Abstract
In the selection of new horticultural crops varieties, fruit shape and size are key agronomic traits targeted by breeders, as well as critical criteria for commercial evaluation and grading. Wild germplasm resources typically exhibit greater genetic diversity in fruit morphology compared to cultivated varieties. The study analyzed fruit shape-related traits of 216 Actinidia eriantha plants from a wild population in Jiangxi Province, China, and identified significant associated single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and candidate genes for the target traits using genome-wide association analysis (GWAS). The results revealed substantial phenotypic variation in fruit shape- and size-related traits. A total of 115 SNPs and 349 putative coding genes were significantly associated with 7 fruit shape-related traits. Within the candidate genomic regions, we identified several key genes linked to specific morphological features, including F-box and MADS4, previously reported to influence fruit shape; WOX, F-box, and OVATE, associated with fruit shape index; RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase, correlated with transverse diameter; and PLATZ, COL, and Aux/IAA, implicated in fruit weight regulation. These findings facilitate the precise identification of genes or quantitative trait loci (QTLs) governing fruit morphology. Furthermore, the associated SNP markers provide valuable tools for marker-assisted breeding, enabling the development of elite cultivars with desirable fruit characteristics.
1. Introduction
China possesses rich and extensive kiwifruit germplasm resources and is thus considered a natural kiwifruit genebank [1]. Out of the 75 taxa (54 species, 21 varieties) in the genus Actinidia, 73 are native to China. Through long-term evolutionary pressures and natural selection, Actinidia species have produced abundant phenotypic and genetic diversity both within and between species, enabling their adaptation and survival. During the domestication and process of breeding new varieties, different cultivated germplasm types with different fruit sizes and shapes have gradually arisen, including the following: from the fruit of Actinidia deliciosa, ‘Hayward’ is elliptic and ‘Monty’ is obovate; from Actinidia chinensis, ‘Hort 16A’ is ovate, ‘Kuimi’ is oblate, and ‘Jinyuan’ is oblate-round; from Actinidia eriantha, ‘Ganlv 1’ is cylindrical; and from Actinidia arguta, ‘Rubystar’ is cylindrical [2], with these fruit shapes exhibiting a rich diversity. Among the various Actinidia species, A. eriantha is a valuable wild species used in kiwifruit breeding programs and is uniquely distributed in various regions of China [3]. Its fruit has extremely high nutritional, medicinal, ornamental, and economic value. It produces a characteristic berry with great potential after A. chinensis and A. deliciosa [4]. Most A. eriantha resources grow in wild or semi-wild environments and differ in fruit size and shape.
Fruit size and shape are some of the most important criteria to be examined for the market quality evaluation, grading, and pricing of horticultural crops whose edible parts are fresh fruits, as they directly affect the economic value of the commodity [5]. Fruits that are esthetically pleasing, regular in shape, and of moderate size tend to be more acceptable in the marketplace. Fruit that is round or oval tends to be more acceptable to consumers, whereas fruit that is misshapen and too small may be perceived by consumers as being of poor quality. Fruit traded on the global market must follow specific criteria, including varietal uniqueness and consistency of the intrinsic quality, size, and shape; deviations from the standardized fruit shape and size are likely to result in lower classification levels [6]. Furthermore, fruit size and shape serve as critical selection criteria in breeding programs and are indispensable target traits for developing new cultivars tailored to market demands.
Researchers have investigated a number of regulatory mechanisms and have made a series of significant advances [7]. Fruit size and shape are complex traits controlled by multiple genes through different pathways [8]. In tomato, FAS and LC control fruit shape mainly by increasing the number of compartments, while SUN, OVATE, sov1, Fs8.1, and globe influence elongation by altering cell division patterns [9,10] and WOX affects fruit shape by controlling the meristem size and locule number [11]. In cucumber, Fs3.2 affected fruit morphogenesis (fruit diameter and length) by regulating ovary development [7,12], and Fs1.2 and Fs2.1 are two main effector quantitative trait loci (QTLs) encoding CsSUN and CsTRM5, respectively. The CsTRM5 mutant inhibits growth by increasing lateral cell division and decreasing longitudinal cell division, leading to a reduction in fruit length, while regulating ABA involved in mediating cell expansion during fruit elongation, leading to the production of spherical fruits [13,14]. Due to their well-characterized fruit shape regulation mechanisms, tomato and cucumber serve as excellent model systems for such studies, yet the genetic and developmental basis for fruit shape regulation in kiwifruit remains limited. Fruit shape-associated genes in kiwifruit have been explored in a few related studies, in which the WUSCHEL-LIKE homeobox gene (a potential regulator of fruit size) and cyclin-dependent kinase (possibly associated with fruit length and shape index) were identified in 140 hybrid offspring of the cultivar ‘White’ [15]. However, fruit size and shape are complex traits controlled by multiple genes through different pathways [8]; further research is needed to identify and characterize the specific genes involved.
With the increasing availability of sequenced genomes for horticultural plants, genome-wide association analysis (GWAS) has emerged as a powerful tool for investigating fruit shape and quality regulation [16,17,18], as well as abiotic and biotic stress resistance [19,20]. Within the genus Actinidia, GWAS approaches have successfully identified SNP loci and candidate genes associated with important agronomic traits such as the fruit size and vitamin C content of A. eriantha [15], the flowers and leaves of male plants [21], SNPs and haplotypes associated with indumentum traits in A. chinensis and A. deliciosa [22], the sex-determining region of A. arguta [23], and QTLs of growth traits in A. chinensis [24]. However, despite these advances, GWAS has rarely been employed to explore the genetic basis of fruit shape in wild Actinidia species, particularly A. eriantha. In this study, we collected fruits and leaves from 216 wild A. eriantha individuals at physiological maturity from a natural population in the Luoxiao Mountains (Ganzhou, Jiangxi Province, China). Building upon a previously established dataset for the comprehensive quality evaluation of this A. eriantha population [25], we incorporated fruit shape, carpophore length, and lateral diameter as additional traits. We constructed seven fruit shape-related trait datasets for the 216 wild A. eriantha accessions and performed GWAS using 1,790,395 high-quality and high-density SNPs (unpublished data from our laboratory) generated via whole-genome resequencing. This study primarily aims to identify SNP loci and candidate genes associated with fruit shape variation. The findings will not only expand the application of GWAS to understudied wild kiwifruit relatives but will also contribute to molecular marker-assisted breeding and germplasm innovation in kiwifruit.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Sample Collection
A wild natural population of A. eriantha was identified in the Luoxiao Mountains of Ganzhou City in Jiangxi Province, China (E 114°1′1.2″–114°03′92″, N 25°46′24.60″–25°48′86″, altitude 1092.98–1282.79 m). Here, 20–40 healthy and undamaged mature fruits and healthy and mature leaf replicates were harvested from each wild A. eriantha individual plant; a total of 216 individual plants of A. eriantha fruits and leaves were intensively harvested from wild populations in mid-October 2022 [25]. The distance between individual plants was at least 50 m [21]. The collected fruits and leaves were then transported to the laboratory for processing.
