Abstract
Laser-driven ion acceleration is a rapidly developing branch of plasma physics and laser science whose primary practical goal is to provide a physical and technological basis for the construction and development of new types of ion accelerators. Laser-driven accelerators can be less complex and more compact than currently used RF-driven accelerators, while the intensities, fluences, and powers of laser-accelerated ion beams can potentially exceed those achieved in RF accelerators. This paper focuses on the generation of very intense ion beams driven by a multi-PW femtosecond laser. The acceleration mechanisms enabling the generation of such beams are characterized, and the properties of multi-PW laser-driven uranium ion beams are discussed in detail based on the results of advanced particle-in-cell numerical simulations. The feasibility of generating sub-picosecond, multi-GeV, mono-charge uranium beams with extreme intensities (~>1020 W/cm2) and fluences (~>GJ/cm2) is demonstrated, and methods for controlling the beam parameters are identified. It is shown that using such beams, extreme states of matter with parameters unattainable with ion beams from conventional accelerators can be created. The prospects for applications of ultra-intense laser-driven ion beams in high-energy density physics, inertial confinement nuclear fusion, and in certain areas of nuclear physics are outlined.
1. Introduction
Energetic ion beams find applications in a variety of scientific and technological fields, including nuclear and particle physics, high-energy density physics (HEDP), inertial confinement fusion (ICF), materials science, cancer therapy, and others. They are routinely produced in conventional accelerators (RF-driven and others), which enable the generation of narrow-spectrum beams with ion energies ranging from MeV to multi-TeV. High-energy ion beams can also be produced in plasma accelerators driven by short (pico- or femtosecond) high-power laser pulses. The electric fields accelerating ions in such accelerators can range from GeV/cm to TeV/cm, and thus ions can be accelerated to very high energies in ~1 ps or less over distances no greater than 1 mm. As a result, these accelerators can be significantly smaller and less complex than conventional accelerators, and the generated ion beams can have significantly shorter durations and higher intensities than those from conventional accelerators.
Research on laser ion acceleration driven by short laser pulses, spanning over two decades, has been focused primarily on maximizing ion energy and minimizing the energy spectrum width and angular divergence of the ion beam (see, for example, review papers [1,2,3]). However, for ion beam applications in fields such as HEDP and ICF, in addition to the energy spectrum and angular distribution of the beam, the energy fluence (Fi) and intensity (Ii) of the ion beam are crucial. At currently achievable laser intensities (~1022–1023 W/cm2 [4,5,6]), the maximum experimentally demonstrated ion energies are in the multi-GeV range [7] and are three orders of magnitude lower than the maximum energies achieved in large RF-driven accelerators. At ultra-high intensities of ~1023–1024 W/cm2 expected in 100-PW lasers [8,9,10,11], the energies of ions produced in laser-driven accelerators are likely to reach sub-TeV values. This will still be at least one order of magnitude lower than those achieved in RF-driven accelerators. The energy spectrum of laser-accelerated ions is relatively broad, much broader than that achieved in conventional accelerators, and methods to narrow this spectrum to the level achieved in these accelerators without dramatically reducing beam efficiency have not yet been developed. The competitiveness of laser-driven accelerators with conventional ones in terms of achievable ion energies and spectral quality seems questionable, not only currently but also in the foreseeable future. The situation is completely different when we compare the fluences, intensities, and powers of ion beams produced in laser accelerators and conventional accelerators. It has been demonstrated in experiments for quite a long time that even at relatively low intensities (~1019 W/cm2) and energies (~10–20 J) of a sub-picosecond laser driver, the intensity of a laser-accelerated ion (proton) beam near the ion source can reach 1018 W/cm2 and the beam power can exceed 1 TW [12,13]. These beam parameters are comparable to those achieved by ion beams produced in large conventional accelerators. An increase in the intensity and power of the laser driver naturally leads to an increase in the intensity and power of the generated ion beam, and at currently achievable laser intensities (~1022–1023 W/cm2) and powers (multi-PW) [4,5,6] of femtosecond lasers, the peak intensities and powers of the generated ion beams can potentially reach very high values, much higher than those achieved even in the largest RF-driven accelerators. Very high intensities and powers of laser-generated ion beams are primarily the result of very short ion pulse durations, which near the ion source can be ~1 ps or shorter [14,15]. Furthermore, the density of the laser-generated ion beam near the source is typically several orders of magnitude higher than that of conventional accelerator beams. As a result, the energy fluences of laser-generated beams could reach GJ/cm2.
Thus, when comparing the intensities, powers, fluences and durations of ion beams, laser-driven accelerators can not only effectively compete with conventional accelerators but, in principle, can also produce ion beams with parameters significantly exceeding those achieved in conventional accelerators. Constructing laser-driven accelerators focused on achieving maximum ion beam intensities, powers, and fluences would open the prospect of exploring new areas of research in HEDP and ICF, and perhaps also in nuclear physics and other fields. Unfortunately, most researchers studying laser-driven ion acceleration have focused their research on maximizing ion energy and improving the quality of the energy and angular spectrum of the ion beam (see review papers [1,2,3]). Only in relatively few works (e.g., [15,16,17,18,19,20]), and mainly in those related to fast ignition of inertial confinement fusion [16,17,18,19], have ion beam parameters such as intensity, fluence, power, and beam duration been analyzed and numerically optimized. However, to produce ion beams enabling thermonuclear ignition, picosecond laser drivers with very high energy (≥100 kJ) are necessary, the prospect of building which is still quite distant.
Very intense ion beams can, in principle, also be produced at currently achievable intensities (~1023 W/cm2) and powers (multi-PW) of femtosecond laser drivers [15,20]. Such beams can be very useful in HEDP research and also in certain areas of nuclear physics. In HEDP, beams of super-heavy ions such as uranium or lead ions [21,22] are particularly desirable, primarily due to their high stopping power in interactions with materials. Collisions of high-energy super-heavy ions also play a very important role in nuclear physics. Therefore, from the point of view of possible applications of laser-generated intense ion beams in these two fields of research, beams of super-heavy ions are of special interest.
This paper demonstrates the feasibility of producing ultra-intense uranium ion beams in a laser accelerator driven by a multi-PW femtosecond laser and presents the results of comprehensive numerical studies of the properties of the generated beams. The studies were conducted using an advanced two-dimensional (2D) particle-in-cell (PIC) computer code, which specifically incorporates dynamic ionization of uranium atoms and ions and the generation of synchrotron radiation accompanying ion acceleration. At a fixed laser intensity of 1023 W/cm2, the effects of the laser focal spot size, dL, and the target thickness, LT, on various ion beam characteristics were investigated. In particular, the influence of dL and LT on the ionization and energy spectrum of the ion beam, on the intensity, fluence, and duration of the ion beam, as well as on the energetic efficiency of ion acceleration was determined. Furthermore, key parameters characterizing the ability of the generated uranium ion beam to create high-energy-density (HED) states of matter—namely, the energy and power deposited per gram of matter—were calculated for a carbon target irradiated by the beam.
The paper is structured as follows. After an introduction (Section 1), Section 2 briefly characterizes the mechanisms of laser-driven ion acceleration that favor the generation of ultra-intense ion beams. Section 3 describes the laser driver and target parameters selected for numerical simulations and the PIC code. The most important simulation results are presented in Section 4, where the influence of the laser focal spot size (Section 4.1) and the uranium target thickness (Section 4.2) on various parameters of the generated uranium ion beam is presented and discussed. Section 5 presents selected results concerning the generation of synchrotron radiation, which is the main source of losses in the ion acceleration process but can also be a source of powerful pulses of short-wavelength radiation Section 6 discusses some limitations and inaccuracies of the computer model used in the simulations, some issues related to plasma instabilities occurring during ion acceleration, the practical achievability of the assumed target and laser parameters, and the possibility of conducting experiments to verify the simulation results. Section 7 outlines some possible applications of ultra-intense laser-generated ion beams, primarily in HEDP. Section 8 summarizes the main results of our research.
2. Ion Acceleration Mechanisms Enabling the Generation of Ultra-Intense Ion Beams
To produce ultra-intense ion beams useful for a variety of applications, the mechanism of laser-driven ion acceleration must meet several requirements. Below, we will discuss the more important of these requirements and attempt to identify mechanisms that can best meet these requirements. The intensity (Ii) and energy fluence (Fi) of an ion beam can be defined as follows: Ii = niviEi = niEi3/2, Fi = σiEi where ni is the ion density, vi and Ei are the ion velocity and energy, respectively, σi = nil is the areal ion density (or ion fluence in units of cm−2), and l is the thickness of the ion layer. To achieve high intensity values, high ion energy and ion density are necessary, and to achieve high energy fluence, the ion layer must also be sufficiently thick. To achieve high values of Ii and Fi, the ion acceleration mechanism should not only be capable of accelerating ions to high energies but also effectively accelerate dense, possibly thick, ion layers.
Most possible ion beam applications require the ion accelerator to be compact, economical, and flexible enough to adapt beam parameters to the specific application. The largest, most complex, and most expensive component of a laser-driven accelerator is the laser driver. Its size, complexity, and cost usually depend largely on the laser energy. From this perspective, a crucial requirement for the usefulness of an ion acceleration mechanism is its ability to ensure high efficiency in converting laser energy into ion beam energy. The higher this efficiency, the lower the laser energy required to achieve the required beam parameters, which in turn allows for minimizing the size and cost of the driver. Lower driver energy also potentially allows for an increase in the driver repetition rate. Thus, the ion acceleration mechanism should ensure high efficiency of transformation of laser energy into ion beam energy.
An important parameter determining the usefulness of an ion beam is the beam angular divergence. A large beam divergence usually hinders or prevents effective studies of ion beam-target interactions, because moving the target away from the ion source by a distance much greater than the source’s size, typically required in research, can lead to a dramatic decrease in the beam intensity and fluence at the target. The ion acceleration mechanism used to produce an ultra-intense ion beam should therefore enable the generation of a beam with a relatively small angular divergence.
A desirable property of an ion beam in many applications is a narrow energy spectrum. Meeting this requirement is particularly important in the potential applications of ultra-intense ion beams in nuclear and particle physics, where relative spectral widths of no more than a few percent are often required. When using these beams in HEDP or ICF research, the requirements for energy spectral width are more lenient, and spectral widths of several dozen percent are typically acceptable. Furthermore, when using heavy ion beams in nuclear/particle physics, HEDP or ICF, a desirable beam property is a narrow ionization spectrum, meaning the beam should be largely mono-charged.
Currently, many ion acceleration mechanisms are known that enable the acceleration of ions of various masses (from protons to super-heavy ions) by laser pulses with intensities ranging from non-relativistic to ultra-relativistic, and under various laser-target interaction conditions (see, for example, review papers [1,2,3,14]). The most common include: target normal sheath acceleration (TNSA) [23,24,25,26,27,28], radiation pressure acceleration (RPA) [29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38], collisionless electrostatic shock acceleration (CESA) [39,40], skin layer ponderomotive acceleration (SLPA) [13,41,42], Coulomb explosion acceleration (CEA) [38,43,44,45], laser afterburner acceleration (BOA, sometimes called relativistic induced transparency acceleration—RITA) [46,47,48,49], and magnetic vortex acceleration (MVA) [50,51]. At high laser intensities, several mechanisms typically participate in the acceleration process (e.g., RPA + TNSA + CEA or RPA + TNSA + CEA + RITA), and the contribution of each is determined by the laser and target parameters. Unfortunately, at the current stage of research on these mechanisms, none of them is capable of simultaneously meeting all the above-mentioned requirements for generating an “ideal” ultra-intense ion beam. It seems that the RPA mechanism comes closest to meeting these requirements. We will discuss this mechanism in more detail below.
In the RPA mechanism, ions are accelerated by ponderomotive forces induced by the laser beam in the skin layer near the critical plasma density (pre-plasma) in front of the target illuminated by the beam. One of these forces is directed forward (in the direction of beam propagation), and the other in the opposite direction (backward). Each of these forces pushes electrons from the skin layer in the direction of the force and locally separates them from the plasma ions. Two so-called double layers are created, each composed of an electron layer and an ion layer, one propagating forward and the other backward. A very strong electric field is generated between the negative electron layer and the positive ion layer, accelerating the ions in the wake of the moving electron layer driven by the ponderomotive force. In this way, two bunches of ions are generated and accelerated in the forward and backward directions. However, when the laser beam intensity is sufficiently high (>1020 W/cm2) and the plasma density gradient near the critical density is high, the forward ponderomotive force (ponderomotive or radiation pressure) is much higher than the backward one, and practically only one high-density forward accelerated ion bunch is generated. This ion acceleration mechanism is commonly called radiation pressure acceleration (RPA) [1,2,3,14].
The RPA mechanism typically consists of two stages (regimes): the hole-boring stage (HB) and the light-sail stage (LS). Which of these regimes dominates depends on the target thickness (LT) and the laser fluence (FL). When the target is thick enough (or the fluence is insufficiently high), ions from the front of the target are accelerated toward the target interior by the charge separation field of the forward-moving double layer driven by the laser radiation pressure. The increase in ion energy is accompanied by an increase in the number and density of accelerated ions, since the positively charged ion layer in the moving double layer acts like a snowplough on the ions in the undisturbed portion of the target. As a result, a dense ion (plasma) block is formed, and almost all the laser energy is used to form and accelerate this block inside the target. In this case, the RPA-HB regime dominates the acceleration process. Optimal conditions for this regime occur when the target thickness LT ≈ LHB = τLVHB, where VHB is the average recession velocity of the ion surface driven by the laser piston and τL is the laser pulse duration. Approximate analytical formulas for estimating the energy of ions accelerated in the RPA-HB regime can be found in [2].
If the target is sufficiently thin (or the laser fluence is sufficiently high), the RPA-LS regime dominates the ion acceleration process. In this case, only a small portion of the laser energy is used to ionize the target and accelerate ions within the target, while the dominant portion is used to accelerate the ionized target in free space behind the initial target position. For the RPA-LS regime to be effectively implemented, the target thickness should meet the following conditions [34]: 1/4 Lskin < LT < 5 Lskin, where Lskin = γ1/2 c/ωp is the relativistic skin depth of the plasma (γ ~ IL1/2—relativistic parameter; ωp—electron plasma frequency; c—speed of light). When LT > 5 Lskin, the TNSA-like mechanism dominates, while when LT < 1/4 Lskin, the acceleration corresponds to the CEA mechanism. Acceleration is most efficient when LT ~ (1–2) Lskin, provided that the transverse expansion of the plasma during the laser pulse is small and the pulse is not very long. An analytical formula for estimating the energy of ions accelerated in the RPA-LS regime when the target areal density, σ, and the laser fluence are known can be found in [2].
From the point of view of generating ion beams with ultra-high fluences and intensities, the following features can be considered the most important advantages of the RPA mechanism (see, e.g., [14]): (a) the areal ion density, σi, of the beam can be very high (up to ~1019 cm−2 close to the source), (b) with ultra-high laser driver intensities already achieved, ion energies can reach multi-GeV energies and higher, (c) the energy efficiency of ion acceleration is high and can reach several dozen percent for both light, heavy, and super-heavy ions, (d) ion pulses generated by the RPA can be very short—from several tens of fs to several ps. The main disadvantages of the RPA mechanism are: (a) achieving high energy efficiency of conventional acceleration requires very high laser intensities (>>1021 W/cm2) and high laser pulse contrast, (b) obtaining high ion beam quality requires high laser beam homogeneity, (c) ion acceleration is usually accompanied by plasma instabilities (Rayleigh-Taylor-like and others), which lead to a deterioration of the ion beam quality. Despite these drawbacks, RPA remains the most effective currently known mechanism for generating ultra-intense ion beams.
RPA typically dominates ion acceleration when laser intensities are very high (>>1021 W/cm2). In the region of relativistic but moderate laser intensities (~1019–1021 W/cm2), acceleration is typically dominated by TNSA—the best-understood and widely used acceleration mechanism. Potentially, TNSA also enables the generation of ion beams of high intensity and fluence, although with parameters significantly lower than those achievable using RPA.
In TNSA, the laser beam interacting with the target generates fast electrons that penetrate the target and, upon exiting, form a negatively charged layer at its rear surface, acting as a moving virtual cathode. Between the cathode and the target surface, a very strong electric field (~tens of GV/cm or higher) is created which ionize atoms located in a thin (~5–10 nm) layer near the target surface. The ions thus produced are then accelerated by this field and move in a direction close to the normal to the target surface. Because only ions from a very thin target layer are accelerated, the areal density σi of the ion source is relatively small, σi < 1017 cm−2, and the ion density in the source ni is moderate, ni < 1019 cm−3. Thus, achieving high ion beam fluences (Fi = σiEi) and intensities (Ii = niviEi) is possible only at very high ion energies, significantly higher than in the RPA mechanism, where the values of σi and ni can be 2–3 orders of magnitude higher. Achieving Ei values much higher with TNSA than with RPA does not seem possible primarily due to the less favorable scaling of Ei with laser intensity IL [14]: Ei ~ IL1/2 for TNSA, while for RPA-LS Ei ~ (ILτL)a, where a = 2 for vi << c, and a = 1 for vi ≈ c. Furthermore, the energy spectrum of TNSA-driven ions is typically much broader than that achievable with RPA, and therefore the ion pulse generated by TNSA is longer than for RPA.
On the other hand, because ions are accelerated primarily in the direction normal to the rear surface of the target, TNSA enables focusing of the ion beam by curving this surface [52,53,54,55]. This enables achieving ion fluences and densities higher than those in the ion source (at the target surface) at distances comparable to the radius of curvature of this surface (e.g., a hemisphere). The increase in Fi and σi values is also facilitated by the fact that the surface from which ions are extracted and accelerated is much larger than the size of the laser beam on the target, and therefore the total number of accelerated and focused ions can be high. Unfortunately, due to the non-uniform distribution of propagation directions and energies of ions in the source, a significant portion of the ions propagate outside the ion focus region, and the efficiency of laser energy transfer into the energy of the dense focused ion beam usually does not exceed a few percent [55]. Moreover, due to the strong dependence of the TNSA mechanism efficiency on the Z/A ratio of the accelerated ions (Z—charge state of the ion, A—atomic mass number of the ion), this mechanism is effective mainly for protons (Z/A = 1) and fully ionized light ions (Z/A = 1/2).
Despite the shortcomings noted above, TNSA can be a useful mechanism for generating ion beams of high fluence and intensity, both when TNSA is the dominant mechanism in the acceleration process and when it merely supports the RPA mechanism in this process.
The remaining acceleration mechanisms mentioned above are usually unable to generate ultra-intense ion beams with useful properties because they do not meet most of the requirements outlined at the beginning of this section. However, some of them can support the RPA and/or TNSA mechanisms in generating such beams if the laser and target parameters are properly selected. These include the RITA mechanism. If the laser pulse is sufficiently long and intense, RITA can accompany RPA in the final stage of acceleration and, by increasing the ion energy at this stage, increases the intensity and fluence of the ion beam. An acceleration scheme combining RPA and RITA, called sheet crossing, has recently been studied and applied to proton acceleration [36,37]. In this scheme, ions from the front part of a relativistically transparent thin target are accelerated by the RPA to high energies, enabling them to cross through the TNSA sheet generated on the rear side of the target. As a result, the mean energy and number of accelerated ions increase, thus increasing the energy fluence and intensity of the produced ion beam. Whether this scheme will be effective for the acceleration of heavy and super-heavy ions remains an open question and requires further research. In turn, the CEA mechanism, which often accompanies RPA, can hinder the generation of ultra-intense ion beams, particularly superheavy ion beams. Although CEA can increase the energy of RPA-driven ions, it also leads to a significant increase in the angular divergence of the ion beam. This results in a rapid decline in the beam fluence, intensity, and density with increasing distance from the ion source, thus reducing the ion beam’s application utility.
The basis of ion acceleration mechanisms such as RPA, TNSA, and the others mentioned above is the electromagnetic forces induced in the plasma by a laser. At relativistic laser intensities, they enable the acceleration of ions to energies in the GeV range and higher, and primarily (but not exclusively) these high ion energies result in high ion beam intensities and fluences. In laser-produced plasma, besides EM forces, other forces also exist, particularly hydrodynamic forces. These forces can also effectively accelerate plasma ions. In laser-produced plasma, they dominate the acceleration process at relatively low, nonrelativistic laser intensities (<1016 W/cm2) and are used to accelerate ions (plasmas), driven primarily by nanosecond or sub-nanosecond laser pulses. The best-known and widely used ion (plasma) acceleration mechanism utilizing laser-induced hydrodynamic (thermal) forces is ablation acceleration (AA) [56]. In the AA mechanism, a hot plasma is generated on the surface of a target illuminated by a laser beam. This plasma expands backward and accelerates the remaining portion of the target forward (via the “rocket effect”). The most important application of AA is in ICF research, where it is used to accelerate and compress DT fuel in fusion targets [57,58]. It is also used to accelerate microprojectiles [59,60,61] and in HEDP research, primarily to generate high pressures [58]. The main drawback of the AA mechanism is the relatively low energy efficiency of acceleration, usually on the order of a few percent [56,59,60]. A much more efficient acceleration mechanism utilizing hydrodynamic forces is the so-called LICPA (laser-induced cavity pressure acceleration) mechanism [62,63]. In LICPA, a target placed in a cavity is irradiated by a laser beam introduced into the cavity through a hole and then accelerated in a guiding channel by the pressure of a hot plasma produced in the cavity by the laser beam. It has been shown [63,64] that the efficiency of acceleration of ion (plasma) flux by LICPA is many times higher than by AA and can reach several dozen percent.
Ions accelerated by hydrodynamic forces have relatively low velocities (<108 cm/s) and energies (<0.1 MeV), many orders of magnitude lower than those achieved in EM acceleration. However, ion densities (ni) and areal ion densities (σi) can reach values significantly higher than those achieved in EM acceleration. In accelerators with flat geometry, these values can reach values of ni ~ 1023 cm−3 and σi ~ 1020–1021 cm−2, while in spherical geometry used for plasma compression in ICF research, these values can be even 1–2 orders of magnitude higher. Although the fluences and intensities of ion fluxes accelerated hydrodynamically are much lower than those accelerated by EM forces (due to the much lower ion energies), they are high enough to play a very important role in HEDP and ICF studies. In particular, by impinging an ion flux generated in flat geometry on a solid target, it is possible to generate very high pressures up to Gbar [65,66], while acceleration and compression of the ion flux in spherical geometry can lead to the initiation of nuclear fusion. The above applications, however, require nanosecond or sub-nanosecond laser drivers with very high energies, from ~1 kJ in flat geometry experiments to ~104–106 J in spherical experiments. In this work, we will focus on the generation of intense ion fluxes driven by EM forces induced in plasma by femtosecond laser drivers with energies ≤ 1 kJ and multi-PW powers.
3. Research Method Used to Demonstrate and Investigate the Properties of Laser-Driven Extreme Ion Beams
To demonstrate the ability to generate ultra-intense ion beams using a multi-PW femtosecond laser and to investigate the properties of these beams in detail, we used the results of a series of numerical simulations performed using an advanced particle-in-cell code. The ion beam driver was a multi-PW laser with parameters achievable with current short-pulse laser technology, specifically: laser pulse duration τL = 30 fs (FWHM), circularly polarized beam intensity focused on the target IL = 1023 W/cm2, and laser wavelength λ = 0.8 µm. The laser pulse interacted with a flat uranium target with a width of 16 µm, composed of a solid part with an atomic density of 4.82 × 1022 atoms/cm3 and a pre-plasma with an exponential change in density and a total thickness of 184 nm. The presence of the pre-plasma in front of the main solid part of the target reflects the fact that the intensity contrast of the laser pulse is finite, and the pre-pulse preceding the main part of the pulse can ionize the target surface and generate a plasma. The uranium target was chosen because beams of high-energy superheavy ions such as uranium can be particularly useful in HEDP and nuclear physics research. To reveal the properties of ultra-intense laser-generated ion beams and to investigate the possibility of controlling their parameters, the size of the laser focal spot on the target (from 3 µm to 6 µm) and the thickness of the target solid part (from 7 nm to 100 nm) were varied in simulations, with fixed values of IL and τL and pre-plasma parameters. It is worth adding that the effective pre-plasma thickness (at the 1/e level of density distribution) is ~20 nm, so the actual initial target thickness (before laser exposure) varied in the simulations from ~27 nm to ~120 nm. With current target fabrication technologies, flat targets with such thicknesses are relatively easily achievable (e.g., [67,68]).
The simulations of uranium ion acceleration in plasma generated by the interaction of the laser pulse with the uranium target were performed using a fully electromagnetic, relativistic multi-dimensional (2D3V) particle-in-cell PICDOM code [69]. This code includes, in particular, the dynamic ionization of the laser-irradiated target and the accelerated ions [34,70], as well as the emission of synchrotron radiation by relativistic electrons produced in the plasma by the laser [71,72,73,74]. To model the ionization process, it was assumed that the process is dominated by field ionization, and its quantitative description was described using the Ammosov-Delone-Krainov formula [75]. This assumption is justified by the fact that the energies of fast electrons generated by lasers in plasma at laser intensities of ~1023 W/cm2 are very high (from tens to even hundreds of MeV [15,76]), while the average plasma density (below 1021 cm−3) and size (~10–20 µm) in the cases studied here are relatively small. As a result, the probability of electron-ion collisions is very low, and therefore processes such as collisional ionization of atoms/ions, electron-ion recombination, or bremsstrahlung radiation can be omitted in numerical modelling ion acceleration (see, e.g., [71,72,73]). This allows simulations to be performed with lower computational power and in much shorter time. For numerical modelling of synchrotron radiation emission accompanying ion acceleration at very high laser intensities and calculations of radiative losses associated with this emission, the well-known Sokolov model [77] was used.
The simulations were carried out in the x-y plane with dimensions of 70 μm × 20 μm (the x-axis is parallel to the direction of laser beam propagation). The time and spatial steps were 2.2 as and 6 nm, respectively, and the number of uranium macroparticles per cell was 50 particles. The total number of uranium particles in the simulation depended on the thickness of the uranium target and ranged from 777,431 to 2,667,000. The number of electron macroparticles changed during the simulation with the change of the ion ionization levels and was equal to the number of uranium macroparticles multiplied by the current average ion ionization level. To account for the fact that the ion beam propagates in three-dimensional (3D) space, a 3D correction [19,76,78] was applied when determining the absolute values of the beam parameters. When calculating this correction, it was assumed that the movement of ions in the x-z plane perpendicular to the x-y simulation plane was identical to that in the simulation plane. As shown in the discussion in Section 6, when RPA is the dominant acceleration mechanism, the differences between the values of beam parameters such as ion energy, beam intensity and beam fluence obtained from 2D and 3D simulations are usually not very large (paradoxically, 2D simulations often give values of these parameters that are slightly lower than those from 3D simulations). Therefore, we can believe that the results of our simulations, enriched with the 3D correction, are sufficiently accurate for the purposes of this work.
