Abstract
During infancy and early childhood, obtaining the adequate amount of appropriate nutrition has paramount importance for the full development of a child’s potential. The focus of this study was to evaluate the complementary food produced by solid-state fermentation of fonio and soybean using Rhizopusoligosporus (2710) and orange-fleshed sweet potatoes (OFSP) using Lactobacillus planterum (B-41621). Solid-state fermentation (SSF) was carried out by inoculating fonio and soybean with a spore suspension (1 × 10⁶ spores/mL) of Rhizopusoligosporus (2710) and OFSP with a spore suspension (1 × 10⁶ spores/mL) of Lactobacillus plantarium (B-41621). The samples were blended in the following ratios: fonio and soybean 100: 100 (AS), fonio/soybean and OFSP 50: 50(ASO). These were compared with a commercial infant formula, which served as the control (CTRL). Quality characteristics of the samples were evaluated. The results showed that moisture, crude protein, fiber, ash content, beta carotene, iron and titratable acidity ranged from 54.97–56.27, 17.10–19.02%, 7.08–7.60%, 2.09–2.38%, 15.80–17.35 mg/100 g, 6.57–8.41 mg/100 g and 0.16–0.48%, respectively. An increase in fermentation time significantly (p < 0.05) increased these contents. In sensory scores, there were no significant (p > 0.05) differences between the average mean scores of the samples. This study shows that nutrient-rich complementary food of acceptable quality can be produced from blends using SSF for the optimum growth and development of infants.
1. Introduction
Childhood malnutrition is one of the primary persistent community health challenges of all developing countries, as well as in Nigeria. Geographic and wellness survey data from twenty-one developing countries suggested that impoverished complementary feeding of infants aged 6–23 months adds to unfavorable growth trends [1]. In sub-Saharan African countries, poor infant eating habits as well as impoverished nutritional attributes of complementary foods and micronutrient deficiencies coexisting with persistent infections adds to high mortality rates among infants and young children [2]. Malnutrition, for example, has been accountable, directly or indirectly, for 10.9 million (60%) of the global yearly under-five infant deaths [3]. African countries have recorded a period of 10 years (1990–2010) of increased numbers of stunted children below five years. According to UNICEF, Nigeria loses 15% of its GDP annually to malnutrition. Oftentimes, malnourishment starts from the mother’s womb. Pregnant women are expected to consume healthy diets, and after delivery, the baby is expected to be placed exclusively on a breastfeeding diet and to be fed nutritious meals afterwards. It is strongly evident that the promotion of appropriate complementary feeding practices reduces the rates of stunting and contributes to better health and growth outcomes in children [4]. For this reason, the WHO and UNICEF recommend the introduction of adequate complementary foods at the sixth (6) month and improving the quantity and quality of foods that children consume while maintaining breastfeeding [5]. Therefore, to decrease the issue of malnutrition amid children in the public, the development of complementary foods that are ample in essential nutrients for the maximum growth and development of infants is crucial. Complementary food has been defined as any healthful and energy-containing solid, semisolid or liquid meal consumed by infants aside from human milk or formula [6]. Complementary foods are essentially introduced from the period of 4–6 months when breast milk, considered the best choice and the safest meal for young babies, can no longer provide the nutrients and energy requirements needed to enable the child to grow and thrive. Adequate nutrition is needed during infancy and early childhood so as to ensure that a child grows optimally and does not have any nutritional deficiencies, as infancy is the most rapid period of growth in human life, as well an important period for cognitive, behavioral and physical development. Inappropriate complementary feeding practices remain one of the most determinant factors that make children susceptible to irreversible outcomes of stunting, poor cognitive development and increased risk of infectious diseases [7]. Given the comparatively insignificant amounts of complementary foods that are ingested at 6–24 months, the nutrient bulkiness of complementary foods needs to be very high to satisfy these needs. One of the important ways of improving the nutritional status of a food is primarily through fortification. Conventional complementary foods are usually fortified to meet the required recommendations and, as such, are usually expensive and are not affordable for half of the world’s population [8]. In many developing countries, and Nigeria in particular, traditional complementary foods have predominantly been produced from cereals or starchy roots and have been reported to be inadequate when compared to estimated needs [9]. Cereal-based gruels are generally low in protein and are limited in some essential amino acids, particularly lysine and tryptophan; likewise, they have low vitamin A quantities, especially in the form of provitamin (B-carotene). Since they are usually prepared as thin gruels, their energy and nutrient content and density are also low. Relative to lysine and sulfur amino acid contents, legume and cereal proteins are nutritionally complementary [10]. Legume seeds have received much attention for their utilization in a variety of food systems due to their availability and high protein content. They provide a relatively affordable source of protein in developing countries. Despite their affordability, legumes are known to cause indigestibility, flatulence and diarrhea [11]. They contain antinutrients, especially phytates, which chelate micronutrients and prevent them from being bioavailable for infants. Due to these constraints, they do not provide the micronutrients needed for good health, thus making micronutrient deficiency a major public health problem in developing countries caused by a lack of essential vitamins and minerals such as vitamin A, iron, zinc, etc. in the diet. Therefore, most infants still suffer from malnutrition because of the inability to utilize the available raw materials to meet their daily requirements. Egounlety et al. [12] evaluated the potential of using solid-state fermentation to improve the nutritional value of cereal and legumes. Solid-state fermentation leads to an increase in soluble proteins and carbohydrates and decreases anti-nutritional factors such as phytic acid, flatulence-producing factors, tannin and protease inhibitors [13]. It can also impart functional and sensorial qualities to the legumes. Acha (Digitariaexilis) is a cereal with very tiny seeds that poses difficulty in processing but is absolutely rich in amino acids [14] and needs to be supplemented with a legume for a higher nutrient-dense product. Soybean (Glycine max L.) is an annual herbaceous legume plant of the pea family Leguminosae and subfamily Papilionnidea [15]. It assumes an important position as a world crop because of its high-quality protein content and rich oil [16]. Soy protein contains all the essential amino acids, most of which are present in amounts that closely match those required for humans or animals, and it is therefore suitable for making high-protein food for children. Orange-fleshed sweet potato (OFSP) is a special type of bio-fortified sweet potato that contains high levels of beta-carotene and is considered valuable due to its high concentration of vitamins and minerals. Ideally, the ingredients for low-cost complementary foods should be derived from dietary staples that are available and affordable in the region of interest [17]. The regularly used substrates for solid-state fermentation are cereal grains, legume seeds, tubers, etc. Orange-fleshed sweet potatoes are used due to their high concentration of vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin A, which is a critical vitamin that has been deficient in most diets in sub-Saharan Africa, thereby leading to vitamin A deficiency in preschool children in Africa and resulting in blindness. Acha/fonio (Hungary rice) and soybean are affordable and available and contain nutrients that are needed by children for optimum growth. The microorganism of choice is used, because they are microorganisms used for solid-state fermentation. Microorganisms that are notably used in solid-state fermentation are mostly filamentous fungi of the genera Aspergillus, Fusarium, Rhizopus and Trichoderma. Bacteria, particularly Lactobacillus spp. such as L. planetarium and L. acidophilus, are used equally. Thus, this work is aimed at investigating the use of solid-state fermentation to improve the nutritional quality of fonio (acha), soybean and orange-fleshed sweet potatoes using Rhizopus oligosporus and Lactobacillus planetarium, thereby enhancing their suitability for use as complementary foods.
