Abstract
The study aimed to optimize an oil-in-water emulsion loaded with the antioxidant extract of Randia monantha using Coccoloba uvifera seed protein (CUSP) as emulsifier and ultrasound-assisted processing. Response surface methodology (RSM) was employed to evaluate the effects of protein concentration (2, 3, and 4%), oil amount (5, 15, and 25%), and ultrasound duration (3, 5, and 7 min) on the polydispersity index (PDI) and droplet size. A total of 21 mg of extract was added to each formulation. The optimal conditions were a 3% protein concentration, 20% oil content, and 7 min of ultrasound. Under these conditions, the emulsion showed low PDI (1.88), D[3,2] (1.11 µm), and D[4,3] (1.60 µm). It remained stable at 4 °C for 15 days within a pH range of 6−10, with NaCl concentrations < 200 mM and at temperatures between 25 and 50 °C. Thermal analysis of the emulsion revealed endothermic transitions and decomposition events at higher temperatures, achieving 100% entrapment efficiency and ~83% photoprotection for the extract. This plant protein stabilizes the extract at the oil/water interface, enhancing thermal stability and protecting against photodamage. These qualities are vital in the food industry for preserving thermolabile compounds. The emulsion can enhance antioxidant properties in semi-solid foods or be spray-dried into a powder for functional formulations.
1. Introduction
Oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions are defined as oil droplets dispersed in an aqueous medium. These emulsions have been used in various sectors, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, materials production, cosmetics, and the petroleum industry, among others [1,2]. In the food industry, emulsions are commonly found in products such as milk, cream, and salad dressings. Due to their biphasic nature, these emulsions enable the incorporation of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic nutrients. This characteristic is ideal for integrating nutraceuticals, minerals, extracts, and vitamins of different polarities [1,3].
A stable emulsion relies on an appropriate emulsifier, which is essential for its production, stabilization, and functionality. Emulsifiers are crucial for the long-term stability of oil-in-water emulsions, as they reduce interfacial tension and prevent droplet coalescence by creating a barrier between oil and water [2,3]. A variety of plant-based protein emulsifiers (pea, canola, soy, chickpea, etc.) have been shown to effectively form and stabilize emulsions, serving as viable alternatives to traditional animal-based emulsifiers and standard synthetic surfactants [1,4,5]. The transition from animal-based emulsifiers to plant-based alternatives represents a significant trend within the food industry, motivated by increasing concerns regarding the sustainability and ethical implications of contemporary food supply chains. In addition, the “clean label” movement encourages food manufacturers to prioritize the use of natural ingredients, such as plant-based protein, over synthetic options [4].
In this sense, the exploration and identification of novel plant proteins derived from food processing byproducts that exhibit emulsifying properties represent a significant and intriguing area of research in today’s scientific landscape. For instance, the C. uvifera plant is widely used in conventional folk medicine worldwide. In Mexico, this plant has been used by traditional Mexican medicine to treat gastrointestinal disorders, and for venereal and kidney diseases [6]. Specifically, the fruit of this plant is edible and contains polyphenols, flavonoids, and anthocyanins, which highlight its therapeutic properties. The pulp is eaten fresh or made into jams, jellies, or fermented to make wine [7,8]. However, following pulp separation, the seeds are disposed of as waste, despite this byproduct representing approximately 70% of the total weight of the fruit. The seeds of this fruit have not been widely recognized for their potential in producing low-cost plant proteins as food ingredients or emulsifiers, mainly due to a lack of research regarding them.
Ragazzo-Calderón et al. [9] reported that C. uvifera seed protein (CUSP) concentrate contained 66.49 g/100 g of protein. The application of high-intensity ultrasound (HIU) to CUSP increased solubility, as well as enhanced foaming, emulsifying, and antioxidant properties. Regarding emulsifying properties, CUSP achieved the creation of O/W emulsions with particle sizes ranging from 22.6 to 29.8 µm. Therefore, the authors indicated that CUSP has the potential to function as a new plant protein emulsifier for the food industry. However, further optimization studies are necessary to improve this specific property.
