Abstract
In the last few decades, lifestyle changes and the awareness of the importance of a balanced diet have led the population to increase the consumption of beverages based on fruit juices and/or vegetables. Fruit and vegetables contain health-related compounds that can impact on physiological processes, thus reducing the risk of certain diseases and improving the overall health status. Consumer demand for more appealing and tasting beverages has also increased. In this sense, fortification of beverages with health-related ingredients and/or flavors arises as a potential strategy for the development of new beverage-based products. Nevertheless, most of those compounds are not soluble in water, thus their incorporation in aqueous food systems, such as beverages, requires an emulsification step. Beverage emulsions are concentrated emulsified systems designed to be further diluted and/or incorporated in beverages and drinks as carriers of water insoluble ingredients. This review article aims at discussing the main key aspects of beverage emulsion formulation and their colloidal stability after being added to complex food systems.
1. Introduction
Fruit and vegetables contain small quantities of water insoluble health-related compounds that are known to have beneficial effects on human health. They mainly belong to families of carotenoids, polyphenols, fatty acids and vitamins which are capable of modulating metabolic processes and can present antioxidant activity [1,2,3]. Therefore, a nutritious, well-balanced diet rich in fruit and vegetables may result in a reduction of diseases such as cardiovascular diseases and cancer [4,5]. Moreover, some of those natural compounds present an attractive color, which would make them useful to obtain visually appealing food. In that sense, food industries have focused on the addition of natural ingredients in order to obtain healthier products which still have attractive characteristics for consumers.
Nevertheless, consumers not only look for healthy and colorful products but also for tastiness and flavor in their choice of diet. Thus, food acceptance by consumers depends, among other factors, on the sensory attributes of the final product [6]. Flavor oils are natural compounds obtained from plants and herbs that are added to food to enhance their taste and aroma [7]. The most commonly used flavor oils in the food industry are citrus oils such as orange and lemon oil. They are isolated from citrus peel by cold pressing and refined by distillation. Besides citrus flavor oils, other aromatic oils from herbs and spices may also be interesting ingredients to be incorporated into beverages. Differences in the origin of each flavor oil implies changes in their physicochemical properties such as water solubility, density, viscosity and optical properties [8].
Beverages are of great importance within the food industry as they are versatile products able to fulfill several consumer needs because of their appearance and their easy storage and distribution. In addition, beverage fortification with health-related compounds and/or flavor oils can increase nutritional value, preventing consumers from contracting certain health-related diseases and improve sensory perceptions [9]. Nevertheless, beverage fortification with these compounds presents some limitations. The beverage matrix consists mainly of water and therefore the incorporation of water insoluble health-related compounds and/or flavor oils to beverages represents a challenge for researchers and requires an emulsification step. In addition, these functional compounds may be degraded after their addition to foods since they may undergo several physicochemical stresses during food manufacturing and storage. In this regard, these functional compounds may be sensitive to environmental changes such as pH, temperature and the presence of minerals, thus their shelf-life depends on processing and storage conditions. As a result, health-related compounds can lose their properties due to oxidative processes and other processes. Similarly, flavor compounds undergo chemical changes such as oxidation, hydrolysis and thermal degradation, resulting in off-flavors. Therefore, designing novel strategies in order to facilitate the dispersion of water insoluble functional ingredients in aqueous food systems as well as protecting them from instability mechanisms and degradation processes is required. Beverage emulsions arise as concentrated emulsified systems designed to carry and protect those water insoluble ingredients to be incorporated in beverages and drinks (Figure 1).
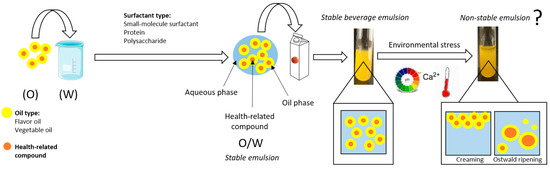
Figure 1.
Scheme of beverage fortification with oil-in-water emulsions and their colloidal stability during manufacturing and storage.
The aim of this contribution is to outline the current developments of beverage emulsion formation as well as discussing the factors affecting their physicochemical and colloidal stability.
