Effects of the Novel Triazole Fungicide Ipfentrifluconazole on Different Endpoints in Zebrafish Larvae
Highlights
- (+)-IFZ exhibited higher acute toxicity than (-)-IFZ and rac-IFZ.
- IFZ exposure led to abnormal growth and development of zebrafish larvae.
- Transcriptomics revealed that IFZ had enantiomer-specific toxicity mechanisms.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Zebrafish Breeding and Embryo Collection
2.3. Detection of Acute Toxicity
2.4. Biochemical Indicators Analysis
2.5. RNA Extraction and Transcriptome Analysis
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis
2.7. Observation of Heart Morphology of Tg(myl7: EGFP)
2.8. Observation of Liver Morphology of Tg(-1.7apoa2: GFP)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
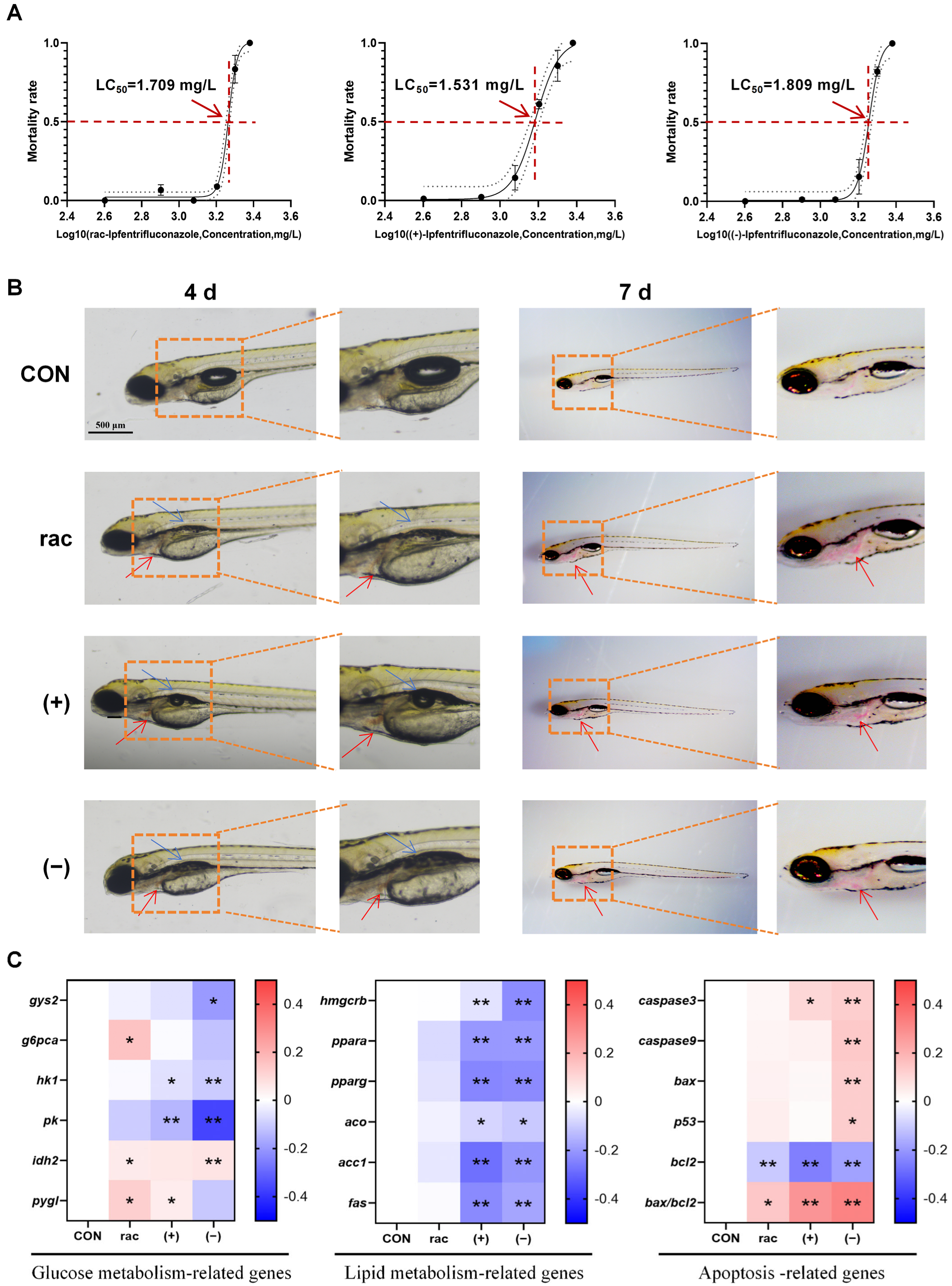
3.1. Developmental Toxicity of IFZ to Zebrafish Larvae
3.2. Cardiotoxicity of IFZ to Zebrafish Larvae
3.3. Hepatotoxicity of IFZ to Zebrafish Larvae
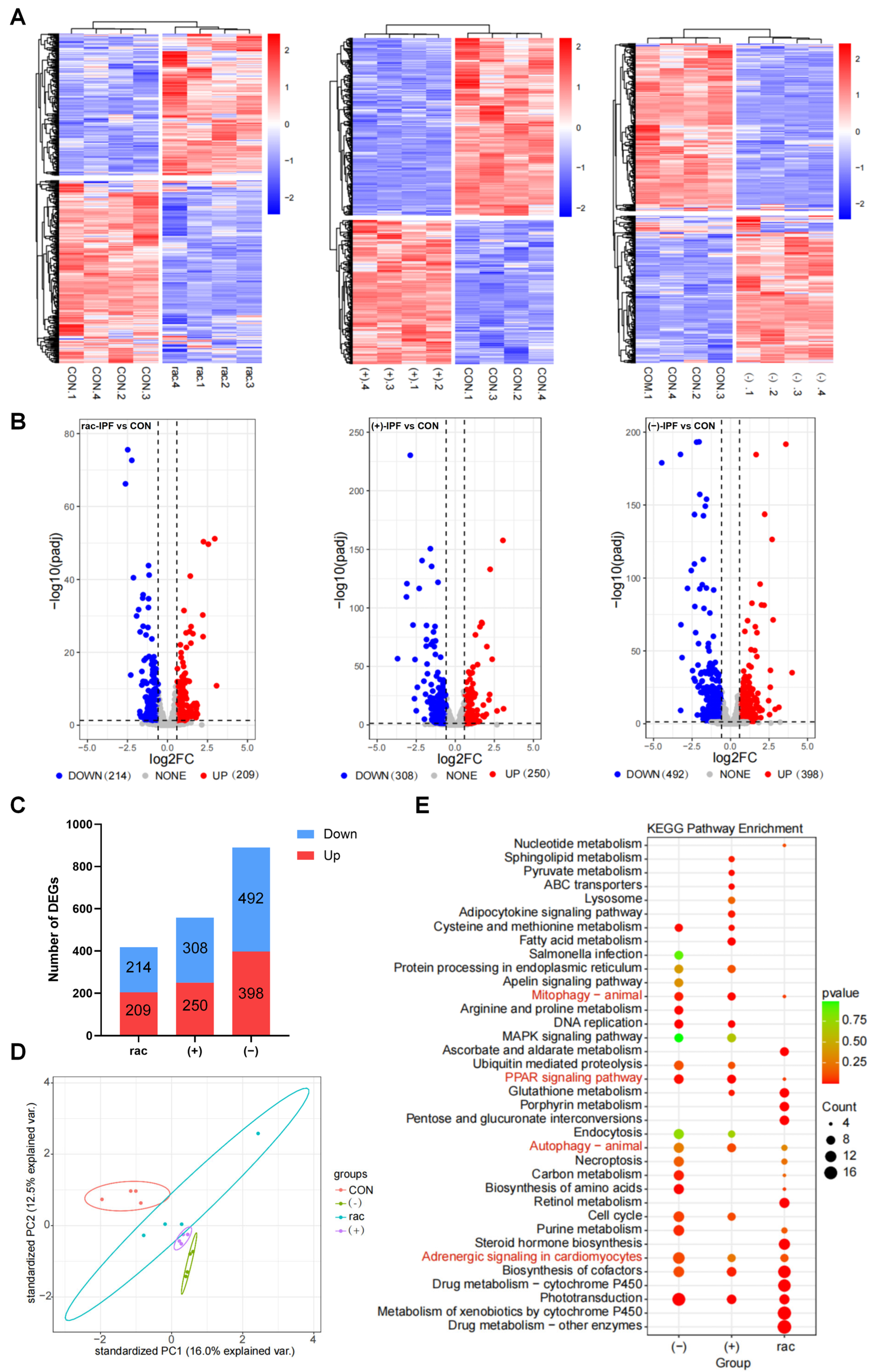
3.4. Transcriptomic Analysis of IFZ Exposed to Larval Zebrafish
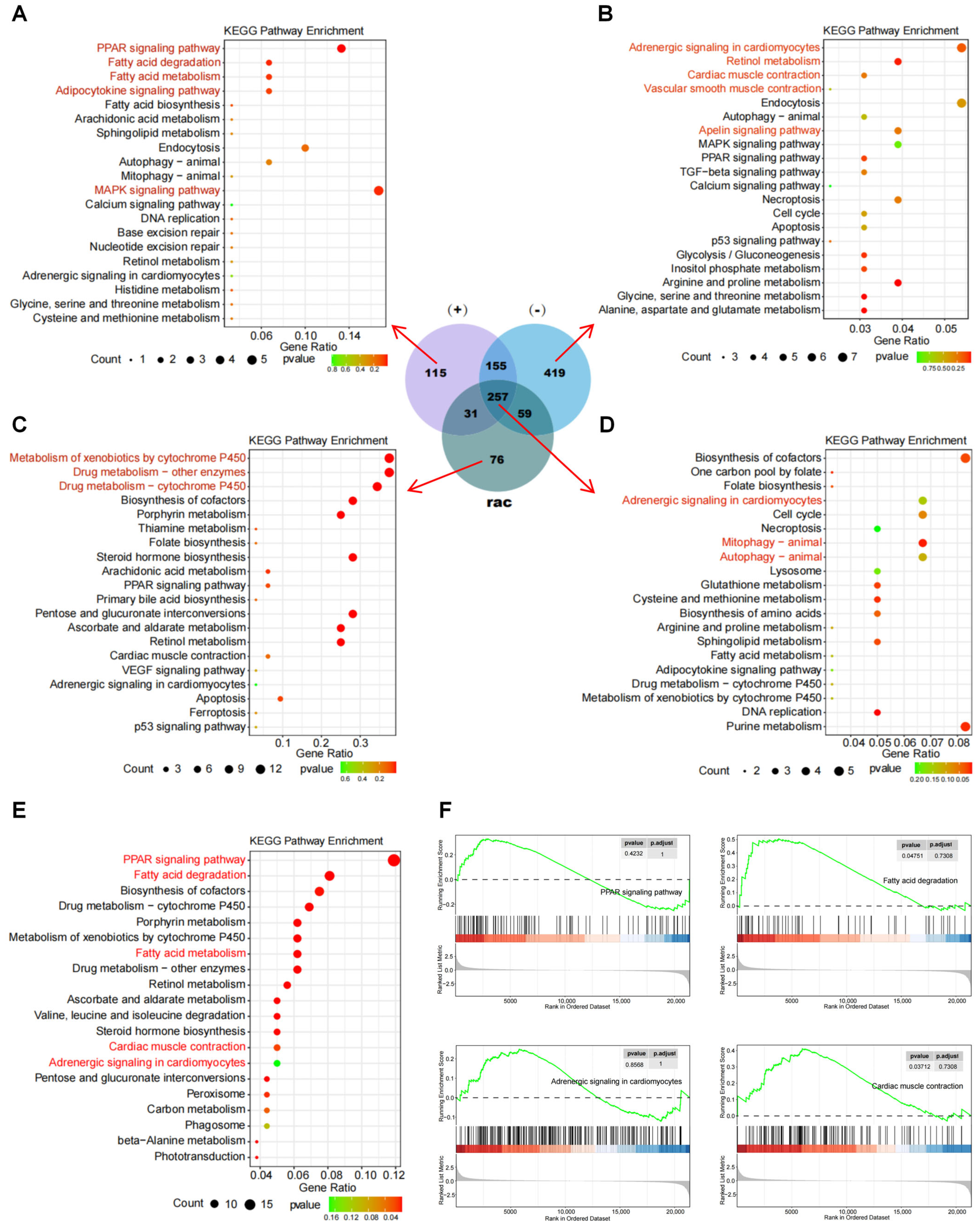
3.5. Comparison of Transcriptomes Between Racemates and Enantiomers of IFZ
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ku, T.; Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Fan, L.; Ren, Z.; Ning, X.; Li, G.; Sang, N. Triazole fungicides exert neural differentiation alteration through H3K27me3 modifications: In vitro and in silico study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Othmène, Y.; Monceaux, K.; Karoui, A.; Ben Salem, I.; Belhadef, A.; Abid-Essefi, S.; Lemaire, C. Tebuconazole induces ROS-dependent cardiac cell toxicity by activating DNA damage and mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2020, 204, 111040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, D.L.; Voiculescu, D.I.; Filip, M.; Ostafe, V.; Isvoran, A. Effects of Triazole Fungicides on Soil Microbiota and on the Activities of Enzymes Found in Soil: A Review. Agriculture 2021, 11, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Deng, P.; Xing, D.; Liu, H.; Shi, F.; Hu, L.; Zou, X.; Nie, H.; Zuo, J.; Zhuang, Z.; et al. Developmental Neurotoxicity of Difenoconazole in Zebrafish Embryos. Toxics 2023, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Paz, J.F.; Beiza, N.; Paredes-Zúñiga, S.; Hoare, M.S.; Allende, M.L. Triazole Fungicides Inhibit Zebrafish Hatching by Blocking the Secretory Function of Hatching Gland Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamanji, R.; Ragothaman, P.; Koigoora, S.; Sivan, G.; Selvin, J. Network analysis of toxic endpoints of fungicides in zebrafish. Toxicol. Res. 2024, 13, tfae087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Liang, C.; Lv, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, Q.; Ding, J.