Abstract
The study examines the influence of humic and amino acid applications on the productivity and nutritional value of white cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata). Two cultivars, ‘Bagočiai’ and ‘Kamienna glowa’, were investigated at the Lithuanian Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry during the 2020–2021 period. The experiment was carried out in the experimental field where four different combinations of humic and amino acids were applied. Productivity and biochemical parameters were evaluated. It was determined that the application of amino and humic acids influenced the productivity of white cabbage. The obtained results showed that biostimulants enhanced the yield of heads up to 25% for cultivar ‘Bagočiai’ and 35% for ‘Kamienna Głowa’ compared with the control. The highest productivity, reaching 72.5–78.6 t ha−1 of cultivar ‘Kamienna Głowa’ and 74.9 t ha−1 to 76.2 t ha−1 of ‘Bagočiai’, was determined in the variants where amino acids and a combination of humic + amino acid were applied. The amount of vitamin C increased when plants were treated with an amino acid solution, while the highest crude protein content was found when plants were treated with humic acid.
1. Introduction
The demand for applying eco-friendly technological tools in crop production, which will ensure the sustainability of agricultural production systems in the mid and long term, is increasing [1]. Biostimulants are of high importance in modern agriculture due to their ability to enhance plant growth, development, and resilience without directly being fertilizers or pesticides. They can be applied to complement the use of chemical inputs, including the use of beneficial rhizosphere microbiomes as plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and advantageous fungi [2,3].
White cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata) is a popular cruciferous vegetable, known for its nutritional value and wide application in the production of various dishes. Cabbage is a rich source of vitamin C, dietary protein, and fiber, which are valuable for the digestive process [4,5,6]. Therefore, it is necessary to find innovative ways to increase the productivity and nutritional quality of these plants.
The use of amino acids (AAs), humic acids (HAs), and their combinations as biostimulants is an effective method for improving plant growth, yield, and quality parameters. Plant biostimulants can act directly on plant physiology by improving soil conditions [7,8,9]. They have a positive effect on plant metabolism and increase plant tolerance to stress factors, especially under unfavorable growth conditions. AAs support stress tolerance at the cellular level, while humic acids improve soil conditions and nutrient availability. It has been observed that treatments with humic substances stimulate plant root growth and development [9,10]. This is reflected in a better uptake of nutrients and water. AAs play an important role in nitrogen (N) metabolism [11] and chlorophyll biosynthesis [12]. Therefore, greater benefits to plants can be achieved when they are combined in a biostimulant formulation. The study by Cerdán et al. [13] showed that plant-derived AAs promote the growth of tomatoes and chlorophyll content under iron deficiency conditions. Koleška et al. [14] stated that the application of a biostimulant product to tomato plants, growing under reduced NPK nutrition, preserved lycopene and chlorophyll content. A similar experiment was performed by Anjum et al. [15] on garlic plants grown with half of the recommended dose of nutrients. Garlic growth and yield were positively affected by the application of a biostimulant in combination with a low dose of macronutrients. Spraying beans foliar with the nutritional products supplemented with AAs and microelements increased the productivity of seeds and the number of pods per plant [16]. El Sheikha et al. showed a highly positive effect on bean productivity and quality under the application of biostimulant and micronutrient fertilizers [17]. The external application of an AA biostimulant (Terra-Sorb® Foliar) on lettuce grown under different cold conditions influenced the increase in plant fresh weight [18]. Parađiković et al. [19] tested four different biostimulant products, including AAs, for their effects on yield and blossom end rot (BER) incidence for pepper. The results obtained revealed that biostimulant applications helped reduce the occurrence of BER, increase yield, and accumulate nutrients in fruits and leaves. These experiments revealed that biostimulant products containing AAs and HAs can be useful for reducing the use of mineral fertilizers, decreasing nutrient deficiencies, and enhancing plant productivity and quality.
Six years ago, Juárez-Maldonado et al. (2019) [20] presented information on biostimulant products, including nanoparticles and nanomaterials. Various experiments have been conducted to assess the effects of growth season and postharvest conditions on a range of bioactive compounds in cabbage, including glucosinolates, vitamins, phenols, and flavonoids [21,22,23,24,25,26]. The results of variability in agronomic characteristics among several cabbage genotypes and the influence of transplanting date on cabbage productivity were presented [27,28]. Godlewska et al. [29] stated that plant-derived biostimulants enhanced plant growth and increased the length of shoots and roots of cabbage seedlings. The dry weight of the plant increases in photosynthetic pigments, and the content of vitamin C in cabbage leaves was also reported [30]. Temperature is another important factor affecting plant growth, nutrient uptake, and the synthesis of biochemical compounds. In white cabbage, temperature significantly influences the accumulation of nitrogen, crude protein, and fiber, factors that determine both yield and quality. They are highly adaptable to different climates and soils. It grows well in cool and humid regions [29]. Lithuanian local conditions are suitable for growing cabbage in the open fields and greenhouses. However, the changes in local climate and the occurrence of extreme temperatures negatively affect plant productivity and quality. Temperature is a factor more difficult to overcome. Therefore, these factors must be taken into consideration before growing cabbage in the open field and choosing optimal agrotechnical measures.
It was assumed that using biostimulants for environmentally friendly cabbage cultivation would increase productivity and improve the biochemical composition. The studies aimed to investigate the influence of meteorological conditions and the effect of AAs and HAs, and their combinations, on the productivity of white cabbage and the potential enhancement of nutritional elements.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Conditions of the Experiment
The two-year investigation was carried out in the experimental field of the Institute of Horticulture, Lithuanian Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry in 2020 and 2021 (Babtai, Kaunas district, Central Lithuania, 55°09′ N, 23°80′ E). The soil of the experimental site is a Calcic Endogleyic Luvisol (LV-gl-n-cc) light loam [31]. Cabbages have been grown in a neutral soil medium rich in potassium (K2O up to 447 mg kg−1 in both years of investigation), phosphorus (P2O5 up to 1008 mg kg−1), and organic matter content reached up to 2.5%.