2. Beverage Emulsions
Oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions consist of an oil phase dispersed into a water phase. Emulsions are thermodynamically unstable systems and they tend to separate over time. In this regard, the use of emulsifiers is required in order to stabilize the oil/water interface and maintain oil droplets dispersed in the aqueous phase. Emulsifiers are surface-active amphiphilic molecules which have water soluble and water insoluble parts. For that reason, they have the ability to adsorb at the oil-in-water interface during emulsification, avoiding droplets re-coalescence. Emulsifiers also decrease the interfacial tension between the oil and the water phase, thus facilitating the oil emulsification. For the dispersion of the oil phase in smaller oil droplets, the application of mechanical forces is needed. During homogenization, the breakdown of droplets occurs, resulting in a decrease in the droplet size, which in turn leads to more stable emulsions [10,11]. This breakdown is typically achieved by high-energy methods, such as high-speed blenders, high-pressure valve homogenizers or microfluidizers. In these types of homogenization devices, high shear stress and compression forces are induced, which result in droplet deformation and subsequent disruption. In addition, the reduction of droplet size and the subsequent increase in surface area of nanodroplets might facilitate the health-related compound and/or flavor oil liberation, increasing the functionality of those compounds [12].
In the particular case of beverage emulsions, a concentrated (10–30%) O/W emulsion is formed to be further diluted and/or incorporated in beverages and drinks as carriers of water insoluble ingredients [13]. One of the most important challenges to be faced for the formulation of beverage emulsions is to guarantee their physicochemical stability. Beverage emulsion instabilities are normally caused by some physicochemical mechanisms, such as creaming, sedimentation, Ostwald ripening and flocculation which normally ends with coalescence. Creaming or sedimentation are gravitational separations caused by density differences between the oil and the water phases. As a result, oil droplets migrate to the top (creaming) or to the bottom (sedimentation), yet the latter is less likely to occur in oil-in-water emulsions. By contrast, flocculation refers to the formation of oil droplet aggregates. Moreover, flocculation may lead to coalescence, the process by which oil droplets merge, resulting in a larger droplets [13]. Finally, Ostwald ripening, consists of the growing of large droplets, via the diffusion of lipid molecules through the water until they deposit into larger oil droplets [13]. In order to avoid such instability mechanisms, the proper selection of the emulsifier and the homogenization mechanism is of crucial importance.
3. Formulation of Beverage Emulsions
Beverage emulsions formulation contain at least three principal components: An aqueous phase, an oil phase and an emulsifier and/or stabilizer. Firstly, the aqueous phase represents the major constituent of an emulsion and might contain a variety of water-soluble constituents, such as minerals, acids, bases, flavors, preservatives, vitamins, sugars, surfactants, proteins or polysaccharides. Secondly, the lipid phase acts as a carrier of the water insoluble compounds to be incorporated into the beverages, such as carotenes, fat-soluble vitamins, plant essential oils, among others. Finally, emulsifiers and stabilizers facilitate the dispersion of oil droplets in water through the reduction of the oil/water interfacial tension. In this section the emulsion main components are discussed in relation with their stability and functionality.
3.1. Effect of Oil Type on Beverage Emulsion Formation and Stability
The dispersed phase of beverage emulsions consists of oil droplets that might in turn act as a carrier of oil-soluble compounds such as flavors, colors, antioxidants, vitamins and/or density-adjusting agents. The most commonly used oils in beverage emulsions are vegetable oils, however flavor oils can also be used as aromatic and flavoring ingredients. Vegetable oils are obtained from a wide range of vegetables, nuts or seeds and their composition and properties largely depend on their origin. Vegetable oils and flavor oils differ in the chain length of the fatty acids of the triglyceride. Vegetable oils are mostly composed of long-chain fatty acids (C18) and medium-chain fatty acids (C12-C14) while flavor oils mainly contain short-chain fatty acids (<C10). This characteristic highly determines their behavior during emulsion formation and stabilization. Moreover, other physicochemical characteristics of the different types of oils, such as viscosity, refractive index, density and water solubility might also have an impact on emulsion properties.
In general, short-chain triglycerides are capable of forming emulsions with droplet sizes as small as 10 nm, while with long-chain triglycerides, the smallest particle size is typically around 100 nm [14]. In this regard, Salvia-Trujillo et al. [11] formed nanoemulsions with different essential oils (lemongrass, clove, tea tree, thyme, geranium, marjoram, palmarosa, rosewood, sage and mint) obtaining droplet sizes in the nano-scale range, with values between 13.16 ± 0.92 and 86.49 ± 4.31 nm. This is due to the fact that the lower the viscosity of the oil phase, the easier to break-up the droplets by mechanical forces [15]. In general, long-chain triglycerides present high viscosity values, thus reducing their droplet size during emulsification by high-energy methods is less efficient than for oils with lower viscosity. Qian and McClements [16] showed that corn oil, with a viscosity of 30 mPa·s, presented particle sizes of 125 nm while increasing the percentage of octadecane in the lipid phase, which reduced the viscosity below 9 mPa·s, and the particle size decreased down to 90 nm.
