Abstract
Electrochemical sensors have been developed based on polyethylene terephthalate track-etched membranes (PET TeMs) modified by photograft copolymerization of N-vinylformamide (N-VFA) and trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate (TMPTMA). The modification, structure and properties of the modified PET TeMs were thoroughly characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, gas permeability measurements and contact angle analysis. Optimal membrane modification was achieved using C = 10% (N-VFA), 60 min of UV irradiation and a UV lamp distance of 10 cm. Furthermore, the modified membranes were implemented in a two-electrode configuration for the determination of Eu3+, Gd3+, La3+ and Ce3+ ions via square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry (SW-ASV). The sensors exhibited a linear detection range from 10−7 M to 10−3 M, with limits of detection of 1.0 × 10−6 M (Eu3+), 6.0 × 10−6 M (Gd3+), 2.0 × 10−4 M (La3+) and 2.5 × 10−5 M (Ce3+). The results demonstrated a significant enhancement in electrochemical response due to the grafted PET TeMs-g-N-PVFA-TMPTMA structure, and the sensor showed practical applicability and consistent performance in detecting rare earth ions in tap water.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, there has been a rapid increase in the use of rare earth elements in a range of industrial sectors, from electronics and renewable energy to metallurgy and medicine. The widespread use of rare earth elements (REEs) is due to their unique magnetic, luminescent and catalytic properties [1]. However, along with technological progress, concerns about their impact on the environment and human health are growing [2]. Due to irrational consumption and insufficient disposal, REE ions are increasingly found in soil, water and living organisms. Although many of these elements were previously considered slightly toxic, recent studies show their ability to cause oxidative stress; disrupt the functionality of the kidneys, liver and central nervous system; and accumulate in biological tissues [2,3].
In this regard, monitoring the content of REEs in the environment is becoming increasingly important. High-precision analytical techniques, such as inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF), laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and atomic emission spectroscopy (AES), are used to determine REEs [4,5]. Despite their high sensitivity, these methods require complex equipment, high costs and significant time for sample preparation. Therefore, alternative approaches are becoming increasingly relevant; of particular relevance are electrochemical methods of analysis that combine sensitivity, portability, ease of use and possibility of automation.
Due to the closely related physical and chemical properties of individual REEs, their accurate detection remains a complex task. This challenge becomes even more pronounced when a specific REE must be detected within a mixture of other lanthanides, as their mutual interferences and overlapping characteristics can significantly hinder selectivity and analytical accuracy [6,7]. Electrochemical methods that combine sensor-based selectivity, operational simplicity and prompt analysis provide a promising platform for real-time monitoring of REEs [8,9]. This platform should ensure reliable, reproducible and operationally efficient detection. The significance of these performance parameters can vary depending on the specific technique employed [7,10]. Efficient control and quantification of the interaction between an analyte and a sensing element is achieved using a wide range of electrochemical methods [11]. Among them, voltammetric and potentiometric techniques stand out as particularly effective methods, offering high sensitivity at a cost-effective and time-efficient rate for identifying specific analytes.
An alternative electrochemical method involves utilizing ion-imprinted electrodes, enabling the accurate measurement of specific metal ions via voltammetry. In this context, Cao et al. created an electrochemical sensor for detecting Eu(III) ions using a modified screen-printed electrode (SPE) [12]. The ease and speed of production for screen-printed electrodes, coupled with their affordability, make them highly suitable for use in electrochemical sensors. Screen-printed electrodes (SPEs) offer the significant advantage of being modifiable, not only in terms of forming metal-sensitive films but also by incorporating functional molecules or nanomaterials. This versatility, combined with their miniaturized format, makes them excellent candidates for on-site analysis using portable instrumentation. As a result, SPEs are progressively used not only in environmental monitoring, but also in food safety, agricultural assessment and biomedical diagnostics. Differential pulse adsorptive stripping voltammetry (DPASV) was employed to detect Eu3+ using the developed sensor, which exhibited a linear response in the concentration range of 1.0 × 10−7 to 1.0 × 10−3 mol/L and achieved a detection limit of 4.0 × 10−8 mol/L under optimized conditions (−0.2 V accumulation potential, 360 s accumulation time) [13]. H. A. Zamani and co-workers reported the development of several gadolinium (III)-selective polyvinyl chloride (PVC) membrane sensors, employing a variety of molecules as ionophores [14]. At the same time, N-vinylformamide (N-VFA) monomer is highly reactive under free-radical conditions, enabling both homo- and copolymerization, typical of many vinyl monomers [15]. In addition, under acidic and basic conditions, homo- and copolymers of N-VFA easily hydrolyze to polymers containing vinylamine units and also have great potential for use in water purification [16]. In this paper, we present an electrochemical sensor based on photografting of PET with N-vinylformamide (N-VFA) and trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate (TMPTMA). This unique copolymerization provides a more stable and controllable measurement platform compared to existing methods, ensuring high REE ion detection efficiency.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Equipment and Materials
N-vinylformamide (N-VFA), trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate (TMPTMA) (Figure 1), benzophenone (BP) and isopropanol (99.9%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Sodium acetate, N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF), europium, gadolinium, lanthanum and cerium standard samples were of analytical-grade quality and applied without prior purification. All solutions were prepared using deionized water obtained from Akvilon-D301 (Podolsk, Russia). Square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry (SW-ASV) experiments were conducted using a PalmSens EmStat3+ potentiostat (Houten, The Netherlands).
