Abstract
Galactomannans (GMs) are polysaccharides with diverse industrial applications due to their functional properties, such as their use in thickeners, stabilizers, and gelling agents. Their use originated in the food industry and has rapidly expanded to other industries due to their biocompatibility, biodegradability, non-toxicity, and low cost. Galactomannans can be extracted from different plant species, resulting in gums with diverse physicochemical properties. Furthermore, there are different methods for their extraction and purification, each with their own advantages and disadvantages. The structure of galactomannans determines their application in industry, so their characterization is also important. This article presents a comprehensive review of galactomannan sources, as well as their extraction, purification, and characterization methods. It also includes the main applications of these polysaccharides in various sectors.
1. Introduction
Galactomannans are polysaccharides found in various plant sources, mainly obtained from a wide variety of tree legume seeds. For example, these include fenugreek (Trigonella spp.), guar (Cyamssopsis tetragonoloba L.), tara (Caesalpinia spinosa), carob (Ceratonia siliqua), or mesquite seeds (Prosopis sp.) to name a few [1,2]. Galactomannans have the ability to absorb water and form highly viscous and stable aqueous solutions. Materials with these types of characteristics are called hydrocolloids, mucilages, or gums [3,4]. GM content varies among different seeds; for example, guar gum seeds contain up to 40–50% by weight. Fenugreek seeds typically have around 20–30%, depending on the species and growing conditions [5].
GMs are composed of galactose and mannose units, forming a linear molecular structure made up of D-mannose chains with β-1,4 linkages. Branches of D-galactose are attached via (1,6) linkages every five or four mannose units [6,7]. GMs show a mannose/galactose (M/G) ratio that varies depending on the extraction source. In their natural form, galactomannans are intertwined with other components of the cellular matrix, which prevents their functional properties from being fully utilized. Therefore, galactomannans must be extracted to release and purify them for use in various industrial applications. The extraction method also influences the M/G ratio [8].
Galactomannans can be extracted using various techniques, including thermal, acid, enzymatic, and microwave extraction, among others. Each technique offers different levels of efficiency as well as advantages and disadvantages in terms of purity and operating costs. The choice of extraction method will largely depend on the final application of the galactomannan. For example, these polysaccharides can be applied in various sectors, where they are used as stabilizers in food. They are used as excipients in the pharmaceutical industry, thickeners in cosmetic products, biopolymers in biodegradable packaging, and reinforcing agents in paper and textile manufacturing (Figure 1) [9].
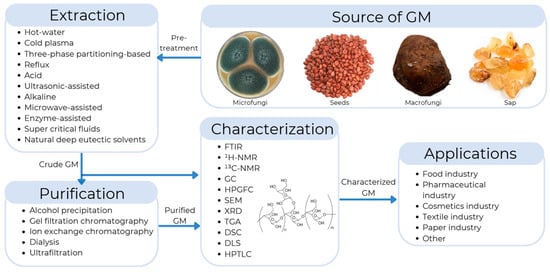
Figure 1.
General representation of the extraction, purification, characterization, and applications of galactomannans (GMs).
This article presents a comprehensive review of the sources of galactomannans. It presents extraction methods such as hot water, ultrasound, microwaves, chemical, and enzymatic methods. It also discusses purification methods such as precipitation, dialysis, ion-exchange chromatography, and ultrafiltration. Various techniques for the characterization of galactomannans are presented, such as Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR and 1C NMR), and high-performance gel filtration chromatography (HPGFC).
2. Galactomannans
Galactomannans are multifunctional polysaccharides found mainly in the endosperm of seeds of various plants such as tara (Caesalpinia spinosa), fenugreek (Trigonella spp.), carob (Ceratonia siliqua), guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.), or mesquite (Prosopis sp.) (Table 1) [1,2].

Table 1.
Different sources of galactomannans.
Galactomannans are synthesized in plants from the products of photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, the Calvin cycle generates glucose. Mannose is synthesized from glucose-6-phosphate via the hexose interconversion pathway, which is converted into GDP-mannose, a fundamental precursor in the formation of β-mannan [80]. Glucose is also transformed into UDP-galactose, which is used by galactosyltransferase to add galactose to the β-mannan chain. The amount of galactose incorporated gives rise to the galactomannan structure and varies depending on the plant species. Galactomannans are stored in the cell wall or in the endosperm of seeds, where they serve as an energy reserve for the plant.
Galactomannans are of great industrial importance [8]. The structural characteristics of galactomannans give them properties such as high solubility in water over a wide range of temperatures. The plant cell wall is composed of various polysaccharides, such as cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin. Among these, cellulose is the most abundant, constituting 30 to 50% of the total dry mass of the cell wall. Hemicellulose constitutes 20 to 35% of it [81]. Hemicelluloses are grouped into xylans, xyloglucans, and mannans. Galactomannans are a subclass of mannans and are multifunctional macromolecular carbohydrates. Galactomannans are made up of the D-mannopyranose main chain linked by β (1→4) glycosidic bonds with D-galactopyranose branches linked to the mannan main chain by α (1→6) bonds (Figure 2) [9].
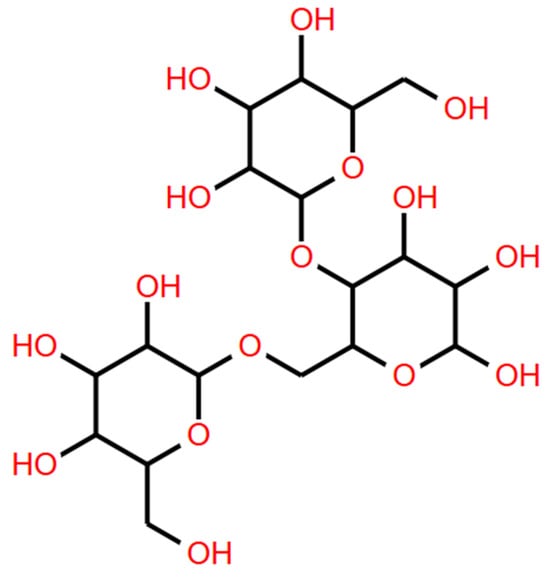
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the chemical structure of galactomannans. (Structure created with the Biomodel program).
The galactose units are organized as random doublets and triplets along the main chain [5,82]. Such random substitution of the galactose units results in regions of high and low substitution in the mannan main chain (Figure 3). In galactose-sparse regions, non-covalent interactions occur between polymer chains. In galactose-abundant areas, high substitution hinders the formation of more organized structures. This is due to steric hindrance of the side chains, which also leads to high solubility in aqueous solutions [83].
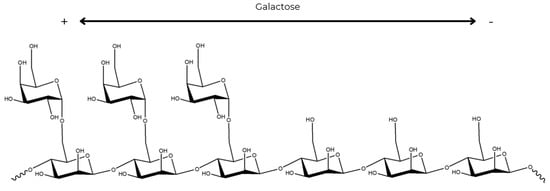
Figure 3.
Representation of the substitution of galactose in the mannose chain. (Structure created with the Chemdraw program).
Galactomannans are distinguished from each other by the M/G ratio, which varies from approximately 1.1 to 3.5. The M/G ratio is directly related to the structure and function of galactomannans.
Furthermore, galactomannans are susceptible to molecular changes due to the number of hydroxyl groups (-OH) and the absence of ionic charges in their structure [84]. Studies indicate that there is a correlation between the bioactivity of these polysaccharides and their structural characteristics. These characteristics include the degree of substitution, the position of the substituent, the molecular weight, and the conformation of the chain [85].
Types of Galactomannans
The basic structure of galactomannans is a mannose backbone with galactose branches. However, significant structural variations may occur depending on the source. These variations include the ratio of galactose to mannose, the distribution of galactose branches, and the molecular weight. These differences directly influence the functional properties of galactomannans, as well as their application. These structural changes allow galactomannans to act as gum, hydrocolloid, or mucilage [86].
The general term to describe the behavior of galactomannans is gum and GMs can be soluble or insoluble in water. This term is also used to refer to polysaccharides of plant origin such as locust bean gum and guar gum. On the other hand, mucilages do not dissolve easily in water and form viscous masses, unlike hydrocolloids, which dissolve easily, forming solutions [87]. Most hydrocolloids offer high viscosity with low concentrations, around 1%, and are capable of forming gels [88]. Galactomannans stand out among other gums because they offer great viscosity retention and great emulsifying and stabilizing capacity. Therefore, they are primarily used to alter rheological behavior [82]. The structural characteristics of galactomannans, mainly hydroxyl groups and hydrogen bonds, provide specific rheological and physicochemical properties, determining their functionality (Figure 4) [10,82].
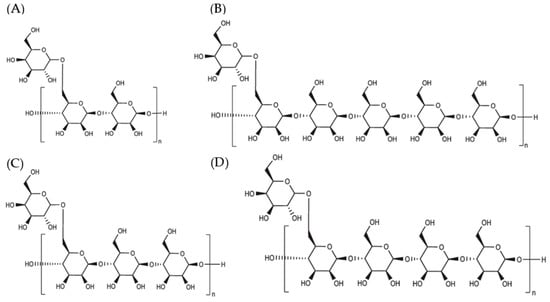
Figure 4.
General chemical structures and repeating units of galactomannans: (A) guar gum, (B) cassia gum, (C) tara gum, and (D) algarroba gum [89].
Water solubility is the basic characteristic affected by the structure of galactomannans. For example, the mannan main chain is insoluble while the galactose side chains are the ones that impart solubility to the molecule. In galactomannans with fewer galactose chains, the mannose units of the main chain come closer together to form intrachain hydrogen bonds, which leads to a decrease in water solubility [86]. Consequently, the solubility of galactomannans will be proportional to the reducing galactose side chains per repeat unit. In turn, this ratio will depend on the source from which the galactomannans are obtained, for example: ~30% for locust bean gum (M/G ratio: 4/1), ~60–70% for guar gum (M/G ratio: 2/1), and ~80% for fenugreek gum (M/G ratio: 1/1) [2,17,31,90,91,92].
These structural changes also affect the basic physical properties of galactomannans: the fiber content is 1% for locust bean gum, followed by tara gum with 2%, guar gum with 2–3%, and fenugreek gum with up to 4–6%. Likewise, the protein content is affected, decreasing as the mannose decreases: for locust bean gum, it is 4.57%, guar gum 3.46%, and fenugreek gum 2.62% [86]. The distribution of galactose branches along the mannose chain also varies according to the source of the galactomannan. For example, uniform branches such as guar gum give rise to a more stable and reproducible viscosity, while galactomannans with an irregular galactose distribution such as locust bean gum offer greater synergy with other gelling agents [85].
After the galactomannans dissolve, the viscosity-producing effect, which is affected by factors such as thermal processing, ionic strength, pH, and the neutral character of the galactomannans, begins to occur [93]. Galactomannans with a lower number of galactose side chains offer lower viscosities, although the thickening capacity also depends on the molecular weight and chain length of the polymers present in the molecule. Due to their different molecular weights, fenugreek gum has the highest thickening capacity, followed by guar gum, tara gum, and locust bean gum [8,10,90,94]. Galactomannans that have fewer galactose chains in their structure have greater gelling properties due to their unsubstituted mannose blocks, which chemically interact with polysaccharides. The gelling capacity in terms of lowest to highest strength is fenugreek gum, guar gum, tara gum, and locust bean gum. Galactomannans with a higher proportion of mannose form stronger gels when combined with other hydrocolloids, while guar gum forms more viscous solutions but with less gelling capacity [10,90,95].
The thickening capacity is related to the applications of galactomannans and will define the required concentration. For example, at low concentrations, the polymers move freely, exhibiting Newtonian behavior with constant viscosity independent of the shear rate. At a critical concentration, the polymer movement is restricted, resulting in non-Newtonian behavior [96].
