The Role of CO2 Levels in High-Oxygen Modified Atmosphere Packaging on Microbial Communities of Chilled Goat Meat During Storage and Their Relationship with Quality Attributes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Sample Preparation and Packaging Conditions
2.3. Determination of Microbial Community (Microbiome Analysis)
2.4. Determination of Total Viable Count (TVC) and Pathogen
2.5. Determination of Quality Attributes
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
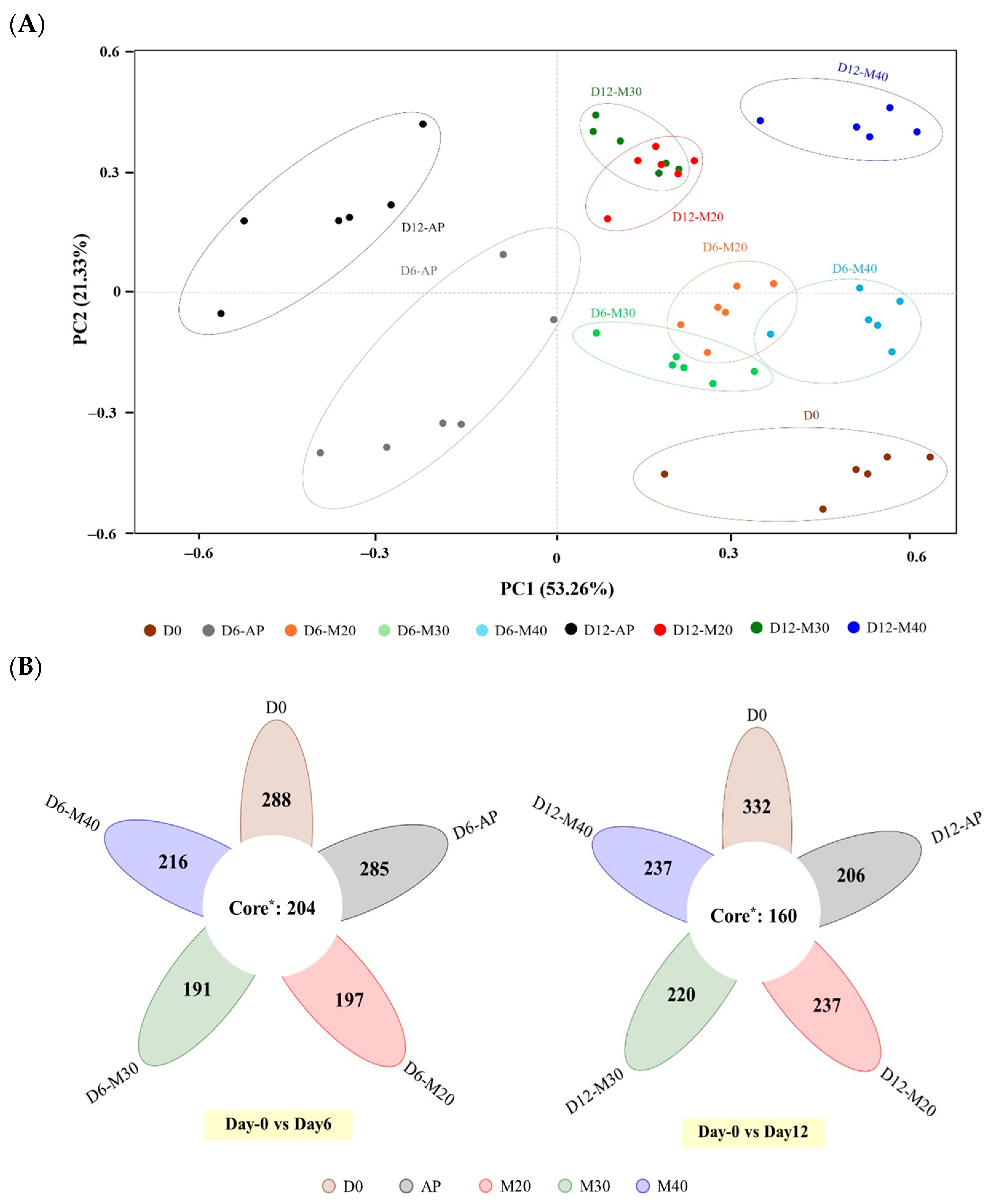
3.1. Dynamic Changes in Microbial Communities During Storage
3.1.1. Microbial Richness and Diversity in Goat Meat Stored Under Map Conditions
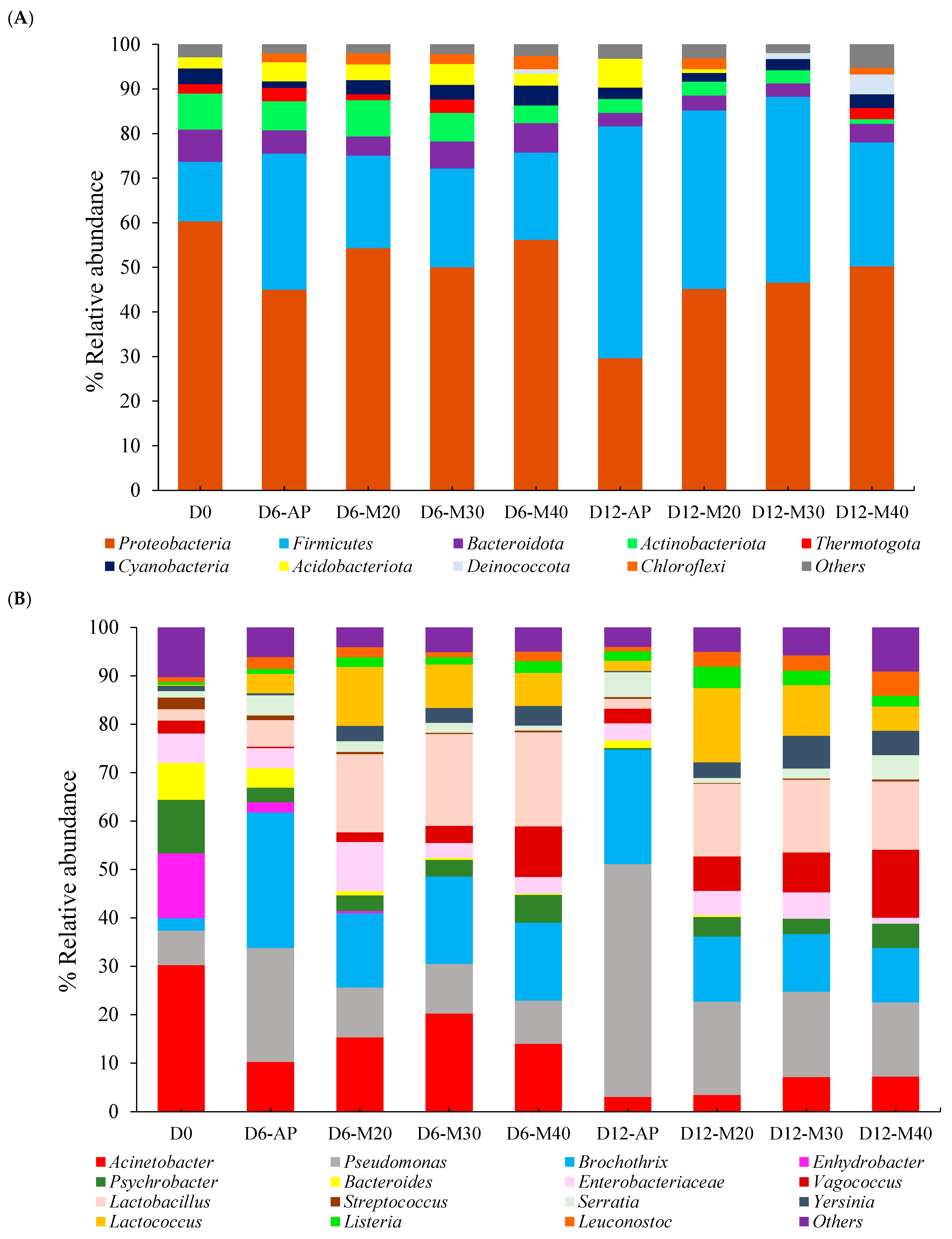
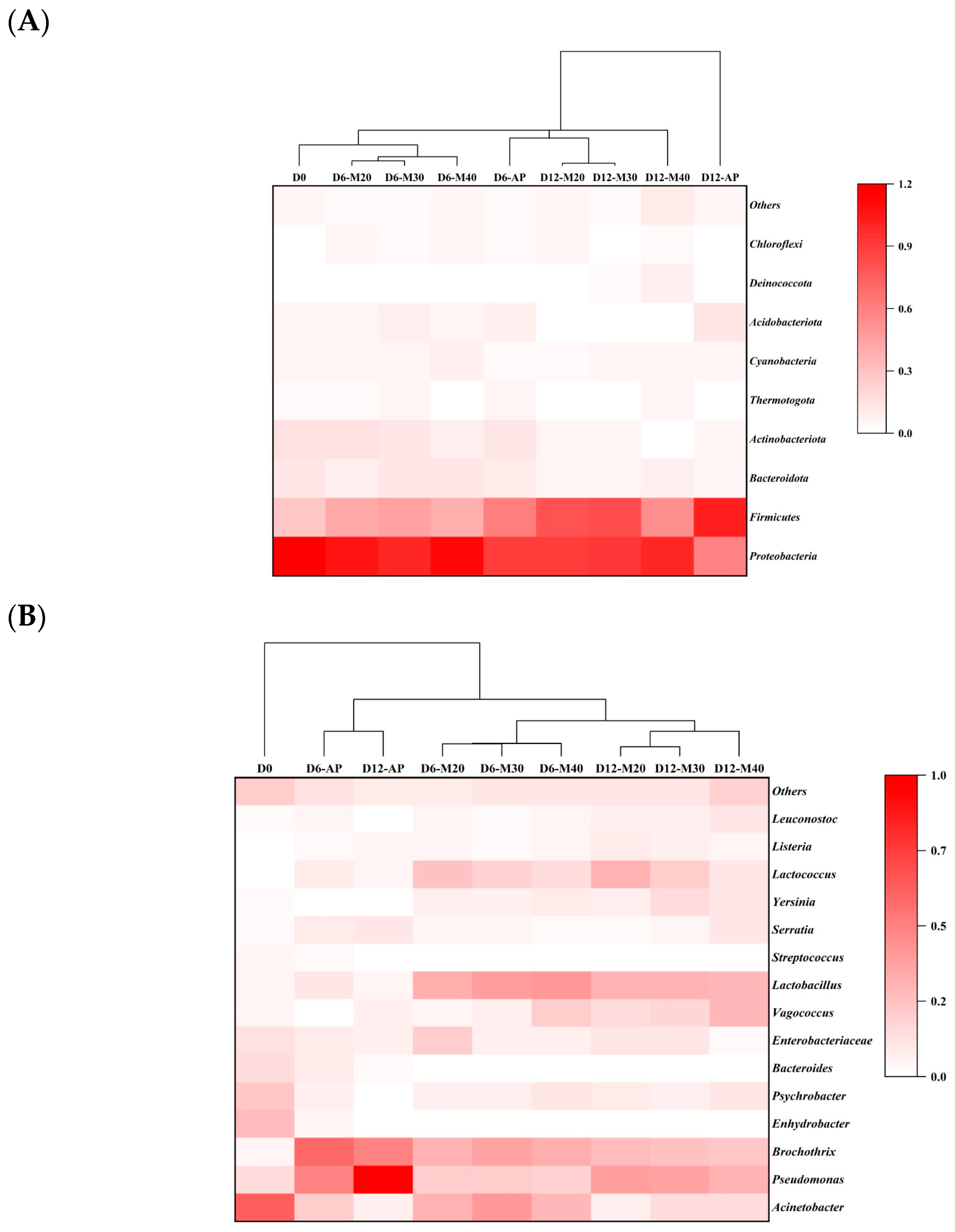
3.1.2. Microbial Community Composition and Abundance
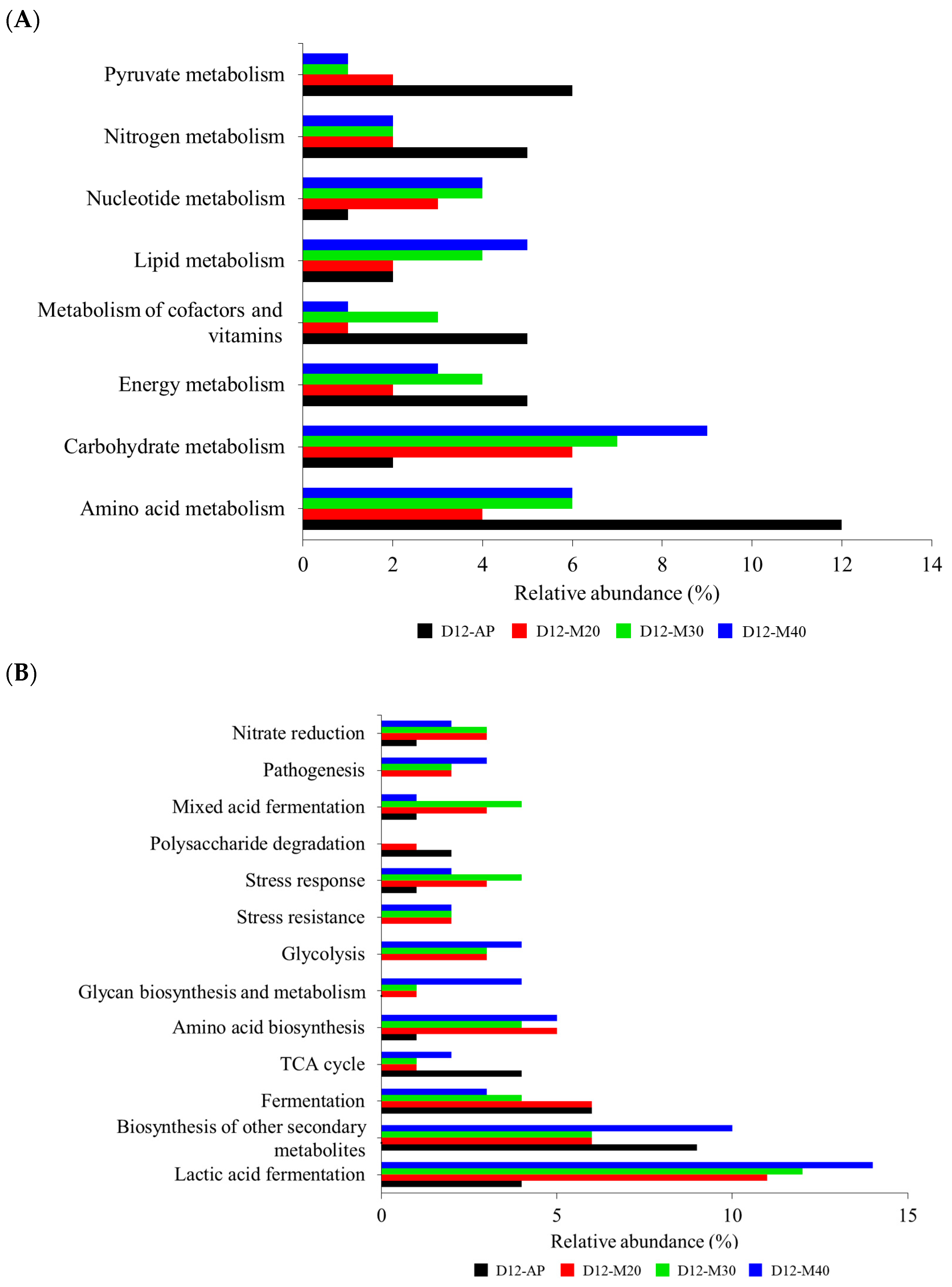
3.1.3. Metagenomic Functional Profiling
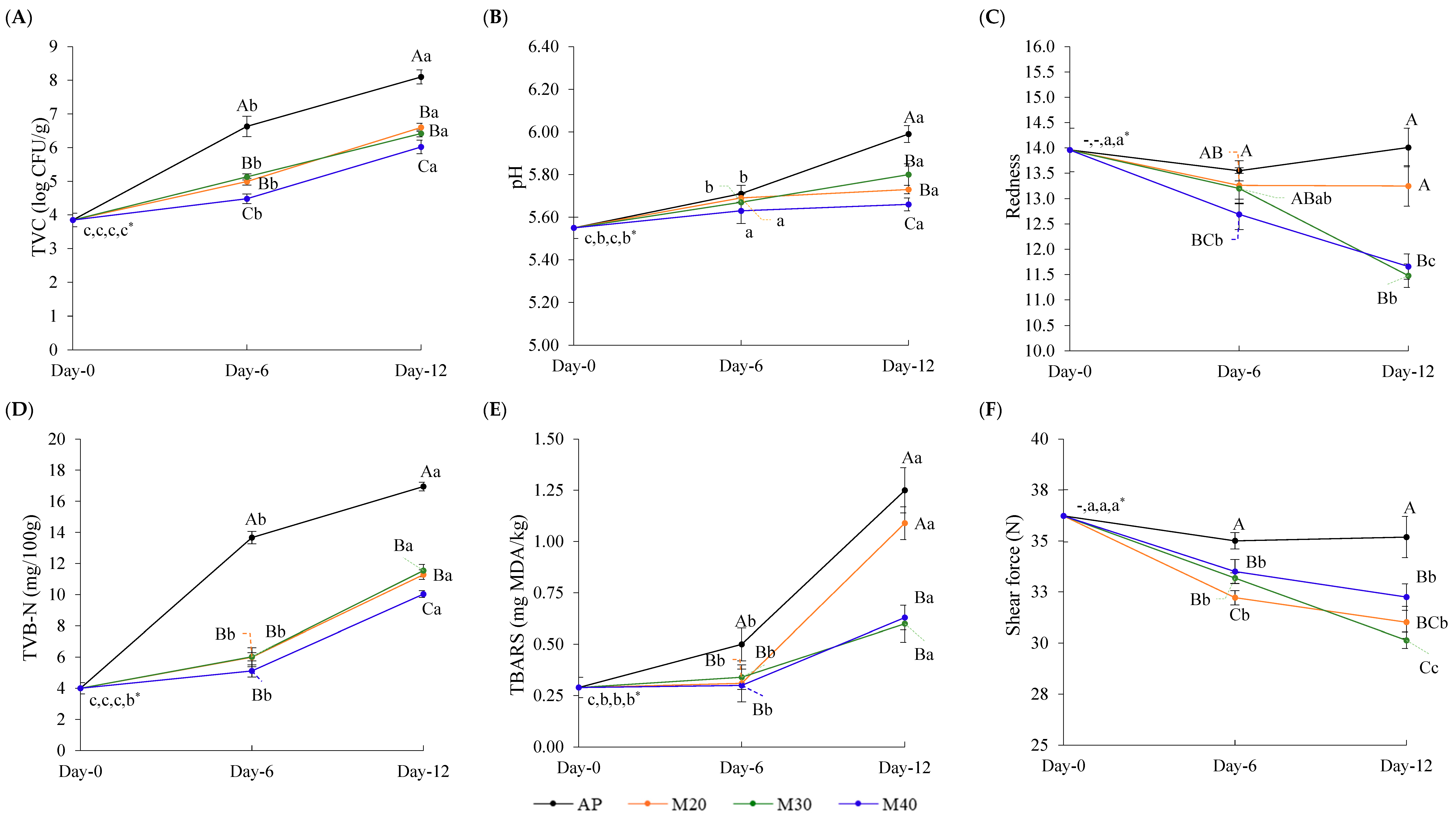
3.2. Changes in TVC and Pathogen of Goat Meat During Storage
3.3. Changes in Quality Attributes of Goat Meat During Storage
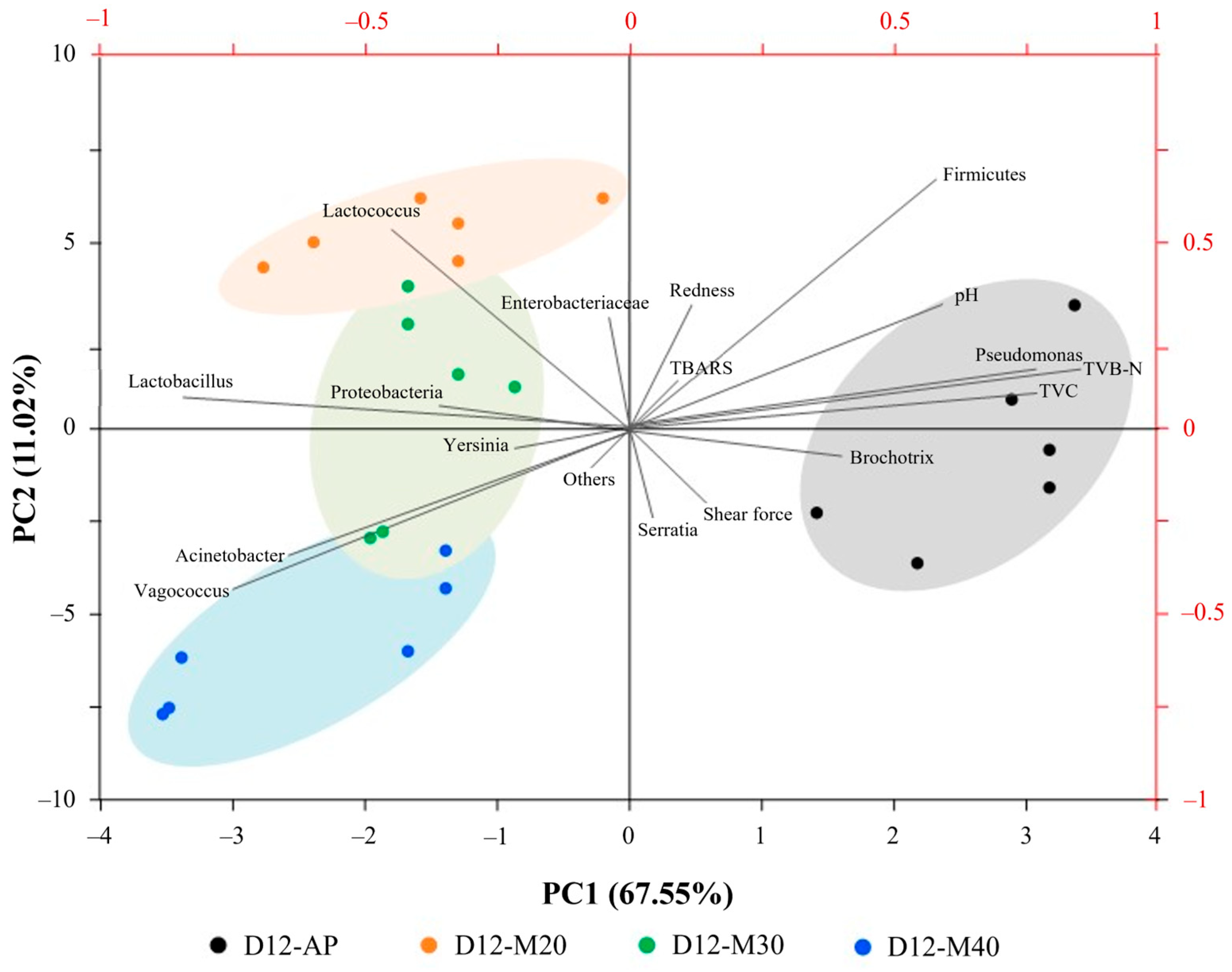
3.4. Correlation Analysis Between Microbial Communities and Quality Attributes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olmo, L.; Van, N.; Nguyen, B.; Bui Thi, N.; Cuc, N.; Don, N.; Hoang, N.; Morales, L.; Walkden-Brown, S. Goat meat supply and demand in Vietnam: Global context and opportunities and risks for smallholder producers. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2024, 64, AN23416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, N. Goat development: An opportunity to strengthen rural economy in Asia and Africa. Asian J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2020, 3, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. FAOSTAT Statistics Database. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Statistics Division. 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Azad, M.; Sayeed, M.; Mukta, S.P.; Parvin, S.; Murshed, H.M.; Rahman, M. Quality of cattle, buffalo, and goat meat keema at different storage temperatures. Meat Res. 2023, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, Y.; Liu, Y. Analysis of quality changes of Hengshan goat hindquarter meat at four storage temperatures. J. Food Comp. Anal. 2023, 117, 105129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indriani, S.; Srisakultiew, N.; Sangsawad, P.; Paengkoum, P.; Pongsetkul, J. Characterization of the non-volatiles and volatiles in correlation with flavor development of cooked goat meat as affected by different cooking methods. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2024, 44, 662–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaspal, M.H.; Ijaz, M.; ul Haq, H.A.; Yar, M.K.; Asghar, B.; Manzoor, A.; Badar, I.H.; Ullah, S.; Islam, M.S.; Hussain, J. Effect of oregano essential oil or lactic acid treatments combined with air and modified atmosphere packaging on the quality and storage properties of chicken breast meat. LWT 2021, 146, 111459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, B.J.; Dobbins, T.W.; Hernandez, M.S.; Barker, S.N.; Loomas, K.R.; Osburn, W.N.; Legako, J.F. Comparison of gas treatments of high oxygen, carbon monoxide, and nitric oxide on ground beef color in modified atmosphere packaging. Foods 2024, 13, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanos, D.; Tørngren, M.; Christensen, M.; Baron, C. Effect of oxygen level on the oxidative stability of two different retail pork products stored using modified atmosphere packaging (MAP). Meat Sci. 2016, 113, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liang, R.; Mao, Y.; Dong, P.; Zhu, L.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X. Potential inhibitory effect of carbon dioxide on the spoilage behaviors of Pseudomonas fragi in high-oxygen packaged beef during refrigerated storage. Food Microbiol. 2023, 112, 104229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrizosa, E.; Benito, M.; Ruiz-Moyano Seco de Herrera, S.; Hernández, A.; Villalobos, C.; Martín, A.; Córdoba, M. Bacterial communities of fresh goat meat packaged in modified atmosphere. Food Microbiol. 2017, 65, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgarth, M.; Lehner, E.M.; Behr, J.; Vogel, R.F. Diversity and anaerobic growth of Pseudomonas spp. isolated from modified atmosphere packaged minced beef. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xiong, Q.; Zhou, H.; Xu, B.; Sun, Y. Analysis of microbial diversity and dynamics during bacon storage inoculated with potential spoilage bacteria by high-throughput sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 713513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, R.; Luo, X. Microbial community dynamics analysis by high-throughput sequencing in chilled beef longissimus steaks packaged under modified atmospheres. Meat Sci. 2018, 141, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequino, G.; Cobo-Diaz, J.F.; Valentino, V.; Tassou, C.; Volpe, S.; Torrieri, E.; Nychas, G.J.; Álvarez Ordóñez, A.; Ercolini, D.; De Filippis, F. Environmental microbiome mapping in poultry processing chain and assessment of microbial dynamics in response to different storage conditions. Food Microbiol. 