Figure 1.
Structures of the monomers: (a) N-VFA and (b) TMPTMA.
2.2. Membrane Preparation and Surface Treatment
The object of this investigation comprised polyethylene terephthalate (PET) films of the Hostaphan® brand, produced by Mitsubishi Polyester Film (Wiesbaden, Germany), with a nominal thickness of 12 μm. Ion irradiation was performed using 84Kr15+ ions at energy of 1.75 MeV/nucleon, using the DC-60 heavy ion accelerator (The Institute of Nuclear Physics, Astana, Kazakhstan). The irradiation fluence was 1 × 108 ions/cm2. Membranes were obtained through photosensitization using a 30 W UV-C lamp (OSRAM HNS G13, Munich, Germany); each side was irradiated for 30 min at a distance of 10 cm. Subsequent chemical etching was conducted in NaOH (C = 2.2 M) solution at 85 °C for 3 min, resulting in the formation of membranes containing pores with diameters of 300 ± 20 nm. Following the etching procedure, the samples were stored at room temperature under standard laboratory conditions.
2.2.1. Surface Modification via UV-Initiated Grafting
Modification of PET track-etched membranes (TeMs) was performed via UV graft polymerization according to the scheme presented in the Figure 2. Prior to the reaction, the membranes were pre-cleaned by sequential washing in deionized water and isopropanol for 10 min. The samples were then immersed in a 5% benzophenone (BP) solution in N, N-dimethylformamide for 24 h, followed by drying and brief washing with isopropanol. Subsequently, the membranes were transferred into isopropanol solutions (99.9%) of the N-VFA monomer at varying concentrations (2.5, 5, 10, 15 and 20%) together with a crossing agent, TMPTMA (trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate, C = 5%). Argon gas was used to purge the reaction mixtures, eliminating dissolved oxygen. UV-induced graft polymerization was conducted using an OSRAM Ultra Vitalux E27 lamp (Munich, Germany) (UVA: 315–400 nm, 13.6 W; UVB: 280–315 nm, 3.0 W) for durations ranging from 15 to 90 min. The temperature was maintained constant at 39–40 °C using a fan. Following irradiation, the modified membranes were washed with water, dried and weighed to quantify the grafting degree.
where m1 and m2 indicate the sample masses before and after grafting, respectively.
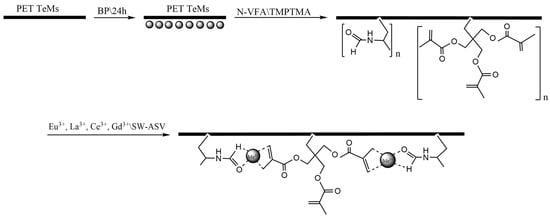
Figure 2.
Scheme of PET TeMs-g-N-PVFA-TMPTMA modification.
2.2.2. Structural and Surface Characterization of Modified Membranes
The surface morphology of the PET TeMs before and after modification was analyzed using a Phenom ProX G6 scanning electron microscope (SEM; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Eindhoven, The Netherlands). Furthermore, membrane pore size was independently assessed using the gas permeability method at a pressure of 20 kPa (data presented in Table 1). To study the chemical functionalities, FTIR spectra were recorded using an InfraLUM FT-08 IR Fourier spectrometer (Saint-Petersburg, Russia) with an ATR attachment (GladiATR from Pike Technologies, Madison, WI, USA). Spectral data were collected within the range of 400 to 4000 cm−1, accumulating 20 scans per spectrum at a controlled temperature between 20 and 25 °C. Spectral acquisition and processing were performed utilizing the SpectraLUM software package (version 2.0.1.295).

Table 1.
Impact of different modification parameters on grafting degree and PET TeM pore sizes.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was performed to investigate the thermal characteristics of the pristine PET TeMs, PET TeMs-g-N-PVFA-TMPTMA and the pure N-PVFA polymer. This technique enabled the assessment of sample thermal stability, the pathway of thermal decomposition and the associated mass loss as a function of temperature. Thermal stability of the samples was tested by using a Themys One+ (Setaram, Caluire-et-Cuire, France) thermogravimetric analyzer. Measurements were conducted under an inert argon atmosphere at a controlled heating rate of 10 °C/min, spanning a temperature range from 25 to 800 °C.
