Abstract
Reclaimed water provides a sustainable and economical alternative for landscape irrigation, but its elevated salinity can negatively impact sensitive plant species. This study evaluated the salinity tolerance of two widely used ornamental grasses, Cymbopogon citratus (lemon grass) and Pennisetum alopecuroides (fountain grass), under three electrical conductivity (EC) levels: 1.2 (control), 5.0, and 10.0 dS·m−1. Visual assessments over 62 days showed that both species maintained an acceptable appearance under saline conditions. C. citratus exhibited no foliar damage, with visual scores above 4.6 even at 10.0 dS·m−1, whereas P. alopecuroides showed slight leaf injury but retained a score of 3.9 or higher. Growth parameters, such as plant height, leaf area, and shoot dry weight, decreased significantly in C. citratus with increasing salinity, particularly at 10.0 dS·m−1, where reductions reached up to 51.1%. In contrast, P. alopecuroides maintained stable growth indices under salt stress, although leaf area and tiller number were notably affected at high EC levels. Both species accumulated substantial amounts of sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−); C. citratus showed more pronounced ion accumulation than P. alopecuroides. These findings suggest that both grasses are suitable for landscaping in saline environments, although they employ different physiological strategies to cope with salt stress.
1. Introduction
The southwestern United States confronts mounting environmental pressures that threaten the long-term viability of its ecosystems and urban landscapes. A particularly pressing challenge is the escalating problem of soil salinization, exacerbated by the arid climate of the region, diminishing freshwater supplies, and growing dependence on marginal-quality irrigation sources, including treated wastewater and brackish groundwater. This progressive salt accumulation disrupts soil physicochemical properties through structural degradation and nutrient imbalances, severely impairing both native vegetation and cultivated ornamental species. With climate projections indicating intensified aridity and water scarcity across the region, developing salinity-resilient landscaping solutions has become an urgent priority. Strategic selection and breeding of salt-tolerant plant species offers a sustainable pathway to maintain landscape functionality while conserving precious freshwater resources, an approach that simultaneously addresses ecological health and water security concerns in this water-stressed region.
The increasing use of ornamental plants in urban landscapes, including streetscapes, parks, schools, and other institutional grounds, has increased the need for salt-tolerant species, as these decorative plants typically exhibit greater salinity sensitivity compared with agricultural crops and forages [1]. Although previous studies have categorized nearly 100 Utah plant species, encompassing field crops, forages, vegetables, fruit and nut crops, flowers, and turfgrasses, the criteria used to assess salt tolerance varied among them. For most plant species, tolerance was evaluated based on yield loss. In contrast, turfgrass species, including ornamental grasses, were assessed using reductions in growth and visual quality. These evaluations classified plants into five salinity tolerance levels based on electrical conductivity (EC) thresholds: salt-sensitive (<3.0 dS·m−1 EC), moderate tolerance (3.0 to 6.0 dS·m−1 EC), moderate to high tolerance (6.0 to 9.0 dS·m−1 EC), high tolerance (9.0 to 12.0 dS·m−1 EC), and extremely salt-tolerant (>12.0 dS·m−1 EC) [1,2]. These classifications relied largely on anecdotal evidence rather than systematic empirical data. This knowledge gap underscores the critical need for rigorous, quantitative evaluation of ornamental plant salt tolerance to support sustainable urban landscape practices, particularly in regions facing increasing soil salinity from irrigation with marginal-quality water sources. Such research will enable landscape designers and urban planners to select appropriate plant species that can maintain aesthetic quality while withstanding saline growing conditions, thereby ensuring the long-term viability of urban green spaces.
Research on salt tolerance in ornamental grass has established baseline data, although significant knowledge gaps remain regarding their performance in southwestern U.S. conditions. Current studies indicate that most grasses cannot survive at sodium chloride (NaCl) concentrations beyond 200 to 300 mM (EC values of approximately 14.6 to 21.9 dS·m−1) [2,3], with notable exceptions like Urochondra setulosa (creek rat-tail grass) thriving at a NaCl concentration of 1000 mM (EC: 73.1 dS·m−1) [2]. Several species demonstrate varying degrees of salt tolerance: Muhlenbergia capillaris (pink muhly grass) tolerates 170 mM NaCl (12.4 dS·m−1 EC) [4,5], whereas Eragrostis spectabilis (purple love grass), Miscanthus sinensis ‘Gracillimus’ (Chinese silver grass), Panicum virgatum ‘Northwind’ (Northwind switchgrass), and Schizachyrium scoparium (little bluestem) maintain good visual quality when irrigated with saline solutions at an EC of 10.0 dS·m−1 [5]. Other species, like Pennisetum alopecuroides ‘Foxtrot’ (fountain grass) and Leymus arenarius (sand ryegrass), show acceptable visual quality under saline conditions despite growth reduction [5,6]. Particularly, Muhlenbergia lindheimeri (Lindheimer’s muhly) performs well at an EC of up to 5.0 dS·m−1 and acceptably at 10.0 dS·m−1 [7], and Cymbopogon citratus (lemon grass), an important multipurpose Poaceae species, demonstrates moderate salinity tolerance up to 80 mM NaCl (EC: 5.8 dS·m−1), while maintaining growth and essential oil production [8,9]. Pennisetum species demonstrate notable drought tolerance and have gained widespread popularity as ornamental plants owing to their striking foliage and distinctive flower spikes [10,11]. Importantly, certain species within this genus exhibit significant salt tolerance, making them promising candidates for phytoremediation of saline-affected soils [12].
However, existing studies present critical limitations: (i) most tolerance assessments rely solely on visual or growth parameters without physiological mechanism analysis [13]; (ii) studies often use single salt types (e.g., CaCl2) rather than ecologically relevant NaCl-dominated solutions [14]; (iii) regional adaptation data for southwestern U.S. conditions are scarce; and (iv) comprehensive evaluations combining morphological, physiological and ion regulation responses are lacking [6,13]. This study addresses these gaps through systematic evaluation of two promising ornamental grass species under controlled saline conditions, examining their morphological adaptation, physiological responses, and ion regulation mechanisms to identify suitable candidates for southwestern U.S. landscapes facing increasing salinity stress.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
The study utilized two ornamental grass species obtained at 10 cm in 32-cell trays (5.5 × 5.5 × 10.5 cm) from Hoffman Nursery (Rougemont, NC, USA) on 14 June 2019. The experiment was conducted in a climate-controlled single-gable glass green-house at Utah State University (USU) (Logan, UT; 41°45′28″ N, 111°48′47″ W, elevation 1409 m) from 14 June to 12 November 2019. Environmental conditions were carefully regulated: the daily light integral averaged 28.8 ± 10.8 mol·m−2·d−1, with supplemental lighting provided by 1000-W high-pressure sodium lamps (Hydrofarm, Petaluma, CA, USA) from 9 September onward when natural intensity dropped below 544 µmol·m−2·s−1 between 0600 and 2200 HR, delivering an average photosynthetic photon flux density of 337 ± 55 µmol·m−2·s−1 at canopy level. Temperatures were maintained at 25 °C (day) and 20 °C (night) using a fan-and-pad evaporative cooling system.
