Abstract
The production of lactic acid (LA) from lignocellulosic biomass is an important route for the exploitation of renewable resources; nevertheless, effective LA production from this feedstock is challenged by several limitations, such as pentose and oligosaccharide utilization. In this study, a new strain, Lactococcus sp. X1, which is capable of fermenting glucose, xylose, and several disaccharides to produce L-lactic acid, was isolated from the gut of a wood-feeding termite, Coptotermes formosanus. Compared to conventional lactic acid bacteria, Lactococcus sp. X1 requires less complex nitrogen sources, which might in turn reduce the cost of LA production. In addition, Lactococcus sp. X1 was able to completely ferment 50 g/L of glucose within 3 days, giving a high LA yield of 99.9%, and its LA yield from 50 g/L of pretreated corncob reached up to 0.34 g/g substrates in the presence of a commercial cellulase. Strain X1 was also capable of excreting two kinds of nutritional factors, namely biotin and vitamin C, indicating its crucial role in the nourishment of the termite. In conclusion, Lactococcus sp. X1 is a new lactic acid bacterium, which may hold promise for application in cost-effective LA production as well as in the field of food additives.
1. Introduction
Lactic acid (LA), also known as 2-hydroxypropionic acid, is an important multi-purpose natural organic acid that can be applied in the chemical industry, food, cosmetics, medicine, and other fields [1]. It exists in three forms: D-, L-, and racemic DL-lactic acid. LA, with high optical purity, is more valuable than the racemic form and has wider applications. In particular, either D- or L-lactic acid can be used as a monomer to polymerize and produce polylactic acid, an environmentally friendly biodegradable polymer material, which is of great importance for better solving the severe environmental problems faced by mankind at present, such as white pollution.
LA is usually manufactured through microbial fermentation, and the economics of the production of both LA and its derivatives rest heavily on the price and source of raw materials [2,3]. With the enlargement of LA production, it is necessary to explore the use of low-cost lignocellulose as an alternative to conventional feedstocks (e.g., glucose and starch). The main components in the enzymatic hydrolysates of lignocellulose are hexoses and pentoses. Most bacteria, including lactic acid bacteria (LAB) can grow well on hexose but poorly on pentose and some disaccharides, such as cellobiose. This drawback has become as one of the major barriers to LA production from the hydrolysates of lignocellulosic biomass [4]. To this end, it is necessary to explore new LAB for better metabolism of pentoses as well as the disaccharides that exist in biomass hydrolysates. Isolation of more efficient microbes from various niches is recognized as one of the possible strategies, and various isolated strains have found their attractive applications in industry [5], with some of them even revealing novel pentose catabolism pathways [6].
Natural cellulolytic systems may be one of the reservoirs of such LAB which cooperate with the cellulolytic partners to decompose lignocellulose. It is well known that many natural biological systems are able to degrade and metabolize lignocellulose to different extents, such as bacteria, fungi, wood-feeding insects, and herbivores; among which wood-feeding termites stand out as an efficient utilization system because of the dual cellulolytic system between host and symbionts [7,8]. Meanwhile, LAB have been identified as the dominant culturable members of the gut microbiota of wood-feeding termites [9]. Recently, a series of LAB with unique phenotypic characteristics have been isolated from the guts of various termites, such as Nasutitermes hainanensis, Reticulitermes speratus, Nasutitermes takasagoensis, and Coptotermes formosanus [9,10,11,12]; and several strains are capable of achieving a high purity L-lactic acid under anaerobic conditions [12]. Apparently, termite gut may harbor unique LAB which have been evolved for efficient utilization of the sugars that generated during the lignocellulose degradation process.
In the present study, we isolated a new strain of Lactococcus sp. X1 from the guts of a termite, C. formosanus, which can produce L-lactic acid from glucose, as well as several pentoses and disaccharides. More importantly, the growth of strain X1 requires little complex nitrogen source, and also produces two kinds of water-soluble vitamins, namely biotin and vitamin C. Therefore, strain X1 may hold promise for application in cost-effective LA production as well as in the field of food additives.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Media Preparation
A wood-feeding termite, C. formosanus, was collected from Suzhou, China. A modified deMan Rogosa Sharpe (mMRS) medium was prepared for LAB isolation. The mMRS medium contains (per liter): tryptone 1 g, yeast extract (YE) 2 g, beef extract 2 g, xylose 5 g, KH2PO4 1.5 g, K2HPO4 × 3H2O 2.9 g, sodium acetate 1 g, triammonium citrate 0.5 g, MgCl2 × 6H2O 0.2 g, CaCl2 × 2H2O 75 mg, and MnSO4 0.05 g. After boiling and nitrogen-flushing for 10 min, L-cysteine was added into the mMRS medium as a reducing reagent at a final concentration of 0.5 g/L. For solid medium, an additional 15 g/L agar was added. A control strain (Lactobacillus pentosus ATCC 8041) was purchased from ATCC (Manassas, VA, USA) and was cultivated using the same method as that for strains X1.
2.2. Isolation Procedures
Several workers of C. formosanus were soaked in 75% ethanol for one minute for surface sterilization, rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 2–3 times under aseptic conditions, and then homogenized using a pestle in an Eppendorf tube. The homogenized liquid was subsequently transferred into the mMRS medium and was incubated at 30 °C under anaerobic conditions overnight. Next, cultures were transferred into fresh mMRS medium and repeated four times at an inoculation ratio of 1:1000. The final culture was gradually diluted with PBS buffer and plated onto solid mMRS medium, incubating anaerobically at 30 °C for 24–48 h. Well separated colonies were picked, purified several times using the same plating method, and stored in 20% glycerol at −80 °C until use. Purified isolates were inoculated into liquid mMRS medium and incubated anaerobically at 30 °C for 24 h for further quantification of LA using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The best LA producer was assigned as strain X1 and deposited into the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC No. 24341).
2.3. Identification of Strain X1
The morphology of strain X1 was observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) as described by Deng et al. [13], and the species identification was carried out using 16S rDNA sequencing. The 16S rDNA fragment was amplified by conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with a universal primer set of Eubac27F (5′-AGAGTTTGATC-CTGGCTCAG-3′) and Eubac1492R (5′-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′) [14]. The 25 μL PCR mixtures contained 23 μL 1× sPfu Master Mix (Biomed, Beijing, China), 0.5 μL of each primer (10 μM), and 1 μL bacterium culture. The PCR products were examined using 1% (w/v) agarose gel electrophoresis, and sequenced by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China). The 16S rDNA sequence was further BLAST against the NR database of GenBank for homology search. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method by MEGA (Version 7.0) for phylogenetic analysis [15].
2.4. Effects of Different Factors on LA Production
In order to determine the effects of different factors on LA production by strain X1, fresh X1 cultures were transferred to 15 mL of mMRS medium at 1% inoculum and incubated anaerobically at 30 °C and 180 rpm for 24 h. Firstly, using the mMRS medium where xylose was replaced by 10 g/L glucose as the carbon source, the effect of some additional acid neutralizers on LA production were tested, such as 10 g/L CaCO3, 5 g/L CaCO3 and 0.05 M KHCO3, 5 g/L CaCO3 and 0.065 M KHCO3, 5 g/L CaCO3 and 0.075 M KHCO3, 0.1 M KHCO3, 0.13 M KHCO3, and 0.15 M KHCO3. Secondly, the effects of various carbon (10 g/L of cellobiose, sucrose, xylose, arabinose) and nitrogen sources (5 g/L of beef extract, 5 g/L of YE, 5 g/L of tryptone, 1 g/L YE, 1 g/L YE and 1 to 5 g/L NH4Cl, 2 g/L YE, 3 g/L YE, and 4 g/L YE) on LA production were investigated. Thirdly, to meet the demand of industrial LA production, X1 was tested during prolonged fermentation of high concentration substrates, such as 50, 100, 150, and 200 g/L sugar for various time spans.
2.5. Simultaneous Saccharification and Fermentation (SSF) of Corncob
Corncob particles (<40 mesh) were treated with 7% sodium hydroxide at 86 °C for 1 h using a solid: liquid (w/v) ratio of 1:7, as described by Zhang et al. [16]. The solid residue was washed with deionized water to remove the residual alkali until neutral pH was achieved. The SSF of corncob was carried out using strain X1 combined with a cellulase, CTec2 (Sigma, Shanghai, China), the latter of which was quantified using a BCA protein quantification kit (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China). The pretreated-corncob (50 g/L), cellulase (10 or 20 mg/g corncob), and bacteria of 1% inoculum were supplemented in 10 mL of medium shaking at elevated temperature (35 °C) and 180 rpm.