2.2.3. Surface Morphology and Mechanical Properties of Membranes Using AFM
Atomic force microscopy was used to study the membrane surface structure (AFM, NT-206, ALC Mikrotesmachines, Gomel, Belarus) in the contact mode of the AFM using standard silicon cantilevers NSG 03 (TipsNano, Tallinn, Estonia), with a stiffness of 1.7 N/m and a radius of curvature of no more than 10 nm.
2.2.4. Nanoroughness Analysis
Based on the AFM scanning results of 5 × 5 μm areas with a resolution of 256 × 256 points in the SurfaceExplorer processing program, the arithmetic mean and root mean square roughness of the sample surfaces were determined. The average values were calculated for 5 scanning areas.
The Ra index characterizes the variability in Z of the membrane surface within the selected area and is calculated using the formula
where N is the number of scanning matrix points, Zi,j is the height at position (x, y) and is the arithmetic mean value of the height in the entire scanning matrix.
The root mean square deviation (Rq) is calculated using the formula
2.2.5. Contact Angle (CA) Measurement
The wettability of the membrane surface was analyzed based on the measured CA values using the DSA 100E setup (KRUSS, Hamburg, Germany) using the sessile drop method. The principle of measuring the CA is based on constructing a tangent at a three-phase point: liquid–substrate–air. Diiodomethane (Sigma-Aldrich, 99%) and distilled water were used as test liquids. Based on the CA values, the free surface energy (γ) and its specific polar component (γp) were measured using the WORK (Ounce, Wendt, Rabel and Kjelble) method. The accuracy of measuring the contact angle was ±0.1°.
2.3. Electrochemical Stripping Voltammetry
Sensors based on PET TeMs-g-N-PVFA-TMPTMA prepared under optimal conditions (t = 60 min, C = 10%, a distance from the UV lamp of 10 cm, T = 38–40 °C) were constructed by magnetron sputtering (Safematic CCU-010 HV, Zizers, Switzerland) of gold with a thickness of 40–50 nm on both surfaces of the membrane through a template-based procedure, as detailed in [17]. Gold was sputtered onto both sides of the PET TeMs using ambient air at a base pressure of 1 × 10−5 mbar and 30 W power, with 300 s of deposition per side. The process was conducted without substrate heating. The size of the gold surfaces was 5 × 10 mm. Electrical connections to these gold surfaces were established using 0.4 mm diameter copper cables secured with silver paste to minimize interfacial resistance and subsequently insulated with layers of fingernail varnish and wax to prevent short circuits and ensure electrochemical isolation. A picture of the prepared sensor is presented in Figure S2. The sensor was configured as a two-electrode system, with one gold surface serving as the working electrode (WE) and the opposing gold surface acting as the counter electrode (CE). Electrochemical measurements were conducted using a PalmSens EmStat3+ potentiostat in conjunction with an external Ag/AgCl reference electrode immersed in KCl (C = 3 M) solution.
SW-ASV was performed using solutions of europium, lanthanum, gadolinium and cerium by dissolving the appropriate amount of their nitrate or chloride in 100 mL of 0.1 M sodium acetate. Prepared sensors were kept in an analyzed solution for 30 min before the measurements. SW-ASV signals were taken at deposition potential of −1.2 V for 60 s, and then scanning from −1 V to 1 V at a frequency of 50 Hz and an amplitude of 20 mV was performed. The concentration of Eu3+, Gd3+, La3+ and Ce3+ ions varied from 10−3 M to 10−7 M. Then, in the presence of a reference electrode (Ag/AgCl), Eu3+, Gd3+, La3+ and Ce3+ ions were precipitated for 60 s. A scan was then performed from −1 to 1 V to oxidize rare earth metal ions at a redox potential of −0.6–0.3 V.
3. Results
3.1. PET TeM Surface Modification
The modification of PET TeMs was achieved through a UV-initiated graft polymerization process involving N-VFA and TMPTMA, where TMPTMA was used as a crosslinking agent. Prior to UV exposure, benzophenone forms reactive species capable of hydrogen abstraction from the PET substrate, initiating radical formation on the surface. As a result of the hydrogen splitting off, active radical centers are formed on the membrane surface, forming initiating centers that ensure controlled covalent grafting of functional polymer layers at the polymerization stage. Subsurface localization of benzophenone increases the mechanical stability and durability of grafted films. These sites initiate the polymerization of N-VFA, leading to the formation of poly(N-vinylformamide) chains covalently bonded to the PET TeMs. Then, TMPTMA monomer, with multiple methacrylate groups, participates in the grafting process and promotes crosslinking due to its multifunctional structure. As a result, a co-grafted layer composed of both N-PVFA and a crosslinked TMPTMA network forms on the membrane surface, combining the functional properties of N-PVFA with the structural stability imparted by TMPTMA. The resulting crosslinked N-PVFA network on the PET membrane surface provides binding sites (carbonyl oxygen atoms and nitrogen, oxygen atoms in the amide groups of PVFA) for the rare earth metal ions. The crosslinked network improved both the durability and the exposure of active binding sites for ion coordination.