Plants were initially watered with tap water (EC = 0.31 dS·m−1; pH 8.19) and transplanted on 5 July 2019 into 2-gallon polypropylene containers (No. 2B, Nursery Supplies, Orange, CA, USA) containing a standardized substrate mix composed of 75% Canadian sphagnum peatmoss (SunGro Horticulture, Agawam, MA, USA) and 25% vermiculite (Therm-O-Rock West, Chandler, AZ, USA), amended with 0.89 kg·m−3 gypsum (92% CaSO4·2H2O, 21% calcium, 17% sulfur, Athletic White Sports Field Marking Gypsum, Western Mining and Minerals, Bakersfield, CA, USA), 1.57 kg·m−3 dolomitic lime (Lhoist North America, Salinas, CA, USA), and 0.65 kg·m−3 wetting agent (AquaGro G; Aquatrols®, Paulsboro, NJ, USA). To ensure experimental uniformity, all plants were trimmed to 15 cm height on 9 August 2019.
2.2. Treatments
The experimental treatments consisted of nutrient and saline solutions applied to the plants. The control treatment was prepared by dissolving 0.8 g∙L−1 of 15N-2.2P-12.5K water-soluble fertilizer (Peters 15-5-15 Cal-Mag Special; Scotts, Marysville, OH, USA) in tap water. Saline treatments were formulated by supplementing the nutrient solution with sodium chloride (NaCl; Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O; Hi Valley Chemical, Centerville, UT, USA) to achieve target electric conductivity (EC) levels of 5.0 and 10.0 dS·m−1. A saline solution with an EC of 10.0 dS·m⁻1 was used based on regional water quality data. Although the majority of irrigation water samples analyzed from 2019 to 2022 by the Utah State University Analytical Laboratories had salinity levels below 2 dS·m⁻1, some samples reached values as high as 20 dS·m⁻1 or more [15]. The detailed composition of the treatment solutions was published by Xing et al. (2021) [16]. The pH of all solutions was adjusted to 6.42 ± 0.05 using 1 mol·L−1 nitric acid. From 9 August to 10 October 2019 (9-week period), each pot received 1.5 L of the assigned treatment solution every four days (approximately 16 irrigation events total). Following each irrigation, leachate was collected using the standardized pour-through technique [17], with the ECs immediately measured using a calibrated EC meter (LAQUA Twin, Horiba, Kyoto, Japan). For quality control, two replicate plants per treatment per species were monitored, with the average EC value of leachate calculated across both species for each irrigation event to ensure representative measurements.
2.3. Plant Harvest and Data Collection
The experiment included two destructive harvests to evaluate treatment effects at different growth stages. The initial harvest occurred on 25 September 2019 (47 days after treatment initiation, following 12 irrigation events), with five replicate plants per treatment per species collected. The final harvest of the remaining five plants was conducted on 10 October 2019 (62 days after treatment initiation, following 16 irrigation events).
Plant quality was assessed using a standardized visual scoring system [18] ranging from 0 (dead plant) to 5 (excellent quality with no damage), with intermediate scores quantifying foliar damage severity: 1 (>90% leaf burn/necrosis), 2 (50–90% damage), 3 (10–50% damage), and 4 (<10% damage). Growth parameters were measured at baseline and for both harvests, including plant height (growing medium surface to tallest point), canopy width (average of two perpendicular measurements), and derived growth index (mean of height and width) [19]. At harvest, tiller counts were recorded, and leaf area was measured using a LI-3100 leaf area meter (LI-COR® Biosciences, Lincoln, NE, USA). Shoot biomass was separated from roots and dried at 80 °C for five days to determine dry weight.
Substrate salinity was assessed after harvest using a modified saturated paste extraction method [20], where air-dried samples (3 replicates per treatment per species) from the top 2–3 cm were mixed with deionized water (1:6 w/v ratio) for EC measurement.
2.4. Determination of Leaf Greenness and Chlorophyll Fluorescence
Leaf chlorophyll content was quantified non-destructively using a SPAD-502 chlorophyll meter (Minolta Camera Co., Osaka, Japan) prior to harvest, with measurements taken from five randomly selected mature leaves per pant and averaged to obtain representative SPAD value for each species.
Photosynthetic efficiency was assessed through chlorophyll fluorescence measurements using a PEA fluorometer (version 12.1; Hansatech Instrument Ltd., Norfolk, UK) to determine both the maximum quantum yield of photosystem II (PSII) and the performance index (PIabs). The Fv/Fm ratio [Fm − Fo)/Fm], representing the maximum photochemical efficiency of PSII, was measured on dark-adapted leaves after a 30-min adaptation period using specialized leaf clips (4 mm diameter; Hansatech Instrument Ltd.), where Fo denotes the minimum fluorescence yield under weak modulated light and Fm indicates the maximum fluorescence yield under saturating light conditions. Measurements were consistently taken from the mid-section of fully expanded leaves to ensure data comparability. Additionally, PIabs was recorded as a comprehensive indicator of the overall functional performance of PSII, reflecting the efficiency of energy conservation from absorbed photons to electron transport.
2.5. Gas Exchange Measurement
Leaf net photosynthetic rate (Pn), stomatal conductance (gs), transpiration rate (E), and water use efficiency (WUE) were measured 2 days before the harvest date using a portable photosynthesis system with an automatic universal PLC3 universal leaf cuvette (CIRAS-3; PP Systems, Amesbury, MA, USA). Fully expanded leaves of six plants in each treatment were used for the measurement. Environmental conditions in the cuvette were controlled at 25 °C, 1000 µmol·m−2·s−1 photosynthetic photon flux and 400 µmol·mol−1 carbon dioxide (CO2). Data were recorded once the environmental conditions and gas exchange parameters in the cuvette became stable. All plants were well-watered before measurement to avoid water stress. Measurements were taken on a sunny day, generally between 1100 and 1400 HR.
2.6. Mineral Analysis
For mineral analysis, three randomly selected plants from each treatment group per species were processed. The dried plant material was ground to a fine powder (0.5 g) using a stainless Wiley mill (Thomas Scientific, Swedesboro, NJ, USA). These powdered samples were subsequently analyzed at the Utah State University Analytical Laboratories (Logan, UT, USA) following established protocols. Elemental concentrations (Na+, Ca2+, K+, P, Mg2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Fe3+, Cu2+, S, B, and Mo3+) were determined through microwave-assisted acid digestion using a modified Gavlak et al. (2005) [20] method: samples were initially digested with 6 mL concentrated HNO3 at 80 °C for 10 min, cooled for 2-min, then treated with 2 mL 30% H2O2 and further digested at 130 °C until the digest volume reduced to 2.0–3.0 mL. After vortexing and cooling, digests were diluted to 25 mL and analyzed via inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (iCAP 6300 ICP-AES; Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), with results reported as mg·g−1 dry weight. Chloride (Cl−) content was separately quantified using 2% acetic acid extraction followed by Flow Injection Analysis with Ion Chromatography (QuikChem 8000; Lachat Instrument, Loveland, CO, USA), also reported as mg·g−1 dry weight.
2.7. Experimental Design and Data Analysis
The experiment design followed a randomized complete block design with 10 replicates (blocks). Each block contained 6 experimental units (pots), representing all combinations of the two grass species and three salinity treatments. Despite observing significant species × treatment interactions in preliminary analyses, we conducted separate analyses of variance (ANOVA) for each species to account for their distinct growth characteristics and response patterns. Post-hoc comparisons between treatment means were performed using Tukey’s honestly significant difference (HSD) test at a significance level of α = 0.05 to control Type I error inflation in multiple comparisons. The statistical analysis was implemented using the ANOVA procedure in JMP software (version 13; JMP Statistical Discovery LLC, Cary, NC, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. EC of Leachate
The EC of leachate served as a key indicator of salt accumulation dynamics in the growing medium under sustained saline irrigation regimes. Although some interspecific variation was observed (p = 0.001), our analysis revealed that EC values of leachate were predominantly determined by the applied salinity treatments (p < 0.0001; Figure 1). The irrigation protocol (1.5 L of saline solution every four days) resulted in progressive salt buildup, with measured EC of leachate demonstrating clear treatment-dependent patterns: control maintained 1.06 to 1.73 dS·m−1; low salinity (5.0 dS·m−1 EC) reached 1.69 to 9.70 dS·m−1, and high salinity (10.0 dS·m−1 EC) ranged from 3.75 to 17.0 dS·m−1 over the 9-week experimental period.