2.6. Chemical Analysis
The concentrations of residual substrates and LA production were analyzed using a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) system (Shimadzu, Japan) equipped with a refractive index detector and a Bio-Rad HPX-87H column [17]. The L-lactic acid content was determined using an L-lactic acid assay kit (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China). The production of vitamins was accessed by liquid chromatography–ion trap mass spectrometry (LC-ITMS; Thermo Fisher, New York, NY, USA) in positive-ion mode according to Zhang et al. [18], with an Agilent ZORBAX Eclipse Plus C18 column (2.1 mm × 100 mm, 1.8 μm) and the mobile phase of formic acid reduced to 0.08%. Raw mass spectrometry data were analyzed using Xcalibur 4.1 software (Thermo Fisher). Unless otherwise stated, all tests were performed in triplicate. Data are given as mean ± standard deviation. Statistical analysis was carried out using Origin 2021 (OriginLab, Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Strain X1
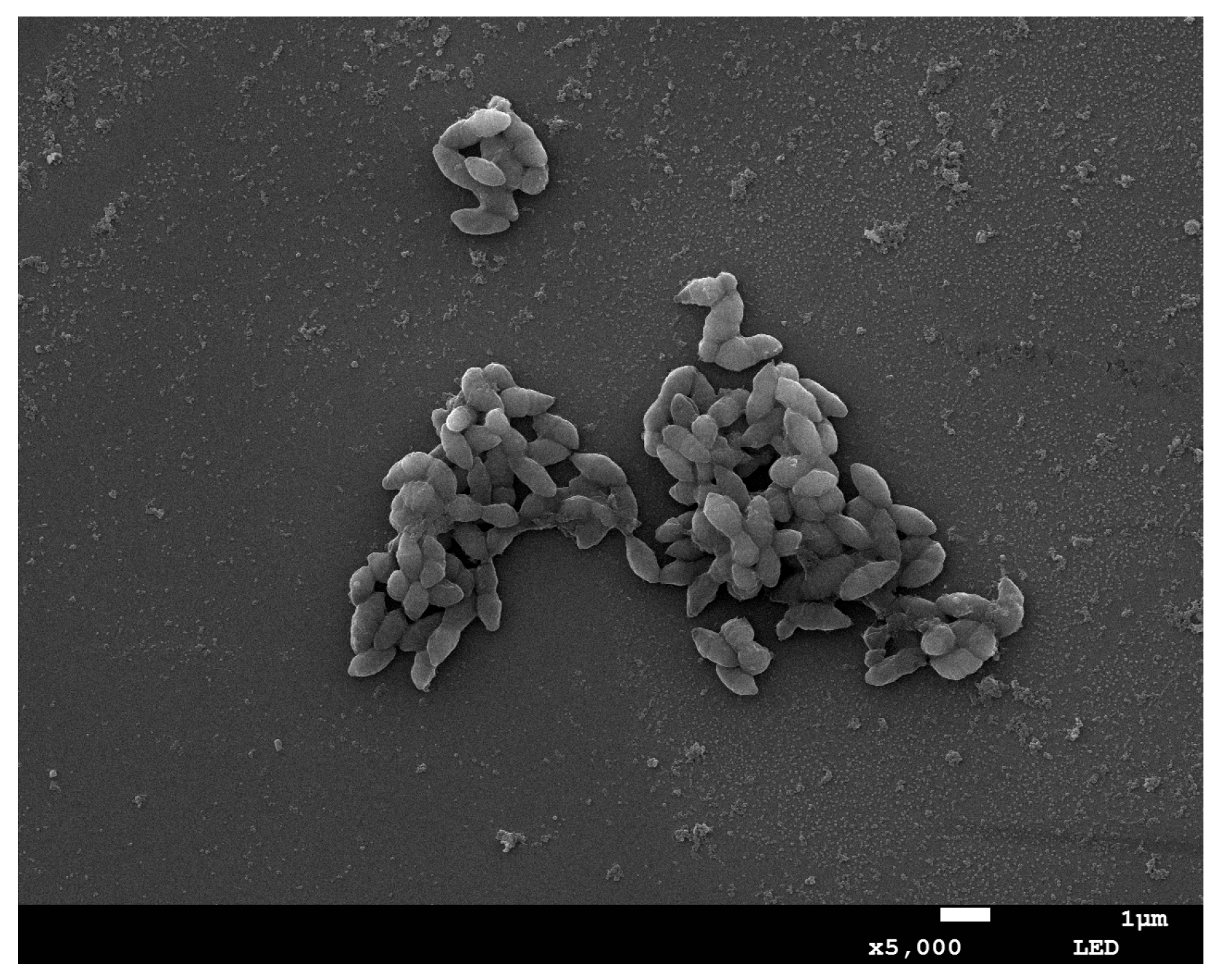
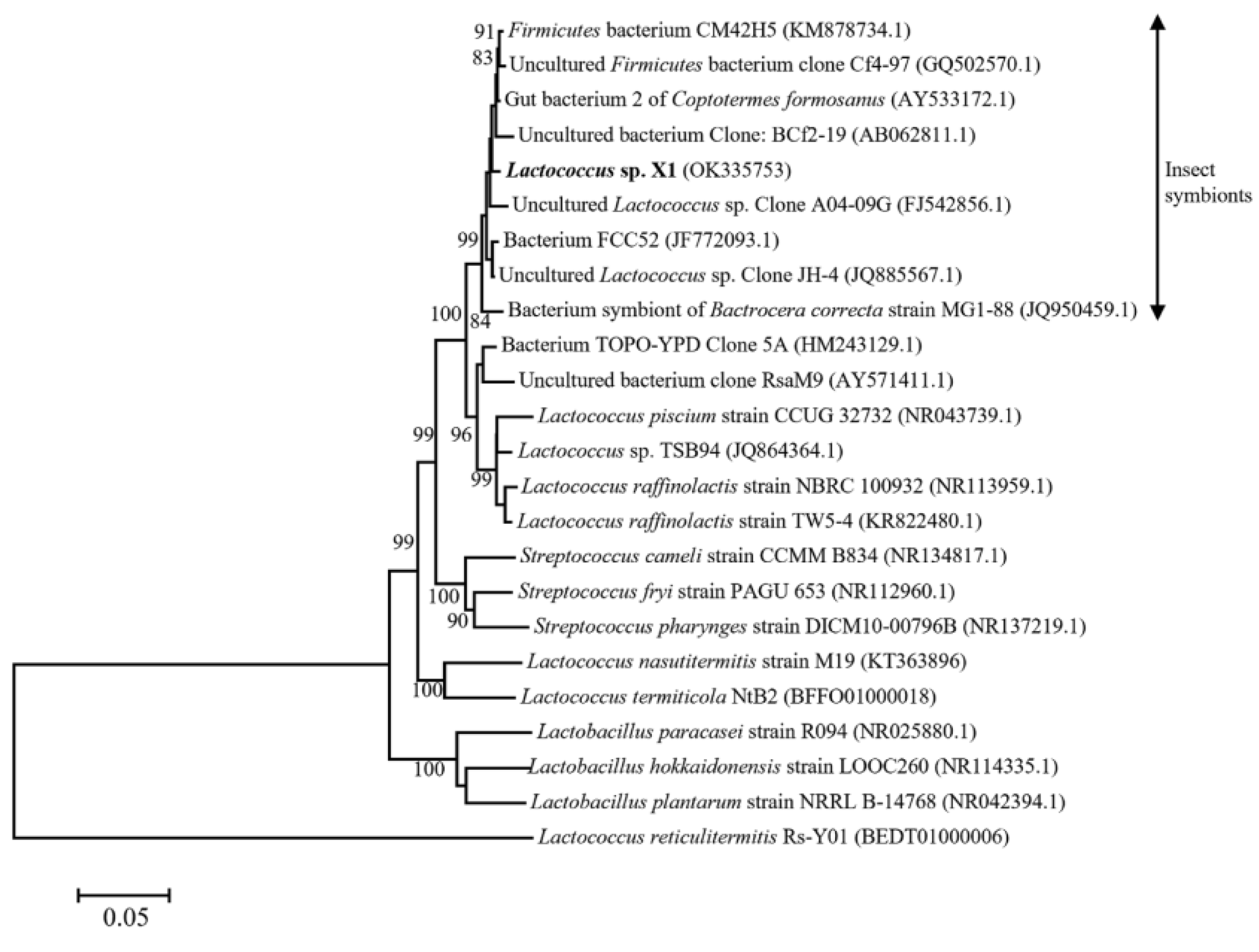
Strain X1 was identified by its morphological characteristic and 16S rDNA sequence. Strain X1 is ovoid in shape (0.5–1.2 μm by 0.5–1.5 μm) as evaluated by means of SEM (Figure 1), matching the description of Lactococcus in the literature [19]. Phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rDNA sequence of strain X1 (GenBank accession: OK335753) suggested that it was a new member of Lactococcus, and that it clustered tightly with some known Lactococcus spp., especially part of those insect-symbionts, but far away from Streptococcus as well as Lactobacillus (Figure 2). In fact, it shared up to 99.1% similarity with some 16S rDNA sequences of uncultured insect-symbionts, while it was at most 95.6% homogenous to cultured Lactococcus spp.