Two white-headed cultivars, ‘Bagočiai’ and ‘Kamienna Głowa’, were tested (Table 1).

Table 1.
Characterization of cabbage cultivars.
Cabbage seeds were sown in multi-pot plastic trays consisting of 45 pots (4 × 4 × 4 cm), containing a mixture of neutral peat (produced by Durpeta, Profi 1, Panevėžys, Lithuania) and sand (3:1 v/v) substrate in the third ten days of April. Plants were grown in the heated greenhouse and watered when necessary. Seedlings with 3–4 leaves (BBCH13-14) were planted in the open field at the end of May in both years. Beans (in 2020) and carrots (in 2021) were the preceding crops for cabbage.
2.2. Experimental Design
The distance between plants was 0.5 m and 0.7 m in inter-rows on a flat surface. The accounted plot area was 6.3 m2. (3 × 2.1). The investigation was carried out in three replications undertaken in a systematic design. Six plants were estimated in a plot, respectively, and 18 plants were evaluated in the treatment. Cabbage was grown under conventional vegetable growing technology adopted by the Institute of Horticulture. These recommendations apply 40 g m−2 of complete mineral fertilizers (YaraMila™, Yara International ASA, Oslo, Norway) (N-12, P205-11, K2O-18) before planting every year. Watering of experimental fields was used 6–15 days after transplanting. No diseases or pests were observed, and plant protection was not used. Harvesting cabbage was performed on the third ten days of August and early September when cabbages had completed head formation at the optimum time for consumption.
2.3. Tested Treatments and the Scheme
The effect of two types of commercial biostimulants based on biologically active free AAs obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis and HAs, and their combinations, was investigated (Table 2). A control variant and four different foliar spray formulas of treatments were applied:

Table 2.
Biostimulant composition.
(1) C (control) spraying with water. Sprayed twice at the same time with the tested products.
(2) T1—HAs (BLACKJAK®) 1 mL L−1 of water, sprayed twice.
(3) T2—AAs (Terra-Sorb® foliar) 1 mL L−1 of water, sprayed twice.
(4) T3—AAs 1 mL L−1 of water, 1st spraying + HAs 1 mL L−1 of water, 2nd spraying.
(5) T4—HAs 1 mL L−1 of water, 1st spraying + AAs 1 mL L−1 of water, 2nd spraying.
The experimental trial’s scheme is presented in Figure 1. Treatments were applied twice at the different plant phenological stages (BBCH). The spraying started when 4–6 leaves developed (1st spraying) at BBCH 16–17. The second spraying (2nd spraying) was performed at the beginning of head formation, when the youngest leaves had not unfolded at the BBCH 41 phenological stage. Spraying was performed manually using a hand sprayer Di Martino Lithium 8, nozzle pressure 2.8–3.8 atm.
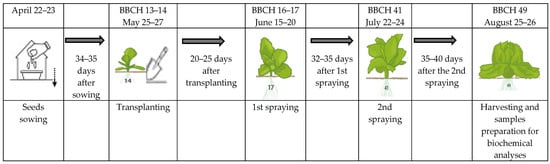
Figure 1.
Methodological development of the experimental trial, 2020–2021.
2.4. Estimation of Data and Analysis
After harvesting, the cabbage heads were divided into marketable and non-marketable, and productivity was evaluated. Once harvested, conjugated samples (from three cabbage heads) were immediately taken for analyses with three analytical replicates. The collected samples were stored in a refrigerator at a temperature of 0 ± 2 °C. For biochemical analysis, 200–400 g of tissue from each sample was taken. The biochemical parameters, vitamin C, nitrogen, crude protein, and crude fiber were analyzed for the fresh cabbage’s whole head (F.W.) at the Laboratory of Agrochemical Research. The sample for analysis was randomly selected from 3 heads of cabbage from each replicate. Vitamin C was estimated by titrating the sample using 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol sodium salt solution [32]. Ascorbic acid was considered the standard, and the formula was used to calculate results.
The total nitrogen content in plants was determined using the Kjeldahl method (Kjeldahl mineralization and distillation system Kjeltec 2200, FOOS, Hillerød, Denmark). Nitrogen was obtained from the dried cabbage leaf material, which was dried at 105 °C to a constant weight before analysis. The results were recalculated and presented in fresh weight (F.W.). Multiplying the total nitrogen (N) content by 6.25 gives the crude protein content (%CP (Dry Matter Basis) = %N (Dry Matter Basis) × 6.25).
The dietary fiber content (%) was determined from 0.5 g pulverized samples based on the detergent method described by Goering and Van Soest [33]. An automatic Fiber Analyzer (ANKOM2000 Fiber Analyzer, ANKOM Technology, Macedon, NY, USA) was used. Acid detergent fiber (ADF, Scharlab S.L., Barselona, Spain) fraction, which includes cellulose and lignin, was used for the crude fiber determinations. This solution removes soluble cell contents and hemicellulose, leaving behind the ADF fraction.