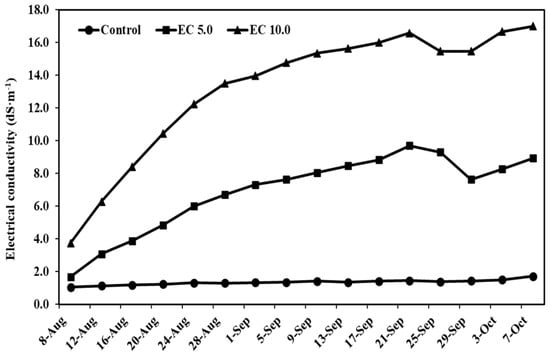
Figure 1.
Leachate electrical conductivity (EC) recorded after ornamental grasses were irrigated with a nutrient solution at an EC of 1.2 dS·m−1 (control) or saline solutions at ECs of 5.0 dS·m−1 (EC 5.0) or 10.0 dS·m−1 (EC 10.0). Two plants per species and treatment were selected for measurement, and the EC values were pooled across species. Leachate EC was monitored during the experimental period from 9 August 2019 to 10 October 2019.
These findings demonstrate that continuous saline irrigation leads to rapid salt accumulation, with leachate EC values eventually exceeding the EC values of input solution after four or five irrigation events because of concentration effect and insufficient leaching volume. After 47 days of irrigation with saline solutions over 12 irrigation events, the substrate EC values of C. citratus were approximately 16 and 22 times higher than the control, whereas those for P. alopecuroides were about 2 and 3 times higher, respectively (Figure 2). Although substrate EC values were not directly measured for C. citratus and P. alopecuroides after 62 days of irrigation with saline solutions over 16 irrigation events, it is reasonable to expect greater salt accumulation in its substrate, as salt remains behind once water is lost through transpiration following saline solution irrigation.
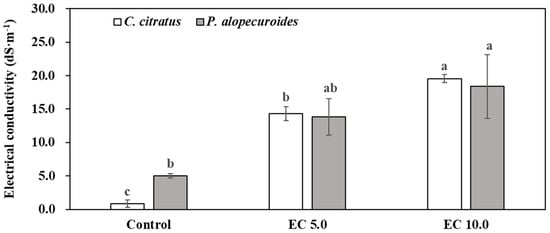
Figure 2.
Substrate electrical conductivity (EC) determined using a modified saturated soil paste technique [20] when ornamental grasses were harvested after they were irrigated with a nutrient solution at an EC of 1.2 dS·m−1 (control) or saline solutions at ECs of 5.0 dS·m−1 (EC 5.0) or 10.0 dS·m−1 (EC 10.0). Three containers per treatment were randomly selected for each species, and error bars represent three measurements for each treatment. Same lowercase letters above columns within species represent no significance among treatments by Tukey’s method for multiplicity at α = 0.05.
This phenomenon aligns with previous container production studies documenting similar salt accumulation patterns [5,21]. It should be noted that, under natural field conditions, soil salinity exhibits greater temporal and spatial variability because of interacting environmental factors, including evapotranspiration rates, irrigation water composition, groundwater dynamics, precipitation events, and inherent soil properties [22,23]. These factors were intentionally controlled in the greenhouse study.
3.2. Visual Quality
Salt stress typically induces foliar damage and compromises aesthetic quality in ornamental plants, as documented in previous studies [24,25,26]. Characteristic symptoms including leaf chlorosis and necrosis serve as reliable morphological indicators of salt stress sensitivity, as observed in species like Melica californica (California melicgrass) and Deschampsia caespitosa (tufted hairgrass) [27]. Our study demonstrated species-specific responses to saline conditions. Cymbopogon citratus (lemongrass) maintained excellent visual quality (score = 5) across all treatments at the first harvest, and P. alopecuroides showed only minimal foliar damage (scores > 4.3) at both EC levels of 5.0 and 10.0 dS·m−1 (Figure 3). At the second harvest, both species displayed increased symptom severity, and C. citratus exhibited superior salt tolerance with maintained high scores (4.6) at both EC levels of 5.0 and 10.0 dS·m−1, compared with P. alopecuroides which showed moderate decline (from 4.3 at an EC of 5.0 dS·m−1 to 3.9 at an EC of 10.0 dS·m−1) (Figure 3). Importantly, neither species developed severe injury symptoms after sustained 9-week saline irrigation, confirming their classification as moderately to highly salt-tolerant species. These findings align with observations on the salt tolerance of P. alopecuroides [6] and underscore the significant horticultural value of both species for landscaping in saline-affected environments, combining aesthetic appeal with functional stress tolerance.
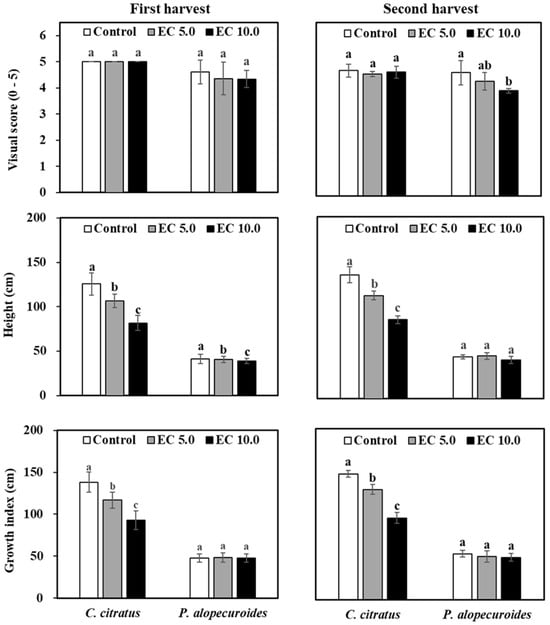
Figure 3.
Visual score, height, and growth index of two ornamental grasses irrigated with a nutrient solution [electrical conductivity (EC) = 1.2 dS·m−1; control] or a saline solution [EC = 5.0 dS·m−1 (EC 5.0) or 10.0 dS·m−1 (EC 10.0)] in a greenhouse. Plants were harvested after 12 irrigation events (first harvest) and 16 irrigation events (second harvest). Same lowercase letters above columns within the harvest date and species represent no significance among treatments by Tukey’s method for multiplicity at α = 0.05. 0 = dead; 1 = severe foliar salt damage (over 90% leaves with burn and necrosis); 2 = moderate foliar salt damage (50 to 90%); 3 = slight foliar salt damage (less than 50%); 4 = good quality with minimal foliar salt damage; and 5 = excellent without foliar salt damage [18].
