Abstract
Extreme rainfall in urban areas can cause major economic damage, a problem expected to intensify with climate change. Despite this, high-resolution studies at the city scale remain limited. This study analyzes rainfall organization and storm dynamics over Barcelona using data from a dense rain gauge network (1994–2019). The aim is to identify dominant spatial patterns and understand how storms evolve in relation to local urban and topographic features. Principal component analysis and simple scaling analysis revealed signs of a rainfall island effect, possibly linked to the urban heat island and modulated by orographic and coastal influences. Tailored rainfall indices highlighted a division between inland areas shaped by orography and coastal zones influenced by the sea. These spatial structures evolved with rainfall duration, shifting from localized contrasts at a 10 min resolution to more homogeneous distributions at daily scales. Storm tracking showed that 90% of speeds ranged from 5 to 60 km/h and intense rainfall events typically moved east–southeast toward the sea and north–northeast. Faster storms tended to follow preferred directions reflecting mesoscale circulations and possible modulations by local terrain. These findings underscore how urban morphology, local relief, and a coastal setting may shape rainfall at the city scale, in interaction with broader Mediterranean synoptic dynamics.
1. Introduction
Understanding the temporal and spatial distribution of intense local and mesoscale rainfall events over urban basins, along with their kinematics and evolution, is crucial for effective urban drainage modeling and flood management. In highly populated cities with complex sewerage systems, such as Barcelona (NE of the Iberian Peninsula), accurately tracking storm movement is essential for minimizing flood risks. The high variability of precipitation characteristic of the Western Mediterranean region [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] makes storm monitoring even more critical.
Urbanization can influence precipitation patterns by modifying land surface characteristics and atmospheric conditions, leading to changes in the behavior of convective storm cells and rainfall distribution [9,10]. Factors such as the urban heat island (UHI) effect [11], increased air pollution, and complex city skylines contribute to these changes by enhancing convective processes and cloud formation [12]. Additionally, urban-induced modifications can affect cloud dynamics and lightning activity, further impacting precipitation patterns [13].
In recent decades, the influence of climate change on precipitation extremes has attracted increasing scientific attention. The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) affirms with high confidence that extreme precipitation events have become more frequent and intense in many regions worldwide, including much of Europe [14]. This intensification is primarily attributed to the atmosphere’s enhanced capacity to hold moisture under warmer conditions, which increases the potential for convective precipitation [15]. The Mediterranean Basin, in particular, has been identified as a climate change hotspot, where both thermodynamic and dynamic factors (including changes in large-scale moisture transport) may contribute to a rise in the frequency of short-duration, high-intensity rainfall events [14,16,17]. However, observed trends in the region have not been spatially uniform. While some studies report a decrease in extreme precipitation in the western Mediterranean, others identify increases in the eastern part of the basin [18,19,20,21,22]. A recent comprehensive European assessment also found no clear signal of intensification of sub-daily extremes in Spain over the past six decades, underscoring the complexity of detecting consistent regional trends [23]. Looking ahead, projections indicate that extreme precipitation is likely to increase across most of Europe under global warming scenarios of up to 2 °C. Nevertheless, regional disparities persist, with the southern regions (particularly the southern Mediterranean) expected to experience little change or even decreases in extreme precipitation [24,25]. Beyond these large-scale patterns, climate change may also reshape rainfall distribution at the urban scale [26,27,28]. Recent studies show that urbanization can amplify local effects of climate change, intensifying atmospheric drying [29,30] and enhancing the risk of compound extreme events, including simultaneous heat and heavy rainfall [31]. These shifting patterns highlight the importance of understanding how urban morphology, land cover, and topography interact with atmospheric processes (particularly in Mediterranean regions) to shape rainfall variability at the city scale.
In the Mediterranean region, such interactions are particularly relevant, as urbanized areas frequently experience intense, localized precipitation events, which are a primary cause of floods [32]. Additionally, the region’s topography, geographical location, and the presence of a warm sea create favorable conditions for the development of hazardous convective systems or the intensification of unsettled Atlantic perturbations [33]. In this context, a related phenomenon known as the urban rain island (URI) effect emerges, wherein urban areas exhibit altered rainfall accumulation [34]. The URI effect can sometimes lead to increased precipitation over urban centers due to UHI-induced convection, enhanced surface roughness, and higher aerosol concentrations acting as cloud condensation nuclei. The URI effect can thus have significant implications for urban hydrology, particularly in regions with high precipitation variability, such as the Western Mediterranean, where small-scale convective storms can lead to intense, localized flooding.
Urban precipitation is shaped by a wide range of interacting factors, including land use, topography, coastal influences, and localized atmospheric conditions. These factors create what we refer to here as complex urban environments, especially in medium to large cities. The Barcelona metropolitan area exemplifies such complexity: the interaction between urban morphology, river corridors, coastal influences, and the surrounding Collserola mountain range plays a central role in shaping storm behavior and rainfall distribution. This study aims to explore how these elements affect local convective organization and precipitation patterns in the city.
Individual convective storms, typically composed of simple convective cells with a short lifespan of around 20–30 min, have been found to generally follow the direction of the prevailing mid-level winds (700 hPa) [35]. However, these cells frequently merge, forming multicellular systems whose movement is no longer dictated solely by the predominant wind. Instead, their propagation results from a combination of individual cell motions and the continuous development of new cells within the system [36]. In regions with complex orography and coastal influence, such as Catalunya (the Spanish region where the city of Barcelona is located), wind shear is commonly observed, further modifying storm propagation by altering cell regeneration patterns and redirecting storm movement relative to the predominant mid-level flow [37]. This effect highlights the crucial role of topography in shaping local convective dynamics.
Beyond these geographic complexities, urban areas add another layer of complexity to convective dynamics. The urban heat island effect enhances atmospheric instability, favoring the initiation and intensification of convective cells [38], while urban breeze circulations and cold pool interactions can further support cell regeneration and influence storm trajectories [39]. These urban-induced processes may increase the frequency, intensity, and spatial extent of convective rainfall, particularly in downwind areas [34,40,41]. While cold pool dynamics associated with mesoscale convective systems have been studied in Catalonia [42,43], their interaction with urban-induced processes remains largely unexplored. In the case of Barcelona, the consolidated urban core presents a notably uniform morphology, which may limit the relative influence of intra-urban variability compared to mesoscale drivers such as orography and coastal proximity. In fact, studies explicitly linking urban-induced convection and rainfall in Barcelona are still limited. Nevertheless, existing research has documented a well-defined UHI across the metropolitan area, shaped by urban morphology and land use [44], and recent work by [12] has begun to explore how urbanization influences mesoscale precipitation organization in various regions, offering valuable insight into urban–convective interactions relevant to complex coastal and urban environments such as Barcelona.
As convective cells continue to organize, they may evolve into larger, long-lived structures, such as mesoscale convective systems (MCSs) and other multicellular storm complexes, which are frequently responsible for significant rainfall episodes in the study area [45]. These systems, sustained by the ongoing interaction and regeneration of convective cells, can produce widespread and intense precipitation, increasing the risk of severe flooding.
To monitor and track storms, different approaches can be used. High-resolution radar images [46,47] provide valuable information about precipitation patterns, but they have known limitations, including beam blockage, attenuation, and difficulties in detecting near-ground precipitation. Therefore, they often need to be complemented with surface rainfall data [45,48,49] to enhance accuracy and improve hydrological models. Among these ground-based methods, a widely used option is a sufficiently dense rain gauge network within the urban area of interest [50,51]. While sparsely distributed rain gauge networks struggle to capture the high spatial and temporal variability of precipitation fields, especially highly convective ones, compared to weather radars [52], this limitation can be overcome with a sufficiently dense network. This ground-based observation method is particularly valuable for large, densely populated cities, where local rainfall intensities can vary significantly [7]. Compared to other ground-based instruments such as standard rain barrels (which lack temporal resolution) or microwave disdrometers (costlier and more complex), dense tipping-bucket networks offer a practical and accurate solution for urban storm monitoring. Even when radar data is available, a sufficiently dense rain gauge network provides direct ground-based rainfall measurements, avoiding uncertainties associated with interpreting radar images at a comparable resolution.
The goal of the present study is to improve the understanding of rainfall variability over the study area, particularly for intense rainfall events, to enhance drainage system management and mitigate urban flooding. Also, to better understand this variability, we analyze the catalogue of storm movements recorded by Barcelona’s rainfall network between 1994 and 2019. Additionally, the role of the URI effect is explored as a potential factor influencing precipitation distribution within the city, providing new insights into the complex interactions between urbanization and rainfall patterns.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Pluviometric Network of Barcelona
The city of Barcelona, with an approximate extension of 101 km2, is located on a small coastal plain bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the east, the Collserola mountain range to the west (512 m in altitude at its highest point), the Llobregat River to the south, and the Besòs River to the north, with various hills scattered throughout the city. Barcelona features a dense rainfall network (Figure 1, Table 1), currently managed by the public company Barcelona Cicle de l’Aigua S.A. (BCASA), Barcelona, Spain, with the participation of the Barcelona City Council through its governing bodies. The pluviometric network, originally deployed and maintained by Clavegueram de Barcelona, S.A. (CLABSA, located in Barcelona, Spain), and now by BCASA, consists of high-resolution tipping bucket rain gauges, most of them operating continuously since 1996 [2,3,49]; for this study, data from twenty-four of them have been used.