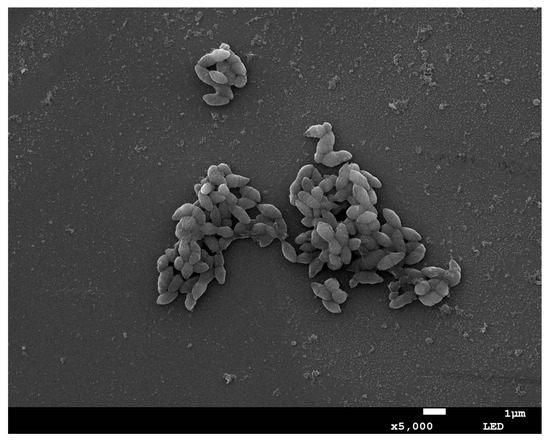

Figure 1.
SEM micrograph of strain X1.
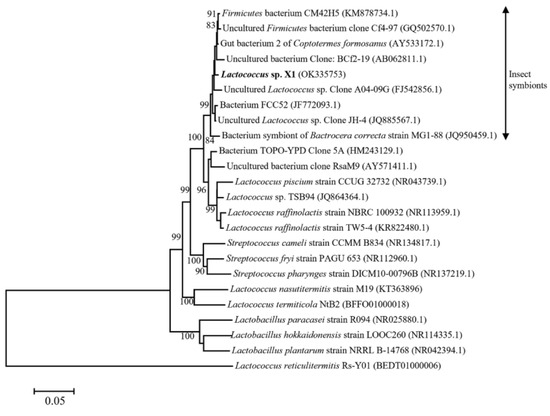
Figure 2.
Neighbor-joining tree of Lactococcus sp. X1 and its closely related species based on nearly complete 16S rDNA sequences. GenBank accession numbers were given in the parentheses.
3.2. Effects of Different Factors on LA Production by Strain X1
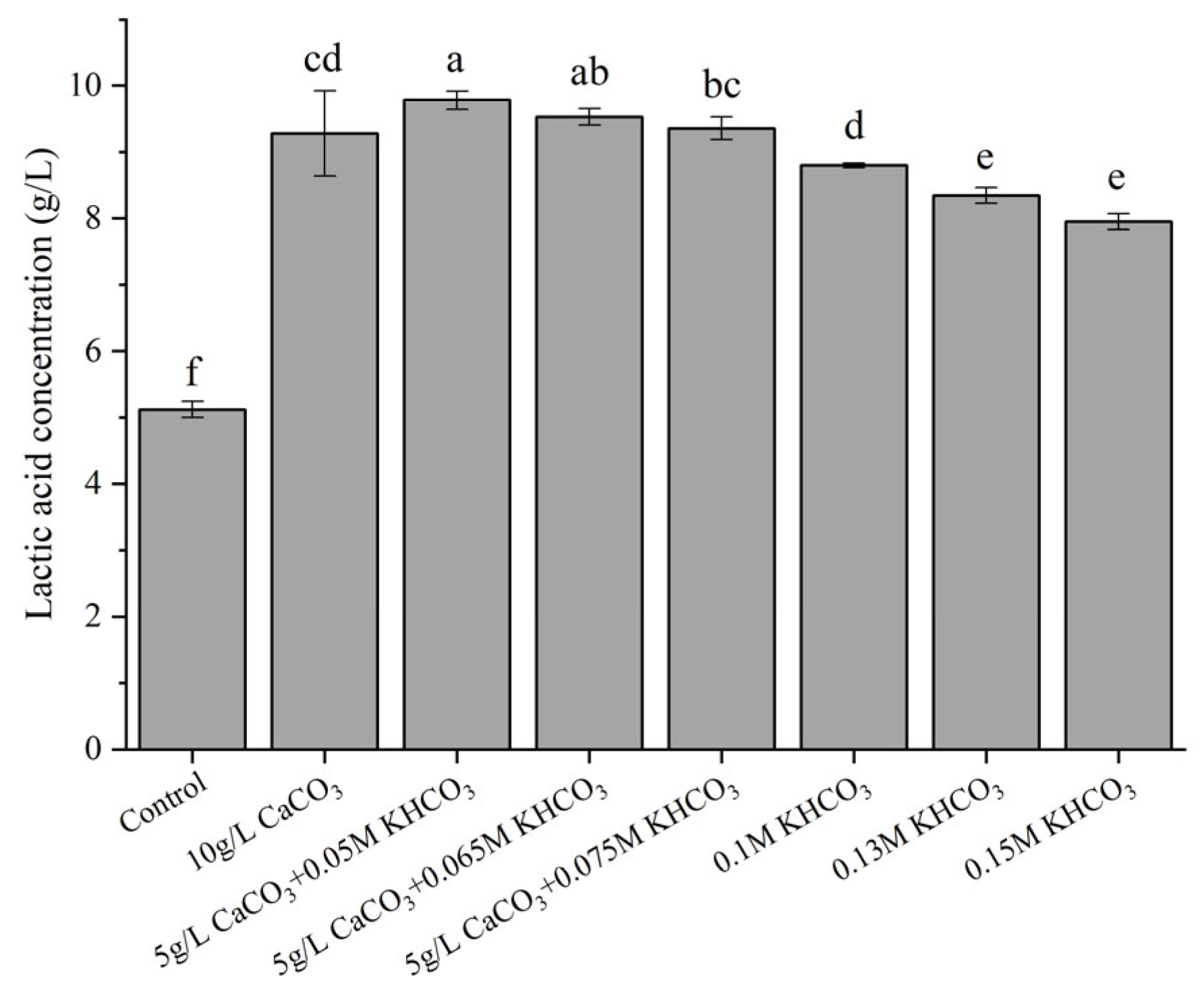
Given that the production of LA would acidify the medium, a series of neutralizers were tested for optimal LA production. As shown in Figure 3, without a neutralizer, the LA production was significantly lower (around 5.0 g/L; p < 0.05) than in those with neutralizers. Moreover, the LA concentration reached the maximum value (9.78 g/L) from 10 g/L glucose, when 5 g/L CaCO3 and 0.05 M KHCO3 was employed as the neutralizer, with the final pH around 5.3. An excessively high alkalinity reduced the LA production. For example, a neutralizer of 0.15 M KHCO3 gave approximately 8.00 g/L LA, and accordingly the final pH increased remarkably to 6.5.
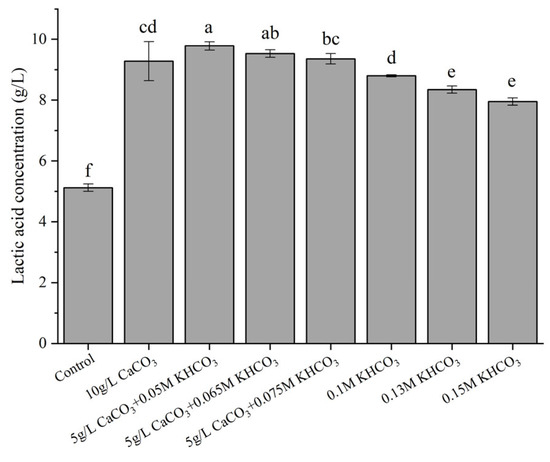
Figure 3.