2.2. Determination of the Fruit Shape-Related Traits and Weight
Additionally, 8–10 uniform-sized and undamaged fruits were selected for the measurement of fruit shape-related traits. These 8–10 selected fruits were randomly divided into triplicates as 3 biological replicates. The fruit shape was assessing according to the National Standard of the People’s Republic of China ‘Guidelines for the conducting of tests for distinctness, uniformity, and stability in Actinidia (Actinidia L.)’ [2]. Carpophore length was measured using digital display vernier calipers (Delixi Electric Power Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China). Detailed methods for the longitudinal, transverse, and lateral diameter and fruit weight have previously been described [25].
2.3. DNA Extraction and Whole-Genome Resequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted and evaluated using previously described methods [21]. The DNA was randomly fragmented into 300–500 bp fragments using a Bioruptor (Diagenode SA, Seraing, Belgium). The sequencing library was constructed using the VAHTS Universal DNA Library Prep Kit for MGI (NDM607, Vazyme, Nanjing, China), following the manufacturer’s recommendations. Sequencing was performed on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform (Illumina, CA, USA) with a PE150 strategy. Whole-genome resequencing was conducted by Wuhan IGENEBOOK Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China) Alignment to the genome of A. eriantha cv. ‘Ganlv 1’ using the Burrows–Wheeler Aligner (BWA) v0.7.15-r1140 soft (Li, USA) with the MEM algorithm [21] was also carried out.
2.4. SNP Calling
Raw sequencing data were assessed for quality using FastQC [26]. Clean data were obtained through quality control and trimming with Fastp [27] and were subsequently mapped to the reference genome. SAM files were converted to the BAM format using Samtools [28]. Duplicates were marked, and SNP calling was performed using GATK (Boulder Institute, Cambridge, MA, USA) [29]. To ensure the accuracy of SNPs, the following parameters were used for filtering: (1) the ratio of the variance confidence to the depth of mass was not less than 2; (2) the p-value in the Fhred format obtained by using Fisher’s exact test to detect strand bias-this item was set to be no greater than 60; (3) RMS comparison quality value of no less than 40; (4) the ratio of the Z-score of the variance nonparametric test, rank sum test, and the quality value of the comparison reads of no less than –12.5; and (5) the ratio of the positional deviation of the Z-score of the variance nonparametric test, rank sum test, and the comparison reads of no less than –8.0. Finally, high-quality SNPs were filtered based on average filtering criteria and were used for downstream GWAS analyses.
2.5. Genome-Wide Association Studies
GWAS was conducted to identify associations between seven fruit shape-related traits and SNPs using GEMMA V0.98.1 (University of Chicago, Chicago, IN, USA). Association analysis was performed for each SNP, with significance thresholds determined through rigorous statistical validation. We established two hierarchical significance levels: 1) a primary threshold of −log10(p) > 6.27 (p < 5.37 × 10−7, 0.05 level of significance) and 2) a more stringent threshold of −log10(p) > 7.54 (p < 2.88 × 10−8, 0.01 level of significance) [15,30]. These thresholds were empirically validated through (1) permutation testing (10,000 iterations), confirming an empirical false discovery rate (FDR) <15%; and (2) Benjamini–Hochberg correction, ensuring q-values < 0.1 for all reported associations [16]. The corrected p values were visualized using Manhattan and Q-Q plots after applying −log10 transformation. For GWAS analyses, both general linear models (GLM and GLM-Q) and mixed linear models (MLM-Q and MLM-QK) were employed [15,16,17,21], with the results interpreted based on the Manhattan and Q-Q plots. SNPs with significant correlation (−log10(p) > 6.27) were identified as candidate loci for specific traits, and genes localized within 50 kb upstream and downstream of these loci were identified as candidate genes and genetically annotated through the KGD database (http://kiwifruitgenome.org/) and NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) [21]. The genetic pleiotropy test using R with PLACO (Pleiotropy Analysis under Composite Null) analysis followed the previous method [31].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Data were collated and analyzed using Microsoft Excel 2019 to calculate the maximum, minimum, median, mean, standard deviation, coefficient of variation, and Shannon–Wiener information index (H’). Correlation and cluster analyses were performed using OriginPro 2024b (OriginLab Inc., Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of Fruit Shape-Related Traits
The present study analyzed 7 fruit shape-related traits in a wild natural population of 216 A. eriantha plants, including fruit shape, fruit shape index, longitudinal diameter, transverse diameter, lateral diameter, carpophore length, and fruit weight (Supplement Table S1). Among the 216 test materials, there are 5 different fruit shapes: ovate, oval, obovate, cylindrical, and short-round (Figure 1). The number distribution of varieties with obovate shape was the largest at 152, follow by cylindrical at 33, oval at 15, short-round at 14, and ovate at 2, with the percentages 70.37%, 15.28%, 6.94%, 6.48%, and 0.93%, respectively. The CV values for the five fruit shape-related traits ranged from 13.47 to 20.72%, with an average of 16.09% (Table 1). The CV values for the fruit weight were 34.09%, significantly higher than other fruit shape traits, demonstrating abundant genetic variation for fruit weight in the wild population. Further analysis revealed that the genetic diversity index (H’) of these six traits ranged from 5.32 to 5.37 (average 5.36), indicating that the fruit appearance traits of the tested samples varied and had large genetic differences. Additionally, the frequency distribution chart for fruit shape (Figure 2A) and the box plots and scatter plots (Figure 2B) for the other six traits displayed near-normal distribution for the data on fruit appearance traits.

Figure 1.
Pictures of fruit shape of some germplasms. Different numbers in the upper right corner of each vignette represent different fruit shapes; specifically, 1 represents ovate, 2 represents oval, 3 represents obovate, 4 represents cylindrical, and 5 represents short-round.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of fruit shape-related traits of 216 wild A. eriantha plants.
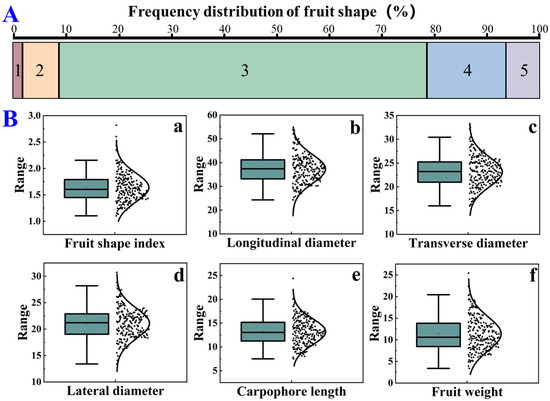
Figure 2.