Galactomannans are a type of polysaccharide that may play a role in the structure of cell walls. They can be broken down into monosaccharides such as galactose and mannose, which can then be used as an energy source by plant cells. Galactomannans have different beneficial activities and can be applied in various industries, so their extraction becomes relevant.
3. Extraction Methods
Existing extraction methods have disadvantages in the process, and in addition, the proteins present in the matrix have an impact on the purity of the galactomannans [97]. Therefore, it is important to eliminate them from the beginning of the process. They can be removed by selective precipitation with 30–50% ethanol or isopropanol. Membranes can also be used to separate proteins (<10 kDa) or enzymes that remove proteins without affecting polysaccharides such as bromelain, pepsin, or trypsin can be used. Adjusting the pH to 4–5 before extraction can also be beneficial [98].
An appropriate extraction method is a critical factor that affects the bioactivity of galactomannans, being a key to having a high yield and maintaining physicochemical characteristics such as functional properties, molecular weight, protein, and galactomannan content [99,100,101,102]. There are various methods for the extraction (Table 2) and purification of galactomannans, and each one produces different structures, which are reflected in a different biological activity [103]. Alternative methods should be used in circumstances more suitable for existing processing techniques [104,105,106].

Table 2.
Different methods of extraction galactomannans.
The main objective of choosing an extraction method should be focused on a fast process that contributes to the economy and the ecosystem.
3.1. Hot Water Extraction
The polysaccharides extracted by this traditional method are mainly neutral polysaccharides or polysaccharides that remove insoluble substances directly or by centrifugation [118,119,120]. The extraction rate depends on the source of galactomannans under different extraction conditions such as extraction temperature, extraction time, and solid–liquid ratios. Each source has different optimal extraction conditions [121]. Extraction temperature and time have a positive effect on extraction yields; high temperature or long extraction time may destroy the structure of polysaccharides. On the other hand, a higher liquid–solid ratio increases the mass transfer from solid to solvent and improves solvent diffusivity in cells. However, increasing the solution volume under a higher liquid–solid ratio also affects the purification process and production costs [122]. You can start with an intermediate ratio (15:1–20:1 mL/g) and adjust according to yield. Applying ultrasound or maintaining constant agitation during extraction can improve solubilization without increasing the amount of water, which would reduce costs. Balancing these factors requires systematic optimization using experimental design techniques, such as response surface methodology (RSM). By analyzing variables such as temperature, time, and cartridge ratio in an integrated manner, it is possible to determine the most efficient extraction conditions for each polysaccharide source.
This method has advantages such as low cost, easy operation, and the lack of requirement for sophisticated equipment, and it can be performed on an industrial scale. However, it is a method with low efficiency and requires a lot of time. This method is usually accompanied by other extraction methods to optimize the extraction, and different factors are considered for the selection of various substances [123].
3.2. Cold Plasma Extraction
This method is also known as non-thermal plasma and is an environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and energy-efficient technique [124]. This method is based on ionization, stimulation, and separation of gases [125]. Basically, it contains electrons with an excessively higher temperature than that of heavy particles (ions and neutrals) [126]. This is because the cooling of ions and uncharged molecules is more effective than the energy transfer of electrons [127]. The temperature of the cold plasma gas does not increase and remains in a state of thermodynamic disequilibrium [128]. Therefore, cold plasma is ideal for application in biological material modifications in terms of surface rupture, wettability, and roughness [129,130]. These are characteristics mainly related to the migration of the substances they contain from the interior to the surface during extraction [131,132]. In this way, according to the plasma parameters (type of gas, input energy, pressure, power) and the inherent characteristics of the substrate, different chemical and physical modifications of the surface are generated [133].
Cold plasma treatment can cause ruptures on the surface of the seeds and decrease the pH of the extraction solution, resulting in an increase in the extraction yield of approximately 67–122%. Galactomannans extracted by this method show higher water binding capacity, higher apparent viscosity, and higher swelling index due to structural disintegration caused by the cold plasma treatment [30].
3.3. Extraction Based on Three-Phase Partitioning
Three-phase partitioning is applied to the extraction and separation of compounds such as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and small-molecule organic compounds. This method involves precipitation interactions with salts, cosolvents, isoionic material, etc. [110]. This technique consists of an upper phase (t-butanol) containing lipids, pigments, and hydrophobic materials, a lower aqueous phase containing polysaccharides and polar components, and an intermediate phase enriched with proteins [109]. The main factors influencing this extraction are the mass fraction (ammonium sulfate), the mass fraction of t-butanol, temperature, and pH. The “salting-out” effect is the force that drives the partitioning of polysaccharides with a low mass fraction of ammonium sulfate. The optimal pH value in this extraction is related to the isoelectric point of the sample. This process is usually carried out at room temperature, but it is of vital importance. For example, an increase to 20 or 40 °C provides an improvement in the mass transfer rate and facilitates hydrogen bond formation. This results in an improvement in the hydrophilicity of the extracted polysaccharides, making them more concentrated in the lower phase. To improve TPP extraction, salt precipitation efficiency can be increased by using an ammonium sulfate concentration of 20% to 40% (w/w). A pH of ~5–6 can improve galactomannan recovery. Additionally, ultrasound (20–40 kHz) can be applied for 5–10 min to increase mass transfer and reduce extraction time. The alcohols in the upper phase can also be replaced with isopropanol or ethanol [121].
3.4. Thermal Reflux Extraction
This method is mainly used for the extraction of polysaccharides and promotes dissolution, solvent penetration, and diffusion of the polysaccharide through thermal effects [102]. The performance of this method commonly depends on the extraction time and the temperature used [134]. It is a method that requires a relatively long extraction reaction time, approximately at least 2 h, and the yield and purity of the product are not ideal [135]. It is a simple and inefficient method that causes the degradation of the polysaccharides and considerably decreases their pharmacological activity if the temperature is not controlled [136,137]. Reflux extraction is an effective extraction method to obtain good yield and bioactivity, with higher polyphenol content and greater weight, presenting better antioxidant properties as long as low temperatures are used [138]. Reflux extraction has the advantage of using little solvent, since, as its name suggests, the solvent itself evaporates and condenses without the need to add more. There are different ways to apply this method: the traditional one (Soxhlet) or combined with other techniques such as MAE. In this way, microwave energy is applied to heat the sample and the solvent, combining these techniques to reduce extraction time. It is also possible to combine this technique with UAE or deep eutectic solvents (DESs) to avoid compound degradation or make it a sustainable method, respectively.
3.5. Alkaline or Acid Extraction
This method is suitable for hard seeds because it is capable of degrading the structure of the thick fibers, destroying the cell walls. It also hydrolyzes the ester bonds between the cell wall protein and the glucan, which further increases the release of polysaccharides [139]. Alkalinity or acidity must be strictly controlled throughout the extraction because glycoside bonds in polysaccharides may be broken, and some polysaccharides are hydrolyzed when alkalinity or acidity is high. Once the extracts are obtained, they must be neutralized or dialyzed, concentrated, and precipitated immediately [140].
The alkaline extraction method increases solubility by forming salts with acidic polysaccharides. Therefore, this method is suitable for the extraction of uronic acid-containing polysaccharides and acidic polysaccharides. The alkali-soluble fractions consist especially of highly branched β-(1→3, 1→6)-glucan [141,142]. The most important factors influencing the extraction rate are alkali concentration, temperature, and extraction time [121].
3.6. Ultrasound Extraction
Ultrasound is one of the most effective techniques for polysaccharide extraction based on applying ultrasonic waves in the frequency range of 20–100 kHz [143]. Ultrasound produces and transfers a large amount of energy, causing the medium to accelerate to a state of high-speed vibration, which produces a cavitation effect in the liquid. In other words, under the action of considerable destructive stress, a cavitation bubble forms; this bubble swells and bursts instantly. The absorbed sound field energy is released in an extremely short time and in an extremely small space, generating high temperature and high pressure at the same time [97]. Strong shock waves, together with micro-sound waves, end up rapidly breaking the cell wall structure. The effective components of plant cells are released into the solvent, where they mix completely, accelerating diffusion and thus improving the extraction rate [144]. This technique produces a coagulation effect, thermal effect, biological effect, chemical effect, emulsification, grinding, and diffusion as side effects. This can result in a product with low solubility, purity, functionality, and viscosity. Therefore, maintaining a controlled temperature, power, and flow rate is essential to minimize these effects. Furthermore, it is recommended to use short pulses instead of continuous ultrasound exposure [143].
This method considerably reduces extraction times, has a high extraction rate, and reduces interference from other solvents. Despite this, it is a technique that is not suited to large-scale application due to the high cost of the required equipment [144].
3.7. Microwave Extraction
The extraction principle of this technique is based on the fact that micro-rays irradiate the solvent and move into the cell through the cell wall. The frequency of the microwaves is between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. As the solvent and the cell absorb the micro-rays, the temperature and pressure increase. The cell wall breaks when the pressure exceeds its capacity, releasing and transferring the components to the solvent. This method offers a high extraction rate, short extraction time, and high heating efficiency and is able to protect the active components from destruction [145]. It can also be combined with other techniques such as enzymatic hydrolysis or hot water extraction.
3.8. Enzymatic Extraction
This method has been widely used in recent years because enzymes help to reduce the extraction condition, are able to degrade plant tissues under subtle conditions, and accelerate the release and extraction of polysaccharides [146]. This technique is very useful because it also breaks down irrelevant compounds such as pectin, protein, and starch, among others. The main condition to consider for an efficient process is to selectively hydrolyze the glycopeptide bonds in the glycoproteins, controlling this aspect in order to not significantly degrade the polysaccharides by using specific enzymes. These are capable of hydrolyzing structurally complex polysaccharides into simple fragments. The most commonly used enzymes are hydrolases that include protease, cellulase, pectinase, papain, α-amylase, β-1,4-xylanase, and β-1,4-mannanase. The most important enzymes for the hydrolysis of mannan includes endo-β-mannanase (EC 3.2.1.78), protease (EC 3.4.21.62), endo-1,4-β-glucanase (EC 3.2.1.4), endo-1,4-β-xylanase (EC 3.2.1.8), exo-β-mannosidase (EC 3.2.1.25), pectinase (EC 3.2.1.15) β-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.21), cellobiohydrolase (EC 3.2.1.91), acetyl mannan esterases (EC 3.1.1.6), and α-galactosidase (EC 3.2.1.22), and 1,4-β-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37) [147]. It is also possible to combine several enzymes to obtain a better performance, taking into account that the type of enzyme, the enzyme concentration, and the pH are highly relevant factors that influence the extraction efficiency. For example, the combination of β-mannanase and α-galactosidase is very efficient in breaking down galactomannans into simple components. The combination of cellulase and pectinase enhances the release of galactomannans from plant matrices [121]. Microorganisms are the sources of the biological production of enzymes that are obtained through microbial fermentation (Table 3). Fermentation offers advantages such as low production costs, high efficiency, and a short production cycle [33].

Table 3.
Different enzymes used for the hydrolysis of galactomannans.
In general, it is an efficient technique because it offers high specificity and broad enzymatic catalytic activity, making it an optimal extraction option [154].
3.9. Extraction with Supercritical Fluids
This extraction technique also has a high extraction rate and provides high product purity, which leads to faster separation, purification, and reduction of the production cycle [155]. The use of this extraction method requires less use of solvents and fast removal times, and it also involves regulating the dissolution force with the help of adjusting its mass since the physicochemical characteristics are between gas and liquid [156]. Taking care of this relationship is vital because even a slight adjustment in the pressure and/or temperature parameters will significantly modify the density of the fluid and increase the dissolution force by approximately 80 to 100 times [157,158]. This is because the molecular propagation rate of supercritical fluids is as high as that of gas and the solubility density is as strong as that of liquids [105]. Overall, it is a non-toxic extraction method and offers higher selectivity and extraction yield by tailoring the operational criteria. More specifically, the selectivity and purity of the final extract can be modulated by varying the temperature, pressure, and flow rate of supercritical fluids [116,159].