Moreover, the visual appearance of emulsions is highly determined by the optical properties of the dispersed phase. The opacity of an emulsion varies depending on the refractive index of the oil phase. In turn, the refractive index varies directly with droplet size [17]. In this regard, small droplets scatter the light more weakly and therefore emulsions remain transparent, whereas larger droplets present an opaque appearance [13]. Thus, Zhao et al. [17] stated that emulsions formulated with orange flavor oil were more transparent than emulsions formulated with a mixture of the flavor oil and canola or corn oil, which had a higher turbidity. In this sense, the development of transparent emulsions may be interesting to meet market demands, as they can be added in clear drinks and beverages without disturbing their original appearance.
In addition, density differences between the oil and the aqueous phases have a direct impact in emulsion stability. Corn oil has a density (0.9188 g/cm3) closer to the aqueous phase density (~0.998 g/cm3) thus leading to stable emulsions [17]. Contrarily, differences between orange oil (0.8423 g/cm3) and aqueous phase densities are more pronounced making the emulsions more susceptible to phase separation (creaming). Nevertheless, the addition of oils mainly composed by long-chain fatty acids may help to equal the density of both phases. Meroni et al. [18] showed a retard creaming phenomena when the oil phase consisted of corn/orange oil with a density of 0.900 g/cm3. Similarly, Zhao et al. [17] showed that the addition of a medium-chain triglycerides (MCT) to orange oil emulsions inhibited destabilization phenomena.
Finally, the water solubility of the oil phase determines the overall stability of the emulsion. Some lipids, such as flavor oils, present a relatively high water solubility due to the presence of monoterpenes in their composition. This type of oils are highly prone to suffer Ostwald ripening, which leads to the diffusion of lipid material from small droplets into larger ones and consequently droplet size increases [19]. However, this destabilization phenomena may be prevented by adding a small amount of an oil with lower polarity into the lipid phase, which prevents the migration of lipid material though the aqueous phase. In fact, the addition of different vegetable oils (canola, coconut, corn, olive and sunflower) to the oil phase has been described in several research papers as an alternative to form more stable emulsions with smaller particle sizes, compared to those emulsions formulated with flavor oils alone (orange, lemon and thyme) [18,19]. Namely, Zhao et al. [17] obtained corn and canola/orange oil stable emulsions compared to those with orange oil or MCT/orange oil. This results confirm that the addition of a vegetable oil leads to a reduction of Ostwald ripening phenomena, thereby conferring the emulsions with higher physical stability [17,18].
3.2. Effect of Emulsifier and Stabilizer Type on Beverage Emulsion Formation and Stability
Emulsions require the presence of emulsifiers, which have the ability to adsorb and remain at the oil/water interface, thus forming a stable layer surrounding the oil droplet surface and preventing the breakdown of emulsions structure once it is formed [20]. There are a wide range of substances that can be potentially used as emulsifiers in food industry. Among them, small-molecule surfactants are those most commonly used to stabilize beverage products, as they adsorb rapidly at the oil/water interface due to the presence of a fatty acid in their molecular structure. Nevertheless, other molecules such as proteins, polysaccharides or other biopolymers may also present emulsion formation capacity even in the absence of fatty acid groups in their structure, since they present other functional groups capable of adsorption at the interface. Most of those emulsifiers used for emulsion stabilization are food-grade and are safe food additives. However, their use and maximum permitted doses are regulated by current legislation (EU 1333/2008).