Frequency distribution (A) or box plots and scatter plots (B) show normal distribution of the fruit shape-related traits in 216 wild A. eriantha plants. (A) Frequency distribution of fruit shape; 1 represents ovate; 2 represents oval; 3 represents obovate; 4 represents cylindrical; and 5 represents short-round. (B) Box plots and scatter plots for fruit shape index (a); longitudinal diameter (b); transverse diameter (c); lateral diameter (d); carpophore length (e); fruit weight (f).
Furthermore, the study found strong correlations among different fruit shape traits and weight (Figure S1). Carpophore length was significant (p < 0.01) and positively correlated with longitudinal, transverse, and lateral diameters; the fruit shape index was highly significant and positively correlated with the longitudinal diameter and highly significant and negatively correlated with the transverse and lateral diameters. The longitudinal, transverse, and lateral diameters and fruit weight were all highly significant and positively correlated with each other, with the fruit weight being more strongly positively correlated with the transverse diameter and lateral diameter; the cluster analysis based on the variables also clustered these three traits into one group. These observations indicated that these appearance traits were closely related to each other and significantly affected the formation of fruit shape.
3.2. Comparison of Different Model for GWAS
To assess the impact of different models on association results, we conducted GWAS using four common models. We compared the association performance of the models using Q-Q plots (Table 2 and Figure 3). The MLM-Q model failed to produce association results for certain traits (e.g., transverse diameter). In contrast, the GLM, GLM-Q, and MLM-QK models yielded satisfactory results across all traits. To identify the optimal model, we compared the number of significant SNPs associated with the GLM, GLM-Q, and MLM-QK models for the seven fruit shape-related traits (Table S2).

Table 2.
SNPs significantly associated with fruit shape-related traits on four correlation models.
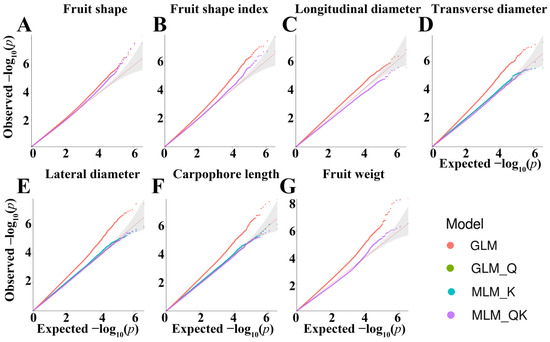
Figure 3.
Q-Q plots of fruit shape-related traits based on four association models for fruit shape (A), fruit shape index (B), longitudinal diameter (C), transverse diameter (D), lateral diameter (E), carpophore length (F), and fruit weight (G).
The GWAS of the seven fruit shape-related traits was conducted by whole-genome resequencing. The Q-Q plot shows that the observed p value is consistent with the expected p value at the front end and only rises at the end, indicating that the SNP false positives are minimal and the results are reliable. Because the Bonferroni significance threshold was too conservative, two slightly lower GWAS signal thresholds were chosen for this study (−log10(p) > 6.27 (0.05 level of significance) and −log10(p) > 7.54 (0.01 level of significance)). Based on the 0.05 significance level (–log10(p) > 6.27, same below), the GLM model identified 115 significant SNPs related to the 7 fruit shape traits, which were located on 25 chromosomes, and a total of 349 putative coding genes were including within the candidate intervals associated with these SNPs (Supplementary Table S2).
3.3. GWAS Results of Fruit Shape
Fruit shape-related quality is a key attribute affecting the preferences of consumers. In this study, seven SNPs significantly associated with fruit shape were detected, with one of them located on chromosome 2 (Chr02:3450573), one on chromosome 7 (Chr07:21565898), one on chromosome 22 (Chr22:10350542), three on chromosome 23 (Chr23:4850550, 4873454, 13176269), and one on chromosome 28 (Chr28:12003167) (Figure 4A,B). The closer the gene is to a significant SNP locus, the more likely it is to be a candidate gene for regulating the target trait. We identified 34 candidate genes for fruit shape. Based on the functional annotation of the genes with previous studies reporting on the regulation of fruit shape-related traits, we recognized some genes that are linked to fruit shape-related traits and fruit development and growth. Specifically, the F-box gene (Chr02g308) and agamous-like MADS-box protein MADS4 (Chr07g1216) were identified as the candidate genes for the fruit shape within the mapping interval 19.31 kb downstream of the associated SNP (Chr02:3450573) [32] and 41.45 kb upstream of the SNP (Chr07:21265898) [33], respectively.
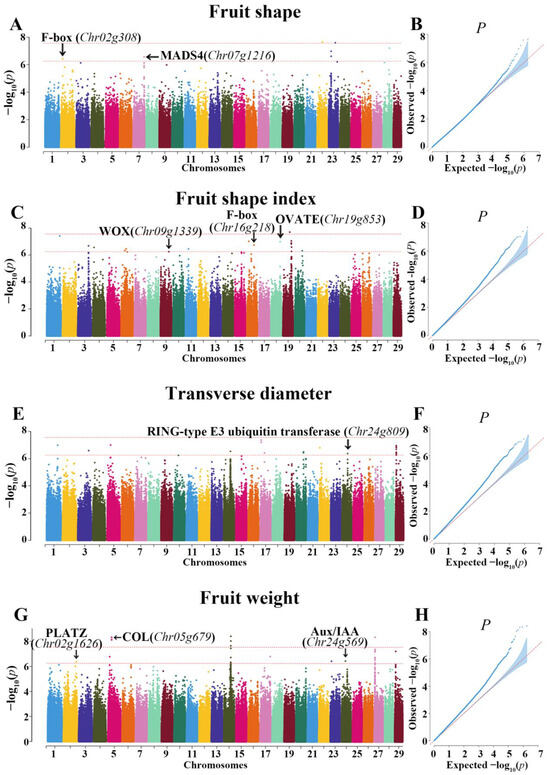
Figure 4.
Manhattan plot and Q-Q plots of genome-wide association studies (GWASs) for fruit shape (A,B), fruit shape index (C,D), transverse diameter (E,F), and fruit weight (G,H).
3.4. GWAS Results of Fruit Shape Index
Additionally, 17 SNPs were significantly associated with the fruit shape index, located on chromosomes 1, 3, 4, 6, 9, 11, 16, 18, 19, and 20. Furthermore, 79 potential coding genes were found within the candidate interval of significant SNP loci that may be associated with the fruit shape index (Figure 4C,D). Three genes were closely related to the fruit shape index, Chr09g1339 (Wuschel-related homeobox (WOX)), Chr16g218 (F-box), and Chr19g853 (transcription repressor OVATE), previously reported to have had significant effects on fruit shape, which were detected on mapping regions 10.66 kb downstream of the associated SNP (Chr09:16698572), 29.64 kb upstream of the SNP (Chr16:3516861), and 9.39 kb downstream of SNPs (Chr19:16547227, 16501891, 16547233, 17032973, 16889348), respectively [11,32,34].