3.3. Height
Growth parameters serve as essential indicators of plant salt stress response, with salinity levels typically exhibiting an inverse relationship with growth performance [28,29]. Our study revealed species-specific growth responses to saline irrigation (p < 0.0001 for both harvests). At the first harvest, C. citratus showed significant height reductions of 15.0% and 35.0% at an EC of 5.0 and 10.0 dS·m−1, respectively, compared with control, whereas P. alopecuroides exhibited only a 5.9% reduction at an EC of 10.0 dS·m−1 (Figure 3). By the second harvest, C. citratus displayed progressive height decreases of 16.7% and 36.3% at an EC of 5.0 and 10.0 dS·m−1, respectively, whereas P. alopecuroides maintained stable growth under saline conditions (Figure 3). These differential responses align with established salt tolerance mechanisms where growth suppression represents an adaptive survival strategy [30]. Previous studies report similar non-linear responses. For example, P. alopecuroides showed an 18.2% height increase at 4.6 dS·m−1 (50 mM NaCl) but declined at higher concentrations [31], a pattern also observed in Ageratum mexicanum (floss flower) [32], Cassia angustifolia (senna) [33], Phaseolus mungo (black gram) [34], and Tagetes patula (French marigold). According to standard classification systems [35,36], which categorize species based on growth reduction thresholds (moderately tolerant: 25% to 50%; tolerant: <25%), our results demonstrate that C. citratus qualifies as moderately salt-tolerant whereas P. alopecuroides exhibits superior salt tolerance. This finding has significant implications for plant selection in saline-affected landscapes.
3.4. Growth Index
Plant growth, the cumulative result of complex metabolic processes, is particularly vulnerable to disruption under salinity stress, often manifesting as reduced shoot development and leaf production, a phenomenon well-documented in species like Sorghastrum nutans (Indian grass) [37]. Our results demonstrated species-growth responses to saline irrigation (p < 0.0001 for both harvests). C. citratus exhibited progressive growth index reductions of 15.5% (first harvest) and 12.4% (second harvest) at an EC of 5.0 dS·m−1, with more pronounced declines of 32.7% and 35.0%, respectively, at an EC of 10.0 dS·m−1 at the first and second harvest (Figure 3). In striking contrast, P. alopecuroides maintained stable growth metrices across all salinity treatments, demonstrating superior salinity tolerance comparable to Chasmanthium latifolium (inland sea oats), which similarly showed no shoot growth inhibition at EC levels ≤ 10.0 dS·m−1 in hydroponic culture [7]. These differential responses highlight the importance of species selection for saline-affected landscapes, where salt-tolerant species like P. alopecuroides can maintain growth and development while moderately tolerant species like C. citratus may require more careful irrigation management.
3.5. Leaf Area
Numerous studies have established that salt stress significantly reduces leaf area development [6,18,38], primarily through salinity-induced physiological drought caused by osmotic stress [22]. Our findings revealed a salinity-level dependent response. Irrigation with saline solution at an EC of 5.0 dS·m−1 showed no significant leaf area reduction in either C. citratus or P. alopecuroides at the first harvest (Figure 4), and exposure to 10.0 dS·m−1 saline solution resulted in substantial decreases of 27.3% and 29.2%, respectively. By the second harvest, progressive leaf area reductions became evident even at an EC of 5.0 dS·m−1 for C. citratus (17.6%), with both species showing more severe impacts at an EC of 10.0 dS·m−1 (38.7% and 31.4% reductions for C. citratus and P. alopecuroides, respectively). These results align with the observation of Sun and Palmer (2018) [6], reporting a 46% leaf area reduction in P. alopecuroides under similar saline conditions (10.0 dS·m−1 for 18 weeks). The underlying mechanism involves initial cellular dehydration and shrinkage during salt stress, followed by complete recovery that ultimately impairs cell expansion and division, thereby limiting leaf growth [30]. Similar salinity-induced growth inhibition has been documented in ornamental shrubs, where combined salt and boron stress reduced photosynthetic activity and altered mineral homeostasis [39], highlighting the widespread nature of these physiological responses across plant species.
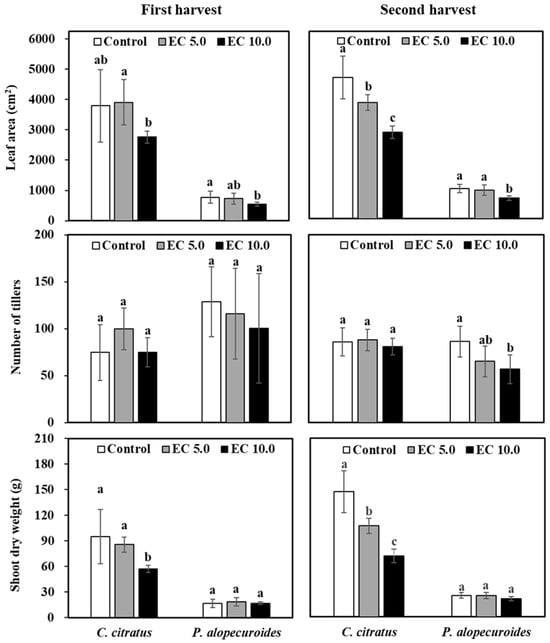
Figure 4.
Leaf area, number of tillers, and shoot dry weight of two ornamental grasses irrigated with a nutrient solution [electrical conductivity (EC) = 1.2 dS·m−1; control] or a saline solution [EC = 5.0 dS·m−1 (EC 5.0) or 10.0 dS·m−1 (EC 10.0)] in a greenhouse. Plants were harvested after 12 irrigation events (first harvest) and 16 irrigation events (second harvest). Same lowercase letters above columns within the harvest date and species represent no significance among treatments by Tukey’s method for multiplicity at α = 0.05.
3.6. Number of Tillers
Tiller formation represents a crucial adaptive mechanism in grasses that directly influences canopy development and productivity. Enhanced tillering increases the leaf area index, improving competitiveness against weeds and boosting photosynthetic capacity, ultimately enhancing forage quality. Our study revealed species-specific tillering responses to saline irrigation. At the first harvest, C. citratus exhibited a 33.7% increase in tiller production at an EC of 5.0 dS·m⁻1 but showed no significant change at EC of 10.0 dS·m⁻1 (Figure 4). No significant change was also observed at ECs of 5.0 and 10.0 dS·m⁻1 at the second harvest. Conversely, P. alopecuroides demonstrated progressive tiller reduction with increasing salinity, which decreased by 10.2% and 22.0% at ECs of 5.0 and 10.0 dS·m⁻1, respectively, at the first harvest, then by 24.6% and 34.1%, respectively, at the second harvest. These differential responses align with previous findings. Wang et al. (2019) [5] observed 27% and 40% tiller reduction in E. spectabilis at comparable salinity levels of 5.0 and 10.0 dS·m⁻1, respectively, whereas Sun and Palmer (2018) [6] reported 23% and 26% decreases in Carex vulpinoidea (fox sedge) and P. alopecuroides after prolonged exposure to saline solution at an EC of 10.0 dS·m⁻1. Similar patterns were documented by Ashraf et al. (1986) [40] in Dactylis glomerata (orchard grass), Festuca rubra (red fescue), Holcus lanatus (common velvet grass), and Lolium perenne (perennial ryegrass) under NaCl stress at 0 to 300 mol·m−3 NaCl (EC ≈ 0 to 21.9 dS·m⁻1) for 7 weeks.