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Procurement of Raw Materials
One kilogram each of fonio/acha (Digitariaexilis) and soybean was obtained from Ogige market, Nsukka in Enugu state, Nigeria and identified in the Department of Plant Science and Biotechnology, University of Nigeria, Nsukka. One kilogram of orange-fleshed sweet potatoes was procured from a research institute in Yenogoa, Bayelsa state, Nigeria, bacterial culture: Rhizopus oligosporus (2710), and Lactobacillus plantarum (B-41621) was obtained from the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), Agricultural Research Service, ARS Culture Collection Center, USA.
2.2. Culture Preparation
The organisms Lactobacillus plantarum (B-41621) and Rhizopus oligosporus (2710) as shown in Figure 1, that were obtained from the USDA were preserved in a dormant state inside tubes. A file scratch was made in the center of the tube and wiped with 70% alcohol. The tube was opened using a paper towel to cushion hands. The organisms were resuscitated by culturing in potato dextrose broth for Rhizopus oligosporus, and suitable broth mediums were used for Lactobacillus plantarum. They were allowed to dissolve for several minutes. The microorganisms inside the medium were homogenized with a finger vortex before using the suspension as inoculum as directed by the USDA for the resuscitation of microorganisms and according to the method described by Petrikkou et al. [18].

Figure 1.
Microbial culture from USDA (Rhizopus oligosporus and Lactobacillus plantarum).
2.3. Preparation of Raw Materials
One kilogram (1 kg) of washed orange-fleshed sweet potatoes (Figure 2) (sliced into 2–3 mm thick flat surfaces) and fonio (acha) (Figure 3) and cleaned seeds of soybean (Figure 4) were soaked separately, each in four (4) volumes of 0.9M acetic acid (pH 3.1) for 16 h at 30 °C. The seeds were drained after 16 h and rinsed with clean water. The seed coat of the soybean was removed manually, and the dehulled seeds were washed with clean water. The raw materials were packed into perforated polythene bags and steam cooked for 7 min at 121 °C. Thereafter, they were allowed to cool to 30 °C. Solid-state fermentation (SSF) was achieved by inoculating fonio and soybean with a spore suspension (1 × 10⁶ spores/mL) of Rhizopus oligosporus (2710) and inoculating OFSP with a spore suspension (1 × 10⁶ spores/mL) of Lactobacillus planterum (B-41621) [19]. Fermentation was carried out for 72 h at a temperature of 30 °C, after which samples were dried in a forced draught oven at 50 °C for 24 h, cooled at room temperature (30 °C) and milled with a hammer millto pass through a 0.2 mm screen. The samples were blended in the following ratios: fonio and soybean 100:100 (AS), fonio/soybean (a blend of fonio and soybean: 25% fonio and 25% soybean to obtain 50%) and OFSP 50:50(ASO), and these were analyzed for adequacy as complementary foods and made into gruel [19] for sensory evaluation.

Figure 2.
Orange-fleshed sweet potato.

Figure 3.
Acha/fonio (Hungary rice).

Figure 4.
Soybean seed.
2.4. Proximate Composition
Moisture content, crude fiber, ash, protein and fat were determined using the AOAC [20] method, and carbohydrate content was determined by difference.
2.5. Determination of Iron Using Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (AAS)
2.5.1. Sample Preparation
Iron was determined using AAS as described by AOAC [20]. One gram (1 g) of the sample was first digested with 30 mL of aqua regia, which is a mixture of concentrated HNO3 and HCL, in a ratio of 1:3. The digested sample was filtered and increased up to 50 mL with deionized water. The aliquots of the digested filtrate were used for AAS using filters that match the different elements.
2.5.2. Determination of Zinc
Zinc content of the sample was determined according to AOAC [20]. An amount of 5 mL of the filtrate was pipetted into duplicate tubes, to which 4.6 mL of actetateacetic acid buffer solution was added, followed by gentle shaking for 10 min. Dithizone (0.4 mL) was added, and the pH was adjusted to 4.5 with 20% NaOH before the absorbance was taken at 520 nm in a spectrophotometer.
2.5.3. Determination of Calcium
The calcium content was determined according to the method of AOAC [20]. An amount of 1 mL of the filtrate was pipetted into duplicate tubes, then 3 mL calcium working reagent consisting of dye solution salt (0.18 g), methythymol blue, 6.0 g polyvinyl pyrolidone, 7.2 g hydroxyquinoline, 10 mL concentrated hydrochloric acid and 1 L of distilled water were added and shaken for 10 min, and the absorbance was taken at 612 nm against a blank using a spectrophotometer.
2.5.4. Determination of Beta-Carotene
Beta-carotene was determined using the method described by AOAC [20]. One gram (1 g) of each of the samples was extracted by mixing with 20 mL of petroleum ether. The extract was evaporated to dryness and the residue dissolved with 0.2 mL chloroform-acetic anhydride mixture. Two milliliters of trichloro-acetic acid (TCA) were also added to the extract and mixed thoroughly, and the absorbance was read at 620 nm within 15 s. With the absorbance value, beta-carotene was calculated as follows:
where Abs = absorbance;
- Df
- = dilution factor;
- E
- = extinction coefficient.
2.5.5. Determination of Vitamin C
Vitamin C content was determined according to the method of Olokodona [21]. Five grams of the sample were weighed into a 100 mL volumetric flask, 2 mL of 20% meta-phosphoric acid was added as a stabilizing agent, and the solution was diluted to volume with distilled water. Ten (10) milliliters of the solution were pipetted into a small flask, and two-and-a-half milliliters of acetone were added. The solution was titrated with indophenols solution until a faint pink color persisted for 15 s. The vitamin C content was calculated as mg/100 mL.
2.5.6. Determination of Vitamin B1
Thiamine was determined using the AOAC [20] method. Seventy-five milliliters (75 mL) of 0.2 N HCl were added to 2 g of sample, and the mixture was boiled over a water bath (Stuart; RE300B, UK). After cooling, 5 mL of phosphatase enzyme solution was then added, and the mixture was incubated at 37 °C overnight. The solution was placed in a 100 mL volumetric flask, and the volume was made up with distilled H2O. The solution was filtered and the filtrate purified by passing through a silicate column. A total of 25 mL of the filtrate was put in a conical flask, and 5 mL of acidic KCl exudate, 3 mL of alkaline ferricyanide solution and 15 mL isobutanol were added and shaken for 2 min. The solution was then allowed to separate, and the alcohol layer was taken. About 3 g of anhydrous sodium sulphate was added to the alcohol layer. Five milliliters of thiamine solution were accurately measured into another fifty milliliter stoppered flask. Oxidation and extraction of thiochrome as already carried out with the sample was repeated using thiamine solution. Three milliliters of 15% NaOH were added to the blank instead of alkaline ferricyanide. The blank sample solution was poured into a fluorescence reading tube, and a reading was taken. Thiamine was calculated as follows:
where W = weight of the sample; X = reading of the sample—reading of the blank; Y = reading of the thiamine standard—reading of the blank standard; V = volume of the solution used for the test on the column.
