Optimization of Pectin-Zein Beads via Response Surface Methodology for Enhanced Colon-Targeted Delivery of p-Coumaric Acid from Rice Husk Extract
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Rice Husk Extract (RHE)
2.3. RHE Encapsulation
2.3.1. Experimental Design
2.3.2. Preparation of RHE Pectin-Zein Hydrogel Beads
2.4. RP-HPLC-DAD Analysis and Method Validation
2.5. Determination of Encapsulation Efficiency
2.6. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion Protocol
2.7. Bioaccessibility Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
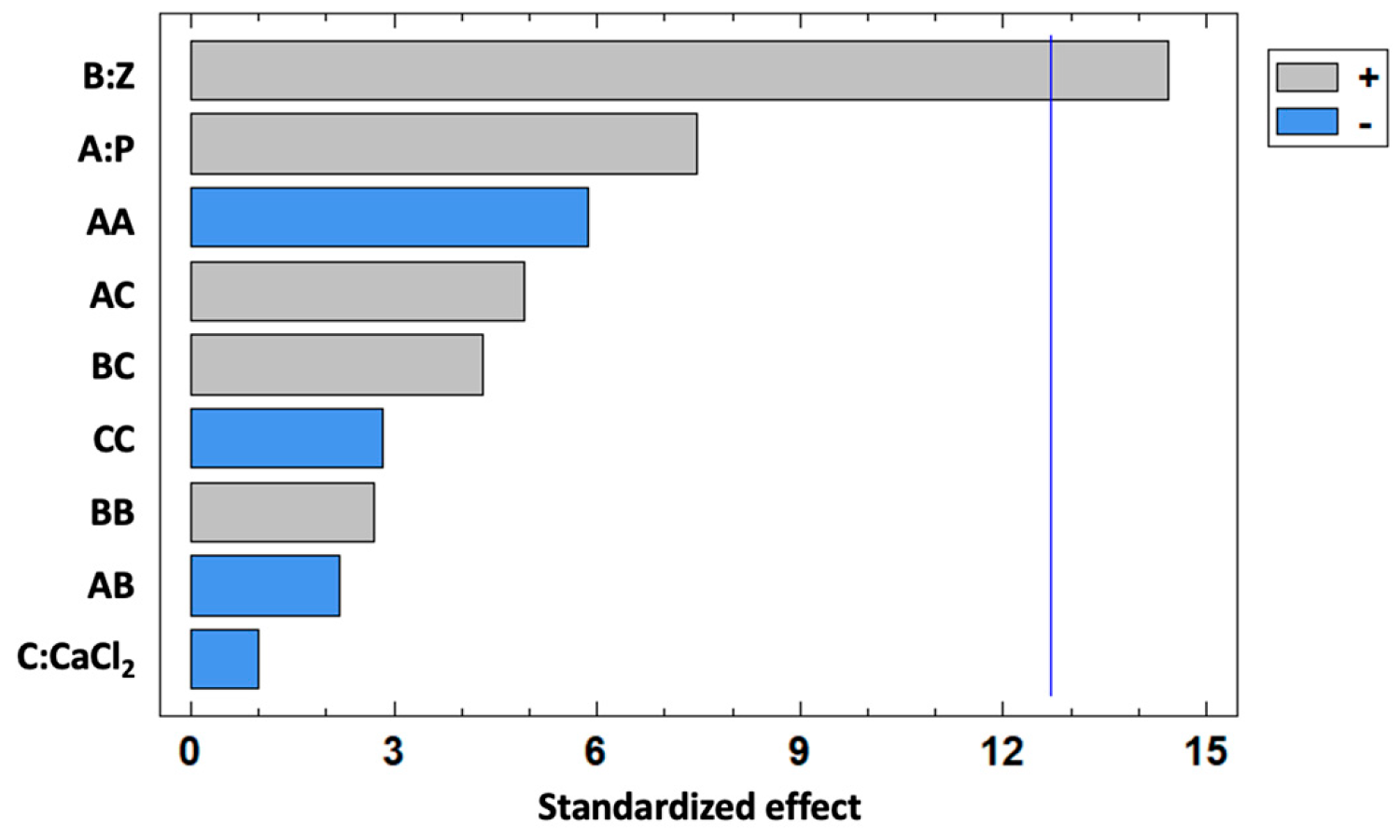
3.1. Optimization of the RHE Formulation
3.2. Bioaccessibility of p-Coumaric Acid in Raw and Encapsulated RHE
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| p-CA | p-coumaric acid |
| DOE | Design of Experiments |
| LMP | Low-methoxylated pectin |
| HMP | High-methoxylated pectin |
| RHE | Rice husk extract |
| MAE | Microwave-Assisted Extraction |
| RSM | Response Surface Methodology |
| ICH | International Council for Harmonisation |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| SSF | Simulated salivary fluid |
| SGF | Simulated gastric fluid |
| SIF | Simulated intestinal fluid |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| GI | Gastro-intestinal |
| EE | Encapsulation efficiency |
References
- Rana, A.; Samtiya, M.; Dhewa, T.; Mishra, V.; Aluko, R.E. Health benefits of polyphenols: A concise review. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, C.; Colombo, F.; Biella, S.; Stockley, C.; Restani, P. Polyphenols and human health: The role of bioavailability. Nutrients 2021, 13, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritzinos, I.; Goula, A. Polyphenols in agricultural byproducts and food waste. In Polyphenols in Plants, 2nd ed.; Watson, R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, L.; McClements, D.J.; Peng, X.; Xu, Z.; Meng, M.; Ji, H.; Qiu, C.; Long, J.; Jin, Z. Encapsulation of polyphenols in protein-based nanoparticles: Preparation, properties, and applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 11341–11355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Bao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Leonidovna Strakh, Y. Encapsulation of three different types of polyphenols in casein using a customized pH-driven method: Preparation and characterization. Food Res. Int. 2024, 189, 114547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buljeta, I.; Pichler, A.; Šimunović, J.; Kopjar, M. Polysaccharides as Carriers of Polyphenols: Comparison of Freeze-Drying and Spray-Drying as Encapsulation Techniques. Molecules 2022, 27, 5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, R.; Lu, X.; Dai, Y.; Chen, T.; Xing, Y.; Xue, L.; Duan, Z.; Zhou, W.; Li, J. Fabrication and characterization of l-ascorbyl palmitate and phospholipid-based hybrid liposomes and their impacts on the stability of loaded hydrophobic polyphenols. Food Chem. 2023, 398, 133953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Antoniadi, L.; Zhou, H.; Chen, H.; Angelis, A.; Halabalaki, M.; Skaltsounis, L.A.; Qi, Z.; Wang, C. Sodium cholate-coated Olea europaea polyphenol nanoliposomes: Preparation, stability, release, and bioactivity. Food Chem. 2025, 469, 142580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishir, M.R.I.; Karim, N.; Gowd, V.; Xie, J.; Zheng, X.; Chen, W. Pectin-chitosan conjugated nanoliposome as a promising delivery system for neohesperidin: Characterization, release behavior, cellular uptake, and antioxidant property. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Chang, Y.H. Structural, physicochemical, and in-vitro release properties of hydrogel beads produced by oligochitosan and de-esterified pectin from yuzu (Citrus junos) peel as a quercetin delivery system for colon target. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Cheng, W.; Liang, Z.; Zhan, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Hu, K. Co-encapsulation of tannic acid and resveratrol in zein/pectin nanoparticles: Stability, antioxidant activity, and bioaccessibility. Foods 2022, 11, 3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosi, I.; Balduzzi, A.; Moretto, G.; Colombo, R.; Papetti, A. Towards valorization of food-waste-derived pectin: Recent advances on their characterization and application. Molecules 2023, 28, 6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, D.A.; Schroeter, B.; Martínez-Abad, A.; Fabra, M.J.; Gurikov, P.; López-Rubio, A. Pectin-based aerogel particles for drug delivery: Effect of pectin composition on aerogel structure and release properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 306, 120604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassino, A.N.; Barba, F.J.; Brnčića, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Lucini, L.; Rimac Brnčić, S. Analytical tools used for the identification and quantification of pectin extracted from plant food matrices, wastes and by-products: A review. Food Chem. 2018, 266, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konrade, D.; Gaidukovs, S.; Vilaplana, F.; Sivan, P. Pectin from fruit- and berry-juice production by-products: Determination of physicochemical, antioxidant and rheological properties. Foods 2023, 12, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, S.; Swami Hulle, N.R. Citrus pectins: Structural properties, extraction methods, modifications and applications in food systems—A review. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib, T.; Pan, H.; Chen, S. Recent advances in pectin-based nanoencapsulation for enhancing the bioavailability of bioactive compounds: Curcumin oral bioavailability. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 3115–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padma Ishwarya, S.; Sandhya, R.; Nisha, P. Advances and prospects in the food application of pectin hydrogels. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 4393–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo, V.R.; Castro Vάzquez, L.I. Pectin—Extraction, Purification, Characterization and Applications. In Pectins—Extraction, Purification, Characterization and Applications; Masuelli, M.A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Q.; Yin, L. Interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels of soy protein isolate and sugar beet pectin as a potential carrier for probiotics. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ke, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z. In vitro release and antioxidant activity of Satsuma mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco cv. unshiu) peel flavonoids encapsulated by pectin nanoparticles. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 2362–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo-Castillo, V.; Rodríguez-Stouvenel, A.; Martínez, R.; Bernal, C. Development of alginate-pectin microcapsules by the extrusion for encapsulation and controlled release of polyphenols from papaya (Carica papaya L.). J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córković, I.; Pichler, A.; Ivić, I.; Šimunović, J.; Kopjar, M. Microencapsulation of chokeberry polyphenols and volatiles: Application of alginate and pectin as wall materials. Gels 2021, 7, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira Silveira, M.; Lucas Chaves Almeida, F.; Dutra Alvim, I.; Silvia Prata, A. Encapsulation of pomegranate polyphenols by ionic gelation: Strategies for improved retention and controlled release. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortorella, S.; Maturi, M.; Vetri Buratti, V.; Vozzolo, G.; Locatelli, E.; Sambri, L.; Comes Franchini, M. Zein as a versatile biopolymer: Different shapes for different biomedical applications. RCS Adv. 2021, 11, 39004–39026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, D.U.; Garg, R.; Gaur, M.; Pareek, A.; Prajapati, B.G.; Castro, G.R.; Suttiruengwong, S.; Sriamornsak, P. Pectin hydrogels for controlled drug release: Recent developments and future prospects. Saudi Pharm. J. 2024, 32, 102002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frosi, I.; Vallelonga, D.; Colombo, R.; Milanese, C.; Papetti, A. Valorization of rice husk (Oryza sativa L.) as a source of in vitro antiglycative and antioxidant agents. Foods 2023, 12, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, K.; Ou, J.; Huang, J.; Ou, S. p-Coumaric acid and its conjugates: Dietary sources, pharmacokinetic properties and biological activities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2952–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, N.; Hathout, R.M.; Abd-Allah, H.; Sammour, O.A. Simplex Lattice Design and Machine Learning Methods for the Optimization of Novel Microemulsion Systems to Enhance p-Coumaric Acid Oral Bioavailability: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. AAPS PharmSciTech 2024, 25, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimbala, J.M. Taguchi Orthogonal Arrays; Pennsylvania State University: State College, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Fishman, M.L.; Hicks, K.B.; Kende, M.; Ruthel, G. Pectin-zein beads for potential colon-specific drug delivery: Synthesis and in vitro evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2006, 13, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICH Q2 (R2) Validation of Analytical Procedures—Scientific Guideline. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-q2r2-validation-analytical-procedures-scientific-guideline (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Contado, C.; Caselotto, L.; Mello, P.; Maietti, A.; Marvelli, L.; Marchetti, N.; Dalpiaz, A. Design a formulation of Eudragit-coated zein/pectin nanoparticles for the colon delivery of resveratrol. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 2417–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. Infogest static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, F.; Ding, B.; Li, Q.; Xi, Y.; Zhai, G. Eudragit® S100 coated calcium pectinate microspheres of curcumin for colon targeting. J. Microencapsul. 2011, 28, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Velázquez, O.A.; Mulero, M.; Cuevas-Rodríguez, E.O.; Mondor, M.; Arcand, Y.; Hernández-Álvarez, A.J. In vitro gastrointestinal digestion impact on stability, bioaccessibility and antioxidant activity of polyphenols from wild and commercial blackberries (Rubus spp.). Food Funct. 2021, 12, 7358–7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.H.I.; Duan, W.; Lee, B.-J.; Tran, T.T.D. Drug stabilization in the gastrointestinal tract and potential applications in the colonic delivery of oral zein-based formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhidinov, Z.M.; Kasimova, G.F.; Bobokalonov, D.T.; Khalikov, D.K.; Teshavev, K.I.; Khalikova, M.D.; Liu, L.-S. Pectin-zein microspheres as drug delivery systems. Pharm. Chem. J. 2011, 44, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotiko, A.; Sathivel, S. Releasing characteristics of anthocyanins extract in pectin–whey protein complex microcapsules coated with zein. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2059–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarioli, A.P.; Giovanini De Oliveira Sartori, A.; Francetto Juliano, F.; Eduardo Pedroso Gomes do Amaral, J.; Cavalcanti dos Santos, R.; Maria De Lima, L.; Matias De Alencas, S. Simulated gastrointestinal digestion/Caco-2 cell model to predict bioaccessibility and intestinal permeability of p-coumaric acid and p-coumaroyl derivatives in peanut. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 134033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiamphun, S.; Chaiyana, W. Enhancing skin delivery and stability of vanillic and ferulic acids in aqueous enzymatically extracted glutinous rice husk by nanostructured lipid carriers. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Kar, A.; Bannerjee, S.; Jana, S.N.; Haldar, P.K.; Sharma, N. Enhanced permeability and photoprotective potential of optimized p-coumaric acid-phospholipid complex loaded gel against UVA mediated oxidative stress. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 2021, 221, 112246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircan, H.; Oral, R.A. Parameters affecting calcium-alginate bead characteristics: Viscosity of hydrocolloids and water solubility of core material. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 236, 124011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chang, G.; Dang, Q.; Liu, C.; Song, H.; Chen, A.; Yang, M.; Shi, L.; Zhang, B.; Cha, D. Preparation and characterization of antibacterial, antioxidant, and biocompatible p-coumaric acid modified quaternized chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 125087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, A.; Roy, A.; Kulandaivel, S.; Natesan, V.; Kim, S.J. p-Coumaric Acid Nanoparticles Ameliorate Diabetic Nephropathy via Regulating mRNA Expression of KIM-1 and GLUT-2 in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Run (No.) | X1 | X2 | X3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 |
| 2 | 0 | −1 | 0 |
| 3 | +1 | −1 | +1 |
| 4 | −1 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | +1 |
| 6 | +1 | 0 | −1 |
| 7 | −1 | +1 | +1 |
| 8 | 0 | +1 | −1 |
| 9 | +1 | +1 | 0 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Run (No.) | P (% w/v) | Z (% w/v) | CaCl2 (% w/v) | EE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.50 | 1.0 | 0.50 | 4.54 |
| 2 | 1.75 | 1.0 | 2.25 | 11.01 |
| 3 | 3.00 | 1.0 | 4.00 | 15.57 |
| 4 | 0.50 | 5.5 | 2.25 | 8.02 |
| 5 | 1.75 | 5.5 | 4.00 | 25.91 |
| 6 | 3.00 | 5.5 | 0.50 | 17.27 |
| 7 | 0.50 | 10.0 | 4.00 | 38.05 |
| 8 | 1.75 | 10.0 | 0.50 | 48.33 |
| 9 | 3.00 | 10.0 | 2.25 | 61.54 |
| 10 | 1.75 | 5.5 | 2.25 | 31.27 |
| 11 | 1.75 | 5.5 | 2.25 | 34.88 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F Ratio | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A:P | 364.39 | 1 | 364.39 | 55.92 | 0.0846 |
| B:Z | 1361.09 | 1 | 1361.09 | 208.88 | 0.0440 |
| C:CaCl2 | 6.28 | 1 | 6.28 | 0.96 | 0.5059 |
| AA | 223.62 | 1 | 223.62 | 34.32 | 0.1076 |
| AB | 30.99 | 1 | 30.99 | 4.76 | 0.2737 |
| AC | 157.52 | 1 | 157.52 | 24.17 | 0.1277 |
| BB | 47.78 | 1 | 47.78 | 7.33 | 0.2252 |
| BC | 121.65 | 1 | 121.65 | 18.67 | 0.1448 |
| CC | 52.27 | 1 | 52.27 | 8.02 | 0.2161 |
| Total error | 6.52 | 1 | 6.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frosi, I.; Colombo, R.; Milanese, C.; Papetti, A. Optimization of Pectin-Zein Beads via Response Surface Methodology for Enhanced Colon-Targeted Delivery of p-Coumaric Acid from Rice Husk Extract. Foods 2025, 14, 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122034
Frosi I, Colombo R, Milanese C, Papetti A. Optimization of Pectin-Zein Beads via Response Surface Methodology for Enhanced Colon-Targeted Delivery of p-Coumaric Acid from Rice Husk Extract. Foods. 2025; 14(12):2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122034
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrosi, Ilaria, Raffaella Colombo, Chiara Milanese, and Adele Papetti. 2025. "Optimization of Pectin-Zein Beads via Response Surface Methodology for Enhanced Colon-Targeted Delivery of p-Coumaric Acid from Rice Husk Extract" Foods 14, no. 12: 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122034
APA StyleFrosi, I., Colombo, R., Milanese, C., & Papetti, A. (2025). Optimization of Pectin-Zein Beads via Response Surface Methodology for Enhanced Colon-Targeted Delivery of p-Coumaric Acid from Rice Husk Extract. Foods, 14(12), 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122034