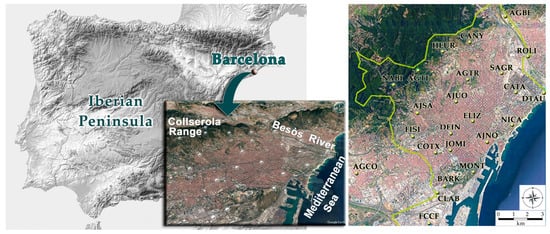
Figure 1.
Pluviometric network of Barcelona. In the right panel, the yellow line indicates the municipal boundaries of the city. The figures showing satellite views of Barcelona have been adapted by the authors from Google Earth imagery © Google.

Table 1.
Location and elevation of the pluviometers in the urban network of Barcelona.
Careful attention has been given to site selection and maintenance to ensure accurate rainfall measurements, minimizing potential sources of error such as nearby obstacles, turbulence, or channeling effects. The volume resolution of the pluviometers is 0.1 mm, their integration time is 5 min, and they feature a digital recording unit equipped with an accurate calendar clock [37]. The network is fairly evenly distributed, with an average density of 0.2 gauges/km2 and an approximate spacing of 1.8 km between rain gauges [53]. Given the relatively homogeneous morphology of the consolidated urban area, dominated by dense, mid-rise buildings and limited green space, no fine-scale analysis of intra-urban morphological variability was included, as its explanatory value was expected to be limited compared to larger-scale geographical features such as coastline and topography. The urbanized area studied lies predominantly on a flat coastal plain known as the Pla de Barcelona, with gentle slopes across most of the rain gauge network, although a few stations are located on more elevated terrain along the Collserola range (Table 1).
Fractal analysis provides a useful framework for evaluating the spatial density and arrangement of rain gauge networks. In an ideal case, such as a fully space-filling system, the fractal dimension would approach 2.0. However, in real-world networks with non-uniform distribution, this value is typically lower. The correlation dimension [54], a specific measure used to characterize the scaling properties of discontinuous networks, has been applied to various cases. For instance, a value of 1.72 was reported for the Barcelona network in [55], in a study where the authors found that the spatial structure exhibits scale-invariant properties over spatial extents ranging from 5 to 100 km2.
From the network registers, a total of 2678 rainfall events recorded between 1994 and 2019 were detected in at least 10 of the pluviometers, with durations longer than 25 min. From this initial set of storms, further filtering steps were introduced to refine the analysis, focusing on subsets of events of interest, for example, those reaching intensities defined by the Meteorological Service of Catalunya (SMC) [56] as heavy (20 mm in 30 min) and torrential (40 mm in 30 min) at least at one of the rain gauges. This filtering resulted in 133 intense rain episodes.
2.2. Spatial Organization of Rainfall in Barcelona
For detailed storm tracking studies over a city, having more rain gauges recording an event improves the ability to investigate storm movement and evolution. However, for other analyses, it is crucial to determine whether all gauges provide independent and relevant information. Closely positioned gauges tend to have highly correlated measurements, meaning that only one effectively contributes new information. In contrast, gauges farther apart are less correlated and more independent, provided they capture the same rainfall event. This dependence varies with the temporal scale of analysis.
To better understand the spatial distribution of independent rainfall information across the city and how it varies with temporal scale, we applied the principal component analysis (PCA) statistical method, widely used in atmospheric studies [3,57]. PCA reduces dataset dimensionality while preserving as much information as possible by transforming original variables into uncorrelated principal components, which are linear combinations of the original ones [58]. Given the long-term observational record available, PCA was chosen for its ability to identify dominant spatial patterns in rainfall variability and its suitability for analyzing datasets at multiple temporal scales. Using rainfall data recorded by the urban network over 26 years (1994–2019) for different durations, this initial analysis helps identify areas where rain gauge data are more independent at each timescale, offering insights into the spatial organization of rainfall patterns in Barcelona. In a subsequent step, we derive a weighted combination of the principal components to produce a single summary field per duration, capturing the dominant spatial structures across the network.
Beyond assessing the independence of rain gauge data, further spatial analyses were conducted to explore how rainfall patterns relate to specific scaling properties and climatic indices. In particular, we examined the spatial distribution of the simple scaling parameter [59,60,61], which describes the fractal scale-invariance properties of rainfall across different durations. This parameter has been shown to correlate with the local rainfall regime, generally aligning with total precipitation while also capturing the irregularity of rainfall patterns. In this study, it may offer valuable insight into rainfall variability within the urban area.
The scaling invariance of rainfall can be described [61] through a relationship that links the probability distribution of rainfall intensity for a given duration, , to that of another duration, , via a scaling factor expressed as a power law of the scale parameter . This relationship is mathematically defined in Equation (1) for the monofractal (or simple scaling) case, where is the scaling parameter mentioned in the previous paragraph, and represents the order of the statistical moments of the probability distributions (Equation (2)).
The parameter can be determined by performing a linear regression of the logarithmic values of the statistical moments against the logarithm of . In the case of scale invariance, the resulting straight lines have a slope of . To ensure the validity of the monofractal hypothesis, the statistical moments were computed using the annual maximum series at each rain gauge.
Additionally, we analyzed the spatial distribution of selected climatic indices, including the mean values over the study period (1994–2019) of PRCPTOT, defined as the total annual precipitation, and Rx1day, the maximum daily precipitation [62]. To capture sub-daily extremes relevant in urban hydrology, we also defined tailored indices: Rx4h, Rx1h, and Rx10min, representing the mean of the annual maximum precipitation values for 4 h, 1 h, and 10 min durations, respectively, over the study period (1994–2019). These indices offer a more detailed understanding of short-duration rainfall events, which are especially critical in assessing flood risks in urban areas. This analysis provides insights into how different timescales of precipitation extremes vary spatially across Barcelona. By integrating these approaches, we aim to identify spatial patterns influenced by orographic and geographic features, including the influence of the coastline and the sea, as well as other urban-related factors that may shape rainfall dynamics.
2.3. Storm-Tracking Technique
The basis of storm-tracking techniques that utilize rainfall network data to estimate storm movement across an area relies on monitoring specific characteristics of the rainfall pattern, often referred to as a reference point [63]. Common reference points include the onset of rainfall at each gauge [64], the peak intensity time, and the centroid of the storm hyetogram. Other approaches involve computing maximum spatio-temporal cross-correlation functions between rain gauges [65] or applying temporal shifts to maximize correlations between pairs of gauges [66]. However, these methods do not perform satisfactorily in cases where multiple rainfall cells are present, as they struggle to account for the complex, evolving structure of convective storms [63,67]. While storms are often composed of multiple evolving and decaying cells, many analyses based on rainfall network data rely on the simplifying assumption that storm movement can be represented by a uniform speed. More recent studies [50,51] have further developed rain gauge-based tracking methods by applying these principles to urban areas, demonstrating their effectiveness in monitoring storm motion. These approaches, based on methods proposed in [53], utilize dense rain gauge networks to capture rainfall variability and track storm propagation, offering a practical alternative for analyzing storm dynamics in regions lacking radar coverage or where simplicity and accessibility are prioritized over more complex radar-based techniques.
The storm-tracking technique chosen to monitor the rainfall events recorded by the urban network is the one proposed in [50,51]. To track these events across the network, the time centroids of the hyetograms and the highest-intensity peaks have been used as reference points (Figure 2). Other techniques, such as the lag-correlation method [65,66,67], were initially tested but later discarded due to unsatisfactory results, possibly caused by this method’s sensitivity to the presence of multiple rain cells within the storm [63].
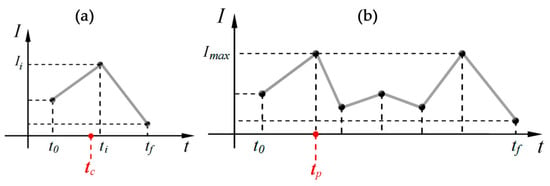
Figure 2.
Examples of a hyetogram (a) time centroid and (b) first maximum intensity peak.
For each rain gauge , the centroid of its hyetogram is a time calculated as Equation (3), where and represent the start and end times of the storm hyetogram, and are its intensity values.
If the reference point for monitoring the storms is the maximum-intensity peak instead of the centroid, the alternative time is selected as the time for which the highest intensity in the hyetogram of rain gauge occurs. If multiple peaks of equal intensity are present, the first recorded one is chosen. Throughout the rest of this paper, denotes the time corresponding to the chosen reference point for tracking the storm, either the centroid or the first maximum peak , depending on the selected method.
For a given storm, once the reference points for each rain gauge in the network have been determined, a set of experimental points is considered, with the coordinates of the gauge , and the time of the storm feature to be tracked. This set of experimental points is then fitted to a plane, defined by Equation (4) by the least squares method (planar regression) [51].