3.10. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent Extraction
Natural deep eutectic solvents are based on hydrogen bond acceptors (HBAs) and hydrogen bond donors (HBDs). These solvents have unique properties of chemical and thermal stability, low vapor pressure, low melting point, non-toxicity, and low costs [160].
NADES are suitable for the extraction of polysaccharides due to their ability to donate or accept external protons or electrons [161]. NADES play a relevant role in the extraction of polysaccharides; water helps to reduce viscosity and facilitate mass transfer, thus improving extraction efficiency. However, excessive water content can destroy hydrogen bonds and decrease the extraction efficiency of the method. This technique shows a higher yield than the thermal method [121].
4. Optimization of the Extraction Method
The application of a single method for the extraction of polysaccharides is limited; a composite method can significantly improve the extraction rate and reduce the cost [97]. For example, studies have shown that ultrasound-assisted enzymatic extraction provides better polysaccharide yields and shortens the extraction time (from 4 h to 32 min). That is, by combining the techniques, higher yields are observed in less time than with the enzymatic technique alone. The average molecular weight of the polysaccharides extracted with ultrasound (343–473 kDa) was lower than the polysaccharide extracted without ultrasound (500–620 kDa), suggesting that some compounds underwent depolymerization [162].
Another technique used in the food industry for the separation of bioactive ingredients is ultrasound-assisted triphasic partitioning. TPP is an environmentally friendly, rapid, and efficient extraction method [163]. The principle of TPP involves mixing crude extracts or suspensions with solid salt and organic solvent to form three distinct phases simultaneously. This method has been used to extract and purify enzymes, lipids, and proteins [164]. The ultrasound-assisted triphasic partitioning process has also been studied and is highly effective in the extraction of polysaccharides. The yield obtained was higher (112%) than with the ultrasound and three-phase partition methods separately with 60 and 93%, respectively.
Furthermore, the extraction time is shorter, at only 10 min. Ultrasonic extraction requires 60 min, while three-phase partition extraction requires 30 min [165]. The ultrasound method can be performed using NADES to improve the extraction yields of polysaccharides. The most important factors are ultrasonic power, temperature, extraction time, and the solvent–solid ratio. In an extraction time of 40 min, high yields were achieved, higher than those achieved with hot water extraction under the same conditions [166].
Techniques such as ultrasound have also been combined in extraction processes with pressurized liquids; although this approach has been little studied, it is a complex process in which different mass and energy transfer mechanisms interact with each other [167]. Understanding the individual and combined impact of each of the process variable extraction processes remains a major challenge for researchers.
To achieve an optimal balance between extraction speed, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability, it is essential to develop combined methods that improve process efficiency while maintaining the integrity of the extracted compounds. Approaches such as enzyme-assisted extraction, environmentally friendly solvents, and emerging technologies such as supercritical fluid extraction or microwave-assisted extraction could help reduce energy consumption and solvent usage while improving galactomannan purity. Furthermore, strategies to minimize protein interference, such as selective precipitation, membrane filtration, or enzymatic hydrolysis, should be integrated into the extraction process to improve purity without compromising yield.
5. Galactomannan Purification Techniques
After the extraction of galactomannans, crude galactomannans are obtained, which may contain a large number of impurities. These impurities generally come from other components present in the plant matrix from which the galactomannans are obtained. Due to the incomplete separation of the germ layer and endosperm, unwanted compounds are partially extracted during the process.
Also, depending on the solvent used for extraction, residues may be present in crude galactomannans. To avoid this contamination, careful manual separation is recommended. The most common impurities are proteins, lignins, salts, minerals, ash, and lipids [168]. These compounds are present in varying amounts depending on the extraction source. For example, protein amounts of 3.74% to 13.9% have been reported for crude fenugreek gum [169,170]. The presence of these compounds can interfere with the functional properties and quality of galactomannans, so a purification process is essential to obtain a high-quality final product [170]. Purification methods must be effective in removing these impurities without damaging the galactomannans or compromising their functional properties.
Among the main methods for the purification of galactomannans are ethanol/isopropanol precipitation, ion exchange chromatography, gel filtration chromatography, dialysis, and ultrafiltration (Table 4). They should be selected based on the nature of the impurities present and the characteristics of the extracted galactomannans. For example, dialysis or precipitation are generally used to remove proteins and salts. For simple sugars, ion exchange chromatography or gel filtration chromatography are used. For lignin, ash, and minerals, ultrafiltration can be used [168].

Table 4.
Different purification techniques of galactomannans.
To obtain a high efficiency in the purification of galactomannans, factors such as sample concentration, flow rate, solvent purity, and solvent selection must be considered [177]. Generally, techniques are combined to remove impurities, proteins, and other components, although this process can be adjusted depending on the final application of the galactomannan. For example, unpurified galactomannans are commonly used in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries [178]. This is due to the fact that during purification, the formation of hydrogen bonds in the galactomannan structure increases, resulting in changes with amorphous transitions, which influence the mobility and functional properties of the gum [179]. Studies have reported that crude galactomannans show higher values of permittivity, conductivity, and losses compared to purified galactomannans [59].
The structure of galactomannans is complex and can be very diverse due to the many variables such as the source of extraction, the extraction method, and the purification method [180]. The characterization of galactomannans is important for their application, because their biological function is directly related to the structural characteristics of the gum [181].
6. Galactomannan Characterization Techniques
Understanding the structure of galactomannans can optimize their applications in industry and improve extraction and purification processes. Furthermore, by understanding their structure, we can understand how they interact with other compounds and design materials with specific properties [117]. For example, polysaccharides with a higher molecular weight have a greater hydrodynamic volume, higher viscosity, and a more complex structure [182]. On the other hand, low molecular weight polysaccharides are more likely to dissolve in water and are easier to absorb [183,184].
There are different techniques for the analysis and characterization of the structure of galactomannans, such as Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) [185]. Table 5 summarizes the main techniques for the structural characterization of galactomannans.

Table 5.
Different techniques for characterization of galactomannans.
7. Applications of Galactomannan
Among the functional properties of galactomannans, their water retention capacity, non-toxicity, non-ionicity, high molecular weight, and solubility stand out, which allows them to be widely used in industry. Galactomannans have different applications, for example, as binders, excipients, fat substitutes, thickeners, gelling agents, plasticizers, emulsifiers, stabilizers, edible coating, and flavor encapsulants, and for the alteration of ice crystallization and the adjustment of freezing and evaporation rates [8,36,90]. All its previous qualities widely allow its use in various industries such as food, cosmetics, textile, paper, and pharmaceutical [41].
7.1. Food Industry
Galactomannans obtained from sources such as tara gum are included in the European Codex Alimentarius Commission (Codex) system. Therefore, their use as a food additive is approved. This includes their use in controlling flavor release and inhibiting sugar crystal formation in various products [189]. In general, galactomannans improve the texture of foods [190].
They are used in dairy products such as cream and yogurt to increase viscosity and texture, resulting in a higher quality product. The concentration of galactomannans is proportional to the creaminess of yogurt; adding gum at 0.41–0.43% increases sensory characteristics and also increases its stability and prevents sediment and whey separation [191].
It is widely used in beverage manufacturing because galactomannans are soluble in cold temperatures and are stable at low pH. Gum is also used as a source of soluble fiber, reducing calories. Adding gum at 0.1% prevents pulp in juices from precipitating, controls viscosity, thickens, and increases shelf life [189].
Galactomannans applied in breadmaking can improve chewiness. Gluten proteins (gliadin and glutenin) interact with galactomannans, creating a more flexible network and improving the bread’s texture. The bread also retains more water, making the crumb moister and softer, which creates a more pleasant chewing sensation [192]. Adding galactomannans to bread extends shelf life because it forms a gel that prevents the formation of crystals that occur during the gluten retrogradation process, leaving the bread with a fresh, soft texture for longer [193,194]. Furthermore, galactomannans have been reported to form a film on the surface of the bread, making it difficult for pathogenic microorganisms to penetrate. Overall, galactomannans improve the acceptability of bread by increasing its softness, dough elasticity, crust characteristics, chewiness, and shelf life, while reducing hardness [11].
Galactomannans present bacteriostatic and antioxidant activity that help preserve food by inhibiting the growth of microorganisms, thus extending the shelf life of various products, showing potential as a natural preservative. Galactomannans have also been applied to sausage manufacturing, improving the products’ texture, sensory characteristics, and storage time [195]. In ice cream, where a concentration of 0.3% is recommended, GMs are also used as a stabilizer due to their water-binding properties, improving texture and homogeneity [196]. Galactomannans are also used in sauces, dressings, and mayonnaise to prevent compounds from settling, improve texture, reduce syneresis, and increase viscosity [197].
In addition, galactomannans have the ability to be used as edible films or coatings such as biodegradable packaging. Polysaccharides applied as coatings contribute to reducing water loss and microbial growth, and they completely degrade non-toxic substances [41,198,199]. These coatings are mainly applied to fresh vegetables and fruits, and it has been shown that they could reduce moisture evaporation from them, improving their quality and extending their shelf life. This is due to the fact that they act as an oxygen barrier, preventing colors, lipid ingredients, and flavors from oxidizing [117]. Galactomannans represent an environmentally friendly alternative by reducing the use of conventional plastics and minimizing their environmental impact.
7.2. Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, the use of galactomannans for medicines stands out due to their important properties such as being chemically inert, non-toxic, cheap, non-immunogenic, and odorless and having better solubility and stability [200]. In addition, polysaccharides are biodegradable and biocompatible. It is difficult for them to penetrate into the blood, which indicates that the appropriate dose of the drug can be administered to the precise organs and tissues at the right time [201].
Polysaccharides are used as a matrix in the formulation of tablets to protect active substances from stomach conditions and small intestine acids, allowing their release into the colon under alkaline conditions [114]. The structure of galactomannans has various functional groups in its structure, which can be converted or modified into hydrogels, allowing different drug delivery systems to be obtained [202]. The interaction of enantiomers with the excipient can lead to differentiated drug delivery rates for each enantiomer of the drug. Hydrogels can then be exploited for slow release and increased drug bioavailability [114]. It has also been shown that they can be used as antibacterial medical dressings that promote wound healing [70].
The controlled release of diclofenac sodium was evaluated in capsules and tablets using galactomannans. The drug release performance was compared with a commercial controlled-release product. The tablets resulted in a zero-order drug release; gel erosion controlled the release rather than the diffusion. On the other hand, the capsules were of a first-order model. The results obtained demonstrate the potential of galactomannans as release-retarding materials. The polymer concentration results in a decrease in drug release, and all formulations with gums demonstrated an excessive sustained release effect [203,204]. Galactomannans were applied in fast-dispersing ibuprofen tablet formulations, which are mainly used in elderly patients and in children who have problems swallowing conventional capsules or tablets. This new technology provides a high drug loading, has an acceptable taste, and leaves a minimal residue in the mouth after administration [205].
A study was conducted comparing the micrometric properties of paracetamol granules using different binders (8% w/w). The tablets in which galactomannans were used showed superior flow properties. They also showed a high resistance to crushing of the granules compared to other binders, which translates into a greater uniformity of the granule size. The use of galactomannans potentially stands out as a pharmaceutical binder [204]. There are companies that develop drugs using the different gums that have been approved. Without a doubt, galactomannans offer a wide potential for use in the pharmaceutical area because their versatility allows their application in novel developments for various drug delivery systems. However, the variability of the molecular weight and the degree of purity of galactomannans derived from the different sources and extraction methods is a problem to be solved.