Effects of various pH neutralizers on LA production. Fermentation was carried out at 30 °C for 24 h, with an initial glucose concentration of 10 g/L. Control represents the LA production by strain X1 in the absence of a neutralizer. Different letters on the bars are significantly different (p < 0.05).
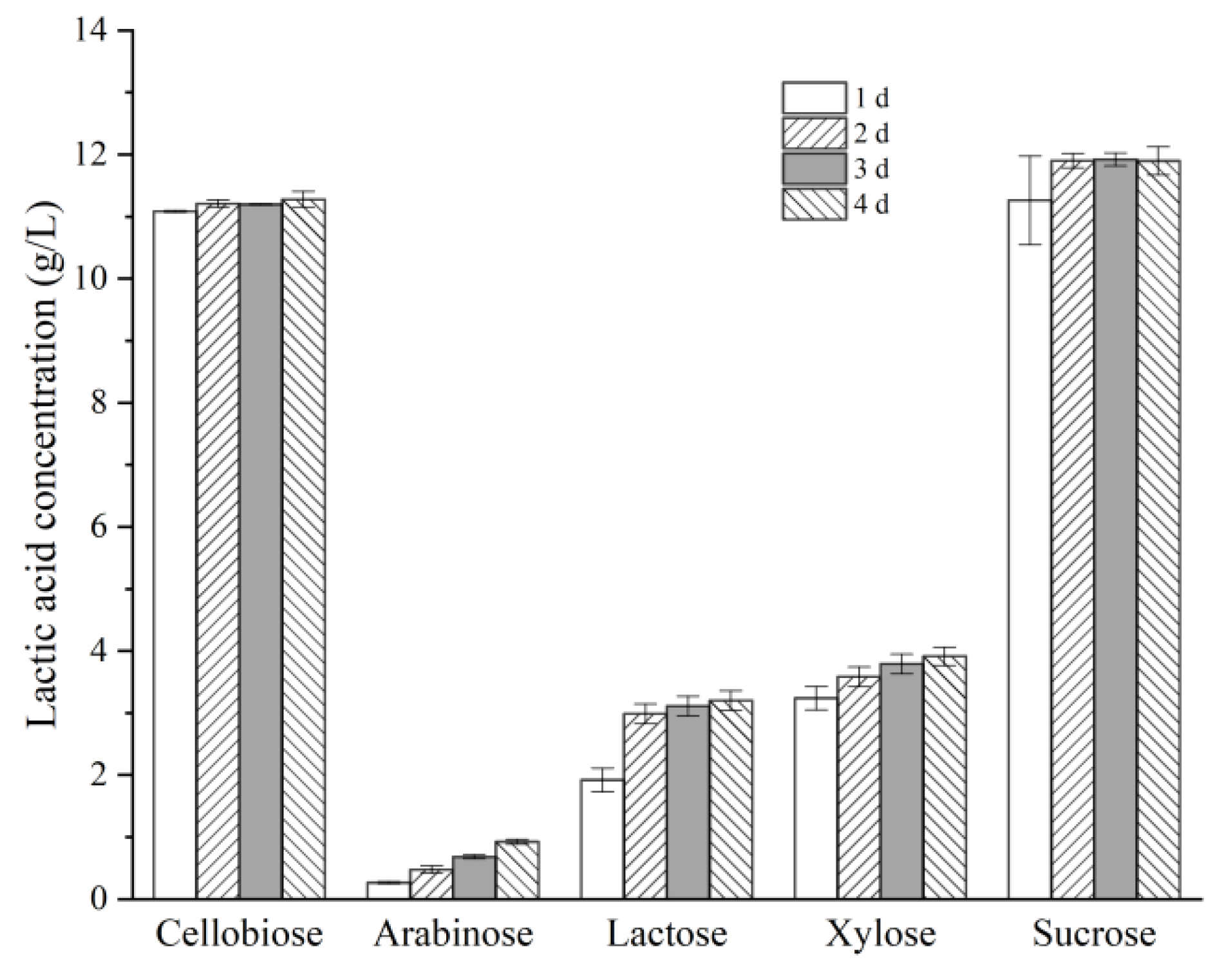
Bacteria usually exhibit distinct responses toward different types of carbon sources, such as hexoses and pentoses, disaccharides, and monosaccharides. Therefore, the effects of several carbon sources, such as: cellobiose, sucrose, xylose, lactose, and arabinose on the LA production by Lactococcus sp. X1 were investigated. As shown in Figure 4, the LA production from either cellobiose or sucrose was much higher than that from xylose, arabinose or lactose (11.0~12.0 g/L vs. below 4.0 g/L) at the same loads of substrates (10 g/L). The relative lower LA productions from these sugars were partially attributed to the low metabolism rates for them by this strain. The productivity of LA from xylose was only 0.14 g/L/h, as opposed to more than 0.46 g/L/h from sucrose as well as cellobiose. Moreover, a gradual accumulation of LA from these pentoses was observed over the course of 4 days. The LA yields from xylose gradually increased from 0.32 to 0.39 g/g during 1 to 4 days of incubation, and similarly the LA yields from arabinose grew from 0.03 to 0.09 g/g within the same time span. In addition, these pentoses were still not fully used after four days’ incubation (92% and 73% utilization for xylose and arabinose, respectively), and acetic acid accumulated along with LA at a molar ratio of approximately 1.3:1 for xylose, and as high as 4.3:1 for arabinose. By comparison, cellobiose and sucrose (10 g/L) were nearly fully depleted within one day, and no acetic acid released. Moreover, that X1 showed quite limited activity on lactose was probably due to its long-term adaptation to lignocellulose-derived sugars in the habitat.
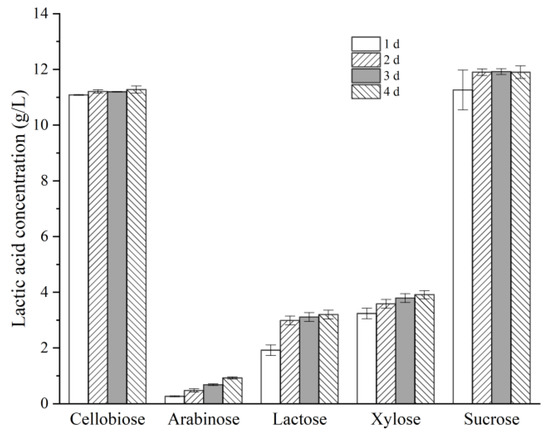
Figure 4.
Effects of different carbon sources on LA production by strain X1. Fermentation was carried out at 30 °C for various time spans, with an initial substrate concentration of 10 g/L.