In particular, the speed of the movement can be estimated by the inverse of the maximum plane slope according to Equation (5), while the direction of movement, which is assumed to be parallel to the direction of the maximum slope, is expressed as an azimuth angle (), measured clockwise from north (0°), and calculated using Equation (6).
In the special case where , then (East) if , and (West) if . If and the direction is undefined, corresponding to a stationary storm [51].
As an example, Figure 3 presents the planar regression for a rainfall event recorded by the urban network of Barcelona on 14 September 2009, where the hyetogram centroids for each of the 15 pluviometers that captured the storm are represented on the t-axis. The parameters of the fitted plane equation in this space (, , ), where longitude is represented by and latitude by , were determined as , and . This corresponds to a movement speed of , that is, towards the south–southwest . See also Figure 4, which presents a sequence of images from the radar operated by the SMC in Vallirana, a nearby town west of Barcelona. The images, captured at 12 min intervals, clearly show the storm moving approximately in a S–SW direction.
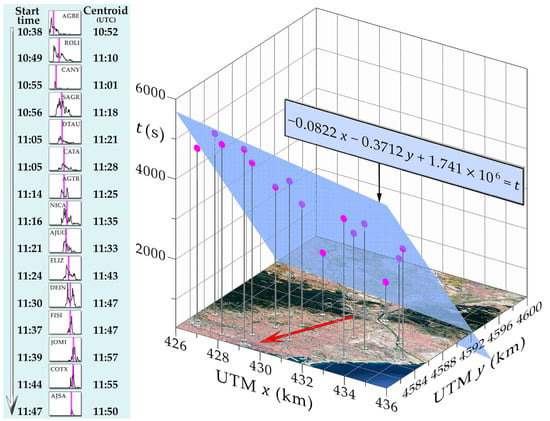
Figure 3.
Example of a planar regression using the hyetogram centroids from the 15 rain gauges of the urban network of Barcelona capturing the storm occurred on 14 September 2009. The fitting gives a movement speed of 9.5 km/h towards the S–SW. On the left, the start times and centroids of the 15 hyetograms are shown. Each hyetogram includes a vertical purple line indicating the time centroid at that station, providing insight into the storm progression. On the right, the vertical axis expresses time in seconds, with t = 0 assigned to 10:30 UTC. Other reference times: t = 2000 s ≈ 11:03 UTC; t = 4000 s ≈ 11:37 UTC; t = 6000 s ≈ 12:10 UTC.
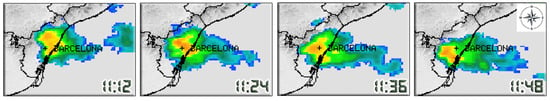
Figure 4.
Sequence of radar reflectivity images from the Vallirana C-band Doppler radar (SMC), capturing the storm that occurred on 14 September 2009 in the Barcelona metropolitan area, shown at 12 min intervals.
This technique has been applied to the 2678 rainfall events recorded between 1994 and 2019 by the urban network, with the aim of compiling a catalog of the main movement directions of the storms moving over the city, as well as their range of speeds.
Equation (7) calculates the value of the significance ratio () [51], a dimensionless metric ranging from 0 (perfect fit) to 1 (no fit), which quantifies the goodness of fit of the planar regression model, where is the number of rain gauges involved in the regression. Lower values indicate better fits, with values under 0.85 typically considered satisfactory. In the example shown in Figure 3, the value is , indicating a very good fit.
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Organization of Rainfall: The Urban Rainfall Island in Barcelona
The PCA technique was applied to the urban network records from 1994 to 2019, using as variables the rainfall quantities recorded by each pluviometer for durations ranging from 5 min to 24 h. To further explore the spatial distribution of the principal components, we interpolated their scores obtained at the rain gauges across a grid covering the study area. This allowed us to generate contour lines (isohyet-like representations), which indicate the spatial variation in the dominant modes of rainfall variability. Figure 5 shows the spatial distribution of the first three principal components of rainfall for a duration of 15 min, explaining 30%, 11%, and 9% of the total variance, respectively.
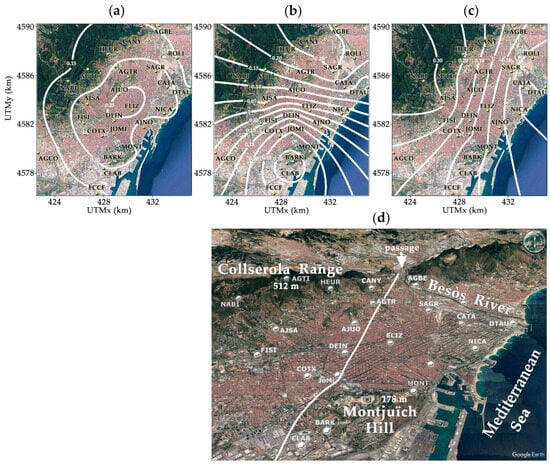
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of the first three principal components (PCA1 to PCA3) of rainfall for a duration of 15 min [53]. Contour lines in panels (a–c) represent interpolated PCA scores, highlighting dominant spatial patterns: (a) first component (PCA1), explaining 30% of the total variance; (b) second component (PCA2), explaining 11% of the variance; (c) third component (PCA3), accounting for 9% of the variance. Panel (d) shows the main orographic and geographic features of the city, along with the zero-contour line of PCA3. This panel uses vertical exaggeration to improve the visualization of relief and to highlight the Collserola corridor. The figures showing satellite views of Barcelona have been adapted by the authors from Google Earth imagery © Google.
In the first principal component (PCA1), which explains 30% of the variance, the rain gauges are grouped into concentric bands that extend across the entire map (Figure 5a). According to this pattern, there is a central area with the highest scores (above 0.25) located in the center of Barcelona, indicating that this region strongly follows the dominant spatial pattern captured by this component. Surrounding this, a second zone forms a ring around the central core, with moderate scores between 0.2 and 0.25. The third ring (with values between 0.15 and 0.20) appears further out, covering areas such as the Collserola range, the Besòs River area, and the central part of the port. Finally, the outermost zone (with scores below 0.15) corresponds to the peripheral rain gauges of the network, where the influence of this component is weakest. Since all scores in this component are positive, it suggests a common spatial mode of rainfall distribution across the city, with its intensity decreasing toward the periphery. The concentric structure of the first principal component values suggests a spatial pattern similar to the urban heat island (UHI) effect [11,68]. Just as the UHI effect leads to higher temperatures in the city center, this pattern may indicate a stronger expression of the dominant rainfall mode in the central area of Barcelona, providing evidence of an urban rainfall island over the city [69,70].
For the second principal component (PCA2), which accounts for 11% of the variance (Figure 5b), we observe a spatial pattern characterized by nearly east–west parallel contours near the city center, reaching both the coast and the mountains of the Collserola range almost perpendicularly, and gradually closing toward the north and south. The central region marks a transition zone with near-zero values, while the scores increase positively toward the south, reaching a maximum near the port (0.30), just behind Montjuïc Hill, suggesting that this small elevation (178 m) may influence the spatial pattern. In contrast, scores decrease negatively toward the north, and the initially east–west-oriented isohyets begin to rotate progressively as they approach the Collserola range in the northwest, aligning perpendicularly to the mountain slope. This reorientation reflects the influence of the topography in modulating rainfall distribution. This pattern suggests two contrasting rainfall regimes. The increasing positive scores toward the southeast indicate that the rain gauges in this region exhibit a stronger correlation with this component, possibly linked to coastal meteorological influences such as sea breezes and convective activity. Conversely, the growing negative scores toward the north, along the Collserola range, suggest that rainfall in this region follows an opposing pattern, likely shaped by orographic effects associated with the mountainous terrain. The transition zone in the central part of the city represents a boundary between these two spatial patterns, highlighting the role of geographical and topographical features in shaping rainfall distribution over Barcelona.
For the third principal component (PCA3), which accounts for 9% of the variance, the spatial pattern is dominated by almost north–south contours, highlighting the influence of the mountainous terrain to the west and the coastal area to the east (Figure 5c). The zero-score line crosses the city from south to north, aligning with the gap or passage created by the Besòs River as it cuts through the Collserola range (Figure 5d). The scores increase positively toward the west, reaching a maximum of 0.30 over the Collserola range, while decreasing negatively toward the east, reaching −0.20 near the coast. This pattern suggests that rainfall in these areas exhibits two contrasting behaviors, with orographic effects shaping the western sector and coastal influences playing a role in the eastern sector. The following principal components (fourth, fifth, and sixth), which explain an additional 6%, 5%, and 4% of the total variance, respectively, were also examined [53]. However, they do not introduce fundamentally new spatial structures. For instance, the fourth component displays concentric patterns similar to the first, while the fifth resembles the third in its west–east contrast, though with slight differences. Due to their limited additional explanatory power and redundancy with previous components, we chose not to include them in the main analysis. This redundancy is also reflected in the number of components required to explain most of the spatial variance at each timescale. For instance, while up to 12 components are needed to reach approximately 80% explained variance at a 10 min resolution, this number decreases with an increasing duration: seven components for 1 h, four for 4 h, and only two for daily accumulations. This progressive reduction aligns with the observed tendency for rainfall structures to become smoother and more spatially coherent as the accumulation duration increases.