The parameters influencing the grafting degree (monomer concentration, reaction time and distance from the UV lamp) were methodically optimized to achieve a high grafting degree while maintaining the porous structure of the membrane. The corresponding results are presented in Table 1 and Figure 3. Isopropanol (IPA) was selected as the solvent due to its effective solubilization of the N-VFA monomer. The grafting degree increased from 1.06% to 12.93% as the reaction time extended from 15 to 60 min, a consistent enhancement in the grafting degree, whereas increasing the monomer concentration beyond 10% resulted in a slight decline in grafting efficiency.
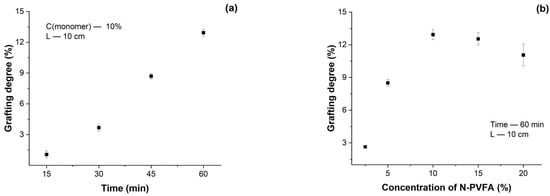
Figure 3.
Grafting degree depending on UV irradiation time (a) and monomer concentration (b).
3.1.1. Characterization of Surface Changes on PET TeMs
The FTIR spectra of the initial PET TeMs, N-PVFA, TMPTMA and PET TeMs-g-N-PVFA-TMPTMA are shown in Figure 4. The initial PET TeMs have main absorption peaks at 2950–3100 cm−1 (aliphatic CH), 1714 cm−1 (C=O), 1634, 1554, 1454 cm−1 (aromatic vibrations of the carbon skeleton), 1242 cm−1 (C(O)-O) and 974 cm−1 (O-CH2). Photograft polymerization of N-PVFA led to the appearance of new peaks at 3300 cm−1; the N-H bond in the amide group leads to wide stretching vibrations in this region. Also, the pronounced shoulder at 1650–1690 cm−1 corresponds to the stretching vibrations of the carbonyl (C-O) group of formamide. FTIR analysis confirms the participation of the carbonyl groups of the formamide fragments in the interaction, as evidenced by the shift in the C=O bond stretching frequency from 1640 to 1620 cm−1. The polymerization of TMPTMA is confirmed by the increased intensity in the C=O region (~1720 cm−1) due to the additional ether carbonyl groups and the appearance of CH2 bending in the region of 1454 and 1386–1408 cm−1.
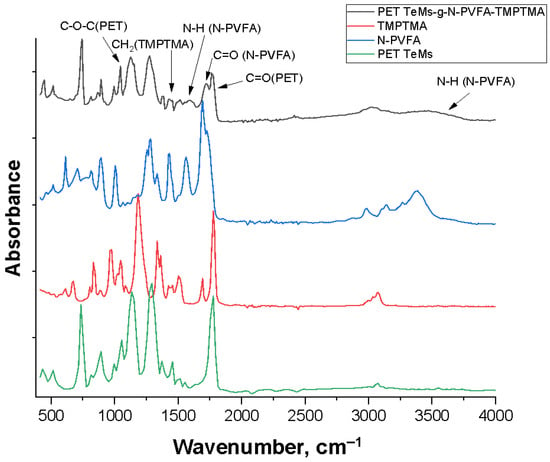
Figure 4.
FTIR spectra of modified PET TeMs-g-N-PVFA-TMPTMA.
Most studies have shown that block copolymers of TMPTMA, along with similar monomers containing carboxyl and hydroxyl groups, can be polymerized and grafted onto various polymers using free-radical or radiation initiation. This process results in the formation of crosslinking networks, which improve the mechanical and thermal properties of the material. The crosslinking significantly enhances the mechanical strength, stability, and chemical resistance of the membrane, making it more durable and suitable for a wide range of applications [18,19].
Figure 2 presents a simplified representation of the PET membrane with a grafted poly(N-VFA) chain. The units of N-VFA and TMPTMA are linked to the PET surface after photoinitiated grafting. TMPTMA was used to form a strong bond between the PET TeM surface and poly(N-VFA) chain. The second part illustrates the coordination of rare earth metal ions to the carbonyl oxygen atoms of the formamide groups on the grafted poly(N-VFA) and TMPTMA chains.