4. Properties of a Uranium Ion Beam Driven by a Multi-PW Femtosecond Laser
In this section, we will demonstrate the feasibility of generating uranium ion beams with ultrahigh intensities and fluences using a multi-PW laser and present the basic properties of these beams. We will also examine whether it is possible to effectively control the parameters of these beams by varying certain laser and target parameters. In Section 4.1, we will examine the effect of the laser focal spot size on the properties of a uranium ion beam, and in Section 4.2, we will demonstrate how the beam properties change with varying the uranium target thickness.
4.1. The Effect of the Laser Focal Spot Size on the Properties of the Uranium Ion Beam
To investigate the effect of the laser focal spot size, dL, on the properties of a uranium ion beam and to assess the effectiveness of beam parameter control by varying the dL value, numerical simulations were performed for four values of this parameter (dL = 3 µm, 4 µm, 5 µm, and 6 µm) at a fixed laser intensity of 1023 W/cm2 and a laser pulse duration of τL = 30 fs. The influence of dL on the ionization and energy spectra of uranium ions, the spatial and angular distributions of ion fluence, the temporal distributions of beam intensity, and the global characteristics of the ion beam, such as peak intensity, peak fluence, and energy, was analyzed.
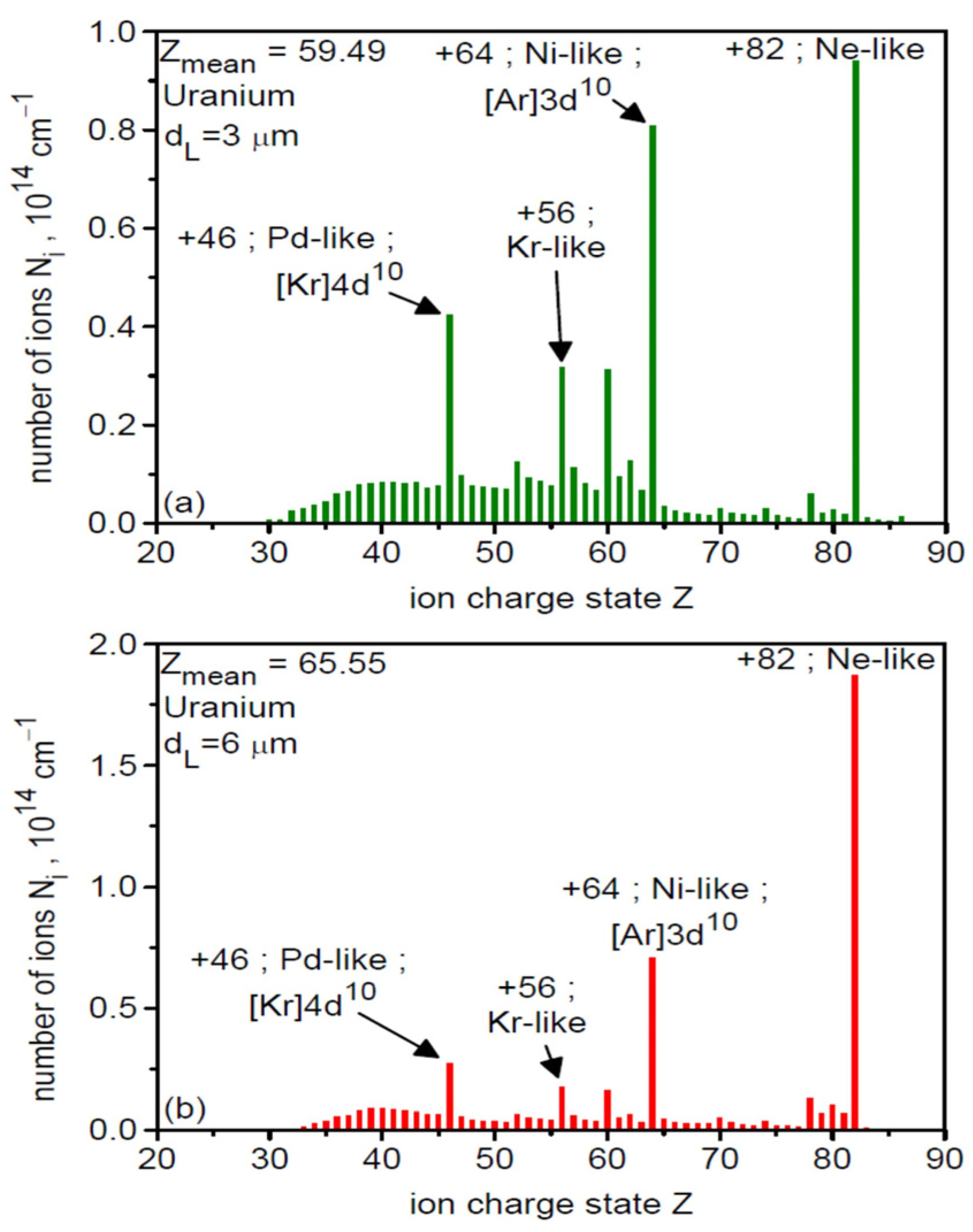
For superheavy ions such as uranium, the ionization spectrum is an important characteristic of the laser-generated ion beam. This is primarily because the efficiency of ion acceleration in laser-induced electric fields in plasma depends significantly on the ratio of the ion charge q to its mass m, i.e., on q/m = Z/A, where Z is the charge state of the ion and A is its atomic mass. In the case of targets with a low atomic number Zat (e.g., a carbon target), even at moderate laser intensities of ~1020–1021 W/cm2, virtually all atoms of the thin target are completely ionized by the laser beam, and for most accelerated ions, Z/A = 1/2. In the case of targets containing super-heavy atoms, even at ultra-high intensities ≥ 1023 W/cm2, the ionization process takes much longer; the atoms are not completely ionized, and there are usually several dozen types of ions with different q/m = Z/A < 1/2. As a result, super-heavy ions are accelerated less efficiently than light ions, and the acceleration efficiency for different ion types (ions with different Z) is different. This is a significant obstacle to achieving high-efficiency acceleration and producing a high-quality ion beam. Detailed knowledge of the ionization spectrum and its possible control towards a monocharged beam is crucial for producing a high-quality super-heavy ion beam.
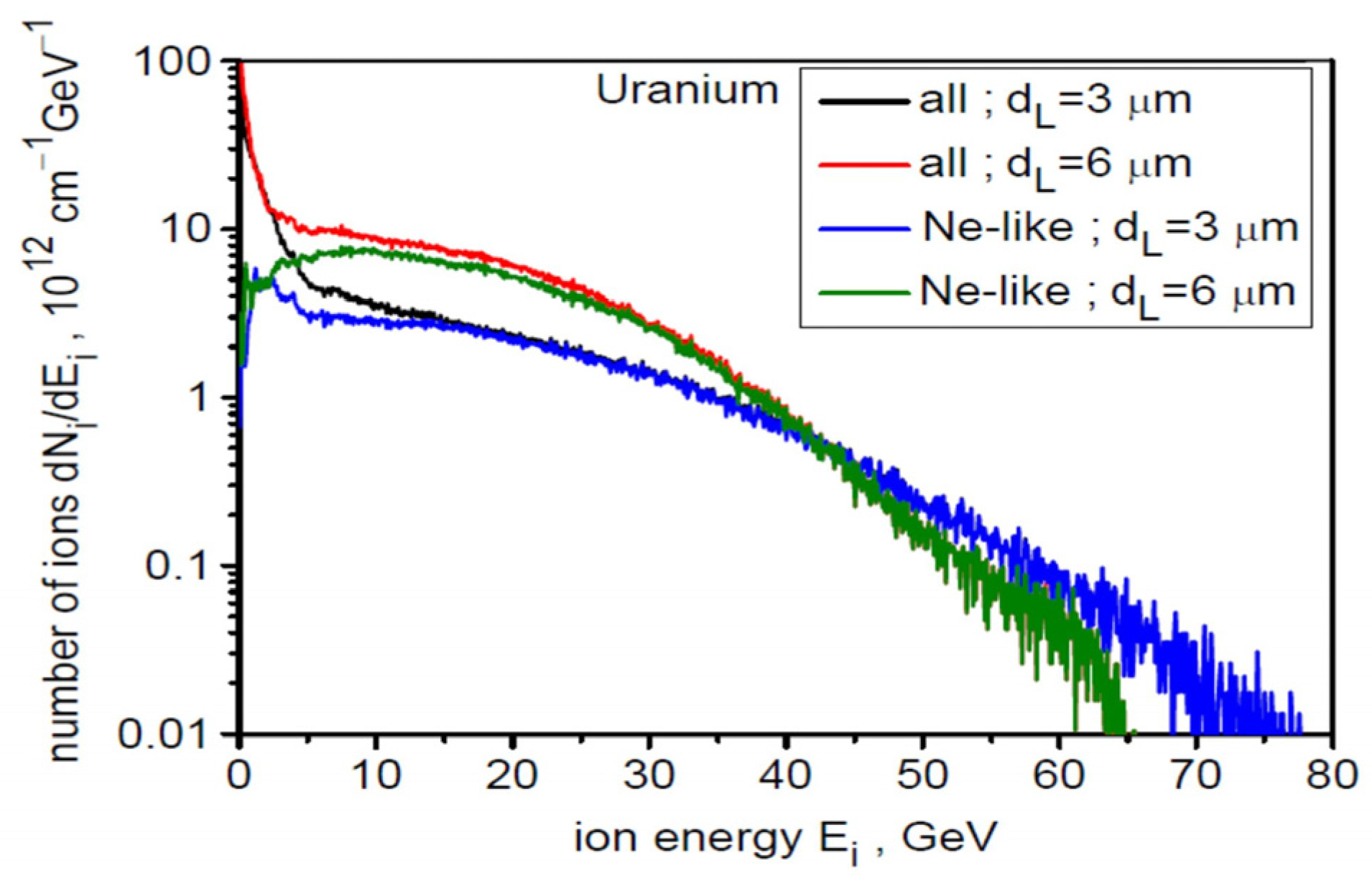
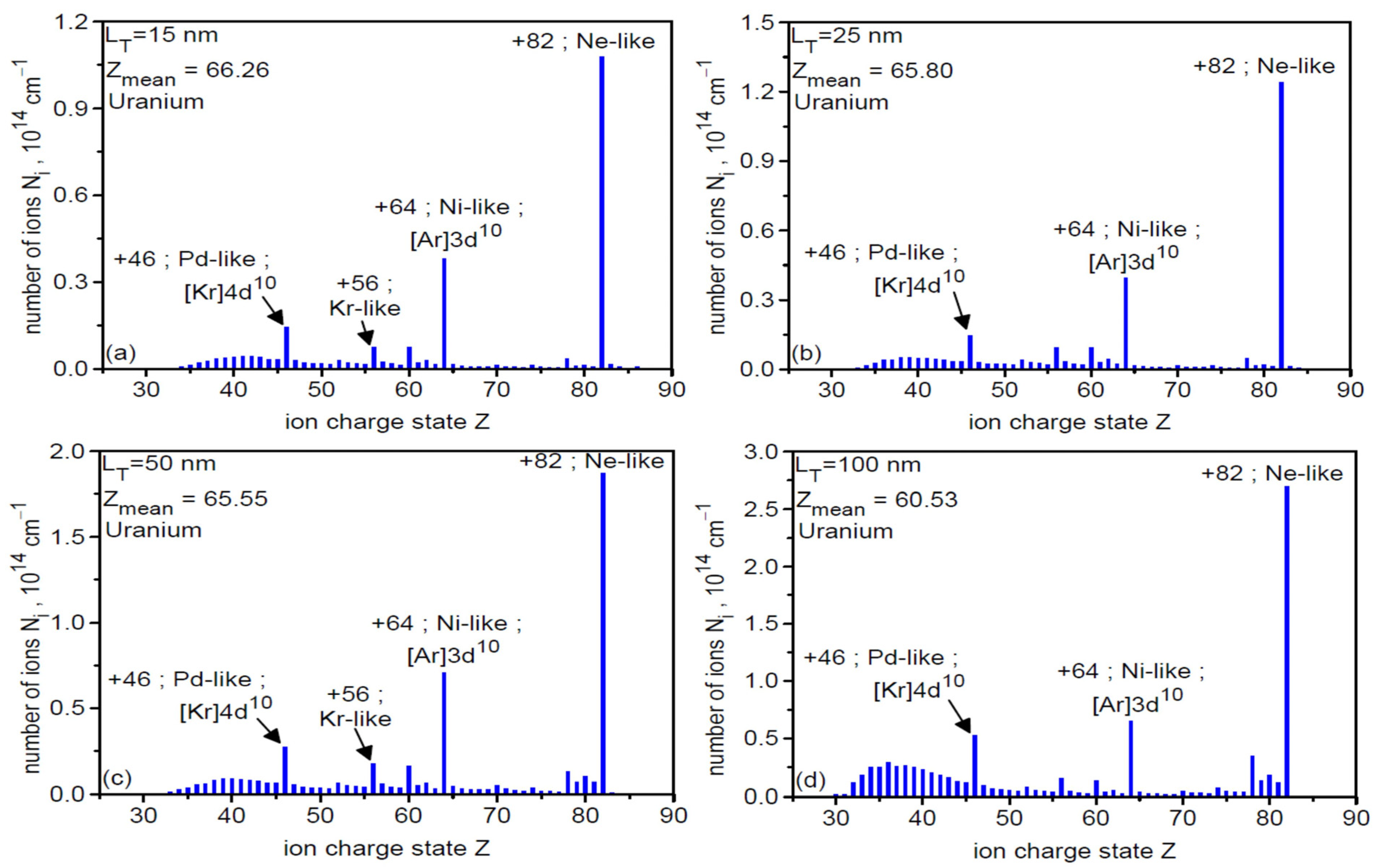
Figure 1 shows the ionization spectra of uranium ions in the final stage of acceleration (t = 8τL = 240 fs) for two laser focal spot sizes of 3 µm (a) and 6 µm (b). As can be seen, the spectral structure is similar in both cases: several dozen ion types with different charge states Z are generated, with the largest population being Ne-like ions with Z = 82. Because Ne-like ions have the highest Z/A ratio among the highly populated ions, they are accelerated most efficiently and thus have the highest energy (both mean and maximum) and carry a substantial portion of the energy deposited by the laser in the ion beam. This is clearly seen in Figure 2, which shows the energy spectra for all ions in the generated beam (red and black curves) and for the Ne-like ion group (green and blue). The high-energy part of the spectrum (Ei > 10 GeV) is completely dominated by Ne-like ions for both dL values, with the maximum energy of these ions being slightly higher for dL = 3 µm and reaching 80 GeV.
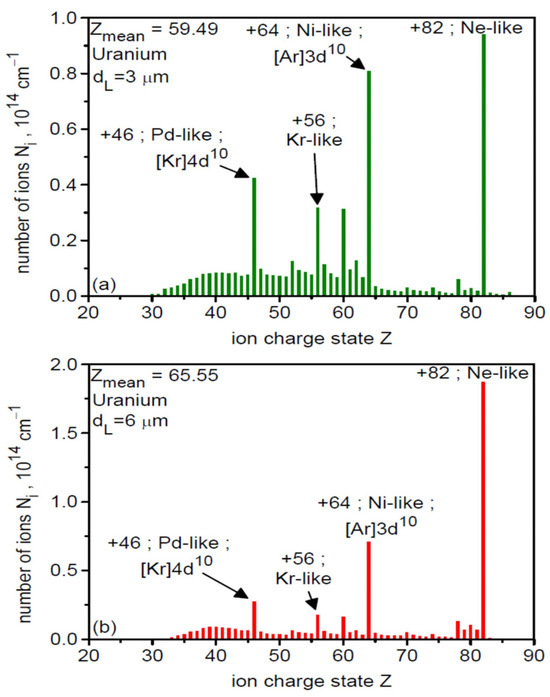
Figure 1.
The ionization spectra of uranium ions in the final stage of acceleration (t = 240 fs) for two laser focal spot sizes of 3 µm (a) and 6 µm (b). The target thickness LT = 50 nm.
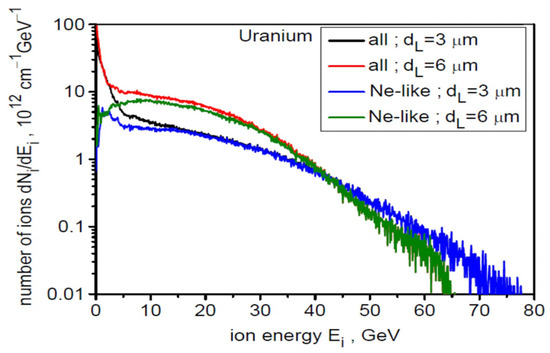
Figure 2.
The energy spectra for all ions in the generated beam (red and black curves) and for the Ne-like ion group (green and blue) for two laser focal spot sizes of 3 µm and 6 µm. LT = 50 nm, t = 240 fs.
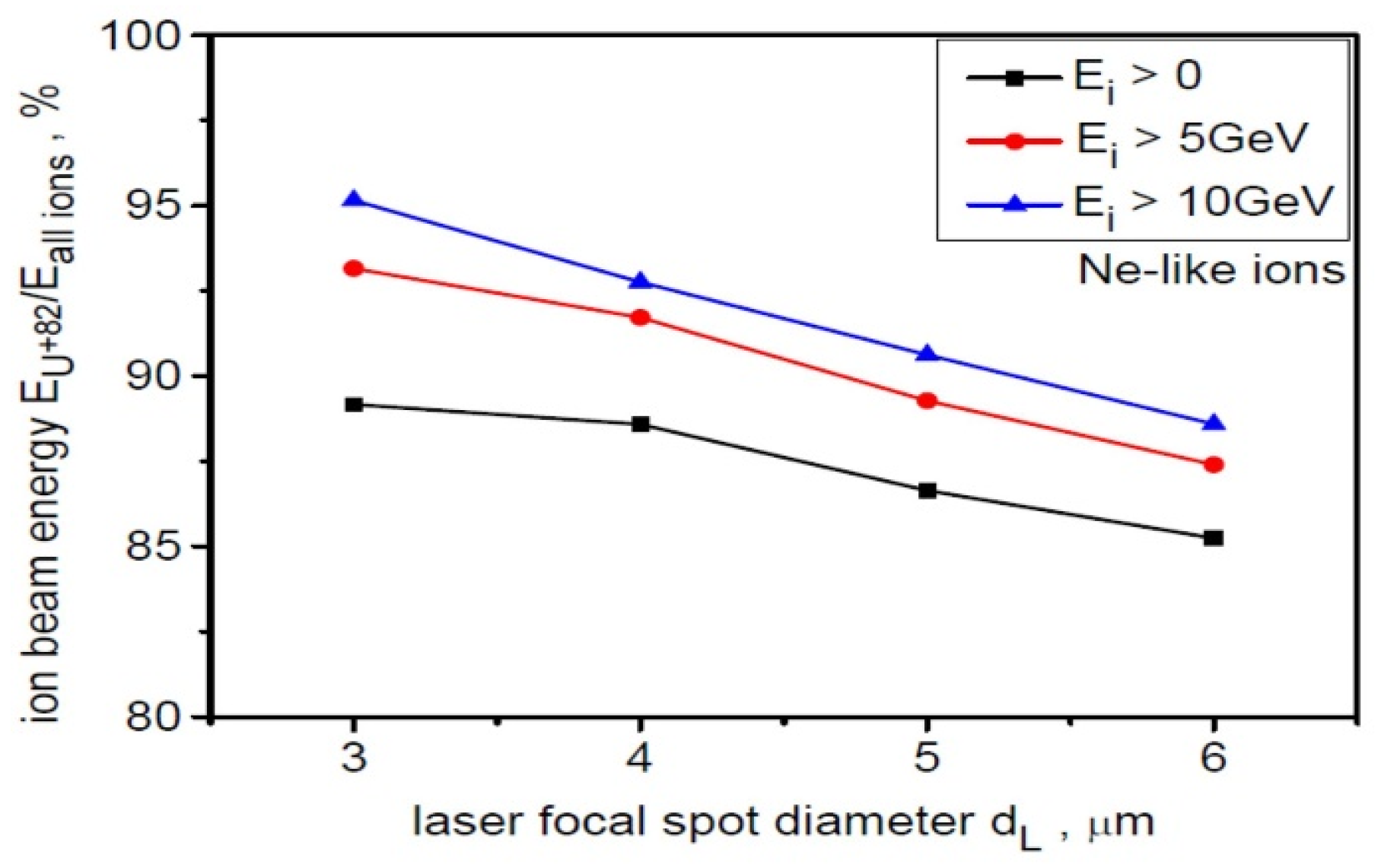
The percentage share of energy carried by Ne-like ions relative to the energy of all ions as a function of the laser focal spot size for various ion energy ranges is shown in Figure 3. This share decreases slightly with increasing dL but increases with increasing ion energy, and for the high-energy part of the energy spectrum, it can significantly exceed 90%. The ion beam is therefore practically mono-charged, with a dominant charge state of Z = 82. As our studies (not presented here) have shown, the mono-charge of the beam can be further increased by separating its paraxial part of size ~ dL from the beam. In this case, Ne-like ions can carry over 98% of the energy stored in the paraxial beam.
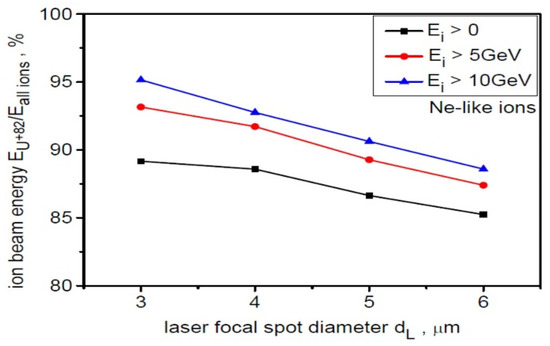
Figure 3.
The percentage share of energy carried by Ne-like ions relative to the energy of all ions as a function of the laser focal spot size for various ion energy ranges. LT = 50 nm, t = 240 fs.
The mono-charged nature of a beam of super-heavy ions such as uranium, demonstrated above, is an important feature from the point of view of their potential applications, for example, in HEDP. It allows for better concentration of the beam energy in the irradiated material and facilitates the interpretation of beam-target interaction measurements. The physical causes and conditions necessary for generating a mono-charged beam of super-heavy ions are discussed in [79]. It has been shown that the generation of such beams is possible when the laser intensity is properly matched to the energy level structure of the super-heavy atom. In the case of uranium, generation of a beam dominated by Ne-like ions is possible at intensities of ~(1–2.4) × 1023 W/cm2, i.e., in a quite wide range of intensities. For super-heavy ions with lower mass numbers (e.g., Au, Pb, Bi), the laser intensities required to generate Ne-like beams are lower than for uranium, but still well above 1022 W/cm2 [79].
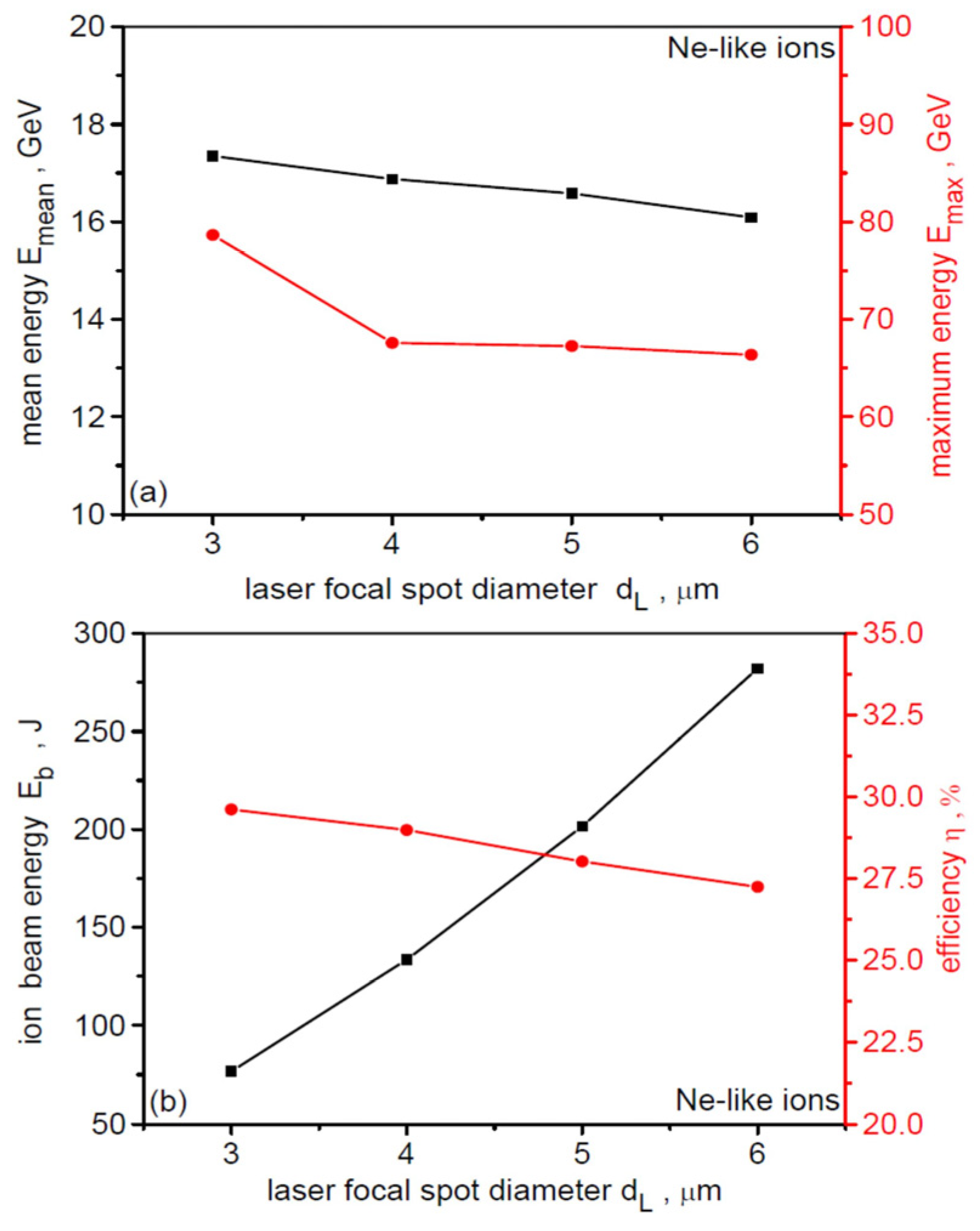
Figure 4 shows the dependence of the mean (Emean) and maximum (Emax) energy of Ne-like ions (a), as well as the Ne-like ion beam energy (Eb) and the laser-to-Ne-like ion energy conversion efficiency (η) (b), on the laser focal spot size. Increasing dL leads to a decrease in the values of Emean and Emax, but the change in these values is small—less than 10% for Emean and ~15% for Emax. Controlling the Ne-like ion energy by changing dL is therefore ineffective. The energy conversion efficiency η is almost independent of dL and is very high—close to 30%. However, the beam energy Eb increases almost parabolically with dL, which is understandable, because at a constant laser intensity, the laser beam energy increases proportionally to dL2.