Next, for each rainfall duration, we compute a weighted sum of the first few principal components for each pluviometer , until their cumulative variance accounts for approximately 80% of the total variance. This yields a composite score per station (Equation (8)), where is the score of the -th principal component at pluviometer , is the weight (fraction of variance explained by component i), and is the number of components needed to reach 80% of explained variance [53,58].
This weighted combination of the first principal components provides a summary signal for each station, capturing the most relevant spatial variation in rainfall intensity while accounting for the proportion of variance explained by each component. Importantly, because the values result from recombining standardized component scores weighted by their contribution to total variance, they partially reconstruct the dominant structure of the original data. As a result, stations with overall similar rainfall behavior across durations tend to yield similar values. This explains the presence of large, relatively uniform zones in the interpolated maps, where only a few distinct areas emerge. Figure 6 displays the interpolated scores of for durations of 10 min and 1, 4 and 24 h, allowing a visualization of the dominant spatial patterns that emerge when multiple principal components are considered together, as well as how these patterns evolve with the rainfall duration. For durations shorter than 30 min (represented in Figure 6 by the 10 min duration), the contour lines of the interpolated values form enclosed zones, distinguishing between the center–south and northern areas of the city. By the 1 h duration, these enclosed areas disappear, giving way to two broad regions: one more influenced by the mountainous orography, and the other closer to the coast. At the 4 h duration, the separation between coastal and orographic influences persists, though the boundary becomes more curved and a localized closed contour appears in the northern sector of the port area. At 24 h, a central enclosed zone emerges, encompassing most rain gauges while only excluding the stations at the periphery of the network.
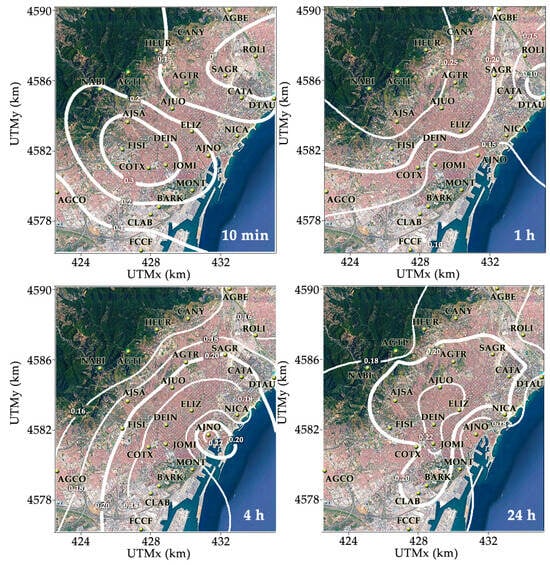
Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of the summary signal , obtained as a weighted combination of the first principal components explaining up to 80% of the total variance, for different rainfall durations (10 min, 1 h, 4 h, and 24 h).
To aid interpretation, auxiliary contour lines have been added in Figure 6 for the 1, 4, and 24 h durations. The range of these added levels becomes progressively narrower as the duration increases, reflecting the greater spatial smoothness of the interpolated fields with longer rainfall durations.
The analysis of spatial patterns across different durations reveals how the scale of observation influences rainfall variability. For the shortest duration (10 min), the patterns are more localized, and the network’s density and distribution allow for a better resolution of small-scale features, characteristic of the local scale. These small-scale features include topography, urban features, and surface properties, which strongly influence rainfall variability. As we move to longer durations, such as 1 and 4 h, the patterns begin to show broader structures and smooth out compared to shorter durations, but still retain some degree of locality. Both durations (1 and 4 h) represent the small mesoscale and mesoscale range [71], where atmospheric processes like local winds and convective activity play a stronger role, while topographic influences remain significant, especially in areas with notable terrain features. Larger-scale meteorological systems also begin to have a more pronounced influence as the scale increases. For the 24 h duration, the scale increases further, approaching the synoptic scale, where the influence of small, local features becomes less apparent. Here, rainfall patterns are more dominated by broader, large-scale weather systems, and the smaller differences between areas in the city are harder to distinguish due to the averaging effect of the longer time frame.
Having explored how the spatial patterns of rainfall variability evolve across different timescales through PCA, we now turn to examining their relationship with conventional rainfall metrics and indices. For instance, the scaling parameter has been calculated for each rain gauge in the network, a parameter that has been related to rainfall irregularity as well as to mean annual precipitation [59,60,61,72]. To explore these characteristics across the city, we interpolated the values from each rain gauge in the network. Figure 7 presents the resulting field, illustrating the spatial variation in this parameter over the study area, along with the interpolated field of average annual total precipitation (PRCPTOT). The comparison between both panels does not appear to reveal a strong similarity between the spatial patterns of and PRCPTOT. Instead, the field exhibits a structure of concentric bands around the center, resembling the typical urban heat island pattern.
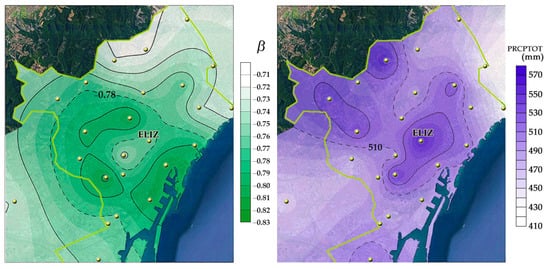
Figure 7.
On the left, the interpolated field, illustrating the spatial variation in rainfall irregularity across the study area. On the right, the interpolated field of average annual total precipitation (PRCPTOT), providing a comparative view of long-term rainfall distribution.
A previous study [59] found that for the Observatori Fabra of Barcelona, located at 411 m above sea level and very close to the AGTI gauge, the exponent value was , using both a Hellmann totalizing rain gauge and a Jardí rain intensity recorder, operating in unison between 1927 and 1992. In the present study, small rainfall differences across various urban areas are detected through simple scale analysis. The values obtained for the different rain gauges range from to (Figure 7). Except for a small central area (ELIZ and DEIN), the spatial distribution of shows values below in the center of the city, increasing towards the outskirts, with values of and in the northeast near the Besòs River basin, and in AGCO, to the southwest, just outside the municipal area of Barcelona (outlined in green in Figure 7).
Conversely, the spatial pattern of PRCPTOT begins to echo features observed in the PCA-derived fields at intermediate durations (1–4 h), where a transition between a mountainous-influenced western zone and a coastal eastern sector becomes discernible (Figure 6). This separation starts to emerge subtly at 1 h, becomes more noticeable at 4 h, and is more clearly defined at 24 h (Figure 6), where higher values begin to cluster around the city center, particularly at stations such as ELIZ and DEIN, as also seen in PRCPTOT (Figure 7). Although this separation is not as clearly maintained at longer durations (e.g., 24 h), some of the spatial structure remains consistent with the broader organization revealed by the PCA. A visible transition area crosses the city with values around the mean of 510 mm or less, dividing it into two regions with maxima (above 530 mm), possibly influenced by different meteorological drivers. In the case of long-term rainfall distribution, one of these influences appears to be orography, as the maxima in the northwest are located in the mountains. The other maximum, located to the east near the city center (ELIZ), does not appear to be solely driven by coastal influences, suggesting that additional meteorological factors are involved. However, notice that since PRCPTOT was computed for annual periods, its resolution is not optimal for detecting the finer-scale spatial structures revealed by PCA. To address this, other indices and tailored metrics adapted to shorter timescales have been calculated. The maritime influence becomes more evident when shifting to shorter timescales, for example, when representing the Rx1day index, which captures the maximum daily rainfall at each gauge. This influence becomes even more pronounced at smaller scales, as seen in the tailored indices Rx4h, Rx1h, and Rx10min, which record the maximum rainfall for each duration (4 and 1 h and 10 min, respectively). At the 10 min scale, a clear difference emerges between the northern and southern parts of the city, highlighting the coastal influence, as previously suggested by the PCA (Figure 8).
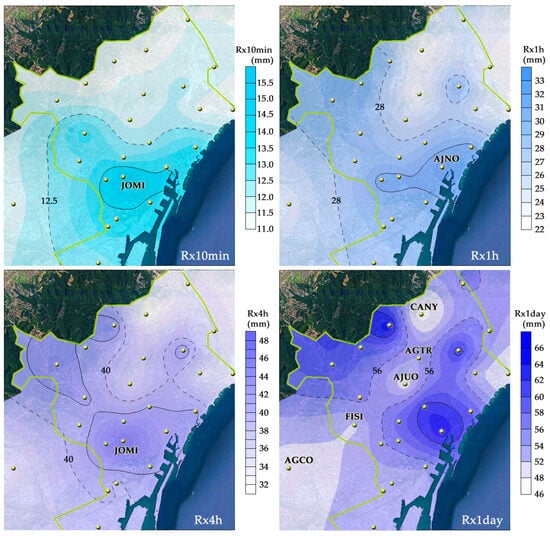
Figure 8.
Interpolated fields of indices Rx10min, Rx1h, Rx4h, and Rx1day.