3.5. GWAS Results of Transverse Diameter
Additionally, 20 SNPs were discovered to be significantly associated with transverse diameter and were located on chromosomes 1, 3, 5, 10, 17, 23, 24, 27, and 29. Mining the reference genome revealed 53 putative protein-coding genes within the candidate regions linked to these SNPs (Figure 4E,F). Among these, Chr24Gg809 (RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase), previously reported to be associated with transverse diameter, was found 20.32 kb upstream of the SNP (Chr24:10979785) [35].
3.6. GWAS Results of Fruit Weight
Furthermore, 27 SNPs were significantly associated with fruit weight, located on chromosomes 2, 5, 14, 17, 23, 24, 27, and 29, with 62 potential candidate genes for fruit weight (Figure 4G,H). Three genes were detected for fruit weight, Chr02g1626 (PLATZ transcription factor), Chr05g679 (zinc finger protein CONSTANS-like (COL)), and Chr24g569 (Aux/IAA), which were located on mapping regions 44.26 kb upstream of the associated SNP (Chr02:25148626), 12.73 kb upstream of the associated SNP (Chr05:6382004, 6382117), and 2.05 kb upstream of the associated SNP (Chr24:7296842), respectively. These three genes play roles in early cell proliferation [36] and the regulation of the cell cycle [37] and cell size [38], respectively.
3.7. GWAS Results of Longitudinal Diameter, Lateral Diameter, and Carpophore Length
Three SNPs significantly associated with longitudinal diameter were detected on chromosome 1 (Chr02:3829846), chromosome 20 (Chr20:5491429), and chromosome 27 (Chr27:12398146) (Figure 5A,B). In addition, 21 SNPs significantly associated with lateral diameter were observed on chromosomes 1, 2, 6, 9, 14, 17, 20, 23, and 29 (Figure 5C,D). Further, 20 SNPs significantly associated with carpophore length were detected on chromosomes 1, 4, 8, 13, 15, 16, and 20. Moreover, 121 coding genes were detected for the 3 traits, particularly, 18 genes for longitudinal diameter, 62 for lateral diameter, and 41 for carpophore length (Figure 5E,F).
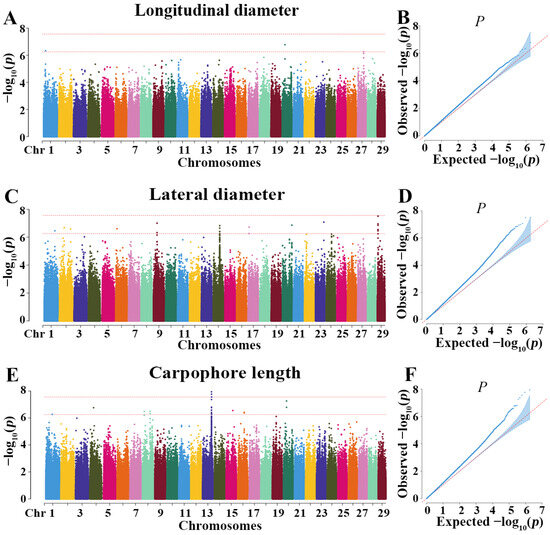
Figure 5.
Manhattan plot and Q-Q plots of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) for longitudinal diameter (A,B), lateral diameter (C,D), and carpophore length (E,F).
Furthermore, we found that the fruit shape trait was significantly associated with multiple SNP loci and that the same SNP locus was associated with multiple fruit shape traits. Chr29:1246434, Chr29:1249368, Chr29:1254797, Chr29:1254798, and Chr29:1256885 were significantly loci co-associated with transverse diameter and lateral diameter; Chr14:13455233, Chr14:13461487, and Chr14:13467221 were significantly loci co-associated with fruit weight and lateral diameter; Chr14:13464442 and Chr29:1252774 were significant co-association loci for fruit weight, transverse diameter, and lateral diameter; and Chr05:6382117 was a significant co-association locus for fruit weight and transverse diameter. The results showed that some of the same SNPs were associated with multiple fruit shape-related traits, indicating that these SNPs may be derived from a pleiotropy or a tight linkage of genes. The p-values of Chr29:1246434, Chr29:1249368, Chr29:1254797, Chr29:1254798, and Chr29:1256885, analyzed by PLACO, were much lower than the threshold of significance (p = 5 × 10−8), which indicated that the pleiotropic of these five SNPs existed in the traits of transverse diameter and lateral diameter. Similarly, Chr14:13455233, Chr14:13461487, and Chr14:13467221 were pleiotropic between single fruit weight and lateral diameter, and Chr05:6382117 was pleiotropic between fruit weight and transverse diameter.
In this study, the mining of candidate genes for fruit shape-related traits mainly included genes related to ubiquitin-protein ligase, transcription factor, pentatricopeptide repeat-containing protein, protein kinase, and isoform X1, indicating that fruit shape-related traits were co-regulated by the morphological regulation pathway of ubiquitin-proteasome, hormonal regulation, and the signaling pathway. Two F-box genes (Chr02g308 and Chr16g218), a transcription factor PLATZ (Chr02g1626), COL (Chr05g679), a MADS4 gene (Chr07g1216), a WOX gene (Chr09g1339), a transcription repressor OVATE (Chr19g853), an Aux/IAA gene (Chr24g569), and a RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase gene (Chr24g809) were identified as candidate genes for fruit shape-related traits.
4. Discussion
For most fruit trees, fruit shape represents the characteristics of a particular species or variety and is one of the most important markers of its appearance and quality, as well as the main target trait for its genetic improvement [6]. Changes in fruit shape are not only the result of natural selection during evolution but also of artificial selection for genetic improvement during domestication. Compared to in-depth studies on fruit shape in tomatoes [11,39,40], peaches [41,42], cucumbers [33], and peppers [34,37], there are still many unknown aspects of the formation and regulation of kiwifruit fruit shape that need to be explored and researched in depth.