Effectiveness of biostimulators for yield. After the assessment of the yield, the biostimulants’ effectiveness (Y) for yield was calculated using the following formula [34]:
where b—yield of variant with biostimulants; a—yield of variant without biostimulants.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Head’s yield kg per plot was converted to t ha−1. Results were mathematically processed using Microsoft Excel, 2010, Software Version 14.0 [35]. The reliability of the data was evaluated using statistical software according to Duncan’s multiple range test for mean separation at 5% level and two-way ANOVA analysis. Similarities and differences in cabbage productivity and nutritional value data depending on the effect of biostimulants in different years of study were assessed using the analysis of principal coordinates PCA within SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, 2002) Software Version 11.5 (SPSS Inc. Chicago, IL, USA).
2.6. Meteorological Conditions
The average air temperature was similar at 16.2 and 16.4 °C during the cabbage vegetation period from May to August in both research years. The amount of precipitation was similar, reaching 75.0 and 78.8 mm, respectively (Figure 2). Differences occurred in different vegetation stages. The average temperature reaching 11.3 °C during the transplanting of cabbage seedlings in May 2020 and 2021 was lower than the multi-year average air temperature. The amount of precipitation this month was observed to be up to 126.8 mm in 2021 and up to 78.4 mm in 2020, while the multiannual average is 52.7 mm. The temperature in June was similar in both years. The highest temperature of 22.9 °C during the vegetation was determined in July 2021, when cabbage heads began to form. The temperature in June and July of 2020 reached 19.2 °C and 17.6 °C. The maximum amount of precipitation was observed in June, up to 134.4 mm in 2020, and up to 136.8 mm in August 2021 during the last phases of cabbage head growth.
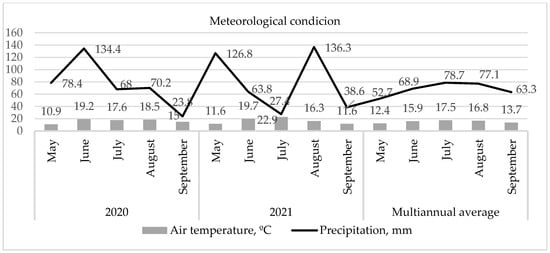
Figure 2.
Meteorological conditions during the vegetation of cabbage (data of Babtai Agrometeorological Station, iMETOS® sm prognostication system).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Meteorological Conditions on Cabbage Productivity and Nutritive Elements Accumulation
Despite cabbage’s ability to adapt to various climatic and soil conditions, local climate conditions greatly affect its production [36]. Cabbage is most often grown in the open field from April to October in Lithuania. According to the literature sources, the optimum air temperature for cabbage head formation varies from 17.0 to 22 °C [37,38,39]. According to Červenski and Takač [40], the temperature that can cause heat stress and adversely affect cabbage head formation and yield is above 25 °C, whereas Gvozdenović et al. [41] stated a temperature above 19 °C, respectively. The average temperature during head formation in July and August reached up to 18 °C in 2020 and 19.6 °C in 2021, respectively, in our investigation. This could have been an important factor affecting cabbage productivity parameters. Our results showed that cabbage yield for both cultivars ranged from 60.4 to 71.8 t ha−1, and the marketable yield output ranged from 77.5 to 82.2% in 2021 and 2020, respectively (Table 3). Cultivar ‘Kamienna Glowa’ produced a significantly higher yield of 70.3 t ha−1 in 2020, when the air temperature during head formation was 1.6 °C lower compared to 2021. Sufficient water is also essential for the cabbage’s absorption of nutrients and productivity. On the other hand, drought can increase the amount of nutrients in production due to reduced biomass, but this often leads to a total decrease in yield and quality. In our study, the amount of precipitation during the cabbage growing season (May–September) differed little between the two study years (348.8 mm in 2020 and 393.4 mm in 2021). But precipitation was higher in July 2020 compared to the same period in 2021. Therefore, this may also have influenced the increase in the yield of the cv. ‘Kamienna Glowa’. Tiwari et al. [42] recommended that 400 mm of water is required for the average seasonal water requirement of cabbage. They presented the yield data up to 106 t ha−1 when full water demand was compensated by a drip irrigation system. Weather conditions almost did not influence the productivity of cv. ‘Bagočiai.’ The yield of cv. ‘Bagočiai’ was similar in both years of investigation. This proves that local plant cultivars are better adapted to the climatic conditions of their place of origin [43,44,45].

Table 3.
Productivity of cabbage.
The mass of a head was similar and reached 2.7 kg for cv. ‘Bagočiai’ and 3.0 kg cv. ‘Kamienna Glowa’ in both years of investigation. A Polish researcher stated the mass of cv. ‘Kamienna Glowa’ head reached up to 2.7 kg, while the harvesting was performed in mid-October [46].
Meteorological conditions during different plant development stages play an important role in the accumulation of nutritive elements, including vitamins, minerals, and secondary metabolites in plants [47]. Cabbage is a good source of vitamin C. Its content ranges from 5 to 23 mg g−1 (F.W.) [48,49]. Cooler growing temperatures, particularly during the final stages before harvest, enhance the accumulation of vitamin C in white cabbage [6,50,51]. This agrees with our results. Significantly higher vitamin C content reaching up to 15.10 mg g−1 for cv. ‘Bagočiai’ and up to 13.50 mg g−1 for cv. ‘Kamienna Glowa’ was observed in 2021 when the air temperature during the cabbages’ last vegetation months (August–September) was 5.6 °C lower compared to 2020 (Table 4). Excessive rainfall can leach nutrients and reduce the mineral content of cabbage heads. Lončcarić et al. [48] reported that, after evaluating four different cultivars, the vitamin C content ranged from 13.45 to 18.52 mg g-1. According to Croatian research, a change in vitamin C from 5.7 to 23.5 mg g−1 was observed in eighteen cultivars [52]. The minimum vitamin C content was recorded in the cv. ‘Golden Acre’ (5.8 mg g−1), which has a shorter growing season than the other cultivars we studied. This indicates a significant effect of genotype on vitamin C accumulation. Optimal temperatures (15–20 °C) enhance enzymatic activity, which is involved in N metabolism. At higher temperatures (>25 °C), N assimilation can be reduced due to enzyme denaturation or increased respiratory losses.