7.3. Cosmetics Industry
There are sixteen galactomannans obtained from different sources that are approved in the international cosmetic ingredient manual. The main function of galactomannans is as hair and skin conditioning agents, and they are also used to increase the viscosity of cosmetic products. The ingredients included are gums extracted from Cyamopsis tetragonoloba, Ceratonia siliqua, Caesalpinia spinosa, Trigonella foenum-graecum, and Cassia tora, among others [206,207].
In this industry, galactomannans fulfill the function of emulsion stabilizers, fragrances, binders, film formers, antistatic agents, adhesives, and emollients. The gums have demonstrated excellent compatibility with almost all the main ingredients used in cosmetics, such as sodium chloride and magnesium sulfate [89]. In tests, it was observed that after 48 h, the viscosity increased slightly, while maintaining the appearance. Galactomannans obtained from Caesalpinia spinosa show stability in a pH range of 3 to 12, without altering the appearance or viscosity. In addition, ethanol can be added at a maximum of 10% to the galactomannans even if the viscosity increases significantly [208].
Caesalpinia spinosa gum demonstrated excellent compatibility in general with natural and synthetic rheology modifiers. In addition, a synergistic effect was observed with xanthan gum, forming a compact gel. In general, Caesalpinia spinosa galactomannans improved the sensory qualities of the gels, providing them with greater smoothness, less stickiness, velvety feel, extension, and thickness [89]. As for surfactants, it offers an improvement in the quality of the foam, without the risk of toxicity, and a thicker and softer sensation during the massage. These qualities make the gum the ideal ingredient in formulations of delicate cleaning products such as baby hygiene products and products for hypersensitive skin.
Also, the gum shows great compatibility with the conditioner cetyltrimethylammonium chloride, making it suitable for the formulation of hair products, such as cleansers and conditioning masks [209]. The gum can also be applied in makeup formulations because it shows ideal compatibility with various pigments, such as iron oxides, titanium dioxide, and zinc oxide. Even inorganic UV filters such as ZnO and silica-coated TiO2 show compatibility with this gum [210]. Hydrotopes such as glycerin, betaine, propylene glycol, 1,3-propanediol, and isopentyldiol show excellent compatibility and higher viscosity is observed in aqueous dispersions. When the gum is moistened with hydrotopes, the water is easily dispersed, facilitating the swelling process [208]. Galactomannans have been used in concentrations of up to 93% in hair straightening products. It is used in powders and sprays at a concentration of up to 0.05%. Likewise, another advantage of using gums is that those products that contain them are safe to apply even several times a day and can come into contact with the skin or hair for long periods after application. For example, hair sprays that contain gums, being in aerosol form, could present a risk of inhalation. Aerosols release particles below 10 mm because traces would be deposited in the respiratory tract, in the nasopharyngeal and bronchial area; therefore, gums would not be respirable; they could not enter the lungs [211].
7.4. Textile Industry
Galactomannans are used in the textile industry for their thickening properties. Galactomannans were initially used primarily in printing pastes, but their other properties such as biocompatibility and biodegradability have been exploited in different textile applications [212].
Printing is an essential technique used for the coloring of textiles. In this technique, a viscous paste is used where thickeners are essential to adhere the dyes to the indicated places according to the pattern [213]. The thickeners used must have a high molecular weight, stability, colorless structure, high viscosity, long hydration duration, and good storage capacity. There are thickeners of synthetic or natural origin. Synthetic thickeners are generally used in pigment printing, but they have different harmful effects on the environment. For example, bottles cannot be dumped in sanitary landfills, produce harmful gases, and cause air pollution [212]. On the other hand, natural thickeners gain importance because they are environmentally friendly, thus minimizing these side effects [214]. For this reason, galactomannans have gained great relevance within the textile industry. Guar gum is the most widely used thickener in printing pastes because it disperses in cold water, representing a great advantage. Guar gum is generally used at concentrations of 0.5% to 2% in printing pastes. For textile finishes, it is used at concentrations of 0.1% to 1% [215]. The viscosity of guar gum decreases when shear rates increase, as in most high molecular weight polymers, making it ideal for carpet printing [216,217].
Guar gum is also used for silk and wool printing, showing great fixing capacity, penetration, and color fastness, comparable with commercial thickeners such as alginate [218,219]. There are studies aimed at modifying the characteristics of galactomannans aimed at increasing the solubility and improving the swelling rate of gums [217]. The suitability of carboxymethyl guar derivatives has also been studied. It has been shown that the color intensity in printed samples varies according to the reactive dye used, the nature of the thickener, and the printing time and fixation. Depending on the degree of substitution (DS), the printed samples exhibit different characteristics such as rough touch (DS: 0.77), soft touch (DS: 1.27), or higher color efficiency [86]. All of the above makes guar gum an ideal thickener for textile printing; it is also economical and does not pose any ecological danger [220]. Locust bean gum, also used as a thickener in the textile industry, is a non-ionic polysaccharide and has a pH of 3 to 11, so it can be used in alkali-resistant printing pastes and is suitable for use with all types of printing pigments. Locust bean gum is effectively removed in post-printing washes, resulting in soft printed textiles [221]. In a study, Indalca gum (modified locust bean gum) and Arabic gum were compared by testing different printing parameters such as colors, touch, fastness, resistance, and costs. Indalca gum showed advantages for silk printing, including higher color resistance compared to gum Arabic gum-treated fabrics [222].
Fenugreek gum and tara gum were also investigated as thickeners. Hebeish et al. (2010) studied tara gum for printing cotton fabrics, resulting in higher color efficiency using tara carbamate than those obtained using conventional thickeners [223]. In another study, it was possible to isolate galactomannan gum and natural dye from tara seeds simultaneously, demonstrating the usefulness of this paste for printing cotton, wool, and silk fabrics [224]. Other sources of galactomannan, such as Cassia obovata seeds, have also been studied and are reported to be an ideal thickening agent for printing on polyester [225]. In parallel, galactomannans from sesbania seeds have proven to be very useful as thickeners [225,226,227].
Textile effluents from dyeing represent a major problem, and current adsorption techniques are not environmentally friendly. Natural polysaccharides are highly effective as adsorbents of dye molecules, providing excellent levels of color removal such as guar gum, locust bean gum, and cassia gum [86]. The use of galactomannans for effluent treatment offers significant advantages, such as their natural origin, being renewable, non-toxic, and biodegradable, and having high availability and high adsorption capacity. Furthermore, they do not require any additional chemical or any other treatment other than the use of the adsorbent [228].
7.5. Paper Industry
In paper manufacturing, it is important to consider costs, efficiency, environmental issues, and paper strength. The process must be clean due to the high speeds of the machines, with lower grammages and greater use of fillers [229].
Virgin wood pulp fibers have been replaced with secondary fibers in the interest of environmental protection [230]. However, products manufactured with secondary fibers as the main ingredient are weaker due to the drying phases [231]. Paper additives are auxiliary chemical products that have the capacity to increase the strength of paper, making their use necessary when working with secondary fibers [232,233]. In the paper industry, huge amounts of chemicals are consumed during the process of making additives for paper manufacturing, which results in serious environmental pollution. This led to the development of green production methods for paper reinforcing agents [234].
Naturally occurring galactomannans such as locust bean gum and guar gum possess cross-linking properties and good water solubility and can form highly viscous stable aqueous solutions at low concentrations, as well as easily combining with cellulose fibers [235]. Gums have previously been used as additives in papermaking, being added to chemical pulps to accelerate the beating process. Galactomannans improve strength and bond formation by increasing the number of bonds, positively affecting paper strength [229]. The sorption capacity of mannans is related to the similarity they share with the structure of cellulose backbones, so the sorption rate will directly depend on their structure. Independently of the chemical environment, mannans are highly useful in closed papermaking systems and in combination with recycled pulps. For papermaking, galactomannans are used in concentrations ranging from 0.1% to 0.5% of the paper weight. For recycled paper, up to 1% can be used to improve fiber retention and the delamination process [229]. When galactose side groups were removed from the galactomannan structure of guar gum, the sorption rate was significantly improved [235]. That is, natural polysaccharides must be chemically modified in order to be more effective when used as a paper-strengthening agent [236,237]. The strength-enhancing qualities of sheet hemicelluloses can be observed in the recycling of chemical pulps as well. During drying and rewetting processes, the strength of chemical pulps deteriorates as the cell wall structure is modified, leading to less swelling of the fibers. As the swelling is reduced, the flexibility and formability of the fibers is also reduced [238].
Derived mannans are already commercially available and their use also provides a reduction in white water BOD (biological oxygen demand), resistance to sheet detachment, and improved drainage. The use of galactomannans within the paper industry offers multiple positive effects [229].
7.6. Other Applications
The application of galactomannans from G. microphylla with borax (0.5%) significantly increases water retention and absorption in sandy soil from 15.68 to 38.12%. Galactomannans also help in water treatment, facilitating the aggregation and sedimentation of suspended particles, which favors their elimination [181]. In cherry cultivation, it was observed that when treated with galactomannans 2 weeks before harvest, the fruits effectively reduced the cracking rate. Galactomannans applied as protective films on seeds promote germination with greater efficiency by retaining moisture and nutrients. In addition, gums help transport microorganisms beneficial to plants, improving symbiosis and agricultural growth [239]. Gums have potential for application in the production of silver nanoparticles to detect bioactive compounds in biological systems [240]. In the oil industry, guar gum is used as a filtration-reducing additive in hydraulic fracturing to increase water viscosity and allow the suspension of solid materials. It also facilitates the lubrication and cleaning of wells during drilling [241]. In combination with other compounds, galactomannans are used to manufacture alternative biodegradable materials from renewable sources [242].
8. Conclusions
The bioactive properties of galactomannans make them highly valuable compounds with enormous potential for industrial applications, particularly in the formulation of food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, textile, and paper products. However, their production remains challenging due to the variability in the chemical structure, which depends on both the source and the extraction method used. Various techniques have been explored for their extraction and purification, but many require high energy consumption or involve the use of solvents and large amounts of water. Therefore, it is crucial to develop processes that maximize galactomannan yield while preserving their functional properties and minimizing environmental impact.
The growing demand for natural biopolymers in industry reinforces the importance of continuing to explore the applications of galactomannans. Future research should focus on the design of more efficient and sustainable extraction and purification methods. Additionally, the chemical or enzymatic modification of these polysaccharides could represent new opportunities for creating advanced materials with specific applications in biomedicine and nanotechnology.
