S.; Yang, Y.G. Dynamic transcriptomic m(6)A decoration: Writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, K. Phytochemical genomics—A new trend. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2013, 16, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, H.; Nie, X.; Yan, Z.; Weining, S. N6-methyladenosine regulatory machinery in plants: Composition, function and evolution. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1194–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sledz, P.; Jinek, M. Structural insights into the molecular mechanism of the m(6)A writer complex. eLife 2016, 5, e18434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Doxtader, K.A.; Nam, Y. Structural Basis for Cooperative Function of Mettl3 and Mettl14 Methyltransferases. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, Z.; Riaz, A.; Chachar, S.; Ding, Y.; Du, H.; Gu, X. Epigenetic Modifications of mRNA and DNA in Plants. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Liang, Z.; Gu, X.; Chen, Y.; Teo, Z.W.; Hou, X.; Cai, W.M.; Dedon, P.C.; Liu, L.; Yu, H. N(6)-Methyladenosine RNA Modification Regulates Shoot Stem Cell Fate in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2016, 38, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruzicka, K.; Zhang, M.; Campilho, A.; Bodi, Z.; Kashif, M.; Saleh, M.; Eeckhout, D.; El-Showk, S.; Li, H.; Zhong, S.; et al. Identification of factors required for m(6) A mRNA methylation in Arabidopsis reveals a role for the conserved E3 ubiquitin ligase HAKAI. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarrow, M.; Chen, N.; Sun, G. Insights into the N(6)-methyladenosine mechanism and its functionality: Progress and questions. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Perez, M.; Aparicio, F.; Lopez-Gresa, M.P.; Belles, J.M.; Sanchez-Navarro, J.A.; Pallas, V. Arabidopsis m(6)A demethylase activity modulates viral infection of a plant virus and the m(6)A abundance in its genomic RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10755–10760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Tian, S.; Qin, G. RNA methylomes reveal the m(6)A-mediated regulation of DNA demethylase gene SlDML2 in tomato fruit ripening. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Addepalli, B.; Hunt, A.G. A novel endonuclease activity associated with the Arabidopsis ortholog of the 30-kDa subunit of cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 4453–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arribas-Hernandez, L.; Bressendorff, S.; Hansen, M.H.; Poulsen, C.; Erdmann, S.; Brodersen, P. An m(6)A-YTH Module Controls Developmental Timing and Morphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 952–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pontier, D.; Picart, C.; El Baidouri, M.; Roudier, F.; Xu, T.; Lahmy, S.; Llauro, C.; Azevedo, J.; Laudie, M.; Attina, A.; et al. The m(6)A pathway protects the transcriptome integrity by restricting RNA chimera formation in plants. Life Sci. Alliance 2019, 2, e201900393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velasco, R.; Licciardello, C. A genealogy of the citrus family. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 640–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Fan, R.; Zeng, J. Comprehensive Analysis of Jumonji Domain C Family from Citrus grandis and Expression Profilings in the Exocarps of “Huajuhong” (Citrus grandis “Tomentosa”) during Various Development Stages. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Zhu, C.; Qiu, D.; Zeng, J. Comparison of the bioactive chemical components and antioxidant activities in three tissues of six varieties of Citrus grandis ‘Tomentosa’ fruits. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1848–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berardini, T.Z.; Reiser, L.; Li, D.; Mezheritsky, Y.; Muller, R.; Strait, E.; Huala, E. The Arabidopsis information resource: Making and mining the “gold standard” annotated reference plant genome. Genesis 2015, 53, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bombarely, A.; Menda, N.; Tecle, I.Y.; Buels, R.M.; Strickler, S.; Fischer-York, T.; Pujar, A.; Leto, J.; Gosselin, J.; Mueller, L.A. The Sol Genomics Network (solgenomics.net): Growing tomatoes using Perl. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D1149–D1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D493–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Artimo, P.; Jonnalagedda, M.; Arnold, K.; Baratin, D.; Csardi, G.; de Castro, E.; Duvaud, S.; Flegel, V.; Fortier, A.; Gasteiger, E.; et al. ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W597–W603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, C.; Liu, H.; Lv, Q.; Chen, Z.; Tian, Y.; Mao, J.; Chu, M.; Ma, Z.; An, Z.; Chen, B. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Apple (Malus domestica) Cysteine-Rich Receptor-Like Kinase (CRK) Family: Annotation, Genomic Organization, and Expression Profiles in Response to Fungal Infection. Plant Mol. Biol. Report. 2019, 38, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; He, Y. Genome-wide investigation of WRKY gene family in pineapple: Evolution and expression profiles during development and stress. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, R.; Qi, G.; Kong, Y.; Kong, D.; Gao, Q.; Zhou, G. Comprehensive analysis of NAC domain transcription factor gene family in Populus trichocarpa. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, J.; Wen, L.; Gao, X.; Jin, C.; Xue, Y.; Yao, X. DOG 1.0: Illustrator of protein domain structures. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Dehais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouze, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Fan, R.; Yang, Q.; Hu, C.; Sheng, O.; Deng, G.; Dong, T.; Li, C.; Peng, X.; Bi, F.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the NAC Transcription Factor Family in Musa Acuminata and Expression Analysis during Fruit Ripening. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, T.; Yamazaki, Y.; Katoh-Fukui, Y.; Tsuchiya, R.; Kondo, S.; Motoyama, J.; Higashinakagawa, T. Gene trap capture of a novel mouse gene, jumonji, required for neural tube formation. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akimoto, K.; Katakami, H.; Kim, H.J.; Ogawa, E.; Sano, C.M.; Wada, Y.; Sano, H. Epigenetic inheritance in rice plants. Ann. Bot. 2007, 100, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Conde, E.S.N.; Audonnet, L.; Servet, C.; Wei, W.; Zhou, D.X. Over-expression of histone H3K4 demethylase gene JMJ15 enhances salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, K.; Almasan, A. Histone H2AX phosphorylation: A marker for DNA damage. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 920, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scutenaire, J.; Deragon, J.M.; Jean, V.; Benhamed, M.; Raynaud, C.; Favory, J.J.; Merret, R.; Bousquet-Antonelli, C. The YTH Domain Protein ECT2 Is an m(6)A Reader Required for Normal Trichome Branching in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 986–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Qi, Y.; Song, J.; Han, Z.; Ma, C. Evolution of the RNA N (6)-Methyladenosine Methylome Mediated by Genomic Duplication. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Manduzio, S.; Kang, H. Epitranscriptomic RNA Methylation in Plant Development and Abiotic Stress Responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Wan, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Jaffrey, S.R.; Qian, S.B. Dynamic m(6)A mRNA methylation directs translational control of heat shock response. Nature 2015, 526, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Wan, J.; Shu, X.E.; Mao, Y.; Liu, X.M.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, X.; Hess, M.E.; Bruning, J.C.; Qian, S.B. N(6)-Methyladenosine Guides mRNA Alternative Translation during Integrated Stress Response. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 636–647.e637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, H.C.; Wei, L.H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Lu, Z.; Chen, P.R.; He, C.; Jia, G. ALKBH10B Is an RNA N(6)-Methyladenosine Demethylase Affecting Arabidopsis Floral Transition. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 2995–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kramer, M.C.; Janssen, K.A.; Palos, K.; Nelson, A.D.L.; Vandivier, L.E.; Garcia, B.A.; Lyons, E.; Beilstein, M.A.; Gregory, B.D. N(6)-methyladenosine and RNA secondary structure affect transcript stability and protein abundance during systemic salt stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Direct. 2020, 4, e00239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, E.; Tong, W.; Hou, Y.; An, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, F.; Li, R.; et al. The Reference Genome of Tea Plant and Resequencing of 81 Diverse Accessions Provide Insights into Its Genome Evolution and Adaptation. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccara, S.; Ries, R.J.; Jaffrey, S.R. Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Yang, Y.; Chen, M. Genome-wide survey of the amino acid transporter gene family in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): Identification, expression analysis and response to abiotic stress. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1372–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellagatti, A.; Boultwood, J. Splicing factor gene mutations in the myelodysplastic syndromes: Impact on disease phenotype and therapeutic applications. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2017, 63, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, X.; Qiao, K.; Fan, S.; Ma, Q. Genome-wide analysis of JMJ-C histone demethylase family involved in salt-tolerance in Gossypium hirsutum L. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 158, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.L.; Liu, M.H.; Hu, J.H.; Su, W.W. Systematic chemical profiling of Citrus grandis ‘Tomentosa’ by ultra-fast liquid chromatography/diode-array detector/quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 90, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Liu, Q.; Xie, Z.; Lam, S.; Xu, X. Chromatographic Fingerprint Analysis of Exocarpium Citri Grandis by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Diode-Array Detector. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 8, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).