Genetic diversity is an important component of biodiversity. It not only clarifies the genetic background of existing materials but also effectively guides the parent selection and hybrid combination selection of conventional breeding, thus significantly improving the efficiency of traditional breeding [24]. Fruit shapes of wild germplasm resources tend to be highly genetically diverse compared to those of cultivars and bred varieties [25]. Among the various Actinidia species, A. eriantha is a valuable wild species used in kiwifruit breeding programs uniquely distributed in various regions of China [3,4]. The Jiangxi Province is one of the areas in China with abundant wild A. eriantha germplasm resources [3,4]. The results of the study showed that the fruit shape-related traits of the tested 216 plants had abundant variation and significant phenotypic diversity, especially carpophore length and fruit weight, which revealed a rich genetic diversity, suggesting that we have constructed a gene pool that is rich in genetic variation. Such abundant phenotypic variation can provide a rich genetic basis for the improvement and breeding of germplasm resources and also implies that the selected germplasm material meets the requirements of GWAS analysis and the corresponding results are expected to be robust, which provides favorable prerequisites for the mining of associated SNP markers and key genes for fruit shape.
Most of the studied traits yielded significant associations based on the GWAS analysis of whole genome resequencing. Our results showed that A. eriantha had a relatively fast decay rate, meaning their short attenuation distance and low-density gene markers typically cannot cover most alleles [43]. We obtained 1.79 million high-quality SNPs using whole-genome resequencing technology, which is a significantly larger number than previous studies on A. deliciosa, A. chinensis, and male plants of A. eriantha [21,24,44]. The high-density and high-quality SNP markers developed in this study based on whole-genome resequencing are a powerful tool for mining excellent alleles, also greatly enriching research on SNPs in A. eriantha. Due to the conserved nature of Bonferroni significance, only a limited number of SNPs surpassed the significance threshold. To balance statistical rigor with biological relevance, we adopted the following slightly less conservative GWAS significance thresholds in this study: p < 5.37 × 10−7 (0.05 significant level) and p < 2.88 × 10−⁸ (0.01 significant level), as previously described [15,30]. Additionally, we applied the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure to control the false discovery rate, which enabled the identification of statistically robust SNP markers and highly correlated candidate genes associated with the target traits. This balanced approach, combining relaxed significance thresholds with false discovery rate correction, has been successfully employed in prior GWAS studies [15,16] and ensures a more comprehensive detection of potential genetic associations. In general, natural population resources are often used to perform GWAS because natural populations undergo multiple generations of recombination and they possess smaller interlocking blocks, which allows for the more precise localization of functional genes. First, the high density of high-quality SNP markers provided a useful precondition for GWAS analysis; second, the phenotypic variability of fruit shape and size among individuals of the test material was large, which was suitable for GWAS analysis; further, the observed values in the simultaneous Q-Q plots were generally consistent with the expected values, suggesting that the population stratification effect had been corrected by principal component analysis; and, lastly, the shape of the fruits was mainly influenced by genetic factors and the candidate genes anchored in this study were closely related to fruit shape and size in previous reports, so the present study has high confidence in the results of GWAS analysis.
Some important fruit shape genes, such as SUN, OVATE, and FAS, were isolated from the abundant fruit shape material of tomato [40], which provides reference and ideas for fruit shape research in other horticultural crops. Fruit shape formation is regulated by a number of factors, of which gene regulation is an important one [8]. In this study, a total of five candidate genes (two F-boxes, MADS4, WOX, and OVATE) highly associated with fruit shape were mined. F-box proteins, as a class of functionally important proteins in plants, are responsible for phosphorylation-mediated ubiquitination in the SCF complex. F-box proteins are involved in cell cycle regulation, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, and cellular signaling in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway because they specifically recognize substrate proteins [45]. The overexpression of SlEBF2-like, a novel F-box gene identified in tomato, resulted in significant fruit elongation [45], and further analyses revealed that this F-box gene is involved in fruit development and maturation by regulating the ethylene response in the fruit. Our findings suggest that the F-box gene may play a regulatory role in determining fruit shape in A. eriantha. Mechanistically, it could influence fruit morphology by targeting key cell cycle regulators for proteasomal degradation, thereby modulating cell division rates. Additionally, the F-box protein may indirectly shape fruit development through its involvement in phytohormone signaling pathways, such as auxin or gibberellin transduction. Agamous-like MADS-box protein gene PpMADS4 was expressed in petals, carpels, fruits, and kernels of peaches, belonging to the MADS box genes controlling the development of floral organs [46]; cucumber CsMADS26 was expressed mainly in reproductive organs including flowers and fruits. The heterologous expression of CsMADS26 in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana showed curly rosette and cauline leaves that were much smaller than those of the wild type [33]. It is implied that the MADS4 gene may indirectly affect fruit shape by regulating genes related to the development of floral organ or fruit. The MADS-box family genes are important transcriptional regulators in the development of reproductive organs, including dry and fresh fruits. In kiwifruit, the MADS4 gene may interact with other transcription factors to form a transcriptional regulatory network that synergistically and finely regulates the development of floral organs and fruits. The WOX gene is a plant-specific homologous heterotrimeric box transcription factor that plays a key role in the regulation of stem cell activity and organ development, affecting fruit shape by controlling the meristem size and locule number in tomato [11]. A mutant with a truncated CsWOX protein in cucumber produced “mango-shaped” fruits with significantly narrower leaves [12]. Fruit morphogenesis involves tightly regulated tissue differentiation processes. During early fruit development in A. eriantha, the WOX transcription factor likely maintains stem cell pluripotency within meristematic tissues, ensuring sustained cell proliferation to establish a cellular foundation for proper fruit growth. As development progresses, WOX may orchestrate cell fate determination by spatially modulating the expression of differentiation-related genes, thereby guiding tissue patterning and ultimately defining final fruit architecture. Notably, among these highly fruit shape-associated candidate genes, WOX positively regulates the expression of MADS4, which co-regulates the number of ovary compartments by inducing MADS expression, thereby affecting the formation of the final fruit shape [47]. Fruit shape is ultimately determined by cell growth and differentiation, and the MADS4 and WOX family of genes may separately or jointly regulate the expression of cell cycle-related genes, affecting the rate and number of cell divisions and ensuring that cells in various parts of the fruit grow and differentiate according to a specific pattern, thus shaping a specific fruit shape. OVATE is an active transcriptional repressor encoding a negative regulatory protein that inhibits cell elongation and regulates fruit shape [10]. In this study, we excavated a gene annotated as transcriptional repressor ovate, which might be related to the regulation of fruit shape in A. eriantha, thereby affecting the fruit shape index. OVATE (sov1), a quantitative trait locus on chromosome 10, controlling the obovate and elongated shape, and OVATE (sov2), a quantitative trait locus on chromosome 11, controlling elongated fruit shape in tomato [48], were both observed. The transcriptional activation of PpOFP1 through chromosomal inversion can inhibit the vertical extension of peach flattened fruits at the early stage of development, leading to the occurrence of flattened fruit shape [42]. The OVATE gene family in kiwifruit may have similar structural features and potential mechanisms by which mutations affect fruit shape.