3.2. Tracking the Rainfall Events Recorded by the Urban Network of Barcelona (1994–2019)
A total of 2678 rainfall events lasting more than 25 min were detected by at least 10 rain gauges in the urban network of Barcelona. A total of 33% of the initially analyzed rainfall events occur in autumn, a proportion that increases to 57% for the selection of 133 intense events. In contrast, summer accounts for just 14% of the events in the initial dataset. This proportion also increases in the more intense selection, rising to 28%, indicating that although less frequent, summer storms are often among the most intense. Altogether, approximately 85% of the most intense rainfall episodes are concentrated in autumn and summer. All these events were analyzed using tracking techniques based on both storm centroids and first maximum peaks as reference points. The estimations of speed and direction of movement obtained from these two approaches were very similar. Although individual storm estimates may differ due to variations in the behavior of centroids and first maximum peaks throughout the storm lifecycle, both methods lead to consistent and comparable conclusions. Table 2 shows the seasonal distribution of total and intense rainfall events, including their respective percentages.

Table 2.
Seasonal distribution of total and intense rainfall events.
In terms of the significance ratio (Equation (2), [51]), 84% of the storms presented a good fit ( ≤ 0.85) when using their centroids, and more than 64% did so when using the first maxima. Building on these findings, an analysis of the rainfall events with a good fit (2245 using the centroid method and 1718 using the first maximum peak method) revealed that the mean motion speed was 30 km/h for events tracked using their centroids, and 24 km/h for those monitored using their first maxima. More than 90% of the speeds fell within the range of 5 to 60 km/h. Moreover, around 65–70% of events moved within a directional range spanning from southeast (SE, towards the coast) to northwest (NW, towards the mountains) through the east (E), northeast (NE), and north (N), while very few moved toward the southwest (SW) (see Figure 9).
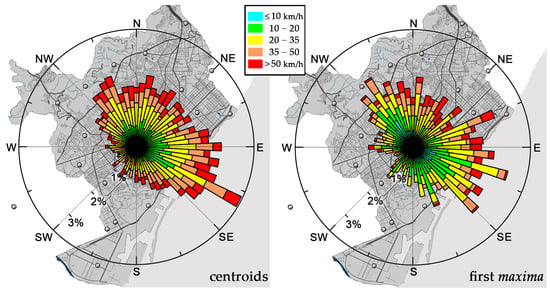
Figure 9.
Diagrams with the motion direction and speeds of the well-fitted rainfall events using the centroid method (left) and those using the first maximum peak method (right).
Figure 10 shows the storm direction and speed diagrams corresponding to the selection of 133 events that reached intensities defined by the SMC [56] as heavy (20 mm in 30 min) and torrential (40 mm in 30 min) at one or more rain gauges. While the full dataset initially displayed a broad range of directions spanning from the northwest (NW) to southeast (SE), the subset of intense events revealed a slightly more balanced distribution. When monitored using the centroid method, this refined selection identified two distinct predominant movements: one toward the east–northeast (ENE), and a more marked one toward the east–southeast (ESE) and southeast (SE), all of them in the direction of the coast. Even so, other quadrants showed relatively higher proportions compared to the full set, indicating a slightly broader diversity in storm trajectories within the subset. In the case of the events tracked using the first maximum, the predominant directions are those toward the coast, with the exception of a subset of events moving toward the north–northwest (NNW), that is, perpendicular to the Collserola range. However, a notable 45% of the intense events recorded by the urban network moved toward the sea, a result consistently observed using both tracking methods.
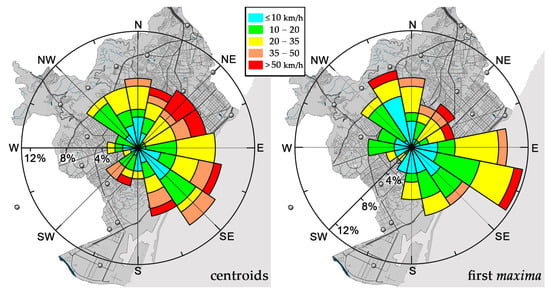
Figure 10.
Diagrams with the motion direction and speeds of the well-fitted rainfall events showing heavy and torrential intensities at one or more rain gauges, using the centroid method (left, 116 episodes) and those using the first maximum peak method (right, 103 events).
Regarding the speeds of the highly intense events, the analysis based on centroid tracking reveals a marked variation across quadrants: in the first quadrant (N to E), the average speed is 32 km/h; in the second (E to S), 24 km/h; in the third (S to W), 25 km/h; and in the fourth (W to N), 15 km/h. The corresponding median speeds for the centroid method are 24, 18, 16, and 14 km/h for quadrants one to four, respectively, reflecting the directional contrasts observed. These median values suggest that the mean speeds, particularly in the first quadrant, are influenced by a few high-velocity outliers. Indeed, more than 11% of the intense events exhibit high velocities (with a mean speed of 32 km/h) clustered in the NNE–NE–ENE range, roughly parallel to the coast. In contrast, the predominant directions moving roughly perpendicular toward the sea, clustered in the ESE–SE–SSE range, have comparatively lower average speeds around 16 km/h.
In comparison, the first maximum method yields generally lower velocities. The median speeds for intense events by quadrant are 21, 13, 10, and 11 km/h for quadrants one through four, respectively. Corresponding mean speeds are 24 km/h in the first quadrant (N to E), 16 km/h in the second (E to S), and 14 km/h in both the third (S to W) and fourth (W to N) quadrants, indicating not only a reduction in overall speeds but also a different distribution pattern across quadrants.
4. Discussion
Accurate analysis of urban precipitation relies on high-quality observational data. Despite the inherent challenges of measuring rainfall in complex urban environments, the dense network used in this study has been carefully maintained for over three decades. Although not all gauges fully meet WMO siting standards, the network was designed with attention to accuracy and has been consistently managed by qualified municipal entities (originally CLABSA, now BCASA) in collaboration with the Barcelona City Council, ensuring reliable data for urban-scale analysis.
Using this robust dataset, the PCA technique applied to the urban network records from 1994 to 2019, along with the resulting interpolated values across a grid covering the study area, has proven highly useful for exploring the spatial distribution of the dominant rainfall patterns in Barcelona. The concentric structure of the first principal component values around the city center revealed a spatial pattern akin to the urban heat island effect (UHI) [11,68], providing the first evidence of an urban rainfall island (URI) over the city. Similarly, the spatial pattern of the scaling parameter , as shown in the Results section, supports this interpretation, further reinforcing the idea of a spatially concentrated urban rainfall effect, with higher β values observed around the urban fringe and gradually decreasing toward the periphery (while showing a slight local dip near the city core), a pattern consistent with the spatial signature expected under an urban rainfall island scenario. The UHI over Barcelona can be represented by the spatial distribution of the annual average nighttime temperature (ANT) calculated by [68] using MODIS satellite data and GIS analysis. It exhibited a concentric band structure around the city center, coinciding with the location of the ELIZ rain gauge in the network, where the highest ANT is 15.4 °C. The temperature gradually decreases toward the periphery, passing through an average ANT value of 13.8 °C, and reaching a lowest ANT of 11.4 °C in the area of the city deeply embedded in the Collserola range (above the NABI gauge). While a comprehensive assessment of the URI would require reference stations beyond the city limits, the observed internal variations, showing decreasing gradients from the urban core to the periphery, suggest that urban-induced factors, such as enhanced convection due to heat and aerosols, may be influencing precipitation distribution within the city. Indeed, Barcelona has been identified among the large southern European cities with notable urban precipitation anomalies [69], reinforcing this interpretation. Although our dataset lacks external observations beyond the municipal boundaries, the internal spatial gradients support the presence of a URI signal. However, this interpretation is limited by the current extent of our gauge network, especially near the city’s edges. For instance, the southwestern periphery, near the mouth of the Llobregat River, may seem to show a rainfall deficit, when in fact this may be due to insufficient observational coverage. As shown by [73], a positive rainfall anomaly was recorded in that area, particularly in autumn, but our network does not detect it, as the nearest station (AGCO, located in the neighboring city of Cornellà) remains several kilometers away from the Llobregat Delta and outside our analysis area.
The second component reveals a north–south contrast, driven by a spatial pattern of nearly east–west-oriented contours, with positive scores increasing toward the south and negative ones toward the north. Small-scale topography (e.g., Montjuïc Hill, 178 m) appears to modulate rainfall patterns on the city’s southern fringe. This is consistent with numerous studies and models [49,74,75], which highlight the significant role of small-scale topographic obstacles in storm initiation, as well as the impact of both sea and topography on storm system movement [49,75]. Meanwhile, the Collserola range appears to modulate the rainfall pattern in the northwest, as suggested by the bending of the contours near the mountains. The observed transition zone aligns with the city center and marks a boundary between two rainfall regimes: one to the north, increasingly influenced by topography, and another to the south, likely shaped by maritime influences (e.g., sea breezes and convective dynamics). While the second component suggests a north–south contrast possibly modulated by Montjuïc Hill on the city’s southern fringe, its interpretation remains more uncertain. For example, the presence of high component values near Montjuïc could be influenced by localized effects or potentially by edge effects of the network, although the spatial context provides some support for a real signal. Similarly, the negative values observed in the northern area are not easily attributable to the Collserola range. This pattern may instead reflect a spatial shift in rainfall intensity linked to urban factors such as storm duration or UHI-induced convection, as shorter-duration events tend to concentrate more toward the urban core. Nevertheless, this interpretation should be considered tentative and subject to the spatial limitations of the observational network. The third component reveals a distinct spatial structure characterized by nearly north–south-oriented contours, clearly separating the mountainous terrain to the west from the coastal plain to the east. The zero-score line is oriented slightly more northward than the general SW–NE orientation of the coastline aligning with the Besòs River corridor, a natural passage through the Collserola range where the orographic barrier briefly weakens.