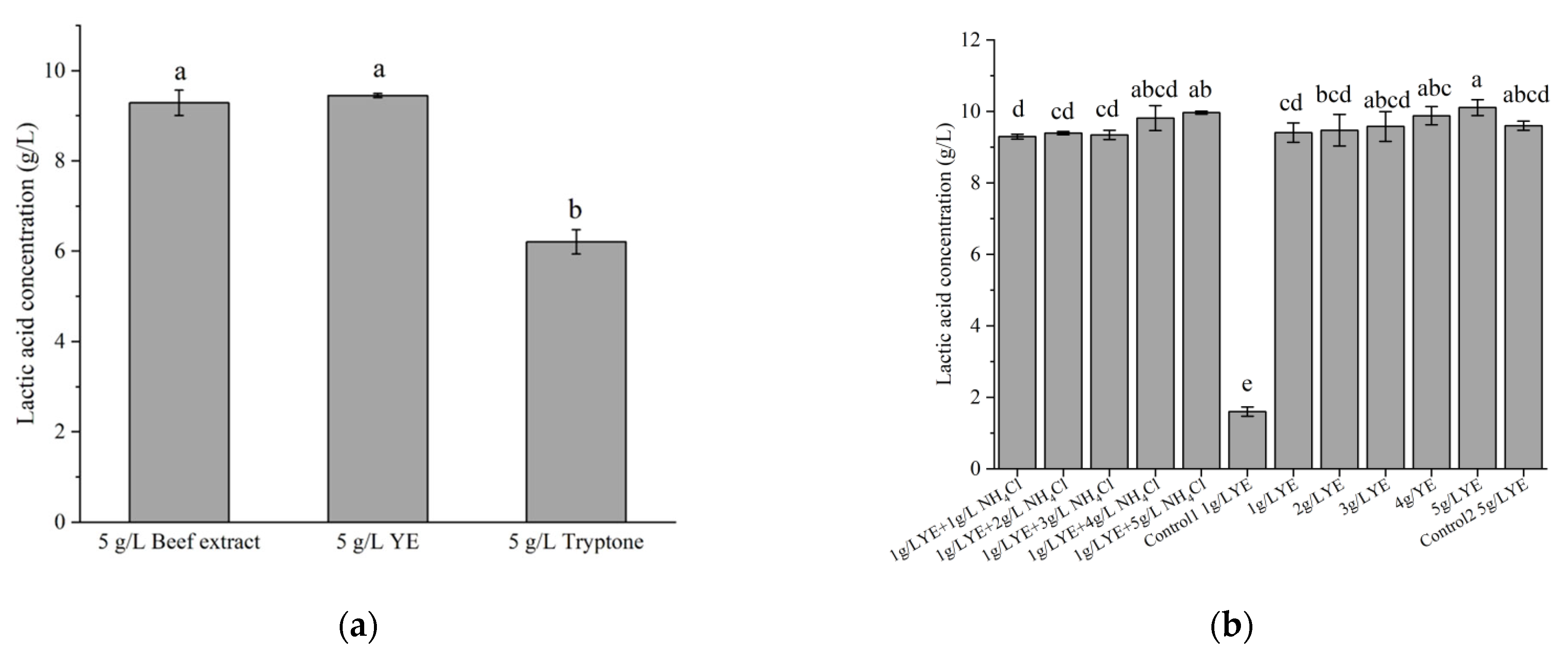
The effects of different types and amounts of nitrogen sources were also evaluated for LA production. Both YE and beef extract were found to be suitable nitrogen sources for the production of LA by strain X1; in contrast, tryptone was not an effective nitrogen source, as its LA production was significantly lower than the former two (p < 0.05). In this work, we chose to use YE as the nitrogen source, although beef extract also allowed very close LA production from 10 g/L glucose (Figure 5a). Subsequently, LA production was tested under low YE conditions. Figure 5b shows that the LA production increased gradually along with YE concentration, and that the LA production at 1 g/L YE was slightly lower (6.9%) than that at 5 g/L YE; meanwhile, the final OD600 were also lower (1.05) than that at 5 g/L YE (1.35), indicating an insufficiency of 1 g/L YE for the cell growth. However, a supplement of 5 g/L of NH4Cl restored the LA production at 1 g/L YE, suggesting that strain X1 can function well at a low load of complex nitrogen sources in the presence of sufficient ammonium; whereas strain X1 did not grow in the absence of YE. By contrast, an industrially important strain, L. pentosus ATCC 8041, was found to produce only 1.6 g/L LA in the presence of 1 g/L YE and 10 g/L glucose, while it produced up to 9.3 g/L LA in the presence of 5 g/L YE and 10 g/L glucose under the same condition. The performances of these two strains at low YE supplement were thus quite different.
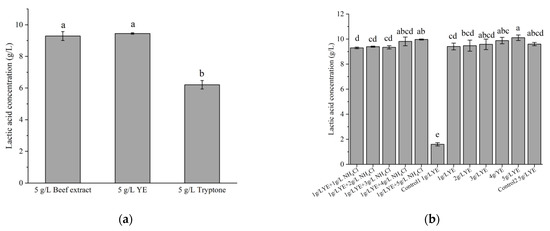
Figure 5.
Effects of some complex nitrogen sources (a) and ammonium salt (b) on LA production. Fermentation was carried out at 30 °C for 24 h, with an initial glucose concentration of 10 g/L. Control1 and Control2 were the LA production using L. pentosus ATCC 8041 in the presence of 1 or 5 g/L YE, respectively. Different letters on the bars are significantly different (p < 0.05).
3.3. Fermentation of High Concentration Substrates
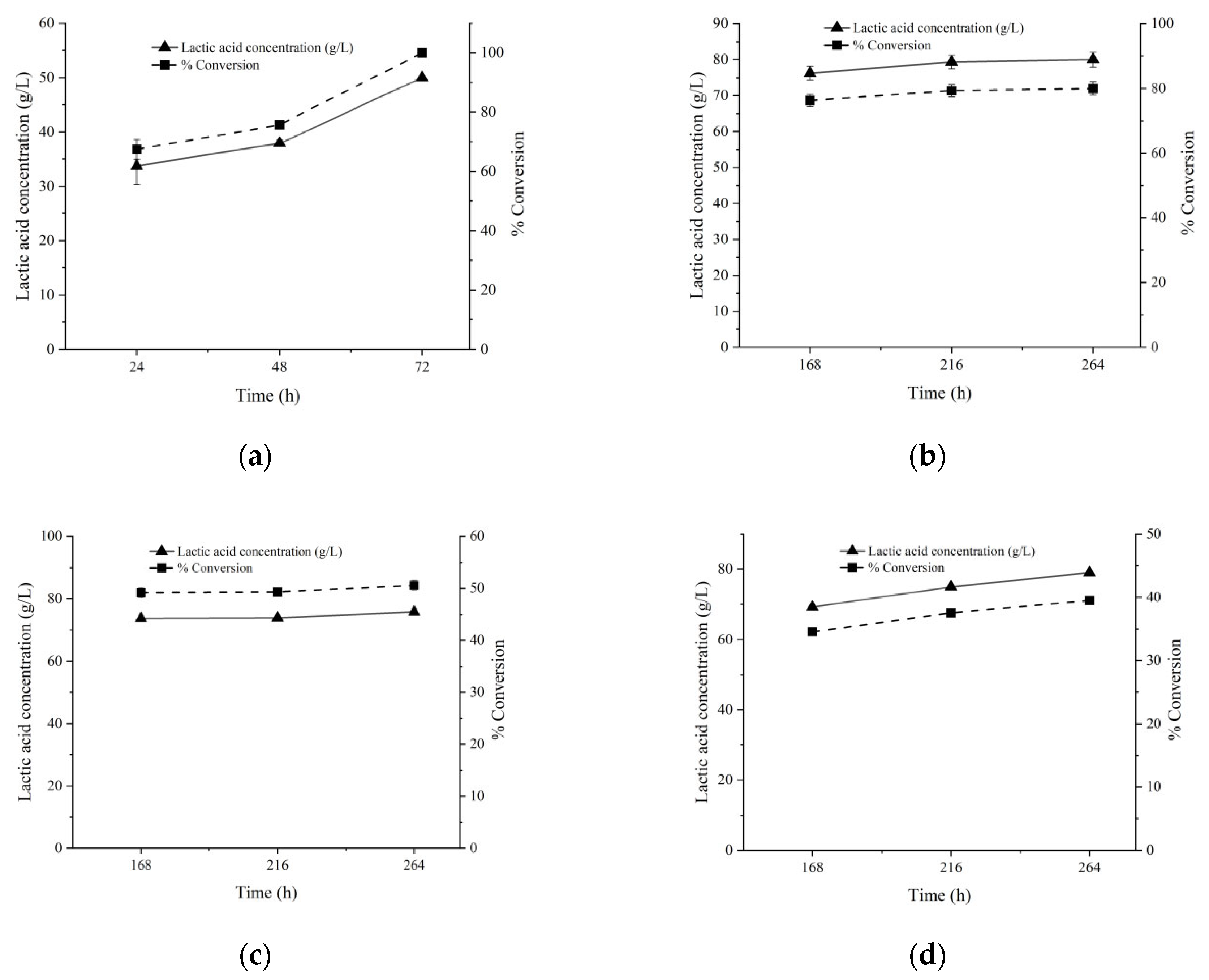
Figure 6 shows the LA production at higher substrate loads. The complete degradation of 50 g/L glucose was achieved within three days, and the LA yield was as high as 99.9% (Figure 6a). In addition, the fermentation product contained essentially L-lactic acid (95.1%), as determined by using an L-lactic acid quantification kit. The LA production from 100 g/L sucrose reached 79.8 g/L (75.8% of the theoretical value) after nine days’ incubation (Figure 6b), but still sucrose was not fully utilized. A prolonged incubation to 11 days only slightly increased the LA production. Furthermore, no more LA production could be obtained from higher substrate loads (150 and 200 g/L sucrose) during the same time span, and the LA productions may be even lower than those from 100 g/L sucrose, suggesting the possibility of inhibition by an overly high load of substrates (Figure 6c,d).