3.7. Shoot DW
Salt stress typically impairs plant water uptake by creating osmotic imbalance in the rhizosphere, ultimately resulting in biomass reduction, a phenomenon well-quantified through dry matter content analysis. Our results demonstrated species-specific biomass responses to saline irrigation (p = 0.01 and <0.0001, respectively, for the first and second harvest). C. citratus showed significant shoot DW reductions of 9.8% (5.0 dS·m−1) and 39.7% (10.0 dS·m−1) at the first harvest, progressing to 27.2% (5.0 dS·m−1) and 51.1% (10.0 dS·m−1) reductions by the second harvest (Figure 4). In contrast, P. alopecuroides maintained stable shoot DW across all salinity treatments, demonstrating superior salt tolerance. These findings align with established patterns of biomass reduction under saline conditions observed in various species, including forage grasses [41,42], cereal crops like Hordeum vulgare (barley) and Zea mays (maize) [43,44,45,46], and turf species such as Cynodon dactylon (Bermuda grass) [47] and P. alopecuroides [31]. Importantly, shoot growth parameters and biomass accumulation serve as reliable proxies for salinity tolerance assessment in graminaceous species [48], with the degree of reduction being species- and cultivar-dependent. The comparative resilience of grasses to salinity stress, as evidenced in our study and previous research, underscores their ecological adaptability and practical value for cultivation in saline-affected environments.
3.8. Leaf Greenness and Chlorophyll Fluorescence
Chlorophyll content assessment revealed species-specific responses to saline irrigation, with SPAD measurements conducted only for C. citratus because of unsuitable leaf morphology of P. alopecuroides. At the first harvest, C. citratus showed a significant 11.6% increase in SPAD values when irrigated with saline solution at an EC of 5.0 dS·m−1, compared with control, but saline solution at an EC of 10.0 dS·m−1 maintained values (Table 1). By the second harvest, SPAD readings showed no treatment differences, suggesting that chlorophyll content was less affected by salinity than morphological parameters, like leaf length reduction and mature leaf wilting. This pattern aligns with observations in Eragrostis spectabilis and Schizachyrium scoparium [5] and contrasts with chlorophyll degradation reported in Viburnum tinus [49] and other species. These interspecific variations are likely to stem from leaf anatomical adaptations (e.g., increased mesophyll thickness) and inherent physiological differences. SPAD values provide indirect chlorophyll estimates and remain valuable for salinity tolerance screening.

Table 1.
SPAD (Soil Plant Analysis Development) reading, chlorophyll fluorescence (Fv/Fm), and PIabs of Cymbopogon citratus irrigated with a nutrient solution [electrical conductivity (EC) = 1.2 dS·m−1; control] or a saline solution [EC = 5.0 dS·m−1 (EC 5.0) or 10.0 dS·m−1 (EC 10.0)] for 47 days (first harvest) and 62 days (second harvest) in a greenhouse z.
Photosynthetic performance analysis of C. citratus showed stable maximum quantum yield of PSII (Fv/Fm = 0.70 to 0.76) and performance index (PIabs = 1.8 to 2.9) across treatments (Table 1), indicating preserved photosystem II functionality under saline conditions. Fv/Fm reflects the optimal light energy conversion efficiency of PSII reaction centers, whereas PIabs quantifies the overall photosystem performance [50,51]. The maintenance of these parameters suggests that the observed growth reductions resulted primarily from osmotic stress rather than photochemical impairment, highlighting the capacity of C. citratus to maintain photosynthetic apparatus integrity despite salinity-induced morphological constraints.
3.9. Gas Exchange
Salinity stress commonly affects plant physiological processes, such as photosynthesis, stomatal conductance, and transpiration. In our study, gas exchange measurements were conducted only for C. citratus, as the leaf morphology of P. alopecuroides was unsuitable for accurate readings. After 47 days of irrigation with saline solutions over 12 irrigation events, C. citratus showed notable reductions in gas exchange parameters. At an EC of 5.0 dS·m−1, Pn, gs, and E decreased by 17.9%, 28.3%, and 21.2%, respectively, compared with control (Table 2). At an EC of 10.0 dS·m⁻1, these reductions were more pronounced, with Pn, gs, and E decreasing by 41.0%, 49.3%, and 37.4%, respectively (Table 2). However, water use efficiency was not affected by saline solution irrigation. Although gas exchange was not collected for C. citratus after 62 days of irrigation with saline solutions over 16 irrigation events, it is reasonable to expect Pn, gs, and E to decrease along with the salinity levels. This pattern aligns with observations in Andropogon ternarius (silver bluestem), Calamagrostis × acutiflora (feather reed grass), Carex morrowii (Japanese sedge), Eragrostis spectabilis, Miscanthus sinensis, Panicum virgatum, Schizachyrium scoparium, and Sporobolus heterolepis (prairie dropseed) [5,16]

Table 2.
Net photosynthetic rate (Pn), stomatal conductance (gs), transpiration (E), and water use efficiency (WUE) of Cymbopogon citratus irrigated with a nutrient solution [electrical conductivity (EC) = 1.2 dS·m−1; control] or a saline solution [EC = 5.0 dS·m−1 (EC 5.0) or 10.0 dS·m−1 (EC 10.0)] for 47 days in a greenhouse z.
3.10. Ion Content
Ion accumulation patterns in the two ornamental grass species revealed distinct physiological responses to saline irrigation (Table 3). C. citratus exhibited 19.6- and 38.2-fold increases in leaf Na+ content at ECs of 5.0 and 10.0 dS·m−1, respectively, whereas P. alopecuroides showed even greater accumulation (25.2- and 45.5-fold increases), reaching a maximum of 3.92 mg·g−1 at an EC of 10.0 dS·m−1. Chloride accumulation followed similar trends. C. citratus exhibited 9.2- and 22.0-fold increases in leaf Cl− content at ECs of 5.0 and 10.0 dS·m−1, respectively, whereas P. alopecuroides had 3.0- and 5.2-fold increases in leaf Cl− content. C. citratus demonstrated particularly high Cl− concentrations (43.2 mg·g−1 at an EC of 10.0 dS·m−1).

Table 3.
Mineral content, Ca2+/Na+, and K+/Na+ ratio of two ornamental grasses irrigated with a nutrient solution [electrical conductivity (EC) = 1.2 dS·m−1; control] or a saline solution [EC = 5.0 dS·m−1 (EC 5.0) or 10.0 dS·m−1 (EC 10.0)] for 62 days in a greenhouse z.
Our study revealed distinct ion regulation strategies between the two grass species. C. citratus exhibited lower Na+ but higher Cl− accumulation compared with P. alopecuroides (Table 3). These findings suggest that P. alopecuroides possesses superior Na+ tolerance mechanisms, whereas C. citratus demonstrates enhanced Cl− tolerance capacity. Both species maintained good visual quality despite elevated leaf ion concentrations, indicating effective activation of known salt tolerance mechanisms including (i) tissue tolerance through vacuolar sequestration, (ii) root-level ion exclusion, and (iii) restricted xylem transport of toxic ions [22,52,53]. This physiological adaptability enables plants to survive saline conditions by managing ion homeostasis while preserving metabolic function and visual appearance.
Calcium dynamics in both grass species exhibited distinct responses to saline irrigation. Compared with control, leaf calcium content significantly increased by 71.5% in C. citratus and 47.1% in P. alopecuroides at an EC of 5.0 dS·m−1 (Table 3). This upward trend intensified at a higher salinity level at an EC of 10.0 dS·m−1, with Ca2+ content rising by 135.9% and 124.7% in C. citratus and P. alopecuroides, respectively, peaking at 12.58 mg·g−1 in P. alopecuroides. Notably, CaCl2 was a component of the saline solution, the observed Ca2+ accumulation was substantially lower than corresponding Na+ and Cl− increases, likely due to Na+-induced competitive inhibition of Ca2+ uptake. This antagonistic relationship was further evidenced by declining Ca2+/Na+ ratios in both C. citratus and P. alopecuroides as the salinity level increased (Table 3). Interestingly, C. citratus maintained relatively higher Ca2+/Na+ ratios than P. alopecuroides at all salinity levels, suggesting species-specific differences in calcium regulation under salt stress.