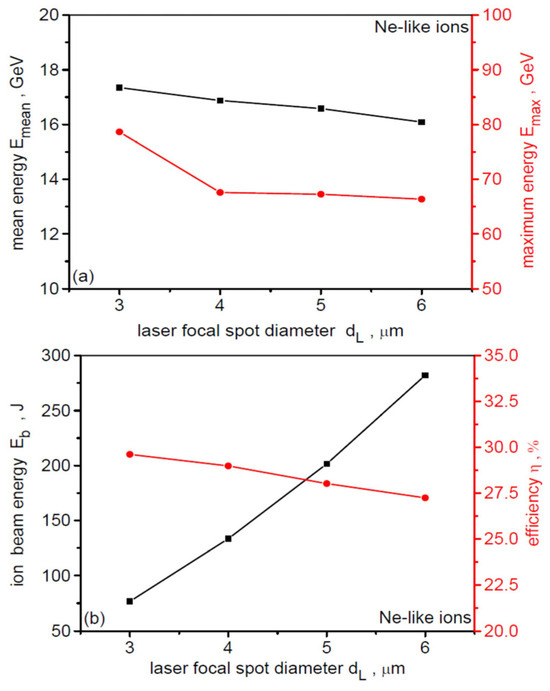
Figure 4.
The dependence of the mean and maximum energy of Ne-like ions (a), as well as the Ne-like ion beam energy and the laser-to-Ne-like ions energy conversion efficiency (b), on the laser focal spot size. LT = 50 nm, t = 240 fs.
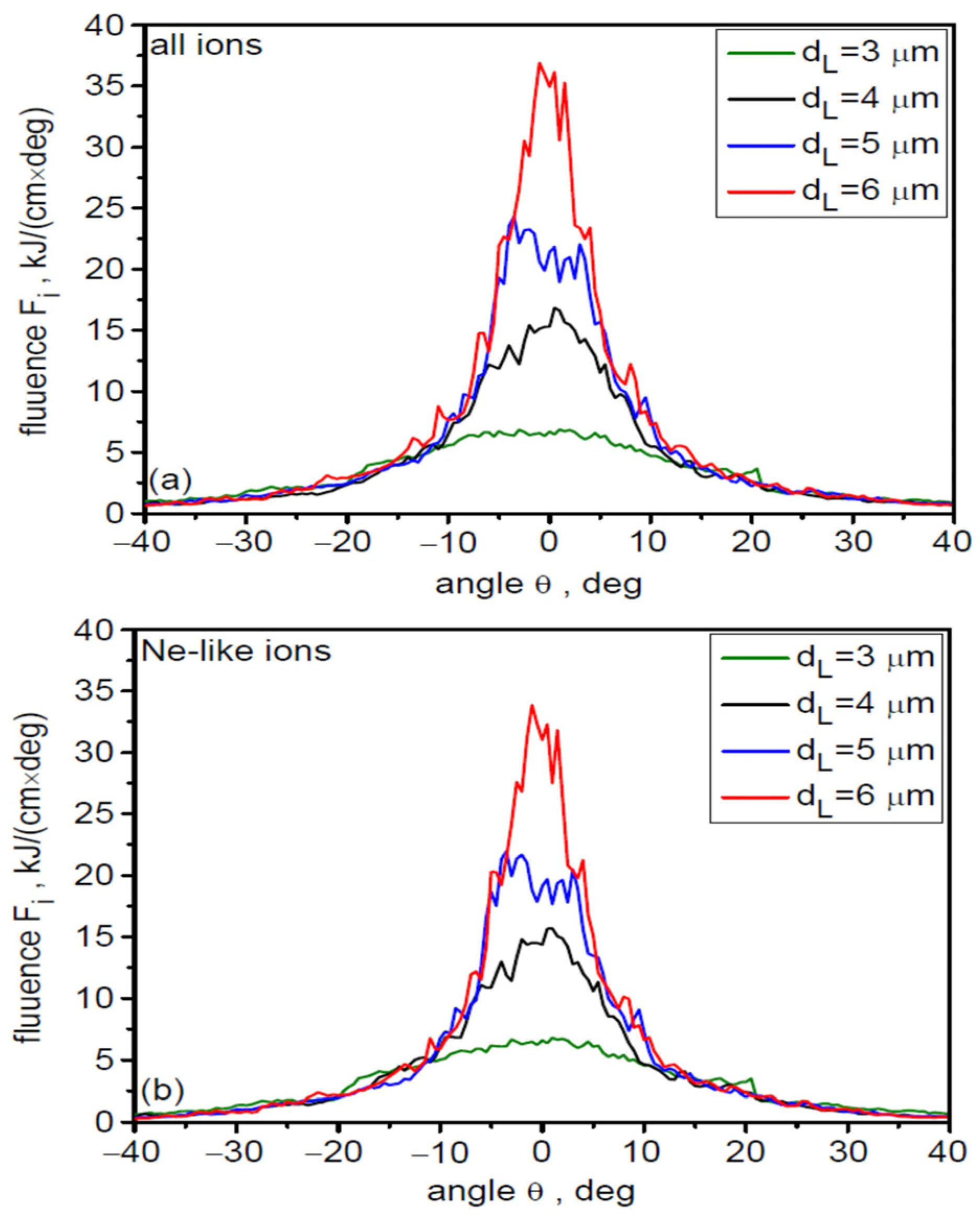
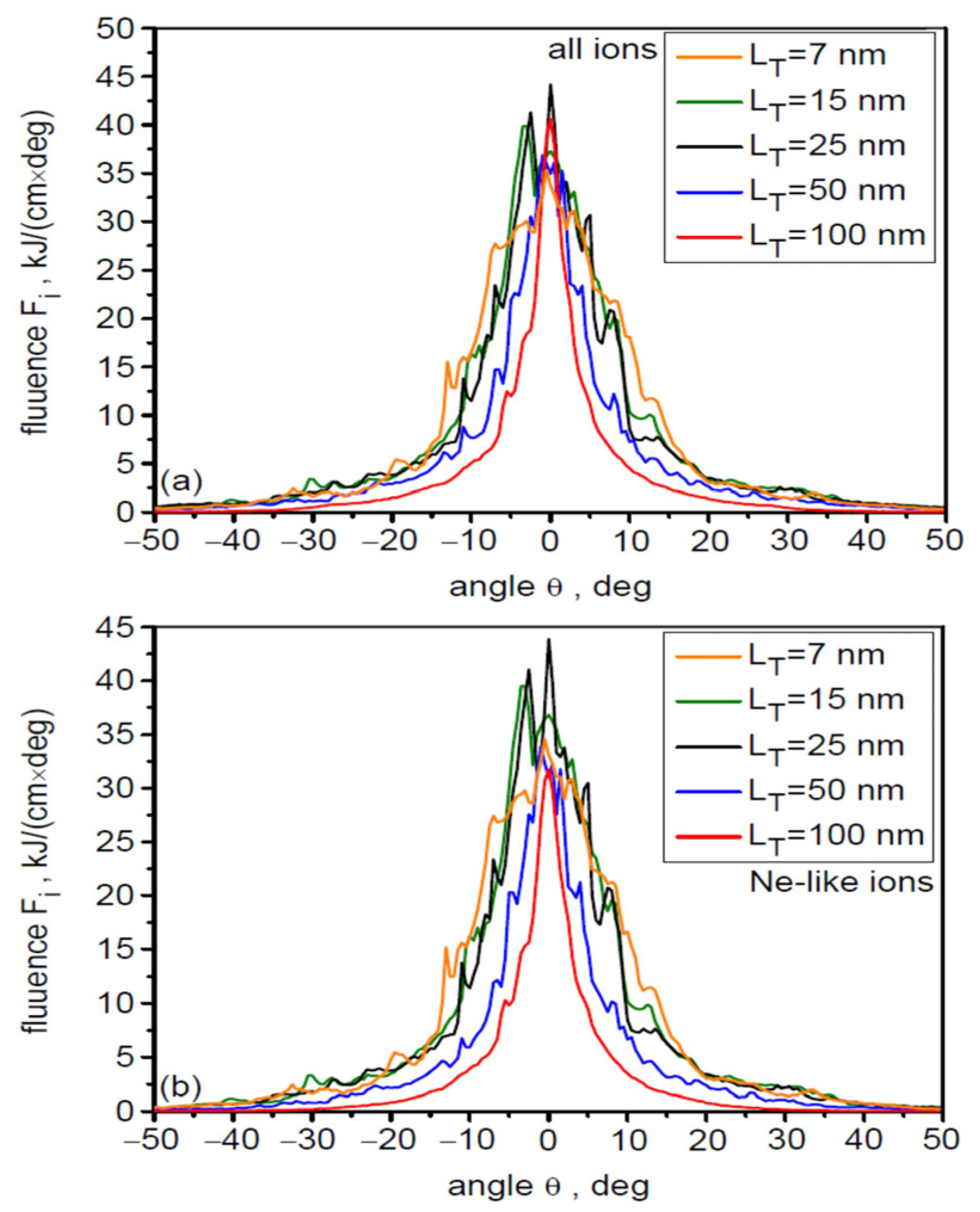
As already mentioned in Section 2, an important parameter of the ion beam, largely determining its practical usefulness, is the beam’s angular divergence. The angular distribution of the fluences of all accelerated uranium ions (a) and Ne-like ions (b) for different values of the laser focal spot size is shown in Figure 5. Both distributions are practically identical. This proves that the beam is mono-charged not only in terms of the energy carried by Ne-like ions, but also that other beam characteristics are completely dominated by this type of ion. The beam’s angular divergence clearly decreases with increasing dL, from ~30 degrees (FWHM) for dL = 3 µm to ~10 degrees for dL = 6 µm. The main cause of the observed changes in angular divergence is the decreasing gradient of laser intensity changes near the laser beam axis with increasing dL. The increase in peak fluence value with dL is primarily the result of increasing beam energy with increasing dL.
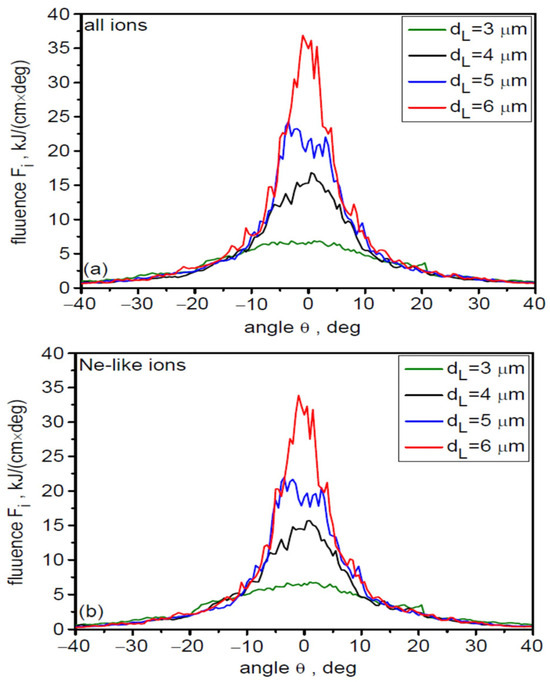
Figure 5.
The angular distribution of the fluences of all accelerated uranium ions (a) and Ne-like ions (b) for different values of the laser focal spot size. LT = 50 nm, t = 240 fs.
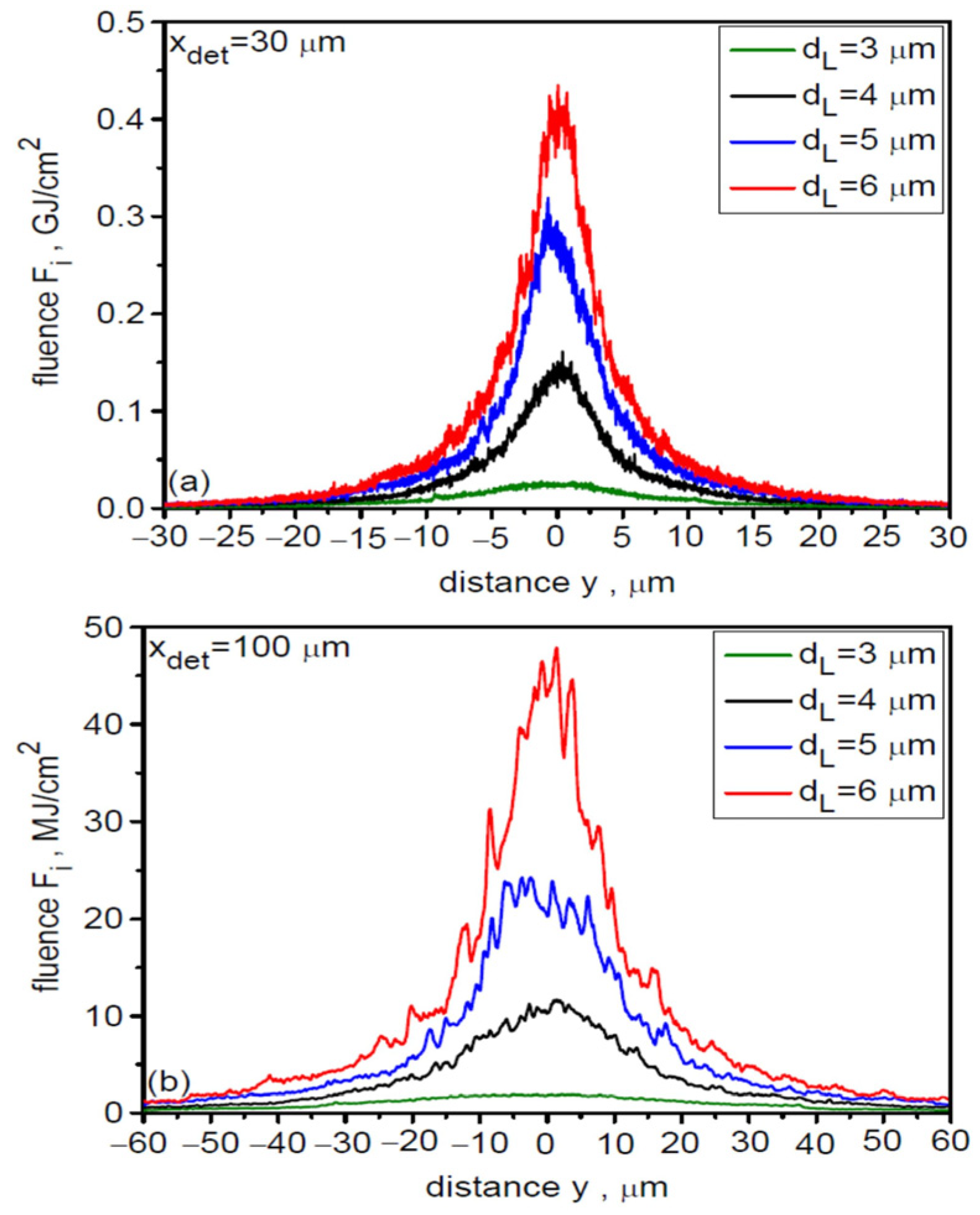
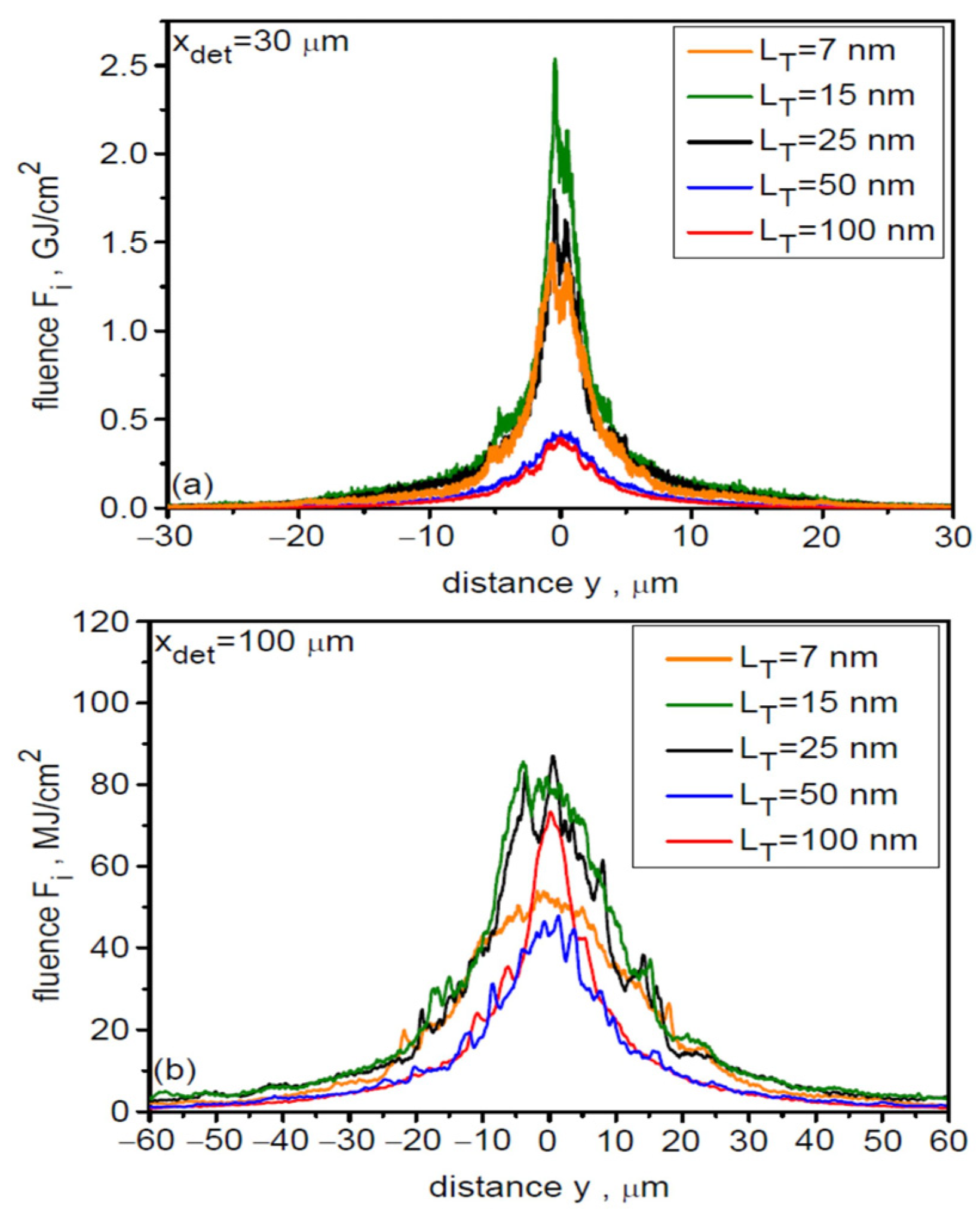
The non-zero angular divergence of the ion beam causes the lateral distribution (along the y and z axes) of the beam fluence to broaden and the peak fluence value to decrease with increasing distance from the target. This is illustrated in Figure 6, which shows the spatial distributions (along the y axis) of fluence for various dL at distances of 30 µm (a) and 100 µm (b) from the target. When determining the absolute fluence values in these distributions, a 3D correction was used to account for the fact that the ion beam propagates in three-dimensional space. With increasing distance from the target, the distribution broadens and the peak fluence decreases quite quickly, but also the difference between the peak fluence for large and small dL increases, which is the result of different angular divergences of beams with different dL.
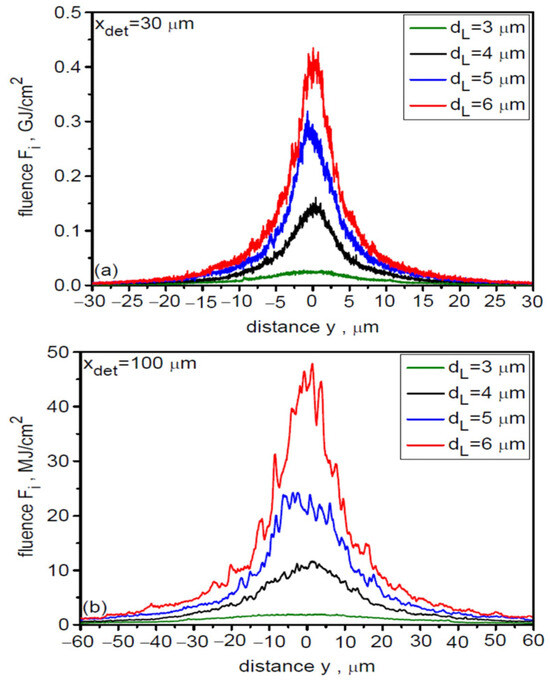
Figure 6.
The spatial distributions of fluence for various laser focal spot sizes at distances of 30 µm (a) and 100 µm (b) from the target. LT = 50 nm, t = 240 fs.
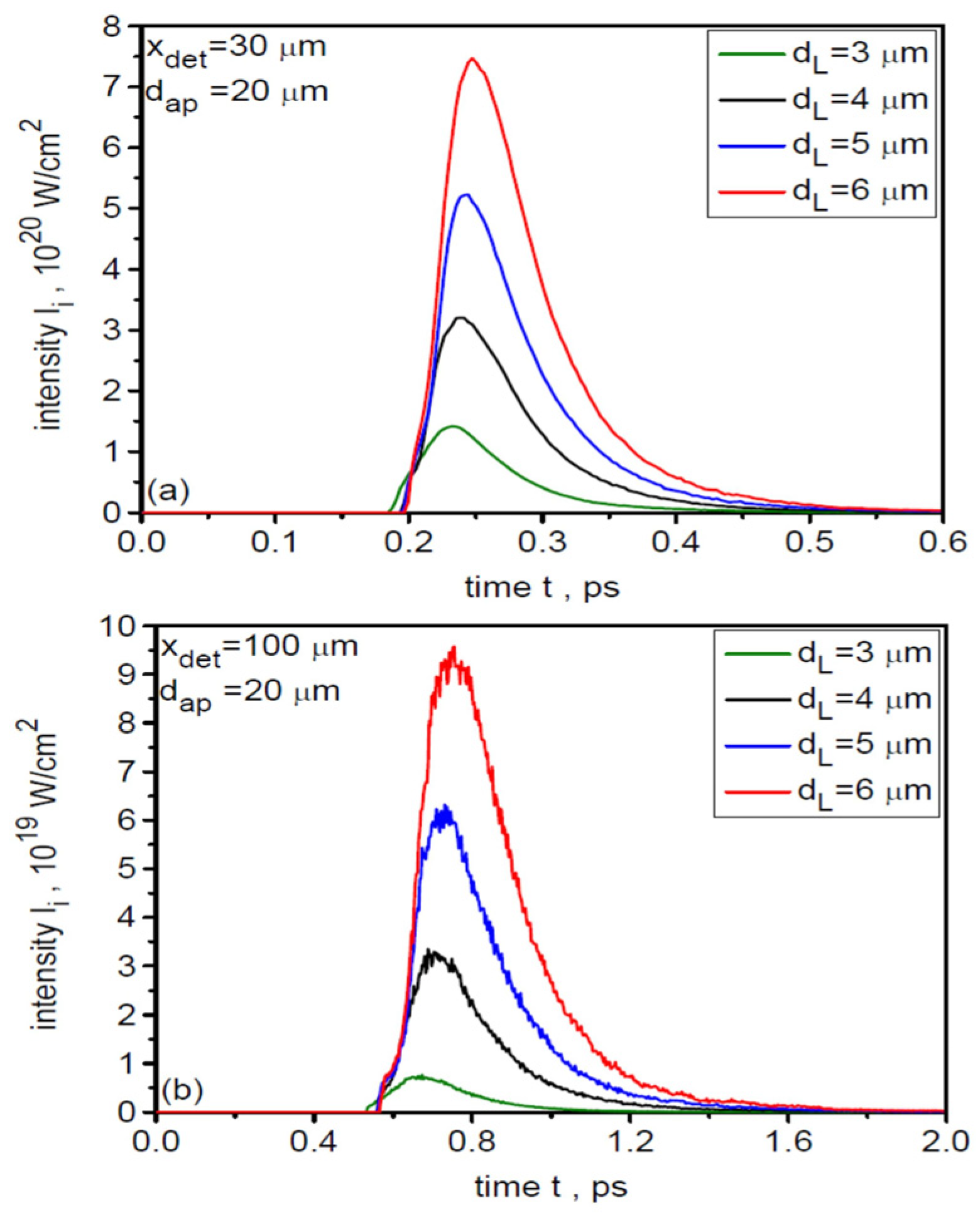
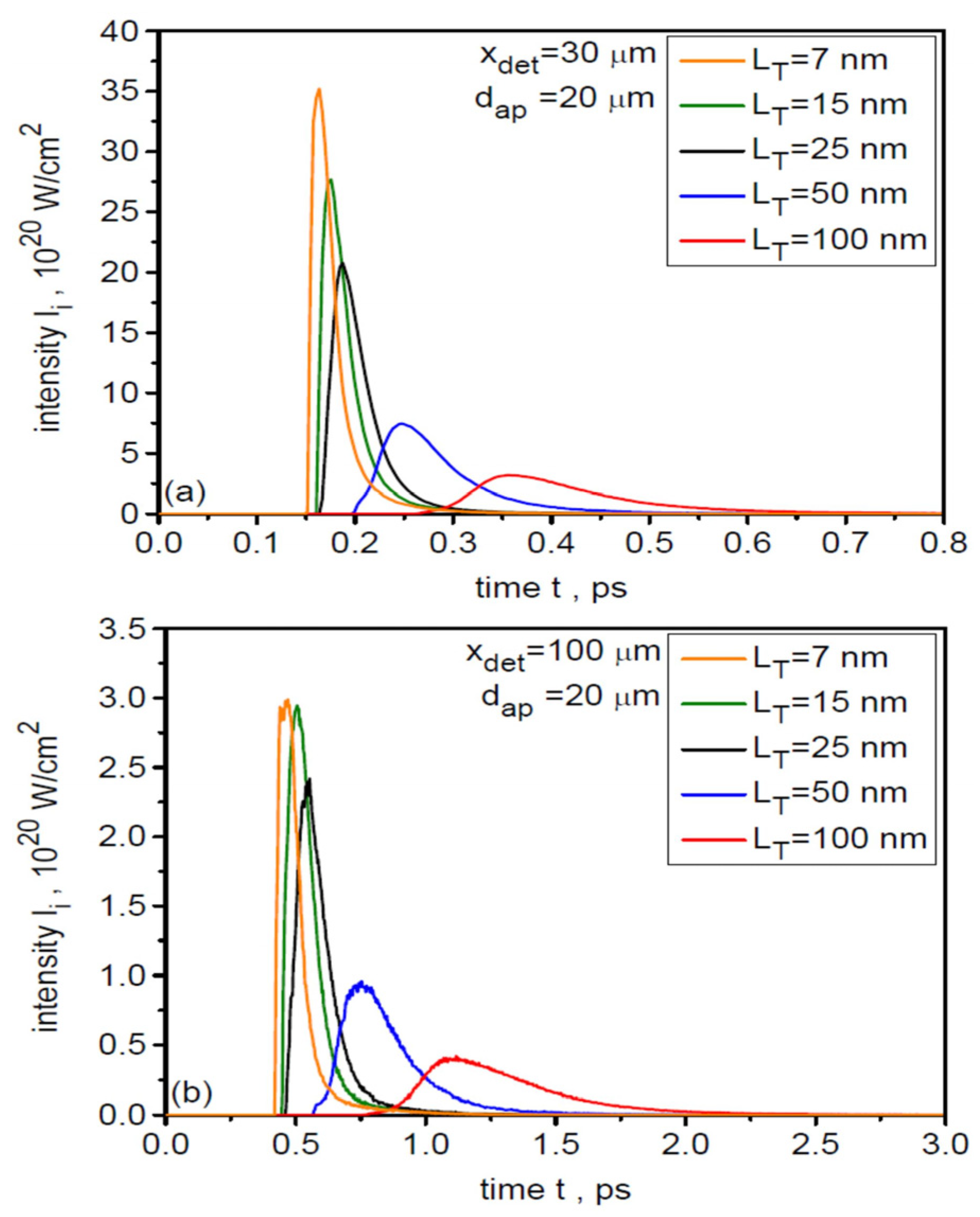
In studies of ion beam interactions with matter, an important beam characteristic that largely determines the course of the interaction process is the temporal shape of the beam intensity and the ion pulse duration. Figure 7 shows the temporal distributions of the uranium ion beam intensity (averaged over a 20-µm region) at distances x = 30 µm and 100 µm from the target for various laser focal spot sizes. A 3D correction was applied to determine the absolute intensity values in these distributions. As dL increases, the peak intensity of the ion pulse increases quite rapidly (primarily due to the increase in laser energy), while its duration changes only slightly and is very short, even shorter than the laser pulse duration. Changing the distance from the target from 30 µm to 100 µm leads to a decrease in the peak intensity by about an order of magnitude and a lengthening of the ion pulse from ~0.08 ps (FWHM) to ~0.25 ps. The change in peak intensity with increasing x is a result of both the non-zero angular divergence of the ion beam and ion velocity dispersion, while the lengthening of the ion pulse is caused by ion velocity dispersion.