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Expanding the insight of ecological risk on the novel chiral pesticide mefentrifluconazole: Mechanism of enantioselective toxicity to earthworms (Eisenia fetida). J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, B.; Zhao, T.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, H.; Liang, H. Enantioselective toxic effects of mefentrifluconazole in the early life stage of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Toxicol. 2022, 37, 1662–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liang, H.; Ren, B.; Zhao, T.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, H. Enantioselective toxic effects of mefentrifluconazole in the liver of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) based on transcription level and metabolomic profile. Toxicology 2022, 467, 153095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Qian, M.; Jin, Y. Mefentrifluconazole exposure disrupted hepatic lipid metabolism disorder tightly associated with gut barrier function abnormal in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, P. Zebrafish as a pharmacological tool: The how, why and when. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2004, 4, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.J.; Teraoka, H.; Heideman, W.; Peterson, R.E. Zebrafish as a model vertebrate for investigating chemical toxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 86, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Sarode, L.P.; Gaddam, R.R.; Kumar, P.; Bhatti, J.S.; Khurana, A.; Navik, U. Zebrafish as an emerging tool for drug discovery and development for thyroid diseases. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2022, 130, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dong, C.; An, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Z.; Jiao, B. Simultaneous Enantioselective Determination of Two New Isopropanol-Triazole Fungicides in Plant-Origin Foods Using Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes in Reversed-Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction and Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5969–5979. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Zhu, J.; Xu, H.; Qian, M.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene microplastics and cypermethrin exposure interfered the complexity of antibiotic resistance genes and induced metabolic dysfunction in the gut of adult zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 374, 126288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Di, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, Y. 6PPD exposure reduced the melanin deposition by inhibiting tyrosinase activity in larval zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 298, 110300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanden Bossche, H.; Marichal, P.; Gorrens, J.; Coene, M.C. Biochemical basis for the activity and selectivity of oral antifungal drugs. Br. J. Clin. Pract. Suppl. 