Fruit size and weight are mainly determined by the number of pulp cells and cell volume, which are contributed to cell division and expansion [48]. Our results indicate that we have identified three genes (PLATZ, COL, and Aux/IAA) within the candidate interval that are most likely to be associated with fruit weight, and that they play a role in regulating fruit growth and development, cell cycle, and phytohormone signaling in previous studies [49,50]. PLATZ (plant AT-rich zinc-binding proteins) are plant-specific transcription factors that are regulated by ABA and are also involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, plant growth, and starch synthesis [51]. The PLATZ transcription factor TaFl3 and OsFl3 genes in wheat and rice interacted with TaPGS1 to positively regulate their expression in wheat and rice; the CRISPR/Cas9 knockdown of rice OsFl3 resulted in a significant decrease in the average thousand-grain weight, grain width, and length of the knockdown lines, as well as a loose and gappy endosperm structure. This is exactly the opposite to the phenotype of TaPGS1 overexpression lines, which further demonstrate that PGS1 affects seed growth and development and, consequently, grain yield by regulating Fl3 [49]. Starch is the main carbohydrate formed by plant photosynthesis to fix carbon, and it is also the main storage metabolite in the fruit; starch accounts for a relatively large proportion of the weight of the fruit. In maize, ZmPLATZ2 binds to the promoters of ZmSSI, ZmISA1, and ZmISA2 and increases their gene expression, promoting starch synthesis and affecting weight [52]. PLATZ transcription factors likely regulate kiwifruit growth-related gene expression through sequence-specific DNA binding. These proteins may directly activate genes involved in cell division, cell wall biosynthesis, and cellular expansion, thereby coordinating fruit cell proliferation and enlargement processes that ultimately determine the final fruit weight. The zinc finger protein family has important functions in plant growth and development, responses to adversity, and the regulation of the cell cycle [50]. Tomato plants with altered expressions of the zinc finger protein gene SlPZF1 produced smaller fruits, and it was demonstrated that it is a new cell size-regulating gene that interacts with several cell cycle regulators and is preferentially expressed in the pericarp of tomato fruits that are developing early; the overexpression of SlPZF1 delays the pericarp cell division phase and is thought to be involved in cell cycle regulation to affect fruit size [50]. In kiwifruit, the COL gene may orchestrate fruit weight determination by modulating the turnover of cell cycle regulators, analogous to their roles in tomato fruit development [50]. Aux/IAA is a regulator of growth hormone signaling at the transcriptional level, and in tomato and apple, there is a direct negative regulatory relationship with fruit weight. Fruits of the tomato SlIAA17 downregulated strain displayed greater diameter, volume, and weight than the wild type [53]; coincidentally, the silencing of MdAux/IAA2 in apple fruits resulted in an increase in apple fruit weight and cell size, and the overexpression of MdAux/IAA2 resulted in a reduction in apple fruit size, weight, and cell size, as well as a reduction in the incremental increase in apple pulp healing tissue and smaller spherical cells [54]. Aux/IAA regulates fruit size by altering the ploidy level of pericarp cells and may also affect cell division and cell expansion by regulating growth hormone signaling, which in turn affects fruit weight. The Aux/IAA family of genes, as growth hormone primary response genes, can affect fruit size by regulating cell elongation and division through the growth hormone signaling pathway in kiwifruit, which promotes vigorous cell division and thus affects fruit weight. RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase has been reported to have a significant regulatory effect on fruit transverse diameter; grain width was increased by 5.02% after silencing the expression of the RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase TaBB in wheat and decreased by 7.32% after overexpression [35]. Coincidentally, in maize, the expression of RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase ZmGW2 was significantly negatively correlated with grain width [55], indicating that RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase is a negative regulator of fruit transverse diameter. In kiwifruit, RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligases may orchestrate fruit weight determination by modulating the turnover of cell cycle regulators and hormone signaling components (e.g., Aux/IAA), analogous to their roles in tomato fruit development [53]. The potential role in kiwifruit may be to promote cell division in the ovary wall and influence initial fruit size by degrading negative cell cycle regulators.
Although the eight candidate genes associated with fruit shape and size identified in this study were functionally linked to known biological pathways, further investigation is needed to elucidate their roles. Specifically, the spatial and temporal expression patterns of these genes should be analyzed across different fruit morphologies and developmental stages. To functionally validate these candidates, genetic transformation techniques—such as overexpression constructs, gene-silencing vectors, or CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis—could be employed in kiwifruit. The phenotypic analysis of transgenic plants would reveal alterations in fruit morphology, followed by cytological examinations to assess changes in cell size, number, and organization so as to explain the mechanism of gene influence on fruit traits and size at the cellular level. Additionally, downstream target genes or upstream transcription factors interacting with the candidate genes could be identified to construct a comprehensive regulatory network governing kiwifruit fruit shape and size.
It is noteworthy that some SNPs were associated with multiple traits, and these interesting findings will provide a basis for subsequent multi-trait GWAS or pleiotropy tests. The next step is to combine more advanced sequencing technologies and functional genomics methods, such as CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing, to validate the specific mechanism of SNP pleiotropy and, at the same time, carry out studies on SNP pleiotropy in kiwifruit under different environmental conditions, so as to comprehensively analyze the interactions between the environment and SNP pleiotropy, which would be helpful to more accurately regulate the kiwifruit’s growth and trait performance and provide the basis for the sustainable development of the kiwifruit industry. This will help to more accurately regulate the growth and development of kiwifruit and provide a more solid theoretical foundation and technical support for the sustainable development of the kiwifruit industry. It is noteworthy that some SNPs were associated with multiple traits, and PLACO analysis confirmed the pleiotropy of these loci. In the process of evolution, the polyvalent loci cause correlations between different traits. In the future, we can verify the specific mechanism of SNP pleiotropy through gene editing technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9 while carrying out research on the polyvalency of kiwifruit SNP loci under different environmental conditions to comprehensively analyze the interaction between the environment and the pleiotropy of SNP loci, which would be helpful to regulate the growth, development, and trait performance of kiwifruit in a more accurate manner. This will help to more accurately regulate kiwifruit growth, development, and trait performance and to provide a more solid theoretical foundation and technical support for the sustainable development of the kiwifruit industry.
5. Conclusions
To identify significant SNP loci and candidate genes associated with fruit shape-related traits in kiwifruit (A. eriantha), we phenotyped 216 wild natural population plants for key morphological characteristics and performed genome-wide association studies (GWAS) based on whole-genome resequencing data. Our analysis revealed 115 SNP loci significantly associated and prioritized 8 high-confidence candidate genes with putative roles in regulating fruit shape and size. These findings enhance our understanding of the genetic basis of kiwifruit fruit morphology and provide valuable resources for future research, including the fine-mapping and functional validation of the identified loci. The SNP markers closely linked to fruit shape and size offer practical tools for molecular breeding programs aimed at developing kiwifruit varieties with desirable fruit characteristics.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae11050538/s1, Table S1. Phenotypic data of fruit shape-related traits in 216 wild A. eriantha plants. Table S2. Significantly associate SNP and candidate genes. Figure S1. Correlation heat map of fruit shape traits and weight.