2.6. Functional Properties Analysis
2.6.1. Measurement of pH
Each flour sample (10 g) was suspended in 100 mL of boiling distilled water. After cooling, the slurry was shaken (1500 rpm, 25 °C, 20 min) using an orbital shaker. The pH values of the flour samples were recorded using a pH meter (Hanna meter model H196107).
2.6.2. Determination of Titratable Acidity
Titratable acidity was determined by dissolving 10 g of the sample in 100 mL of distilled water and titrating 10 mL aliquots with 0.1 N NaOH to the phenolphthalein end point.
2.6.3. Determination of Viscosity
The viscosity was determined using a torsion viscometer (Gallenkamp, England), as described by the method of Sathe and Salunkhe [22]. Ten percent (10%) (w/v) of each of the flour blends was heated for 10 min at 100 °C to form a gruel; each gruel was cooled to 28 °C before a viscosity measurement was taken from the viscometer.
2.7. Determination of Water Activity (Aw)
The water activity of the samples was determined using a standard water activity meter according to AOAC [20]. About 2 g of the sample was placed in stainless steel bowl of the water activity-measuring instrument, such that it took three-quarters of the volume of the container, and was covered tightly and allowed to stand for three hours before taking the reading. Before taking the water activity value, the measuring instrument was standardized. The value of the standard was used to calculate the water activity.
2.8. Determination of Water Absorption Capacities (WAC)
WAC was determined using the method of Lin et al. [23]. One gram (1 g) of the sample was dispensed into a weighed centrifuge tube with 10 mL of distilled water and mixed thoroughly. The mixture was allowed to stand for 1 h before being centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 30 min. The excess water (unabsorbed) was decanted, and the tube was inverted over an adsorbent paper to drain dry. The weight of water absorbed was determined by difference. The water absorption capacity was calculated as:
2.9. Determination of Swelling Capacity
The centrifuge tube was weighed alone. Five grams (5 g) of the sample were weighed into the centrifuge tube and mixed with 30 mL of distilled water, heated at 120 °C for 15 min and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min, and the supernatant was decanted. The tube was dried and weighed, and the swelling capacity was calculated as:
where
- W1
- = the weight of the centrifuge tube;
- W2
- = the weight of the centrifuge plus the sample.
2.10. Microbial Analysis
2.10.1. Total Viable Count
The pour plate method as described by Harrigan et al. [24] was used. One gram of the sample was macerated into 9 mL of Ringers solution and mixed thoroughly by shaking. Then, 0.1 mL dilution was transferred from each dilution bottle into the corresponding plate, and 15 mL of sterile nutrient agar medium was poured and mixed thoroughly with the inoculum by rocking the plates. The plates were incubated at 38 °C for 24 h, after which the colonies that formed were counted and expressed as colony-forming units per gram (cfu/g).
2.10.2. Mold Count
The pour plate method as described by Harrigan et al. [24] was used. The sample dilution weighing 0.1 mL was transferred from each dilution into corresponding plates, and 15 mL of sterile Sabourand dextrose agar (SDA) medium was poured and mixed thoroughly with the inoculum by rocking the plates. The plates were incubated at ambient temperature for three days, after which the colonies that formed were counted and expressed as colony-forming units per gram (cfu/mL).
2.11. Determination of Selected Anti-Nutrient Content of Samples
2.11.1. Determination of Tannin Content
The tannin content of the samples was determined by the method described by Pearson [25]. One gram (1 g) of the sample was dispersed in 10 mL of distilled water, allowed to stand and shaken at 5 min intervals for 30 min before being filtered using a Whatman no. 42 grade of filter paper. Then, 2.5 mL of the extract was transferred into a test tube. Similarly, 2.5 mL of standard tannic acid solution was transferred into a 50 mL flask to serve as a blank standard. Then, 1.0 mL of Folin–Denis reagent was added into the flask, followed by 2.5 mL of saturated Na2CO3 solution and made up the solution to the mark. The respective absorbance was measured after 90 min incubation at room temperature.
where
- An
- = absorbance of the test sample;
- As
- = absorbance of the standard solution;
- C
- = concentration of the standard solution;
- W
- = weight of the sample used;
- Vf
- = total volume of the extract;
- Va
- = volume of the extract analyzed.
2.11.2. Determination of Phytate Content
Phytate content was determined using the spectrophotometric method described by Kirk and Sawyer [26]. Two grams (2 g) of the sample were weighed into a five-hundred-milliliter (500 mL) flat-bottom flask. The flask with the sample was laced in a shaker and extracted with one hundred milliliters (100 mL) of 24% HCL for one hour at 25 °C. The aliquot was decanted and filtered. Five milliliters (5 mL) of 0.1 M sodium chloride were added to ten milliliters (10 mL) of the diluted sample and passed through a Whatman no. 1 filter paper to elute in organic phosphorus, and fifteen milliliters (15 mL) of 0.7 sodium chloride were also added to elute the phytate, which was mixed on a vortex mixer for 5 s. The mixture was centrifuged for 10 min, and the supernatant was read at a 520 nm wavelength in a UV spectrophotometer. The phytate concentration was read off from the standard curve prepared with standard inositol phytate, and the value was expressed in mg/100 g using the following formula:
2.12. Sensory Evaluation
The complementary food samples were made into gruel and evaluated for color, taste, texture, mouthfeel, aftertaste and overall acceptability on a 9-point hedonic scale, where 1 = dislike extremely, 5 = neither like nor dislike and 9 = like extremely, as described by Ihekoronye and Ngoddy [27]. The evaluation was performed by 20 semi-trained man panelists selected randomly from among nursing mothers and students of Ziks Flat University of Nigeria, Nsukka.
2.13. Statistical Analysis
Data analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and least significance difference (LSD) at p < 0.05 to test the differences among the nutritional value of the blends. The design of the experiment for blends was achieved using completely randomized design (CRD). Mean separation was calculated using Duncan’s new multiple range test using SPSS version 23.0 computer software [28]. The experiments were performed in duplicate.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Fermentation (SSF) Time on the Proximate Composition (%) of the Fermenting Raw Material
Table 1 shows the effect of fermentation (SSF) time on the proximate composition of the fermenting raw materials.

Table 1.
Effect of fermentation (SSF) time on the proximate and physical composition (%) of the fermenting raw materials (wet basis).
The moisture content of the fermenting raw materials ranged from 54.97–56.27%, with sample AS0 having the least moisture content and AS72 the highest value. From the result, it can be deduced that as fermentation progressed, there was an increase in moisture content. The increase in moisture content is consistent with the findings of [29], the authors of which observed that fermentation increased the moisture content of pigeon pea flour. This could be credited to the catabolic breakdown of substrates due to fermentation, which releases water [29]. There were significant (p < 0.05) differences among the samples.
The protein content of the fermenting raw materials ranged from 17.10–19.02%, with sample AS0 having the lowest protein value and sample AS72 having the highest protein content. There was a gradual increase in the protein content as the fermentation time increased. There was a significant (p < 0.05) difference among the protein content of the samples at different fermentation times. The observed increase in the protein content of the samples is similar to that observed by [30]. The author reported that solid-state fermentation (SSF) increased the protein content of common bean flour to 21.7%.