Salt stress typically disrupts plant ion homeostasis by promoting excessive Na+ influx while impairing K+ uptake, ultimately compromising cellular functions [54]. Although our study did not detect statistically significant variations in K+ content across treatments, we observed a consistent decreasing trend corresponding with increasing salinity levels. Notably, C. citratus maintained higher K+/Na+ ratios than P. alopecuroides under saline conditions (Table 3), although both species exhibited significant ratio reductions at ECs of 5.0 and 10.0 dS·m−1 compared with controls. These findings suggest limited capacity for Na+ exclusion in leaf tissues, as maintenance of optimal cytosolic K+/Na+ ratio is crucial for enzymatic activity and metabolic processes [55]. The observed ratio declines, particularly at higher salinity levels, indicate potential disruption of normal cellular functions despite the overall salt tolerance of two species used in the study.
The two grass species exhibited distinct patterns of micronutrient accumulation under saline conditions (Table 4). P. alopecuroides maintained stable Mg2+ concentrations (2.78 to 3.01 mg·g−1) across all salinity levels, remaining within the sufficiency range (2.63 to 6.00 mg·g−1) [56]. In contrast, C. citratus displayed progressive Mg2+ deficiency, with concentrations declining to 2.22 and 1.90 mg·g−1, representing 20.8% to 32.1% reductions from control at ECs of 5.0 and 10.0 dS·m−1, respectively. This deficiency likely explains the observed leaf chlorosis, as Mg2+ serves multiple critical physiological functions: (i) as the central atom in chlorophyll molecules, (ii) as an activator for more than 300 enzymes including RuBP carboxylase, and (iii) as a regulator of photosynthetic carbon metabolism [57,58]. In C. citratus, the combination of salinity stress and Mg2+ deficiency appears to disrupt chloroplast ultrastructure, leading to photoinhibition through multiple mechanisms: impaired photosynthate export, elevated reactive oxygen species production (superoxide and H2O2), and increased oxygenase activity of Rubisco [57,58]. These metabolic disturbances ultimately manifest as the characteristic yellowing observed in Mg-deficient leaves, particularly under high salinity conditions.

Table 4.
Mineral content of two ornamental grasses irrigated with a nutrient solution [electrical conductivity (EC) = 1.2 dS·m−1; control] or a saline solution [EC = 5.0 dS·m−1 (EC 5.0) or 10.0 dS·m−1 (EC 10.0)] for 62 days in a greenhouse z.
This study revealed distinct P and Zn2+ accumulation patterns between the two grass species under saline conditions. P. alopecuroides maintained consistently higher P concentrations (3.45 to 3.99 mg·g−1) than C. citratus (1.99 to 2.33 mg·g−1) (Table 4), with values remaining within the optimal sufficiency range (2.0 to 5.0 mg·g−1) for both species [56]. Although P. alopecuroides showed stable P levels across salinity treatments, C. citratus exhibited a significant reduction of 14.6% at an EC of 5.0 dS·m⁻1 compared with control, suggesting potential salinity-induced P uptake inhibition despite maintaining adequate concentrations. This is physiologically significant, as P plays crucial roles in nucleic acid synthesis, energy transfer, and carbohydrate metabolism, all critical for salinity stress responses [59].
Zn2+ distribution showed contrasting trends, with P. alopecuroides accumulating higher concentrations (0.06 to 0.08 mg·g−1) than C. citratus (0.02 to 0.03 mg·g−1) (Table 4), although both remained within normal ranges (0.02 to 0.1 mg·g−1) [56]. Interestingly, Zn2+ levels in P. alopecuroides showed a non-significant increasing trend with salinity, whereas C. citratus demonstrated significantly higher Zn2+ accumulation under saline conditions compared with control. This may reflect species-specific activation of Zinc-dependent stress responses, as Zn2+ is vital for antioxidant defense (superoxide dismutase), membrane stabilization, and phytohormone (auxin) biosynthesis [60]. The differential Zn2+ accumulation patterns suggest distinct metabolic adaptations to saline stress between the two species.
Iron (Fe3+) and manganese (Mn2+) dynamics in the two grass species revealed distinct responses to saline solution irrigation. Although no significant treatment effects were observed for Fe3+ accumulation, baseline concentrations differed substantially between species: P. alopecuroides maintained 0.38 to 0.65 mg·g−1 Fe3+, approximately 5 to 13 times higher than C. citratus (0.05 to 0.07 mg·g−1) (Table 4). This interspecific variation may reflect differential iron uptake efficiency, as high salinity can impair Fe3+ assimilation through cation competition at root surfaces [61]. Notably, Mn2+ accumulation showed clear salinity dependence in both species. P. alopecuroides exhibited 57.0% to 106.4% increases in leaf Mn2+ (0.56 to 0.73 mg·g−1) at elevated EC levels, whereas C. citratus showed even greater relative increases (127.2% to 357.2%; 0.19 to 0.38 mg·g−1) compared with controls (Table 4). These Mn2+ accumulation patterns are physiologically significant given essential roles of manganese in chlorophyll synthesis, photosystem II oxygen-evolving complex, and antioxidant enzyme activation [62].
Copper (Cu2+) and sulfur (S) homeostasis remained stable under saline conditions in both grass species, despite their distinct metabolic roles. Cu2+, a critical component of photosynthetic electron transport (plastocyanin) and redox enzymes [63], maintained consistent concentrations across treatments (C. citratus: 0.004 to 0.005 mg·g−1; P. alopecuroides: 0.013 to 0.017 mg·g−1) (Table 4). Similarly, S levels, essential for stress-responsive compounds like glutathione and phytochelatins, showed no salinity-induced variations (C. citratus: 1.21 to 1.42 mg·g−1; P. alopecuroides: 2.21 to 2.91 mg·g−1) (Table 4).
