Abstract
We employ an extreme ultraviolet (XUV) pulse to impulsively excite dipole polarization in atoms or molecules, which corresponds to coherently prepared superposition of excited states. A delayed near infrared (NIR) pulse then perturbs the fast evolving polarization, and the resultant absorbance change is monitored in dilute helium, dense helium, and sulfur hexafluoride (SF) molecules. We observe and quantify the time-dependence of various transient phenomena in helium atoms, including laser-induced phase (LIP), time-varying (AC) Stark shift, quantum path interference, and laser-induced continuum structure. In the case of dense helium targets, we discuss nonlinear macroscopic propagation effects pertaining to LIP and resonant pulse propagation, which account for the appearance of new spectral features in transient lineshapes. We then use tunable NIR photons to demonstrate the wavelength dependence of the transient laser induced effects. In the case of molecular polarization experiment in SF, we show suppression of XUV photoabsorption corresponding to inter-valence transitions in the presence of a strong NIR field. In each case, the temporal evolution of transient absorption spectra allows us to observe and understand the transient laser induced modifications of the electronic structure of atoms and molecules.
1. Introduction
The quantum mechanical motion of electrons and their interaction with light is at the heart of most photophysical and photochemical processes. Examples include light harvesting in photosynthesis, photocatalytic charge transfer, and the initiation of vision, etc. [1,2,3]. In real life, the evolution of electronic processes involves complicated couplings between electrons or holes, nuclei, external electromagnetic fields, or a mixture of above. As a result, tracking the electronic evolution of non-equilibrium systems is a highly non-trivial task. Measuring charge dynamics in complex systems is challenging even with advanced techniques such as quantum process tomography [4]. As the natural electronic timescale lies in the range of a few femtoseconds (10 s) to attoseconds (10 s), ultrafast light sources are needed to probe these process in real time. In addition, the use of high energy (short-wavelength) photons from extreme ultraviolet (XUV) to the X-rays (∼100 nm to few nm) range can provide additional benefits in terms of spatially localized excitation and imaging of the dynamical process [5,6].
The above mentioned requirements to investigate the electron dynamics have been met by advances in table-top laser high-harmonic generation (HHG), which have led to femtosecond to attosecond laser-like pulses in the XUV range [7,8]. The ultrashort and broadband XUV pulses enable coherent preparation of the excited quantum states of an atomic or a molecular system. The resulting wavepacket dynamics can be probed, perturbed, or controlled using a second ultrafast pulse. One of the common approaches is to use a time-delayed near-infrared (NIR) or visible laser pulse to conduct temporal and energetically resolved spectroscopy of excited electronic states by measuring photofragments, photoabsorption, or photoemission. Among these approaches, the attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy (ATAS) is an emergent all-optical technique that can be applied to study many interesting coherent laser induced phenomena such as Autler–Townes splitting, electromagnetically induced transparency, light induced virtual states, quantum beats, spectral line shape manipulations, and resonant pulse propagation, etc. [9,10,11,12,13,14].
This paper is intended to summarize some of our recent experimental investigations that demonstrate how a general ATAS scheme can be utilized to study laser-induced modification of electron dynamics in single-atom and the collective regime, as well as in molecules. This paper is organized as follows: after the introduction in Section 1, we discuss our experimental methods in Section 2 and provide a comparison of two XUV generation schemes used in this research. In Section 3, we focus on the helium Rydberg series as an example of impulsive XUV initiated atomic polarization, and we explore the time-dependence of various NIR photon induced effects such as quantum-path interference and laser-induced continuum structure, using XUV photons that are commensurate in energy to an integer multiple of NIR photons. In Section 4, we studied XUV transient absorption in optically thick helium targets in the case of both short and long wavelength NIR perturbation. The interplay between NIR imposed quantum phase as well as macroscopic resonant XUV pulse propagation effect are systematically investigated. In Section 5, we discuss a demonstrative example of how ATAS studies can be extended to polyatomic molecules by probing the XUV initiated molecular polarization in sulfur hexafluoride (SF). We end the paper with concluding remarks in Section 6.
2. Experimental Methods
In our experiment, as shown in Figure 1, a single-stage multi-pass Ti:Sapphire laser amplifier is used to produce ∼35 fs NIR pulses at 1 kHz repetition rate with pulse energy 2 mJ, with tunable central wavelength 778–788 nm and 26 nm full width at half maximum (FWHM) bandwidth. The NIR pulse after the amplifier is split into two paths by a low dispersion ultrafast beamsplitter. In one path, the NIR pulse is used as a phase-locked and delayed strong-field perturbing pulse with controllable intensity. The NIR pulse in this arm can generate a peak intensity of 1–2 TW/cm at the target sample. In addition, there is a shutter equipped in this NIR beamline. In additional to fundamental NIR wavelength, an optional optical parametric amplifier (OPA) is implemented to convert the original NIR to longer wavelengths in the range of 1200–1800 nm at a peak intensity of ∼0.1 TW/cm.
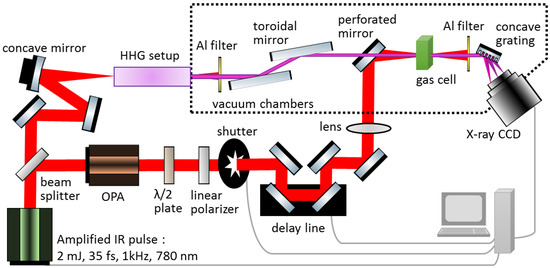
Figure 1.