The fat content of the fermenting raw materials ranged from 5.81–4.52%, with sample AS0 having the highest value and AS72 having the lowest value. The fat content of the fermented samples decreased with increasing fermentation time (Table 1). Ruiz-Teran and Owen [31] reported that during SSF of soybean, a considerable depletion in crude lipids took place during the initial stages of fermentation. They attributed this reduction to the oxidation and utilization of fatty acids by the fungus as a source of energy. Fatty acids present in glycerides have been reported to decrease during fermentation of soybean from 30% natural lipids by the action of lipases activity [32]. Rubina et al. [33] reported a reduction in the fat content of barley during SSF by R. oligosporus from 2.13–1.62%.
The ash content of the blends ranged from 2.09–2.38%, with sample AS0 having the least ash content and AS72 having the highest value. The ash content is the index of the mineral content of food samples, which is vital for infant growth and development. There was a significant (p < 0.05) difference between the samples. The ash content increased as the fermentation time increased. This observation is in agreement with that of [34], the authors of which observed an increase in the ash content of fermented maize-cowpea blends. The increase in the ash content could be attributed to the reduction in carbohydrate and fat content of the sample, thereby increasing other dry matter [35]. Fermentation improves the nutrient composition of food. The increase in ash content as fermentation progressed could be an indication that the minerals present in the samples were released from the chelated complex compound through the activities of microorganisms, since ash content is an index of the mineral content of food [36].
The carbohydrate content of the fermenting raw materials ranged from 12.95–10.21%, with AS0 having the highest value and AS72 having the lowest value. The carbohydrate content of the samples decreased with increased fermentation time. A decrease in carbohydrate levels during fermentation could be due to the incomplete removal of non-starch components in the course of the solid-state fermentation process. It has also been reported that during the fermentation process of cereals, proteases, lipases, phytases and a variety of carbohydrases are created, resulting in the breaking down of macromolecules into lower-weight products, thereby enhancing the nutritional quality of fermented products [32]. There was a significant (p > 0.05) difference among the samples.
The pH of the fermenting samples decreased as the fermentation progressed from 0 h to 72 h of fermentation. This decrease in pH is attributed to the production of organic acids in the fermenting samples. A similar result was observed by the authors of [37]. The pH ranged from 4.72–3.11, with sample AS0 having the highest value and AS72 having the lowest value. There were significant (p < 0.05) differences among the samples.
Titratable acidity (TTA) increased with time over the entire fermentation period. A similar increase in acid production was observed by the authors of [34] during the production of weaning food from maize-cowpea blends. The increase in acidity is of great significance, as it is reported to reduce the incidence of diarrhea in infants.
3.2. Proximate Composition (%) of Complementary Food Formulated from Fonio, Soybean and Orange-Fleshed Sweet Potato Flour Blends
Table 2 shows the proximate composition of the formulated complementary food from fonio, soybean and orange-fleshed sweet potato flour blends.

Table 2.
Proximate composition (%) of the complementary food blends (dry basis).
The protein content of the complementary food blend ranged from 22.5–30.52%, with the control sample having the lowest protein value and sample AS (fonio/soybean) having the highest protein content. The result showed that solid-state fermentation increased the protein content of the blends compared to the control sample, which did not undergo the same treatment. The recommended daily allowance for protein intake by infants is within the range of 9–14%, and all the samples ranked above this range. The SSF process increased the total protein quality of maize flour from 9.1 g/100 g to 13.4 g/100 g [38]. Lena et al. [39] have also reported an increase in the crude protein content of wheat bran during SSF with white-rot fungus.
The moisture content of the complementary food blend ranged from 2.42–3.39%, with the control sample (commercial product) having the least moisture content and sample ASO having the highest value. Drying significantly (p < 0.05) reduced the moisture content of the samples. The moisture content is a function of the drying time and the loading depth during the drying operation. A higher moisture content indicates increased susceptibility to spoilage and thus reduces shelf life. The low moisture content of the flour sample was within the acceptable limit of not more than 10% for the long storage of flour. The samples varied significantly (p < 0.05). The values obtained in this study agreed with the report of [40], which reported that low moisture content of flour prevents food spoilage and the growth of pathogenic organisms, thus extending the shelf life of the product. The samples met the required moisture content of the Codex Alimentarius Commission for complementary foods [41].
The fat content of the blends ranged from 6.25–8.40%, with the control sample (commercial product) having the least value and sample AS having the highest value. Fat plays a role in determining the shelf life of foods [42]. A high amount of fat could accelerate spoilage by promoting rancidity, which could lead to the production of off-flavors and -odors. The values obtained in this study are in line with the recommended fat content of not less than 6% for complementary diets [12]. Ruiz-Teran and Owen [31] demonstrated that during SSF of soybean, a substantial reduction in the fat content occurs. The reduction is attributed to the oxidation and utilization of fatty acids by the fungus as a source of energy. The observed increase in fat content after fermentation and drying of the blends may be attributed to the decrease in carbohydrate and moisture content, which increased other dry matter present in the samples [43] The samples varied significantly (p < 0.05).
The ash content of the blends ranged from 1.5–3.4%, with sample CTRL (commercial product) having the least ash content and samples AS and ASO having the highest value. The ash content is the index of the mineral content of food samples, which is vital for infant growth and development. Mineral content is important in fighting infections and for other metabolic activities in infants [44]. The results obtained indicated that the complementary food contained an appreciable amount of important minerals for proper growth and development. There was a significant (p > 0.05) difference between the samples. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) value for infants is between 2–5%. Samples AS and ASO met the requirements.
The carbohydrate content of the samples ranged from 49.34–64.53%, with AS having the lowest value and sample CTRL (commercial product) having the highest value. Carbohydrates in foods provide energy. The decrease in carbohydrates could be attributed to the ability of the micro-organisms to hydrolyze and metabolize the carbohydrate as carbon sources or substrate to synthesize cell biomass. The observed increase in the protein content of the blends may be attributed to the decrease in carbohydrate content [44]. There was a significant (p > 0.05) difference among the blends.
3.3. Effects of SSF on the Functional Properties of the Complementary Food
The functional properties of the complementary food formulated from blends of fonio, soybean and orange-fleshed sweet potato flour are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Functional properties of the formulated complementary food (dry basis).
The viscosity ranged from 8200 ± 1.71–15400 ± 0.71 cP, with sample CTRL (commercial product) having the lowest value and sample ASO having the highest value. There were significant (p < 0.05) differences among the samples. Their variations in viscosity could be due to the effect of solid-state fermentation, as SSF could be applied in the modification of flour. Lactic acid bacteria fermentation enhanced the viscosity of kefir grain flour. The kefiran that was produced increased the binding ability of the kefir grain flour with water and increased the interaction of flour with water in the presence of protein [45].
The water absorption capacity represents the ability of a product to associate with water under conditions in which water is limited [46]. It is desirable for food systems to improve yield and consistency and to give body to the food. The values for the water absorption capacity ranged from 450–551.3%. There were significant (p < 0.05) differences between sample CTRL (commercial product) and the other samples. Samples AS and ASO had the highest content as a result of the effect of SSF on the flour blends. SSF increased the water absorption index of QPM flour from 1.25 to 2.93 g gel/g dry flour [38]. The water absorption capacity is a critical function of protein in various food products such as soups, dough and baked products [47]. The increase in protein content had a positive influence on the water absorption capacity of the samples.