Boron (B) and molybdenum (Mo3+) exhibited species-specific responses. P. alopecuroides maintained stable B and Mo3+ levels (Table 4), which are important for the cell wall integrity and nitrate reductase cofactor [64]. However, C. citratus showed significant Mo3+ reduction under salinity stress, potentially leading to Mo3+ deficiency and impairing plant growth and development, as well as nitrogen metabolism, which correlated with observed growth inhibition.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrated that both C. citratus and P. alopecuroides exhibit considerable tolerance to salinity stress, making them promising candidates for urban landscaping where reclaimed water is used. However, their adaptive mechanisms differ markedly. C. citratus maintained excellent visual quality across all salinity treatments, with no observable foliar damage even at an EC of 10.0 dS·m−1. Its strategy appears to involve reducing growth as a means to limit salt accumulation, which is reflected in significant decreases in plant height, leaf area, and shoot dry weight under increasing salinity. At the same time, this species accumulated high Cl− level in their tissues, suggesting tolerance to Cl−. Notably, K+/Na+ and Ca2+/Na+ ratios decrease, indicating potential disruptions in nutrient balance and possible regulation of ion toxicity. These physiological responses highlight the ability of C. citratus to adapt to salt stress by limiting visible damage through internal biochemical adjustments. P. alopecuroides, on the other hand, shows less impact on morphological indices such as plant height and shoot dry weight, maintaining relatively stable structural performance under salt stress. Although some decline in visual quality was observed at an EC of 10.0 dS·m−1, the species appears to tolerate salinity by distributing salt more evenly throughout its tissues, thereby diluting harmful effects. This is supported by significant increases in Cl− contents, along with decreasing K+/Na+ and Ca2+/Na+ ratios as salinity increases. The lack of significant changes in growth traits suggests that P. alopecuroides may have a higher capacity to maintain biomass production under saline conditions compared with C. citratus. The differential responses between these two species highlight the importance of considering not only visual tolerance but also physiological adaptability when selecting plants for saline environments. These findings provide valuable insights for landscape professionals, horticulturists, and policymakers in developing resilient and sustainable urban green spaces under water scarcity conditions with increasing salinity stress. Future studies could further explore long-term acclimation responses, field performance under real-world reclaimed water irrigation scenarios, and the molecular or genetic basis of salt tolerance in these species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S.; Methodology, H.X., J.H. and Y.S.; Formal analysis, H.X. and A.P.; Data curation, H.X., J.H. and Y.S.; writing—original draft preparation, H.X.; writing—review and editing, H.X., A.P. and Y.S.; Supervision, Y.S.; Project administration, H.X. and Y.S.; Funding acquisition, H.X. and Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Science and Technology Planning Project of Inner Mongolia (2022YFDZ0067), the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) National Institute of Food and Agriculture Hatch projects UTA01381 and UTA01666, the USDA Agricultural Marketing Service Specialty Crop Block Grant Program, New Faculty Start-Up Funds from Utah State University’s (USU) Office of Research and Graduate Studies, USU’s Center for Water-Efficient Landscaping, and the Utah Agricultural Experiment Station (UAES). Additional support was provided by the University of Georgia’s Center for Applied Nursery Research, a nonprofit research center in Dearing, GA.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed at the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the kind contribution of plant materials from Hoffman Nursery (Rougemont, NC, USA), and we appreciate the valuable feedback provided by anonymous reviewers. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agencies. Mention of a trademark, proprietary product, or vendor does not constitute a guarantee or warranty of the product by the USDA and does not imply its approval to the exclusion of other products or vendors that also may be suitable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- Amacher, J.K.; Rich, K.; Boyd, K. Salinity and Plant Tolerance. All Archived Publications 2000. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237537841_SALINITY_AND_PLANT_TOLERANCE (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Gulzar, S.; Khan, M.A.; Ungar, I.A. Salt tolerance of a coastal salt marsh grass. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2003, 34, 2595–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearen, J.R.; Pahl, M.D.; Wolynetz, M.S.; Hermesh, R. Association of salt tolerance at seedling emergence with adult plant performance in slender wheatgrass. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1997, 77, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCompte, J.S.; Wright, A.N.; LeBleu, C.M.; Kessler, J.R. Saline irrigation affects growth and leaf tissue nutrient concentration of three native landscape plant species. HortTechnology 2016, 26, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Sun, Y.P.; Niu, G.H.; Deng, C.Y.; Wang, Y.; Gardea-Torresdey, J. Growth, gas exchange, and mineral nutrients of ornamental grasses irrigated with saline water. HortScience 2019, 54, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.P.; Palmer, A.L. Responses of ornamental grass and grasslike plants to saline water irrigation. HortTechnology 2018, 28, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenney, C.B.; Mahato, T.R.; Schuch, U.K. Salinity tolerance of ornamental grasses adapted to semi-arid environments. Horticulturae 2016, 1112, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, H.S.; Ali, A.; Zahra, S.; Hassan, Z.U.; Kubra, K.T.; Azam, M.; Zahid, H.F. Phytochemical composition and pharmacological potential of lemongrass (Cymbopogon) and impact on gut microbiota. AppliedChem 2022, 2, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukarram, M.; Khan, M.M.A.; Zehra, A.; Petrik, P.; Kurjak, D. Suffer or survive: Decoding salt-sensitivity of lemongrass and its implication on essential oil productivity. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 903954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Allington, G.R.H.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Zhang, R.; Luo, Y.; Xu, Z. Photosynthesis and growth of Pennisetum centrasiaticum (C4) is superios to Calamagrostis pseudophragmites (C3) during drought and recovery. Plants 2020, 9, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mircea, D.M.; Estrelles, E.; Hassan, M.A.; Soriano, P.; Sestras, R.E.; Boscaiu, M.; Sestras, A.F.; Vicente, O. Effect of water deficit on germination, growth and biochemical responses of four potentially invasive ornamental grass species. Plants 2023, 12, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, A.; Panuccio, M.R.; Eshel, A. Ecophysiology of Pennisetum clandestinum: A valuable salt tolerant grass. Envionmental Exp. Bot. 2013, 92, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.A.; Rasheed, M.; Hyder, S.I. Medicinal plant lemon grass (Cymbopogon citratus) growth under salinity and sodicity. Korean J. Food Health Converg. 2020, 6, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yoon, Y.H.; Ju, J.H. Desalinization effect of Pennisetum Alopecuroides and characteristics of leachate depending on Calcium Chloride (CaCl2) concentration. J. People Plants Environ. 2020, 4, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, B.; Yost, M.; Rivers, E.; Miller, R.; Taylor, K.; Evans, T. Irrigation Water Quality Sampling Guide; Utah State University Extension: Logan, UT, USA, 2023; Available online: https://extension.usu.edu/irrigation/research/irrigation-water-quality-sampling-guide (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- Xing, H.F.; Julie, H.; Asmita, P.; Sun, Y.P.; Chen, J.J.; Dai, X.; Matthew, C. Morphological and physiological responses of ornamental grass to saline water irrigation. HortScience 2021, 56, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.P.; Mickelbart, M.V.; Lopez, R.G. Leachate volume effects on pH and electrical conductivity measurements in containers obtained using the pour-through method. HortTechnology 2010, 20, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.P.; Niu, G.; Perez, C. Relative salt tolerance of seven of Texas Superstar perennials. HortScience 2015, 50, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalk, G.T.; Bi, G.; Stafne, E.T.; Li, T. Fertilizer type and irrigation frequency affect plant growth, yield, and gas exchange of containerized strawberry cultivars. Technol. Hortic. 2023, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavlak, R.G.; Horneck, D.A.; Miller, R.O.B. Soil, Plant and Water Reference Methods for the Western Region, 3rd ed.; Western Regional Extension Publication (WREP-125): San Jose, CA, USA, 2005; Available online: https://www.naptprogram.org/files/napt/western-states-method-manual-2005.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Liu, Q.; Sun, Y.P.; Niu, G.H.; Altland, J.; Chen, L.; Jiang, L. Morphological and physiological responses of ten ornamental taxa to saline water irrigation. HortScience 2017, 52, 1816–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carla, C.; Daniela, R.; Timothy, J.F. The response of ornamental plants to saline irrigation water. Irrig.