Table 4.
Biochemical composition of cabbage (F.W.).
Cabbage absorbs N most actively around the early head formation stage and more slowly in the head fill stage [49]. Our results showed that the N amount up to 0.20–0.25% was similar in both years of investigation for both cultivars (Table 4).
Crude protein content in cabbage is a function of N assimilation [53]. Low to moderate temperatures favor protein synthesis by supporting enzymatic activity and reducing protein degradation. In contrast, higher temperatures can lead to protein denaturation and reduced N use efficiency, a decrease in crude protein content [54]. The studied cultivars showed different capabilities for crude protein accumulation. Cultivar ‘Bagočiai’ accumulated a higher amount of crude protein up to 1.81% in 2020, significantly, when the air temperature during the vegetation was 2 °C lower compared to 2021. Air temperature had a lesser effect on the accumulation of crude protein in cv. ‘Kamienna Glowa’ cabbage, and no significant differences were found in different years of study.
Fiber is a complex of heterogeneous substances of cell walls, indigestible in the human alimentary tract [55]. Higher temperatures tend to increase crude fiber content. In contrast, cooler temperatures often lead to more tender tissues with lower fiber concentrations [55]. Adequate rainfall ensures optimal cell expansion and reduces the need for excessive structural reinforcement, thus maintaining lower fiber content. Drought conditions, however, promote lignification as a protective response, thereby increasing the accumulation of crude fiber. Our result showed that the amount of crude fiber ranged from 0.42 to 0.79% in the cabbage heads of cv ‘Bagočiai’, in 2020 and 2021, respectively. The amount of crude fiber was significantly higher in 2021, when the rainfall amount during the plant vegetation was 12% higher compared to 2020. Meanwhile, no significant differences were found in different years in cv. ‘Kamienna Glowa’.
3.2. Effect of Biostimulants on Productivity Enhancement
Amino and humic acids can improve fertilizer assimilation, nutrients, water uptake, and photosynthesis of various vegetable plants [11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. The summarized two-year productivity results showed that the productivity of both cultivars was very similar and did not differ significantly, while biostimulants significantly enhanced the yield of cabbage heads (up to 23%) compared with the control (Table 5). The effects of biostimulants and their combinations, except T4 variant (HAs, first spraying + AAs, second spraying), were similar, but the highest productivity, reaching 74.4–76.8 t ha−1, was determined in the variants where HAs+ AAs (T3) and AAs (T2) were applied. In our previous investigations with hybrid ‘Socrates’ H, the highest marketable yield (80.5 t ha−1) of white cabbages was obtained by applying granular poultry manure fertilizer in the autumn and mineral fertilizer in the spring [56].

Table 5.
Effect of biostimulants on the productivity of the cabbage, t ha−1, 2020–2021 mean values.
The studied cultivars differed significantly in the formation of marketable yield. The marketable yield output of cv. ‘Bagočiai’ reached up to 82.2% and up to 78.9% of cv. ‘Kamienna Głowa’, respectively. Biostimulants also significantly increased marketable yield output.
A two-year study and evaluation of cabbage yields showed that meteorological conditions, genotype, and the combination of biostimulants had an impact on plant productivity and quality. Principal component analysis (PCA), an unsupervised pattern recognition technique, is an effective tool for visualizing similarities and dissimilarities in multivariate data [57,58]. This analysis was used to comprehensively evaluate the nutritional quality of the studied cabbage cultivars depending on growth conditions. The scatter plot of PCA displayed a wide range of cabbage productivity depending on genotype and applied biostimulant treatment in different years of investigation. According to the PCA results of the cabbage productivity, including total and marketable yield, it is possible to classify the investigated samples into several groups. The variants of both cultivars, which were treated with biostimulants and their combinations (12—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T1, 2020; 13—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T2, 2020; 14—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T3, 2020; 15—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T4, 2020; and 8—‘Bagočiai’ T2, 2021), characterized by the highest productivity, were scattered in one group on the area of the PC scatter plot (Figure 3). Cultivar ‘Kamienna Głowa’ samples (variants T2, T3, T4 in 2021), with the lowest productivity, were in another group at the front side of the scatter plot.
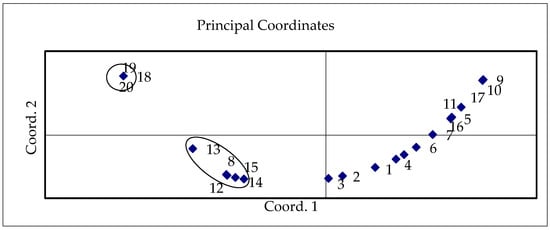
Figure 3.
Scatter plot of cabbage productivity applying different AAs and HAs, and their combinations in different study years. 1—‘Bagočiai’ C, 2020; 2—‘Bagočiai’ T1, 2020; 3—‘Bagočiai’ T2, 2020; 4—‘Bagočiai’ T3, 2020; 5—‘Bagočiai’ T4, 2020; 6—‘Bagočiai’ C, 2021; 7—‘Bagočiai’ T1, 2021; 8—‘Bagočiai’ T2, 2021; 9—‘Bagočiai’ T3, 2021; 10—‘Bagočiai’ T4, 2021; 11—‘Kamienna Głowa’ C, 2020; 12—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T1, 2020; 13—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T2, 2020; 14—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T3, 2020; 15—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T4, 2020; 16—‘Kamienna Głowa’ C, 2021; 17—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T1, 2021; 18—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T2, 2021; 19—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T3, 2021; 20—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T4, 2021.