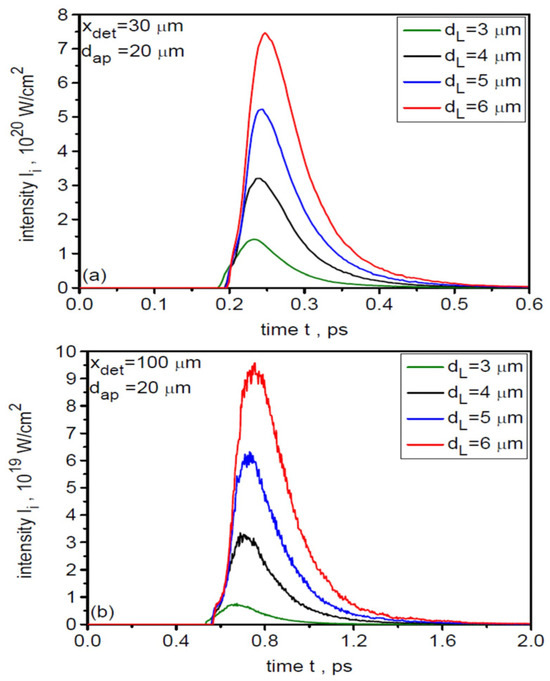
Figure 7.
The temporal distributions of the uranium ion beam intensity (averaged over a 20-µm region) at distances x = 30 µm (a) and 100 µm (b) from the target for various laser focal spot sizes. LT = 50 nm.
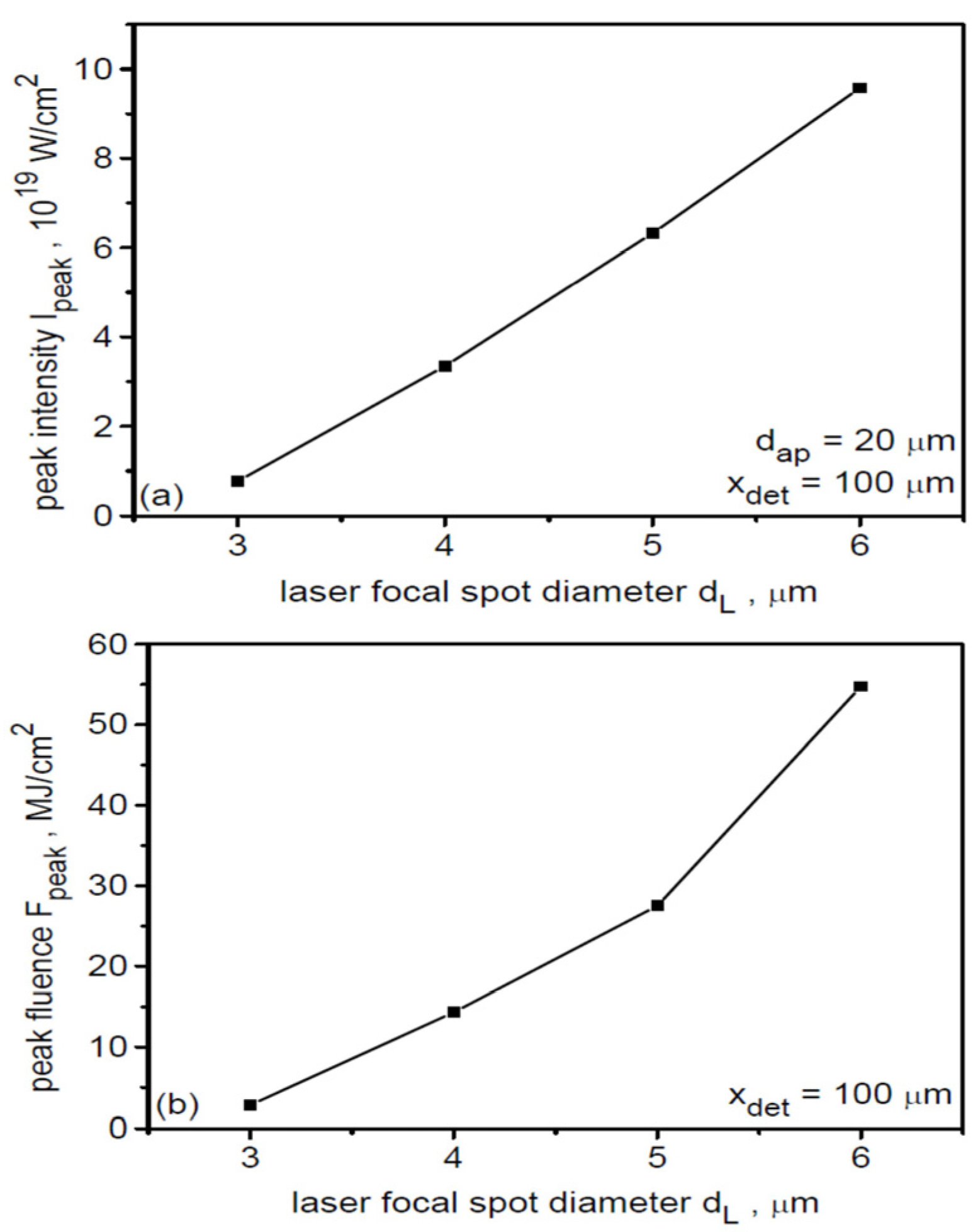
A quantitative summary of the changes in the peak intensity and peak fluence of the ion beam with variations in the laser focal spot size at distances from the target much larger than the initial ion source size (x = 100 µm > 10 dL) is presented in Figure 8. Both parameters increase very rapidly with increasing dL: changing dL from 3 μm to 6 μm results in increases in Ipeak and Fpeak by more than an order of magnitude.
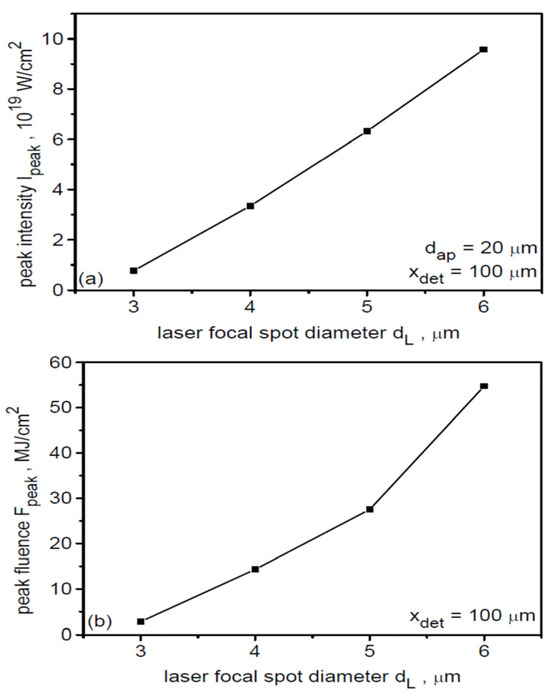
Figure 8.
The peak intensity (a) and peak energy fluence (b) of the ion beam as a function of the laser focal spot size at the distance of 100 µm from the target. LT = 50 nm, t = 240 fs.
In summary, changing the laser focal spot size dL at a fixed laser intensity and target thickness leads to small changes in the mean and maximum energy of uranium ions and the laser-to-ions energy conversion efficiency. Therefore, changing dL is not an effective way to control ion energy over a wide range. On the other hand, the dL variation results in very rapid changes in the peak intensity and peak fluence of the ion beam and can generally be used to control these beam parameters in possible beam-target interaction studies. It should be noted, however, that rapid changes in ion beam fluence and intensity with dL at fixed IL and LT require changes in laser energy, which is a definite disadvantage of this method of controlling these ion beam parameters.
4.2. The Effect of the Target Thickness on the Properties of the Uranium Ion Beam
Modern target technology enables the production of high-quality targets of various thicknesses, shapes, and structures [67,68], including flat high-Z metal targets with thicknesses ranging from a few nm to several hundred nm, which are particularly desirable for laser acceleration of super-heavy ions [7]. It is well known that changing the target thickness leads to changes in the properties of the generated ion beam, but the magnitude and dynamics of these changes strongly depend on the laser parameters and the type of accelerated ions. To assess whether varying the target thickness allows for effective control of ion beam parameters, it is necessary to analyze the quantitative changes in these parameters at fixed laser parameters. In this subsection, we will investigate how changing the thickness of a uranium target illuminated with a 30-fs laser pulse with an intensity of 1023 W/cm2 and a laser focal spot size of 6 µm affects the uranium ion beam parameters crucial for ultra-intense ion beams and their possible applications. Given a fixed uranium pre-plasma density profile and its total thickness of 184 nm (see Section 3), the thickness of the solid part LT of the target was varied from 7 nm to 100 nm. Since the effective pre-plasma thickness (at 1/e maximum density) was ~20 nm, the effective uranium target thickness Leff varied from ~20 + 7 nm to ~20 + 100 nm.
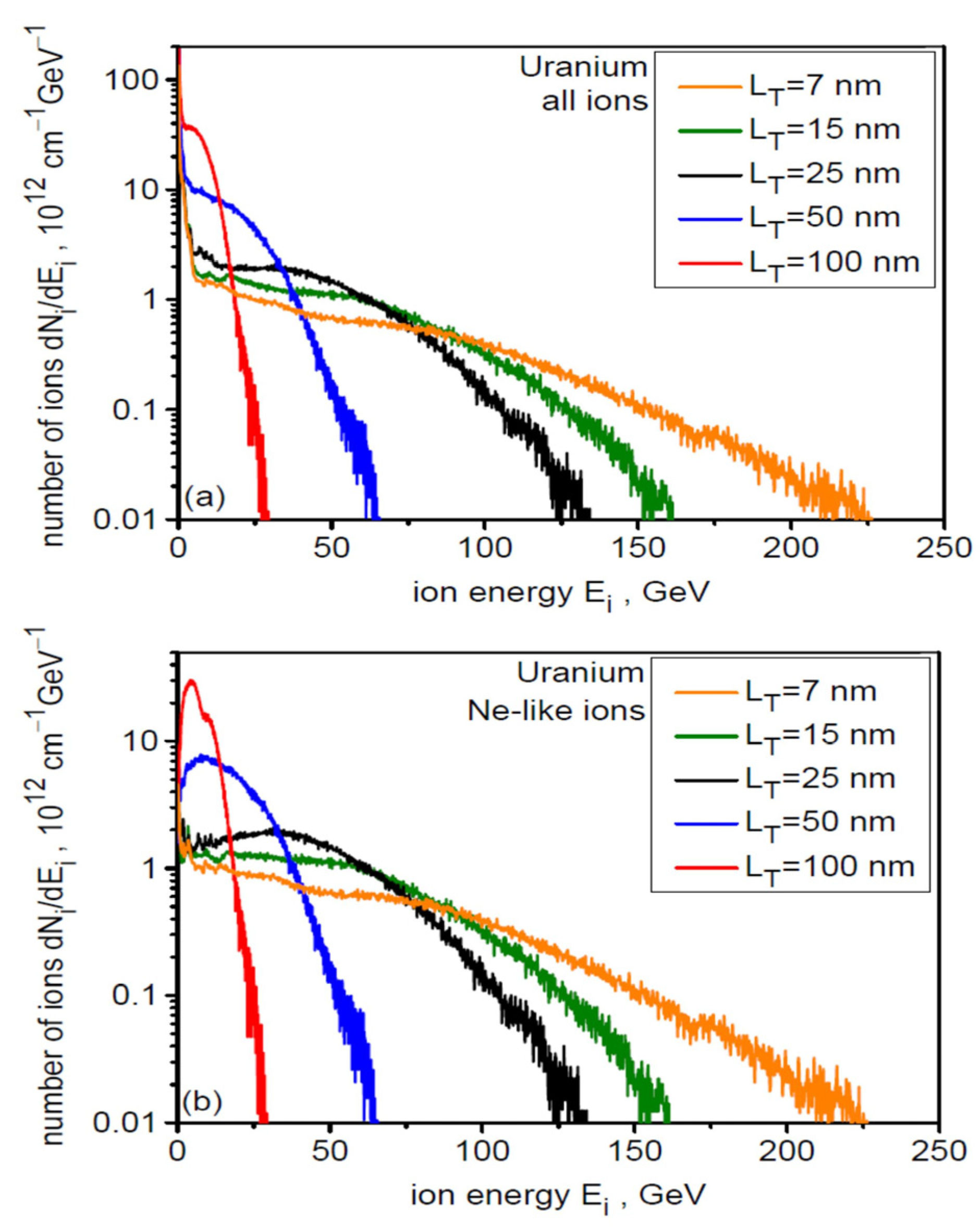
Figure 9 presents the ionization spectra of U ions in the final stage of acceleration for four different uranium target thicknesses (its solid part) LT. The general structure of the spectrum is practically independent of LT, whereas the populations of individual ion species (ions with a given Z) depend on the target thickness. In all cases considered, the most numerous are Ne-like ions (Z = 82), which, due to the highest Z/A ratio, should be accelerated most efficiently. This is confirmed by Figure 10, which presents the energy spectra for all accelerated ion species (a) and for Ne-like ions (b) for six thicknesses of the constant target part LT. As can be seen from the figure, the high-energy part of the spectrum is completely dominated by Ne-like ions regardless of the target thickness, with the highest ion energies achieved with the thinnest targets.
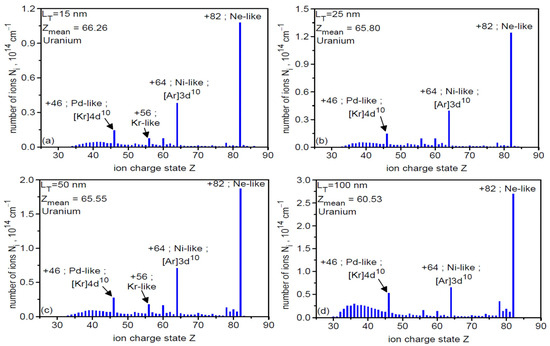
Figure 9.
The ionization spectra of uranium ions in the final stage of acceleration for four different uranium target thicknesses (LT = 15 nm (a), LT = 25 nm (b), LT = 50 nm (c), LT = 100 nm (d)). The laser focal spot size dL = 6 µm, t = 240 fs.
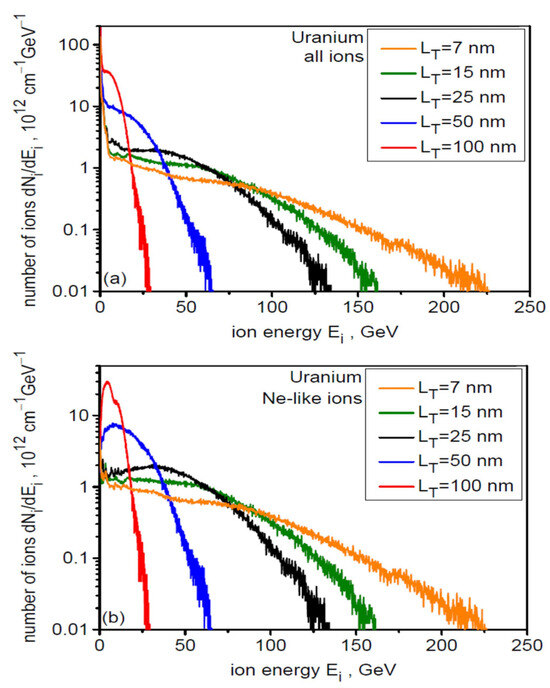
Figure 10.
The energy spectra for all accelerated ion species (a) and for Ne-like ions (b) for different uranium target thicknesses LT. dL = 6 µm, t = 240 fs.
The quantitative contribution (in percentage) of the energy carried by Ne-like ions to the energy of the entire uranium beam as a function of target thickness for three ion energy ranges is presented in Figure 11. The upper scale bar in this figure also provides the effective target thicknesses Leff (including the pre-plasma thickness) in Lop units. In the theoretical description of the RPA mechanism, Lop is the optimal target thickness ensuring the highest RPA acceleration efficiency and is described by the formula [2]:
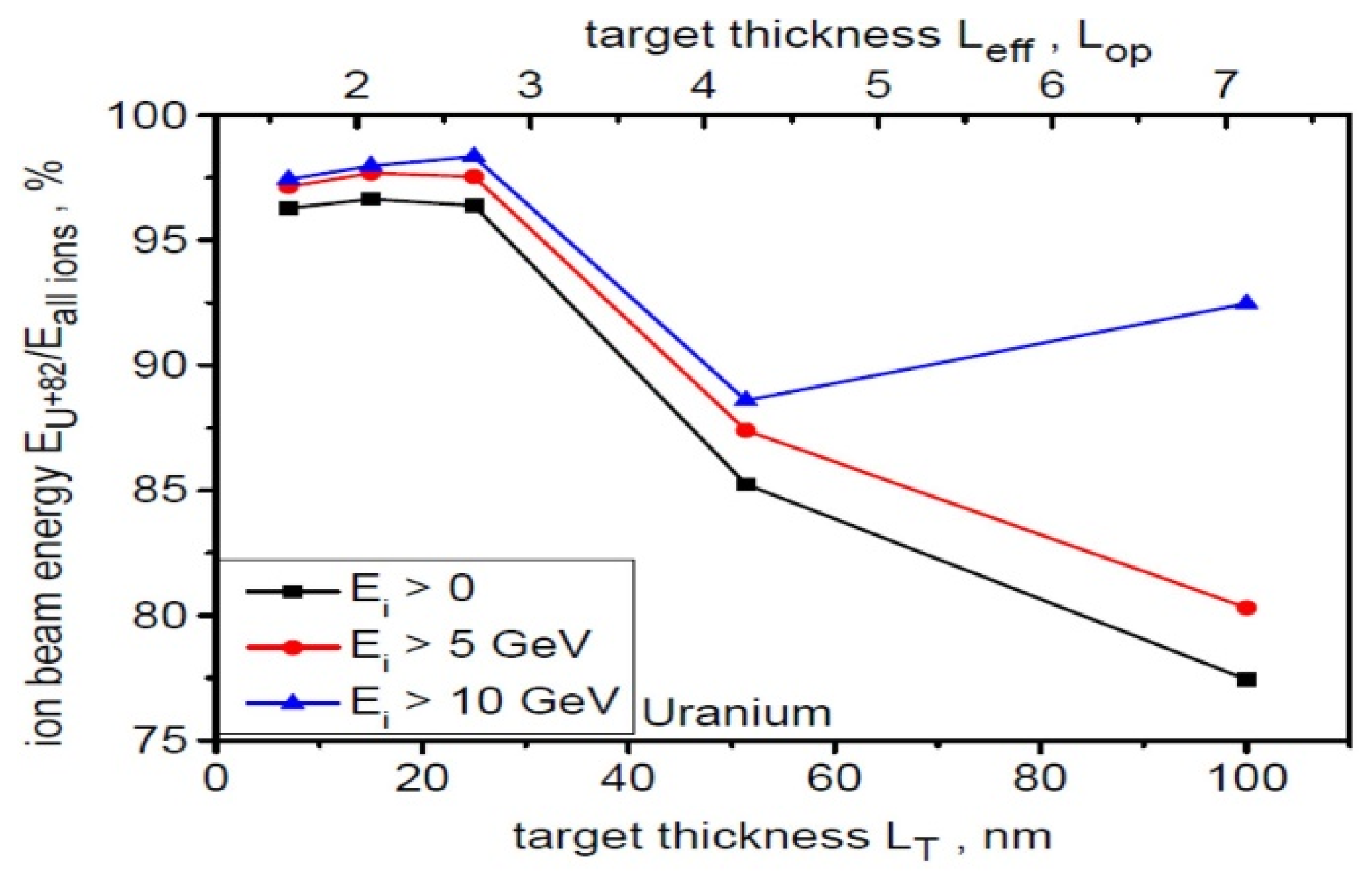
where is a dimensionless amplitude of the laser pulse, is critical plasma density, ne is electron density, is the laser wavelength, is amplitude of the electric field of the laser pulse, is angular frequency of the laser pulse, is electro charge, is electron mass and is speed of light. For a uranium target and for laser intensity equal of 1023 W/cm2 and , . As can be seen from Figure 11, the contribution of the energy carried by Ne-like ions to the entire beam energy is highest for the thinnest targets used () and, depending on the assumed ion energy range, ranges from 96% (for Ei > 0) to 98% (for Ei > 10 GeV). For thicker targets, the contribution of Ne-like ion energy to the overall beam energy is noticeably lower, reaching values of ~80–90%. Changing the target thickness therefore enables quite effective control of the ion beam’s mono-charge degree without changing the laser parameters.
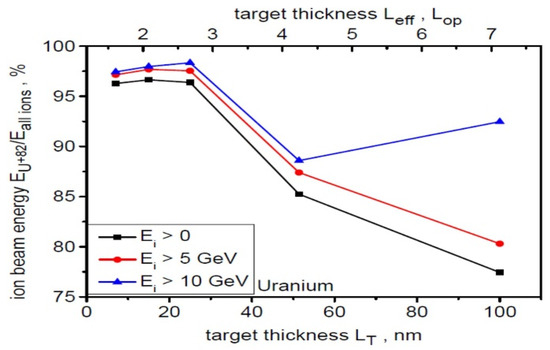
Figure 11.
The quantitative contribution (in percentage) of the energy carried by Ne-like ions to the energy of the entire uranium beam as a function of target thickness for three ion energy ranges. dL = 6 µm, t = 240 fs.