The schematic of the experimental apparatus for extreme ultraviolet (XUV) attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy (ATAS). An amplified near infrared (NIR) femtosecond pulse is split into two, where one of the pulses is used to generate XUV via the high-harmonic generation (HHG) process. The HHG setup is illustrated in detail in Figure 2. The other NIR pulse is delayed and used as a pump pulse to induce strong-field modifications. A home-made spectrometer is used to resolve the XUV spectrum transmitted through a gas cell for ATAS experiments.
The NIR pulse in the second arm is focused by a 500 mm focal length concave mirror into a high harmonic generation (HHG) setup. Figure 2a,b shows two types of geometry that we used to produce XUV attosecond pulse trains (APTs) by the HHG process; namely, a gas cell [15,16] and a gas-filled capillary waveguide [17,18]. The geometry of the gas cell can be described as a semi-infinite gas cell (SIGC), where a thin aluminum plate can be used as a gas–vacuum barrier with a hole drilled in situ by NIR pulses. On the other hand, the waveguide has 150∼250 m inner core diameter and 30 mm length, with two holes on the top of the waveguide as the inlet of the gas. In our design, we can easily swap between the waveguide and the SIGC with the least amount of disruption to the vacuum systems and optical alignment. A 200 nm thick aluminum thin film filter is used to block residual NIR pulse after a waveguide or a SIGC.
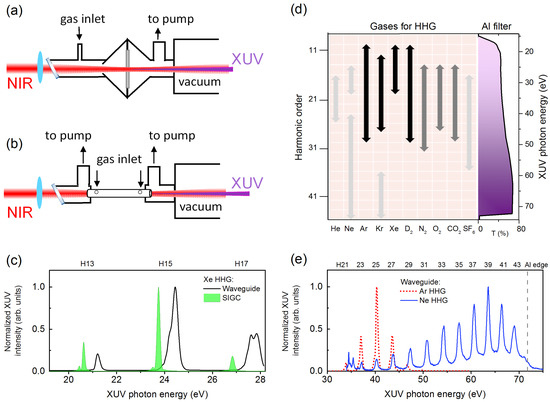
Figure 2.
The schematic setup for HHG in (a) a semi-infinite gas cell (SIGC), and in (b) a gas-filled capillary waveguide; (c) a typical HHG spectra generated from Xe gas in a SIGC (green) and a waveguide (black), respectively; (d) experimental survey of HHG spectral range from various gases based on our laser parameters and HHG setup. The aluminum filter transmission (T%) for XUV is shown on the side for reference. The length of the arrows indicates the spectral range in which we can generate reasonably strong XUV (few nJ per NIR pulse). Black, dark gray, and light gray arrows indicate relative intensity of the XUV emission; (e) representative HHG spectra for higher XUV photon energies from Ar (red dotted) and Ne (blue solid) gases, respectively.
Depending on different gases introduced in the HHG chamber, we can produce XUV over a wide energy range with tunable harmonics in each case. A brief experimental survey on HHG spectra generated from many common gases is shown in Figure 2d. The length of the arrows in this figure represents the spectral range in which we can produce reasonably strong XUV, which is roughly at the level of few nJ per NIR pulse. The color (black, dark gray, light gray) of the arrows represents relative spectral intensity of that XUV, from the most strong (black), moderately strong (dark gray), to weak (light gray). We also show aluminum filter transmission spectrum (T%) on the right-hand side of the Figure 2d, where we calculated the transmission assuming 2 nm AlO oxidization layer on the top of 200 nm thick aluminum filter. The transmission data are calculated using Ref. [19]. Some representative HHG spectra covering the XUV energy range from 20 eV to 70 eV (∼62 nm to 18 nm) are shown in Figure 2c,e.
The XUV emission is in the form of odd harmonics due to the centro-symmetric nature of atomic gases, where the nth harmonic will have photon energy , where is the fundamental driving NIR frequency corresponding to the central wavelength in the range 778–788 nm. The use of molecular gases, however, can include weak ‘even’ harmonic emission as well. It should be mentioned that the reported XUV spectral ranges and the relative intensities are based on our femtosecond NIR pulse parameters, as well as our focusing and interaction geometry in the form of a waveguide or an SIGC. In general, the waveguide and the SIGC produce a similar HHG spectral profile. However, individual harmonics from a waveguide will have slightly higher photon energy, i.e., , where the blue shift is typically <0.5 eV, as shown in Figure 2c. The origin of blue shift is the stronger plasma generation in the gas when using a waveguide, which changes the phase match conditions for HHG. In addition, from Figure 2c, we can observe that each individual harmonic from the waveguide has a broader bandwidth compared to that from a SIGC. As for the spectral intensity, the HHG from a SIGC usually has stronger peak intensity comparing to that from a waveguide, and this is due to the coupling losses in a waveguide based HHG. The mechanisms behind the spectral range tuning of XUV emission from various gases in a waveguide or an SIGC can be attributed to the detailed phase matching considerations, which is beyond the scope of this paper. Detailed discussion of HHG phase match conditions can be found in Refs. [17,20,21].