Small-molecule surfactants include sucrose esters, polyoxyethylene sorbitan esters of monoglycerides (Tweens) and sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS), among others. Typically, low concentrations of small-molecule surfactants are capable of oil droplet emulsification as they have the ability to easily adsorb to the oil/water interface, lower the interfacial tension and therefore facilitate droplet disruption during mechanical processes [20,21]. In this sense, Salvia-Trujillo et al. [22] obtained lemongrass essential oil-Tween 80 emulsions with an average droplet size of 7.35 ± 1.67 nm. In addition, the strong adsorption of the surfactant at the oil/water interface contribute to enhance the stability via steric repulsions. Accordingly, Guerra et al. [23] showed that lemongrass and mandarin nanoemulsions presented no significant changes in particle size during storage (56 days). In general, the higher the surfactant concentration, the smaller the particle size of emulsions. Smaller particles have a larger interfacial area thus higher surfactant concentration is needed in order to cover all the interfacial surface [21]. Nevertheless, an excess of surfactant concentration may induce the opposite effect and cause droplet destabilization [24]. The presence of non-adsorbed small-molecule surfactant form micelles in the continuous phase, which may lead to an increase in attraction forces between the droplets and cause oil droplet destabilization. Therefore, proper selection of the ratio between oil and surfactant is crucial when formulating emulsions.
Although small-molecule surfactants are very effective emulsifiers, they are typically obtained synthetically. In this sense, there is a trend to replace them by emulsifiers of natural origin. Proteins from natural origin as well as certain types of polysaccharides have shown interfacial properties, thus being able to act as natural emulsifiers. Proteins especially from milk and eggs can act as emulsifiers, since it has been demonstrated that they can adsorb at the oil/water interface to protect emulsions from the destabilization phenomena. Nevertheless, proteins tend to adsorb less effectively at the oil/water interface in comparison with small molecule surfactant, so higher amounts of proteins need to be used for emulsion stabilization [25,26]. Recently, Raikos et al. [26] observed gravitational separation in sodium caseinate (SC)-stabilized emulsions mainly caused by a lack of surfactant concentration, whereas Tween 80-stabilized emulsions were stable at the same concentration. On the other hand, when the concentration of protein is enough to cover all the surface area, protein-stabilized emulsions are highly stable. Proteins exhibit a partial denaturation during adsorption, thus strengthening intramolecular interactions, which results in a higher emulsion stability via steric repulsion [24,27]. For instance, Whey Protein Isolate (WPI) and SC led to an increase of surface coverage with increasing protein concentration [27]. Nevertheless, despite their potential to adsorb at the oil/water interface, the electrostatic properties of proteins play a major role in the stabilization of oil-in-water emulsions. In fact, changes in the pH result in changes in the ionization degree of the functional groups of proteins and therefore determining the electrical charge of droplets. In this regard, charged droplets exhibit highly electrostatic repulsions between them and therefore, flocculation may be avoided. Finally, protein-stabilized emulsions typically exhibit higher droplets sizes compared to those emulsions stabilized by a small-molecule surfactant, since their large molecular size occupies an space at the interface that contributes to the final oil droplet size [20]. Accordingly to Jo et al. [21], protein-stabilized emulsions showed larger droplets (175.3–309.8 nm) than small-molecule surfactant-stabilized emulsions (111.7–120.7 nm).
In general, polysaccharides do not present a strong interfacial activity, but it is described that they can contain protein moieties in their molecular structure [20], which confers on them emulsification properties. Specifically, gum arabic (GA), octenyl succinic anhydride (OSA) starch and purified modified galactomannans have shown to effectively contribute to the emulsification of oil droplets [20,28,29,30,31]. In a recent work, GA, which is widely used in beverage emulsion formulation, could adsorb at the interface forming a thick layer surrounding the droplets and conferring a great steric stability (up to 3 weeks) to droplet flocculation and coalescence [26]. Nevertheless, polysaccharide-stabilized emulsions normally led to higher particle size emulsions than small-molecule surfactants or protein-stabilized emulsions [21,26]. Recently, Raikos et al. [26] obtained Tween 80 and WPI-stabilized emulsions with particle sizes of 1.88 and 2.14 µm, respectively, while GA-stabilized emulsion had particle sizes of about 4.10 µm.
Finally, several papers have been published regarding the emulsifying capacity of some biopolymers as they can present surface-active properties. Namely, Artiga et al. [32] obtained submicron essential oil emulsions with pectin concentrations above 1% in the absence of a small-molecule surfactant. Besides their activity as emulsifiers, hydrocolloids may be used as emulsion stabilizers. Emulsion stabilization may be enhanced due to the presence of thickening agents in the water phase [20]. Biopolymers often provide a significant increase of the aqueous phase viscosity, minimizing oil droplets movement and thus providing kinetic stability to the system [20,23]. Table 1 summarizes different emulsifiers that can be used to form emulsions found in the literature.

