The Spatial Distribution and Bioaccumulation of Anatoxin-A in Hulun Lake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
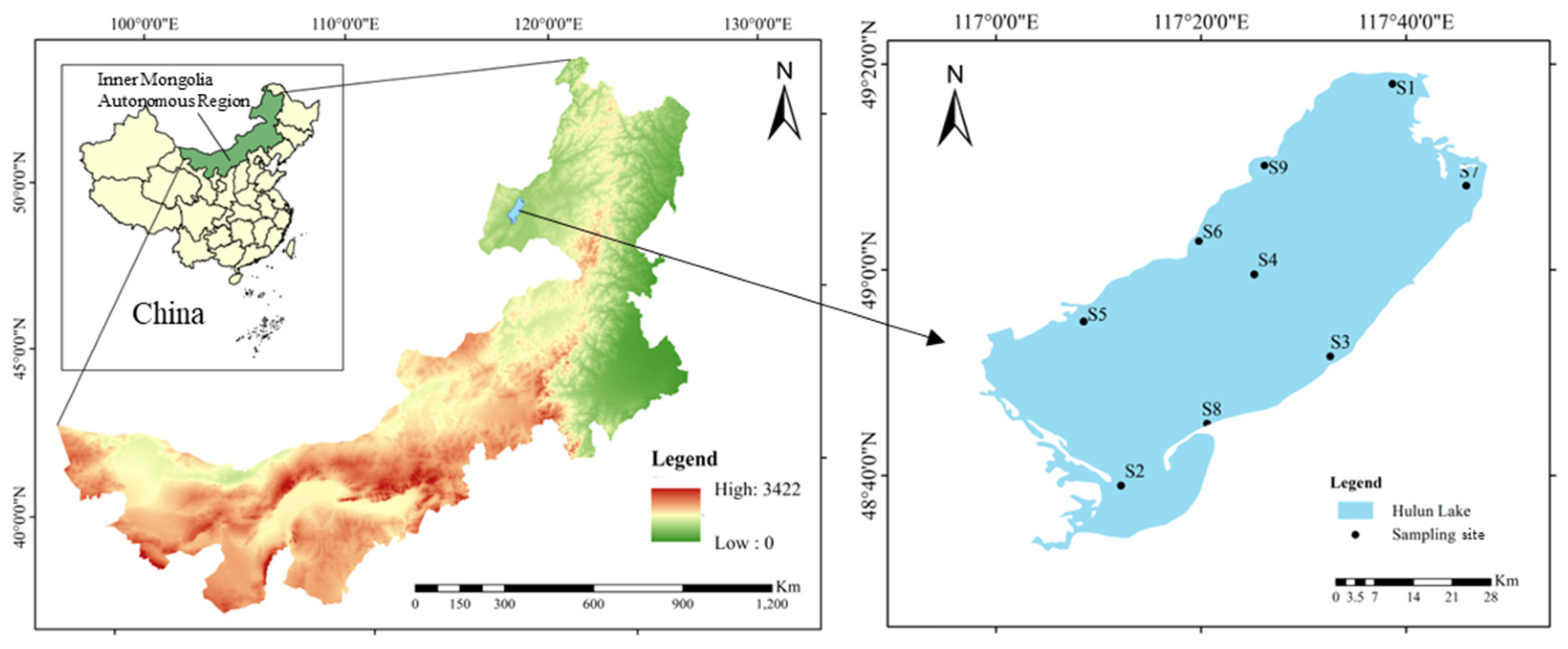
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Density and Identification of Phytoplankton
2.3. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.4. Chemicals and Standards
2.5. Extraction of ATX-A from Samples
2.6. ATX-A Detection and Quantification
2.7. The Total Length and Weight of the Fish
2.8. Calculation of Biological Magnification Effects
2.9. Risk Assessment
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Species Abundances
3.2. Detection of ATX-A Concentration in Cyanobacterial Cells
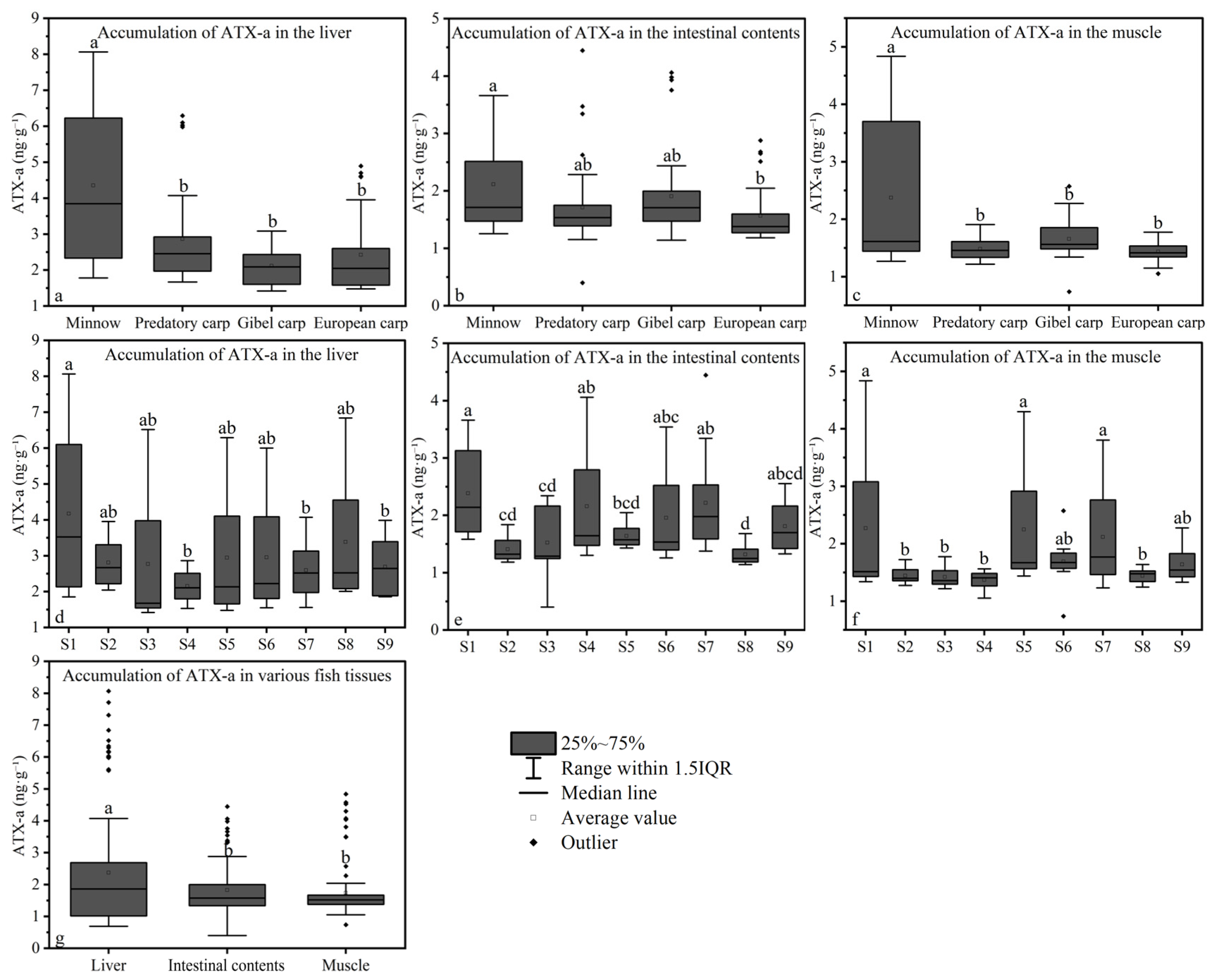
3.3. Spatial Distribution of ATX-A
3.4. Measurement of Fish Total Length and Weight
3.5. Bioaccumulation of ATX-A
3.6. Subsection Biomagnification of ATX-A
3.7. Correlations of Environmental Concentrations and Biological Accumulation of ATX-A
3.8. Risk Assessment Reveals Low Human Health and Ecological Risks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hallegraeff, G.M. A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 1993, 32, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajan, K.; Osterholz, H.; Stegen, J.; Udovič, M.G.; Orlić, S. Mechanisms shaping dissolved organic matter and microbial community in lake ecosystems. Water Res. 2023, 245, 120653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, D.; Gan, N.; Geng, R.; Cao, Q.; Song, L.; Yu, G.; Li, R. Cyanobacterial blooms in China: Diversity, distribution, and cyanotoxins. Harmful Algae 2021, 109, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerasino, L.; Salmaso, N. Co-occurrence of anatoxin-a and microcystins in Lake Garda and other deep subalpine lakes. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2020, 11, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk-Woźniak, E.; Krztoń, W.; Budziak, M.; Walusiak, E.; Žutinič, P.; Udovič, M.G. Harmful blooms across a longitudinal gradient in central Europe during heatwave: Cyanobacteria biomass, cyanotoxins, and nutrients. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Feng, L.; Dai, Y.; Hu, C.; Gibson, L.; Tang, J.; Lee, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cai, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Global mapping reveals increase in lacustrine algal blooms over the past decade. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Wang, G.; Yao, Y.; Peng, Z.; Dou, H.; Jiang, G. Warming-driven shifts in ecological control of fish communities in a large northern Chinese lake over 66 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 144722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dreher, T.W.; Li, R. An overview of diversity, occurrence, genetics and toxin production of bloom-forming Dolichospermum (Anabaena) species. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.P.; Edwards, O.E.; Gorham, P.R.; Hunter, N.R.; Pike, R.K.; Stavr, B. Anatoxin-a, a toxic alkaloid from Anabaena flos-aquae NRC-44h. Can. J. Chem. 1976, 55, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Molloy, L.; Wonnacott, S.; Gallagher, T.; Brough, P.A.; Livett, B.G. Anatoxin-a is a potent agonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor of bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 289, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, S.; Cohen, M.; Hugon, F.C.; Pichon, V.; Mazmouz, R.; Méjean, A.; Ploux, O. Synthesis, configuration assignment, and simultaneous quantification by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry, of dihydroanatoxin-a and dihydrohomoanatoxin-a together with the parent toxins, in axenic cyanobacterial strains and in environmental samples. Toxicon 2012, 60, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, I.Y.; Yang, F.; Ding, Z.; Yang, S.; Guo, J.; Tezi, C.; Osman, M.A.; Kamegni, R.B.; Zeng, W. Exposure routes and health effects of microcystins on animals and humans: A mini-review. Toxicon 2018, 151, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biré, R.; Bertin, T.; Dom, I.; Hort, V.; Schmitt, C.; Diogène, J.; Lemée, R.; Haro, L.D.; Nicolas, M. First evidence of the presence of anatoxin-a in sea figs associated with human food poisonings in France. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backović, D.D.; Tokodi, N. Cyanotoxins in food: Exposure assessment and health impact. Food Res. Int. 2024, 184, 114271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoffersen, K. Ecological implications of cyanobacterial toxins in aquatic food webs. Phycologia 1996, 35, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, S.; Duval, C.; Marie, B. Toxicity, transfer and depuration of anatoxin-a (cyanobacterial neurotoxin) in medaka fish exposed by single-dose gavage. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 222, 105422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitman, P.; Schaeffer, B.; Salls, W.; Coffer, M.; Mishra, S.; Seegers, B.; Loftin, K.; Stumpf, R.; Werdell, P.J. A validation of satellite derived cyanobacteria detections with state reported events and recreation advisories across U.S. lakes. Harmful Algae 2022, 115, 102191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, J.S.; Stockley, N.; Harvey, K.; Mcfarland, M.; Gordon, S.C.; Schaefer, A.M. Symptom frequency and exposure to a cyanobacteria bloom in Florida. Harmful Algae 2023, 129, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, D.; Koehler, H.; Mcgirr, S.; Parkes, R.; Lucy, F.E.; Touzet, N. Seasonal community dynamics and toxicity potential of cyanobacteria in Lough Arrow, an oligo-mesotrophic lake in the north-west of Ireland. Limnologica 2023, 103, 126124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, V.G.; Khan, E. Freshwater neurotoxins and concerns for human, animal, and ecosystem health: A review of anatoxin-a and saxitoxin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 39515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffersen, K.; Kaas, H. Toxic cyanobacteria in water. A guide to their public health consequences, monitoring, and management. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 1013–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, A.; Bober, B.; Lechowski, Z.; Bialczyk, J. Determination of anatoxin-a stability under certain abiotic factors. Harmful Algae 2013, 28, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.K.; Krieger, R.I. Stability studies on the cyanobacterial nicotinic alkaloid snatoxin-A. Toxicon 1991, 29, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapala, J.; Lahti, K.; Sivonen, K.; Niemelä, S.I. Biodegradability and adsorption on lake sediments of cyanobacterial hepatotoxins and anatoxin-a. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1994, 19, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Cyanobacterial Toxins: Anatoxin-a and Analogues. 2020. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/338060 (accessed on 11 November 2025).