The ATAS studies discussed below predominantly rely on HHG generated in xenon gas. In the case of xenon HHG, we produce XUV APTs with ∼440 attosecond bursts and ∼4 fs envelope. Our APTs are dominated by 13th harmonics (H13), 15th harmonics (H15), and 17th harmonics (H17). Before going to the target sample, the XUV and NIR pulses are combined using a perforated annular mirror at 45 degrees. The target gas under investigation is introduced into a 1 cm long cell with a backing pressure of 200–1600 Pa, which is covered by aluminum foils as gas barriers with entrance and exit holes drilled by the NIR pulse. The XUV and NIR pulses propagate collinear with the same linear polarization. The analysis is conducted using a home-made spectrometer, which consists of a concave reflective grating (1200 lines/mm, 1 m radius of curvature) and a back-illuminated cooled X-ray charge-coupled device camera. A 200 nm thick aluminum filter is used in front of the camera to block the NIR. The shutter on the NIR beamline is synchronized and triggered by the camera to get background (NIR free) XUV spectra at each camera exposure. The spectrometer detects transmitted XUV spectra with a resolution of ∼10 meV at 24 eV. As our spectrometer cannot resolve the very narrow static XUV absorption lines at field-free resonances, the transmitted XUV only spectrum in the absence of NIR field is essentially the same as the input XUV spectrum . We therefore can use it as a reference for evaluating measured optical density (OD) change due to the presence of strong NIR field, namely, , where is the XUV and NIR time delay, and we define negative delay as the case when XUV arrives at the target sample first. The experimental OD is obtained by calculating near-simultaneously measured XUV spectrum with the NIR, and without the NIR at 0.1 s exposure time per camera exposure. We then average tens to hundreds of exposures at each delay step.
3. Laser Modification of Dipole Polarization in Helium: Temporal and Spectral Properties
As a first example, we discuss the basic phenomena underlying XUV transient photoabsorption in helium atoms exposed to strong NIR fields—a topic that forms the basis of understanding most ATAS measurements. The experimental spectrogram is shown in Figure 3a, where we clearly observe time-dependent transient absorption corresponding to helium levels excited from the ground state by XUV pulse, ranging from 1s2p, 1s3p, 1s4p, 1s5p, to the continuum. The field-free locations of helium energy levels below single electron ionization potential (Ip) are labeled on the right side of the figure for reference. In Figure 3b, we show the transient absorption lineshapes corresponding to atomic resonances, which are obtained by taking the lineouts of the spectrogram in Figure 3a at a delay of –5 optical cycles . It should be noted that we averaged over two cycles to generate these lineouts. In addition, due to the discreteness of our XUV spectrum, there are very few XUV photons at 3p energy and we observe very weak signal (not shown) from that state. Transient absorption lineshape details are determined by the NIR laser parameters as we discuss below.
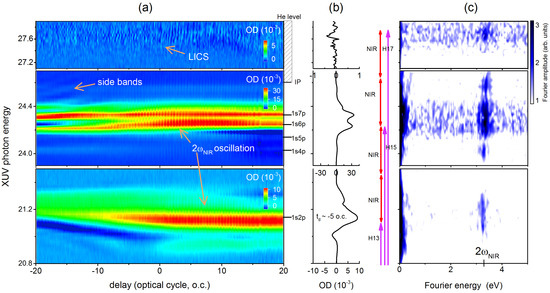
Figure 3.
(a) experimental transient photoabsorption spectrogram obtained in the helium gas, where relevant energy levels are labeled on the side of the figure. The NIR photon energy used here is 1.59 eV (780 nm); (b) lineouts showing transient absorption lineshapes near –5 optical cycles (averaged over two cycles). The purple and red arrows indicate XUV and NIR coupling pathways. (c) Fourier analysis of the spectrogram from (a). The Fourier amplitude is in arbitrary units and on a logarithmic scale.
In the single-atom response assumption (dilute gas limit), we can discuss the XUV initiated dipole polarization in helium Rydberg states as the collection of time-dependent electric dipoles, which can be analyzed using a semi-classical treatment. The XUV initiated ringing and exponentially decaying dipoles, , will show conventional Lorentzian absorption line shapes in the frequency domain in the absence of the NIR field. The static photoabsorption cross section of this dipole can be represented as [22], where and are the Fourier transform of the time-dependent dipole and the total applied electric field, respectively. When an NIR pulse is applied to these dipoles, it effectively kicks (phase shifts) oscillating dipoles. If NIR arrives at large time delays, the NIR perturbed free-induction decay (FID) [23] manifests as broadened Lorentzian line shape with sidebands, as seen from the middle panel in Figure 3a. Then, the XUV and the NIR pulses overlapped, strong modifications, resulting in a Fano-like line shape, can be observed. The line shape modification can be explained qualitatively in terms of laser-induced phase (LIP) shift on dipoles, and this phase shift can be estimated from the pondermotive or Stark shift [13,24], i.e., , where is pondermotive energy. The experimentally observed absorbance change due to the NIR can then be obtained as .