An assessment of the effect of biostimulants on cabbage productivity showed that their overall effectiveness ranged from 11 to 40% (Table 6). Foliar spraying with the AAs (T2) and AAs + HAs (T3) provided maximum efficiency on both tested cultivars. The highest effectiveness of biostimulators for yield was observed for the cv. ‘Kamienna Głowa’ in the T2 variant when the plants were sprayed with AAs. When spraying cabbage with AAs + HAs solution, a biostimulant efficiency of 29% was observed in both cultivars (T3 variant).

Table 6.
Biostimulants’ effectiveness on the productivity of cabbage, 2020–2021.
3.3. Effect of Biostimulants for the Accumulation of Nutritive Elements
Beyond productivity, the influence of AAs and HAs extends to the nutritional quality of white cabbage. Research suggests that these biostimulants may enhance the synthesis of phytochemicals and antioxidants in plants [59,60]. Haghighi et al. [59] demonstrated that the exogenous application of AAs enhances the nutritional profile of cabbage, including increased levels of phenols, total protein, and vitamins. The effect of biostimulants on vitamin C, N, crude protein, and fiber accumulations is presented in Figure 4.
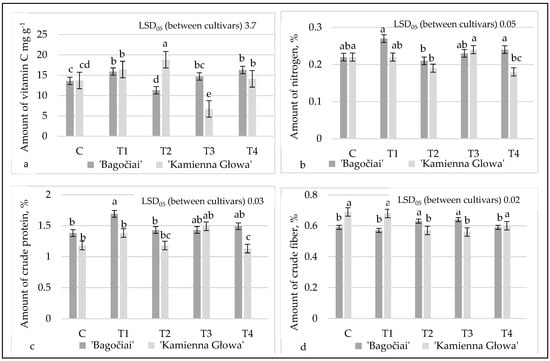
Figure 4.
Effect of biostimulants on the quantitative parameters of nutritive elements ((a)—vitamin C, (b)—N, (c)—crude protein, (d)—crude fiber) of the cabbage, 2020—2021 mean values. C (control)-spraying with water; T1-HAs, sprayed twice; T2-AAs, sprayed twice; T3-AAs, 1st spraying + HAs, 2nd spraying; T4-HAs, 1st spraying + AAs, 2nd spraying. Means followed by the same letter do not differ significantly within the column at p = 0.05 (Duncan’s multiple range test).
Cabbage is a good source of vitamin C, a major antioxidant in Brassica spp. The amount of vitamin C, from 6.7 to 18.8 mg g−1, was determined in our investigation (Figure 4a). Cultivar ‘Kamienna Głowa’ had the highest level of vitamin C, where plants were treated with AAs twice (T2). Cultivar ‘Bagočiai’ accumulated the highest amount of vitamin C, reaching 15.9 and 16.3 mg g−1 when the plants were treated with HA (T1) and HA+AA (T4) solutions, respectively. Lončaric et al. [48] investigated four different cultivars of cabbage in Croatia and presented results when vitamin C content ranged between 13.5 and 18.5 mg g−1. Kavaliauskaitė et al. [56] have stated the amount 7.80 mg g−1 of vitamin C by applying the granular poultry manure fertilizer in the autumn and mineral fertilizer in the spring.
Analyses of N showed that N accumulation was similar up to 0.22 and 0.27% in all variants, except T2, where AAs were applied (Figure 4b). Both cultivars in this variant accumulated at least an amount of N.
Vegetables, except legumes, nuts, and seeds, are not a rich source of protein. But people have started following a healthy diet and paying more attention to vegetarian food. So, they expect to receive good-quality vegetable protein. Our results showed that HA and AA applications increased protein concentration in the cabbage heads. The highest amount of crude protein, reaching 1.69% was determined in the cv. ‘Bagočiai’ in the T1 variant, in which HAs were sprayed twice (Figure 4c). Significantly, the crude protein increases were observed in the cv. ‘Kamienna Głowa’ when the plant foliar was sprayed with HAs (T1 variant) and AA+HA combination (T3 variant) compared to the untreated plants (C variant).
Song et al. [61] stated similar results when conventional plant growing conditions were applied. The crude protein content of 35 Chinese cabbage materials in their experiment was 1.06–1.69%. The results obtained showed that the use of biostimulants did not affect the accumulation of crude fiber in cabbage. The amount of crude fiber when using biostimulants in both tested varieties was similar and averaged up to 0.61% in cv. ‘Bagočiai’ and up to 0.60% in the cv. ‘Kamienna Głowa’, while in the control variant, the amount of crude fiber in these cultivars was 0.59 and 0.69%, respectively (Figure 4d). It was presented that the amount of crude fiber reached up to 0.53% in Chinese cabbage growing under conventional conditions [61].
The nutritional quality of cabbage is determined by the content and distribution ratio of nutrients, likely vitamin C, crude protein, fiber, organic acids, and mineral elements. Our PCA results showed similar locations of nutritive element parameters depending on the genotype and applied biostimulants in different years of investigation, except for a few results of cv. ‘Kamienna Glowa’ in 2021. Samples of the cv. ‘Kamienna Glowa’ (18,19,20) treated with AAs (T2), AAs+HAs (T3), and HAs+AAs (T4) were located at the individual point on the PC scatter plot (Figure 5). The plants of these samples had accumulated a high amount of N up to 0.19–0.26%, crude protein up to 1.3–1.6%, and crude fiber up to 0.65–0.88%.