2025, 128, 104734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, H.; Zhu, W.; Chen, S.; Zou, Y.; Xia, X. Studies on quality deterioration and metabolomic changes in oysters induced by spoilage bacteria during chilled storage. Foods 2025, 14, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indriani, S.; Srisakultiew, N.; Boonchuen, P.; Kingwascharapong, P.; Sai-ut, S.; Benjakul, S.; Pongsetkul, J. Investigating the relationship between microbial community dynamics and flavor profiles in Korat chicken breast fillets under varied packaging conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2025, 435, 111157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Weber, C.F. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langille, M.G.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BAM. Aerobic plate count. In Bacteriological Analytical Manual; Bryce, J., Ed.; U.S. Food and Drug Administration, E-Con Publishing: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2001; pp. 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Thai Agricultural Commodity and Food Standard. Microbiological criteria. In Safety Requirements for Agricultural Commodity and Food; National Bureau of Agricultural Commodity and Food Standards, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives: Bangkok, Thailand, 2005; pp. 1–34. ISBN 974-403-356-8. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, E.J.; Byrne, A. An absorption apparatus for the micro-determination of certain volatile substances I: The micro-determination of ammonia. Biochem. J. 1936, 27, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongsetkul, J.; Benjakul, S.; Takeungwongtrakul, S.; Sai-Ut, S. Impact of stocking density during live transportation on meat quality of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and their changes during storage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e16523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanachant, S.; Benjakul, S.; Ledward, D.A. Composition, color, and texture of Thai indigenous and broiler chicken muscles. Poult. Sci. 2004, 83, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Xu, J.; Sun, F.; Liu, H.; Kong, B. Effects of modified atmosphere packaging with various CO2 concentrations on the bacterial community and shelf-life of smoked chicken legs. Foods 2022, 11, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Niu, Y.; Wang, J. Physicochemical property, bacterial diversity, and volatile profile during ripening of naturally fermented dry mutton sausage produced from Jianzhou big-eared goat. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 961117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Zhao, H.; Yan, L.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Fan, J. Effect of CO2 on the preservation effectiveness of chilled fresh boneless beef knuckle in modified atmosphere packaging and microbial diversity analysis. LWT 2023, 187, 115262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caleb, O.J.; Mahajan, P.V.; Al-Said, F.A.; Opara, U.L. Modified Atmosphere Packaging Technology of Fresh and Fresh-cut Produce and the Microbial Consequences-A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2023, 6, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Munekata, P.E.; Dominguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Saraiva, J.A.; Franco, D. Main groups of microorganisms of relevance for food safety and stability: General aspects and overall description. In Innovative Technologies for Food Preservation; Barba, F.J., Sant’Ana, A.M., Orlien, V., Koubaa, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 53–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, H. Comprehensive evaluation of the bacterial adhesion and spoilage capacity of meat-borne Acinetobacter spp. Food Res. Int. 2025, 203, 115831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, N.; Ravensdale, J.; Coorey, R.; Chandry, S.; Dykes, G. The predominance of psychrotrophic Pseudomonads on aerobically stored chilled red meat. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1541–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanth, S.; Feng, S.; Patra, D.; Pradhan, A.K. Linking microbial contamination to food spoilage and food waste: The role of smart packaging, spoilage risk assessments, and date labeling. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1198124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcenilla, C.; Ducic, M.; López, M.; Prieto, M.; Álvarez-Ordóñez, A. Application of lactic acid bacteria for the biopreservation of meat products: A systematic review. Meat Sci. 2022, 183, 108661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelli, V.; Osimani, A.; Aquilanti, L. Research progress in the use of lactic acid bacteria as natural biopreservatives against Pseudomonas spp. in meat and meat products: A review. Food Res. Int. 2024, 196, 115129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.M.; Merquior, V.L.C.; Shewmaker, P.L. Vagococcus. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaburi, A.; Piombino, P.; Nychas, G.J.; Villani, F.; Ercolini, D. Bacterial populations and the volatilome associated with meat spoilage. Food Microbiol. 2015, 45 Pt A, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, S.M.H.; Kaur, M.; Farahnaky, A.; Torley, P.J.; Osborn, A.M. The pathogenic and spoilage bacteria associated with red meat and application of different approaches of high CO2 packaging to extend product shelf-life. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1733–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, S.; Tian, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Amino acid degradation and related quality changes caused by common spoilage bacteria in chill-stored grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Food Chem. 2023, 399, 133989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruxton, C.H.S.; Gordon, S. Animal board invited review: The contribution of red meat to adult nutrition and health beyond protein. Animal 2024, 18, 101103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.A.; Ayivi, R.D.; Zimmerman, T.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Altemimi, A.B.; Fidan, H.; Esatbeyoglu, T.; Bakhshayesh, R.V. Lactic acid bacteria as antimicrobial agents: Food safety and microbial food spoilage prevention. Foods 2021, 10, 3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CAC/RCP 58-2005; Codex Alimentarius Commission. Code of Hygienic Practice for Fresh Meat. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2020. Available online: http://www.fao.org (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Donenko, F.V.; Gruber, I.M.; Semenova, I.B.; Priyatkin, R.G.; Ziganshin, R.H.; Zaryadyeva, E.A.; Efferth, T. Growth-dependent release of carbohydrate metabolism-related and antioxidant enzymes from Staphylococcus aureus strain 6 as determined by proteomic analysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2011, 2, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhang, W.X.; Chen, X.L. Mechanisms for induction of microbial extracellular proteases in response to exterior proteins. Appl. Envi. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01036-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, M.; Svenarud, P.; Flock, J.I.; van der Linden, J. Carbon dioxide inhibits the growth rate of Staphylococcus aureus at body temperature. Surg. Endosc. 2005, 19, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, D.; Thames, H.T.; Zhang, L.; Dinh, T.T.N.; Schilling, W.; White, S.B.; Ramachandran, R.; Theradiyil, S.A. Roles of aerotolerance, biofilm formation, and viable but non-culturable state in the survival of Campylobacter jejuni in poultry processing environments. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, M.; Bertelsen, G. The use of CO2 in packaging of fresh red meats and its effect on chemical quality changes in the meat: A review. J. Muscle Foods 2020, 13, 143–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, M.C.; Mancini, R.A.; Hachmeister, K.; Kropf, D.; Merriman, M.; Leduca, G.; Milliken, G. Carbon monoxide in modified atmosphere packaging affects color, shelf life, and microorganisms of beef steaks and ground beef. J. Food Sci. 2008, 69, FCT45–FCT52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.; Djenane, D.; Cilla, I.; Beltrán, J.; Roncalés, P. Effect of different concentrations of carbon dioxide and low concentration of carbon monoxide on the shelf-life of fresh pork sausages packaged in modified atmosphere. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anumudu, C.K.; Miri, T.; Onyeaka, H. Multifunctional Applications of Lactic Acid Bacteria: Enhancing Safety, Quality, and Nutritional Value in Foods and Fermented Beverages. Foods 2024, 13, 3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhit, A.E.; Holman, B.W.B.; Giteru, S.G.; Hopkins, D.L. Total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) and its role in meat spoilage: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 280–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, B.; Sun, R.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q.; Ma, Y. Bacterial changes in boiled crayfish between different storage periods and characterizations of the specific spoilage bacteria. Foods 2023, 12, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piranavatharsan, U.; Jinadasa, B.K.K.K.; Jayasinghe, C.V.L. Validation of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) method for measuring secondary lipid oxidation products in fresh Indian mackerel (Rastrelliger kanagurta). Food Humanit. 2023, 1, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Fu, Y.; Tan, J.; Gagaoua, M.; Bak, K.H.; Soladoye, O.P.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, W. Effects of intramuscular fat on the flavor of fresh sheep and goat meat: Recent insights into pre-mortem and post-mortem factors. Food Chem. X 2025, 25, 102159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongsetkul, J.; Kingwascharapong, P.; Senphan, T. Biochemical changes of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) meat during ice storage: A comparison between slurry ice vs flake ice. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2022, 31, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbeck, S.; Kienberger, H.; Kleigrewe, K. Effect of high levels of CO2 and O2 on membrane fatty acid profile and membrane physiology of meat spoilage bacteria. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, C. Effects of oxygen concentration in modified atmosphere packaging on water holding capacity of pork steaks. Meat Sci. 2019, 148, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, L.; Hui Seah, X.; Morton, J.D.; Kaur, R.; Chian, F.M.; Boland, M. Endogenous proteolytic systems and meat tenderness: Influence of post-mortem storage and processing. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2021, 41, 589–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yang, R.; Fan, X.; He, G.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Han, M.; Ullah, N.; et al. Changes in the quality of myofibrillar protein gel damaged by high doses of epigallocatechin-3-gallate as affected by the addition of amylopectin. Foods 2023, 12, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasałka-Czarna, N.; Stachniuk, A.; Fornal, E.; Montowska, M. Proteomic analysis of wild boar meat: Effect of storage method and time on muscle protein stability. Food Chem. 2025, 464 Pt 3, 141774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanborough, T.; Fegan, N.; Powell, S.; Singh, T.; Tamplin, M.; Chandry, P. Genomic and metabolic characterization of spoilage-associated Pseudomonas species. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 268, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Ren, F.; Xie, X. The implication of viability and pathogenicity by truncated lipopolysaccharide in Yersinia enterocolitica. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 7165–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Villamizar, S.; Chica Cárdenas, L.A.; Morales Mancera, L.T.; Vives Florez, M.J. naerobiosis, a neglected factor in phage-bacteria interactions. App. Envi. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0149123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Read no. | OTUs * | Chao1 ** | ACE ** | Simpson ** | Shannon ** | Coverage *** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | 57,340 | 492 | 922 | 980 | 0.96 | 6.02 | 0.9997 | |
| Day 6 | AP | 57,002 | 489 | 801 | 1002 | 0.96 | 5.28 | 0.9997 |
| M20 | 55,413 | 401 | 800 | 903 | 0.93 | 5.02 | 0.9998 | |
| M30 | 54,678 | 395 | 789 | 888 | 0.95 | 5.21 | 0.9997 | |
| M40 | 55,293 | 420 | 822 | 965 | 0.95 | 5.39 | 0.9998 | |