Author Contributions
X.X., D.J. and J.M.: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition, and project administration; L.C.: methodology, investigation, formal analysis, and writing—original draft; Y.L. and H.G.: methodology, investigation, validation, and formal analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32160692, 32460742), Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation Youth Fund Project (20232BAB215040), and the Key Research and Development Plan from Jiangxi Science and Technology Department, China (20192ACB60002).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors. The data are not publicly available due to privacy restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SNP | single nucleotide polymorphisms |
| GWAS | genome-wide association analysis |
| CV | coefficient of variation |
| QTLs | quantitative trait loci |
References
- Huang, H.W.; Liu, Y.F. Natural hybridization, introgression breeding, and cultivar improvement in the genus Actinidia. Tree Genet. Genomes 2014, 10, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 19557.11-2022; Guidelines for the Conduct of Test for Distinctness, Uniformity and Stability-Actinidia (Actinidia L.). Chinese National Standard: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Liao, G.L.; Xu, X.B.; Huang, C.H.; Zhong, M.; Jia, D.F. Resource evaluation and novel germplasm mining of Actinidia eriantha. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 282, 110037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.B.; Liao, G.L.; Huang, C.H.; Zhong, M. Germplasm Resources of Actinidia eriantha; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rouphael, Y.; Kyriacou, M.C.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Pascale, S.D.; Colla, G. Improving vegetable quality in controlled environments. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 234, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Liu, F.Z.; Chen, Y.H.; Lian, Y. Research progress on inheritance of fruit shape in horticultural crops. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2011, 38, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.P.; Wang, Y.H.; McGregor, C.; Liu, S.; Luan, F.S.; Gao, M.L.; Weng, Y.Q. Genetic architecture of fruit size and shape variation in cucurbits: A comparative perspective. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunthawodtiporn, J.; Hill, T.; Stoffel, K.; Van, D.A. Quantitative trait loci controlling fruit size and other horticultural traits in bell pepper (Capsicum annuum). Plant Genome 2018, 11, 160125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, B.Y.; Keyhaninejad, N.; Rodríguez, G.R.; Kim, H.J.; Chakrabarti, M.; Illa-Berenguer, E.; Taitano, N.K.; Gonzalo, M.J.; Díaz, A.; et al. A common genetic mechanism underlies morphological diversity in fruits and other plant organs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Han, X.; Antonio, C.; Tea, M.; Esther, V.D.K. SUN regulates vegetative and reproductive organ shape by changing cell division patterns. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Knaap, E.; Chakrabarti, M.; Chu, Y.H.; Clevenger, J.P.; Illa-Berenguer, E.; Huang, Z.; Keyhaninejad, N.; Mu, Q.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. What lies beyond the eye: The molecular mechanisms regulating tomato fruit weight and shape. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 227. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.Z.; Fu, W.Y.; Wang, Y.Z.; Qin, X.D.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Lou, Q.F.; Chen, J.F. Rapid identification of fruit length loci in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) using next-generation sequencing (NGS)-based QTL analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.Q.; Colle, M.; Wang, Y.H.; Yang, L.; Rubinstein, M.; Sherman, A.; Ophir, R.; Grumet, R. QTL mapping in multiple populations and development stages reveals dynamic quantitative trait loci for fruit size in cucumbers of different market classes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.P.; Liang, X.J.; Gao, M.L.; Liu, H.Q.; Meng, H.W.; Weng, Y.Q.; Cheng, Z.H. Round fruit shape in WI7239 cucumber is controlled by two interacting quantitative trait loci with one putatively encoding a tomato SUN homolog. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.L.; Ren, W.M.; Chen, Q.Y.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhang, F.; Lin, Y.Z.; Yue, J.Y.; Liu, Y.S. Genome wide association analysis identifies candidate genes for fruit quality and yield in Actinidia eriantha. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Xue, C.; Hu, H.J.; Li, J.M.; Xue, Y.S.; Wang, R.Z.; Fan, J.; Zou, C.; Tao, S.T.; Qin, M.F.; et al. Genome-wide association studies provide insights into the genetic determination of fruit traits of pear. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.W.; Wu, S.Q.; Jia, Z.Q.; Zhang, J.H.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.Y.; Fan, B.L.; Wang, P.Q.; Gao, Y.N.; Ye, Z.B.; et al. Exploring the influence of a single-nucleotide mutation in EIN4 on tomato fruit firmness diversity through fruit pericarp microstructure. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2024, 22, 2379–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Xu, T.; Cai, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, T.; Gong, L.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Identifying candidate genes for grape (Vitis vinifera L.) fruit firmness through genome-wide association studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 8413–8425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidan, I.R.; Ferreira, M.F.; Pereira do Couto, D.; Santos, J.G.; Silva, M.A.; Canal, G.B.; Bernardes, C.; Azevedo, C.F.; Ferreira, A. Genome-wide association analysis of traits related to development, abiotic and biotic stress resistance in Coffea canephora. Sci. Hortic. 2025, 341, 114004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitt, L.; Bennett, J.S.; Collum, T.D.; Evans, B.; Raines, D.; Gutierrez, B.; Janisiewicz, W.J.; Jurick, W.M.; Gottschalk, C. Genome-wide associations within diverse wild apple germplasm for postharvest blue mold resistance to Penicillium expansum. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 225, 113513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.L.; Zhong, M.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Tao, J.J.; Jia, D.F.; Qu, X.Y.; Huang, C.H.; Liu, Q.; Xu, X.B. Genome-wide association studies provide insights into the genetic determination of flower and leaf traits of Actinidia eriantha. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 730890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Qu, D.; Sun, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Study on population structure of kiwifruit and GWAS for hairiness character. Gene 2022, 821, 146276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.M.; Yu, X.F.; Li, G.Q.; Qu, M.H.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Man, Y.P.; Jiang, X.H.; Li, M.Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome assembly of autotetraploid Actinidia arguta highlights adaptive evolution and enables dissection of important economic traits. Plant Commun. 2024, 5, 100856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.K.; Wang, R.; Lin, M.M.; Gu, H.; Li, Y.K.; Zhang, M.; Feng, X.; Qi, X.J. Construction of a high-density genetic map and QTL mapping of growth traits in kiwifruit. Sci. Hortic. 