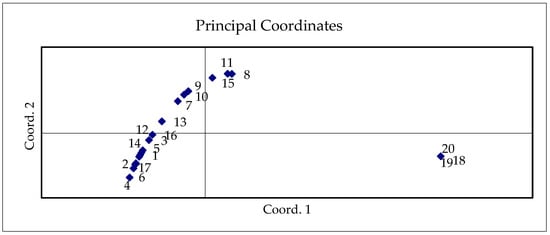
Figure 5.
Scatter plot of cabbage nutritive elements (vitamin C, N, crude protein, crude fiber) applying different AAs and HAs and their combinations in different study years. 1—‘Bagočiai’ C, 2020; 2—‘Bagočiai’ T1, 2020; 3—‘Bagočiai’ T2, 2020; 4—‘Bagočiai’ T3, 2020; 5—‘Bagočiai’ T4, 2020; 6—‘Bagočiai’ C, 2021; 7—‘Bagočiai’ T1, 2021; 8—‘Bagočiai’ T2, 2021; 9—‘Bagočiai’ T3, 2021; 10—‘Bagočiai’ T4, 2021; 11—‘Kamienna Głowa’ C, 2020; 12—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T1, 2020; 13—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T2, 2020; 14—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T3, 2020; 15—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T4, 2020; 16—‘Kamienna Głowa’ C, 2021; 17—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T1, 2021; 18—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T2, 2021; 19—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T3, 2021; 20—‘Kamienna Głowa’ T4, 2021.
4. Conclusions
The study highlights the influence of genotype and humic and amino acids on the productivity and nutritional value of white cabbage. Biostimulants are an important tool for reducing the use of chemical fertilizers. Spraying the cabbages’ foliage with nutritional products supplemented with humic and amino acids increased the productivity of heads to 23%. The highest effectiveness of biostimulators for yield was observed for the cultivar ‘Kamienna Głowa’ when the amino acid was applied. When using biostimulants, the cultivar ‘Bagočiai’ is distinguished for its highest marketable yield. The amount of vitamin C increased when plants were treated with the amino acid solution, while the highest crude protein content was found when plants were treated with humic acid.
Meteorological conditions also had an impact on productivity and nutritional value. Higher yields and crude protein content were observed when the growing season was cooler and more precipitation in July. A higher amount of precipitation during the vegetation period promoted crude fiber accumulation in cultivar ‘Bagočiai’ heads.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.K. and D.J.; methodology, R.K.; software, D.J.; validation, R.K., A.R. and D.J.; formal analysis, D.J.; investigation, D.J.; resources, D.J. and R.K.; data curation, R.K.; writing—original draft preparation, D.J.; writing—review and editing, A.R.; visualization, R.K.; supervision, D.J.; project administration, R.K.; funding acquisition, R.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the manuscript. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out within the framework of the long-term research program ‘Horticulture: agro-biological basics and technologies’ implemented by the Lithuanian Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry. We thank Danguolė Kavaliauskaitė for her assistance in conducting experiments and collecting data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Cheng, Q.; Sun, W. Using bacteria and fungi as plant biostimulants for sustainable agricultural production systems. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2023, 17, 206–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W. Sustainable approaches to boost yield and chemical constituents of aromatic and medicinal plants by application of biostimulants. Recent Adv. Food Nutr. Agric. 2022, 13, 72–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Sun, W. Survey of the Influences of Microbial Biostimulants on Horticultural Crops: Case Studies and Successful Paradigms. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.H. Dietary fibre in Europe: An overview. In COST 92—Dietary Fibre Intakes in Europe; Cummings, J.H., Frolich, W., Eds.; Commission of European Communitres, Directorate-General: Luxembourg, 1993; pp. 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Elkner, K. Effect of cultivar and nitrogen fertilization on the content of dietary fibre and its composition in some cruciferous vegetables. Veg. Crops Res. Bull. 2000, 53, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kovalikova, Z.; Kubes, J.; Skalick, M.; Kuchtickova, N.; Maskova, L.; Tuma, J.; Vachova, P.; Hejnak, V. Changes in Content of Polyphenols and Ascorbic Acid in Leaves of White Cabbage after Pest Infestation. Molecules 2019, 24, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, K.; Sorrentino, M.; Lucini, L.; Rouphael, Y.; Cardarelli, M.; Bonini, P.; Reynaud, H.; Canaguier, R.; Trtílek, M.; Panzarová, K. Understanding the Biostimulant Action of Vegetal-Derived Protein Hydrolysates by High-Throughput Plant Phenotyping and Metabolomics: A Case Study on Tomato. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgari, R.; Morgutti, S.; Cocetta, G.; Negrini, N.; Farris, S.; Calcante, A.; Spinardi, A.; Ferrari, E.; Mignani, I.; Oberti, R.; et al. Evaluation of Borage Extracts As Potential Biostimulant Using a Phenomic, Agronomic, Physiological, and Biochemical Approach. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canellas, L.P.; Olivares, F.L.; Okorokova-Facanha, A.L.; Facanha, A.R. Humic Acids Isolated from Earthworm Compost Enhance Root Elongation, Lateral Root Emergence, and Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase Activity in Maize Roots. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 1951–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, S.; Francioso, O.; Quaggiotti, S.; Nardi, S. Humic substances biological activity at the plant-soil interface: From environmental aspects to molecular factors. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miflin, B.J.; Lea, P.J. The pathway of nitrogen assimilation in plants. Phytochemistry 1976, 15, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porra, R.J. Invited Review Recent Progress in Porphyrin and Chlorophyll Biosynthesis. Regulation 1997, 65, 492–516. [Google Scholar]