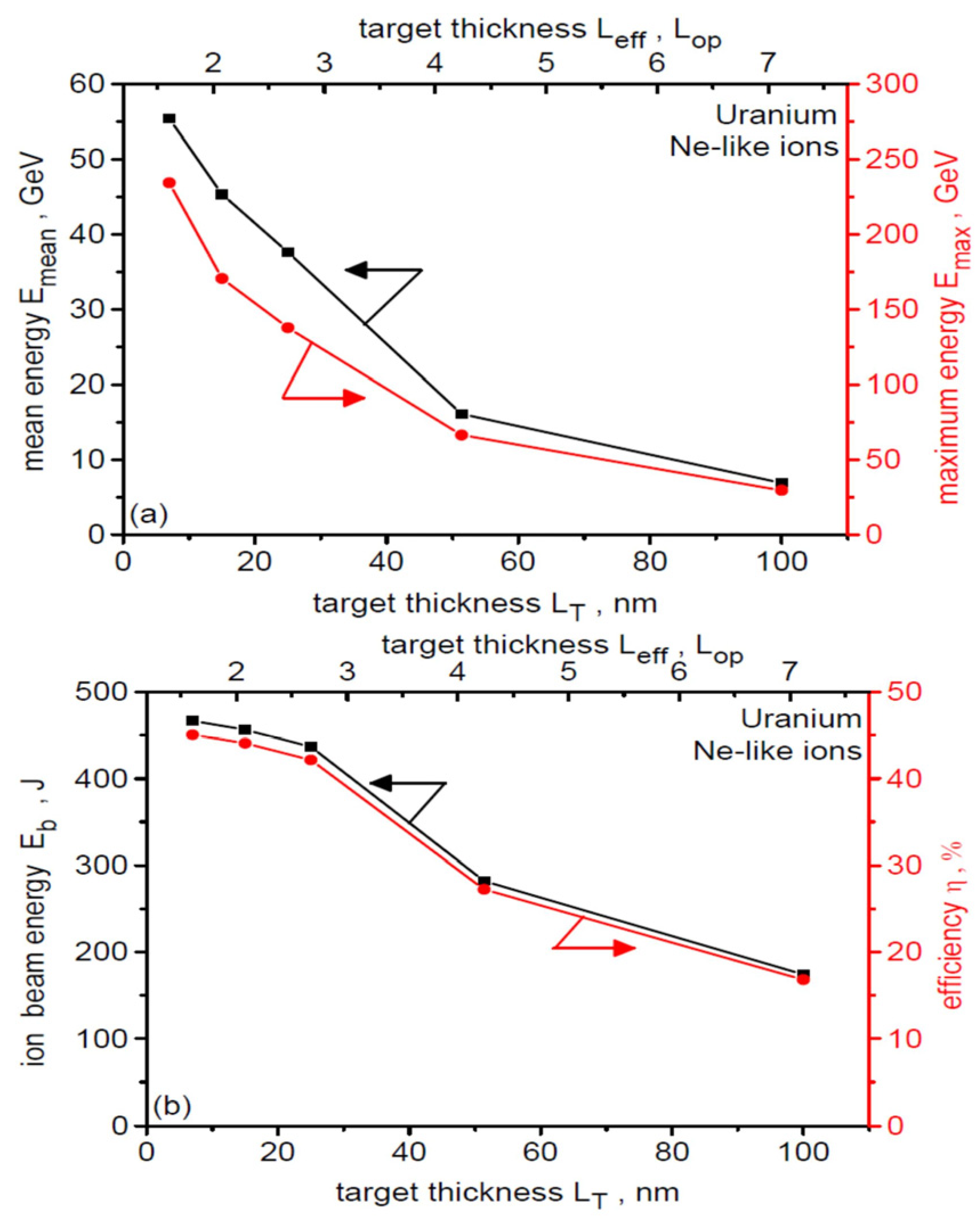
The effect of target thickness on the mean and maximum energy of Ne-like ions (a) and on the total energy of these ions and the energy efficiency of their acceleration (b) is illustrated in Figure 12. Both Emean and Emax of Ne-like ions increase quite rapidly with decreasing target thickness (a change in Leff by a factor of 4.4 leads to a change in ion energy by an order of magnitude), and for the thinnest target with Leff = 1.6 Lop, they reach 55 GeV and 234 GeV, respectively. Decreasing target thickness also results in an increase in the energetic efficiency of Ne-like ion acceleration, and for the thinnest target, this efficiency reaches a very high value of close to 45%. Variation of target thickness can therefore be a simple and effective way to control the mean and maximum energy of uranium ions.
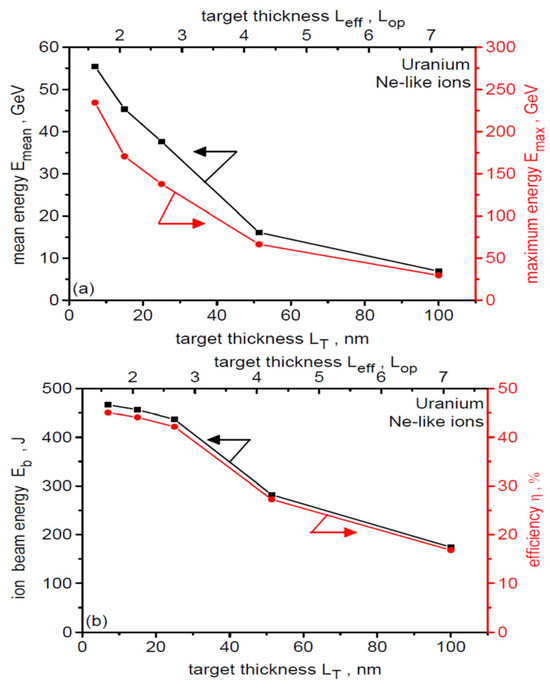
Figure 12.
The effect of target thickness on the mean and maximum energy of Ne-like ions (a) and on the total energy of these ions and the laser-to-Ne-like ions energy conversion efficiency (b). The arrows in the figure assign a given graph to the appropriate y-axis. dL = 6 µm, t = 240 fs.
The target thickness has a significant effect on the angular and spatial (transverse) distributions of ion energy fluence and the temporal shape of the ion pulse, as well as the peak values of fluence and intensity of the ion beam. This is illustrated in Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15. Figure 13 shows the angular distributions of fluence for all accelerated uranium ions (a) and Ne-like ions (b) for the five considered target thicknesses LT. These distributions for all ions and Ne-like ions are practically identical, which is the result of the clear dominance of Ne-like ions in the ion beam. An increase in LT leads to a decrease in the beam angular divergence, the main reason for which in the considered cases is the decreasing contribution of the CEA mechanism in the acceleration process. As LT increases, the spatial distribution of the ion beam fluence also narrows, as illustrated in Figure 14 for two distances from the target (x = 30 µm and 100 µm). Increasing the distance from the target leads to a broadening of the distribution and a significant reduction in the peak fluence.
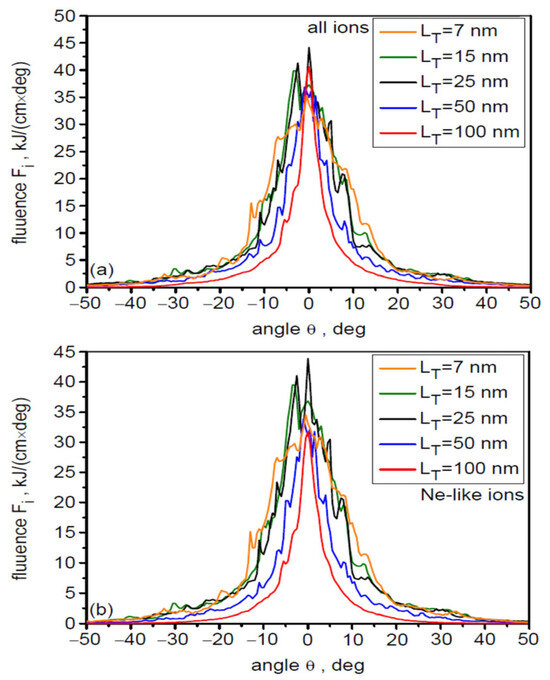
Figure 13.
The angular distributions of ion beam energy fluence for all accelerated uranium ions (a) and Ne-like ions (b) for five target thicknesses LT. dL = 6 µm, t = 240 fs.
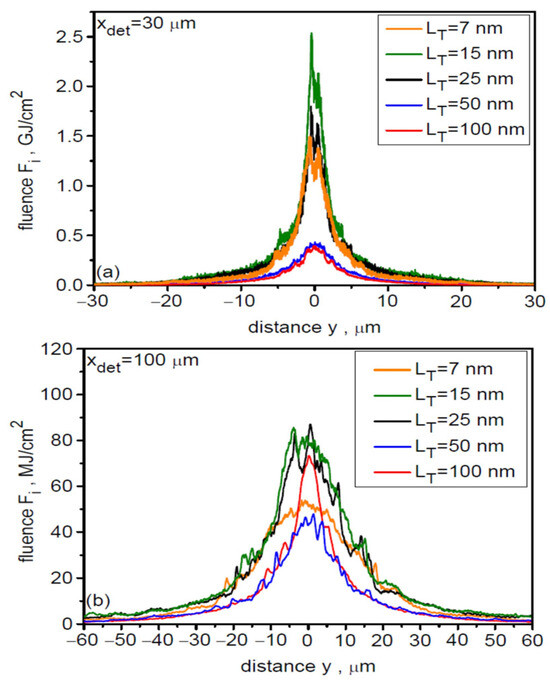
Figure 14.
The spatial distributions of ion beam energy fluence for all accelerated uranium ions at distances x = 30 µm (a) and 100 µm (b) from the targets with various thicknesses. dL= 6 µm.
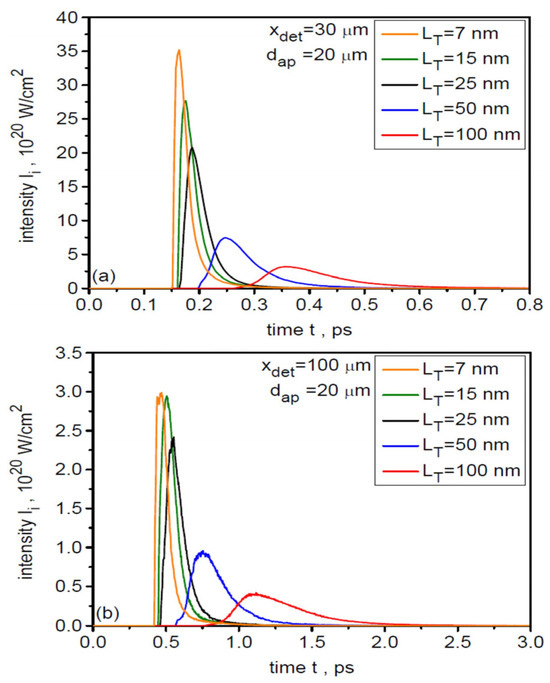
Figure 15.
The temporal distributions of ion beam intensity (averaged over a 20-µm region) for all accelerated uranium ions at distances x = 30 µm (a) and 100 µm (b) from the targets with various thicknesses. dL = 6 µm.
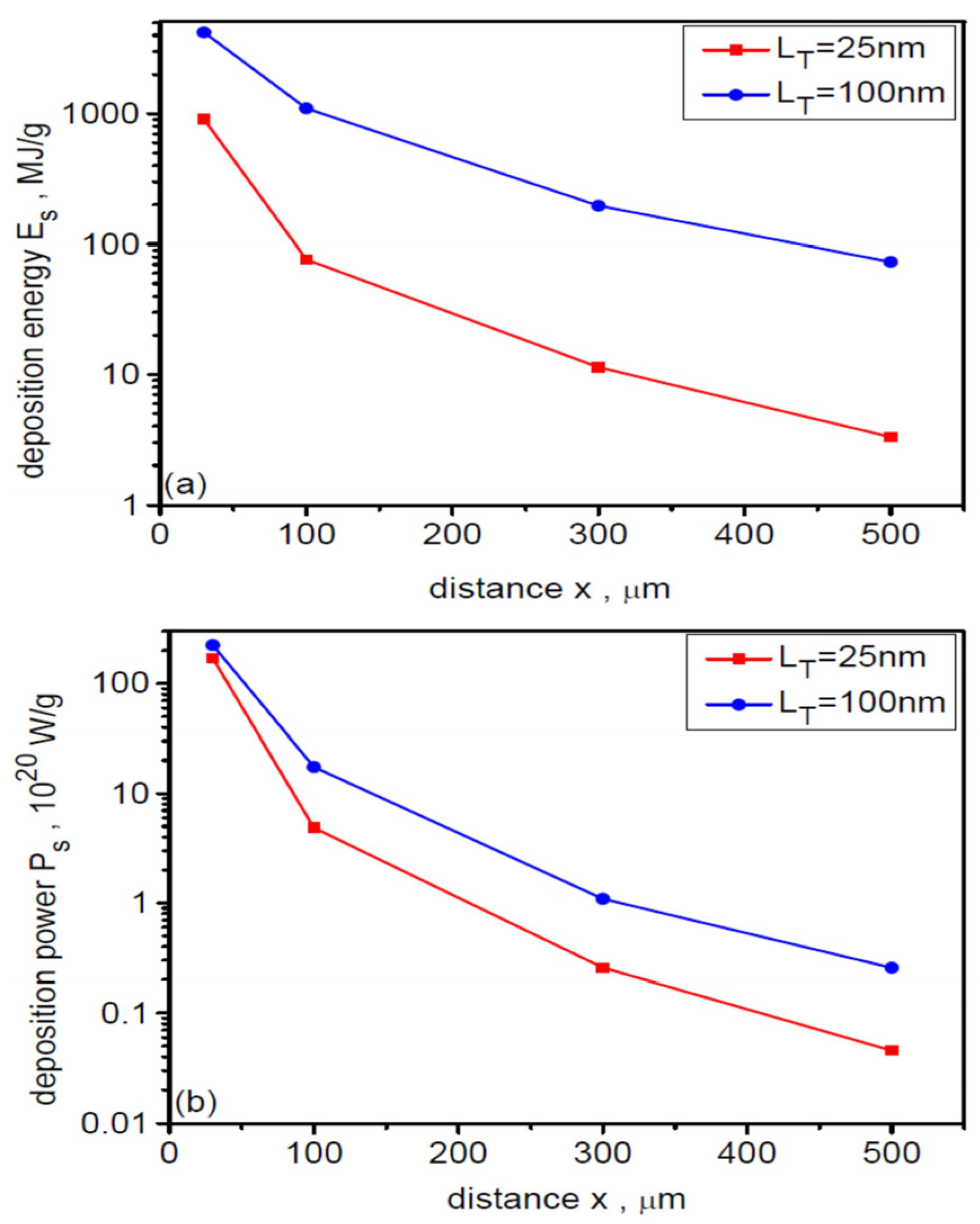
In the case of temporal distributions of the ion beam intensity, increasing the target thickness leads to a broadening of the temporal distribution (ion pulse duration) and a reduction in the peak intensity (Figure 15). This is due to the decreasing ion energy with increasing dL. As the distance from the target x increases, the peak ion pulse intensity decreases (due to both the angular divergence of the beam and ion velocity dispersion) and its duration increases (due to ion velocity dispersion). For the thinnest targets with LT ≤ 15 nm (Leff ≤ 35 nm), the ion pulse peak intensity decreases from ~30 × 1020 W/cm2 at x = 30 μm to ~3 × 1020 W/cm2 at x = 100 µm, while its duration increases from ~50 fs to ~200 fs (FWHM). Considering that the ion pulse energy is >400 J (Figure 12b), the ion pulse power is ~8 PW at x = 30 µm and ~2 PW at x = 100 µm, thus being in the multi-PW range in both cases.
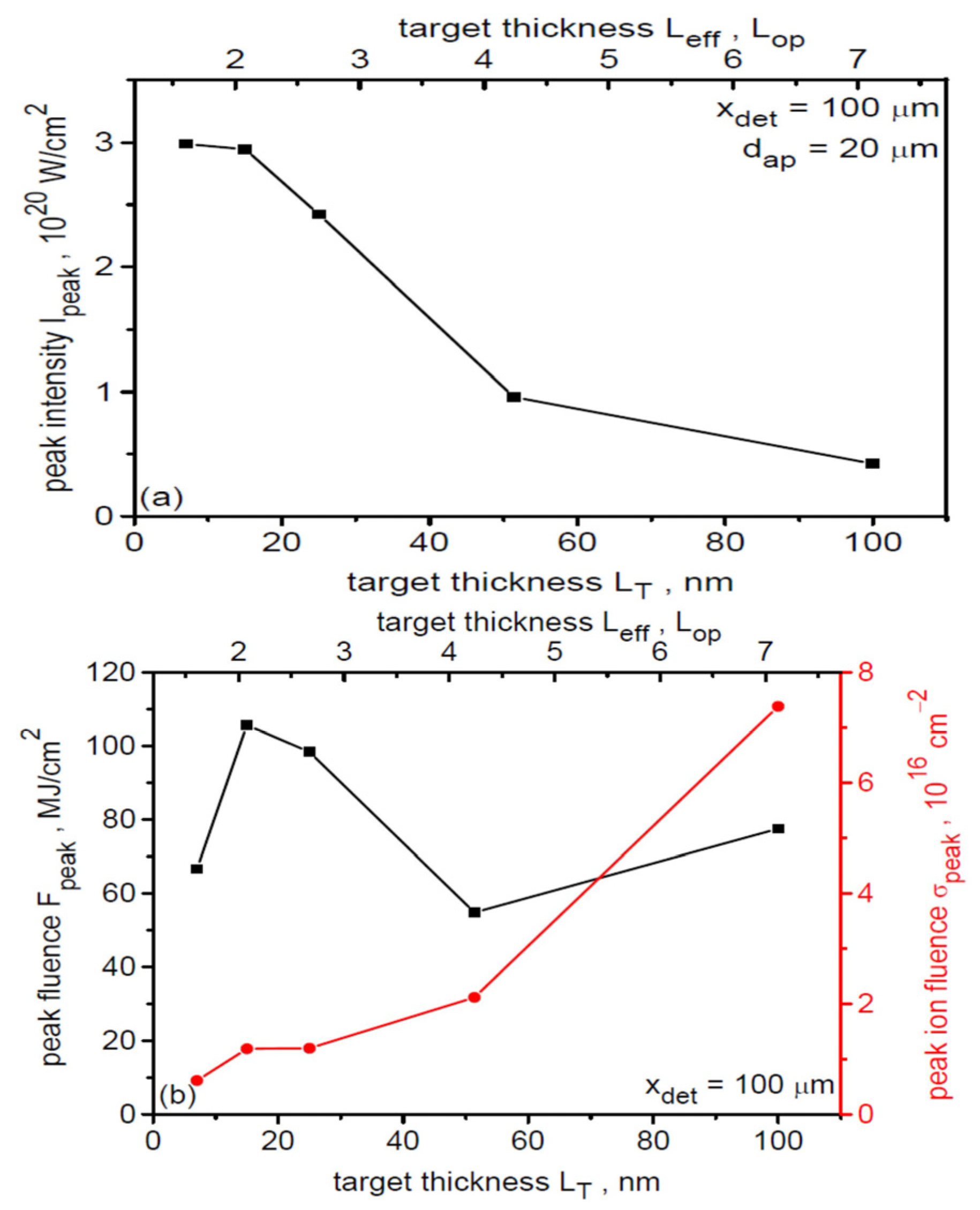
The dependence of the peak values of the intensity (a) as well as energy and ion fluences (b) of the ion beam on the target thickness is presented for 100 µm from the target in Figure 16. A 3D correction was used to determine these values (also for the graphs in Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15). The beam intensity decreases from ~3 × 1020 W/cm2 for LT = 7 and 15 nm to ~0.5 × 1020 W/cm2 for LT = 100 µm. This course of the dependence is primarily determined by the relatively rapid reduction of ion energy with increasing dL (Figure 12), which has a greater impact on the change in beam intensity than possible increase in ion density ni accompanying increasing LT (Ii = niEi3/2). In the case of peak energy fluence of the beam, its dependence on dL is nonmonotonic with a clear maximum at LT = 15 nm (Leff ~ 2 Lop). This is because energy fluence linearly depends on both the areal ion density (ion fluence) σi and the ion energy Ei, i.e., Fi = σiEi, and for sufficiently small target thicknesses, the increase in Ei accompanying the reduction in dL cannot compensate for the reduction in ion areal density. On the other hand, the peak ion fluence σpeak increases with increasing LT because a higher number of ions is accelerated in the case of thicker targets. It should be added that also in the case of Ipeak (dL) dependence on target thickness, a decrease in intensity can be expected for very thin targets with Leff < Lop. For such targets, the sharp decrease in σi due to the relativistic transparency of the plasma could not be compensated by the increase in ion energy and thus the peak beam intensity would decrease. With the fixed effective pre-plasma thickness assumed to be Leff ~ 20 nm > Lop ~ 15 nm, it is not possible to demonstrate this case.
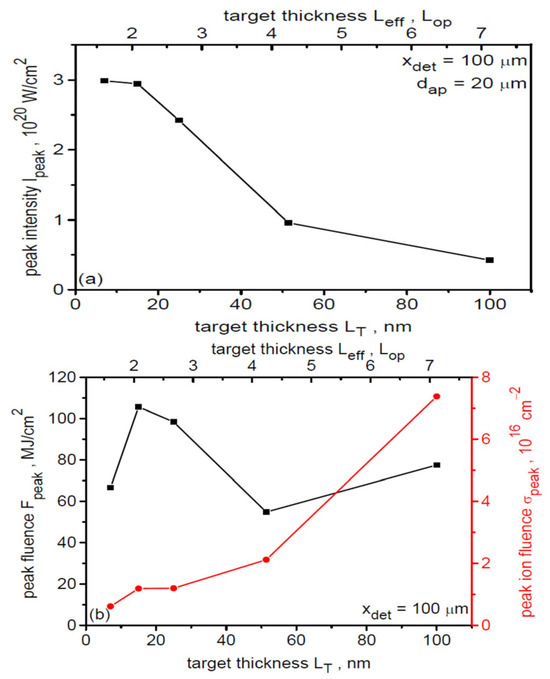
Figure 16.
Dependence of the peak intensity (a) and peak energy fluence and peak ion fluence (b) of the ion beam on the target thickness. dL = 6 µm, x = 100 µm.
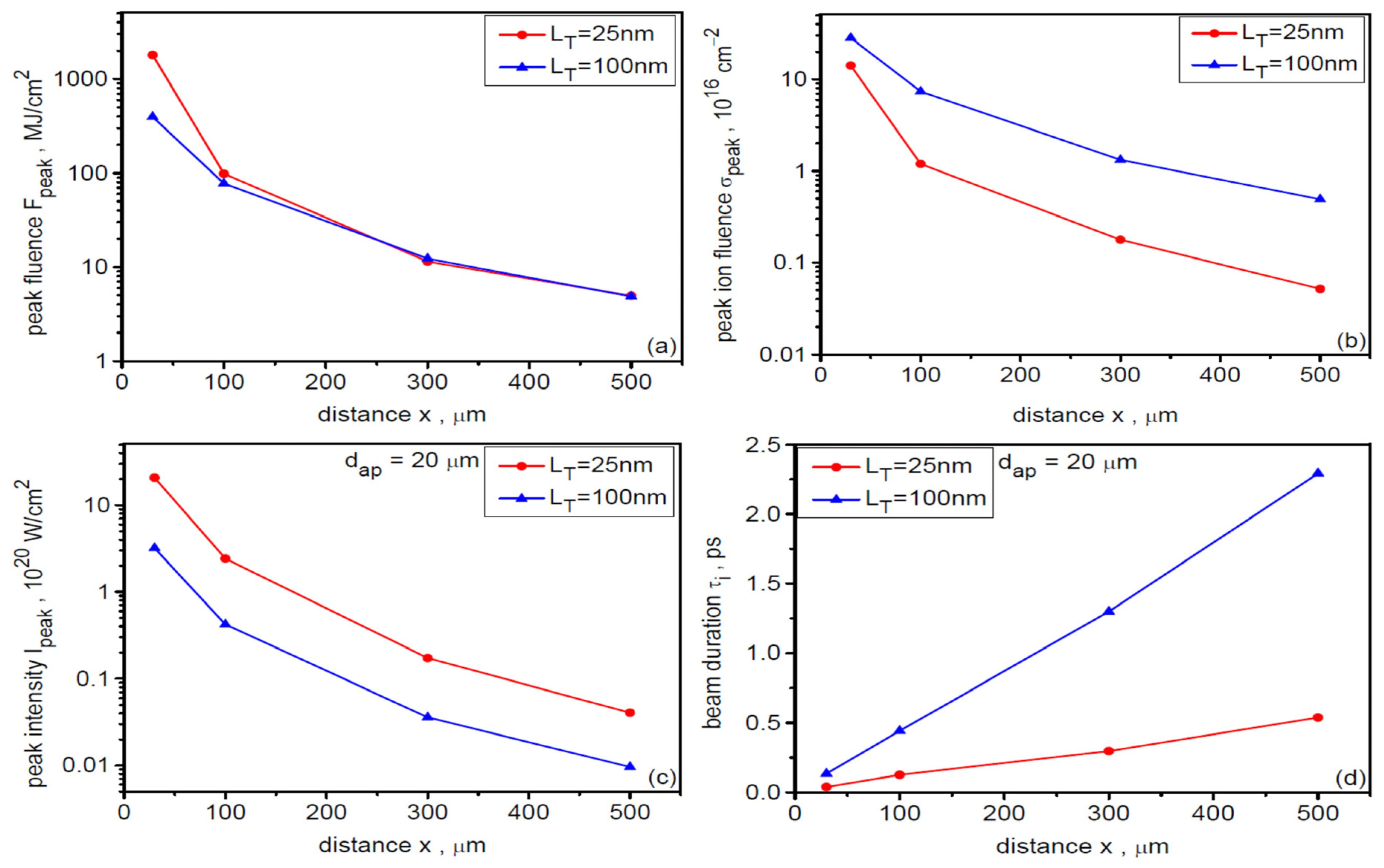
As demonstrated in Figure 14 and Figure 15, the peak intensity and peak energy fluence of the ion beam as well as the ion pulse duration depend on the distance of the beam detection point, x, from the target. The dependence of these values as well as peak ion fluence on x over a wide range from x = 30 µm to x = 500 µm for three target thicknesses LT is shown in Figure 17. With increasing x, the Ipeak, Fpeak and σpeak values decrease quite rapidly, while the ion pulse length increases. For thinner targets, the intensity decreases from very large values exceeding 1021 W/cm2 at x = 30 µm to ~5 × 1018 W/cm2 at x = 500 µm. For the thickest target, the peak intensity also changes by nearly three orders of magnitude, but the intensities are several times lower. As mentioned earlier, this strong intensity decrease with increasing x is the result of the combined effect of beam angular divergence and ion velocity dispersion on beam propagation. Due to beam angular divergence, the peak beam fluence changes from ~2 GJ/cm2 for x = 30 µm to ~5–7 MJ/cm2 for x = 500 µm. The differences in fluence values for targets of different thicknesses are not very large, especially for x > 100 µm. However, the changes in ion pulse duration with increasing x are very large for different dL: for thinner targets, these changes range from several tens of fs to several hundred fs, while for the thickest target, the ion pulse duration varies from ~100 fs for x = 30 µm to ~2.3 ps for x = 500 µm. It is worth adding that the considered changes in Ipeak, Fpeak, σpeak and τi with increasing x occur with practically unchanged ion energy, because at x > 50 μm the fields accelerating the ions are so small that very heavy uranium ions are insensitive to these fields and move ballistically.