2025, 339, 113816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Y.S.; Gao, H.; Cao, J.L.; Qian, J.Q.; Zheng, K.X.; Jia, D.F.; Gao, Z.; Xu, X.B. A model for selecting kiwifruit (Actinidia eriantha) germplasm resources with excellent fruit quality. Foods 2024, 13, 4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartavya, V.; Caroline, G.; Simon, A.; Christel, K. Librarian: A quality control tool to analyse sequencing library compositions. F1000Res 2022, 11, 1122. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.F. Ultrafast one-pass FASTQ data preprocessing, quality control, and deduplication using fastp. Imeta 2023, 2, e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.D.; Huang, L.Y.; Xu, C.Y.; Qi, L.; Wu, Z.Y.; Li, J.; Chen, H.X.; Wu, Y.; Fu, T.; Zhu, H.; et al. Chromosome-scale genome assembly of areca palm (Areca catechu). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 2504–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warden, C.D.; Adamson, A.; Neuhausen, S.L.; Wu, X.W. Detailed comparison of two popular variant calling packages for exome and targeted exon studies. Peerj 2014, 2, e600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.W.; Levine, D.; Shen, J.; Gogarten, S.M.; Laurie, C.; Weir, B.S. A high-performance computing toolset for relatedness and principal component analysis of SNP data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3326–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, P.; Tan, H.; Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Quan, R.; Hu, Z.; Zeng, M.; Greenbaum, J.; Shen, H.; Deng, H.; et al. Dissecting the shared genetic architecture between anti-Müllerian hormone and age at menopause based on genome-wide association study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2024, 231, 634.e1–634.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cui, L.W.; Fang, J.G. Genome-wide association study of the candidate genes for grape berry shape-related traits. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ge, L.; Hu, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S. A cucumber AGAMOUS-LIKE 15 (AGL15) MADS-Box gene mediates abnormal leaf morphology in Arabidopsis. Agronomy 2018, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaballa, A.; Pasentsis, K.; Darzenta, N.; Tsaftaris, A. Multiple evidence for the role of an Ovate-like gene in determining fruit shape in pepper. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C. Analysis of the Mechanism of Wheat RING typeE3 Ubiquitin Ligase TaBB Regulating Grain Size. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.X.; Cheng, M.P.; Li, M.L.; Guo, X.J.; Wu, Y.R.; Wang, J.R. Identification and characterization of PLATZ transcription factors in wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovsky, Y.; Raz, A.; Doron-Faigenboim, A.; Zemach, H.; Karavani, E.; Paran, I. Pepper fruit elongation is controlled by capsicum annuum ovate family protein 20. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 815589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dujak, C.; Alcudia, V.C.; Aranzana, M.J. Genomic analysis of fruit size and shape traits in apple: Unveiling candidate genes through GWAS analysis. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhad270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, B.; Barrero, L.S.; Tanksley, S.D. Regulatory change in YABBY-like transcription factor led to evolution of extreme fruit size during tomato domestication. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, G.; Muños, S.; Anderson, C.; Sim, S.C.; Michel, A.; Causse, M.; Gardener, B.M.; Francis, D.; Knaap, E. Distribution of SUN, OVATE, LC, and FAS in the tomato germplasm and the relationship to fruit shape diversity. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.P.; Liu, X.; Gao, H.R.; Xiao, W.; Chen, X.D.; Fu, X.L.; Li, L.; Li, D.M.; Gao, D.S. Comparison between flat and round peaches, genomic evidences of heterozygosity events. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 592. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Ma, R.; Gao, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, X.; Ren, F.; Zhang, W.; Liao, L.; Yang, Q.; et al. A 1.7-Mb chromosomal inversion downstream of a PpOFP1 gene is responsible for flat fruit shape in peach. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 19, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, J.M.; Crossa, J.; Babu, R.; Campos, G.D.L. Factors affecting the accuracy of genotype imputation in populations from several maize breeding programs. Crop Sci. 2012, 52, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macnee, N.; Hilario, E.; Tahir, J.; Currie, A.; Warren, B.; Rebstock, R.; Hallett, I.C.; Chagné, D.; Schaffer, R.J.; Bulley, S.M. Peridermal fruit skin formation in Actinidia spp. (kiwifruit) is associated with genetic loci controlling russeting and cuticle formation. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.K.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, Y.; Wang, Y.Z.; Cheng, W.J.; Yang, Y.W. Overexpression of an EIN3-binding F-box protein2-like gene caused elongated fruit shape and delayed fruit development and ripening in tomato. Plant Sci. 2018, 272, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Xu, Y.; Chang, F.Q.; Li, X.D.; Ma, R.C. Cloning and characterization of two MADS box genes from peach (Prunus persica). J. Genet. Genom. 2004, 30, 908–918. [Google Scholar]
- Lenhard, M.; Bohnert, A.; Jürgens, G.; Laux, T. Termination of stem cell maintenance in Arabidopsis floral meristems by interactions between WUSCHEL and AGAMOUS. Cell 2001, 105, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, G.R.; Kim, H.J.; Knaap, V.D.E. Mapping of two suppressors of OVATE (sov) loci in tomato. Heredity 2013, 111, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.J.; Fu, Y.X.; Lee, Y.R.J.; Chern, M.; Li, M.L.; Cheng, M.; Dong, H.X.; Yuan, Z.W.; Gui, L.X.; Yin, J.J.; et al. The PGS1 basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) protein regulates Fl3 to impact seed growth and grain yield in cereals. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1311–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.F.; Zhang, J.J.; Weng, L.; Li, M.; Wang, Q.H.; Xiao, H. Fruit size control by a zinc finger protein regulating pericarp cell size in tomato. Mol. Hortic. 2021, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Rong, H.; Tian, Y.T.; Qu, Y.S.; Xu, M.; Xu, L. Genome-wide Identification of PLATZ transcription factors in ginkgo biloba L. and their expression characteristics during seed development. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 946194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Xiao, Q.L.; Luo, L.; Zhang, C.X.; Mao, C.Q.; Du, J.; Long, T.D.; Cao, Y.; Yi, Q.; et al. Transcription factor ZmPLATZ2 positively regulate the starch synthesis in maize. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 93, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.Y.; Audran, C.; Bouzayen, M.; Roustan, J.P.; Chervin, C. The Aux/IAA, Sl-IAA17 regulates quality parameters over tomato fruit development. Plant Signal. Behav. 2015, 10, e1071001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, H.D.; Sun, X.H.; Yue, P.T.; Qiao, J.L.; Sun, J.M.; Wang, A.D.; Yuan, H.; Yu, W.Q. The MdAux/IAA2 transcription repressor regulates cell and fruit size in apple fruit. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.F.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, Y.Y.; Jing, J.Z.; Wang, L.F.; Li, J.J.; Wang, H.; Li, H.Y. Expression pattern assay of ZmGW2,a RING-domain E3 ubiquitin ligase gene in maize. J. Maize Sci. 2013, 21, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).