Table 1.
Review of the published works reporting emulsions produced with different emulsifiers used in food industry.
4. Emulsion Incorporation in Complex Beverages
The incorporation of concentrate emulsions to beverages represents a challenge for the beverage industry. In this regard, the processing treatments applied to beverages as well as the physicochemical characteristics of the food matrix might cause colloidal destabilization of beverage emulsions. On one hand, beverages processing provides shelf-stable products and guarantees the quality and safety of the final product. Several stabilization treatments are applied, such as heat or chemical treatments. Heat treatments are used to inactivate microorganisms as well as enzymes that might cause detrimental effects to the quality and safety of beverages. However, heat might disturb the thermodynamic stability of emulsions, thus causing the emulsion breakup. Moreover, acidification of the food matrix is often required in order to prevent microbial growth among other detrimental physicochemical changes in foods. This may change the ionization degree of emulsifiers and therefore compromise the dispersion of oil droplets. On the other hand, once emulsions are incorporated into beverages, the presence of minerals, which are cations ionized in the aqueous phase, might have an impact on emulsion stability. Overall, this section aims at discussing the main challenges to prevent emulsion destabilization once they are incorporated in formulated beverages, such as the effect of heat, pH changes or the presence of minerals.
4.1. Thermal Treatment
Stability of emulsions upon heat treatments may be affected by the surfactant type. In the case of non-ionic small-surfactants, the temperature at which a phase separation occur upon heating is known as cloud point. At that temperature, the surfactant becomes insoluble due to dehydration of their polar head groups and after this point, phase separation occurs. Teo et al. [24] studied the influence of different temperatures in emulsion physicochemical stability. They observed that droplets of Tween 20-stabilized emulsions heated at 90 °C presented coalescence, as it has a cloud point of about 76 °C [24]. This phenomenon is immediate, because it does not depend to the duration of the thermal treatment. Contrarily, proteins depend not only on the denaturation temperature, but also the treatment duration. In the case of proteins, when short-term thermal treatments are applied, emulsions are stable against droplet aggregation, due to the strong electrostatic repulsions between their charged droplets. For instance, WPI-stabilized emulsions did not present droplet aggregation upon a heat treatment at 90 °C for 15 min [24]. Nevertheless, when long-term heat treatments are applied, it has been reported that an extensive denaturation and unfolding of non-adsorbed proteins occurs on the droplet surface, thus leading to droplet aggregation. This effect is due to the intermolecular interactions between the non-polar groups of the unfolded proteins [35]. Contrarily, polysaccharide-stabilized emulsions may be more stable in front of thermal treatments. Ozturk et al., [31], showed invariable particle size of GA-stabilized emulsions at thermal treatments between 30 °C and 90 °C during 30 min. This may be related to the fact that polysaccharides do not have any hydrophobic groups that may react at elevated temperatures.
4.2. pH
Fruit juices are mainly acidic with a pH ranging from 2 to 5 units. The pH, and therefore the presence of hydrogen ions, determine the degree of ionization of surfactant molecules. Thus, as a consequence, it determines the electrostatic stability of the emulsions. In that sense, emulsions stabilized with ionisable emulsifiers (proteins and polysaccharides) are more susceptible to pH changes than those small-molecule surfactants-stabilized emulsions, as they present charged interfaces. Globular proteins stabilize emulsions mainly by electrostatic repulsions at pH below or above the pI. Nevertheless, they tend to form aggregates via hydrophobic attractions and van der Waals interactions when the electrostatic repulsion is not strong enough to overcome these attractive forces at pH close to their pI [24,36]. In that sense, WPI-stabilized emulsions showed stable emulsions at a wide pH range, except for pH values close to its pI (around 4.9), where sedimentation occurred [24]. Oppositely, lactoferrin (LF)-stabilized emulsions remain stable even at pH close to its pI, which could be attributed to the strong steric stabilization [24,33]. Furthermore, polysaccharides stabilize emulsions primarily by steric repulsions and therefore, they are highly stable across the entire range of pH [31].