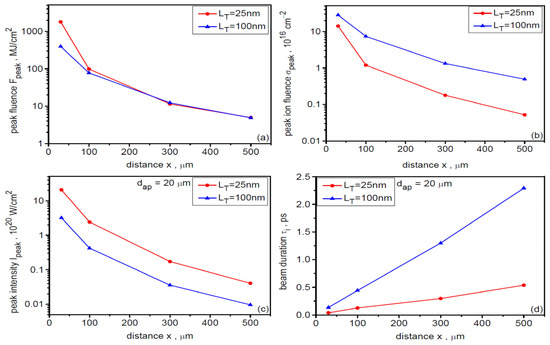
Figure 17.
Dependence of the peak values of energy fluence (a), ion fluence (b), intensity (c), and duration (d) of the ion beam on the distance from the uranium target with a thickness of 25 µm and 100 µm. dL = 6 µm.
In summary, reducing the uranium target thickness LT at fixed laser pulse parameters leads to an increase in (a) mean and maximum ion energy, (b) energetic acceleration efficiency, (c) beam intensity, and (d) the percentage of Ne-like ions in the beam (the beam becomes more mono-charged), as well as to shortening the ion pulse duration. Simultaneously, reducing the target thickness results in an increase in the beam’s angular divergence and a reduction in ion fluence (the number of ions per unit area). Changes in these beam parameters with changes in target thickness are relatively rapid, which allows for control of these parameters by varying the target thickness.
The energy fluence, ion fluence, and beam intensity decrease rapidly (faster than linearly), while the ion pulse duration increases with increasing distance between the beam detection point and the target (these changes occur while the ion energy remains constant). Changing this distance can therefore be a simple and effective way to control these parameters, e.g., in ion beam-target interaction experiments.
5. Synchrotron Radiation Accompanying the Generation of Ultra-Intense Ion Beams
At very high laser intensities ~>1023 W/cm2, ion acceleration is accompanied by the emission of short-wavelength synchrotron radiation (SR) (typically gamma radiation with photon energy > 1 MeV), the sources of which are relativistic electrons produced in laser-plasma interactions [71,72,73,74]. The efficiency of laser energy conversion into the radiation energy depends not only on the laser intensity (it increases with IL) but also on various laser and target parameters and can range from ~1% to several dozen percent [71,72,73,74,76,78]. Because SR emission consumes some of the laser energy that could otherwise be used to accelerate ions, it can lead to reduced acceleration efficiency and lower ion beam parameters.
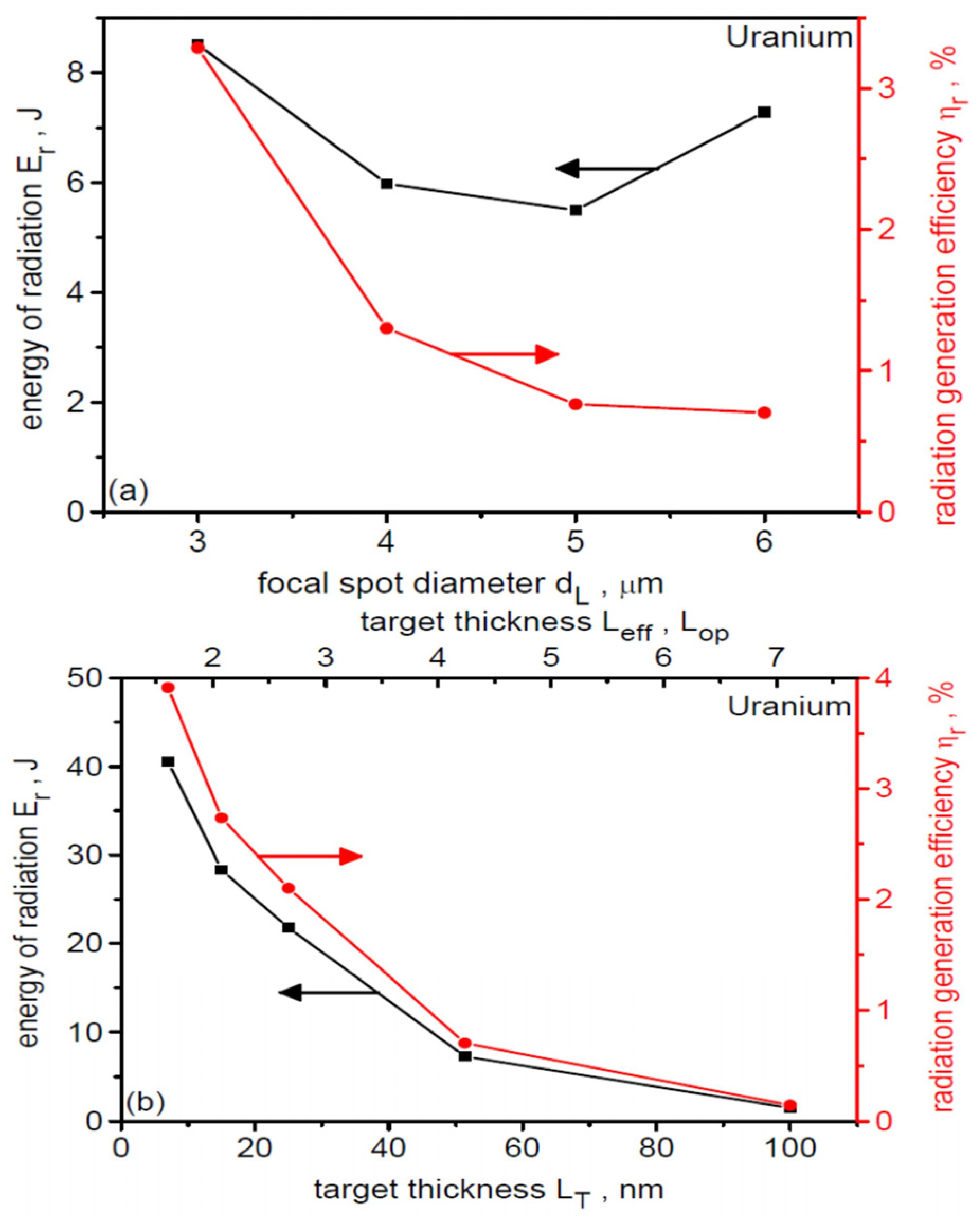
Figure 18 shows the synchrotron radiation energy, Er, and the laser-to-radiation energy conversion efficiency, ηr, as a function of the laser focal spot size (a) and uranium target thickness (b) at IL = 1023 W/cm2 with other laser and target parameters fixed (see Section 3). As dL increases, the conversion efficiency decreases, suggesting that despite the increase in laser energy (proportional to dL2) and the number of accelerated electrons, the temperature of the relativistic electrons decreases. As a result, the energy of the generated radiation changes only slightly (by ~30%). However, changing the target thickness leads to much faster changes in the SR energy. Reducing LT leads to an increase in the temperature of the relativistic electrons (laser energy is used to accelerate fewer electrons), and as a result, the energy of the emitted radiation and the conversion efficiency increase rapidly. For the thinnest target, the SR energy reaches 40 J, and the conversion efficiency ηr is 4%. However, when we compare the ηr values with the efficiency of converting laser energy to accelerated ion energy, which is over 40% (Figure 12b), we see that no more than 1/10 of the laser energy that could be used to accelerate ions is wasted in SR emission. Therefore, in the cases considered in this work, the influence of radiation losses caused by SR emission on the parameters of the uranium ion beam is small.
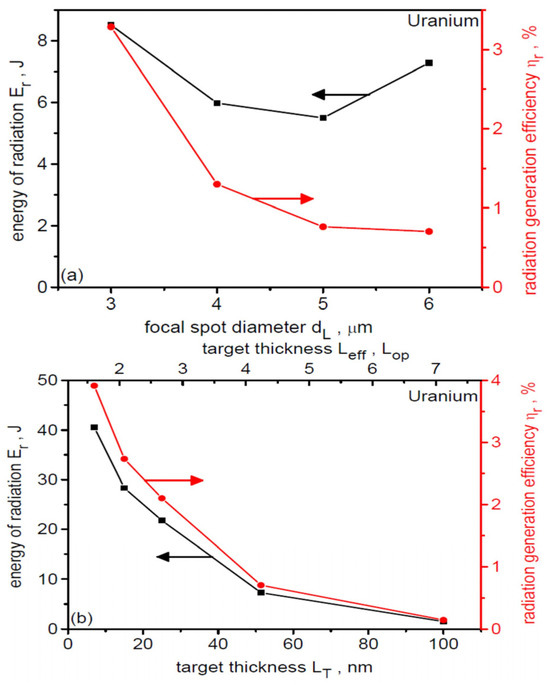
Figure 18.
The synchrotron radiation energy and the laser-to-radiation energy conversion efficiency as a function of the laser focal spot size (a) and uranium target thickness (b). IL = 1023 W/cm2. For (a) LT = 50 nm, for (b) dL = 6 µm. The arrows in the figure assign a given graph to the appropriate y-axis.
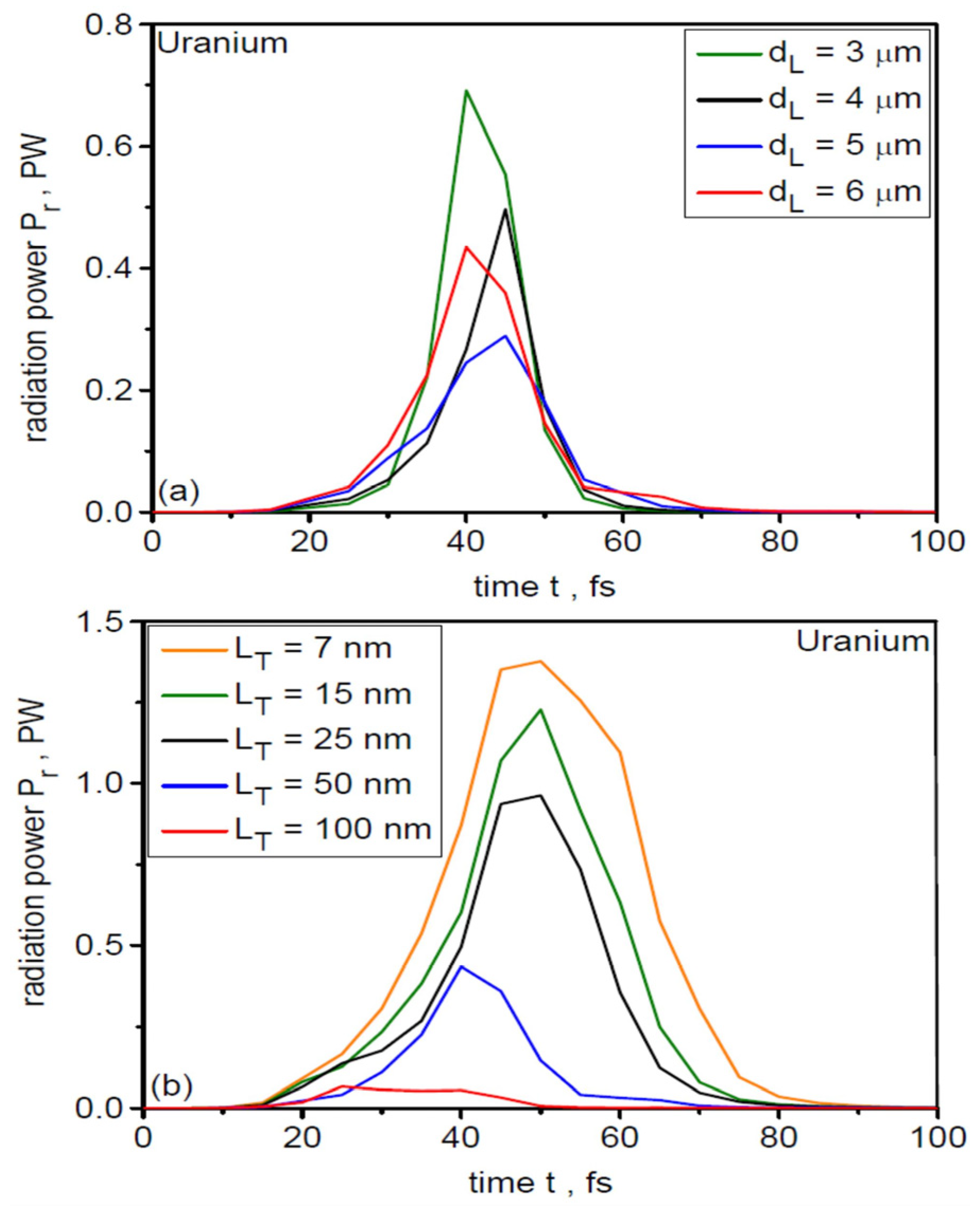
As demonstrated, for example, in [76], synchrotron radiation is emitted primarily from the region of direct interaction of the laser field with the laser-produced plasma electrons. Therefore, the intensity of SR emission is highest near the laser beam axis, where the beam intensity is highest, and the emission duration is comparable to the laser pulse duration. The energy of SR photons increases with the energy (Ee) of the emitting electrons, and at Ee >> 1 MeV, the electrons emit gamma radiation [72,73]. In the cases considered in this work, the energy of relativistic electrons reaches several tens of MeV, and synchrotron radiation is therefore gamma radiation. Figure 19 shows gamma radiation pulses accompanying uranium ion acceleration for various sizes of the laser focal spot at LT = 50 µm (a) and various target thicknesses at dL = 6 µm (b). The duration of the gamma pulses ranges from ~15 fs to ~30 fs, and their power exceeds 1 PW (for LT ≤ 15 nm). It is worth adding that, unlike ion pulses, the duration of gamma pulses in vacuum does not depend on the distance from the SR source, and even at large distances from the target, the duration and power of the gamma pulse will be the same as near the target. Of course, due to the angular divergence of the radiation, the intensity of gamma radiation will decrease with increasing distance from the target.
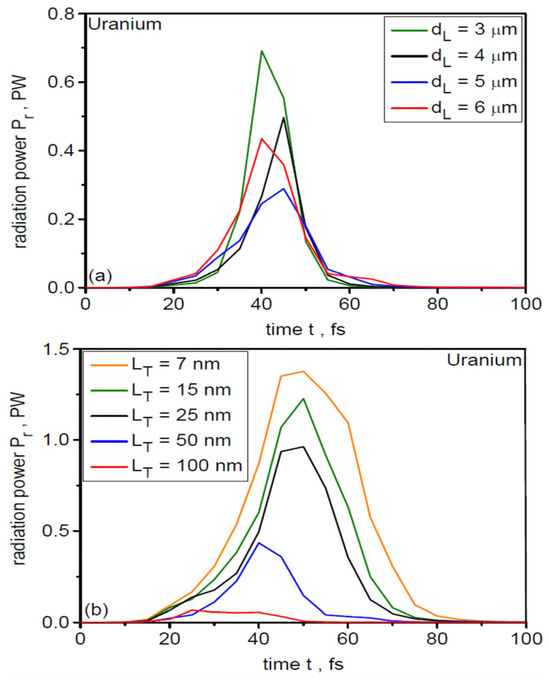
Figure 19.
Temporal shapes of gamma-ray pulses for different laser focal spot sizes (a) and different uranium target thicknesses (b). IL = 1023 W/cm2. For (a) LT = 50 nm, for (b) dL = 6 µm.
In conclusion, under the considered laser-target interaction conditions, the efficiency of converting laser energy into synchrotron radiation energy does not exceed a few percent and is an order of magnitude lower than the efficiency of converting laser energy into the energy of accelerated ions. The effect of SR emission on ion beam parameters is therefore small. Despite this, the emitted ultra-short (~30 fs) gamma radiation pulses have high power (~PW) and can be used in various applications, such as nuclear physics or materials science.
6. Discussion
In this section, we will discuss some limitations and inaccuracies of the computer model used in the simulations, as well as some issues related to plasma instabilities occurring during ion acceleration, the practical achievability of the assumed target and laser parameters, and the possibility of performing experiments to verify the results of the simulations.
The studies of ultra-intense beam generation conducted in this paper are based on the results of numerical simulations using the advanced, two-dimensional particle-in-cell computer code PICD0M. Although this code accounts for most of the physical phenomena relevant to the problem under study, the simulation results are subject to inaccuracies, primarily due to the limited computing power available to the authors. These inaccuracies arise from both technical and physical reasons. Technical inaccuracies result primarily from limitations on the time and space steps used in the simulations, the simulation time, and the size of the simulation box. The PICDOM code has been optimized so that, despite these limitations, the simulations can reveal the physical phenomena crucial to the problem being studied while keeping quantitative errors as small as possible. Another reason for simulation inaccuracy is the use of a 2D code instead of a 3D code, which potentially better reflects reality. In the case of laser-driven ion acceleration, omitting one of the spatial dimensions can result not only in quantitative but also qualitative inaccuracies, including the omission of some phenomena whose full significance is not reflected in the 2D code. Both quantitative and qualitative differences between 2D and 3D simulation results depend on the laser and target parameters, and on the type of acceleration mechanism dominant in the ion beam generation.
Acceleration mechanisms such as RPA, TNSA, CEA, or RITA, crucial for producing ultra-intense ion beams, can be modelled quite well with 2D simulations, as confirmed by many papers investigating ion acceleration using these mechanisms. When determining the basic parameters of the generated ion beam, such as the energy spectrum, ionization spectrum, mean angular divergence of the beam, or the intensity, fluence, and energy of the beam, we are primarily (though not exclusively) dealing with quantitative differences between the results of 2D and 3D simulations. Particularly large differences are observed in the energies of ions accelerated by TNSA. In this case, the energies of ions determined using 2D PIC can be more than twice as high as those determined using 3D codes [80,81,82]. As a result, the intensity, fluence, and energy of the ion beam are also overestimated. This is primarily because the decrease in electron density in the sheet at the target rear surface caused by the lateral expansion of the plasma is slower in two dimensions than in three. Also, in ion acceleration using the CEA mechanism, the acceleration efficiency and ion energy calculated in 2D can be higher than in 3D, because the Coulomb energy (repulsion energy) stored in the ions is dispersed in a plane rather than in three-dimensional space. This applies particularly to ion acceleration in directions close to the laser beam axis, i.e., in the forward direction, supporting the RPA acceleration, and in the backward direction, counteracting the RPA acceleration.
In the case of ion acceleration using RPA, and especially RPA-LS, the situation is different from that for TNSA and CEA. Transverse expansion of the plasma (ions) causes successive decrease in the areal mass density, σ, of the ion (plasma) bunch accelerated by laser light pressure and the decrease in σ is faster in 3D than in 2D. The ion bunch becomes lighter and therefore its velocity increases faster in 3D. As a result, at the end of the RPA acceleration stage, the bunch velocity and the energy of the ions accumulated in the bunch are higher in 3D simulations. On the other hand, if the laser pulse is long enough (or the target is thin enough), a faster decrease in plasma density can lead to faster penetration (transparency) of the bunch by the laser pulse and a shortening of the RPA acceleration stage. This can result in a lower mean ion energy and, therefore, lower intensity and energy fluence of the ion beam in the 3D simulation compared to 2D. In such a case, the increase in ion velocity and energy due to the lower areal density of the ion bunch can be compensated by the shortening period of effective ion acceleration. The picture outlined above is confirmed by works [33,83] which compared the results of 2D and 3D simulations for both RPA-LS and RPA-HB. In these works, the energies of ions driven by RPA are usually higher in 3D simulations than in 2D. The observed differences do not exceed several dozen percent and are much smaller than the typical differences in ion energies observed in the case of TNSA acceleration [80,81,82].
In the uranium ion acceleration studied in this paper, the dominant acceleration mechanism is RPA-LS, and relativistic transparency of the accelerated target is not observed. Considering the argument presented above, the mean ion energies, as well as the intensity, fluence, and energy of the ion beam, may be slightly underestimated compared to the results of possible 3D PIC simulations. In turn, the lower ion acceleration efficiency via the CEA mechanism (which is the main source of increased beam angular divergence) may result in a smaller beam divergence in 3D. On the other hand, the maximum ion energy, which is largely determined by the TNSA mechanism, may be overestimated in our simulations. However, the value of this energy is of secondary importance in the generation of ultra-intense ion beams.
Laser-driven ion acceleration, including that driven by the RPA mechanism, is usually accompanied by the development of plasma instabilities, Rayleigh-Taylor-like (R-T) instabilities [84,85,86,87] and Weibel-like (WB) instabilities [88,89,90]. WB instabilities are favored by targets with rather low densities, comparable to the critical plasma density [89,90] (although they also occur at higher densities), where ion acceleration is dominated by the RPA-HB mechanism (if the laser intensities are sufficiently high). In such targets, WB instabilities have enough space and time to develop and create small-scale inhomogeneities (filamentations) in the plasma, which deteriorate the quality of the generated ion beam. In the case of solid-state targets, WB instabilities are observed primarily in the pre-plasma generated on the target surface by the laser pre-pulse. RT instabilities accompany both RPA-HB acceleration (thick targets) and RPA-LS acceleration (thin targets). They are particularly dangerous for very thin targets, where RT instabilities can lead to complete destruction of the target and the generated ion beam even before the acceleration process is complete. In the case of a high-quality solid target (without surface irregularities), the main source of RT instabilities is inhomogeneity in the lateral intensity distribution of the laser beam. Even for high-quality beams, the formation of these inhomogeneities is difficult to avoid, as they result from diffraction of laser light at the target surface and interference between the incident beam and the beam reflected from the target (from the critical plasma surface). As a result, the laser light intensity distribution on the target surface has a non-uniform periodic structure with a non-uniformity scale of the order of λL. In the initial phase of laser-target interaction, the laser beam produces a periodic density disturbance on the target surface (near the critical plasma surface) with a non-uniformity scale comparable to λL. During ion acceleration, the amplitude of these non-uniformities increases exponentially due to RT instabilities. The growth rate (g) of these instabilities depends on the acceleration (A) of the surface driven by the light pressure and increases with increasing A [56]. If the value of g is sufficiently high and/or the acceleration duration is sufficiently long, the RT instabilities can destroy the accelerated plasma object.
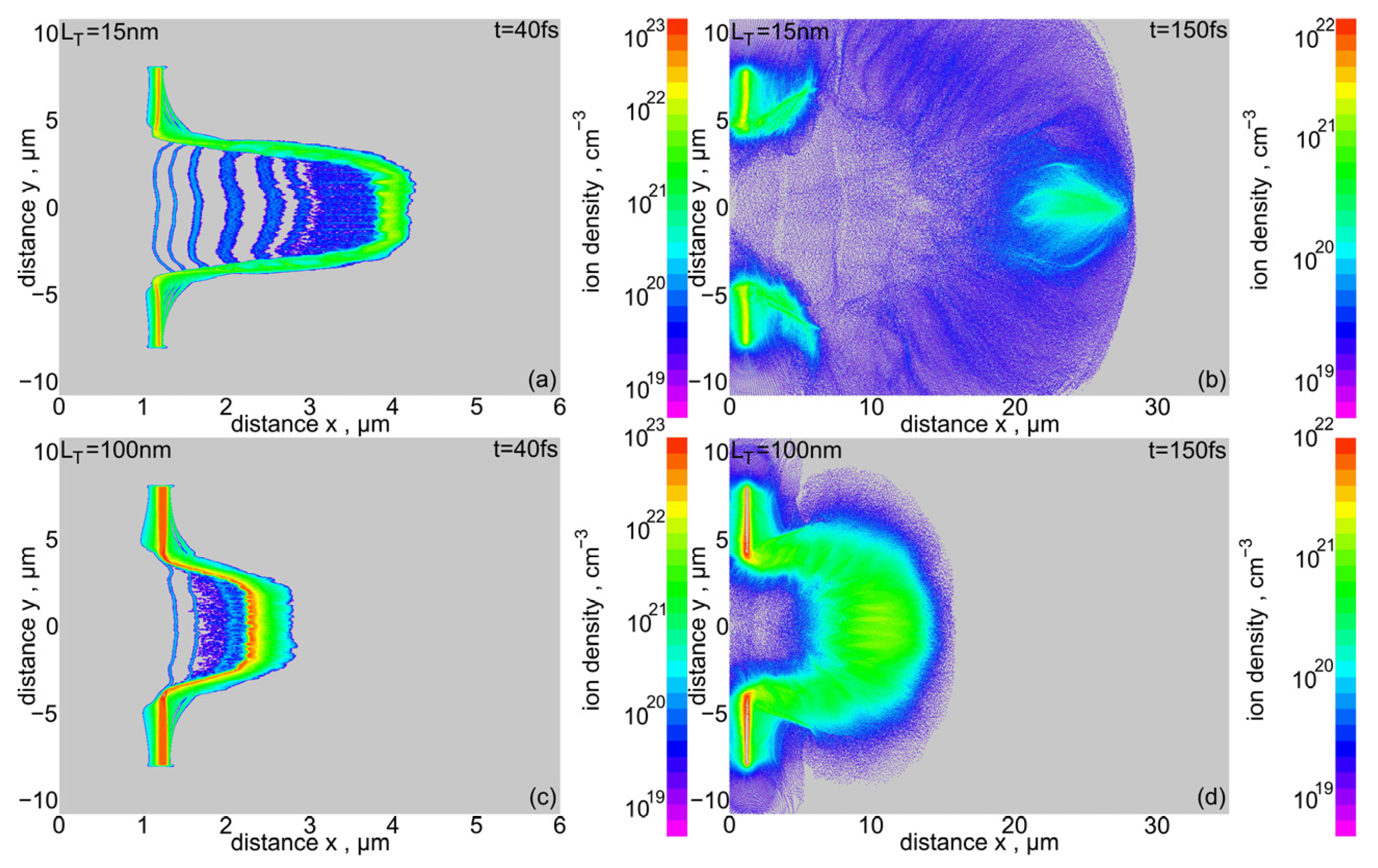
Figure 20 shows the density distributions of uranium ions in the final stage of acceleration by RPA-LS (t = 40 fs) and in the final stage of post-RPA acceleration (t = 150 fs) driven by CEA and TNSA. Figure 20a,b illustrates the density distributions for a target with a thickness of LT = 15 nm (Leff ~ 35 nm), while Figure 20c,d for a target with LT = 100 nm (Leff ~ 120 nm). A more detailed analysis of these distributions showed that, at t = 40 fs in the pre-plasma region, there are many longitudinal filamentations with a width not exceeding λL/10. This suggests that WB-type instabilities occur and dominate in this region. Such filamentations are not observed in the final stage of post-RPA acceleration (t = 150 fs). In the dense plasma region, both in the final RPA stage (Figure 20a) and in the post-RPA stage (Figure 20d), density modulations are observed with a mean distance between density peaks of ~0.5 μm. This inhomogeneity scale is quite close to λL/2 = 0.4 μm, i.e., the scale of the transverse inhomogeneity of the standing wave of laser light irradiating the target. This suggests that the sources of these inhomogeneities are RT instabilities, which dominate here in the dense region of accelerated plasma. Despite the observed instabilities, even with a very thin target (LT = 15 nm), the uranium ion beam was not destroyed, and a fairly compact ion bunch entered the ballistic propagation stage (see also Figure 14) with a density of up to ~5 × 1020 cm−3, areal ion density ~(3–4) × 1017 cm−2, energy fluence > 1 GJ/cm2 (Figure 14a), and intensity > 1021 W/cm2 (Figure 15a). For a 100 nm target, the density and areal ion density are even higher, but—due to the lower ion energy—the energy fluence and beam intensity are slightly lower (Figure 14 and Figure 15). It is worth noting that the relatively high resistance of the uranium ion beam to the destructive effects of RT instability, demonstrated above, is primarily due to the very high mass of the uranium ions. First, due to the high ion mass, the acceleration factor A, which largely determines the growth rate of the instability g, is significantly lower than for light ions accelerated by a laser beam of the same intensity. Second, due to their high mass, uranium ions are less sensitive than light ions to the magnetic and electric fields accompanying the development of instabilities (both RT and WB) and the destructive influence of these fields on the ion beam.