3.1.2. Morphological and Structural Characterization via SEM, AFM and TGA
The surface morphology of PET TeMs and PET TeMs-g-N-PVFA-TMPTMA coated on PET TeMs before and after modification was observed by scanning electron micrographs. It can be seen from Figure 5 that the modified membrane (b) is smooth and homogeneous. The SEM micrographs clearly demonstrate that the modification of the PET TeMs with N-PVFA-TMPTMA leads to a substantial change in the surface morphology, characterized by the covering of the original pores, resulting in a partial clogging of these pores.
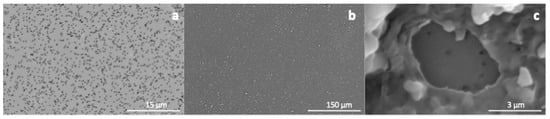
Figure 5.
SEM micrographs of the original PET TeMs (a) and the modified PET TeMs-g-N-PVFA-TMPTMA (t = 60 min, N-VFA (C = 10%), L = 10 cm) at different magnifications: 1000× (b) and 50,000× (c).
The thermogram of the PET TeMs demonstrates (Figure 6) notable thermal stability up to 380 °C, beyond which a significant mass loss event is observed within the temperature range of 380–450 °C, indicative of the primary polymer backbone degradation. A residual mass of 9.6% of the initial weight remains at the maximum analyzed temperature of 800 °C, attributable to the formation of thermally stable char. Conversely, the N-PVFA homopolymer (blue line) exhibits a multi-stage degradation process. An initial gradual mass loss commences around 100 °C, likely due to the release of volatile byproducts or moisture, followed by a more pronounced decomposition phase between 250 °C and 450 °C, corresponding to the thermal scission of the polymer chains. Near-complete decomposition is observed by 800 °C, with minimal residual mass [20]. The PET TeMs-g-N-PVFA-TMPTMA (t = 60 min, N-VFA concentration 10%, L = 10 cm UV distance, T = 38–40 °C) composite (red line) displays a thermal degradation profile that is intermediate between the pristine PET TeMs and the N-PVFA homopolymer, reflecting the successful grafting of the N-PVFA-based polymer onto the PET TeMs. The thermogram shows a slight mass loss at lower temperatures, followed by significant decomposition beginning at 380 °C and continuing up to 450 °C. At 600 °C, 8.58% of the modified membrane’s mass remains. In comparison, the residual mass of pure N-PVFA is 16.5%. The residue at 450 and 600 °C is lower than that of unmodified PET TeMs but higher than that of the N-PVFA monomer, confirming the composite nature of the grafted membrane.
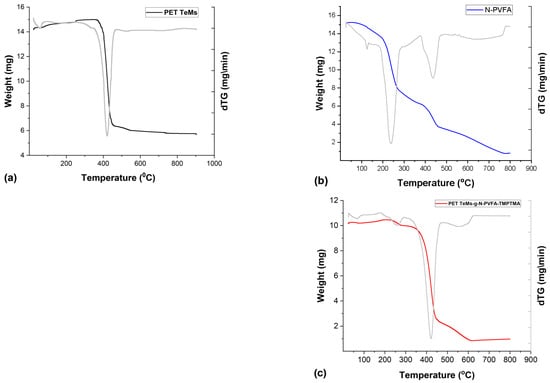
Figure 6.
Thermogravimetric (TGA) analysis results for samples PET TeMs (a), N-PVFA (b) and PET TeMs-g-N-PVFA-TMPTMA (c).
AFM data on the surface structure of the PET TeM samples after modification are shown in Figure 7. It is shown that samples s1 and s2 are characterized by a developed surface. The highest nanoroughness values were found for sample s1 (Ra = 15.66 nm, Rq = 20.72 nm) (Table 1). The pore boundaries of sample 2 are not clearly defined (Ra = 4.12 nm, Rq = 5.64 nm). With an increase in the monomer concentration to 10% (s3 (Ra = 6.18 nm, Rq = 9.02 nm)) and 15% (s4), the degree of polymerization reaches values of about 13%. The pore boundaries are uniform; the interpore space is characterized by a dense uniform structure (s3, s4). The lowest surface roughness values were noted for sample s4, which indicates the uniformity of the studied surface (Ra = 2.88 nm ± 10%, Rq = 4.24 nm ± 10%).