- Zhang, H.; Yao, B.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y. Understanding the changes of optically active substances (OACs) in Hulun Lake in the past 35 years and its indication to the degradation of aquatic ecology. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 377, 134286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wei, Q.; Pang, B.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G.; Dou, H.; et al. Microcystin exposure alters gut microbiota composition in fish: An in-Situ analysis of post-bloom effects in Hulun Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, F.; Lu, Y.; Ha, X. Feedbacks between phytoplankton and global changes in a riverine source-mainstem-estuary continuum. Water Res. 2025, 268, 122746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, M.M.; Hii, K.S.; Kassim, N.S.; Azmi, N.F.M.; Baharudin, S.N.; Gu, H.; Leaw, C.P.; Lim, P.T. Diversity and distribution of micro-phytoplankton and harmful microalgae along the Malaysian coasts of Malacca Strait and South China Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2025, 81, 103947. [Google Scholar]
- Turland, N.J.; Wiersema, J.H.; Barrie, F.R.; Greuter, W.; Hawksworth, D.L.; Herendeen, P.S.; Knapp, S.; Kusber, W.H.; Li, D.Z.; Marhold, K. International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants. In Proceedings of the Nineteenth International Botanical Congress, Shenzhen, China, 23–29 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Zhao, C.; Mwagona, P.C.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Dou, H.; Zhou, X.; Bhadha, J.H. Bottom-up and top-down effects on phytoplankton functional groups in Hulun Lake, China. Ann. Limnol. 2021, 57, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Bai, D.; Li, T.; Li, J.; Jia, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Cao, X.; Song, L. Understanding filamentous cyanobacteria and their adaptive niches in Lake Honghu, a shallow eutrophic lake. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 152, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekar, H.; Westerberg, E.; Bruno, O.; Lääne, A.; Persson, K.M.; Thim, L.F. Fast, rugged and sensitive ultra high pressure liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for analysis of cyanotoxins in raw water and drinking water—First findings of anatoxins, cylindrospermopsins and microcystin variants in Swedish source waters and infiltration ponds. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1429, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, M.A.; Cordeiro-Araújo, M.K.; Bittencourt-Oliveira, M.D.C. Growth and antioxidant response of Microcystis aeruginosa (Cyanobacteria) exposed to anatoxin-a. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Gu, X.; Zeng, Q. The structure of fish community and changes of fishery resources in Lake Hulun. J. Lake Sci. 2016, 28, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saijirahu, B. Folk medicine among the Mongols in Inner Mongolia. Asian Med. 2008, 4, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisk, A.T.; Hobson, K.A.; Norstrom, R.J. Influence of chemical and biological factors on trophic transfer of persistent organic pollutants in the Northwater Polynya marine food web. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hop, H.; Borga, K.; Gabrielsen, G.W.; Kleivane, L.; Skaare, J.U. Food web magnification of persistent organic pollutants in poikilotherms and homeotherms from the Barents Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2589–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xie, P.; Guo, L.; Li, L.; Miyabara, Y.; Park, H. Organ distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in freshwater fish at different trophic levels from the eutrophic Lake Chaohu, China. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Havens, K.E. Cyanobacterial toxins: A qualitative meta-analy sis of concentrations, dosage and effects in freshwater, estuarine and marine biota. In Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Hudnell, H.K., Ed.; Springer Science: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 675–732. [Google Scholar]
- Skowrońska, B.P.; Kalinowska, R.; Skowroński, T. Cyanotoxin diversity and food web bioaccumulation in a reservoir with decreasing phosphorus concentrations and perennial cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 2013, 28, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, F.J.; Johnson, A.; Hamel, K.; Preece, E. Cyanotoxin bioaccumulation in freshwater fish, Washington State, USA. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, B.K.; Wilson, A.E.; Filho, A.D.S.F. Biomagnification or biodilution of microcystins in aquatic foodwebs? Meta-analyses of laboratory and field studies. Harmful Algae 2012, 18, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Bruning, K.; Jonge, J.D.; Wolfstein, K.; Pires, L.M.D.; Postma, J.; Burger, T. Distribution of Microcystins in a Lake Foodweb: No Evidence for Biomagnification. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 49, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Gardner, W.S.; Havens, K.E.; Joyner, A.R.; McCarthy, M.J.; Newell, S.E. Mitigating cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in aquatic ecosystems impacted by climate change and anthropogenic nutrients. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, A.S.; Araújo, M.K.C.; Chia, M.A.; Oliveira, M.D.C.B. Cyanotoxin contamination of semiarid drinking water supply reservoirs. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.F.; Tsuji, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Harada, K.I.; Suzuki, M. Release of heptapeptide toxin (microcystin) during the decomposition process of Microcystis aeruginosa. Nat. Toxins 2006, 1, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Wang, P.; Jia, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, X.; Wang, Y. A review on factors affecting microcystins production by algae in aquatic environments. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordahi, M.A.; Ayoub, G.M.; Zayyat, R.M. A critical review of current research on cyanobacterial cells and associated toxins in aquatic environments: Occurrence, impact, and treatment methods. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Chorus, I. Accumulation of cyanobacterial toxins in freshwater “seafood” and its consequences for public health: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotton, B.; Guillard, J.; Anneville, O.; Maréchal, M.; Savichtcheva, O.; Domaizon, I. Trophic transfer of microcystins through the lake pelagic food web: Evidence for the role of zooplankton as a vector in fish contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, H.G.; Tõnno, I.; Agasild, H.; Kõiv, T.; Freiberg, R.; Nõges, P.; Nõges, T. Algal diet of small-bodied crustacean zooplankton in a cyanobacteria-dominated eutrophic lake. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 0154526. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Luo, W.; Lu, Y.; Giesy, J.P. Bioaccumulation of microcystins (MCs) in four fish species from Lake Taihu, China: Assessment of risks to humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Jia, R.; Ding, W.; Du, J.; Yin, G. Establishment of the acute hepatic injury model and antioxidant effects of extract from Angelica sinennsis in common carp Cyprinus carpio var. Jian. J. Dalian Fish. Univ. 2012, 27, 551–557. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Z. Microcystin pollution in lakes and reservoirs: A nationwide meta-analysis and assessment in China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, G.; Chen, Y.; Jia, N.; Li, R. Four decades of progress in cylindrospermopsin research: The ins and outs of a potent cyanotoxin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, E.; Manganelli, M.; Buratti, F.M.; Testai, E. Cyanobacteria blooms in water: Italian guidelines to assess and manage the risk associated to bathing and recreational activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Q.; Zhang, X. Are fish fed with cyanobacteria safe, nutritious and delicious? A laboratory study. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.S. Off-flavor problems in aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2000, 8, 45–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, S.; Marie, B.; Lance, E.; Quiblier, C.; Tricoire-Leignel, H.; Mattei, C. Anatoxin-a: Overview on a harmful cyanobacterial neurotoxin from the environmental scale to the molecular target. Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Steinman, A.D.; Xie, L.; Yao, L.; Su, X.; Cao, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, Y. Seasonal variation and potential risk assessment of microcystins in the sediments of Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gu, X.; Chen, H.; Mao, Z.; Shen, R.; Zeng, Q.; Ge, Y. Co-occurrence of multiple cyanotoxins and taste-and-odor compounds in the large eutrophic Lake Taihu, China: Dynamics, driving factors, and challenges for risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbalah, A.; Chidya, R.; Jadoon, W.; Sakugawa, H. Temporal trends in organophosphorus pesticides use and concentrations in river water in Japan, and risk assessment. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 79, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Steinman, A.D.; Zhang, K.; Lin, Q.; Xue, Q.; Wang, X.; Xie, L. Risk assessment and identification of factors influencing the historical concentrations of microcystin in Lake Taihu, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 127, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| English Name | Scientific Name | Diet | Habitat Strata |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minnow | Hemiculter bleekeri | Planktivore | Upper |
| Predatory carp | Cultrichthys erythropterus | Piscivore | Middle |
| Gibel carp | Carassius auratus gibelio | Omnivore | Upper |
| European carp | Cyprinus carpio | Omnivore | Bottom |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Liu, R.; Guo, S.; Chen, X.; Wu, W.; Pang, B.; Liu, Z.; Ying, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The Spatial Distribution and Bioaccumulation of Anatoxin-A in Hulun Lake. Toxics 2025, 13, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110996
Li S, Liu R, Guo S, Chen X, Wu W, Pang B, Liu Z, Ying H, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, et al. The Spatial Distribution and Bioaccumulation of Anatoxin-A in Hulun Lake. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110996
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shiyu, Rui Liu, Shuhao Guo, Xiaoxuan Chen, Wenxue Wu, Bo Pang, Zixuan Liu, Haiming Ying, Yanlong Zhang, Yuanyuan Zhang, and et al. 2025. "The Spatial Distribution and Bioaccumulation of Anatoxin-A in Hulun Lake" Toxics 13, no. 11: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110996
APA StyleLi, S., Liu, R., Guo, S., Chen, X., Wu, W., Pang, B., Liu, Z., Ying, H., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., & Ma, C. (2025). The Spatial Distribution and Bioaccumulation of Anatoxin-A in Hulun Lake. Toxics, 13(11), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110996