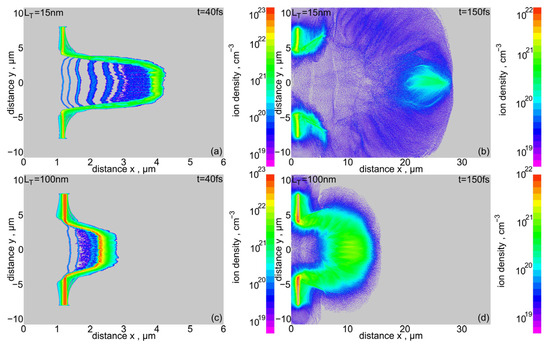
Figure 20.
2D spatial distributions of uranium ion density in two acceleration stages for a uranium target with a thickness LT equal to 15 μm (a,b) and 100 μm (c,d). IL = 1023 W/cm2, dL = 6 μm.
In 3D simulations, the influence of plasma instabilities on the generated uranium beam can potentially be greater than in 2D. The three-dimensional structure of the field, especially the magnetic field, can intensify the development of instabilities and thus increase their destructive effect on beam quality. However, for the reasons indicated above, the impact of including the third dimension in simulations on the degree of beam degradation by these instabilities should be much smaller for the uranium beam than for a light ion beam. Therefore, it can be expected that even in 3D simulations, the uranium beam will not be destroyed for the laser and target parameters considered in this paper. To verify this assumption and to quantitatively assess the impact of the additional dimension in simulations on ion beam parameters, we would need to compare the results of our simulations with the results of the corresponding 3D simulations. However, this is beyond the current capabilities of the authors of this paper.
A crucial issue for experimental verification of our numerical results and the use of super-heavy ion beams in possible applications is the achievability of the laser and target parameters assumed in the simulations. In particular, this concerns the level of laser pulse intensity contrast required under the laser-target interaction conditions considered in this work.
The leading edge of every real laser pulse has a low-intensity part—the pulse “background”—that irradiates the target before the main pulse, carrying almost all the pulse’s energy, reaches the target. If the intensity level of this “background” is sufficiently high, it generates pre-plasma on the target surface. The shape and thickness of the pre-plasma depend not only on the intensity but also on the background structure. This structure is complex and usually includes: a long-term part (from a few to several dozen ns) determined mainly by ASE, an intermediate (sub-ns) part with possible ps or fs pre-pulses, and a short-term (ps, sub-ps) part in the immediate vicinity of the main high-intensity part of the laser pulse. The detailed structure of the pulse “background” in each laser system is different and depends on the detailed technical solutions used in the system. The concept of laser contrast, understood as the ratio of the average intensity of the “background” to the peak intensity of the pulse, is therefore not unambiguous, because the average intensity of each of the three mentioned parts of the “background” is different (the differences can reach several orders of magnitude). In this way, we can talk about three types of laser contrast: long-term contrast, medium-term contrast and short-term contrast. As the numerical values of these contrasts may differ by orders of magnitude, a credible answer to the question of what laser contrast is necessary for the implementation of the laser-target interaction conditions assumed in our simulations does not seem possible without knowing the detailed structure of the laser pulse “background”. This makes it even more difficult to reliably determine (e.g., using hydrodynamic simulations) the characteristics of pre-plasma without knowledge of this structure.
For the reasons mentioned above, to mimic the interaction between the laser pulse “background” and the target in theoretical and numerical studies, the thickness and shape of the pre-plasma density distribution are usually assumed a priori. These pre-plasma parameters have a significant impact on the laser-driven ion acceleration, and on the type and efficiency of the mechanism that dominates acceleration. When the peak intensity of the laser pulse is very high and RPA is the dominant acceleration mechanism, the pre-plasma thickness should be as small as possible, and the pre-plasma density gradient should be high [1,2,14]. If this requirement is not met, the RPA acceleration efficiency may be low, and therefore the parameters of the generated ion beam may be unsatisfactory. In particular, an increase in the pre-plasma thickness and/or a decrease in the pre-plasma density gradient may lead to: (a) a decrease in the ponderomotive force driving ions and thus a decrease in the ion energy and the intensity, fluence and energy of the ion beam, (b) an increase in the angular divergence of the beam, (c) a broadening of the energy spectrum, (d) a deterioration in the quality of the spatial distribution of ion density and energy (e.g., due to the intensification of WB instability or filamentation of the laser beam in the pre-plasma).
Based on our earlier studies (e.g., [20,79]), in this work, we assumed uranium pre-plasma parameters conducive to achieving high RPA acceleration efficiency, namely: an exponential pre-plasma density profile, a total thickness of 184 nm, and an effective thickness (at the level of 1/e of the maximum density) of ~20 nm. These uranium pre-plasma parameters correspond to a CH pre-plasma with a total thickness of ~0.8 μm (plasma expansion velocity is inversely proportional to the square root of the ion mass). The effective target thicknesses (Leff) assumed in the simulations range from 27 nm to 120 nm. They correspond to CH target thicknesses with an areal mass density like that of the uranium target, ranging from ~0.5 μm to ~2 μm. The parameters of the pre-plasma and the thickness of the uranium targets are therefore not particularly sophisticated. Flat targets made of heavy metals (Au, Pb, U, …) with such thicknesses are easily achievable with current target fabrication technologies [67,68] and have been used in experiments for many years [4,7,44].
For the reasons discussed earlier, it is difficult to assess how high the contrast of a 30-fs pulse with a peak intensity of 1023 W/cm2 should be to prevent the targets used in our simulations from being destroyed (or significantly deformed) by the pulse “background”. One can only speculate, based on experiments already conducted, such as [4], that a contrast of ~1010–1011 for the picosecond “background” part and ~1014–1015 for the intermediate (sub-ns) and long (ns) “background” parts of the pulse would be sufficient to avoid damaging the target and changing its intended parameters. Such or even higher contrast levels have already been demonstrated. For example, in [91], a contrast of ~1017 up to 160 ps and 1012 up to 2 ps before the main multi-PW laser pulse was achieved. However, achieving the required laser pulse parameters (power, intensity, and contrast) simultaneously remains a challenge. Considering the current rapid development of high-power femtosecond laser technology, including the development of methods for enhancing laser pulse contrast [91,92], we can believe that we will not have to wait too long to overcome this challenge.
Experimental verification of some of the properties of super-heavy ion beams demonstrated in this work is generally possible using existing (e.g., ELI-NP [6], Corel [4,5]) or emerging [8] multi-PW femtosecond lasers. However, the parameters of operating currently multi-PW lasers should be improved to bring them closer to those designed for these lasers. Methods for measuring the parameters of high-energy heavy ion beams are known and have been used in laser-accelerated heavy ion experiments for many years. Popular devices used to measure heavy ion beams include various types of time-of-flight (TOF) detectors [93], Thomson parabola spectrometers (TPS) [4,44], electrostatic ion energy analyzers (IEA) [93,94], solid-state track detectors, and radiochromic films. One challenge in these measurements can be measuring the ionization spectrum of super-heavy ions with high resolution, enabling assessment of the degree to which the generated beam is mono-charged. IEA analyzers may prove more useful for this purpose than the commonly used TPS spectrometers, as they typically provide significantly higher resolution in measuring the ionization spectrum of heavy ions than TPS. Another challenge is measuring the duration of the ion pulse at a short distance from the target, which may lie in the picosecond or sup-picosecond range. Direct measurement of this duration is problematic using the ion beam measurement techniques known to the authors. However, it is possible to estimate this duration indirectly using a TOF ion detector and numerical or analytical transformation of the time distribution recorded by the detector near the ion source [13,41,95]. This method could also estimate the energy fluence and intensity of the ion beam near the source.
7. Prospects for Applications of Ultra-Intense Ion Beams Driven by a Multi-PW Femtosecond Laser
Laser-driven ultra-intense ion beams, including heavy ion beams, have the potential to be used in various fields of scientific research, as well as in certain technologies (e.g., materials technology) and medicine (e.g., cancer therapy, isotope production). Below, we outline the possibilities and benefits of using such beams in HEDP, inertial confinement fusion, and nuclear physics.
7.1. High Energy-Density Physics
HEDP focuses on creating and studying extreme states of matter in which the pressure p > 1 Mbar or, equivalently, the energy density ε > 0.1 MJ/cm3 [96]. Producing such states of matter in the laboratory and understanding their properties is highly desirable for planetary science and astrophysics, as well as for ICF and materials science. High- energy-density (HED) states are produced by intense ion beams generated in conventional accelerators, intense laser beams, chemical explosions, pulsed-power devices such as Z-pinch, or hypervelocity projectile impacts. Among these methods, the highest pressures and energy densities are currently achieved using lasers in ICF experiments, in which the target is spherically compressed by multiple laser beams or X-rays generated by these beams. Record pressures of hundreds Gbar were achieved in this way in a highly compressed plasma at the National Ignition Facility (USA), where X-rays generated by ~200 laser beams with a total energy above 1 MJ were used for spherical compression of the fusion target [57,58]. Pressures generated by other methods, including accelerator ion beams, are many orders of magnitude lower and are typically in the range of 1 Mbar–1 Gbar. The use of ion beams to produce HED states has a few advantages, including the possibility of deep beam penetration into virtually any dense material and relatively good uniformity of the distribution of energy deposited in the material. In the case of beams produced in large accelerators, this also includes the ability to generate HED states in relatively large volumes (~mm), as well as the ability to generate such states with a high repetition rate. Therefore, the generation of HED states using ion beams is increasingly being proposed and is included in the research programs of the largest accelerators [21,22].
Important parameters characterizing the ability of an ion beam to create HED states are the energy deposited per gram of matter, Es, and the deposited power, Ps = Es/td, where td is the energy deposition time. Es can be determined from the formula [22]:
where dEi/dx is the ion stopping power of the material irradiated by the beam and Fi is the ion fluence (in cm−2).
Figure 21 shows the energy Es (a) and power Ps (b) deposited in a carbon target by a uranium ion beam as a function of the distance x between the carbon target and the uranium target. The uranium beam is generated by a 30-fs laser pulse with an intensity of 1023 W/cm2 from a target with a thickness LT of 25 or 100 nm. To determine the Es and Ps values, the ion fluence values Fi = σpeak from Figure 17b were used and it was assumed that the energy deposition time in the carbon target td was equal to the ion pulse duration (Figure 17d). To determine the stopping power of uranium ions in carbon, the mean energies for all generated ions calculated for the target with LT = 25 nm (Emean = 20.6 GeV) and LT = 100 nm (Emean = 3.5 GeV) were used. For these energies, dEi/dx were calculated using the SRIM code [97]. The calculated stopping power values for uranium ions were compared with those for Pb ions in carbon presented in [98] (p. 124) (Figure 5). As expected, for the assumed ion energies, the stopping power value for U ions is ~20% higher than for Pb ions, while the shapes of the stopping power-energy dependencies for U and Pb ions are very similar. It can therefore be assumed that the Es and Ps values presented in Figure 21 for U ions are representative also for other super-heavy ions (Pb, Th, Au, etc.).
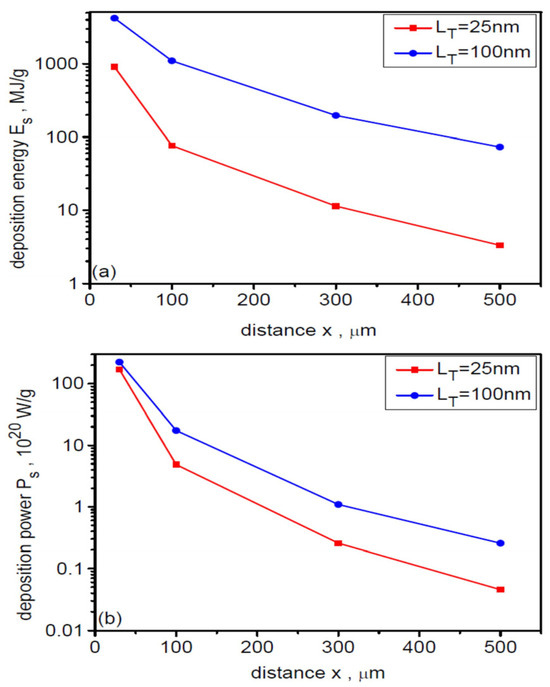
Figure 21.
The energy Es (a) and power Ps (b) deposited in a carbon target by a uranium ion beam as a function of the distance x between the carbon target and the uranium target. The uranium ion beam is produced by a laser pulse with IL = 1023 W/cm2, τL = 30 fs, and dL = 6 µm.
Figure 21 shows that although the peak energy fluence for the thinner target is higher than for the thicker one (Figure 17a), the energy deposited by the uranium ion beam in the carbon target is significantly higher for the 100 nm target than for the 25 nm one. This results firstly from the fact that the ion fluence Fi = σpeak (the number of ions per cm2) is higher for the thicker target (Figure 17b) and secondly from the fact that the ion energy decreases with increasing dL (Figure 12a); for lower energies, the stopping power is higher in the considered ion energy range (see [98] (p. 124)). The deposited power Ps is also higher for the 100 nm target than for the 25 nm target; however, these differences are smaller than for Es. This is due to the longer duration of the ion pulse generated from the thicker target (Figure 17d). The absolute values of Es and Ps decrease quite rapidly with increasing distance from the uranium target. For a 100 nm target, a change in x from 30 µm to 500 µm results in a change in Es from ~4 GJ/g to ~70 MJ/g and a change in Ps from ~2 × 1022 W/g to ~2.5 × 1019 W/g.
To realize how high the absolute values of Es and Ps shown in Figure 21 are, it is worth comparing these values with those predicted for the largest conventional heavy ion accelerators, such as HIAF (High Intensity Heavy Ion Accelerator Facility, Institute of Modern Physics, Lanzhou) and FAIR (Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research, GSI, Darmstadt). According to [22] the predicted values of Es and Ps are for HIAF: Es ~ 1 MJ/g, Ps ~ 1013 W/g and for FAIR: Es ~ 0.1 MJ/g, Ps ~ 1012 W/g (td ~ τi ~ 100 ns was assumed when estimating the deposited power). Therefore, even at a relatively large distance between the uranium and carbon targets of ~500 μm, the energies Es and powers Ps deposited in the target by a uranium ion beam driven by a multi-PW laser are, respectively, 2–3 orders of magnitude and 6–7 orders of magnitude higher than those achievable in the largest heavy ion accelerators. It should be noted that the Es and Ps values were estimated using stopping power values calculated based on the Bethe-Bloch theory, commonly used for accelerator ion beams. However, the laser-driven uranium ion beams considered here have a significantly higher intensity and density than accelerator beams. Research on the interaction of such intense ion beams with matter is in its early stages, so it is difficult to assess the error in the Es and Ps estimates resulting from using stopping power values calculated or measured for accelerator beams.
Figure 21 also suggests a method for controlling the energy and power deposited by the ion beam in the material. If we want to change the Es and Ps values simultaneously while changing the ion energy, this can be achieved by changing the thickness of the ion target. However, when a controlled change in Es and Ps is desired at a fixed ion energy, this is most easily achieved by changing the distance between the ion target and the target irradiated by the ion beam. In the latter case, the Es and Ps values can be easily varied over several orders of magnitude.
Besides very high intensities and fluences, laser-driven ion beams have another feature unattainable for accelerator beams: an ultrashort, pico- or femtosecond ion pulse duration, many orders of magnitude shorter than those of accelerator beams. This enables the creation and study of various non-stationary processes in dense matter occurring at picosecond or shorter times. Ultrashort, high-intensity ion pulses enable, among other things, isochoric heating of matter to high temperatures (~keV or higher), where the energy deposition time td in the material is significantly shorter than the time th over which the parameters of the heated material change due to hydrodynamic motions. The generation of such states of matter is particularly important for inertial confinement fusion (see below) and for astrophysical research.
The examples briefly discussed in this subsection demonstrate that laser-driven ultra-intense ion beams, including heavy ion beams, can be an innovative tool in HEDP research, enabling the exploration of entirely new areas of beam-target interactions and the generation of extreme states of matter that are unattainable or difficult to achieve using other known methods. However, realizing this possibility requires addressing numerous challenges, primarily related to improving the quality of the generated ion beams, as well as improving the parameters of the laser drivers, including increasing their repetition rate.
7.2. Inertial Confinement Fusion
Inertial confinement fusion (ICF) and magnetic confinement fusion (MCF) are currently the two main paths toward an energy source based on controlled thermonuclear fusion. Unlike MCF, where energy from fusion reactions of light elements (usually deuterium and tritium) is produced continuously or over long periods of time, ICF produces energy in short (sub-ns) repeated explosions of nuclear fuel stored in a spherical target, compressed to very high densities by multi-ns laser beams or soft X-rays generated by these beams. In the classic version of ICF (used, for example, at the NIF facility, USA [57,58]), ignition of the nuclear fuel occurs spontaneously as a result of the fuel temperature increase (up to multi-keV) accompanying its compression. Currently, other versions of ICF are also being intensively researched. One of the most promising is the so-called ion fast ignition (IFI), in which the ignition of compressed nuclear fuel is initiated by a very intense beam of laser-driven ions [12,16,17,18,76,78,99]. This innovative ICF option potentially enables thermonuclear ignition at lower laser driver energies than the classical option and ensures a significantly higher fusion energy gain, which is essential for the operation of a fusion reactor. Both light [12,16,17,18,76] and heavy [78,99] ion beams can be used to ignite the fuel, but the ion beam parameters required for IFI are extremely high, in particular [16,17,18,19,78]: intensity ~1020 W/cm2, energy fluence ~GJ/cm2, and beam energy ~10–20 kJ. Generating an ion beam of such high energy requires a laser driver with energy > 100 kJ [76,78,98] and is currently unattainable. However, as the results of this work demonstrate, the required ion beam intensities and fluences, as well as the required ion energies of ~100 MeV/u [17,18], can be achieved using a multi-PW femtosecond driver with parameters achievable with current high-peak-power laser technology, including improved versions of the ELI laser infrastructure [6,8]. Therefore, the ultra-intense ion beams demonstrated in this work can be used for various fundamental research related to IFI, benchmarking theoretical and computational models, and testing measurement methods and systems designed for ICF. Strong ultrashort gamma radiation pulses accompanying ion beam generation (Section 5) may also play a useful role in some aspects of these studies. However, effective implementation of the ion beams considered in this paper in ICF-related research requires further numerical and experimental studies aimed at improving the quality of these beams, especially at narrowing their energy spectrum.
7.3. Nuclear Physics
Heavy ion beams with high energies ranging from multi-GeV to multi-TeV are among the fundamental research tools in nuclear and particle physics. They are routinely produced in large accelerators such as the LHC (Large Hadron Collider), FAIR, or HIAF. Collisions of such ions play a key role in quantum chromodynamics (QCD) research and provide crucial information about the structure of matter at the subnuclear level. They also enable the production of quark-gluon plasma (QGP), an exotic state of matter containing interacting quarks, antiquarks, and gluons. Studying QGP can be a valuable source of information that helps answer fundamental questions in nuclear and particle physics, as well as those concerning the early stages of the evolution of the universe. The ion energies required to produce quark-gluon plasma decrease with increasing ion mass, so beams of super-heavy ions, such as uranium ions, are especially useful in QGP studies. The maximum energies of uranium Ne-like ions demonstrated in Section 4 reach 230 GeV, while the mean energies are ~60 GeV (Figure 12), which is not much lower than those achieved in large accelerators such as FAIR and HIAF [21,22]. These are high enough, for example, to study the equations of state of nuclear matter and to observe certain QCD phenomena such as kaon and pion production [100]. The energy of uranium ions can be increased by increasing the laser intensity, but achieving energies ≥ 1 TeV required for QGP creation is an open question, as the required intensities are likely ~1024 W/cm2, at which radiative losses (Section 5) as well as various quantum effects (creation of electron-positron pairs and others [101,102]) can significantly hinder achieving such ion energies. Another serious problem hindering the use of laser-driven ion beams in this type of research is the broad energy spectrum of the ions, which can significantly complicate or even prevent the interpretation of results obtained with these beams.
An advantage of using laser-driven ion beams in this type of research is the high ion fluence of the beam, which can be up to several orders of magnitude higher than that of accelerator beams. This potentially enables the detection of some QCD effects using a “laser collider” operating at a significantly lower repetition rate than that of RF accelerators, achievable by lasers. Furthermore, a “laser collider” could be a more compact, less complex, and less expensive device than a conventional accelerator, making it possible to build and operate in academic laboratories.
Ultra-intense laser-driven heavy ion beams could also be useful in nuclear astrophysics research. Such studies are included in the ELI-Nuclear Physics laser infrastructure program with a 10-PW femtosecond laser. The goal of one branch of this program is to investigate the feasibility of producing neutron-rich heavy ions by a new reaction mechanism called fission–fusion, using laser-generated thorium ion beams [103,104]. Successful results of these studies would be a significant step toward understanding the nature of heavy element production in the universe. The thorium ion beam parameters required for these studies are as follows [103]: mean ion energy ~1.6 GeV, beam intensity ~1020 W/cm2, ion fluence ~1018 cm−2, ion number ~1011. These parameters are like those presented in this paper for the uranium beam (the atomic numbers of U and Th are very close). By adjusting the target thickness and the size of the laser focal spot, they are achievable for thorium ion beams with the energy and power of the femtosecond laser considered in this paper. The main problem, however, is the broad energy spectrum of the generated beams. Achieving the required thorium ion beam parameters with a narrow energy spectrum requires further comprehensive studies and will likely be possible with higher laser energies and powers, achievable only in currently designed femtosecond lasers [8,10,11].
This section provides only examples of possible applications of ultra-intense laser-generated ion beams. The range of potential applications for these beams is much broader, but research into their implementation is still at a very early stage. This research should be directed in two directions. On the one hand, it should consist of general research—cognitive and innovative—and on the other, specific research tailored to the needs of a given application. The development of this research requires the development of research infrastructure, including laser drivers (increasing laser energy, power, intensity, and repetition rate), as well as target technology and measurement methods and equipment.
8. Summary and Conclusions
Laser-driven ion acceleration is a relatively new, rapidly developing branch of plasma physics and laser science. The main practical goal of research in this field is to establish the physical and technological foundations for the construction and development of a new type of accelerator, more compact and less complex than the commonly used RF-driven accelerators. Although the energies of ions accelerated in laser accelerators are currently, and likely will be in the foreseeable future, lower than the energies of ions from these conventional accelerators, the intensities, fluences, and powers of laser-accelerated ion beams can potentially exceed those achieved in RF accelerators. This paper focuses on the generation of very intense ion beams driven by a multi-PW femtosecond laser. The acceleration mechanisms enabling the generation of such beams are identified and characterized, and the properties of multi-PW laser-driven uranium ion beams are discussed in detail based on the results of advanced two-dimensional particle-in-cell numerical simulations. At a fixed laser intensity currently achievable equal to 1023 W/cm2, the effects of the laser focal spot size, dL, and the target thickness, LT, on various ion beam characteristics were investigated. In particular, the influence of dL and LT on the ionization and energy spectrum of the ion beam, on the intensity, fluence, and duration of the ion beam, as well as on the energetic efficiency of ion acceleration was determined. Furthermore, key parameters characterizing the ability of the generated uranium ion beam to create high-energy-density (HED) states of matter—namely, the energy and power deposited per gram of matter—were calculated for a carbon target irradiated by the beam. The prospects for applications of ultra-intense laser-driven ion beams in high-energy density physics (HEDP), inertial confinement fusion (ICF), and in certain areas of nuclear physics are outlined. Detailed conclusions from the conducted research are summarized below.
- Changing the laser focal spot size dL at a fixed laser intensity and target thickness leads to rather small changes in the mean and maximum energy of uranium ions and the laser-to-ion energy conversion efficiency. On the other hand, the dL variation results in very rapid changes in the peak intensity and peak fluence of the ion beam; however, these changes are mainly caused by the increase in laser energy accompanying the increase in the laser focal spot size.
- Reducing the uranium target thickness LT at fixed laser pulse parameters leads to an increase in (a) mean and maximum ion energy, (b) beam intensity, (c) energetic acceleration efficiency, and (d) the percentage of Ne-like ions in the beam (the beam becomes more mono-charged), as well as to shortening the ion pulse duration. Simultaneously, reducing the target thickness results in an increase in the beam’s angular divergence and a reduction in ion fluence (the number of ions per unit area). Changes in these beam parameters with changes in target thickness are relatively rapid, which allows for control of these parameters by varying the target thickness.