- Cerdán, M.; Sánchez-Sánchez, A.; Jordá, J.D.; Juárez, M.; Sánchez-Andreu, J. Effect of commercial amino acids on iron nutrition of tomato plants grown under lime-induced iron deficiency. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2013, 176, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleška, I.; Hasanagić, D.; Todorović, V.; Murtić, S.; Klokić, I.; Paradiković, N.; Kukavica, B. Biostimulant prevents yield loss and reduces oxidative damage in tomato plants grown on reduced NPK nutrition. J. Plant Interact. 2017, 12, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, K.; Ahmed, M.; Baber, J.K.; Alizai, M.A.; Ahmed, N.; Tareen, M.H. Response of Garlic Bulb Yield To Bio-Stimulant (Bio-Cozyme) Under Calcareous Soil. Life Sci. Int. J. 2014, 8, 3058–3062. [Google Scholar]
- Juškevičienė, D.; Karklelienė, R.; Radzevičius, A.; Kavaliauskaitė, D. Effect of nutritional elements on the productivity of common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Acta Hortic. 2023, 1375, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sheikha, A.F.; Allam, A.Y.; Taha, M.; Varzakas, T. How Does the Addition of Biostimulants Affect the Growth, Yield, and Quality Parameters of the Snap Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.)? How Is This Reflected in Its Nutritional Value? Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, A. Enhancing plant tolerance to temperature stress with amino acids: An approach to their mode of action. Acta Hortic. 2012, 1009, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parađiković, N.; Vinković, T.; Vinković Vrček, I.; Tkalec, M. Natural biostimulants reduce the incidence of BER in sweet yellow pepper plants (Capsicum annuum L.). Agric. Food Sci. 2013, 22, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Maldonado, A.; Ortega-Ortíz, H.; Morales-Díaz, A.; González-Morales, S.; Morelos-Moreno, Á.; Cabrera-De la Fuente, M.; Sandoval-Rangel, A.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Benavides-Mendoza, A. Nanoparticles and Nanomaterials as Plant Biostimulants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Park, S.; Lim, Y.P.; Kim, S.-J.; Park, J.T.; An, G. Metabolite profiles of glucosinolates in cabbage varieties (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) by season, color, and tissue position. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2014, 55, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciska, E.; Drabinska, N.; Narwojsz, A.; Honke, J. Stability of glucosinolates and glucosinolate degradation products during storage of boiled white cabbage. Food Chem. 2016, 203, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, M.F.; Scotti-Campos, P.; Pais, I.; Feteiro, A.; Canuto, D.; Simoes, M. Nutritional profile of the Portuguese cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. costata) and its relationship with the elemental soil analysis. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2016, 28, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.R.; Rhee, J.; Choi, C.S.; Jo, J.S.; Shin, Y.K.; Lee, J.G. Profiling of individual desulfo-glucosinolate content in cabbage head (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) germplasm. Molecules 2020, 25, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yue, Z.; Zhong, X.; Lei, J.; Tao, P.; Li, B. Distribution of primary and secondary metabolites among the leaf layers of headed cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata). Food Chem. 2020, 312, 126028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kałuzewicz, A.; Krzesiński, W.; Spizewski, T.; Zaworska, A. Effect of biostimulants on several physiological characteristics and chlorophyll content in broccoli under drought stress and re-watering. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2017, 45, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Pathak, K.A.; Sarma, K.A.; Thapa, M. Effect of Transplanting Dates on Plant growth, Yield and Quality Traits of Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.). Indian J. Hill Farming 2010, 23, 1–5. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235650323_Effect_of_transplanting_dates_on_plant_growth_yield_and_quality_traits_of_cabbage_Brassica_oleracea_var_capitata_L_cultivars (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Parker, A.; Namuth-Covert, D. Cabbage, TG/48/7. In Guidelines for the Conduct of Tests for Distinctness, Uniformity and Stability; International Union For The Protection of New Varieties of Plants (UPOV): Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Godlewska, K.; Biesiada, A.; Michalak, I.; Pacyga, P. The effect of Plant-Derived Biostimulants on White Head Cabbage Seedlings Grown under Controlled Conditions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlewska, K.; Pacyga, P.; Michalak, I.; Biesiada, A.; Szumny, A.; Pachura, N.; Piszcz, U. Effect of Botanical Extracts on the Growth and Nutritional Quality of Field-Grown White Head Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata). Molecules 2021, 26, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WRB: World Reference Base for Soil Resources. International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. In World Soil Resources Reports, 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; pp. 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz, W.; Latimer, G.W. AOAC Official Methods of Analysis. In Official Analytical Chemists, 17th ed.; AOAC: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Goering, H.K.; Van Soest, P.J. Forage Fiber Analysis: Apparatus, Reagents, Procedures and some Applications; USDA-ARS Agricultural Handbook No. 379; US Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1970.