4.3. Presence of Minerals
Commercial beverages contain different mineral ions due to the leakage of citoplasmatic content from vegetable tissues during juice extraction. Moreover, minerals might also be added to formulate beverages to provide isotonic balance and taste. The presence of those minerals can affect the emulsion stability through two principal mechanisms. Firstly, the presence of cations neutralizes the emulsion negative interfaces and therefore, a reduction of the electrostatic repulsion forces between droplets occurs (screening effect). Secondly, ion bridging effects may happen as cations have the ability to form bridges between the adsorbed proteins on the droplets, leading to an extensive droplet aggregation. Thus, negatively charged surfactants are more likely to form emulsions highly susceptible to destabilization phenomena in the presence of mineral cations. In this way, negatively charged WPI-stabilized emulsions were physically unstable in the presence of CaCl2 at concentrations above 10 mM, whereas those stabilized by LF and Tween 20, which are positively charged and neutral at pH far from the pI, remained stable [24]. Similarly, KCl addition to WPI-stabilized emulsions also presented phase separation [37]. Nevertheless, it is possible to add concentrations up to 200 mM of KCl before observing phase separation, as ion-binding is stronger with divalent Ca2+ cations than monovalent K+ cations. These results show a strong relationship between the charge of the droplets and emulsion stability.
5. Conclusions
Beverage emulsions fortified with water insoluble health-related compounds and/or flavor oils are considered an excellent source of nutrients, health-related compounds and a potential strategy for conferring attractive flavor, color and aroma to beverages and drinks. Nevertheless, emulsions may present instability phenomena since they are thermodynamically unstable systems. On the one hand, the proper selection of the ingredients for beverage emulsion formulation and the emulsification conditions determines the initial physicochemical characteristics and in turn their stability over time. On the other hand, the further addition of beverage emulsions in complex foods might cause critical colloidal destabilization. In this regard, the possible application of thermal treatments and changes in pH and mineral composition of complex foods can compromise the stability of emulsions. Therefore, the formulation of emulsions needs to be considered and selected according to the final product composition and industrial processing required. Besides the colloidal stability of beverage emulsions, other aspects such as the chemical stability of the functional ingredients and their health benefits after being digested need attention. Overall, beverage emulsions are excellent potential tools to incorporate functional ingredients into beverages and drinks to obtain healthier and more attractive products.
Author Contributions
A.M.-R. wrote the paper as principal author; and O.M.-B. and L.S.-T. contributed to the writing and correction of the paper.
Funding
This work was supported by the Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER) and Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (AGL2015-65975-R).
Acknowledgments
A.M.-R. thanks the University of Lleida for the predoctoral Research Funds. L.S.-T. thanks the ‘Secretaria d’Universitats i Recerca del Departament d‘Empresa i Coneixement de la Generalitat de Catalunya’ for the Beatriu de Pinós post-doctoral grant (BdP2016 00336).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ignat, I.; Volf, I.; Popa, V.I. A critical review of methods for characterisation of polyphenolic compounds in fruits and vegetables. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulueta, A.; Esteve, M.J.; Frasquet, I.; Frígola, A. Vitamin C, vitamin A, phenolic compounds and total antioxidant capacity of new fruit juice and skim milk mixture beverages marketed in Spain. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Nile, S.H.; Park, S.W. Carotenoids from fruits and vegetables: Chemistry, analysis, occurrence, bioavailability and biological activities. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 735–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarmeas, N.; Stern, Y.; Tang, M.X.; Mayeux, R.; Luchsinger, J.A. Mediterranean diet and risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 59, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Covas, M.I.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with a mediterranean diet. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costell, E.; Tárrega, A.; Bayarri, S. Food acceptance: The role of consumer perception and attitudes. Chemosens. Percept. 2010, 3, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, N.T.M.; Thanh, L.X.; Une, A.; Ukeda, H.; Sawamura, M. Volatile constituents of Vietnamese pummelo, orange, tangerine and lime peel oils. Flavour Fragr. J. 2002, 17, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; McClements, D.J. Impact of lemon oil composition on formation and stability of model food and beverage emulsions. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunathilake, K.D.P.P.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V.; Pitts, N.L. Formulation and characterization of a bioactive-enriched fruit beverage designed for cardio-protection. Food Res. Int. 2013, 52, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Rao, J. Food-Grade nanoemulsions: Formulation, fabrication, properties, performance, biological fate, and potential toxicity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 285–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Rojas-Graü, A.; Soliva-Fortuny, R.; Martín-Belloso, O. Physicochemical characterization and antimicrobial activity of food-grade emulsions and nanoemulsions incorporating essential oils. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Rojas-Graü, M.A.; Solivia-Fortuny, R.; Martín-Belloso, O. Use of antimicrobial nanoemulsions as editable coatings: Impact on safety and quality attributes of fresh-cut Fuji apple. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2015, 105, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions: Principles, Practices, and Techniques, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Komaiko, J.; McClements, D.J. Low-energy formation of edible nanoemulsions by spontaneous emulsification: Factors influencing particle size. J. Food Eng. 2015, 146, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.M.; Gumus, C.E.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Improvements in the formation and stability of fish oil-in-water nanoemulsions using carrier oils: MCT, thyme oil, & lemon oil. J. Food Eng. 2017, 211, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; McClements, D.J. Formation of nanoemulsions stabilized by model food-grade emulsifiers using high-pressure homogenization: Factors affecting particle size. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, F.; Ma, C.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Effect of carrier oils on the physicochemical properties of orange oil beverage emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2015, 74, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meroni, E.; Raikos, V. Physicochemical stability, antioxidant properties and bioaccessibility of β-carotene in orange oil-in-water beverage emulsions: Influence of carrier oil types. Food Funct. 2017, 9, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of lipid type on gastrointestinal fate of oil-in-water emulsions: In vitro digestion study. Food Res. Int. 2015, 75, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, E. Hydrocolloids at interfaces and the influence on the properties of dispersed systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.J.; Kwon, Y.J. Characterization of β-carotene nanoemulsions prepared by microfluidization technique. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Rojas-Graü, M.A.; Soliva-Fortuny, R.; Martín-Belloso, O. Effect of processing parameters on physicochemical characteristics of microfluidized lemongrass essential oil-alginate nanoemulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Rosas, M.I.; Morales-Castro, J.; Ochoa-Martínez, L.A.; Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Martín-Belloso, O. Long-term stability of food-grade nanoemulsions from high methoxyl pectin containing essential oils. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, A.; Goh, K.K.T.; Wen, J.; Oey, I.; Ko, S.; Kwak, H.S.; Lee, S.J. Physicochemical properties of whey protein, lactoferrin and tween 20 stabilised nanoemulsions: Effect of temperature, pH and salt. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanafusa, S.; Chu, B.S.; Nakajima, M. Factors affecting droplet size of sodium caseinate-stabilized O/W emulsions containing β-carotene. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2007, 109, 1038–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikos, V.; Duthie, G.; Ranawana, V. Comparing the efficiency of different food-grade emulsifiers to form and stabilise orange oil-in-water beverage emulsions: Influence of emulsifier concentration and storage time. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornacchia, L.; Roos, Y.H. Stability of β-carotene in protein-stabilized oil-in-water delivery systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7013–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Yao, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, K.; Fang, Y.; Nishinari, K.; Phillips, G.O.; Jiang, F. Gum arabic-stabilized conjugated linoleic acid emulsions: Emulsion properties in relation to interfacial adsorption behaviors. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 48, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweedman, M.C.; Tizzotti, M.J.; Schäfer, C.; Gilbert, R.G. Structure and physicochemical properties of octenyl succinic anhydride modified starches: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.; Shoemaker, C.F.; Yang, X.; Zhong, F.; Huang, Q. Stability and bioaccessibility of β-carotene in nanoemulsions stabilized by modified starches. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, B.; Argin, S.; Ozilgen, M.; McClements, D.J. Formation and stabilization of nanoemulsion-based vitamin E delivery systems using natural biopolymers: Whey protein isolate and gum arabic. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artiga-Artigas, M.; Guerra-Rosas, M.I.; Morales-Castro, J.; Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Martín-Belloso, O. Influence of essential oils and pectin on nanoemulsion formulation: A ternary phase experimental approach. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokle, T.; McClements, D.J. Physicochemical properties of lactoferrin stabilized oil-in-water emulsions: Effects of pH, salt and heating. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.; Aserin, A.; Svitov, I.; Garti, N. Enhanced stabilization of cloudy emulsions with gum arabic and whey protein isolate. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 77, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, B.S. Stability of protein-stabilised β-carotene nanodispersions against heating, salts and pH. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 1764–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnsilawat, T.; Pongsawatmanit, R.; McClements, D.J. Characterization of β-lactoglobulin-sodium alginate interactions in aqueous solutions: A calorimetry, light scattering, electrophoretic mobility and solubility study. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keowmaneechai, E.; McClements, D.J. Effect of CaCl2 and KCl on physiochemical properties of model nutritional beverages based on whey protein stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).