- The energy fluence, ion fluence, and beam intensity decreases rapidly, while the ion pulse duration increases with increasing distance between the beam detection point and the ion target (these changes occur while the ion energy remains constant). Changing this distance can therefore be a simple and effective way to control these parameters, e.g., in ion beam-target interaction experiments.
- At high laser intensities ~> 1023 W/cm2, ion acceleration is accompanied by the emission of synchrotron gamma radiation (SR). Under the considered laser-target interaction conditions, the efficiency of converting laser energy into SR is an order of magnitude lower than the laser-to-ion energy conversion efficiency, and therefore the effect of SR emission on ion beam parameters is small. Despite this, the emitted ultra-short (~30 fs) gamma radiation pulses have high power (~PW) and can be used in various applications.
- The energy and power deposited in the solid target by the ion beam driven by a laser can be easily controlled by changing the distance of this target from the ion target (ion source). Even with relatively large distances between these targets (~0.5 mm), the energies and powers deposited in the carbon target by the multi-PW laser-driven uranium ion beam are several orders of magnitude higher than those predicted for large heavy ion accelerators such as FAIR and HIAF.
- Based on the results of our earlier work [79], it can be assumed that the general properties of ultra-intense ion beams driven by a multi-PW femtosecond laser demonstrated in this paper for uranium ions will be similar for beams of other super-heavy ions such as gold, lead or thorium ions.
In conclusion, the feasibility of generating sub-picosecond, multi-GeV, mono-charge super-heavy ion beams with extreme intensities (~>1020 W/cm2) and fluences (~>GJ/cm2) has been demonstrated, and methods for controlling the beam parameters have been identified. It has been shown that the energies and powers deposited by these beams in a solid target can be orders of magnitude higher than those of ion beams produced in the largest RF-driven heavy ion accelerators. Such ultra-intense laser-driven ion beams could be a unique research tool for exploring new areas of research in HEDP and nuclear physics inaccessible to ion beams from conventional accelerators. To make this possible, further comprehensive studies on laser-driven generation of ultra-intense ion beams, aimed primarily at improving the quality of these beams and controlling their parameters, are necessary.
Author Contributions
J.B.: Conceptualization (lead); Formal analysis (equal); Writing—original draft (lead). J.D.: Formal analysis (equal); Software (lead); Visualization (lead). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been carried out, in part, within the framework of the EUROfusion Consortium, funded by the European Union via the Euratom Research and Training Programme (Grant Agreement No. 101052200—EUROfusion). Views and opinions expressed are, however, those of the authors only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Commission. This scientific work was also supported by Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education within the program called “PMW” for 2022 under the Contract No. 5246/HEU-Euratom/2022/2. The simulations were carried out with the support of the Poznan Supercomputing and Networking Centre under Grant pl0111-02.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
References
- Daido, H.; Nishiuchi, M.; Pirozhkov, A.S. Review of laser driven ion sources and their applications. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 056401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchi, A.; Borghesi, M.; Passoni, M. Ion acceleration by superintense laser-plasma interaction. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2013, 85, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Shen, X.F.; He, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, C.T.; Zhu, S.P.; He, X.T. Revisit on ion acceleration mechanisms in solid targets driven by intense laser pulses. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2019, 61, 014039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gong, Z.; Lee, S.G.; Shou, Y.; Geng, Y.; Jeon, C.; Kim, I.J.; Lee, H.W.; Yoon, J.W.; Sung, J.H.; et al. Super-Heavy Ions Acceleration Driven by Ultrashort Laser Pulses at Ultrahigh Intensity. Phys. Rev. X 2021, 11, 021049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.W.; Kim, Y.G.; Choi, I.W.; Sung, J.H.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, S.K.; Nam, C.H. Realization of laser intensity over 1023 W/cm2. Optica 2021, 8, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radier, C.; Chalus, O.; Charbonneau, M.; Thambirajah, S.; Deschamps, G.; David, S.; Barbe, J.; Etter, E.; Matras, G.; Ricaud, S.; et al. 10 PW peak power femtosecond laser pulse at ELI-NP. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badziak, J.; Domański, J. Acceleration of Heavy Ions by Ultrafast High-Peak-Power Lasers: Advances, Challenges, and Perspectives. Photonics 2025, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danson, C.N.; Haefner, C.; Bromage, J.; Butcher, T.; Chanteloup, J.-C.F.; Chowdhury, E.A.; Galvanauskas, A.; Gizzi, L.A.; Hein, J.; Hillier, D.I.; et al. Petawatt and exawatt class lasers worldwide. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourou, G. Nobel Lecture: Extreme light physics and application. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2019, 91, 030501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazanov, E.; Shaykin, A.; Kostyukov, I.; Ginzburg, V.; Mukhin, I.; Yakovlev, I.; Soloviev, A.; Kuznetsov, I.; Mironov, S.; Korzhimanov, A.; et al. Exawatt Center for Extreme Light Studies (XCELS). High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Lu, X.; Chen, J.; Long, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Bai, P.; Li, Y.; et al. 13.4fs, 0.1 Hz OPCPA Front End for the 100PW-Class Laser Facility. Ultrafast Sci. 2022, 2022, 9894358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badziak, J.; Jabłoński, S.; Wołowski, J. Progress and prospect of fast ignition of ICF targets. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2007, 49, B651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badziak, J.; Jabłoński, S.; Parys, P.; Rosiński, M.; Wołowski, J.; Szydłowski, A.; Antici, P.; Fuchs, J.; Mancic, A. Ultraintense proton beams from laser-induced skin-layer ponderomotive acceleration. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 063310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badziak, J. Laser-driven ion acceleration: Methods, challenges and prospects. J. Phys. Conf. Series 2018, 959, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badziak, J.; Domanski, J. Towards ultra-intense ultra-short ion beams driven by a multi-PW laser. Laser Part. Beams 2019, 37, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honrubia, J.J.; Fernandez, J.C.; Temporal, M.; Hegelich, B.M.; Meyer-ter-Vehn, J. Fast ignition of inertial fusion targets by laser-driven carbon beams. Phys. Plasmas 2009, 16, 102701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.C.; Albright, B.J.; Beg, F.N.; Foord, M.E.; Hegelich, B.M.; Honrubia, J.J.; Roth, M.; Stephens, R.B.; Yin, L. Fast ignition with laser-driven proton and ion beams. Nucl. Fusion 2014, 54, 054006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honrubia, J.J.; Murakami, M. Ion beam requirements for fast ignition of inertial fusion targets. Phys. Plasmas 2015, 22, 012703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badziak, J.; Domański, J. Laser-driven acceleration of ion beams for high-gain inertial confinement fusion. Nucl. Fusion 2021, 61, 046011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domański, J.; Badziak, J. Towards single-charge heavy ion beams driven by an ultra-intense laser. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2022, 64, 085002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, D.H.H.; Fortov, V.E.; Kuster, M.; Mintsev, V.; Sharkov, B.Y.; Tahir, N.A.; Udrea, S.; Varentsov, D.; Weyrich, K. High energy density physics generated by intense heavy ion beams. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2009, 322, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkov, B.Y.; Hoffmann, D.H.H.; Golubev, A.A.; Zhao, Y. High energy density physics with intense ion beams. Matter Radiat. Extrem. 2016, 1, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, S.C.; Langdon, A.B.; Cowan, T.E.; Roth, M.; Singh, M.; Hatchett, S.; Key, M.H.; Pennington, D.; McKinnon, A.; Snavely, R.A. Energetic proton generation in ultra-intense laser-solid interactions. Phys. Plasmas 2001, 8, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinnon, A.J.; Borghesi, M.; Hatchett, S.; Key, M.H.; Patel, P.K.; Campbell, H.; Schiavi, A.; Snavely, R.; Wilks, S.C.; Willi, O. Effect of Plasma Scale Length on Multi-MeV Proton Production by Intense Laser Pulse. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badziak, J.; Woryna, E.; Parys, P.; Platonov, K.Y.; Jabłoński, S.; Ryć, L.; Vankov, A.B.; Wołowski, J. Fast Proton Generation from Ultrashort Laser Pulse Interaction with Double-Layer Foil Targets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 215001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghesi, M.; Mackinnon, A.J.; Campbell, D.H.; Hicks, D.G.; Kar, S.; Patel, P.K.; Price, D.; Romagnani, L.; Schiavi, A.; Willi, O. Multi-MeV Proton Source Investigations in Ultraintense Laser-Foil Interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 055003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.B.; Zhuo, H.B.; Yang, X.H.; Yu, T.P.; Shao, F.Q.; Pukhov, A. Control of target-normal-sheath-accelerated protons from a guiding cone. Phys. Plasmas 2015, 22, 063103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saxena, V. Enhanced target normal sheath acceleration with a grooved hydrocarbon target. Phys. Plasmas 2023, 30, 063102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esirkepov, T.; Borghesi, M.; Bulanov, S.V.; Mourou, G.; Tajima, T. Highly Efficient Relativistic-Ion Generation in the Laser-Piston Regime. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 175003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchi, A.; Cattani, F.; Liseykina, T.V.; Cornalti, F. Laser Acceleration of Ion Bunches at the Front Surface of Overdense Plasmas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 165003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A.P.L.; Zepf, M.; Kar, S.; Evans, R.G.; Bellei, C. Radiation pressure acceleration of thin foils with circularly polarized laser pulses. New J. Phys. 2008, 10, 013021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grech, M.; Skupin, S.; Diaw, A.; Schlegel, T.; Tikhonchuk, V.T. Energy dispersion in radiation pressure accelerated ion beams. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 123003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgattoni, A.; Sinigardi, S.; Macchi, A. High energy gain in three-dimensional simulations of light sail acceleration. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 084105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, G.M.; McGuffey, C.; Thomas, A.G.R.; Krushelnick, K.; Beg, F.N. Generation of heavy ion beams using femtosecond laser pulses in the target normal sheath acceleration and radiation pressure acceleration regimes. Phys. Plasmas 2016, 23, 063108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.J.; Pae, K.H.; Choi, I.W.; Lee, C.-L.; Kim, H.T.; Singhal, H.; Sung, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, H.W.; Nickles, P.V.; et al. Radiation pressure acceleration of protons to 93 MeV with circularly polarized petawatt laser pulses. Phys. Plasmas 2016, 23, 070701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Shou, Y.; Tang, Y.; Hu, R.; Yu, J.; Ma, W.; Lin, C.; Yan, X. Proton sheet crossing in thin relativistic plasma irradiated by a femtosecond petawatt laser pulse. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 013207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Y.; Gong, Z.; Pae, K.H.; Yoon, J.W.; Sung, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Wu, X.; Yan, X.; et al. Proton Acceleration Associated with Sheet Crossing in Petawatt-Laser-Irradiated Nanometre Foils. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2025, 135, 215002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Y.; Wu, X.; Pae, K.H.; Ahn, G.-E.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, J.W.; Sung, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; Gong, Z.; et al. Laser-driven proton acceleration beyond 100 MeV by radiation pressure and Coulomb repulsion in a conduction-restricted plasma. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.O.; Marti, M.; Davies, J.R.; Fonseca, R.A. Proton shock acceleration in laser-plasma interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.S.; Mangles, S.P.D.; Najmudin, Z.; Walton, B.; Gopal, A.; Tatarakis, M.; Dangor, A.E.; Clark, E.L.; Evans, R.G.; Fritzler, S.; et al. Ion acceleration by collisionless shocks in high-intensity-laser–underdense-plasma interaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 155003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badziak, J.; Głowacz, S.; Jabłoński, S.; Parys, P.; Wołowski, J.; Hora, H. Laser-driven generation of high-current ion beams using skin-layer ponderomotive acceleration. Laser Part. Beams 2005, 23, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głowacz, S.; Hora, H.; Badziak, J.; Jabłoński, S.; Cang, Y.; Osman, F. Analytical description of rippling effect and ion acceleration in plasma produced by a short laser pulse. Laser. Part. Beams 2006, 24, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esirkepov, T.; Bingham, R.; Bulanov, S.; Honda, T.; Nishihara, K.; Pegoraro, F. Coulomb explosion of a cluster irradiated by a high intensity laser pulse. Laser Part. Beams 2000, 18, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braenzel, J.; Andreev, A.A.; Platonov, K.; Klingsporn, M.; Ehrentraut, L.; Sandner, W.; Schnurer, M. Coulomb-Driven Energy Boost of Heavy Ions for Laser-Plasma Acceleration. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 124801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, M.; Choudhury, J.; Das, N. Laser driven ion acceleration due to Direct Coulomb Explosion from hydrogen target using PIC simulations. Appl. Phys. B 2025, 131, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Albright, B.J.; Hegelich, B.M.; Fernandez, J.C. GeV laser ion acceleration from ultrathin targets: The laser breakout afterburner. Laser Part. Beams 2006, 24, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Albright, B.J.; Hegelich, B.M.; Browers, K.J.; Flippo, K.A.; Kwan, T.J.T.; Fernandez, J.C. Monoenergetic and GeV ion acceleration from the laser breakout afterburner using ultrathin targets. Phys. Plasmas 2007, 14, 056706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegelich, B.M.; Pomerantz, I.; Yin, L.; Wu, H.C.; Jung, D.; Albright, B.J.; Gautier, D.C.; Letzring, S.; Palaniyappan, S.; Shah, R.; et al. Laser-driven ion acceleration from relativistically transparent nanotargets. New J. Phys. 2013, 15, 085015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higginson, A.; Gray, R.J.; King, M.; Dance, R.J.; Williamson, S.D.R.; Butler, N.M.H.; Wilson, R.; Capdessus, R.; Armstrong, C.; Green, J.S.; et al. Near-100 MeV protons via a laser-driven transparency-enhanced hybrid acceleration scheme. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Bulanov, S.V.; Esirkepov, T.Z.; Kando, M. High-Energy Ions from Near-Critical Density Plasmas via Magnetic Vortex Acceleration. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 135002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Bulanov, S.S.; Bin, J.; Ji, Q.; Steinke, S.; Vay, J.-L.; Geddes, C.G.R.; Schroeder, C.B.; Leemans, W.P.; Schenkel, T.; et al. Ion acceleration in laser generated megatesla magnetic vortex. Phys. Plasmas 2019, 26, 103108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.K.; Mackinnon, A.J.; Key, M.H.; Cowan, T.E.; Foord, M.E.; Allen, M.; Price, D.F.; Ruhl, H.; Springer, P.T.; Stephens, R. Isochoric heating of solid-density matter with an ultrafast proton beam. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 125004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartal, T.; Foord, M.E.; Bellei, C.; Key, M.H.; Flippo, K.A.; Gaillard, S.A.; Offermann, D.T.; Patel, P.K.; Jarrott, L.C.; Higginson, D.P.; et al. Focusing of short-pulse high-intensity laser-accelerated proton beams. Nat. Phys. 2012, 8, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuffey, C.; Kim, J.; Wei, M.S.; Nilson, P.M.; Chen, S.N.; Fuchs, J.; Fuchs, P.; Fitzsimmons, P.P.; Foord, M.E.; Mariscal, D.; et al. Focussing protons from a kilojoule laser for intense beam heating using proximal target structures. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, A.J.; Wilks, S.C.; Tabak, M.; Higginson, D.P. On the role of self-generated magnetic fields in focused ion beams driven by intense picosecond laser pulses. Phys. Plasmas 2025, 32, 093102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, S.; Meyer-ter-Vehn, J. The Physics of Inertial Fusion; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Betti, R.; Hurricane, O.A. Inertial-confinement fusion with lasers. Nat. Phys. 2016, 12, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurricane, O.A.; Patel, P.K.; Betti, R.; Froula, D.H.; Regan, S.P.; Slutz, S.A.; Gomez, M.R.; Sweeney, M.A. Physics principles of inertial confinement fusion and U.S. program overview. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2023, 95, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasik, M.; Weaver, J.L.; Aglitskiy, Y.; Watari, T.; Arikawa, Y.; Sakaiya, T.; Oh, J.; Velikovich, A.L.; Zalesak, S.T.; Bates, J.W.; et al. Acceleration to high velocities and heating by impact using Nike KrF laser. Phys. Plasmas 2010, 17, 056317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, M.; Chu, G.; Zhu, B.; He, W.; Xi, T.; Fan, W.; Xin, J.; Gu, Y. Hypervelocity launching of flyers at the SG-III prototype laser facility. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 035903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, M.; Chu, G.-B.; Xin, J.-T.; Wu, Y.-C.; Zhu, B.; He, W.-H.; Xi, T.; Gu, Y.-Q. Laser-driven flier impact experiments at the SG-III prototype laser facility. Chin. Phys. B 2015, 24, 094701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badziak, J.; Borodziuk, S.; Pisarczyk, T.; Chodukowski, T.; Krousky, E.; Masek, K.; Skala, J.; Ullschmied, J.; Rhee, Y.-J. Highly efficient acceleration and collimation of high-density plasma using laser-induced cavity pressure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 251502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badziak, J.; Jabłoński, S.; Pisarczyk, T.; Rączka, P.; Krousky, E.; Liska, R.; Kucharik, M.; Chodukowski, T.; Kalinowska, Z.; Parys, P.; et al. Highly efficient accelerator of dense matter using laser-induced cavity pressure acceleration. Phys. Plasmas 2012, 19, 053105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badziak, J.; Krousky, E.; Marczak, J.; Parys, P.; Pisarczyk, T.; Rosiński, M.; Sarzynski, A.; Chodukowski, T.; Dostal, J.; Dudzak, R.; et al. Efficient acceleration of a dense plasma projectile to hyper velocities in the laser-induced cavity pressure acceleration scheme. Laser Part. Beams 2018, 36, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauble, R.; Phillion, D.W.; Hoover, T.J.; Holmes, N.C.; Kilkenny, J.D.; Lee, R.W. Demonstration of 0.75 Gbar planar shocks in X-ray driven colliding foils. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 70, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badziak, J.; Krousky, E.; Kucharik, M.; Liska, R. The LICPA-driven collider—A novel efficient tool for the production of ultra-high pressures in condensed media. JINST 2016, 11, C03043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prencipe, I.; Fuchs, J.; Pascarelli, S.; Schumacher, D.W.; Stephens, R.B.; Alexander, N.B.; Briggs, R.; Büscher, M.; Cernaianu, M.O.; Choukourov, A.; et al. Targets for high repetition rate laser facilities: Needs, challenges and perspectives. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2017, 5, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jipa, F.; Ionel, L.; Zamfirescu, M. Advances in Design and Fabrication of Micro-Structured Solid Targets for High-Power Laser-Matter Interaction. Photonics 2024, 11, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domański, J.; Badziak, J. Generation of ion beams from a high-Z target irradiated by a laser pulse of ultra-relativistic intensity. Acta Phys. Polon. A 2020, 138, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Arefiev, A.V.; Bulanov, S.S.; Kawahito, D.; Bailly-Grandvaux, M.; Petrov, G.M.; McGuffey, C.; Beg, F.N. Ionization injection of highly-charged copper ions for laser driven acceleration from ultra-thin foils. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, M.; Pegoraro, F.; Di Piazza, A.; Keitel, C.H.; Macchi, A. Radiation reaction effects on radiation pressure acceleration. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 123005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgers, C.P.; Brady, C.S.; Duclous, R.; Kirk, J.G.; Bennett, K.; Arber, T.D.; Robinson, A.P.L.; Bell, A.R. Dense electron-positron plasmas and ultraintense γ rays from laser-irradiated solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 165006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, C.S.; Ridges, C.P.; Arber, T.D.; Bell, A.R. Synchrotron radiation, pair production, and longitudinal electron motion during 10-100 PW laser solid interaction. Phys. Plasmas 2014, 21, 033108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capdessus, R.; McKenna, P. Influence of radiation force on ultraintense laser-driven ion acceleration. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 91, 053105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammosov, M.V.; Delone, N.B.; Krainov, V.P. Tunnel ionization of complex atoms and of atomic ions in an alternating electromagnetic field. Sov. Phys. JETP 1986, 64, 1191. [Google Scholar]
- Badziak, J.; Domański, J. Laser-driven acceleration of ion beams for ion fast ignition: The effect of the laser wavelength on the ion beam properties. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2021, 63, 055005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, I.V.; Nees, J.A.; Yanovsky, V.P.; Naumova, N.M.; Mourou, G.A. Emission and its back-reaction accompanying electron motion in relativisticaly strong and QED-strong laser fields. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 036412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badziak, J.; Domański, J. Ultra-intense laser-accelerated ion beams for high-gain inertial fusion: The effect of the ion mass on the beam properties. Nucl. Fusion 2022, 62, 086040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domański, J.; Badziak, J. Super-heavy ion beams generated by a multi-PW femtosecond laser. Phys. Plasmas 2024, 31, 023110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Humières, E.; Brantov, A.; Bychenkov, V.Y.; Tikhonchuk, T. Optimalization of laser-target interaction for proton acceleration. Phys. Plasmas 2013, 20, 023103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-L.; Chen, M.; Zheng, J.; Sheng, Z.-M.; Liu, C.-S. Three dimensional effects on proton acceleration by intense laser solid target interaction. Phys. Plasmas 2013, 20, 063107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.D.; Zhou, C.T.; Jiang, K.; Yang, Y.C.; Li, R.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, B.; Huang, T.W.; Cao, J.M.; Cai, T.X.; et al. Multidimensional effects on proton acceleration using high-power laser pulses. Phys. Plasmas 2018, 25, 023103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psikal, J.; Matys, M. Dominance of hole-boring radiation pressure acceleration regime with thin ribbon of ionized solid hydrogen. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2018, 60, 044003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C.A.J.; Schreiber, J.; Nagel, S.R.; Dover, N.P.; Bellei, C.; Beg, F.N.; Bott, S.; Clarke, R.J.; Dangor, A.E.; Hassan, S.M.; et al. Rayleigh-Taylor Instability of an Ultrathin Foil Accelerated by the Radiation Pressure of an Intense Laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 225002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgattoni, A.; Sinigardi, S.; Fedeli, L.; Pegoraro, F.; Macchi, A. Laser-driven Rayleigh-Taylor instability: Plasmonic effects and three-dimensional structures. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 91, 013106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, B. Instability of thin conducting foil accelerated by a finite wavelength intense laser. New J. Phys. 2015, 17, 033026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Pai, C.-H.; Zhang, C.J.; Li, F.; Wu, Y.P.; Hua, J.F.; Lu, W.; Gu, Y.Q.; Silva, L.O.; Joshi, C.; et al. Physical Mechanism of the Transverse Instability in Radiation Pressure Ion Acceleration. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 23480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibel, E.S. Spontaneously Growing Transverse Waves in a Plasma Due to an Anisotropic Velocity Distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1959, 2, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, N.; Schoeffler, K.; Boella, E.; Vieira, J.; Fonseca, R.; Silva, L.O. Interplay between the Weibel instability and the Biermann battery in realistic laser-solid interactions. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 023129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Tikhonchuk, V.; Yi, L.; Araudo, A.; Weber, S. Weibel instability mediated laser hole boring and ion acceleration in an electrostatic shock. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2021, 63, 085013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.W.; Jean, C.; Lee, S.G.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, I.J.; Lee, H.W.; Yoon, J.W.; Sung, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; et al. Highly efficient double plasma mirror producing ultrahigh-contrast multi-petawatt laser pulses. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 6342 and references therein. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zigler, A.; Xie, X.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Q.; Sun, M.; Papeer, J.; Kang, J.; Gao, Q.; Liang, X.; et al. Temporal contrast enhancement of ultrashort pulses using a spatiotemporal plasma-lens filter. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 2279 and references therein. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woryna, E.; Parys, P.; Wołowski, J.; Mróz, W. Corpuscular diagnostics and processing methods applied in investigations of laser-produced plasma as a source of highly ionized ions. Laser Part. Beams 1996, 14, 293–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woryna, E.; Parys, P.; Wołowski, J.; Laska, L.; Krasa, J.; Masek, K.; Pfeifer, M.; Kralikova, B.; Skala, J.; Straka, P. Au49+, Pb50+, and Ta48+ ions from laser-produced plasmas. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domański, J.; Badziak, J. Properties of heavy ion beams produced by a PW sub-picosecond laser. J. Instrum. 2020, 15, C05037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, R.P. High-Energy-Density Physics; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Hidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, J.F. SRIM 2003. 2004. Available online: http://www.srim.org (accessed on 15 December 2025).
- Paul, H. The Stopping Power of Matter for Positive Ions, Modern Practices in Radiation Therapy; Natanasabapathi, G., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2012; p. 124. ISBN 978-953-51-0427-8. Available online: https://cdn.intechopen.com/pdfs/34244/InTech-The_stopping_power_of_matter_for_positive_ions.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Badziak, J.; Domański, J. In search of ways to improve the properties of a laser-accelerated heavy ion beam relevant for fusion fast ignition. Phys. Plasmas 2023, 30, 053107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, C.; Böttcher, I.; Dȩbowski, M.; Förster, A.; Grosse, E.; Koczoń, P.; Kohlmeyer, B.; Laue, F.; Mang, M.; Naumann, L.; et al. Evidence for a Soft Nuclear Equation-of-State from Kaon Production in Heavy-Ion Collisions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Piazza, A.; Müller, C.; Hatsagortsyan, K.Z.; Keitel, C.H. Extremely high-intensity laser interactions with fundamental quantum systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2012, 84, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonoskov, A.; Blackburn, T.G.; Marklund, M.; Bulanov, S.S. Charged particle motion and radiation in strong electromagnetic fields. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2022, 94, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negoita, F.; Roth, M.; Thirolf, P.G.; Tudisco, S.; Hannachi, F.; Moustaizis, S.; Pomerantz, I.; McKenna, P.; Fuchs, J.; Sphor, K.; et al. Laser driven nuclear physics at ELI_NP. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2016, 68, S37–S144. [Google Scholar]
- Gales, S.; Tanaka, K.A.; Balabanski, D.L.; Negoita, F.; Stutman, D.; Tesileanu, O.; Ur, C.A.; Ursescu, D.; Andrei, I.; Ataman, S.; et al. The extreme light infrastructure-nuclear physics (ELI-NP) facility: New horizons in physics with 10 PW ultra-intense lasers and 20 MeV brilliant gamma beams. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2018, 81, 094301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.