The swelling capacities of the samples ranged from 2.25–3.31%, with sample AS having the highest value and sample CTRL (commercial product) having the lowest value. The high swelling capacity value of samples AS and ASO could be due to the effect of SSF on the samples. There were significant (p < 0.05) differences among the samples. SSF increased the swelling power and solubility of finger millet flour from 12 to 20.04 and from 17.25 to 13.25 due to a change in the gelatinization properties of the flour [48].
3.4. Micronutrient Content of the Formulated Complementary Food
Minerals
Table 4 shows the mineral and vitamin composition of the complementary food formulated from blends of fonio, soybean and orange-fleshed sweet potato flour.

Table 4.
Micronutrient value of the formulated complementary food (dry basis).
The iron content of the complementary food ranged from 6.57–8.41 mg/100 g, with sample ASO having the least value and sample CTRL (commercial product) having the highest value. Although sample CTRL had the highest value due to fortification, samples AS and ASO also contained good amounts of iron, as soybean, which is a constituent of the formulated food, is a rich plant source of iron. Iron is crucial for cognitive development and transportation of oxygen in the body [49]. The recommended daily allowance of iron intake by infants is between 0.27 and 11 mg [50]. All the samples contained acceptable quantities of iron when compared to the recommended daily allowance. There was a significant (p > 0.05) difference among the samples. Iron deficiency, which is the most common and widespread nutritional disorder in both industrialized and non-industrialized countries, results in anemia, which affects more than 3.5 million people in developing countries [51].
Calcium is necessary for the optimal growth and development of infants and young children [52]. The calcium content of the complementary food ranged from 96.23–327.12 mg/100 g, with sample ASO having the lowest value and sample CTRL (commercial product) having the highest value. The samples contained significant amounts of the element, and as such, this makes it an ideal meal for children and adults alike. Srkita et al. [53] reported calcium values of 111 to 356 mg/100 g in weaning food supplemented with moringa leaf powder.
Zinc is an indispensable micronutrient that is necessary for protein synthesis, cell growth and differentiation, immune function and intestinal transport of water and electrolytes [54]. Symptoms of zinc deficiency include dermatitis, retarded growth, diarrhea, etc. All age groups of the population are at risk of zinc deficiency, but infants and young children are the most vulnerable. Zinc supplementation trials conducted over the last few decades in children from developing countries have clearly demonstrated the positive benefits of improved zinc status, including improved growth rates and reductions in the incidence of various infectious diseases [55]. The zinc content in this work ranged from 2.43–5.52 mg/100 g, with sample CTRL (commercial product) having the highest value and sample ASO having the lowest value. The recommended daily intake of zinc in infants (6–12 months) is 0.6 mg [56], and the values observed in this study are higher than the recommended zinc intake.
The vitamin A content of the complementary food blend ranged from 1134–2560 (µg/100 g), with sample ASO having the highest value and sample AS the lowest value. There was a significant (p < 0.05) difference among the samples. Sample ASO had the highest content because it contained orange-fleshed sweet potato, which is a rich source of pro vitamin A. One of the easiest ways to introduce more vitamin A into an infant’s diet is by the addition of carotene-rich plant-based foods. Vitamin A is an essential nutrient that helps to build up the immune system of infants against a number of infections and sustains the integrity of the epithelial linings [57]. These values were higher than the 1380.00 to 1623.33 (µg/100 g) reported by the authors of [58] for moringa-fortified orange-fleshed sweet potato complementary food.
The vitamin C content ranged from 18.32–65.07 mg/100 g, with sample CTRL (commercial product) having the highest value and sample AS having the lowest value. There were significant (p < 0.05) differences among the samples, and their content was generally low. Vitamin C helps to form and repair red blood cells, bones and tissues; it also helps cuts and wounds to heal, boosts the immune system and keep infections away. The RDI of vitamin C for infants of 7–12 months is 50 mg/day. Samples AS and ASO contained less than the required intake, but sample CTRL (commercial product) contained more than the RDI; this could be because it is a fortified food.
The vitamin B1 content ranged from 0.5–1.05 mg/100 g, with sample CTRL (commercial product) having the lowest value and sample ASO having the highest value. There were significant (p < 0.05) differences among the samples. The inclusion of orange-fleshed sweet potato flour to the blend significantly (p < 0.05) increased the vitamin B1 content of the food. The high values obtained could be a result of the SSF process used. Sultana et al. [59] reported that solid-state fermentation using Rhizopus oligosporus on dehulled cereal and legumes (Bengal gram or chola or chickpea) increased the B vitamins (thiamine, niacin and vitamin B6). However, the samples were all above the RNI of thiamine, which is set to a 0.5 mg/100 g standard by the USDA [60].
3.5. Effect of SSF on the Retention of Beta-Carotene Content in OFSP
Sweet potatoes, especially orange-fleshed sweet potato (OFSP) varieties, contain significant amounts of β-carotene [61]. The effect of SSF on the retention of β-carotene content in OFSP is shown in Figure 5. The content ranged from 15.80–17.35 (µg β-carotene/g), with sample OFSP0 having the lowest value and sample OFSP72 having the highest value. There was a significant (p > 0.05) difference between the samples. The β-carotene content increased significantly (p < 0.05) as fermentation time increased. This was similar to the findings of [62], the authors of which reported that lactic acid fermentation using Lactobacillus plantarum produced lacto-pickles from Zapallo OFSP with 93.97% β-carotene retention and an adequate shelf life.
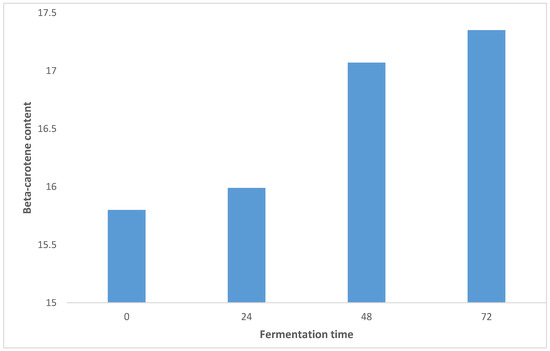
Figure 5.
Effect of SSF on the retention of beta-carotene content of OFSP.
3.6. Effects of Solid-State Fermentation on the Anti-Nutritional Content of the Fermented Complementary Food
3.6.1. Phytate
The phytate content is shown in Table 5. It ranged from 0.06–0.18 mg/g, with the CTRL sample having the lowest value and sample AS having the highest value. There were no significant (p < 0.05) differences among the samples. SSF decreased the phytic acid levels in the complementary food. This could be attributed to the activities of phytase, which reduced the phytic acid level in the fermented product [63]. The relationship between the decrease in phytic acid content and fermentation could be explained by phytase enzyme synthesis by Rhizopus, which hydrolyzes phytic acid [64].

Table 5.
Anti-nutritional content of the fermented complementary food.
3.6.2. Tannin
The tannin content is shown in Table 5, ranging from 0.09–0.13 mg/g, with the CTRL sample having the lowest value and sample AS having the highest value. There were no significant (p > 0.05) differences between samples CTRL and ASO, but they differed (p < 0.05) significantly from sample AS. Soaking, dehulling and discarding of the cooking water have been observed to reduce the tannin content in beans [65]. Tannins depress the absorption of iron, the availability of amino acids and protein digestibility [66]. Their reduction has important implications for the final nutritional properties of the developed product.