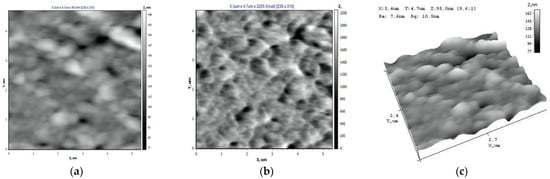
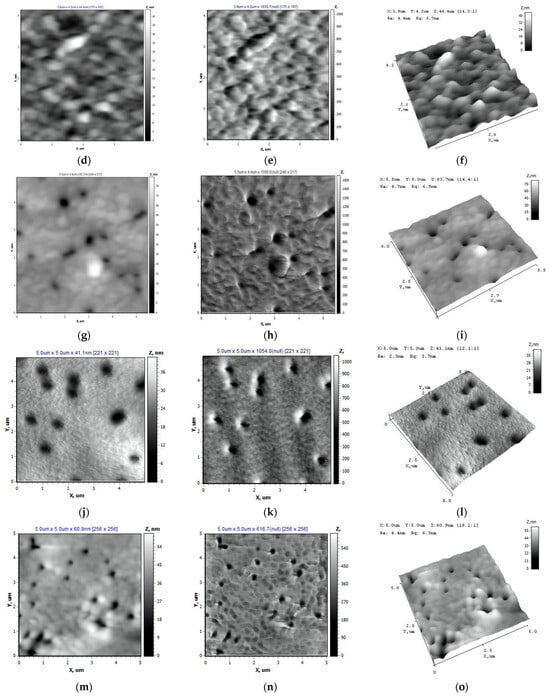
Figure 7.
The surface structure of PET TM in the AFM operating modes “Topography” (a,d,g,j), “Torsion” (b,e,h,k), and “3D” (c,f,i,l) and the initial PET TeMs (m,n,o). (a–c) Sample s1, (d–f) sample s2, (g–i) sample s3, (j–l) sample s4, (m–o) sample s0.
All types of samples are hydrophilic (Table 2); the CA is about 40° and does not depend on the monomer concentration (pictures of the water droplets are presented in Figure S1). However, the dispersion component contributes a significant specific weight (2/3) to the surface energy values, which is due to the nature of the polymers used.

Table 2.
Change in the CA and specific surface energy (γ) of PET TeM samples after modification.
3.2. Electrochemical Measurement
Voltammetric Properties of Eu3+, Gd3+, La3+, Ce3+ on Track-Etched Membrane Sensor Surfaces
Among the rare earth ions studied, europium (Eu3+) exhibited the most significant enhancement in peak height and analytical sensitivity under acidic conditions, particularly at pH 6. As illustrated in Figure 8, the square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry (SW-ASV) peak current (I, mA) displayed a strong dependence on the solution pH. Beyond pH 7, a pronounced decrease in peak current was observed, possibly due to the formation of weaker coordination complexes between REE ions and functional groups of the polymer chains. By comparison, at lower pH values, electrochemical detection of REE ions becomes increasingly compromised by the onset of hydrogen evolution, typically occurring in the potential range of −0.9 to −0.8 V. To balance sensitivity and signal clarity, optimal pH values were selected for each ion in subsequent analyses: pH 6 for Eu3+, pH 5 for Gd3+, pH 4 for La3+ and pH 7 for Ce3+.
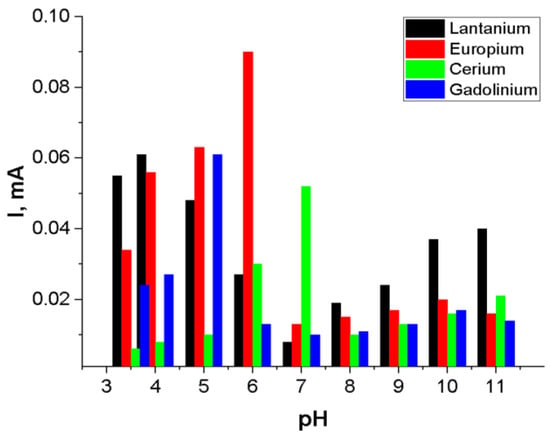
Figure 8.
Adsorption kinetics versus peak height of Eu3+, Gd3+, La3+ and Ce3+ ion (10−3 M) deposition at −1.2 V for 60 s.
To optimize the adsorption time for electrochemical detection, PET TeMs modified via photograft polymerization with N-PVFA and TMPTMA were immersed in 10−3 M solutions of Eu3+, Gd3+, La3+ and Ce3+ ions prepared in 0.1 M sodium acetate for 30 min. Electrochemical deposition and reduction of these rare earth metal ions were subsequently carried out with an applied potential of −1.2 V for 60 s using the Ag/AgCl reference electrode. Following deposition, a potential sweep from −1 V to +1 V was performed to record the oxidation signals corresponding to each ion species.
Subsequent sensor performance evaluation was conducted across a concentration range of 10−3 to 10−7 M for the target rare earth elements. The resulting calibration curves (depicted in Figure 9) demonstrated the following limits of detection (LODs): Eu3+—1.0 × 10−6 M (R2 = 0.95); Gd3+—6.0 × 10−6 M (R2 = 0.99); La3+—2.0 × 10−4 M (R2 = 0.90); Ce3+—2.5 × 10−5 M (R2 = 0.93). The results demonstrate that photografting N-PVFA and TMPTMA onto PET TeMs substantially improves their surface reactivity and sensing capabilities. The repeatability of the PET TeMs-g-N-PVFA-TMPTMA-based sensor was evaluated by conducting ten consecutive measurements of rare earth elements at a concentration of 10−3 M in wastewater. The standard deviation remained below 6%, demonstrating a good reproducibility and stability of the sensor under complex conditions.