The spatial patterns derived from the summed PCA components across different rainfall durations reveal how dominant modes of variability evolve with time. For the shortest duration (e.g., 10 min), the interpolated scores form distinct enclosed zones that separate the center–south from the northern part of the city, an organization that echoes the contrast observed in the second principal component at 15 min, where orographic and maritime influences begin to diverge. As the duration increases to 1 and 4 h, the spatial patterns evolve from localized features to broader structures. At 1 h, the inland–coastal division becomes more apparent, following a relatively straight trajectory, as was found by [3]. By 4 h, the separation acquires a more curved configuration, and a secondary closed structure appears near the northern edge of the port area. By 24 h, a single large, enclosed zone emerges at the center of the network, reflecting the increasing dominance of synoptic-scale processes that override finer-scale urban and topographic variability.
This gradual shift in spatial structure mirrors what is seen in the interpolated fields of climatic indices such as PRCPTOT, Rx1day, and others. However, it is important to note that such indices are typically designed to capture long-term climate variability and change [62], and are often computed over seasonal or annual periods. As such, they are less sensitive to the fine spatial structures that emerge at sub-daily scales. In fact, it is only when these indices are computed at shorter durations, such as 24 h or less, that the patterns hinted at by the PCA become more discernible. For instance, in the Rx1day field, a clear division, roughly following the path of several rain gauges (CANY, AGTR, AJUO, FISI, AGCO), starts to emerge between the part of the city more influenced by the mountains (Collserola) and the sector closer to the coast. As we further reduce the duration to 4 and 1 h, this topographic–maritime contrast becomes more defined, although the influence of the coast progressively gains strength. At 10 min, the spatial organization once again reflects a strong north–south separation, very much in line with the structure captured by the summed PCA components for the same short duration. This parallelism across independent methods underscores the robustness of the observed spatial divisions, and highlights the importance of analyzing rainfall at sub-hourly scales when aiming to resolve the interaction between urban structure, topography, and coastal dynamics.
In order to contextualize the storm speeds observed in Barcelona, the ranges obtained using our tracking methods were compared with values reported in other European studies [50,63,66,67,75]. The speed ranges obtained using tracking methods over the city of Barcelona are consistent with results reported by other authors [37,55], with 90% of the well-fitted storms ( 0.85) falling within a speed range of 5 km/h to 60 km/h. Specifically, using the centroid method, we found an average speed of 30 km/h, while the first maximum peak method yielded an average of 24 km/h. For the selection of highly intense events, the averaged velocities were 27 km/h and 23 km/h, respectively. For comparison, the estimated average speed for 400 storms in Lund (Sweden) was 37 km/h [63], while in England, average speeds of 41 km/h for 110 storms in Cardington and 42 km/h for 133 storms in Winchcombe were reported by [66]. Using data from 107 storms recorded by a network of 20 rain gauges distributed over a 600 km2 area in northwest England, an average storm speed of 34.5 km/h was estimated by [67]. Based on a 10-gauge rain network in Palermo (Italy), it was found by [50] that 60% of the monitored storms had speeds below 30 km/h, with approximately 30% of the events falling within the 20–30 km/h range.
However, although these comparisons provide useful context, direct contrasts should consider differences in latitude, topography, and prevailing meteorological conditions. Latitude may influence synoptic-scale wind patterns and storm propagation, but local geographic factors, such as the presence of coastal influences and orographic features, also play a crucial role in modulating storm dynamics. Consequently, variations in storm speeds across different regions likely result from a combination of these factors rather than latitude alone.
Maintaining a more local focus, an earlier work [37], based on the initial years of measurements from the Barcelona rainfall network and a selection of 32 storms, identified a predominant eastward propagation direction, with speeds estimated between 3 and 12 m/s (10.8 to 43.2 km/h). Subsequently, and also using data from the rainfall network, ref. [55] analyzed a more limited set of 15 storms and identified predominant propagation directions along the SW–NE and NW–SE axes (parallel and perpendicular to the coastline, respectively), with speeds ranging between 3 and 25 km/h. While limited in scope, both works provided early insights into storm behavior in the region. The results from [37] partially align with the eastward component observed in our current analysis, whereas [55] shows a closer correspondence with the NW–SE propagation paths we found. Based on radar observations, some mesoscale systems with convective cells have been documented to traverse the entire Catalan littoral (approximately 580 km) in under three hours [75,76], which would imply very high speeds. In contrast, other mesoscale systems can remain almost stationary over specific areas, with reported speeds of less than 8.6 km/h [45,75]. More locally, a study conducted in Salou, a coastal town located about 100 km southwest of Barcelona, reported storm propagation speeds ranging between 9 and 61 km/h based on radar measurements and hourly/daily rainfall records during the 2014–2018 period [75]. These findings align well with the speed range observed in our analysis over the city of Barcelona.
The observed difference in average storm speeds obtained by the centroid and first maximum methods can be attributed to their fundamentally different definitions and sensitivities. The first maximum peak method tracks the movement of the localized maximum rainfall intensity, which is spatially and temporally constrained to the convective core of the storm, thereby reflecting primarily the propagation speed of this core. Conversely, the time centroid method computes a weighted average timing over the entire rainfall hyetogram, integrating both convective and stratiform precipitation components, thus representing the overall motion of the storm system. This integration allows the centroid to reflect contributions from diffuse precipitation areas and trailing features that may move more freely or faster than the convective core, leading to higher average speeds estimated by the centroid method.
Regarding the general propagation directions for all analyzed events, two dominant trends emerged consistently with both tracking methods: movement toward the sea and toward the northeast. While centroid-based tracking suggests a slightly more pronounced seaward propagation, this difference mainly reflects the centroid’s sensitivity to storm growth dynamics fueled by marine moisture inflow, as previously discussed. The first maximum peak method, focused on the convective core displacement, tends to show somewhat less pronounced movement toward the sea, due to its structural constraints. Focusing specifically on intense events, the predominant motion directions become more structured. Notably, about 45% of these high-intensity storms moved toward the sea, a result consistently observed with both centroid and peak tracking methods. However, only the centroid-based analysis revealed a second pronounced clustering, with a substantial proportion of fast-moving intense storms concentrated in the NNE–NE–ENE directions, nearly parallel to the coastline. This cluster accounted for over 11% of the intense centroid-tracked events, with an average speed of 32 km/h, and it aligns with the gap created by the Besòs River in the Collserola mountain range. Although a direct channeling effect is unlikely given the relatively low elevation of the ridge (~500 m) compared to convective altitudes, the topography and river corridor may still modulate surface-level flows, potentially facilitating inland breeze penetration during sea-breeze regimes. In general, the average speed of events moving in the first quadrant (N to E) was significantly higher than in the others: 32 km/h for the centroid method (with all other quadrants below 25 km/h) and 24 km/h for the first maximum method (others below 16 km/h). Nonetheless, this preferential NE orientation is also observed at broader spatial scales, suggesting a link to mesoscale circulation patterns rather than local orographic forcing alone. For instance, when studying mesoscale convective systems (MCSs) across Catalunya between 2012 and 2016, [76] found that most systems moved predominantly within a directional range from west to east or roughly from WSW to NE. The range of directions reported in that study closely matches those identified in our full dataset, spanning from NNE to SSE, with practically no MCSs moving from east to west.
5. Conclusions
Principal component analysis (PCA) has proven useful in identifying dominant spatial patterns of rainfall variability over the urban area of Barcelona, based on high-resolution data from a dense rain gauge network. The first principal component suggests the presence of a pattern that may be consistent with an urban rainfall island (URI), whose spatial configuration resembles that of the urban heat island (UHI) over the city. This urban-related signal is also reflected in the spatial distribution of the scaling parameter , calculated from the records of each rain gauge. Topographic influences, particularly from the Collserola mountain range and smaller features like Montjuïc Hill, play a key role in shaping rainfall variability across the city. The second and third principal components highlighted distinct contrasts between inland and coastal areas.
The spatial organization of dominant rainfall modes, as identified through the PCA, varies notably with event duration. At shorter durations (e.g., 10 min), a clear north–south contrast is observed across the city. As the duration increases to 1 h and 4 h, the spatial structure shifts to reveal a more distinct inland mountains versus coastal differentiation. At the 24 h timescale, rainfall patterns appear largely homogeneous across the urban area. These evolving spatial structures are broadly consistent with those observed in climatic indices such as Rx1day, where a similar inland–coastal differentiation is present, with the maritime influence progressively becoming more prominent when computed at a sub-daily resolution, especially for Rx10min.