In our experiment, we used SIGC to generate XUV, which is focused on the target helium gas along with NIR peak intensity 1 () TW/cm, and the helium backing pressure in the sample cell is ∼267 Pa. From the spectrogram in helium (Figure 3a), we can observe the development of structures in 1s2p state due to AC Stark shift [9], which results from NIR induced one photon coupling from a bright state such as a 1s2p state to a nearby dark 1sns or 1snd state. The delay axis of spectrogram is calibrated in optical cycles, such that one cycle corresponds to ∼2.6 fs of 780 nm (∼1.59 eV) NIR laser used in this experiment, and we can clearly observe sub-cycle oscillations in the transient absorption spectrogram. These subcycle oscillations, also called 2 oscillation, are a common feature in attosecond transient absorption experiments [9,12], especially when commensurate energy XUV and NIR photons are used. These oscillations can be observed in our data by performing Fourier transform along time delay axis from the spectrogram to get Figure 3c. For 1s2p energy and some high-lying 1snp states, the Fourier analysis shows strong signals at ∼3.2 eV, which is the 2 oscillation. This oscillation can be understood as two-photon NIR coupling between the polarizations created by H13 and H15, leading to beating at a frequency corresponding to the energy difference between 1snp and 1s2p states. As indicated in Figure 3b, there are two pathways to 1s2p state (by H13 or H15-2), and similarly to 1snp polarization (by H15 or H13 + 2).
Note that, from the spectrogram in Figure 3, we can also observe very weak signal at around 27.7 eV. In this energy range, there are no known energy levels, or autoionizing states, embedded in helium continuum, so it should show featureless continuum absorption. On the contrary, we observe features in this range that can be attributed to the so-called laser-induced continuum structure (LICS). This effect was first discussed in the 1970s [25,26], and it has been reviewed in Ref. [27]. The subcycle oscillation in LICS is due to two pathways of photoexcitation, where one is excitation directly from ground state by H17 and the other is the promotion of an electron from 1snp state polarization with two NIR photons. As a result, we can again observe quantum beat signal in Fourier analysis similar to 2 oscillation in the case of 1s2p and 1snp polarizations.
4. Laser Modification of Dipole Polarization in Helium: Pressure and Wavelength Dependence
Most experiments in recent years assume single-atom response in their transient absorption experiments. However, the experimental densities in these experiments often approach a limit where the simple Beer-Lambert law is no longer valid and macroscopic effects should be taken into account. We have explored this regime in our recent studies [14,28], where we show that the collective macroscopic XUV pulse propagation effect, also called the resonant pulse propagation (RPP) effect, should be considered. We also laid out the criteria for consideration of gas target as an optically thick medium. Here, we provide a simple overview of the complex interplay between LIP effect and RPP effect by summarizing it in a schematic of Figure 4. The first column indicates experimental conditions, and the second column is the physical picture of the interaction, followed by its temporal description on the third column, and its corresponding spectral profile in the last column. In single-atom response picture—as explained in Section 3 and shown in Figure 4a—when XUV pulse alone (E) excites the dipole polarization (P) of a resonant medium, the Fourier transform of this oscillating and decaying polarization shows a Lorentzian spectrum in the frequency domain. The introduction of strong, time delayed NIR pulse (E) (Figure 4b) imparts an additional phase on the polarization, and this LIP effect results in a Fano spectral line shape. When an XUV propagation alone in a dense medium is considered (Figure 4c), the polarization created by the incident XUV is strong enough to radiate XUV light, and this emission could further excite secondary polarization. In this self-consistent dipole-field interaction picture, the final polarization will be temporally reshaped and it can be described by a Bessel function of the first kind (J) [29] as , where Γ is the decay lifetime, P is the gas pressure, and z is the propagation distance. Therefore, the pressure-length product determines the reshaping of XUV pulse in a dense resonant medium. The temporal reshaping manifests as broadened spectral lineshape. An important feature of the reshaped XUV pulse profile is that the first sub-pulse will be out-of-phase compared to the original pulse, the second sub-pulse will be out of phase compared to the first sub-pulse, and so on. These temporal phase variations can be brought to light using the presence of delayed NIR pulse, where the NIR pulse samples the π phase jumps between sub-pulses, and the LIP effect serves to broaden the fine spectral structure associated with these phase jumps. The non-linear interplay between RPP and LIP can thus be clearly seen through the appearance of new spectral features in the experimental transient absorption lineshape. It should be noted that, for this to happen, the duration of the first XUV sub-pulse has to be comparable or smaller than the NIR pulse duration, which means that pressure-length product has to be high enough to significantly reshape the XUV pulse through RPP effect.
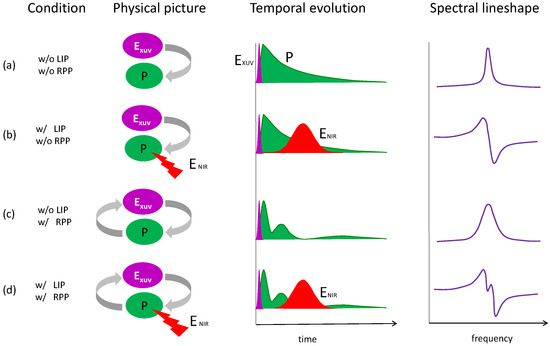
Figure 4.
A schematic that summarizes various phenomena that determine the temporal and spectral properties of XUV excited dipole polarization in a simplified two-level resonant system. (a) The impulsive XUV field (E) prepares dipole polarization (P), which decays exponentially, leading to Lorentzian spectral lineshape. (b) When laser-induced phase (LIP) shift is applied by a time-delayed NIR field (E), a Fano-like dispersive lineshape is observed. (c) The polarization is temporal reshaped by resonant pulse propagation (RPP) effect in a dense medium. (d) The interplay between RPP and LIP effects leads to the appearance of new spectral features in the lineshape.