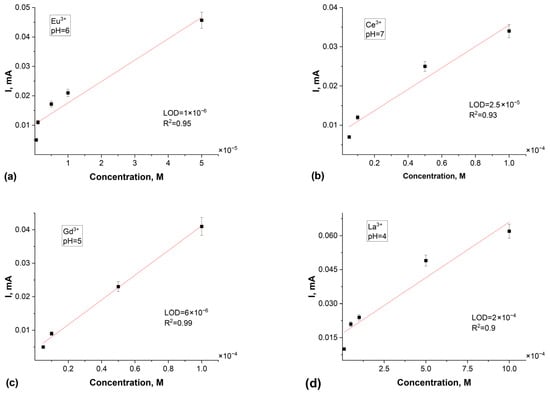
Figure 9.
Calibration curves of peak currents for Eu3+ (a), Ce3+ (b), Gd3+ (c) and La3+ (d) concentration for SW-ASV after 30 min of adsorption in appropriate Eu3+, Gd3+, La3+ and Ce3+ solution in 0.1 M sodium acetate electrolyte.
The developed electrochemical sensor was evaluated for its practical applicability by individually detecting REE ions in tap water. Results are presented in the Table 3. For validation, the PET TeMs-g-N-PVFA-TMPTMA sensor was used to measure REE concentrations in tap water after membrane-based filtration. The results demonstrate that the PET TeMs-g-N-PVFA-TMPTMA-modified sensor offers high analytical sensitivity and reliable performance in selectively identifying Eu3+, Gd3+, La3+ and Ce3+ ions.

Table 3.
Results of determination of REE ions in water samples.
The adsorption behavior of Ce3+, Eu3+, La3+ and Gd3+ ions was analyzed by fitting the experimental data to the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models. The correlation coefficients (R2) for both models indicated a good fit, with the Langmuir model generally exhibiting slightly higher R2 values, suggesting monolayer adsorption on a homogeneous surface (Figure S3).
In the Langmuir model, the maximum current response Imax, which reflects the theoretical saturation capacity of the electrode surface, ranged from 0.05285 mA (Ce3+) to 0.08710 mA (Eu3+). Notably, the Langmuir constant KL, which quantifies the binding affinity, was highest for Gd3+ (144.17 L/μM), indicating a significantly stronger interaction with the adsorbent compared to the other ions.
In the Freundlich model, the adsorption intensity n was greater than 1 for all ions, suggesting favorable adsorption. The highest Freundlich constant KF was also observed for Gd3+ (4.528), supporting the Langmuir-based conclusion about its high affinity.
Overall, both models consistently identified Gd3+ as the most strongly adsorbed ion on the surface, followed by Eu3+, La3+, and Ce3+. These results suggest that the electrode material has a higher selectivity toward Gd3+ under the experimental conditions applied.
Table 4 presents a comparative analysis of various REE sensing methods, highlighting their target ions, LOD, response time and selectivity. The obtained results are comparable to those reported for other REE sensing methods, as presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Comparison of REE sensing methods.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we presented that UV polymerization of N-vinylformamide, followed by crosslinking with trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate on poly(ethylene terephthalate) track-etched membranes, significantly enhances the functional properties of electrochemical sensors. The developed sensors were tested for the electrochemical detection of Eu3+, Gd3+, La3+ and Ce3+ ions using SW-ASV over a concentration range of 10−3 to 10−7 M. By controlling the modification conditions, effective complexation of rare earth ions on the sensor surface was achieved. The calibration curves demonstrated that the sensor exhibits reliable sensitivity for REE detection, with limits of detection of 1.0 × 10−6 M for Eu3+ (R2 = 0.95), 6.0 × 10−6 M for Gd3+ (R2 = 0.99), 2.0 × 10−4 M for La3+ (R2 = 0.90) and 2.5 × 10−5 M for Ce3+ (R2 = 0.93). The obtained results confirm the efficiency of the developed sensor, which enables selective and sensitive detection of rare earth element ions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemengineering9040088/s1, Figure S1: Water contact angles; Figure S2: Picture of electrochemical sensors based on modified PET track-etched membranes; Figure S3: Isotherm models fitting of electrochemical adsorption data; Table S1: Fitted parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models for Ce3+, Eu3+, La3+, and Gd3+ ions; Table S2: Summary of linear range and sensitivity for REE detection using PET TeMs-g-N-PVFA-TMPTMA sensor.