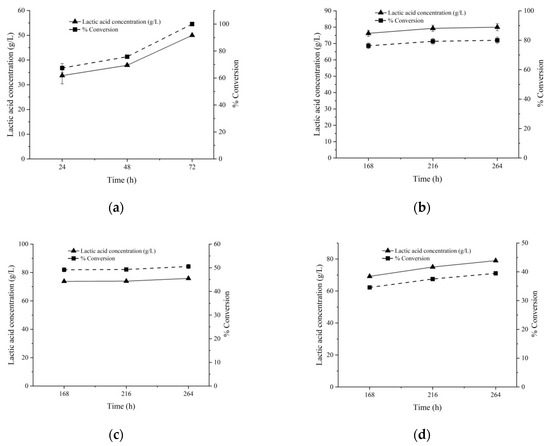
Figure 6.
Effects of high loads of substrates on LA production. Either 50 g/L Glucose (a), 100 g/L sucrose (b), 150 g/L sucrose (c), or 200 g/L sucrose (d) was supplemented as substrates. Calcium carbonate was supplemented at 0.5 g/g substrate, and an additional 0.05 M KHCO3 was also added together as the pH neutralizer.
3.4. SSF of Corncob for LA Production
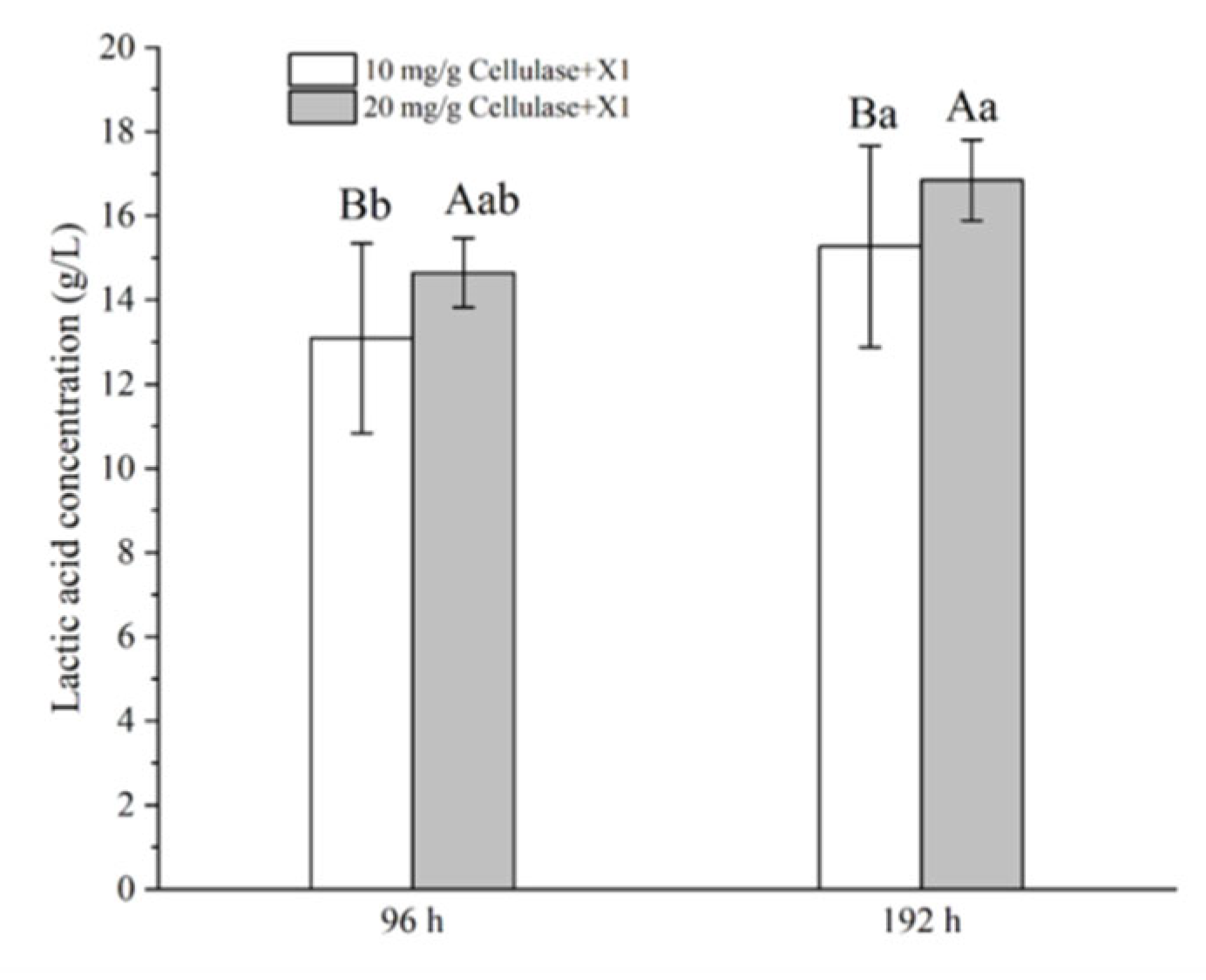
Strain X1 was also tested for the potential of direct LA production from biomass by a strategy of SSF. As shown in Figure 7, the LA productions were 13.1 and 14.6 g/L after 96 h of SSF of 50 g/L pretreated corncob at 35 °C in the presence of a cellulase, CTec2, at 10 and 20 mg/g substrate, respectively. Moreover, the LA production increased significantly further to 15.3 and 16.8 g/L after 192 h of SSF, respectively, namely 306 and 336 mg/g corncob, respectively (p < 0.05). These results suggested that strain X1 functioned well under the SSF strategy, and either an elevated enzyme load or a prolonged incubation period benefited the LA accumulation.
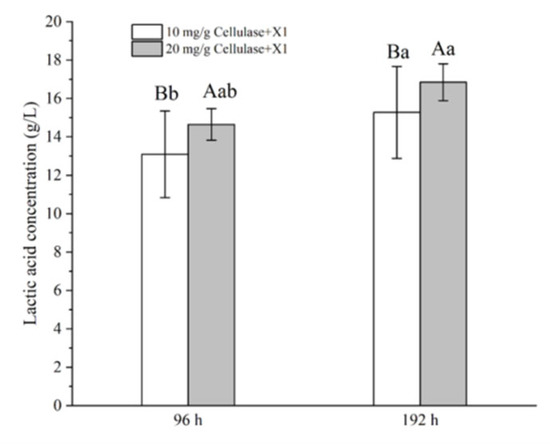
Figure 7.
SSF of pretreated corncob for LA production by Lactococcus sp. X1 supplemented with a cellulase, CTec2. SSF was carried out at 35 °C for 96 or 192 h, with an initial substrate concentration of 50 g/L. Calcium carbonate was supplemented at 0.5 g/g substrate, and an additional 0.05 M KHCO3 was also added together as the pH neutralizer. Different letters on the bars are significantly different.
3.5. Vitamin Identification
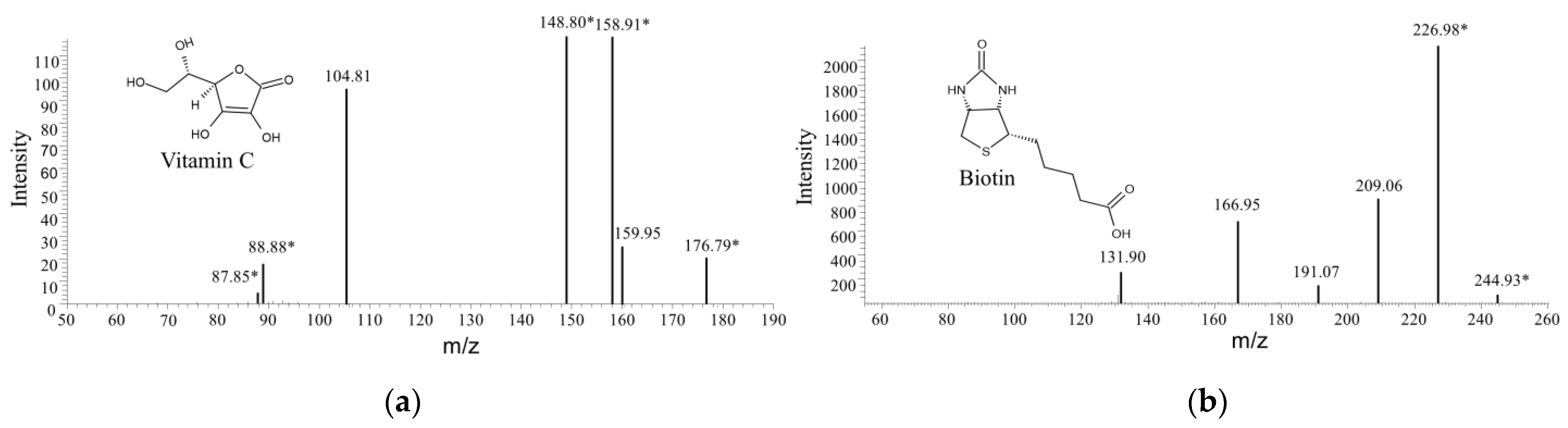
LAB are known probiotic microbes and some of them are able to produce one or more kinds of vitamins; therefore, the water-soluble vitamins that were produced by strain X1 during the fermentation process were determined by LC-ITMS. Molecules were readily protonated during ionization process to form a protonated molecular ion [M + H]+ under acidic condition in positive-ion mode. Ions at m/z of 177.1 and 245.10 were identified as vitamin C and Biotin, respectively, and were further justified by the secondary fragments according to the human metabolome database (Figure 8). By contrast, these two compounds were not detected in the blank control medium. The strong intensity of biotin in the mass spectrometry demonstrated it to be a major vitamin product by strain X1.