In order to experimentally demonstrate the interplay between RPP and LIP effects, in Figure 5a, we show 1s2p state evolution, at 400 Pa and 1200 Pa backing pressure for 786 nm laser wavelength, at –30 fs time delay, and ∼2 TW/cm laser intensity. As gas pressure is increased, we clearly observe the appearances of new spectral features (indicated by vertical dashed line) near the line center of an otherwise simple Fano like profile. We also used an OPA to convert original NIR pulse to 1428 nm NIR pulse with similar pulse duration but weaker peak intensity at ∼0.2 TW/cm. The bottom curve in Figure 5a shows the 1s2p line profile evolution under 1428 nm NIR imposed LIP effect at the same backing pressure (1200 Pa) and time delay (–30 fs). Although this intensity is an order of magnitude weaker, the LIP effect depends on the pondermotive energy shift that is proportional to , where I is the peak intensity of the laser and λ is the laser wavelength, so the LIP effect in the case of longer wavelength should only be three times smaller. We observe that the dispersive effect of 1428 nm light is actually similar compared to the 786 nm case, as seen from the overall broadening of the spectral lineshapes in the two cases. The quantitative comparison between these two cases requires calculation of the LIP effect by including one-photon couplings to nearby states. In our case, NIR couplings pathways to nearby dark 1sns states from the bright 1s2p state are shown in Figure 5b. Depending on the detuning, the dipole strength of these transitions and the NIR intensity dependent Rabi Frequency, we will observe different AC Stark shift and line profiles in two cases. The calculations for 1s2p states reported in [23] do show that it is possible to have wider lineshape for higher detuning cases. The overall line shape in 1428 nm case also shows an especially strong RPP peak when compared to the 786 nm NIR case. Detailed understanding of exact spectral features is not trivial, and it requires macroscopic calculations where a time-dependent Schrödinger equation calculation is coupled to the Maxwell wave equation based propagation.
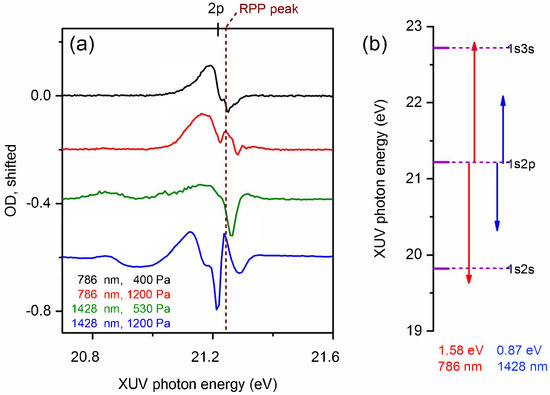
Figure 5.
(a) experimental spectra of helium 1s2p state evolution which show both LIP and RPP effects at 786 nm NIR wavelength at gas pressure of 400 Pa (black) and 1200 Pa (red), and 1428 nm NIR wavelength at gas pressure of 530 Pa (green) and 1200 Pa (blue). Field free states are labeled at the top, and the RPP induced feature is shown by the dashed line. (b) NIR one-photon coupling pathways leading to different amounts of LIP effect for the two NIR wavelengths.
If we continue looking at the long wavelength (1428 nm) case and further increasing helium gas backing pressure to 1600 Pa, we can enhance the main RPP peak so that it becomes comparable or greater in strength than the original Fano profile peaks as seen in Figure 6a. Importantly, we can observe that, as the time delay is varied, the RPP strength changes monotonically; however, the dispersive Fano profile around the RPP peak changes its nature quite dramatically and going to positive to negative time delay results in complete reversal of the signal of OD. As for 1snp states in helium, including n = 4, 5, 6, 7,… to ionization potential (IP), the transition strength is much smaller, and hence the RPP effect is not very significant; therefore, most states show Fano-like profiles even with dense gas as shown in Figure 6b. Note that vertical gray dash lines are field-free energy level, and the ’real’ 1s2p and 1snp state under strong field dressing will be pondermotively shifted toward higher energy as shown in Ref. [30].
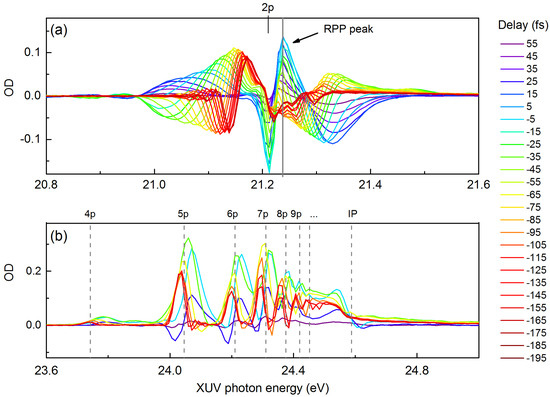
Figure 6.
Overlaid transient absorption spectra at dense helium 1s2p state (a) and 1snp states (b), dressed by 1428 nm NIR pulse at ∼0.2 TW/cm and 1600 Pa backing pressure. Vertical gray dashed lines are field-free energy level.