| Day 12 | AP | 55,465 | 366 | 799 | 993 | 0.95 | 5.20 | 0.9998 |
| M20 | 53,890 | 397 | 503 | 785 | 0.93 | 4.99 | 0.9998 | |
| M30 | 49,299 | 380 | 565 | 703 | 0.92 | 4.89 | 0.9999 | |
| M40 | 50,400 | 397 | 745 | 902 | 0.95 | 5.55 | 0.9998 | |
| Sample | E. coli | S. aureus | Salmonella spp. | C. perfringens | C. jejuni | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | <10 CFU/g | ND * | ND | <10 CFU/g | ND | |
| Day 6 | AP | <10 CFU/g | 30 CFU/g | ND | <10 CFU/g | ND |
| M20 | <10 CFU/g | ND | ND | <10 CFU/g | ND | |
| M30 | <10 CFU/g | ND | ND | <10 CFU/g | ND | |
| M40 | <10 CFU/g | ND | ND | <10 CFU/g | <10 CFU/g | |
| Day 12 | AP | 53 CFU/g | 69 CFU/g | ND | <10 CFU/g | ND |
| M20 | <10 CFU/g | ND | ND | <10 CFU/g | ND | |
| M30 | <10 CFU/g | ND | ND | <10 CFU/g | <10 CFU/g | |
| M40 | <10 CFU/g | ND | ND | <10 CFU/g | 22 CFU/g | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sai-Ut, S.; Indriani, S.; Srisakultiew, N.; Kingwascharapong, P.; Suriyarak, S.; Issara, U.; Phongthai, S.; Rawdkuen, S.; Pongsetkul, J. The Role of CO2 Levels in High-Oxygen Modified Atmosphere Packaging on Microbial Communities of Chilled Goat Meat During Storage and Their Relationship with Quality Attributes. Foods 2025, 14, 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111837
Sai-Ut S, Indriani S, Srisakultiew N, Kingwascharapong P, Suriyarak S, Issara U, Phongthai S, Rawdkuen S, Pongsetkul J. The Role of CO2 Levels in High-Oxygen Modified Atmosphere Packaging on Microbial Communities of Chilled Goat Meat During Storage and Their Relationship with Quality Attributes. Foods. 2025; 14(11):1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111837
Chicago/Turabian StyleSai-Ut, Samart, Sylvia Indriani, Nattanan Srisakultiew, Passakorn Kingwascharapong, Sarisa Suriyarak, Utthapon Issara, Suphat Phongthai, Saroat Rawdkuen, and Jaksuma Pongsetkul. 2025. "The Role of CO2 Levels in High-Oxygen Modified Atmosphere Packaging on Microbial Communities of Chilled Goat Meat During Storage and Their Relationship with Quality Attributes" Foods 14, no. 11: 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111837
APA StyleSai-Ut, S., Indriani, S., Srisakultiew, N., Kingwascharapong, P., Suriyarak, S., Issara, U., Phongthai, S., Rawdkuen, S., & Pongsetkul, J. (2025). The Role of CO2 Levels in High-Oxygen Modified Atmosphere Packaging on Microbial Communities of Chilled Goat Meat During Storage and Their Relationship with Quality Attributes. Foods, 14(11), 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111837