The results are in agreement with Mugula [67], who reported a similar phytic acid and tannin content in SSF from a maize–soybean mixture, and also the work of Onilude et al. [68], who also observed a reduction in both the polyphenol and tannin content of cereal–soyabean blends as a result of malting and roasting. Reyes-Moreno et al. [19] reported a decrease in phytic acid content of SSF of chickpea from 10.85–1.1 g/kg and in tannin content from 21.95–2.65 g/kg.
3.7. Effects of Fermentation (SSF) Time on the Total Viable Count and Mold Counts of the Fermenting Raw Materials
Table 6 shows the effect of fermentation time on the total viable and mold counts of the fermenting samples.

Table 6.
Effect of SSF on the microbial count of the complementary food (wet basis).
The total viable count gives a quantitative idea about the presence of microorganisms in the sample. The total viable count (cfu/mL)) for the blends ranged from 2.8 × 105 (AS0), 2.2 × 105 (AS24), 4.0 × 104 (AS48) to 1.7 × 104 (AS72), and the values for the finished products ranged from 2.0 × 104 (AS) to 2.4 × 104 cfu/mL (ASO). It was observed that the value was highest at the 48th h. This could be the result of the microbial organisms growing and multiplying, as this was the peak of the fermentation period. After 48 h of the fermentation period, the microbial count of the blends decreased gradually. In the final product, it was observed that the TVC count increased. This could be a result of the mild heat treatment used in drying, which still allows the microbial strains to thrive. The microbial strains are beneficial to the intestinal guts of children, as they are probiotic. However, the samples were within the safe limits recommended for foods [69].
The mold count in (cfu/mL) for the fermented complementary food ranged from 2.0 × 10 (AS0), 4.0 × 10 (AS24), 2.0 × 10 (AS48) to 1.0 × 10 (AS72). The mold count was recorded throughout the fermentation time. This was a result of the microbial strain (Rhizopus oligosporus) used to ferment the samples, which is a fungus. The growth of mold during the fermentation process signifies that the fermentation is progressing. The mold count increased at the 24th h of fermentation and decreased at the 72nd h. On the final product, the mold count ranged from 1.8 × 10–2.0 × 10. This could be a result of the mild heat treatment used in drying, which still allows the microbial strains to thrive. The microbial strains are beneficial to the intestinal guts of children, as they are probiotic. The microbial contents in the samples were within the safe limits recommended for foods [69].
3.8. Sensory Properties of Complementary Food Formulated from Fonio, Soybean and Orange-Fleshed Sweet Potato Flour Blends
Figure 6 and Figure 7, shows complementary food produced from blends of Fonio, Soybean and Orange-fleshed Sweet Potato flour blends, alongside with the control.

Figure 6.
Flour blends of samples packaged in plastic containers.

Figure 7.
Different blends of the cooked formulated complementary food. They are arranged from left to right (CTRL, AS and ASO).
Table 7 shows the average mean sensory scores of the complementary food samples from the blends of fonio, soybean and orange-fleshed sweet potato flour.

Table 7.
Sensory scores of complementary food produced from blends of fonio, soyabean and orange-fleshed sweet potatoes with a commercial control (wet basis).
The sensory scores for color ranged from 7.15–7.70. All the samples had a rating of seven points for color. Sample CTRL (commercial product) scored 7.15, sample AS scored 7.70, and sample ASO scored 7.55. However, no significant (p > 0.05) differences existed among all the samples. Sample CTRL (commercial product) and sample AS had a milky color, whereas sample ASO had slightly orange color as a result of the addition of OFSP. Fermentation produced a slightly darker color, which may be attributed to the influence of mycelia color and drying. However, all the colors were generally accepted by the panelists. Color is one of the most important parameters in any new developed food product, because it can affect the acceptability of the product [70]. The color of a food is very important as an eating quality parameter. It is the first and instant indicator of quality.
The sensory scores for taste (as shown in Table 7) indicated that the differences in the tastes between products were not significant (p > 0.05). Although no significant differences in taste could be established between products, the products containing orange-fleshed sweet potatoes had the lowest scores. The scores for taste ranged from 6.45–7.65. The CTRL sample had the highest score for taste as a result of the additional artificial flavors added, whereas the developed product had no addition of artificial flavor.
The sensory scores for the aftertaste ranged from 5.80–7.35, with the control sample having the highest score. There was no significant (p > 0.05) difference between samples AS and ASO. The sample CTRL was preferred compared to the other samples, because it had a sweeter aftertaste.
The sensory scores for flavor ranged from 6.20–7.85. The control sample had the highest score for flavor, and sample ASO had the lowest score. There was no significant (p > 0.05) difference in the flavors of sample CTRL and AS. The results obtained in this study are higher than the values (5.92 to 6.58) reported by [71] for orange-fleshed sweet potato–sorghum–soy flour complementary food.
The sensory scores for the mouthfeel ranged from 5.75–6.80. Sample AS had the highest score, and there was a significant (p < 0.05) difference between the samples. The panelists preferred sample AS, because it had a smoother texture than the other samples. The texture of the weaning food indicates how coarse, rough or smooth the samples were. The sensory scores for texture ranged from 5.75–6.85, with sample ASO having the lowest score and sample CTRL having the highest score. There was no significant (p < 0.05) difference between the samples, and they were generally accepted by the panelists.
The sensory scores for consistency ranged from 7.40 to 7.05. Sample CTRL had the highest score, whereas sample ASO had the lowest score. The low values of consistency for sample ASO could be a result of the high percentage of OFSP in the blends, which resulted in high viscosity. The pseudo-plastic nature of OFSP feels sticky in the mouth after eating [72]. The results obtained in this study are higher than the values (5.10 to 6.68) reported by [57] for orange-fleshed sweet potato–sorghum–soy flour complementary food.
The sensory scores for the overall acceptability of the formulated complementary food ranged from 6.20–7.80. Sample CTRL had the highest score, whereas sample ASO had the lowest score. There was no significant (p > 0.05) difference between samples CTRL and AS. From the results, it can be deduced that the panelists least preferred sample ASO as a result of the addition of OFSP, as it has a less sweet taste compared to the other samples and is less smooth in the mouth than sample AS.
4. Conclusions
The results from this study have shown that acceptable, high-protein, nutritious complementary foods can be produced from combinations of cereals (fonio), legumes (soybean) and tubers (orange-fleshed sweet potato) using solid-state fermentation. Acceptable results were obtained for functional properties, such as the water absorption capacity and viscosity, which are important parameters that determine the texture and energy density of products. The use of soybean in the formulation of complementary food would help to alleviate problems of protein energy malnutrition, and the use of OFSP would be beneficial for micro-nutrient deficiencies in Nigeria and other developing countries. The complementary food produced could be used to replace the predominant carbohydrate-based complementary foods. Soybean, a protein of high biological value, can be used as a replacement for animal protein (which is usually expensive) in complementary food formulas. Although the commercial sample (a combination of Cerelac maize and soya) was most strongly preferred, the sensory scores indicated that sample AS (100% fonio/soybean blend) could be recommended compared to the other blends, as there were no significant (p < 0.05) difference between the sample and the control. The use of probiotic microorganisms Rhizopus oligosporus (2710) and Lactobacillus plantarum (B-41621) in the production process will benefit the intestinal guts of children and help to prevent complementary food-associated childhood diarrhea, which kills about 525,000 children under 5 years of age every year in low- and middle-income countries due to unhygienic practices by mothers/caretakers.