5. Probing Dipole Polarization in a Polyatomic SF Molecule
Numerous ATAS based experiments, focusing on atomic systems, have been conducted over the past few years. However, there have been only a few experimental attempts to investigate laser modification of molecular polarization, except for some initial studies in diatomic systems such as H, N, and O [31,32,33], and to the best of our knowledge, no work has been conducted in polyatomic molecules. Here, we demonstrate an application of ATAS to investigate the polyatomic SF molecule that exhibits octahedral geometry. The SF has been the focus of recent investigations that probed the ultrafast vibrational modes and shape resonances through study of its photoelectron spectrum and HHG spectrum [34,35], as well as the light-induced chemical reactions at sulfur L-edges by soft X-ray transient absorption [36].
Figure 7a shows a schematic of the effective molecular potential of SF adapted from Ref. [37], where the radial distance is shown for illustrative purposes only. The excited state potential is partitioned into an inner well and an outer well. Inside the inner well, there are many virtual valence orbitals in which shape resonances have been identified. The assignments of these resonances embedded in the ionization continuum has been under debate because of the ambiguity in the ordering of valence orbitals [38,39]. Here, we adopt accepted orbital configuration 4tt3e(5t + 1t)6t. It is known that the photoabsorption cross section of SF is unusual, in that the most prominent features are due to the inter-valence transitions, whereas Rydberg series are strongly suppressed in a few eV ranges [39,40].
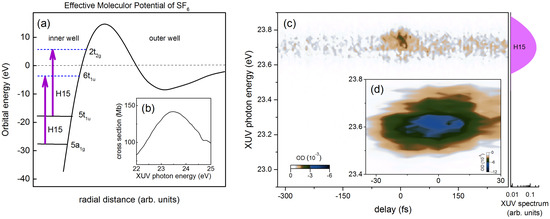
Figure 7.
(a) a schematic effective molecular potential of SF adapted from [37]. Dashed (solid) horizontal lines indicate vacant (occupied) virtual orbitals. Two purple arrows indicate two possible inter-valence photoexcitation pathways by H15. (b) Total photoabsorption cross section adapted from Ref. [41]; (c) our experimental transient absorption spectrogram in SF. The XUV spectrum of H15 is also shown on the side for reference; and (d) the transient absorption spectrogram of SF near delay zero taken with smaller delay step size.
The absolute photoabsorption cross section in XUV range has been measured by Holland et al. [41] using a synchrotron source and is shown in Figure 7b. The H15 excites one of the most intense features in the inner well peaked around 23.5 eV, which could be attributed to two shape resonance enhanced inter-valence transitions [42,43]. The first one is 5a → 6t, which is correlated with the 3s and 3p orbitals, and the second one is 5t → 2t, which arises from the fluorine 2pπ orbitals and the sulfur 3d orbitals, respectively [37]. These two possible photoexcitation pathways are indicated by purple arrows in Figure 7a. However, it was suggested based on ab initio calculation that the first transition, 5a → 6t, is expected to be much stronger in its oscillator strength [37,44].
Similar to the experimental scheme used in previous sections, our XUV pulse first impulsively excites the superpositions of molecular polarizations corresponding to 5a → 6t and/or 5t → 2t transitions. A subsequent NIR pulse is applied to perturb these dipole polarizations. The NIR pulse used here has its wavelength centered at 780 nm with peak intensity at 1 () TW/cm, and the SF target gas cell has backing pressure 267 Pa. The measured transient absorption spectrogram of SF is shown in Figure 7c. Unlike the ATAS spectrogram of helium, here we only observe the change in OD around delay zero, indicating short-lived molecular polarization. A different set of data taken near delay zero with smaller delay step (5 fs) is shown in Figure 7d. This transient OD signal’s spectral width is limited by the XUV bandwidth, as the broad static absorption feature shown in the inset of Figure 7c is wider than the H15 bandwidth shown on the right side of the figure. We note that, at H13 or H17 energies, we did not observe any transient signal within the detection limits of our method.
In the presence of strong-field NIR, only negative OD is observed in our experiment, which implies that the static XUV absorption is suppressed. Since the initial state is tightly bound, we believe the laser induced modification of the final states is responsible for causing this effect. Considering the complexity of these shape resonance enhanced inter-valence transitions, the exact physical mechanism of this absorption suppression on these excited states due to NIR pulse is still unclear. In contrast to the study of atomic polarization and relatively simple diatomic polarization in previous ATAS studies, neither the laser-induced phase model nor the laser induced attenuation model [33] is sufficient to give us physical insight on this complex molecular system. More experimental as well as theoretical investigations are needed to fully understand these observations. The study of SF serves as a starting point for future studies on complex molecular systems where excited state dynamics resulting from electronic and nuclear motions can be resolved.
6. Conclusions
In summary, we have applied XUV ATAS to study the laser induced modification of excited states in atomic and molecular systems, such as helium and SF. We have explored a range of gas density, laser wavelength and time-delay parameters in these studies. In the dilute helium experiment with the standard pump–probe setup, we observed the AC Stark shift, the quantum path interference, the laser-induced continuum structure, etc. In the dense helium target, we observe new and complex spectral features due to the interplay between laser-induced phase shift effect and the resonant pulse propagation effect. We discussed the comparison between a long and short wavelength NIR perturbation. Extending the transient absorption technique to complex molecular targets, we investigated SF molecular polarization evolution. We observed that the presence of a strong NIR field suppresses the inter-valence transitions inside the inner well of the effective molecular potential, and thus the OD change is reduced. Further work along these directions will serve to demonstrate the power and applicability of the ATAS, as the XUV research and attosecond science community moves to study complex systems, where correlation and couplings’ driven charge and energy transfer mechanisms remain open questions.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) under Contract No. PHY-1505556 and the U. S. Army Research Laboratory under Grant No. W911NF-14-1-0383. C.T.L. acknowledges support from the Arizona TRIF Imaging/Photonics Fellowship.