Storm tracking analyses revealed a wide range of propagation speeds over the city of Barcelona, with average values and variability consistent with those reported in other European studies. The time centroid method consistently produced higher average propagation velocities compared to the first maximum peak method, reflecting its sensitivity to the integrated motion of the entire precipitation system rather than just the convective core. Additionally, the centroid approach yielded a larger proportion of well-fitted storm tracks, demonstrating its robustness and reliability for capturing storm dynamics at the urban scale. Despite these methodological differences, both tracking techniques revealed spatial propagation patterns broadly consistent with the dominant rainfall variability modes identified by the PCA, effectively capturing the key hydrometeorological features shaping rainfall over Barcelona. Among the most intense events, two predominant storm movement directions were identified for both methods: a dominant flow toward the sea (45% of the intense events), and a faster cluster oriented roughly toward the northeast (NNE–NE–ENE), almost parallel to the coast, which was much more pronounced when using the centroid method. This directional clustering aligns with the gap created by the Besòs River in the Collserola mountain range, although a direct channeling influence is unlikely given the relatively low elevation of the Collserola ridge (~500 m) compared to typical convective altitudes. Moreover, this NE direction is also commonly observed at broader spatial scales, reflecting mesoscale circulation patterns. However, the topography of Collserola and the low-lying corridor formed by the river may still play a role in modulating surface-level flows, potentially favoring inland breeze penetration during sea-breeze regimes.
These findings deepen our understanding of rainfall dynamics in complex urban and coastal environments and underscore the value of high-resolution, long-term observational networks in hydrometeorological research. The analysis of intense rainfall events highlights the capacity of dense urban rain gauge networks to effectively capture storm motion and variability at the city scale.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/hydrology12070178/s1, Table S1: Date, fitting parameters, speed (v) and direction (θ) of the storms monitored using the time centroid. Table S2: Date, fitting parameters, speed (v) and direction (θ) of the storms monitored using the first maximum.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.R.-S. and M.d.C.C.-C.; methodology, R.R.-S. and X.N.; software, R.R.-S. and X.N.; validation R.R.-S. and M.d.C.C.-C.; formal analysis, M.d.C.C.-C., R.R.-S., and X.N.; investigation, R.R.-S. and M.d.C.C.-C.; resources, M.d.C.C.-C.; data curation, X.N.; writing—original draft preparation, M.d.C.C.-C.; writing—review and editing, M.d.C.C.-C. and R.R.-S.; visualization, M.d.C.C.-C. and R.R.-S.; supervision, M.d.C.C.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request. In addition, selected results are provided in two Supplementary Tables included with the article. The urban rainfall data used in this study can be obtained upon request to info.bcasa@bcn.cat (Departament d’Explotació de BCASA) [77].
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Barcelona Cicle de l’Aigua, SA (BCASA) for providing the high-resolution urban rainfall data used in this study. We also extend our sincere thanks to Tomeu Rigo, Anna Rius, and the Servei Meteorològic de Catalunya (SMC) for kindly sharing the radar imagery.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Martín-Vide, J. Spatial Distribution of a Daily Precipitation Concentration Index in Peninsular Spain. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, M.C.; Rodríguez, R.; Redaño, À. Analysis of extreme rainfall in Barcelona using a microscale rain gauge network. Meteorol. Appl. 2010, 17, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.; Navarro, X.; Casas, M.C.; Redaño, À. Rainfall spatial organization and areal reduction factors in the metropolitan area of Barcelona (Spain). Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 114, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramblay, Y.; El Adlouni, S.; Servat, E. Trends and variability in extreme precipitation indices over Maghreb countries. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 3235–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Zanón, N.; Casas-Castillo, M.C.; Rodríguez-Solà, R.; Peña, J.C.; Rius, A.; Solé, J.G.; Redaño, À. Analysis of extreme rainfall in the Ebre Observatory (Spain). Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 124, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribes, A.; Thao, S.; Vautard, R.; Dubuisson, B.; Somot, S.; Colin, J.; Planton, S.; Soubeyroux, J.M. Observed increase in extreme daily rainfall in the French Mediterranean. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 1095–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lana, X.; Rodríguez-Solà, R.; Martínez, M.D.; Casas-Castillo, M.C.; Serra, C.; Burgueño, A. Characterization of standardized heavy rainfall profiles for Barcelona city: Clustering, rain amounts and intensity peaks. Theor. Appl. Climatol 2020, 142, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Hidalgo, J.C.; Beguería, S.; Peña-Angulo, D.; Trullenque, V. Catalogue and analysis of extraordinary precipitation events in the Spanish mainland, 1916–2022. Int. J. Climatol. 2025, 45, e8785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, J.; Sexton, A. The Relationship between Severe Weather Warnings, Storm Reports, and Storm Cell Frequency in and around Several Large Metropolitan Areas. Weather Forecast. 2018, 33, 1339–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Niyogi, D. Meta-analysis of urbanization impact on rainfall modification. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Vide, J.; Moreno-García, M.C. Probability values for the intensity of urban heat island (Spain). Atmos. Res. 2020, 240, 104877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torelló-Sentelles, H.; Marra, F.; Koukoula, M.; Villarini, G.; Peleg, N. Intensification and changing spatial extent of heavy rainfall in urban areas. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2024EF004505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.M.; Stallins, J.A.; Jin, M.L.; Mote, T.L. Urbanization: Impacts on Clouds, Precipitation, and Lightning. In Urban Ecosystem Ecology; Aitkenhead-Peterson, J., Volder, A., Eds.; Agronomy Monographs; ASA, CSSA, SSSA Books: Madison, WI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; 2391p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Alterskjær, K.; Stjern, C.W.; Hodnebrog, Ø.; Marelle, L.; Samset, B.H.; Sillmann, J.; Schaller, N.; Fischer, E.; Schulz, M.; et al. Frequency of extreme precipitation increases extensively with event rareness under global warming. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobinski, P.; Ducrocq, V.; Alpert, P.; Anagnostou, E.; Béranger, K.; Borga, M.; Braud, I.; Chanzy, A.; Davolio, S.; Delrieu1, G.; et al. HyMeX: A 10-Year Multidisciplinary Program on the Mediterranean Water Cycle. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 1063–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ínsua-Costa, D.; Senande-Rivera, M.; Llasat, M.C.; Míguez-Macho, G. A global perspective on western Mediterranean precipitation extremes. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, M.; Lionello, P. Synoptic climatology of winter intense precipitation events along the Mediterranean coasts. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 1707–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, M.I.P.; Santo, F.E.; Ramos, A.M.; Trigo, R.M. Trends and correlations in annual extreme precipitation indices for mainland Portugal, 1941–2007. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunyer, M.A.; Hundecha, Y.; Lawrence, D.; Madsen, H.; Willems, P.; Martinkova, M.; Vormoor, K.; Bürger, G.; Hanel, M.; Kriaučiūnienė, J.; et al. Inter-comparison of statistical downscaling methods for projection of extreme precipitation in Europe. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1827–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Notivoli, R.; Beguería, S.; Saz, M.Á.; de Luis, M. Recent trends reveal decreasing intensity of daily precipitation in Spain. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 4211–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittis, G.; Almazroui, M.; Alpert, P.; Ciais, P.; Cramer, W.; Dahdal, Y.; Fnais, M.; Francis, D.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Howari, F.; et al. Climate change and weather extremes in the Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East. Rev. Geophys. 2022, 60, e2021RG000762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Tramblay, Y.; Reig, F.; González-Hidalgo, J.C.; Beguería, S.; Brunetti, M.; Kalin, K.C.; Patalen, L.; Kržič, A.; Lionello, P.; et al. High temporal variability not trend dominates Mediterranean precipitation. Nature 2025, 639, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionello, P.; Scarascia, L. The relation of climate extremes with global warming in the Mediterranean region and its north versus south contrast. Reg. Environ. Change 2020, 20, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vautard, R.; Kadygrov, N.; Iles, C.; Boberg, F.; Buonomo, E.; Bülow, K.; Coppola, E.; Corre, L.; van Meijgaard, E.; Nogherotto, R.; et al. Assessment of the European Climate Projections as Simulated by the Large EURO-CORDEX Regional and Global Climate Model Ensemble. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2021, 126, e2019JD032356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.; Navarro, X.; Casas, M.C.; Ribalaygua, J.; Russo, B.; Pouget, L.; Redaño, À. Influence of climate change on IDF curves for the metropolitan area of Barcelona (Spain). Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Castillo, M.C.; Rodríguez-Solà, R.; Lana, X.; Serra, C.; Martínez, M.D.; Biere, R.; Arellano, B.; Roca, J. Consecuencias hidrológicas del cambio climático en entornos urbanos. In Proceedings of the XIII International Conference on Virtual City and Territory: Challenges and Paradigms of the Contemporary City, Barcelona, Spain, 2–4 October 2019; p. 8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monjo, R.; Locatelli, L.; Milligan, J.; Torres, L.; Velasco, M.; Gaitán, E.; Pórtoles, J.; Redolat, D.; Russo, B.; Ribalaygua, J. Estimation of future extreme rainfall in Barcelona (Spain) under monofractal hypothesis. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 4047–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Hao, L.; Sun, G.; Yang, Z.-L.; Li, W.; Chen, D. Urbanization aggravates effects of global warming on local atmospheric drying. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL095709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Fatichi, S.; Mascaro, G.; Manoli, G.; Peleg, N. Intensification of sub-daily rainfall extremes in a low-rise urban area. Urban Clim. 2022, 42, 101124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, N.; Wang, C.; Gu, X.; Ma, J.; Niyogi, D. Urbanization amplified asymmetrical changes of rainfall and exacerbated drought: Analysis over five urban agglomerations in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Earth’s Future 2023, 11, e2022EF003117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llasat, M.C.; Marcos, R.; Turco, M.; Gilabert, J.; Llasat-Botija, M. Trends in Flash Flood Events versus Convective Precipitation in the Mediterranean Region: The Case of Catalonia. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doswell, C., III; Ramis, C.; Romero, R.; Alonso, S. A Diagnostic Study of Three Heavy Precipitation Episodes in the Western Mediterranean Region. Weather Forecast. 1998, 13, 102–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, P.; Radian, R.; Halfon, N.; Levin, Z. Urban Rainfall Anomaly under Intensive Development, 1949–2018, Case of Tel-Aviv, Israel. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.; Crook, N.; Mueller, C.; Sun, J.; Dixon, M. Nowcasting thunderstorms: A status report. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 2079–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, C.W.; Fankhauser, J.C. Movement and propagation of multicellular convective storms. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1975, 113, 747–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente, J.; Redaño, À. Rainfall rate distribution in a local scale: The case of Barcelona city. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1990, 41, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Miao, S.; Dai, Y.; Bornstein, R. Numerical simulation of urban land surface effects on summer convective rainfall under different UHI intensity in Beijing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 7851–7868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Jin, H.G.; Han, J.Y.; Baik, J.J. Initiation and evolution of urban-induced precipitation under different background wind speeds: Roles of urban breeze circulation and cold pool. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2024, 155, 9457–9470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fowler, H.J.; Argüeso, D.; Blenkinsop, S.; Evans, J.P.; Lenderink, G.; Yan, X.; Guerreiro, S.B.; Lewis, E.; Li, X.F. Strong intensification of hourly rainfall extremes by urbanization. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Gao, Y.; Wilby, R.; Yu, D.; Wright, N.; Yin, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Guan, M. Urbanization further intensifies short-duration rainfall extremes in a warmer climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL108565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigo, T.; Llasat, M.-C. Analysis of mesoscale convective systems in Catalonia using meteorological radar for the period 1996–2000. Atmos. Res. 2007, 83, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigo, T.; Farnell, C. Quasi-Linear Convective Systems in Catalonia Detected Through Radar and Lightning Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano Ramos, B.; Roca-Cladera, J. Urban-CLIMPLAN: La Isla de Calor Urbana en la Región Metropolitana de Barcelona. ACE-Archit. City Environ. 2021, 15, 10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigo, T.; Llasat, M.C. A methodology for the classification of convective structures using meteorological radar: Application to heavy rainfall events on the Mediterranean coast of the Iberian Peninsula. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 4, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berne, A.; Krajewski, W.F. Radar for hydrology: Unfulfilled promise or unrecognized potential? Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorndahl, S.; Einfalt, T.; Willems, P.; Nielsen, J.E.; ten Veldhuis, M.-C.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Rasmussen, M.R.; Molnar, P. Weather radar rainfall data in urban hydrology. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 1359–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Rodríguez, S.; Wang, L.-P.; Willems, P.; Onof, C. A review of radar-rain gauge data merging methods and their potential for urban hydrological applications. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 6356–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esbrí, L.; Rigo, T.; Llasat, M.C.; Aznar, B. Identifying storm hotspots and the most unsettled areas in Barcelona by analysing significant rainfall episodes from 2013 to 2018. Water 2021, 13, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Conti, F.; Noto, L.; Quatrosi, A.; La Loggia, G. Using high resolution raingauge data for storm tracking analysis in the urban area of Palermo, Italy. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Precipitation in Urban Areas “Rainfall in the Urban Context: Forecasting, Risk and Climate Change”, St. Moritz, Switzerland, 10–13 December 2009; pp. 166–171. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10447/41562 (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Carbone, M.; Garofalo, G.; Tomei, G.; Piro, P. Storm Tracking based on Rain Gauges for Flooding Control in Urban Areas. Procedia Eng. 2014, 70, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, I.; Tchiguirinskaia, I.; Schertzer, D. Rain gauge networks’ limitations and the implications to hydrological modelling highlighted with a X-band radar. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, X. Organització Espacial i Temporal de la pluja a l’àrea Metropolitana de Barcelona. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Vilanova I La Geltrú, Spain, 13 October 2021. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10803/673995 (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Olsson, J.; Niemczynowicz, J. Multifractal analysis of daily spatial rainfall distributions. J. Hydrol. 1996, 187, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enjamio, C.; Vilar, E.; Redaño, À.; Fontán, F.P.; Ndzi, D. Experimental analysis of microscale rain cells and their dynamic evolution. Radio Sci. 2005, 40, RS3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servei Meteorològic de Catalunya: Divulgacio/La Predicció Meteorològica/Predicció/. Available online: https://www.meteo.cat/wpweb/divulgacio/la-prediccio-meteorologica/prediccio/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Platikanov, S.; López, J.F.; Martrat, B.; Martín-Vide, J.; Tauler, R. Temporal and Spatial Relationships Between Climatic Indices and Precipitation Zones in Europe, Spain and Catalonia. Int. J. Climatol. 2025, 45, e8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I. Principal Component Analysis. In International Encyclopedia of Statistical Science; Lovric, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Solà, R.; Casas-Castillo, M.C.; Navarro, X.; Redaño, À. A study of the scaling properties of rainfall in Spain and its appropriateness to generate intensity-duration-frequency curves from daily records. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Castillo, M.C.; Llabrés-Brustenga, A.; Rius, A.; Rodríguez-Solà, R.; Navarro, X. A single scaling parameter as a first approximation to describe the rainfall pattern of a place: Application on Catalonia. Acta Geophys. 2018, 66, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Castillo, M.C.; Llabrés-Brustenga, A.; Rodríguez-Solà, R.; Rius, A.; Redaño, À. Scaling properties of rainfall as a basis for intensity-duration-frequency relationships and their spatial distribution in Catalunya, NE Spain. Climate 2025, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Nicholls, N.; Ghazi, A. (Eds.) CLIVAR/GCOS/WMO workshop on indices and indicators for climate extremes: Workshop summary, Weather and Climate Extremes. In Weather and Climate Extremes; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 42, pp. 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemczynowicz, J. Storm tracking using rain gauge data. J. Hydrol. 1987, 93, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diskin, M.H. The Speed of Two Moving Rainfall Events in Lund. Hydrol. Res. 1990, 21, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadski, I.I. Statistical properties of precipitation patterns. J. Appl. Met. 1973, 12, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.J. The estimation and distribution of storm movement and storm structure, using a correlation analysis technique and rain gauge data. J. Hydrol. 1980, 48, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, G.J.G. A correlation–regression method for tracking rainstorms using rain-gauge data. J. Hydrol. 2002, 261, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, C.; Lana, X.; Martínez, M.D.; Roca, R.; Arellano, B.; Biere, R.; Moix, M.; Burgueño, A. Air temperature in Barcelona metropolitan region from MODIS satellite and GIS data. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 139, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Yang, Z.; Shepherd, M.; Niyogi, D. Global scale assessment of urban precipitation anomalies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2311496121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, J.; Xu, Z.; Zou, L.; Qiao, Y.; Li, P. Impact of urban expansion on rain island effect in Jinan City, North China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndtsson, R.; Niemczynowicz, J. Spatial and temporal scales in rainfall analysis—Some aspects and future perspectives. J. Hydrol. 1988, 100, 293–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Castillo, M.C.; Rodríguez-Solà, R.; Llabrés-Brustenga, A.; García-Marín, A.P.; Estévez, J.; Navarro, X. A Simple Scaling Analysis of Rainfall in Andalusia (Spain) under Different Precipitation Regimes. Water 2022, 14, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazón, J.; Pino, D. Pluviometric anomaly in the Llobregat Delta. Tethys Rev. Meteorol. Climatol. Mediterr. 2009, 6, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gascón, E.; Laviola, S.; Merino, A.; Miglietta, M.M. Analysis of a Localized Flash-Flood Event over the Central Mediterranean. Atmos. Res. 2016, 182, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Moral, A.; Llasat, M.C.; Rigo, T. Connecting Flash Flood Events with Radar-Derived Convective Storm Characteristics on the Northwestern Mediterranean Coast: Knowing the Present for Better Future Scenarios Adaptation. Atmos. Res. 2020, 238, 104863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigo, T.; Berenguer, M.; Llasat, M.C. An improved analysis of mesoscale convective systems in the western Mediterranean using weather radar. Atmos. Res. 2019, 227, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelona Cicle de l’Aigua, SA. 9. Sol·Licitud d’informació Pluviomètrica. Available online: https://www.bcasa.cat/CAT/solicitud-informacio.asp (accessed on 14 April 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).