Author Contributions
Investigation, N.Z., A.B.Y. and G.B.M.; writing—original draft preparation, N.Z.; resources, A.T.Z. and S.A.C.; supervision, I.V.K.; visualization, A.B.Y.; data curation, G.B.M., S.A.C. and A.T.Z.; writing—review and editing, I.V.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Energy of the Republic of Kazakhstan (BR23891691).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the authors.
Acknowledgments
In preparing this manuscript, the authors utilized ChatGPT (version 4o) to enhance the English grammar and style for improved clarity and readability. The original draft and subsequent revisions were written by the authors themselves. Following the use of these tools, the authors thoroughly reviewed and edited the output and assume full responsibility for the final content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
References
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Buchert, M. Recycling of rare earths: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 51, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, L. Toxic effects of rare earth elements on human health: A review. Toxics 2024, 12, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi, W.; Mangori, L.; Danha, C.; Chaukura, N.; Dunjana, N.; Sanganyado, E. Sources, behaviour, and environmental and human health risks of high-technology rare earth elements as emerging contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardini, F.; Soggia, F.; Rugi, F.; Udisti, R.; Grotti, M. Comparison of inductively coupled plasma spectrometry techniques for the direct determination of rare earth elements in digests from geological samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 678, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Rare earth elements: A review of applications, occurrence, exploration, analysis, recycling, and environmental impact. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vito, I.; Olsina, R.; Masi, A. Enrichment method for trace amounts of rare earth elements using chemofiltration and XRF determination. Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 2000, 368, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; Majumdar, S. Polymers in sensor applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2004, 29, 699–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawisza, B.; Pytlakowska, K.; Feist, B.; Polowniak, M.; Kita, A.; Sitko, R. Determination of rare earth elements by spectroscopic techniques: A review. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 2373–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.J.C.; Milton, M.J.T. Analytical techniques for trace element analysis: An overview. Trends Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, C.M.A. Electrochemical sensors for environmental monitoring: Strategy and examples. Pure Appl. Chem. 2001, 73, 1969–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Sun, Y.P. Evaluation of ionic imprinted polymers by electrochemical recognition of rare earth ions. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 87, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Bai, H.; Xia, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Cao, Q. Electrochemical sensor for detection of europium based on polycatechol and ion-imprinted sol–gel film modified screen-printed electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 824, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Bai, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P.; Cao, Q. Stripping voltammetric determination of europium via ultraviolet-trigger synthesis of ion imprinted membrane. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 271, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, H.A.; Mohammadhosseini, M.; Mohammadrezazadeh, S.H.; Faridbod, F.; Ganjali, M.R.; Meghdadi, S.; Davoodnia, A. Gadolinium(III) ion selective sensor using a newly synthesized Schiff’s base as a sensing material. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek, E.; Pazdro, M.; Bortel, E. Mechanism for Base Hydrolysis of Poly(N-vinylformamide). J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2007, 44, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinschmidt, R. Polyvinylamine at last. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 2257–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolkov, V.; Mashentseva, A.A.; Guven, O.; Taltenov, A.A. UV-induced graft polymerization of acrylic acid in the sub-micronchannels of oxidized PET track-etched membrane. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2015, 365, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebi, S.; Jahani, Y.; Arabi, H. Trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate functionalized polypropylene/polyhexene-1 blend with enhanced melt strength. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2019, 59, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi-Saghandikolaei, S.; Frounchi, M.; Dadbin, S.; Augier, S.; Passaglia, E.; Ciardelli, F. Modification of isotactic polypropylene by the free-radical grafting of 1,1,1-trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sütekin, S.D.; Demirci, S.; Kurt, S.B.; Güven, O.; Sahiner, N. Tunable fluorescent and antimicrobial properties of poly(vinyl amine) affected by the acidic or basic hydrolysis of poly(N-vinylformamide). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 140, e51234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P.; Alizadeh, T.; Tadjarodi, A.; Hanifehpour, Y. Fabrication of a highly selective and sensitive Gd(III)-PVC membrane sensor based on N-(2-pyridyl)-N′-(4-nitrophenyl)thiourea. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 120, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanty, B.; Srivastava, A.; Verma, P.K.; Leoncini, A.; Huskens, J.; Verboom, W.; Mohapatra, P.K. A highly efficient sensor for europium(III) estimation using a poly(propylene imine) diaminobutane diglycolamide dendrimer as the ionophore: Potentiometric and photoluminescence studies. Microchem. J. 2024, 196, 109530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Yousefi, M.; Hosseini, M.; Ganjali, M.R. Lanthanum(III) PVC membrane electrodes based on 1,3,5-trithiacyclohexane. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5538–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).