Author Contributions
C.T.L. performed the experiment. A.S. supervised the research. All authors contributed to the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| APTs | attosecond pulse trains |
| ATAS | attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy |
| FID | free-induction decay |
| FWHM | full width at half maximum |
| H13 | 13th harmonics |
| H15 | 15th harmonics |
| H17 | 17th harmonics |
| HHG | high-harmonic generation |
| LICS | laser-induced continuum structure |
| LIP | laser-induced phase |
| NIR | near infrared |
| OD | optical density |
| OPA | optical parametric amplifier |
| SIGC | semi-infinite gas cell |
| RPP | resonant pulse propagation |
| XUV | extreme ultraviolet |
References
- Sarovar, M.; Ishizaki, A.; Fleming, G.R.; Whaley, K.B. Quantum entanglement in photosynthetic light-harvesting complexes. Nat. Phys. 2010, 6, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presti, D.; Delbrück, M. Photoreceptors for biosynthesis, energy storage and vision. Plant Cell Environ. 1978, 1, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhao, J.; Onda, K.; Jordan, K.D.; Yang, J.; Petek, H. Ultrafast interfacial proton-coupled electron transfer. Science 2006, 311, 1436–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belsley, M. Ultrafast spectroscopy: Quantum information and wavepackets, by Joel Yuen-Zhou, Jacob J. Krich, Ivan Kassal, Allan S. Johnson and Alán Aspuru-Guzik: Scope: Monograph. Level: Postgraduate, early career researcher, researcher, specialist. Contemp. Phys. 2016, 57, 281–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, D.T.; Heyl, C.M.; Thomson, R.R.; Trebino, R.; Steinmeyer, G.; Fielding, H.H.; Holzwarth, R.; Zhang, Z.; Del’Haye, P.; Südmeyer, T.; et al. Roadmap on ultrafast optics. J. Opt. 2016, 18, 093006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Ishikawa, T.; Robinson, I.K.; Murnane, M.M. Beyond crystallography: Diffractive imaging using coherent X-ray light sources. Science 2015, 348, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, J.L.; Schafer, K.J.; Kulander, K.C. High-order harmonic generation from atoms and ions in the high intensity regime. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corkum, P.B. Plasma perspective on strong field multiphoton ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 71, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chini, M.; Zhao, B.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, S.; Chang, Z. Subcycle ac stark shift of helium excited states probed with isolated attosecond pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 073601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Bell, M.J.; Beck, A.R.; Mashiko, H.; Wu, M.; Pfeiffer, A.N.; Gaarde, M.B.; Neumark, D.M.; Leone, S.R.; Schafer, K.J. Light-induced states in attosecond transient absorption spectra of laser-dressed helium. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 86, 063408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, Z.H.; Greene, C.H.; Leone, S.R. Femtosecond induced transparency and absorption in the extreme ultraviolet by coherent coupling of the He 2s2p (1 Po) and 2p 2 (1 Se) double excitation states with 800 nm light. Chem. Phys. 2008, 350, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holler, M.; Schapper, F.; Gallmann, L.; Keller, U. Attosecond electron wave-packet interference observed by transient absorption. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 123601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, C.; Kaldun, A.; Raith, P.; Meyer, K.; Laux, M.; Evers, J.; Keitel, C.H.; Greene, C.H.; Pfeifer, T. Lorentz meets Fano in spectral line shapes: a universal phase and its laser control. Science 2013, 340, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.T.; Sandhu, A.; Camp, S.; Schafer, K.J.; Gaarde, M.B. Beyond the single-atom response in absorption line shapes: probing a dense, laser-dressed helium gas with attosecond pulse trains. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 143002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadogiannis, N.; Kalpouzos, C.; Goulielmakis, E.; Nersisyan, G.; Charalambidis, D.; Augé, F.; Weihe, F.; Balcou, P. Kilohertz extreme-ultraviolet light source based on femtosecond high-order harmonic generation from noble gases. Appl. Phys. B 2001, 73, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, P.M.; Toma, E.; Breger, P.; Mullot, G.; Augé, F.; Balcou, P.; Muller, H.; Agostini, P. Observation of a train of attosecond pulses from high harmonic generation. Science 2001, 292, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durfee, C.G., III; Rundquist, A.R.; Backus, S.; Herne, C.; Murnane, M.M.; Kapteyn, H.C. Phase matching of high-order harmonics in hollow waveguides. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundquist, A.; Durfee, C.G.; Chang, Z.; Herne, C.; Backus, S.; Murnane, M.M.; Kapteyn, H.C. Phase-matched generation of coherent soft X-rays. Science 1998, 280, 1412–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henke, B.L.; Gullikson, E.M.; Davis, J.C. X-ray interactions: Photoabsorption, scattering, transmission, and reflection at E = 50–30,000 eV, Z = 1–92. Atom. Data Nuclear Data Tables 1993, 54, 181–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterfeldt, C.; Spielmann, C.; Gerber, G. Colloquium: Optimal control of high-harmonic generation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, T.; Vrakking, M. Attosecond and XUV Spectroscopy: Ultrafast Dynamics and Spectroscopy; John Wiley & Sons: Somerset, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gaarde, M.B.; Buth, C.; Tate, J.L.; Schafer, K.J. Transient absorption and reshaping of ultrafast XUV light by laser-dressed helium. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 83, 013419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Chen, S.; Camp, S.; Schafer, K.J.; Gaarde, M.B. Theory of strong-field attosecond transient absorption. J. Phys. B Atom. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2016, 49, 062003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wu, M.; Gaarde, M.B.; Schafer, K.J. Laser-imposed phase in resonant absorption of an isolated attosecond pulse. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 88, 033409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, L., Jr.; Beers, B.L.; Feneuille, S. Resonant multiphoton ionization via the Fano autoionization formalism. Phys. Rev. A 1975, 12, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, Y.I.; Popov, A. Parametric generation and absorption of tunable vacuum-ultraviolet radiation controlled by laser-induced autoionizing-like resonances in the continuum. Opt. Commun. 1976, 18, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, P.L.; Lauder, M.; Dalton, B.J. Laser-induced continuum structure. Phys. Rep. 1990, 190, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.T.; Sandhu, A.; Camp, S.; Schafer, K.J.; Gaarde, M.B. Attosecond transient absorption in dense gases: Exploring the interplay between resonant pulse propagation and laser-induced line-shape control. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 93, 033405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisp, M.D. Propagation of small-area pulses of coherent light through a resonant medium. Phys. Rev. A 1970, 1, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaram, N.; Timmers, H.; Tong, X.M.; Sandhu, A. Attosecond-resolved evolution of a laser-dressed helium atom: interfering excitation paths and quantum phases. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 193002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Chini, M.; Wang, X.; Gonzalez-Castrillo, A.; Palacios, A.; Argenti, L.; Martin, F.; Chang, Z. Reconstruction of an excited-state molecular wave packet with attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 023403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrick, E.R.; Cao, W.; Neumark, D.M.; Leone, S.R. Probing the Dynamics of Rydberg and Valence States of Molecular Nitrogen with Attosecond Transient Absorption Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 3165–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.T.; Li, X.; Haxton, D.J.; Rescigno, T.N.; Lucchese, R.R.; McCurdy, C.W.; Sandhu, A. Probing autoionizing states of molecular oxygen with XUV transient absorption: Electronic symmetry dependent lineshapes and laser induced modification. ArXiv 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ferré, A.; Staedter, D.; Burgy, F.; Dagan, M.; Descamps, D.; Dudovich, N.; Petit, S.; Soifer, H.; Blanchet, V.; Mairesse, Y. High-order harmonic transient grating spectroscopy of SF6 molecular vibrations. J. Phys. B Atom. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2014, 47, 124023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.L.; Wüest, A.; Christov, I.P.; Popmintchev, T.; Zhou, X.; Murnane, M.M.; Kapteyn, H.C. Monitoring molecular dynamics using coherent electrons from high harmonic generation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13279–13285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertot, Y.; Schmidt, C.; Matthews, M.; Chauvet, A.; Huppert, M.; Svoboda, V.; von Conta, A.; Tehlar, A.; Baykusheva, D.; Wolf, J.P.; et al. Time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy with a water window high-harmonic source. Science 2017, 355, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuke, K.; Suzuki, S.; Imamura, T.; Koyano, I. Negative-ion mass spectrometric study of ion-pair formation in the vacuum ultraviolet. III. J. Chem. Phys. 1990, 93, 8717–8724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, T. Partial photoionization cross sections of SF6 between 20 and 54 eV: An interpretation of the photoelectron spectrum. Phys. Rev. A 1978, 18, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehmer, J.L.; Parr, A.C.; Wallace, S.; Dill, D. Photoelectron branching ratios and angular distributions for the valence levels of SF6 in the range 16 ≤ hν ≤ 30 eV. Phys. Rev. A 1982, 26, 3283–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefedov, V. Quasistationary states in X-ray absorption spectra of chemical compounds. J. Struct. Chem. 1970, 11, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, D.; Shaw, D.; Hopkirk, A.; MacDonald, M.; McSweeney, S. A study of the absolute photoabsorption cross section and the photoionization quantum efficiency of sulphur hexafluoride from the ionization threshold to 420 A. J. Phys. B Atom. Mol. Opt. Phys. 1992, 25, 4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, K.; Brion, C. Inner-shell and valence-shell electronic excitation of SF6, SeF6 and TeF6 by high energy electron impact: An investigation of potential barrier effects. Chem. Phys. 1990, 140, 439–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrett, T.; Lindle, D.; Heimann, P.; Piancastelli, M.; Kobrin, P.; Kerkhoff, H.; Becker, U.; Brewer, W.; Shirley, D. Shape-resonant and many-electron effects in the S 2p photoionization of SF6. J. Chem. Phys. 1988, 89, 4726–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamatsu, H.; Mukoyama, T.; Adachi, H. Theoretical X-ray absorption spectra of SF6 and H2S. J. Chem Phys. 1991, 95, 3167–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).