Considering the above, this study was undertaken to optimize a CUSP-based O/W emulsion by ultrasound and to incorporate a hydro-ethanolic extract of Randia monantha. This extract contains high-value biological compounds (HVBCs) such as chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, quercetin, gallic acid, ferulic acid, rutin, and scopoletin, which confer antioxidant and antifungal properties. These compounds, with their potential health benefits, could be the key to developing innovative food emulsions that meet the growing demand for natural antioxidants. This potential application could inspire creativity and innovation in food development [10,11]. However, it is imperative to develop an effective delivery system to protect these compounds from adverse environmental conditions. Thus, the potential of this protein as a promising alternative emulsifier and photoprotective agent for HVBCs in the extract of R. monantha constitutes a central focus of this research. Furthermore, the utilization of seeds from this fruit aims to revitalize byproducts and inspire the transformation of these byproducts into functional, plant-based components for food applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vegetal Material and Chemical Subtances
Sea grape (Coccoloba uvifera) fruits were collected in January 2025 from the coastal region of Tecolutla, Veracruz, Mexico (22°28′ N, 17°09′ S, 93°36′ E, 98°39′ W). After collection, the fruits were manually depulped, washed, and dried in a convection oven (Novatech, HS60-AID, Guadalajara, Jalisco, Mexico) at 45 °C for 72 h. The dried material was initially ground using an electric mill (Gutstark 2000G, Mexico City, Mexico), followed by further grinding in a blender (NutriBullet Series 900, Los Angeles, CA, USA). The resulting powder was sieved through a No. 100 mesh and stored until use.
Chemical substances such as potassium persulfate, the ABTS+ reagent (2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)), and Trolox were sourced from Sigma Chemical Co. in St. Louis, MO, USA. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), sodium chloride (NaCl), ethanol, and hydrochloric acid (HCl) were obtained from Jalmek® (Monterrey, Nuevo León, Mexico). Extra virgin olive oil (brand: Great Value) was purchased from a local market.
2.2. Protein Concentrate Extraction
Protein extraction was performed using the methodology described by Ragazzo-Calderón et al. [9], with slight modifications. A total of 60 g of sea grape seed powder were mixed with 1126 mL of distilled water and 372 mL of 0.2 M NaOH (solution with a final concentration of 0.049 M), and stirred for 2 h. The mixture was then placed in an ultrasonic bath (Digital Ultrasonic Cleaner, CD-4820, Shenzhen, China) operating at 42 kHz for 20 min. After sonication, the mixture was centrifuged (Hermle Labortechnik GmbH, Z 326 K, Wehingen, Germany) at 10,000 rpm and 10 °C for 15 min. The supernatant was recovered, and the pH was adjusted to 4.0 using 1N HCl until protein precipitation occurred. The solution was left to rest for 24 h at room temperature (25 ± 2 °C) to allow complete precipitation. The resulting precipitate was recovered and subjected to a second centrifugation under the same conditions. The obtained protein concentrate was then neutralized to pH 7.0 using 0.2 M NaOH, and stored at 4 °C until use.
2.3. Spray Drying of Protein
A 20% (w/v) protein solution was prepared in distilled water and processed using a mini spray dryer (Büchi B-290, Labortechnik, Flawil, Switzerland), according to the methodology of Ruiz-Montañez et al. [12] with modifications. Atomization was carried out using a nozzle (Labortechnik, Büchi B-290, Flawil, Switzerland) under the following operating conditions: inlet air temperature of 107 °C, feed rate of 4 mL/min, air flow rate of 45 m3/h, and air pressure of 0.5 MPa. During the drying process, the solution was continuously stirred at 350 rpm and maintained at a temperature of 22 ± 1 °C. The resulting powder was recovered from the collection vessel and stored in Falcon tubes inside a desiccator until use.
2.4. Extracting High-Value Biological Compounds (HVBCs) from Randia Monantha
The extraction of HVBCs from R. monantha followed the method described by Vilchis-Gomez et al. [11]. The dried fruits were ground using a mechanical mill, and the resulting powder was sieved through a No. 100 mesh. The powder was mixed with 80% ethanol in a solid-to-solvent ratio of 1:30 (w/v). The mixture was subjected to ultrasound-assisted extraction using a probe-type sonicator (Branson Ultrasonics Corporation, 150D, Brookfield, CT, USA) for 7.5 min at 60% amplitude. The sonicated mixture was then filtered through Whatman No. 1 filter paper (150 mm diameter). The filtrate was concentrated using a rotary evaporator (RV10, IKA, Flawil, Switzerland) under a vacuum pressure of 90 kPa at 50 °C.