-Water Manag. Pollut. Altern. Strateg. 2012, 131, 131–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.H.; Cabrera, R.I. Growth and physiological responses of landscape plants to saline water irrigation: A review. HortScience 2010, 45, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.H.; Rodriguez, D.S. Relative salt tolerance of five herbaceous perennials. HortScience 2006, 41, 1493–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, K.A.M.; Wu, L. Morphological and physiological response of five California native grass species to moderate salt spray: Implications for landscape irrigation with reclaimed water. J. Plant Nutr. 2005, 28, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Motos, J.R.; Ortuño, M.F.; Álvarez, S.; López-Climent, M.F.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; Sánchez-Blanco, M.J. Changes in growth, physiological parameters and the hormonal status of Myrtus communis L. plants irrigated with water with different chemical compositions. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 191, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triston, H.; Niu, G.H. Relative salt tolerance of four Herbaceous Perennial ornamentals. Horticulturae 2019, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, T.; Shen, G.; Esmaeili, N.; Zhang, H. Plants response to salinity stress. Plants 2023, 12, 2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, A.V.; Karadge, B.A.; Samant, J.S. Salt stress induced alteration in growth characteristics of a grass Pennisetum alopecuroides. J. Environ. Biol. 2011, 32, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, M.; Panda, S.K. Salt stress induced changes in growth and enzyme activities in germinating phaseolus mungo seeds. Biologia. Plant. 2001, 44, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Pandey, V. Antioxidant enzyme responses to NaCl stress in Cassia angustifolia. Biologia. Plant. 2004, 48, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapryanova, N.; Atanassova, B. Effects of salt stress on growth and flowering of ornamental annual species. Biotechnol. Biotechnological. Eq. 2009, 23 (Suppl. S1), 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S. Salt Tolerance of Landscape Plants Common to the Southwest; Texas Agrilife Research Center: El Paso, TX, USA, 2008; Volume 316, Available online: https://agrilife.org/elpaso/files/2011/10/TR-316-FINAL-TOLERANCE-REPORT_updated_.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- WateReuse Foundation. Salinity Management Guide. 2007. Available online: https://watereuse.org/salinity-management (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Henschke, M. Growth of ornamental grasses under salinity stress. J. Hortic. Res. 2016, 24, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paudel, A.; Sun, Y.P. Effect of salt stress on the growth, physiology, and mineral nutrients of two penstemon species. HortScience 2024, 59, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banon, S.; Miralles, J.; Ochoa, J.; Sanchez-Blanco, M.J. The effect of salinity and high boron on growth, photosynthetic activity and mineral contents of two ornamental shrubs. Hort. Sci. 2012, 39, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; McNeilly, T.; Bradshaw, A.D. The response of selected salt-tolerant and normal lines of four grass species to NaCl in sand culture. New Phytol. 1986, 104, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belligno, A.; Cutore, L.; Leo, M.D.; Sardo, V.; Brancato, R. Response of two grasses to irrigation with diluted seawater. Proc. IS Salination Hort. Prod. Hortic. 2022, 573, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belligno, A.; Loggia, F.L.; Sambuco, F.; Sardo, V.; Brancato, R. Salinity tolerance in Elytrigia (Agropyron elongatum). Acta Hortic. 2002, 573, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicek, N.; Cakirlar, H. The effect of salinity on some physiological parameters in two maize cultivars. Bulg. J. Plant Physiol 2002, 28, 66–74. Available online: http://www.bio21.bas.bg/ipp/gapbfiles/v-28/02_1-2_66-74.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Jaleel, C.A.; Beemarao, S.; Ramalingam, S.; Rajaram, P. Soil salinity alters growth, chlorophyll content and secondary metabolite accumulation in Catharanthus roseus. Turk. J. Biol 2008, 32, 79–83. Available online: https://journals.tubitak.gov.tr/biology/vol32/iss2/2 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Khosravinejad, F.; Heydari, R.; Faboodnia, T. Growth and inorganic solute accumulation of two barley varieties in salinity. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 12, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantawy, A.S.; Abdel-Mawgoud, A.M.R.; El-Nemr, M.A.; Chamoun, Y.G. Alleviation of salinity effects on tomato plants by application of amino acids and growth regulators. Eur. J. Sci. Res 2009, 30, 484–494. Available online: https://www.eurojournals.com/ejsr.htm (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Rodriguez, I.; Miller, G.L. Using a chlorophyll meter to determine the chlorophyll concentration, nitrogen concentration, and visual quality of St. Augustine grass. HortScience 2000, 35, 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammary, S.F.; Qian, Y.L.; Wallner, S.J. Growth response of four turfgrass species to salinity. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 66, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Bellot, M.J.; Ortuño, M.F.; Nortes, P.A.; Bernavé, A.; Fernández, F.; Sánchez-Blanco, M.J. Effectiveness of bacterial inoculation in alleviation of salinity on water status, mineral content, gas exchange and photosynthetic parameters of Viburnum tinus L. plants. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 237, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, H.; Athar, H.U.; Zafar, Z.U.; Kalaji, H.M.; Ashraf, M. Linking changes in chlorophyll a fluorescence with drought stress susceptibility in mung bean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek]. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 172, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.K.; Bhandari, S.R.; Lee, J.G. Monitoring of salinity, temperature, and drought stress in grafted watermelon seedlings using chlorophyll fluorescence. Front. Plant Sci 2021, 12, 786309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmer, T.D.; Muniz, R.; Flowers, T.J. Improving salt tolerance of wheat and barley: Future prospects. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2005, 45, 1425–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Amador, B.; Troyo-Diegues, E.; Garcia-Hernandez, J.L.; Lopez-Aguilar, R.; Avila-Serrano, N.Y.; Zamora-Salgado, S.; Rueda-Puente, E.O.; Kaya, C. Effect of NaCl salinity in the genotypic variation of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) during early vegetative growth. Sci. Hortic 2006, 108, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, Y.E. Effect of high light, water and salt stress on photosynthetic characteristics and antioxidant enzyme system in wheat. J Triticeae Crops 2018, 38, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, I. Magnesium as a Nutrient for Crops and Grass; Potash Development Association: York, UK, 2017; Available online: https://www.pda.org.uk/magnesium-nutrient-crops-grass/ (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Esechie, H.A.; Rodriguez, V. Does salinity inhibit alfalfa leaf growth by reducing tissue concentration of essential mineral nutrients? J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2001, 182, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candan, N.; Tarhan, L. Relationship among chlorophyll and carotenoid content, antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation levels by Mg2+ deficiency in the Mentha pulegium leaves. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2003, 41, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozlu, I.; Moore, A.G.; Guy, L.C. Effects of increasing NaCl concentration on stem elongation, dry mass production, and macro- and micro-nutrient accumulation in Poncirus trifoliata. Funct. Plant Biol. 2000, 27, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadley, M.; Brown, P.; Cakmak, I.; Rengel, Z.; Zhao, F. Function of nutrients: Micronutrients. In Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 3rd ed.; Elsevier/Academic Press: London, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 191–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Rasheed, R.; Rizwan, M.; Hussain, I.; Aslam, R.; Qureshi, F.F.; Hafiza, B.S.; Bashir, R.; Ali, S. Effect of exogenous taurine on pea (Pisum sativum L.) plants under salinity and iron deficiency stress. Env. Res 2023, 223, 115448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salar, F.; Kazem, G. Changes in soil properties and salt tolerance of safflower in response to biochar-based metal oxide nanocomposites of magnesium and manganese. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safesy 2021, 211, 111904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Gao, Y.; Luo, J.; Yan, S.H.; Wang, T.; Liu, L.Z.; Zhang, Z.H. Interactive effects of Tetracyclines and copper on plant growth and nutrient uptake by Eichhornia crassipes. CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2016, 44, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K.; Stone, L.F.; Santos, A.B. Molybdenum requirements of dry bean with and without limiting. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2015, 46, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).