As galactomannan production methods improve, their industrial applications are expected to expand further, consolidating their position as a sustainable alternative to synthetic polymers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.F.G. and Z.Y.E.-G.; formal analysis Y.F.G., J.D.P.d.l.R., J.H.G.-A., and J.M.S.-J.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.F.G., M.F.M.d.C.S., J.H.G.-A., A.H.M.P., J.D.P.d.l.R., J.M.S.-J., and Z.Y.E.-G.; writing—review and editing, Y.F.G., M.F.M.d.C.S., A.H.M.P., and Z.Y.E.-G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the University of Guadalajara for their support; Biotechnology Laboratory (CUNORTE) and Biotechnology Processes Laboratory (CUCEI). The first author is grateful to the Consejo Nacional de Humanidades, Ciencias y Tecnologías (CONAHCyT) for the doctoral scholarship, CVU 845878.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wielinga, W.C. 10—Galactomannans. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids, 2nd ed.; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2009; pp. 228–251. [Google Scholar]
- López-Franco, Y.L.; Cervantes-Montaño, C.I.; Martínez-Robinson, K.G.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Robles-Ozuna, L.E. Physicochemical characterization and functional properties of galactomannans from mesquite seeds (Prosopis spp.). Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Hussain, S.; Ahmed, Z. Extraction purification and characterization of galactomannan from fenugreek for industrial utilization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharafi, S.; Nateghi, L.; Eyvazzade, O.; Taj Abadi, M.E. Optimization and evaluation of textural properties of ultra-filtrated low-fat cheese containing galactomannan and novagel gum. Mljekarstvo 2019, 69, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, D.; Barak, S.; Khatkar, B. Guar gum: Processing, properties and food applications—A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 409–418. [Google Scholar]
- Vilaró, P.; Bennadji, Z.; Budelli, E.; Moyna, G.; Panizzolo, L.; Ferreira, F. Isolation and characterization of galactomannans from Prosopis affinis as potential gum substitutes. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 711–719. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Z. Physical properties and antidiabetic potential of a novel galactomannan from seeds of Gleditsia japonica var. delavayi. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 46, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, S.; Ramakrishna, G.; Srivastava, H.; Gaikwad, K. A comprehensive review on leguminous galactomannans: Structural analysis, functional properties, biosynthesis process and industrial applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 443–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Rodriguez, G.H.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Argüelles-Monal, W.; Álvarez-Bajo, O.; López-Franco, Y.L. Chemical modifications of galactomannans: Synthesis and structure-function analysis. Biotecnia 2023, 25, 126–135. [Google Scholar]
- Prajapati, V.D.; Jani, G.K.; Moradiya, N.G.; Randeria, N.P.; Nagar, B.J.; Naikwadi, N.N.; Variya, B.C. Galactomannan: A versatile biodegradable seed polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 60, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, S.; Mudgil, D. Locust bean gum: Processing, properties and food applications—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 66, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz, L.; Grenha, A.; Corvo, M.C.; Lourenço, J.P.; Ferreira, D.; Sarmento, B.; da Costa, A.M. Synthesis and characterization of Locust Bean Gum derivatives and their application in the production of nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lei, F.; He, L.; Xu, W.; Jiang, J. Comparative study on the monosaccharides of three typical galactomannans hydrolyzed by different methods. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 157, 112895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.B.; Garcia-Rojas, E.E. Recent advances in the encapsulation of bioactive ingredients using galactomannans-based as delivery systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, N.; Mattu, P.; Kaur, G. Extraction and derivatization of Leucaena leucocephala (Lam.) galactomannan: Optimization and characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida, R.R.; Magalhães, H.S.; de Souza, J.R.R.; Trevisan, M.T.S.; Vieira, Í.G.P.; Feitosa, J.P.A.; Araújo, T.G.; Ricardo, N.M.P.S. Exploring the potential of Dimorphandra gardneriana galactomannans as drug delivery systems. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 69, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, S.; Abidi, N.; Auld, D.; Moussa, H. Chemical and physical characterization of galactomannan extracted from guar cultivars (Cyamopsis tetragonolobus L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 74, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.R.; Silva, C.M.M.; Nunes, R.M.; Cunha, P.L.R.; de Paula, R.C.M.; Feitosa, J.P.A.; Girão, V.C.C.; Pompeu, M.M.L.; Leite, J.A.D.; Rocha, F.A.C. Structural characteristics are crucial to the benefits of guar gum in experimental osteoarthritis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresta, F.; Ceravolo, G.; Presti, V.L.; D’Agata, A.; Rao, R.; Chiofalo, B. Seed yield, galactomannan content and quality traits of different guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.) genotypes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 107, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani Soltani, M.; Meftahizadeh, H.; Barani, M.; Rahdar, A.; Hosseinikhah, S.M.; Hatami, M.; Ghorbanpour, M. Guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.) plant gum: From biological applications to advanced nanomedicine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 1972–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, T.I.M.; Badawi, K.R.M.; Naeem, M.A.; Helmy, W.A.; Gamal Shalaby, A.S. Enhancement of the quality attributes and health benefits synbiotic yoghurt from cow’s milk. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tel-Çayan, G.; Muhammad, A.; Deveci, E.; Duru, M.E.; Öztürk, M. Isolation, structural characterization, and biological activities of galactomannans from Rhizopogon luteolus and Ganoderma adspersum mushrooms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2395–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yang, T.; Wang, T.; Qiu, L. Thermosensitive behavior of hydrophobically associating anionic guar gum solutions and gels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Li, R.; Zhu, S.; Hu, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Kong, W.; Liang, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. A comparative study of sulfated tara gum: RSM optimization and structural characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huamaní-Meléndez, V.J.; Mauro, M.A.; Darros-Barbosa, R. Physicochemical and rheological properties of aqueous Tara gum solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha Jácome Marques, F.; da Silva Pantoja, P.; Matos, V.E.A.; Silva, R.O.; Damasceno, S.R.B.; Franco, Á.X.; Alves, R.C.; Justino, P.F.C.; de Souza, M.H.L.P.; Feitosa, J.P.A.; et al. Galactomannan from the seeds of Caesalpinia pulcherrima prevents indomethacin-induced gastrointestinal damage via neutrophil migration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadkari, P.V.; Tu, S.; Chiyarda, K.; Reaney, M.J.T.; Ghosh, S. Rheological characterization of fenugreek gum and comparison with other galactomannans. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, T.; Zhang, H.; Liang, J.; Kong, W.; Yao, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Synthesis and structure characterization of sulfated galactomannan from fenugreek gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshy, E.; Zarinkamar, F.; Nazari, M. Isolation, qualitative and quantitative evaluation of galactomannan during germination of Trigonella persica (Fabaceae) seed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Bao, Y.; Ahmed, Z.; Huang, J.-Y. Effect of high voltage atmospheric cold plasma on extraction of fenugreek galactomannan and its physicochemical properties. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhull, S.B.; Sandhu, K.S.; Punia, S.; Kaur, M.; Chawla, P.; Malik, A. Functional, thermal and rheological behavior of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum–graecum L.) gums from different cultivars: A comparative study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, W.; Feng, C.; Zhu, L.; Ji, L.; Wang, K.; Jiang, J. Study on structure and properties of galactomannan and enzyme changes during fenugreek seeds germination. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 327, 121653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, R.; Gao, M.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus fermentation on the structural feature, physicochemical property, and bioactivity of plant and fungal polysaccharides: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 148, 104492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashurov, A.; Dzhonmurodov, A.; Usmanova, S.; Kholov, S.E.; Muhidinov, Z. Characterization of polysaccharides from Eremurus hissaricus roots by FTIR spectroscopy. Proc. Univ. Appl. Chem. Biotechnol. 2021, 11, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwokocha, L.M.; Senan, C.; Williams, P.A.; Yadav, M.P. Characterisation and solution properties of a galactomannan from Bauhinia monandra seeds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidabadi Sherahi, M.; Fathi, M.; Zhandari, F.; Hashemi, S.M.B.; Rashidi, A. Structural characterization and physicochemical properties of Descurainia sophia seed gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwokocha, L.M.; Williams, P.A.; Yadav, M.P. Physicochemical characterisation of the galactomannan from Delonix regia seed. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 78, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Canto, W.; Chel-Guerrero, L.; Fernandez, V.V.A.; Aguilar-Vega, M. Delonix regia galactomannan hydrolysates: Rheological behavior and physicochemical characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.R.M.; de Lima Ramos, E.L.; Silva, M.F.S.; Ribeiro, F.D.O.S.; Sousa, J.S.; Pessoa, C.; Silva, D.A.; Feitosa, J.P.A.; Paula, H.C.B.; de Paula, R.C.M. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/galactomannan from Delonix regia seed thermal responsive graft copolymer via Schiff base reaction. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, I.C.; Castro, R.R.; Adjafre, B.L.; Sousa, S.H.A.F.; de Paula, D.S.; Alves, A.P.N.N.; Silva, P.G.B.; Assreuy, A.M.S.; Mota, M.R.L. Galactomannan of Delonix regia seeds modulates cytokine expression and oxidative stress eliciting anti-inflammatory and healing effects in mice cutaneous wound. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 203, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamir, K.; Badithi, N.; Venumadhav, K.; Seshagirirao, K. Characterization and comparative studies of galactomannans from Bauhinia vahlii, Delonix elata, and Peltophorum pterocarpum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Singhal, R.S. Hydrogel formulation based on galactomannan from residual spent coffee ground confers bioactivities and viscosifying properties in milkshake. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 102958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, P.B.S.; Soares, P.A.G.; Aragão-Neto, A.C.; Albuquerque, G.S.; Silva, L.C.N.; Lima-Ribeiro, M.H.M.; Neto, J.C.S.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; Correia, M.T.S.; Teixeira, J.A.C.; et al. Healing activity evaluation of the galactomannan film obtained from Cassia grandis seeds with immobilized Cratylia mollis seed lectin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prada, A.L.; Amado, J.R.R.; Keita, H.; Zapata, E.P.; Carvalho, H.; Lima, E.S.; de Sousa, T.P.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Cassia grandis fruit extract reduces the blood glucose level in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, R.; Pedrosa, C.; Leal, A.; Palermo, L.; Mansur, C. Extraction, characterization and rheological behavior of galactomannans in high salinity and temperature conditions. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2021, 26, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.A.; Ribeiro, K.A.; Seixas, J.R.P.C.; Silva Neto, J.C.; Santiago, M.G.P.F.; Aragão-Neto, A.C.; Lima-Ribeiro, M.H.M.; Borba, E.F.O.; Silva, T.G.; Kennedy, J.F.; et al. Effects including photobiomodulation of galactomannan gel from Cassia grandis seeds in the healing process of second-degree burns. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.D.A.L.; da Silva, M.G.; Porto, A.L.F.; de Albuquerque Wanderley, M.C.; da Silva, S.S.S.; de Andrade, A.F.; Bezerra, R.P.; Converti, A.; Ramos, D.G.; Marques, D.D.A.V.; et al. Application of the galactomannan gel from Cassia grandis seeds for biomedical purposes: Study of the incorporation of collagenases and their release profile. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 334, 122061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Yin, J.; Nie, S.; Wan, Y.; Xie, M. Structure and conformation characterization of galactomannan from seeds of Cassia obtusifolia. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 76, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Rimpy; Ahuja, M. Carboxymethyl modification of Cassia obtusifolia galactomannan and its evaluation as sustained release carrier. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3823–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannadi, A.; Movahedian, A.; Jannesary, Z. Hypocholesterolemic effects of Balangu (Lallemantia royleana) seeds in the rabbits fed on a cholesterol-containing diet. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2015, 5, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salehi, M.; Tabarsa, M.; Amraie, M.; Anvari, M.; Rezaei, M.; Smith, B.M. Characterization of rheological and structural properties of a gum from Balangu seeds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Peng, X.; Xu, J.; Deng, J.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, X.; Kan, H. A polysaccharide from the seed of Gleditsia japonica var. delavayi: Extraction, purification, characterization and functional properties. LWT 2024, 191, 115660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z. Isolation, fine structure and morphology studies of galactomannan from endosperm of Gleditsia japonica var. delavayi. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangi, D.; Mattoo, M.; Kumar, V.; Sharma, P. Synthesis and characterization of galactomannan polymer hydrogel and sustained drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2022, 4, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, R.; Mousavi, M.; Kiani, H. Effect of ultrasonication on rheological aspects and storage stability of O/W emulsions containing Gleditsia caspica galactomannan–Trigonella foenum–graceum galactomannan mixtures. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, I.G.P.; Mendes, F.N.P.; da Silva, S.C.; Paim, R.T.T.; da Silva, B.B.; Benjamin, S.R.; Florean, E.O.P.T.; Guedes, M.I.F. Antidiabetic effects of galactomannans from Adenanthera pavonina L. in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2018, 11, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, A.A.C.; Teixeira Sá, D.M.A.; Andrade, P.L.; Barreto, J.J.S.; dos Santos, N.L.; das Chagas, R.M.M.; Alves, T.d.B.; Chaves, M.J.L.; Maciel, J.d.S.; do Egito, A.S.; et al. Partially hydrolyzed galactomannan from Adenanthera pavonina seeds used as stabilizer, fat substitute, and food fiber source for mousses. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 2951–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Neto, J.F.; Pereira, W.O.; Cavalcante, L.A.; Oliveira Neto, J.G.; Graça, M.P.F.; Gavinho, S.R.; Amaral, F.M.B.; Santos, A.O.; Sombra, A.S.B.; Mendes, F.; et al. Extraction, Purification and Electrical Characterization of Gross Galactomannan and Purified Galactomannan Obtained from Adenanthera pavonina L. Seeds. Chem Biodivers 2023, 20, e202200888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devesa, S.; Graça, M.P.F.; Pereira, W.O.; Santos, G.L.; da Silva Neto, J.F.; Amaral, F.M.B.; Hammami, I.; Mendes, F.; Macedo, A.A.M. Dielectric Characterization of Solutions of Galactomannan Extracted from Adenanthera pavonina L.: Effects of Purification and Ethanol Concentration. Polymers 2024, 16, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.M.; Araújo, L.F.S.; Alvez, R.C.; Ono, L.; Sá, D.A.T.; da Cunha, P.L.R.; de Paula, R.C.M.; Maciel, J.S. Promising alternative gum: Extraction, characterization, and oxidation of the galactomannan of Cassia fistula. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, L.; Aouadi, S.; Gouzi, H. Characterization of Galactomannan Isolated from Algerian Gleditsia triacanthos L. Seeds. Nat. Prod. J. 2020, 10, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Barrera, G.N.; Galimberti, P.I.; Ribotta, P.D.; Alvarez Igarzabal, C.I. Development of edible films prepared by soy protein and the galactomannan fraction extracted from Gleditsia triacanthos (Fabaceae) seed. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, G.N.; Piloni, R.V.; Moldenaers, P.; Iturriaga, L.B.; Ribotta, P.D. Rheological behavior of the galactomannan fraction from Gleditsia triacanthos seed in aqueous dispersion. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 132, 107848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouaibi, M.; Rezig, L.; Lakoud, A.; Boussaid, A.; Hassouna, M.; Ferrari, G.; Hamdi, S. Exploring potential new galactomannan source of Retama reatam seeds for food, cosmetic and pharmaceuticals: Characterization and physical, emulsifying and antidiabetic properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Yang, L.; Yang, S.; Zhao, F.; Xu, L.; Yong, Q. Isolation, characterization and in vitro anticancer activity of an aqueous galactomannan from the seed of Sesbania cannabina. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Tang, N.; Jia, X.; Nirasawa, S.; Bian, X.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, Y. Isolation, physical, structural characterization and in vitro prebiotic activity of a galactomannan extracted from endosperm splits of Chinese Sesbania cannabina seeds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Tao, Y.; Huang, C.; Lai, C.; Yong, Q. Using One-pot Fermentation Technology to Prepare Enzyme Cocktail to Sustainably Produce Low Molecular Weight Galactomannans from Sesbania cannabina Seeds. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 3016–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Ma, J.; Huang, C.; Lai, C.; Ling, Z.; Yong, Q. The immunomodulatory activity of degradation products of Sesbania cannabina galactomannan with different molecular weights. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lei, F.; He, L.; Xu, W.; Jiang, J. Physicochemical characterization of galactomannans extracted from seeds of Gleditsia sinensis Lam and fenugreek. Comparison with commercial guar gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E, Y.; Chang, Z.; Lu, J.; Ju, Y.; Jiang, J.; Duan, W.; Li, P.; Lei, F.; Yao, X.; Wang, K. Enzymatically mediated Gleditsia sinensis galactomannan based hydrogel inspired by wound healing process. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Han, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Lei, F.; Wang, K.; Ji, L.; Jiang, J. Changes in structure and physicochemical properties of Sophora japonica f. pendula galactomannan in late growth stage. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 304, 120496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.M.; Mallik, B.; Sakhare, S.D.; Murthy, P.S. Prebiotic oligosaccharide enriched green coffee spent cookies and their nutritional, physicochemical and sensory properties. LWT 2020, 134, 109924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elangovan, S.M.; Muthu Kumar, S.; Sindhu, V.; Mahendiran, B.; Muthusamy, S.; Krishnakumar, G.S. Extraction, characterization and biological activity of Galactomannan rich endosperm of Borassus flabellifer (Linn.) suitable for biofabrication of tissue scaffolds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Han, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; Lei, F.; Wang, K.; Jiang, J. Production of manno-oligosaccharide from Gleditsia microphylla galactomannan using acetic acid and ferrous chloride. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Cao, N.; Wu, Y.; Wu, J. Optimized extraction and molecular characterization of polysaccharides from Sophora alopecuroides L. seeds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouana, T.; Pierre, G.; Vial, C.; Gardarin, C.; Wadouachi, A.; Cailleu, D.; le Cerf, D.; Boual, Z.; Hadj, M.D.O.; Michaud, P.; et al. Structural characterization and rheological properties of a galactomannan from Astragalus gombo Bunge seeds harvested in Algerian Sahara. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, G.; Pandey, I.P.; Joshi, G. Carboxymethylation of Cassia angustifolia seed gum: Synthesis and rheological study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, V.M.; Kolender, A.A.; Santagapita, P.R.; Buera, M.P. Vinal gum, a galactomannan from Prosopis ruscifolia seeds: Physicochemical characterization. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavudi, H.N.; Kottapalli, S.; Goycoolea, F.M. Extraction and physicochemical characterization of galactomannans from Dichrostachys cinerea seeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 82, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaud, F.; Pizzut-Serin, S.; Tarquis, L.; Ladevèze, S.; Morel, S.; Putaux, J.-L.; Potocki-Veronese, G. In Vitro Synthesis and Crystallization of β-1,4-Mannan. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, M.; Keegstra, K. Cell-wall carbohydrates and their modification as a resource for biofuels. Plant J. 2008, 54, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Variyar, P.S. Chapter 12—Guar Gum: A Versatile Polymer for the Food Industry. In Biopolymers for Food Design; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 383–407. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, S.R.; Shrivastava, P.S.; Ramasamy, J. Role of self-care in management of diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2013, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geronço, M.; Ramos, I.; Filho, E.; dos Rizzo, M.; Ribeiro, A.; Costa, M. Are Structurally Modified Galactomannan Derivatives Biologically Active? Polysaccharides 2021, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Sharma, R. Modeling the blockchain enabled traceability in agriculture supply chain. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 101967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özen, İ.; Bahtiyari, M.İ.; Haji, A.; ul Islam, S.; Wang, X. Properties of galactomannans and their textile-related applications—A concise review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemiller, J. Gums and Related Polysaccharides. In Glycoscience; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; p. 1513. ISBN 978-3-540-36154-1. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, D.; Bhattacharya, S. Hydrocolloids as thickening and gelling agents in food: A critical review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 47, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilbur Johnson, J.; Heldreth, B.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G., Jr.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; et al. Safety Assessment of Galactomannans as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2015, 34, 35S–65S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, V.; Mathur, N.K. Fenugreek and other less known legume galactomannan-polysaccharides: Scope for developments. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2005, 64, 475–481. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Ding, W.; Jia, L.; He, Q. The rheological properties of tara gum (Caesalpinia spinosa). Food Chem. 2015, 168, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidan, H.; Stankov, S.; Petkova, N.; Petkova, Z.; Iliev, A.; Stoyanova, M.; Ivanova, T.; Zhelyazkov, N.; Ibrahim, S.; Stoyanova, A.; et al. Evaluation of chemical composition, antioxidant potential and functional properties of carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.) seeds. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 2404–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sittikijyothin, W.; Torres, D.; Gonçalves, M.P. Modelling the rheological behaviour of galactomannan aqueous solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 59, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdani, A.; Wani, I.; Bhat, N. Effect of gamma irradiation on the physicochemical and structural properties of plant seed gums. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 106, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, M.; Kapoor, V.P. Seed galactomannans: An overview. Chem. Biodivers. 2005, 2, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.A.; Phillips, G.O. 1—Introduction to food hydrocolloids. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids, Second Edition; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2009; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Chen, F.; Yang, W.; Huang, H. Preparation, deproteinization and comparison of bioactive polysaccharides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, R.R. Chapter 20 Protein Precipitation Techniques. In Methods Enzymol; Burgess, R.R., Deutscher, M.P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 331–342. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, H.; Tian, L.; Sun, H.; Li, D.; Wu, W. Comparison in structural, physicochemical and functional properties of sweet potato stems and leaves polysaccharide conjugates from different technologies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 247, 125730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.A.R.; Coimbra, M.A. The antioxidant activity of polysaccharides: A structure-function relationship overview. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 314, 120965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Xiong, X.; Huang, G. Ultrasound-assisted extraction and characteristics of maize polysaccharides from different sites. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 95, 106416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; He, X.; Liu, G.; Wei, Z.; Sheng, J.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Xin, M.; Li, L.; Yi, P. Effects of different extraction methods on the structural, antioxidant and hypoglycemic properties of red pitaya stem polysaccharide. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zou, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhai, S.; Chang, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Luan, F.; Shi, Y. Extraction, purification, structural features, and pharmacological properties of polysaccharides from Houttuynia cordata: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmaz, Y.; Kilicli, M.; Toker, O.S.; Konar, N.; Palabiyik, I.; Tamtürk, F. Using spray-dried microalgae in ice cream formulation as a natural colorant: Effect on physicochemical and functional properties. Algal Res. 2020, 47, 101811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, A.; Mehariya, S.; Di Sanzo, G.; Larocca, V.; Martino, M.; Leone, G.P.; Marino, T.; Chianese, S.; Balducchi, R.; Musmarra, D. Recent developments in supercritical fluid extraction of bioactive compounds from microalgae: Role of key parameters, technological achievements and challenges. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 36, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat Aron, N.S.; Khoo, K.S.; Chew, K.W.; Veeramuthu, A.; Chang, J.-S.; Show, P.L. Microalgae cultivation in wastewater and potential processing strategies using solvent and membrane separation technologies. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Yu, J.; Ji, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Extraction of a Novel Cold-Water-Soluble Polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus and Its Antitumor and Immunological Activities. Molecules 2018, 23, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirabadi, S.; Milani, J.M.; Sohbatzadeh, F. Application of dielectric barrier discharge plasma to hydrophobically modification of gum arabic with enhanced surface properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 104, 105724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.-J.; Wang, C.-Y.; Yi, Y.-J.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zhou, W.-L.; Tan, S.-Y.; Li, F. Three phase partitioning for simultaneous purification of aloe polysaccharide and protein using a single-step extraction. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-K.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Qiu, W.-Y.; Wang, Z.-B.; Ma, H. Ultrasound synergized with three-phase partitioning for extraction and separation of Corbicula fluminea polysaccharides and possible relevant mechanisms. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-Z.; Tan, L.; Jin, C.-G.; Lu, J.; Tian, L.; Chang, Q.-Q.; Wang, K. Extraction, isolation, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 77, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campia, P.; Ponzini, E.; Rossi, B.; Farris, S.; Silvetti, T.; Merlini, L.; Brasca, M.; Grandori, R.; Galante, Y.M. Aerogels of enzymatically oxidized galactomannans from leguminous plants: Versatile delivery systems of antimicrobial peptides and enzymes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 158, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Juhaimi, F.; Adiamo, O.Q.; Ghafoor, K.; Babiker, E.E. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) seed. CyTA J. Food 2015, 14, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, H.-L.; Zhu, L.-W.; Zhang, W.-M.; Sun, D.-F.; Jiang, J.-X. Enzymatic production and characterization of manno-oligosaccharides from Gleditsia sinensis galactomannan gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 55, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Nakagawa, M.; Cheng, S. Emerging Trends in Green Extraction Techniques for Bioactive Natural Products. Processes 2023, 11, 3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.L.B.; de Aguiar, A.C.; Rostagno, M.A. Extraction of natural products using supercritical fluids and pressurized liquids assisted by ultrasound: Current status and trends. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 74, 105584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.; Cerqueira, M.; Souza, B.; Avides, M.; Vicente, A. Shelf Life Extension of Ricotta Cheese Using Coatings of Galactomannans from Nonconventional Sources Incorporating Nisin against Listeria monocytogenes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1884–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chen, F.; Huang, G. Extraction and analysis of polysaccharide from Momordica charantia. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 153, 112588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Huang, G.; Huang, H. Preparation and structure of polysaccharide selenide. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 154, 112630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Huang, G.; Huang, H. Preparation, analysis, antioxidant activities in vivo of phosphorylated polysaccharide from Momordica charantia. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ma, X.; Jin, W.; Cheng, H.; Xu, G.; Wen, H.; Xu, P. Shellfish polysaccharides: A comprehensive review of extraction, purification, structural characterization, and beneficial health effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, Y.K.; Yang, F.-C.; Chang, J.-S. Extraction of polysaccharides from edible mushrooms: Emerging technologies and recent advances. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Huang, G. Extraction, separation, modification, structural characterization, and antioxidant activity of plant polysaccharides. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2020, 96, 1209–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Geyter, N.; Morent, R. 7—Cold plasma surface modification of biodegradable polymer biomaterials. In Biomaterials for Bone Regeneration; Dubruel, P., Van Vlierberghe, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2014; pp. 202–224. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, N.N.; Keener, K.M.; Bourke, P.; Cullen, P.J. Generation of In-Package Cold Plasma and Efficacy Assessment Using Methylene Blue. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2015, 35, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.; Berganza, C.; Zhang, J. Cold Atmospheric Plasma: Methods of production and application in dentistry and oncology. Med. Gas Res. 2013, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, G.; Friedman, G.; Gutsol, A.; Shekhter, A.B.; Vasilets, V.N.; Fridman, A. Applied Plasma Medicine. Plasma Process. Polym. 2008, 5, 503–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.N.; Martynenko, A.; Chemat, F.; Paniwnyk, L.; Barba, F.J.; Jambrak, A.R. Thermodynamics, transport phenomena, and electrochemistry of external field-assisted nonthermal food technologies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1832–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deynse, A.; Van Morent, R.; De Geyter, N. Surface modification of polymers using atmospheric pressure cold plasma technology. In Polymer Science: Research Advances, Pratical Applications and Educational Aspects; Formatex Research Center: Norristown, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.-C.; Wu, J.S.-B.; Wu, J.-S.; Ting, Y. Effect of novel atmospheric-pressure jet pretreatment on the drying kinetics and quality of white grapes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5102–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Reddivari, L.; Huang, J.-Y. Enhancement of phenolic compounds extraction from grape pomace by high voltage atmospheric cold plasma. LWT 2020, 133, 109970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Reddivari, L.; Huang, J.-Y. Development of cold plasma pretreatment for improving phenolics extractability from tomato pomace. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 65, 102445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaka, K.; Jacob, M.V.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Plasma-assisted surface modification of organic biopolymers to prevent bacterial attachment. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2015–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Lan, W.; Li, H.; He, J.; Qin, W. Effect of extraction methods on the properties and antioxidant activities of Chuanminshen violaceum polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yi, W.; Wang, Z.; Fu, C.; Fan, X.; Du, B.; Cheng, L.; Lu, W.; Zhuo, J. Ultrahigh pressure extraction of polysaccharide from Morinda officinalis and effect on the polysaccharide structure. Sep. Sci Technol. 2021, 56, 1741–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, R.; Tan, L.; Bai, H.; Tian, L.; Lu, J.; Gao, M.; Bai, C.; Sun, H.; Li, D.; et al. Effect of extraction technology on physicochemical properties and biological activities of passion fruit peel polysaccharides. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 2797–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Ren, H.; Gong, G.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S. Effects of extraction methods on the antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Agaricus blazei Murrill. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lv, G.; Song, T.; Xu, Z.; Wang, M. Effects of different extraction methods on the structural and biological properties of Hericium coralloides polysaccharides. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getachew, A.T.; Lee, H.J.; Cho, Y.J.; Chae, S.J.; Chun, B.S. Optimization of polysaccharides extraction from Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) using subcritical water: Structural characterization and biological activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Huang, G.; Zhao, F.; Zhou, L.; Huang, S.; Li, H. The antioxidant activities of six (1→3)-β-d-glucan derivatives prepared from yeast cell wall. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Tang, Q.; Huang, G.; Long, R.; Huang, H. Preparation, structural analysis and antioxidant activities of phosphorylated (1 → 3)-β-d-glucan. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.; Song, Z.; Hu, W.; Liang, J.; Jing, Y.; He, L.; Huang, S.; Wang, X.; Hou, S.; Xu, T.; et al. Methods of extraction, separation, purification, structural characterization for polysaccharides from aquatic animals and their major pharmacological activities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Yu, S.; Luo, L.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y. Optimization of ultrasonic extraction of polysaccharides from Ziziphus jujuba Mill. by response surface methodology. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Qi, X.; Li, L.; Zhu, J.; Brennan, C.S.; Yan, J.-K. Application of nonthermal processing technologies in extracting and modifying polysaccharides: A critical review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4367–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.-C.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, H.; Jia, L.-R.; Chen, W.-Y. Characterization of antioxidant polysaccharides from Auricularia auricular using microwave-assisted extraction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; You, Q.; Jiang, Z. Optimization of enzyme assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Tricholoma matsutake by response surface methodology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangoria, P.; Divecha, J.; Shah, A.R. Production of mannooligosaccharides producing β-Mannanase by newly isolated Penicillium aculeatum APS1 using oil seed residues under solid state fermentation. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 34, 102023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; He, Z.; Ong, S.-L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ng, J. Optimization of agitation, aeration, and temperature conditions for maximum β-mannanase production. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2003, 32, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paludetti, L.F.; Kelly, A.L.; Gleeson, D. Effect of thermoresistant protease of Pseudomonas fluorescens on rennet coagulation properties and proteolysis of milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 4043–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solis, J.; Ayala-Borda, P.; Alvarez, W.; Soto, R.; Vargas, V.A. Protease Production by Bacteria Isolated from Laguna Chiar Khota, Potosi-Bolivia, for Protein Hydrolysates Production. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2022, 13, 3171–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valášková, V.; Baldrian, P. Degradation of cellulose and hemicelluloses by the brown rot fungus Piptoporus betulinus—Production of extracellular enzymes and characterization of the major cellulases. Microbiology 2006, 152, 3613–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, R.; Farooq, I.; Kaleem, A.; Iqtedar, M.; Iftikhar, T. Pectinase production from Aspergillus niger IBT-7 using solid state fermentation. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2018, 47, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, P.A.; de Rezende, S.T.; Passos, F.M.L.; Machado, S.G.; Maitan, G.P.; da Silva Coelho, V.T.; Guimaraes, M.V. α-Galactosidases production by Debaryomyces hansenii UFV-1. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Yu, Q.; Ai, C.; Fu, Y.; Yan, C.; Wen, C.; Zhu, Z. Structural characterization and anticoagulant activity of two polysaccharides from Patinopecten yessoensis viscera. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Liu, Y.; Tao, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Wu, J.; Lv, Z. CO2 supercritical fluid extraction and characterization of polysaccharide from bamboo (Phyllostachys heterocycla) leaves. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.K.; Srivastav, P.P. Extraction, Identification and Quantification Methods of Rice Aroma Compounds with Emphasis on 2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline (2-AP) and Its Relationship with Rice Quality: A Comprehensive Review. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 111–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaw, K.-Y.; Parat, M.-O.; Shaw, P.; Falconer, J. Solvent Supercritical Fluid Technologies to Extract Bioactive Compounds from Natural Sources: A Review. Molecules 2017, 22, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmortazavi, S.M.; Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M.; Hajimirsadeghi, S. Supercritical Fluid Technology in Analytical Chemistry. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2014, 10, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Verma, D.K.; Thakur, M.; Tripathy, S.; Patel, A.R.; Shah, N.; Utama, G.L.; Srivastav, P.P.; Benavente-Valdés, J.R.; Chávez-González, M.L.; et al. Supercritical fluid extraction (SCFE) as green extraction technology for high-value metabolites of algae, its potential trends in food and human health. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Tan, Z. Extraction and purification of grape seed polysaccharides using pH-switchable deep eutectic solvents-based three-phase partitioning. Food Chem. 2023, 412, 135557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdanowicz, M.; Wilpiszewska, K.; Spychaj, T. Deep eutectic solvents for polysaccharides processing. A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 200, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, N.; Zhong, J.; Ye, X.; Lu, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Xu, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, D. Ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction of polysaccharide from Corbicula fluminea: Characterization and antioxidant activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panadare, D.C.; Gondaliya, A.; Rathod, V.K. Comparative study of ultrasonic pretreatment and ultrasound assisted three phase partitioning for extraction of custard apple seed oil. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 61, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chen, K.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, L.; Yu, D.; Dai, Y.; Wang, L. Ultrasound-assisted three phase partitioning for simultaneous extraction of oil, protein and polysaccharide from pumpkin seeds. LWT 2021, 151, 112200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-K.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Qiu, W.-Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.-B.; Wu, J.-Y. Three-phase partitioning as an elegant and versatile platform applied to nonchromatographic bioseparation processes. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2416–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Wu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Dong, Q.; Yang, H.; Dai, C. An efficient approach for extraction of polysaccharide from abalone (Haliotis Discus Hannai Ino) viscera by natural deep eutectic solvent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Rombaut, N.; Sicaire, A.-G.; Meullemiestre, A.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.-S.; Abert-Vian, M. Ultrasound assisted extraction of food and natural products. Mechanisms, techniques, combinations, protocols and applications. A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 540–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Xu, F.; Liu, F.; Masamba, K.G.; Chen, M.; Zhong, F. A comparative study of crude and refined tara gum in terms of structural parameters and rheological properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 162, 110986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Kakuda, Y.; Cui, S. Hydrocolloids in emulsions: Particle size distribution and interfacial activity. Food Hydrocoll. 2001, 15, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Cui, S.W.; Barbut, S. Purification and partial physicochemical characteristics of protein free fenugreek gums. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 2049–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbon, A.I.; Pinheiro, A.C.; Ribeiro, C.; Miranda, C.; Maia, J.M.; Teixeira, J.A.; Vicente, A.A. Characterization of galactomannans extracted from seeds of Gleditsia triacanthos and Sophora japonica through shear and extensional rheology: Comparison with guar gum and locust bean gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cheng, H.; Wu, D.; Linhardt, R.J.; Zhi, Z.; Yan, L.; Chen, S.; Ye, X. Green recovery of pectic polysaccharides from citrus canning processing water. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 144, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, S.; Beck, A.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Guillarme, D. Ion-exchange chromatography for the characterization of biopharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 113, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ó’Fágáin, C.; Cummins, P.; O’Connor, B. Gel-Filtration Chromatography. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 681, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, R.; Nicolas, P.; Vincent, S.J.F.; Fischer, M.; Reymond, S.; Redgwell, R.J. Purification and characterisation of a galactoglucomannan from kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa). Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 331, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.M.; Ahmad, A.S.; Yin, Y.Y.; Yahya, N.; Ibrahim, N. Extraction, purification and characterization of durian (Durio zibethinus) seed gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, J.; Zhao, G.; Koidis, A.; Wei, X.; Huang, W.; Guo, Z.; Wu, S.; Huang, R.; Lei, H. Isolation, structural, biological activity and application of Gleditsia species seeds galactomannans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 334, 122019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üner, M.; Altınkurt, T. Evaluation of honey locust (Gleditsia triacanthos Linn.) gum as sustaining material in tablet dosage forms. Farmaco 2004, 59, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakimets, I.; Paes, S.S.; Wellner, N.; Smith, A.C.; Wilson, R.H.; Mitchell, J.R. Effect of Water Content on the Structural Reorganization and Elastic Properties of Biopolymer Films: A Comparative Study. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1710–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wen, C.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Y. Review of isolation, structural properties, chain conformation, and bioactivities of psyllium polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Tang, M.; Zhang, F.; Lei, F.; Li, P.; Wang, K.; Zeng, H.; Jiang, J. Facile Access to Gleditsia microphylla Galactomannan Hydrogel with Rapid Self-Repair Capacity and Multicyclic Water-Retaining Performance of Sandy Soil. Polymers 2022, 14, 5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, F.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Xue, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B. Antithrombotic activity of oral administered low molecular weight fucoidan from Laminaria Japonica. Thromb Res. 2016, 144, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Cao, Y.X.; Jiao, S.M.; Du, G.H.; Du, Y.G.; Qin, X.M. Structural characterization and immune activity screening of polysaccharides with different molecular weights from Astragali Radix. Front Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 582091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, H. Characterization and antioxidant activities of degraded polysaccharides from two marine Chrysophyta. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Guo, D.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, P.; Huang, L. Isolation, structures and bioactivities of the polysaccharides from Radix Hedysari: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 199, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Yin, M.; Lan, P.; Wang, H.; Nie, H.; Ji, X. Recent progress in the research of Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels polysaccharides: Extraction, purification, structure and bioactivities. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2021, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, Q.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, L. Anti-fatigue activity of polysaccharide fractions from Lepidium meyenii Walp. (maca). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 95, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, H.A.; Lalitha, K.G. Isolation, purification and characterization of galactomannans as an excipient from Senna tora seeds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 65, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, G.; Arya, S.K. Mannans: An overview of properties and application in food products. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavudi, H.N.; Suthari, S. Application of Legume Seed Galactomannan Polysaccharides. Sustain. Agric. Rev. 2020, 45, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spotti, M.J.; Perduca, M.; Loyeau, P.; Rubiolo, A.; Carrara, C. Espina Corona (Gleditsia amorphoides) Seed Gum. In Emerging Natural Hydrocolloids: Rheology and Functions; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 225–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciarini, L.S.; Palavecino, P.M.; Ribotta, P.D.; Barrera, G.N. Gleditsia triacanthos Galactomannans in Gluten-Free Formulation: Batter Rheology and Bread Quality. Foods 2023, 12, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, S.; Oliveira, V.; Oliveira, A.; Holanda Araújo, M.; Feitosa, J.; Paula, R.; de Sousa, F.D.; Moreira, A.C.; Beserra, F.J.; Moreira, R.A. Caesalpinia pulcherrima seed galactomannan on rheological properties of dairy desserts. Ciênc. Rural 2020, 50, e20190176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mæhre, H.K.; Weisensee, S.; Ballance, S.; Rieder, A. Guar gum fortified white breads for prospective postprandial glycaemic control—Effects on bread quality and galactomannan molecular weight. LWT 2021, 152, 112354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.-K.; Ha, S.-R.; Choi, J.-S. Effect of the Ratio of Raw Material Components on the Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Emulsion-Type Pork Sausages. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 29, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, D.; Barak, S.; Patel, A.; Shah, N. Partially hydrolyzed guar gum as a potential prebiotic source. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (ANS); Mortensen, A.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Di Domenico, A.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Lambré, C.; et al. Re-evaluation of guar gum (E 412) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazón, P.; Velazquez, G.; Ramírez, J.A.; Vázquez, M. Polysaccharide-based films and coatings for food packaging: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 68, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbaljoo, H.; Sani, I.K.; Sani, M.A.; Rahati, S.; Mansouri, E.; Molaee-Aghaee, E.; Fatourehchi, N.; Kadi, A.; Arab, A.; Sarabandi, K.; et al. Advances in plant gum polysaccharides; Sources, techno-functional properties, and applications in the food industry—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 2327–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, A.; Tyagi, S.; Gupta, R.K.; Tyagi, Y.K. Natural gums of plant origin as edible coatings for food industry applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 959–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Gao, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Fan, X.; Wang, W.; et al. Structural basis for the severe adverse interaction of sofosbuvir and amiodarone on L-type Cav channels. Cell 2022, 185, 4801–4810.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.H.; Ismail, M.M.A.; Mohammed, H.S. The effect of dexamethasone on postoperative blood glucose levels in diabetic and nondiabetic Patients who are undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. SVU-Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 3, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Vendruscolo, C.W.; Andreazza, I.F.; Ganter, J.L.M.S.; Ferrero, C.; Bresolin, T.M.B. Xanthan and galactomannan (from M. scabrella) matrix tablets for oral controlled delivery of theophylline. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 296, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, J.; Bresolin, T. Pharmaceutical use of galactomannans. Quim. Nova 2010, 34, 292–299. [Google Scholar]
- Schiermeier, S.; Schmidt, P. Fast dispersible ibuprofen tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 15, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tara, E.; Gottschalck, G.N. McEwen. In International Cosmetic Ingredient Dictionary and Handbook, 10th ed.; Cosmetic, Toiletry, and Fragrance Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, I.; Bergfeld, W.; Heldreth, B.; Fiume, M.; Gill, L. The Cosmetic Ingredient Review Program—Expert Safety Assessments of Cosmetic Ingredients in an Open Forum. Int. J. Toxicol. 2017, 36, 5S–13S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigano, L.; Deola, M.; Zaccariotto, F.; Colleoni, T.; Lionetti, N. A New Gelling Agent and Rheology Modifier in Cosmetics: Caesalpinia spinosa Gum. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisel, M.; Aguni, Y.; Renou, F.; Malhiac, C. Impact of fine structure of galactomannans on their interactions with xanthan: Two co-existing mechanisms to explain the synergy. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ding, W.; He, Q. The gelation properties of tara gum blended with κ-carrageenan or xanthan. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothe, H.; Fautz, R.; Gerber, E.; Neumann, L.; Rettinger, K.; Schuh, W.; Gronewold, C. Special aspects of cosmetic spray safety evaluations: Principles on inhalation risk assessment. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 205, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, R. Textiles and Fashion: Materials, Design and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1–845. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M. Influence of Binders and Thickeners of Pigment Printing paste on Light Fastness and Crocking Fastness of the Fabric. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2018, 3, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Harlapur, S.; Airani, N.; Gobbi, S. Appliance of Natural Gums as Thickeners in the Process of Cotton Printing. Adv. Res. Text. Eng. 2020, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, L.W.C. The Production and Properties of Printing Pastes. 2003. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=http://182.160.97.198:8080/xmlui/bitstream/handle/123456789/1169/Chapter%25207%2520-%2520The%2520production%2520and%2520properties%2520of%2520printing%2520pastes.pdf%3Fsequence%3D8&ved=2ahUKEwj7h4aY3sSMAxVDh1YBHaDaJ1kQFnoECBIQAQ&usg=AOvVaw35BxLkF6rHDvMQdM8Uxgc6 (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Dawson, T.L.; Miles, L.W.C. Carpet and Yarn Printing. 2003. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=http://182.160.97.198:8080/xmlui/bitstream/handle/123456789/1169/Chapter%25204%2520-%2520Carpet%2520and%2520yarn%2520printing.pdf%3Fsequence%3D5&ved=2ahUKEwjfy83A3sSMAxVMsVYBHYjGL5sQFnoECB0QAQ&usg=AOvVaw3JMWRo1qTwl2Vhw5amVs0b (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- Hassabo, A.; Othman, H. Natural thickener in textile printing (A Mini Review). J. Text. Color. Polym. Sci. 2021, 18, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Fijan, R.; Šostar-Turk, S.; Lapasin, R. Rheological study of interactions between non-ionic surfactants and polysaccharide thickeners used in textile printing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldaro, E.; Gallucci, M.; Formantici, C.; Issi, L.; Cheroni, S.; Galante, Y.M. Enzymatic improvement of guar-based thickener for better-quality silk screen printing. Color. Technol. 2012, 128, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, D.N.; Nazir, A.; Iqbal, M.; Yameen, M. Green synthesis and characterization of carboxymethyl guar gum: Application in textile printing technology. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, F.; Hassabo, A.; Othman, H.; Mosaad, M.; Mohamed, A. A Valuable Observation on Thickeners for Valuable Utilisation in the Printing of Different Textile Fabrics. Egypt. J. Chem. 2021, 65, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlot, M.; Dubey, P.; Sharma, E. Screen printing of silk, using gum Indalca and gum Arabic thickeners. Int. Dye. 2003, 188, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Hebeish, A.; Ragheb, A.A.; Nassar, S.H.; Allam, E.; Abd El-Thalouth, J.I. Tara Gum Carbamate: A New Thickening System for Cotton Printing Using Vat Dyes. J. Am. Sci. 2010, 6, 623–631. [Google Scholar]
- Hebeish, A.; Ragheb, A.; Nassar, S.; Allam, E.E.; El-Thalouth, J.I.A. Eco-friendly technology for textile printing using innovative self printing paste. Egypt. J. Chem. 2011, 54, 663–678. [Google Scholar]
- El-Molla, M. Preparation and characterization of carboxymethyl cassia obovata gum and their utilization in textile printing. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2000, 282, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekaby, M.; Hermina, I.; El-Rahman, A.; Elkhabiry, S. Technological evaluation of carboxymethyl sesbania galactomannan gum derivatives as thickeners in reactive printing. Bioresources 2010, 5, 517–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Thalouth, I.; Rekaby, M.; Abdel-Rahman, A.H.; El-khabery, S.A. Preparation and Characterization of Phosphorylated Sesbania Galactomannan Gum Derivatives and Their Applications in Textile Printing. Res. J. Text. Appar. 2012, 16, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, R.S. Natural Polysaccharides and Their Interactions with Dye Molecules: Applications in Effluent Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4905–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannuksela, T.; Holmbom, B.; Lachenal, D. Effect of sorbed galactoglucomannans and galactomannans on pulp and paper handsheet properties, especially strength properties. Nord. Pulp Pap. Res. J. 2004, 19, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A.; Lucia, L. A New Class of Biobased Paper Dry Strength Agents: Synthesis and Characterization of Soy-Based Polymers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbe, M.; Venditti, R.; Rojas, O. What happens to cellulosic fibers during papermaking and recycling? A Review. Bioresources 2007, 2, 739–788. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbe, M. Bonding between cellulosic fibers in the absence and presence of dry-strength agents—A review. Bioresources 2006, 1, 281–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Li, K. Development of wet strength additives from wheat gluten. Holzforschung 2005, 59, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.-Y.; Li, S.-Y.; Song, X.-L. Preparation of Paper Strengthening Agent by Esterification of Cellulosic Fines. Bioresources 2016, 12, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Liu, B.; Song, X. The Galactose Oxidase Air Oxidation of Galactomannans for Use as Paper Strengthening Agents. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2020, 40, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Hu, H.; Xu, J. Influences of configuration and molecular weight of hemicelluloses on their paper-strengthening effects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; He, W.; Yan, R.; Song, X. A study of cationic glucomannan as a paper strength agent. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2017, 54, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.I.N.; Hubbe, M.; Venditti, R. Can recycled kraft fibres benefit from chemical addition before they are first dried? Appita J. 2002, 55, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Mihaela Gabriela, D.; Nicolae Ionut, V.; Baciu, A. The Use of Natural Biopolymer Derived from Gleditsia triacanthos in Reducing the Cracking Process of Cherries. Rev. Chim. 2015, 66, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, N.; Dang, N.; Doan, L.; Nguyen, H. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: From Conventional to ‘Modern’ Methods—A Review. Processes 2023, 11, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.M.A.; Abdel-Raouf, M.E. Applications of guar gum and its derivatives in petroleum industry: A review. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.; Fronza, P.; Gonçalves, I.; da Silva, W.; Oliveira, L.; Franca, A. Development of Polymeric Films Based on Sunflower Seed Proteins and Locust Bean Gum. Polymers 2024, 16, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).