Author Contributions
Supervision: N.C.O.; Writing—Review and Editing: C.F.O.; Conceptualization: N.C.O. and I.E.M.-N.; Investigation: C.P.A.; Methodology and Software: C.R.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the assistance of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), the Agricultural Research Service, and the ARS Culture Collection Center, USA, who provided the microbial culture used in this research work. Your impact cannot be overemphasized.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dewey, K. Guiding Principles for Complementary Feeding of the Breastfed Child; Pan American Health Organization: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Black, R.E.; Allen, L.H.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Caulfield, L.E.; De Onis, M.; Ezzati, M. Maternal and Child Under-nutrition: Global and Regional Exposures and Health Consequences. Lancet 2008, 371, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO; UNICEF. Global Strategy for Infant and Young Child Feeding; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9241562218 (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- Bhutta, Z.A.; Das, J.K.; Rizvi, A.; Gaffey, M.F.; Walker, N.; Horton, S. Evidence-Based Interventions for Improvement of Maternal and Child Nutrition: What Can Be Done and At What Cost? Lancet 2013, 383, 452–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Feeding and Nutrition of Infants and Young Children: Guidelines for the WHO European Region with Emphasis on the Former Soviet Countries; WHO Region Publication, European Series no. 87; WHO—Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Krebs, N.F. Food Based Complementary Feeding Strategies for Breastfed Infants: What’s the Evidence that it matters? Nutr. Today 2014, 49, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.; Dewey, K.; Allen, L. Complementary Feeding of Young Children in Developing Countries: A Review of Current Scientific Knowledge; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Jorge, E.M.; Wolfgang, H.P.; Beyer, P. Bio-fortified Crops to Alleviate Micronutrient Malnutrition. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, R.A.; Vanderjagt, J.D.; Williams, M.; Huang, Y.S.; Chuang, L.-F.; Millson, M.; Andrew, R.; Pastuszyn, A.; Glew, H.R. Fatty acid, amino acid and trace element analysis of five weaning food from Jos, Nigeria. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2002, 57, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranti, M. Grain Legume Proteins and Nutraceutical Properties—Review. Fitoterapia 2006, 77, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojinnaka, M.C.; Ebinyasi, C.S.; Ihemeje, A.; Okorie, S.U. Nutritional Evaluation of Complementary Food Gruels Formulated from Blends of Soybean Flour and Ginger Modified Cocoyam Starch. Adv. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 5, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egounlety, M. Production of Legume-fortified Weaning foods. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachmeister, K.A.; Fung, D.Y.C. Tempeh: A mold-modified indigenous fermented food from soybeans and/or cereal-grains. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 1993, 19, 137–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodouhe, S.R.; Zannou, A.; Achigan-Dako, G.E. Actes du premier atelier sur la diversite genetique du fonio (Digitaria exilis Stapf. en Afrique de l’Ouest. In Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Genetic Diversity of Fonio (Digitaria exilis staph) in West Africa, Conakry, Guinea, 4–6 August 1998; IPGRI: Rome, Italy. [Google Scholar]
- Pampluna, G.D.; Roger, M.D. Health Foods; Ibegraphi: San Feranado, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dashiell, K.E. Soybean production and utilization in Nigeria. In Proceedings of the National Workshop on Small Scale and Industrial Level for Processing of Soybean, Ibadan, Nigeria, 27–29 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Alian, M.M.M.; Isreal, M.P.; Rene, M.S. Improving the nutritional quality of cowpea and Bambara bean flours use in infant feeding. Pak. J. Nutr. 2007, 6, 660–664. [Google Scholar]
- Petrikkou, E.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Gomez, A.; Molleja, A.; Mellado, E. Inoculum standardization for antifungal susceptibility testing of filamentous fungi pathogenic for humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1345–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Moreno, C.; Cuevas-Rodríguez, E.O.; Milán-Carrillo, J.; Cárdenas-Valenzuela, O.G.; Barrón-Hoyos, J. Solid State Fermentation Process for Producing Chickpea (Cicerarietinum L.) Tempeh Flour. Physicochemical and Nutritional Characteristics of the Product. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A.O.A.C. Official Methods of Analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 18th ed.; AOAC International: Washinton, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Olokodona, F.A. Analysis of Fruit Drinks and Fruit Juices. Institute of Public Analysts of Nigeria. IPAN Bull. 2005, 6, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sathe, S.K.; Salunkhe, D.K. Functional Properties of the Great Northern Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Proteins: Emulsion, Foaming, Viscosity and Gelation Properties. J. Food Sci. 1981, 46, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.J.Y.; Humbert, E.S.; Sosulski, F. Certain Functional Properties of Sunflower Meal Products. J. Food Sci. 1974, 39, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrigan, W.F.; McCance, M.E. Laboratory Methods in Food and Dairy Microbiology; Academic Press Inc. Limited: London, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, D.A. Chemical Analysis of Foods, 7th ed.; Churchill Living Stone: Edinburgh, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, H.; Sawyer, R. Frait Pearson Chemical Analysis of Food, 8th ed.; Longman Scientific and Technical: Edinburgh, UK, 1998; pp. 211–212. [Google Scholar]
- Ihekoronye, A.I.; Ngoddy, P.O. Integrated Food Science and Technology for the Tropics; Macmillian Publishers Limited: London, UK, 1985; pp. 236–253. [Google Scholar]
- Steel, G.D.; Torrie, J.H. Principles and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Book Company Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, A.; Frias, J.; Granito, M.; Vidal-Valverde, C. Fermented Pigeon Pea (Cajanuscajan) Ingredients in Pasta Products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6685–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Bastidas, M.; Reyes-Fernández, E.Z.; López-Cervantes, J.; Milán-Carrillo, J.; Loarca-Piña, G.F. Physicochemical, Nutritional and Antioxidant Properties of Tempeh Flour from Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2010, 16, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Teran, F.; Owens, J.D. Chemical and Enzymatic Changes during the Fermentation of Bacteria-free Soya Bean Tempe. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1996, 71, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nout, M.J.R.; Kiers, J.L. Tempeh Fermentation, Innovation and Functionality: Update into the third millinium. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 789–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubina, N.; Muhammad, N.; Muhammad, I.; Quratulain, S. Nutritional Enhancement of Barley in Solid state Fermentation by Rhizopus Oligosporus ML-10. Nutr. Food Sci. Int. J. 2018, 6, 555700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefa-Dedeh, S.; Kluvitse, Y.M. Development of cowpea-fortified weaning foods: Functional and chemical properties. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Institute of Food Technologists, Atlanta, GA, USA, 3–7 June 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Obadina, A.O.; Akinola, O.J.; Shittu, T.A.; Bakare, H.A. Effect of Natural Fermentation on the Chemical and Nutritional Composition of Fermented Soymilk Nono. Niger. Food J. 2015, 31, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, R.A.O.; Akinyosoye, F.A.; Adetuyi, F.C. Nutritional composition of Canavaliaensiformis (L.) (Jack Beans) as affected by the use of Mould starter cultures for fermentation. Trends Appl. Sci. Res. 2011, 6, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanni, A.I.; Onilude, A.A.; Ibidapo, O.F. Physicochemical Characteristics of Weaning Food Formulated from Different Blends of Cereal and Soybean. Z. Für Lebensm. Forsch. A 1999, 208, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Rodríguez, E.O.; MiIán-Carrillo, J.; Mora-Escobedo, R.; Cárdenas-Valenzuela, O.G.; Reyes-Moreno, C. Quality Protein Maize (Zea mays L.) and Tempeh Flour through Solid State Fermentation Process. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 37, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lena, G.I.; Patroni, E.; Quaglia, G. Improving the nutritional value of wheat bran by a white-rot fungus. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 32, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Origbemisoye, B.A.; Ifesan, B.O.T. Chemical Compostion of Kiaat (Pteropcarpusangolensis) bark and the effect of herb pastes on the quality changes in marinated cat fish during chilled storage. Food Biol. 2019, 82, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codex, A.C. Corn Soya Sugar Blend for Young Children and Adults; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Brons, C.; Jensen, C.B.; Storggard, H.; Alibegovic, A.; Jacobsen, S.; Nilsson, E.; Astrup, A.; Quistroff, B.; Vaag, A. Mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle is normal and unrelated to insulin action in young men born with low birth weight. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 3885–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, P.E.; Amoaful, E.F. Healthy Eating for Mothers, Babies and Children: Facilitator Guide for use By Community Health Workers in Ghana; International Potato Center (CIP): Lima, Peru; Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)—Nutrition Department of the Ghana Health Service: Accra, Ghana, 2015; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Oboh, G. Nutrient Enrichment of Cassava Peels Using a Mixed Culture of Saccharomyces cerevisae and Lactobacillus spp. Solid Media Fermentation Techniques. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 9, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piermaria, J.; Mariano, L.; Abraham, A.G. Gelling properties of Kefiran, a food-grade polysaccharide obtained from Kefir grain. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U. Functional properties of grain legume flours. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 38, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Adeyeye, E.I.; Aye, P.A. The Effect of Sample Preparation on Proximate Composition and the Functional Properties of African Yam Bean Flours (Sphenostylisstenocarpa Hoshst ex A. rich) Flours. Ital. Rev. Fat. Subst. 1998, 75, 253–261. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekar, V.; Ganapathy, S.; Karthikeyan, S. Enhancing Alpha Amylase Activity of Finger Millet (Eluesinecoracana) for Improving Baking Property through Solid State Fermentation. Adv. Life Sci. 2016, 5, 4069–4076. [Google Scholar]
- John, L. Why Iron is Important in Infant Development. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 2534–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Nutrition and Your Health: Dietary Guidelines for Americans; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA; US Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- UNICEF; UNU; WHO; MI. Preventiing iron dficiency in women and children. Technical consensus on key issues. In Proceedings of the Technical Workshop, New York, NY, USA, 7–9 October 1998; International Nutrition Foundation: Boston, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lucretia, L.; Patience, C.E.; Enobong, M. Proximte Composition, Micronutrient and Sensory Properties of Complementary Food Formulated from Fermented Maize, Soybeans and Carrot flours. Sky J. Food Sci. 2017, 6, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shiriki, D.; Igyor, M.A.; Gernah, D.I. Effect of Moringa oleifera leaf powder supplementation on the micronutrient and toxicant content of maize-soybean-peanut complementary food formulations. Int. J. Food Process. Technol. 2014, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Waquas, U.; Daniel, W. Zinc Supplementationin the Management of Diarrhoea; World Healh Organization (WHO): Toronto, ON, Canada, 2011; Available online: https://www.who.int/elena/titles/bbc/zinc_diarrhoea/en/ (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- Shankar, A.H. Influence of zinc supplementation on morbidity due to plasmodium falciparum: A randomized trial in preschool children in Papua New Guinea. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 62, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO; WHO. Essential amino acid and minerals. In Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Experts Consultations; Food and Agricultural Organizations of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1991; p. 280. [Google Scholar]
- Ekweagwu, E.; Awu, A.E.; Madukwe, E. The role of micronutrients in children health: A review of the Literature. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 3804–3810. [Google Scholar]
- Kolawole, F.L.; Balogun, M.A.; Sanni-Olayiwola, H.O.; Abdulkadir, S.O. Physical and chemical characteristics of moringa-fortified orange sweet potato flour for complementary food. Croat. J. Food Technol. Biotechnol. Nutr. 2017, 12, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, N.; Azam, M.Z.; Amin, M.Z.; Shams, B.; Satter, M.A.; Masum, S.M. Vitamin B and Essential minerals contents of mixed solid state fermented millet (Steria italic) and Bengal gram by Rhizopus oligosporus. Bangladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2011, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Nutrition and Your Health: Dietary Guidelines for Americans; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA; US Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- CIP. International Potato Centre. 2017. Available online: www.internationalpotatocentre.com (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- Oloo, B.O.; Shitandi, A.A.; Mahungu, S.; Malinga, J.B.; Rose, O.B. Effects of Lactic Acid Fermentation on the Retention of Beta-carotene Content in Orange Fleshed Sweet Potatoes. Int. J. Food Stud. 2014, 3, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Khetarpaul, N. Effect of Fermentation on Phytic Acid Content and Invitro Digestibility of Starch and Protein of Rice-Black Gram Dhal-Wheat Blends. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 34, 20–30. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes-moreno, C.; Romero-urias, C.; Milan-Carrillo, J.; Valdez-Torres, B.; Zarate-Marquez, E. Optimization of the Solid State Fermentation Process to Obtain Tempeh from Hardened Chickpea (Cicerarietinum L.). Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2000, 55, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, N.R.; Pierson, M.D.; Sathe, S.K.; Salunkhe, D.K. Dry Beans Tannins: A Review of Nutritional Implications. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1985, 62, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.S.; Sathe, S.K.; Salunkhe, D.K.; Cornforth, D.P. Effect of Dehulling on Phytic acid, Polyphenols and Enzyme Inhibition of Dry Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J. Food Sci. 1982, 47, 1846–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugula, K. Evaluation of the Nutritive Value of Maize-Soybean Tempe as a Potential Food in Tanzania. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 1992, 43, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onilude, A.A.; Sanni, A.I.; Ighalo, M.I. Process Upgrade and the Microbiological, Nutritional and Consumer Acceptability of Infant Weaning Food from Fermented Composite Blends of Cereals and Soybean. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2004, 2, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Centre for Food Safety. Microbiological Guidelines for Food: For Ready to Eat Foods in General and Specific Food Items; Revised ed.; Food and Environmental Hygiene Department: Hong Kong, China, 2014.
- Kikafuda, J.K.; Abenakyo, L.; Lukwago, F.B. Nutritional and sensory properties of high energy/nutrient dense composite flour porridges from germinated maize and roasted beans for child-weaning in developing countries: A case for Uganda. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2006, 45, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawode, E.K.; Idowu, M.A.; Adeola, A.A.; Oke, E.K.; Omoniyi, S.A. Some quality attributes of complementary food produced from flour blends of orange flesh sweet potato, sorghum, and soybean. Croat. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 9, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.A. Changes in Nutrient Composition, Trypsin inhibitor, Phytate, Tannins and Protein Digestibility of Dolichos Lablab Seeds (Lablab purpureus (L) sweet) occurring during Germination. J. Food Technol. 2007, 5, 294–299. Available online: https://medwelljournals.com/abstract/?doi=jftech.2007.294.299 (accessed on 25 December 2020).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).