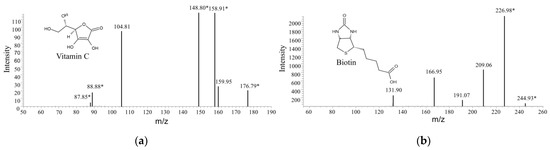
Figure 8.
Secondary ion mass spectrometry of two kinds of water-soluble vitamins in the supernatant of culture of Lactococcus sp. X1. (a) vitamin C, and (b) biotin. Asterisks after the m/z values indicate potential secondary ion fragments.
4. Discussion
Our work suggested that Lactococcus sp. X1 is a mutualistic bacterium for termite C. formosanus. The latter, along with some cellulolytic symbionts, decomposes wood particles into cellobiose, glucose, xylose, etc., which could be utilized by the former; meanwhile, the former releases two kinds of vitamins, which could be valuable nutrition factors for the latter (Figure 8). As a matter of fact, some very close Lactococcus spp. have also been identified through uncultured 16S rDNA sequencing method in the gut of C. formosanus, which were sampled from North America [20]. Moreover, the nearest neighbors of strain X1 were essentially insect symbionts (Figure 2), suggesting a close relation between this Lactococcus cluster and insects. In addition, some Lactococcus species have been reported to produce vitamin B2 [21], K2 [22], or folate [23]. By contrast, Lactococcus X1 was found to be able to produce quite different kinds of nutrition factors, including biotin and vitamins C. Furthermore, some Lactococcus may even consume vitamins [24]. To this end, the unique vitamin production capability of strain X1 thus might play crucial role in the nourishment of termites, and thus is also of great interest for application as a food additive.
Lactococcus sp. X1 could be classified as a facultative heterofermentative bacterium. It was able to convert 1 mol of hexoses into approximately 2 mol of lactic acid, and 1 mol of xylose into approximately 1 mol of lactic acid as well as 1 mol of acetic acid. Furthermore, as a prevalent gene regulator, arabinose may have further triggered the partial decomposition of LA into acetic acid, leading to a much higher ratio of acetic acid to LA (4.3:1). Hence, it is most probable that strain X1 metabolizes hexoses via the Embden-Meyerhoff-Parnas pathway, and pentoses via the phosphoketolase pathway (PK) [25]. Like most microbes, strain X1 consumes pentoses much slower than hexoses, and some Lactococcus were even found unable to uptake xylose [26,27]. The reason for this is probably the low expression levels of several genes involved in the PK pathway. The performance of strain X1 on xylose might be improved by adaptive evolution in xylose medium. For example, adaptive evolution during repeated growth and transfer among high loads of xylose medium resulted in a mutant that up-regulated the expression of a xylose isomerase gene, and in turn significantly increased the utilization speed of xylose in Escherichia coli [28].
Strain X1 holds great potential for the conversion of sugars into lactic acids under high-load conditions (~100 g/L). Table 1 compares the LA-fermentation profiles of several kinds of efficient LA-producers under high substrate loads, and the performance of strain X1 was comparable to these species. However, LA production increased to a minor extent when the substrate concentration was further increased from 100 to 200 g/L (Figure 6b); probably because high concentration of substrate (150~200 g/L) and products might have inhibited the activity of the strain. As a matter of fact, the inhibition effect by high concentration of substrates and products of a closely related species, Lactococcus lactis, had been revealed and modeled by Åkerberg et al. [29]. In addition, the low requirement of nutrition is a valuable factor of strain X1, which accomplished the full fermentation of 100 g/L of glucose in the presence of a total amount of 5 g/L complex nitrogen sources, compared to at least 10 g/L by other strains [25,29,30,31]. Moreover, the complex nitrogen sources could be further substituted by 1 g/L YE plus 4 g/L NH4Cl (Figure 5b), which might in turn cut down the cost of LA production.

Table 1.
Literature reported for lactic acid production by lactic acid bacteria.
Strain X1 is also a good candidate for the SSF of lignocellulose biomass for LA production. It is known that one of the major bottlenecks in the hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass by cellulase is the inhibition of cellulase by glucose, cellobiose, and other oligo sugars, which significantly slows down the hydrolysis rate [32]. To circumvent this bottleneck, it is advantageous to use an SSF strategy where the biomass is synchronously hydrolyzed and fermented into various products. To the best of our knowledge, quite few wild LAB were able to uptake both cellobiose and xylose, except for some genetically modified strains [32,33]. It was good to see that Lactococcus sp. X1 can substantially utilize these sugars, which demonstrated that Lactococcus sp. X1 is a potential candidate strain for effective LA production from lignocellulose by employing the SSF strategy. It is known that a series of bacteria were able to produce LA from different kinds of lignocellulosic biomass in the SSF or in the separate hydrolysis and fermentation (SHF) mode (Table 2). Some Bacillus were able to grow at elevated temperatures, which fit well with the optimal condition of commercial cellulases [34,35,36]. In contrast, LAB usually produce LA in SSF mode at 30 to 35 °C. Nevertheless, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. delbrueckii IFO 3202 managed to produce LA from defatted rice bran in the presence of amylase and cellulase at a yield of 0.28 g/g [37], and Lc. lactis IO-1 achieved an LA yield of 0.36 g/g from acid-hydrolyzed sugarcane bagasse [38]. In this study, the LA yield (0.34 g/g) from the SSF of corncob by strain X1 is comparable to them. Furthermore, remarkably higher yields of LA might be achieved by employing harsher and more efficient pretreatment methods. For example, Hu et al. [36] obtained a high LA yield of 0.68 g/g by using finely milled corncob (<100 mesh); and similarly Karnaouri et al. [39] achieved an LA yield of 0.69 g/g through oxidative organosolv pretreatment of beech wood. Meanwhile, biomass itself is also an unneglectable factor on LA yields. For instance, distinct LA yields on beech wood and pine (0.69 vs. 0.40 g/g, respectively) were observed by employing the same pretreatment method as well as an identical strain [39] (Table 2). It should be mentioned that a high LA yield may correlate not only to the metabolic engineering of a specific microbe, but also to the biomass types, pretreatment efficiency, saccharification yields, etc. Furthermore, future studies may focus on random mutagenesis of strain X1 by various mutagens to improve its performance, such as its pentose metabolism capabilities, as well as the yield on pentose.

Table 2.
Literature reported for LA fermentation of different types of lignocellulosic biomass by various strains.