1990, 71, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ning, X.; Li, G.K.; Sang, N. New insights into potential estrogen agonistic activity of triazole fungicides and coupled metabolic disturbance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424 Pt B, 127479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, M.Y.; Yang, Y.S.; Shi, H.H.; Zhou, J.L.; He, D.F. Strong lethality and teratogenicity of strobilurins on Xenopus tropicalis embryos: Basing on ten agricultural fungicides. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busquet, F.; Strecker, R.; Rawlings, J.M.; Belanger, S.E.; Braunbeck, T.; Carr, G.J.; Cenijn, P.; Fochtman, P.; Gourmelon, A.; Hubler, N.; et al. OECD validation study to assess intra- and inter-laboratory reproducibility of the zebrafish embryo toxicity test for acute aquatic toxicity testing. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 69, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, J.; Zhang, J.; Ruan, T.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, G. Impaired gas bladder inflation in zebrafish exposed to a novel heterocyclic brominated flame retardant tris(2,3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9750–9757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinckens, E.; Vergauwen, L.; Ankley, G.T.; Blust, R.; Darras, V.M.; Villeneuve, D.L.; Witters, H.; Volz, D.C.; Knapen, D. An AOP-based alternative testing strategy to predict the impact of thyroid hormone disruption on swim bladder inflation in zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 200, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, P. The impaired swim bladder via ROS-mediated inhibition of the Wnt/Hedgehog pathway in zebrafish embryos exposed to eight toxic chemicals and binary chemical mixtures. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, E.R.; Mager, E.M. The effects of exposure to crude oil or PAHs on fish swim bladder development and function. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 238, 108853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jeon, H.J.; Kim, K.; Kim, C.; Moon, J.K.; Hwang, K.W.; Lee, S.E. Enantioselective effect of trifloxystrobin in early-stage zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos: Cardiac abnormalities impacted by E,E-trifloxystrobin enantiomer. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Qi, S.; Wu, P.; Wang, C.; Wang, C. Toxic effects of boscalid in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, J.; Zuo, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, C. Chronic exposure to paclobutrazol causes hepatic steatosis in male rockfish Sebastiscus marmoratus and the mechanism involved. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Song, T.T.; Chen, J.F.; Lv, G.Y. Recovery of a hypolipidemic polysaccharide from artificially cultivated Sanghuangporus vaninii with an effective method. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1095556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Wang, G.; Zhao, H. Exposed to Sulfamethoxazole induced hepatic lipid metabolism disorder and intestinal microbiota changes on zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 253, 109245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Di, S.; Wang, C.; Hu, Q.; Jin, Y. Tire rubber-derived contaminant 6PPD had the potential to induce metabolism disorder in early developmental stage of zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 287, 110062. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Lin, W.; Zha, Q.; Guo, H.; Zhang, D.; Yang, L.; Li, L.; Li, D.; Tang, R. Persistent Exposure to Environmental Levels of Microcystin-LR Disturbs Cortisol Production via Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Interrenal (HPI) Axis and Subsequently Liver Glucose Metabolism in Adult Male Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxins 2020, 12, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; He, Q.; Yue, C.; Xu, T.; Hang, X. Effects of dechlorane plus on hepatic pathology, metabolic health and gut microbiota in male mice. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 957, 177532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaumer, S.; Guenal, I.; Brun, S.; Theodore, L.; Mignotte, B. Bcl-2 and Bax mammalian regulators of apoptosis are functional in Drosophila. Cell Death Differ. 2000, 7, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stainier, D.Y. Zebrafish genetics and vertebrate heart formation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkerk, A.O.; Remme, C.A. Zebrafish: A novel research tool for cardiac (patho)electrophysiology and ion channel disorders. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, G.C.; Franco, R.; Lloyd, S.G.; Moura, I.; Moura, J.J.; Huynh, B.H. Structure and function of ferrochelatase. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1995, 27, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijerathna, H.; Shanaka, K.; Raguvaran, S.S.; Jayamali, B.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, M.J.; Jung, S.; Lee, J. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated fech Knockout Zebrafish: Unraveling the Pathogenesis of Erythropoietic Protoporphyria and Facilitating Drug Screening. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensaad, K.; Favaro, E.; Lewis, C.A.; Peck, B.; Lord, S.; Collins, J.M.; Pinnick, K.E.; Wigfield, S.; Buffa, F.M.; Li, J.L.; et al. Fatty acid uptake and lipid storage induced by HIF-1alpha contribute to cell growth and survival after hypoxia-reoxygenation. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Song, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Kong, X.; Sheng, Y.; Cao, K.; Qian, L. Silencing of FABP3 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis in embryonic carcinoma cells. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 66, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Kong, X.; Sun, Y.; Dai, X.; Yu, W.; Chen, R.; Ma, L.; Jiang, L. FABP3 overexpression promotes vascular fibrosis in Takayasu’s arteritis by enhancing fatty acid oxidation in aorta adventitial fibroblasts. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 3071–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, W. Isoflucypram cardiovascular toxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, R.; Fallatah, W.; Qaryoute, A.A.; Ryon, M.; Jagadeeswaran, P. Knockdown and Knockout of Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor in Zebrafish. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 122, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.G. Hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Fang, S.; Wu, Z.; Han, C.; Shi, W.; Bao, Y. Effects of early florfenicol exposure on glutathione signaling pathway and PPAR signaling pathway in chick liver. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 237, 113529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Song, Q.; Shaw, P.C.; Zuo, Z. Dendrobium officinale regulate lipid metabolism in diabetic mouse liver via PPAR-RXR signaling pathway: Evidence from an integrated multi-omics analysis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 173, 116395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Chen, X.; Xiang, Y.K. Compartmentalization of beta-adrenergic signals in cardiomyocytes. Trends. Cardiovasc. Med. 2013, 23, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Huang, T.; Li, X.; Shen, C.; Ren, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, T.; Fu, X.; Deng, S.; Feng, Z.; et al. Retinol dehydrogenase 10 reduction mediated retinol metabolism disorder promotes diabetic cardiomyopathy in male mice. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanger, U.M.; Schwab, M. Cytochrome P450 enzymes in drug metabolism: Regulation of gene expression, enzyme activities, and impact of genetic variation. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 138, 103–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guengerich, F.P. Mechanisms of Cytochrome P450-Catalyzed Oxidations. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 10964–10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guengerich, F.P. Cytochrome p450 and chemical toxicology. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Feng, M.; Li, Z.; Zhou, M.; Xu, L.; Pan, K.; Wang, S.; Su, W.; Zhang, W. ETV5 Regulates Hepatic Fatty Acid Metabolism Through PPAR Signaling Pathway. Diabetes 2021, 70, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayourian, J.; Ceholski, D.K.; Gonzalez, D.M.; Cashman, T.J.; Sahoo, S.; Hajjar, R.J.; Costa, K.D. Physiologic, Pathologic, and Therapeutic Paracrine Modulation of Cardiac Excitation-Contraction Coupling. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, A.; Kushner, J.; Marx, S.O. Adrenergic Regulation of Calcium Channels in the Heart. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2022, 84, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Biochemical Indicators | Ipfentrifluconazole | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | Rac-Ipfentrifluconazole | (+)−Ipfentriflucona-zole | (−)−Ipfentriflucona-zole | |
| TG (mmol/gprot) | 0.016 ± 0.001 | 0.023 ± 0.001 ** | 0.028 ± 0.001 ** | 0.024 ± 0.000 ** |
| TC (mmol/gprot) | 0.083 ± 0.002 | 0.087 ± 0.001 | 0.089 ± 0.002 | 0.098 ± 0.003 ** |
| Gluscode (mmol/gprot) | 0.086 ± 0.003 | 0.084 ± 0.002 | 0.091 ± 0.003 | 0.099 ± 0.003 * |
| Pyruvate (mmol/gprot) | 0.027 ± 0.003 | 0.026 ± 0.002 | 0.025 ± 0.002 | 0.024 ± 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.; Huang, Y.; Qian, M.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, H. Effects of the Novel Triazole Fungicide Ipfentrifluconazole on Different Endpoints in Zebrafish Larvae. Toxics 2025, 13, 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100830
Xu M, Huang Y, Qian M, Jin Y, Zhang H. Effects of the Novel Triazole Fungicide Ipfentrifluconazole on Different Endpoints in Zebrafish Larvae. Toxics. 2025; 13(10):830. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100830
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Mingfei, Yilin Huang, Mingrong Qian, Yuanxiang Jin, and Hu Zhang. 2025. "Effects of the Novel Triazole Fungicide Ipfentrifluconazole on Different Endpoints in Zebrafish Larvae" Toxics 13, no. 10: 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100830
APA StyleXu, M., Huang, Y., Qian, M., Jin, Y., & Zhang, H. (2025). Effects of the Novel Triazole Fungicide Ipfentrifluconazole on Different Endpoints in Zebrafish Larvae. Toxics, 13(10), 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100830