- Dabkevičius, Z.; Brazauskienė, I. Plant Pathology; IDP Solution: Klaipėda, Lithuania, 2007; p. 493. (In Lithuanian) [Google Scholar]
- Tarakanovas, P.; Raudonius, S. Agronomic Research, Statistical Analysis Using Computer Programs ANOVA, STAT, SPLIT-PLOT from Program Package SELEKCIJA and IRRISTAT; Dotnuva–Akademija, Lithuanian Institute of Agriculture: Dotnuva, Lithuania, 2003; 56p. (In Lithuanian) [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, I.; Peer, Q.J.A.; Saraf, S.A.; Farooq, F.; Aziz, T. Assessment of the Knowledge Level of Cabbage Growers for an Enhanced Production Technology. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2020, 39, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurhidayati, N.; Ali, U.; Murwani, I. Yield and quality of cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. Capitata) under organic growing media using vermicompost and earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus inoculation. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2016, 11, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žnidarčič, D.; Kacjan-Maršić, N.; Osvald, J.; Požrl, T.; Trdan, S. Yield and quality of early cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.) in response to within-row plant spacing. Acta Agric. Slov. 2007, 89, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranhos, L.G.; Barrett, C.E.; Zotarelli, L.; Darnell, R.; Migliaccio, K.; Borisova, T. Planting date and in-row plant spacing effects on growth and yield of cabbage under plastic mulch. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 202, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Červenski, J.; Takač, A. Growing cabbage as a double crop. Ratar. Povrt. 2012, 49, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvozdenović, Đ.; Bugarski, D.; Gvozdanović-Varga, J.; Červenski, J.; Takač, A. Posebno povrtarstvo. In Knjiga-Udžbenik, 1-383; Megatrend Universitz: Belgrade, Serbia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, K.N.; Singh, A.; Mal, P.K. Effect of Drip Irrigation on Yield of Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. Capitata) under Mulch and Non-mulch Conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 58, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karklelienė, R.; Juškevičienė, D.; Radzevičius, A. Application of genetic resources in the development of new Lithuanian vegetable cultivars. Plants 2023, 12, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karklelienė, R.; Juškevičienė, D.; Radzevičius, A.; Sasnauskas, A. Productivity and adaptability of the new carrot and garlic cultivars in Lithuania. Zemdirb.-Agric. 2018, 105, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juškevičienė, D.; Karklelienė, R.; Radzevičius, A. Biodiversity and productivity of potato onions (Allium cepa var. Aggregatum g. Don). Acta Hortic. 2019, 1251, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiński, P. An evaluation of some morphological traits in doubled haploid lines and their F, hybrids of head cabbage Kamienna Głowa in the vegetative phase. J. Appl. Genet. 2000, 41, 247–252. [Google Scholar]
- Červenski, J.; Vlajić, S.; Ignjatov, M.; Tamindžić, G.; Zec, S. Agroclimatic conditions for cabbage production. Ratar. Povrt. 2022, 59, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lončarić, A.; Marček, T.; Šubarić, D.; Jozinović, A.; Babić, J.; Miličević, B.; Sinković, K.; Šubarić, D.; Babić, J.; Ačkar, Ð. Comparative Evaluation of Bioactive Compounds and Volatile Profile of White Cabbages. Molecules 2020, 25, 3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Upadhyay, A.K.; Prasad, K.; Bahadur, A.; Rai, M. Variability of carotenes, vitamin C, E and phenolics in Brassica vegetables. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2007, 20, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmižić, D.; Pinterić, M.; Lazarus, M.; Šola, I. High Growing Temperature Changes Nutritional Value of Broccoli (Brassica oleracea L. convar. botrytis (L.) Alef. var. cymosa Duch.) Seedlings. Foods 2023, 12, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seung, K.; Lee, A.; Kader, A. Preharvest and postharvest factors influencing vitamin C content of horticultural crops. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2000, 20, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M.; Feller, C. An empirical model for describing growth and nitrogen uptake of white cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata). Sci. Hortic. 1998, 73, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsuo, H.; Sonoda, Y. Cabbage-head development as affected by nitrogen and temperature. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1982, 28, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempelos, L.; Baranski, M.; Sufar, E.K.; Gilroy, J.; Shotton, P.; Leifert, H.; Srednicka-Tober, D.; Hasanaliyeva, G.; Rosa, E.A.S.; Hajslova, J. Effect of Climatic Conditions, and Agronomic Practices Used in Organic and Conventional Crop Production on Yield and Nutritional Composition Parameters in Potato, Cabbage, Lettuce and Onion; Results from the Long-Term NFSC-Trials. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komolka, P.; Górecka, D.; Dziedzic, K. The effect of thermal processing of cruciferous vegetables on their content of dietary fiber and its fractions. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2012, 11, 347–354. [Google Scholar]
- Kavaliauskaitė, D.; Karklelienė, R.; Jankauskienė, J. Impact of organic fertilizer on yield of white cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) and soil productivity. Hortic. Sci. 2023, 50, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung-Hoon, K.; Chang-Seob, S.; Seong-Sil, K.; Hyeun-Kyoo, S. Quality Assessment of Ojeok-San, a Traditional Herbal Formula, Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography Combined with Chemometric Analysis. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2015, 2015, 607252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.-L.; Qin, M.-J.; Qi, L.-W.; Wu, G.; Shu, P. Improved quality evaluation of Radix Salvia miltiorrhiza through simultaneous quantification of seven major active components by high-performance liquid chromatography and principal component analysis. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, M.; Saadat, S.; Abbey, L. Effect of Exogenous Amino Acids Application on Growth and Nutritional Value of Cabbage under Drought Stress. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 272, 109561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarojnee, D.Y.; Navindra, B.; Chandrabose, S. Effect of naturally occurring amino acid stimulants on the growth and yield of hot peppers (Capsicum annum L.). J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2009, 5, 414–424. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283086040_Effect_of_naturally_occurring_amino_acid_stimulants_on_the_growth_and_yield_of_hot_peppers_Capsicum_annum_L (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Song, C.; Ye, X.; Liu, G.; Zhang, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Sun, R.; Wang, C.; Xu, D.; et al. Comprehensive Evaluation of Nutritional Qualities of Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis) Varieties Based on Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).