5. Conclusions
Lactococcus sp. X1 is an efficient facultative heterofermentative LA producer that can utilize a series of disaccharides and monosaccharides. It is also an important symbiont for termites due to its unique vitamin excretion capability. Considering the merits of vitamin generation and the relatively lower requirement of complex nitrogen sources, Lactococcus sp. X1 holds promise for multipurpose application in industry.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.L. and A.G.; data tabulation, Y.F. and X.L.; formal analysis, Z.T. and R.X.; supervision, J.S.; writing—original draft preparation, N.L. and A.G.; writing—review and editing, A.G. and X.L.; funding acquisition, J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFE0107100). X.L. acknowledges the support of the Jiangsu Agriculture Science and Technology Innovation Fund (JASTIF) (CX(22)2045). R.X. and X.L. acknowledges the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31900367 and 32101444, respectively).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data sets used and analyzed are available on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rawoof, S.A.A.; Kumar, P.S.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Devaraj, K.; Mani, Y.; Devaraj, T.; Subramanian, S. Production of optically pure lactic acid by microbial fermentation: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tashiro, Y.; Sonomoto, K. Fermentative production of lactic acid from renewable materials: Recent achievements, prospects, and limits. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 119, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, N.; Oba, M.; Iwamoto, M.; Tashiro, Y.; Noguchi, T.; Bonkohara, K.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Zendo, T.; Shimoda, M.; Sakai, K.; et al. L-Lactic acid production from glycerol coupled with acetic acid metabolism by Enterococcus faecalis without carbon loss. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 121, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhvi, M.; Zendo, T.; Sonomoto, K. Free lactic acid production under acidic conditions by lactic acid bacteria strains: Challenges and future prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 5911–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, J.; Kim, J.-S.; Choi, K.R.; Eun, H.; Yang, D.; Ko, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-J. Application of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) in sustainable agriculture: Advantages and limitations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.R.; Gauttam, R.; Fong, B.; Chen, Y.; Lim, H.G.; Feist, A.M.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Petzold, C.J.; Simmons, B.A.; Singer, S.W. Revealing oxidative pentose metabolism in new Pseudomonas putida isolates. Environ. Microbiol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, S.K.; Dhawaria, M.; Tripathi, D.; Raturi, V.; Adhikari, D.K.; Kanaujia, P.K. Investigation of lignin biodegradation by Trabulsiella sp. isolated from termite gut. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 112, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsegaye, B.; Balomajumder, C.; Roy, P. Isolation and characterization of novel lignolytic, cellulolytic, and hemicellulolytic bacteria from wood-feeding termite Cryptotermes brevis. Int. Microbiol. 2019, 22, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Aihara, C.; Yuki, M.; Katsuhara, M.; Ohkuma, M. Lactococcus termiticola sp. nov., isolated from the gut of the wood-feeding higher termite Nasutitermes takasagoensis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3832–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashiguchi, D.T.; Husseneder, C.; Grace, J.K.; Berestecky, J.M. Pilibacter termitis gen. nov., sp. nov., a lactic acid bacterium from the hindgut of the Formosan subterranean termite (Coptotermes formosanus). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.M.; Yang, H. Lactococcus nasutitermitis sp. nov. isolated from a termite gut. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, M.; Sakamoto, M.; Nishimura, Y.; Ohkuma, M. Lactococcus reticulitermitis sp. nov., isolated from the gut of the subterranean termite Reticulitermes speratus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhu, J.; Tong, Y.; Kong, Y.; Tan, C.; Wang, M.; Wan, M.; Meng, X. Antibacterial characteristics and mechanisms of action of Aronia melanocarpa anthocyanins against Escherichia coli. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 150, 112018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajabadi, N.; Mardan, M.; Abdul Manap, M.Y.; Shuhaimi, M.; Meimandipour, A.; Nateghi, L.J.A. Detection and identification of Lactobacillus bacteria found in the honey stomach of the giant honeybee Apis dorsata. Apidologie 2011, 42, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Yong, Q.; Yang, S.-T.; Ouyang, J.; Yu, S. Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of xylo-oligosaccharides manufacturing waste residue for L-lactic acid production by Rhizopus oryzae. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 94, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, A.; Wu, J.; Xie, R.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Chang, F.; Sun, J. Highly thermostable GH51 α-arabinofuranosidase from Hungateiclostridium clariflavum DSM 19732. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3783–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Pan, S.; Yu, X. Simultaneous determination of eight water-soluble vitamins in formula food for special medical purpose using ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Mod. Food 2021, 27, 164–167. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, J.; Cho, H.; Tamura, T.; Saitou, S.; Park, K.; Kim, J.S.; Hong, S.B.; Kwon, S.W.; Kim, S.J. Lactococcus allomyrinae sp. nov., isolated from gut of larvae of Allomyrina dichotoma. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 3682–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhe, C.V.; Sethi, A.; Delatte, J.; Husseneder, C. Isolation and assessment of gut bacteria from the Formosan subterranean termite, Coptotermes formosanus (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae), for paratransgenesis research and application. Insect Sci. 2017, 24, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, C.; O’Connell-Motherway, M.; Sybesma, W.; Hugenholtz, J.; van Sinderen, D. Riboflavin production in Lactococcus lactis: Potential for in situ production of vitamin-enriched foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5769–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Van Bennekom, E.O.; Zhang, Y.; Abee, T.; Smid, E.J. Long-chain vitamin K2 production in Lactococcus lactis is influenced by temperature, carbon source, aeration and mode of energy metabolism. Microb. Cell Fact. 2019, 18, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangadharan, D.; Nampoothiri, K.M. Folate production using Lactococcus lactis ssp cremoris with implications for fortification of skim milk and fruit juices. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1859–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.Y.; Lee, C.; Seo, M.J.; Roh, S.W.; Lee, S.H. Characterization of a potential probiotic bacterium Lactococcus raffinolactis WiKim0068 isolated from fermented vegetable using genomic and in vitro analyses. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wischral, D.; Arias, J.M.; Modesto, L.F.; de Franca Passos, D.; Pereira, N., Jr. Lactic acid production from sugarcane bagasse hydrolysates by Lactobacillus pentosus: Integrating xylose and glucose fermentation. Biotechnol. Prog. 2019, 35, e2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yang, J.; Pang, H.; Kitahara, M. Lactococcus fujiensis sp. nov. A lactic acid bacterium isolated from vegetable matter. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 1590–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passerini, D.; Coddeville, M.; Le Bourgeois, P.; Loubiere, P.; Ritzenthaler, P.; Fontagne-Faucher, C.; Daveran-Mingot, M.L.; Cocaign-Bousquet, M. The carbohydrate metabolism signature of Lactococcus lactis strain A12 reveals its sourdough ecosystem origin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5844–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.M.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.J. Efficient anaerobic consumption of D-xylose by E. coli BL21(DE3) via xylR adaptive mutation. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerberg, C.; Hofvendahl, K.; Zacchi, G.; Hahn-Hägerdal, B. Modelling the influence of pH, temperature, glucose and lactic acid concentrations on the kinetics of lactic acid production by Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis ATCC 19435 in whole-wheat flour. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 49, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, K.; Zhang, Q.; Shinkawa, S.; Yoshida, S.; Tanaka, T.; Fukuda, H.; Kondo, A. Efficient production of optically pure D-lactic acid from raw corn starch by using a genetically modified L-lactate dehydrogenase gene-deficient and α-amylase-secreting Lactobacillus plantarum strain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, G.; Moldes, A.B.; Alonso, J.L.; Vázquez, M. Optimization of D-lactic acid production by Lactobacillus coryniformis using response surface methodology. Food Microbiol. 2004, 21, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adsul, M.; Khire, J.; Bastawde, K.; Gokhale, D. Production of lactic acid from cellobiose and cellotriose by Lactobacillus delbrueckii mutant Uc-3. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5055–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhvi, M.; Joshi, D.; Adsul, M.; Varma, A.; Gokhale, D. D-(−)-Lactic acid production from cellobiose and cellulose by Lactobacillus lactis mutant RM2-2 4. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, K.M.; Liu, S.; Hughes, S.R.; Rich, J.O. Fermentation of corn fiber hydrolysate to lactic acid by the moderate thermophile Bacillus coagulans. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, J.; Qi, B.; Wan, Y. An efficient process for lactic acid production from wheat straw by a newly isolated Bacillus coagulans strain IPE22. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 158, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, S.; Mei, Y.; Liang, Y.; Peng, N. High-titer lactic acid production from NaOH-pretreated corn stover by Bacillus coagulans LA204 using fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and fermentation under non-sterile condition. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Hoshina, M.; Tanabe, S.; Sakai, K.; Ohtsubo, S.; Taniguchi, M. Production of D-lactic acid from defatted rice bran by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laopaiboon, P.; Thani, A.; Leelavatcharamas, V.; Laopaiboon, L. Acid hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse for lactic acid production. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnaouri, A.; Asimakopoulou, G.; Kalogiannis, K.G.; Lappas, A.; Topakas, E. Efficient D-lactic acid production by Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus through conversion of organosolv pretreated lignocellulosic biomass. Biomass Bioenerg. 2020, 140, 105672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).