2.5. Optimization of the Ultrasound-Assisted Emulsification (UAEm) Parameters
The optimization of the UAEm parameters was conducted using a Box–Behnken Design (BBD) with three independent variables evaluated at three levels: low (−1), medium (0), and high (+1). Protein concentration (2, 3, and 4%), oil concentration (5, 15, and 25%), and ultrasound-assisted emulsification (UAEm) time (3, 5, and 7 min) were used as independent variables. A total of 15 experimental runs (in triplicate) were generated to assess the effects of these factors on emulsion stability indicators (Table 1).

Table 1.
Box–Behnken design with experimental data of PDI, D[3,2] (µm) and D[4,3] (µm).
The dependent variables selected for optimization were the polydispersity index (PDI), surface-weighted mean diameter D[3,2] (µm), and volume-weighted mean diameter D[4,3] (µm), all of which were minimized to improve emulsion uniformity and droplet size distribution. The system behavior was modeled using a second-order polynomial equation, as shown in Equation (1).
where y represents the predicted response; b0 is the intercept; b1, b2, and b3 are the linear coefficients; b12, b13, and b23 represent the interaction coefficients; and b11, b22, and b33 are the quadratic coefficients. The independent variables x1, x2, and x3 correspond to protein concentration, oil concentration, and sonication time, respectively. The experimental design and statistical analyses were conducted using Statistica version 12.0 software (StatSoft, Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA). Optimization was performed through Response Surface Methodology (RSM), and the best conditions were determined by applying ANOVA and a desirability function. This approach identified the formulation that minimized PDI and droplet size, both considered critical parameters for enhancing emulsion stability.
2.6. Preparation of the Emulsion (O/W)
Emulsions were prepared following the methodology of Vilchis-Gómez et al. [11] with some modifications. Emulsions were prepared in a final volume of 6 mL. Initially, 21 mg of Randia monantha extract corresponding to 0.5% w/v were added to glass vials. The protein powder (obtained in Section 2.3) was then incorporated to achieve final concentrations of 2, 3, or 4% (w/v). Distilled water was added to adjust the aqueous phase volumes to 5.70, 5.10, and 4.50 mL, respectively. Olive oil, used as the lipid phase, was then added gradually at concentrations of 5, 15, and 25% (v/v), corresponding to 0.30, 0.90, and 1.50 mL of oil, respectively. While mixing the solution with an Ultra-Turrax homogenizer (IKA T10 basic, Staufen, Germany) for 1 min at 10,000 rpm to form a pre-emulsion. Subsequently, it was subjected to ultrasound treatment using a probe sonicator (model S-150D, Branson Ultrasonics Corporation, Danbury, CT, USA) at 50% amplitude, varying durations for 3, 5, and 7 min.
2.7. Particle Size Distribution
The particle size distribution of the emulsion was determined following the methodology described by Vilchis-Gómez et al. [11] using a laser diffraction analyzer (Mastersizer 3000 Hydro EV, Malvern, Worcestershire, UK). Measurements were conducted at 25 °C, employing a refractive index of 1.46 for the dispersed phase (oil) and 1.33 for the dispersant (water). Prior to analysis, 400 mL of distilled water were added to the Hydro EV unit, and the emulsion was added drop by drop until the laser obscuration value reached between 8% and 12%.
Each sample was analyzed in five consecutive runs, and the results were averaged to obtain a representative particle size distribution curve. The results were reported as the Polydispersity Index (PDI), surface-weighted mean diameter (D[3,2]), and volume-weighted mean diameter (D[4,3]). All values were calculated using the Mastersizer 3000 software version 3.60.
2.8. Entrapment Efficiency of the Emulsion (EEE)
Entrapment efficiency of the emulsion was defined as the proportion of Randia monantha extract successfully retained within the emulsion after processing. The amount of Randia monantha extract in the final emulsion was determined by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The efficiency of entrapment of the emulsion was assessed by comparing the mass fraction of extract initially incorporated in the formulation with the mass fraction detected in the thermogram of the final emulsion. EEE was calculated using the following Equation (2):
where the total fraction corresponds to the initial amount of extract added to the emulsion, and the final fraction is the amount of extract quantified in the final emulsion via TGA.
2.9. Radical Scavenging Activity (RSA) Assessment
The RSA was evaluated using the ABTS+ assay. A stock solution of ABTS+ was prepared by reacting 7 mM ABTS with 2.45 mM potassium persulfate, and the mixture was allowed to stand in complete darkness at 25 °C for 15 h to generate the radical. The solution was then diluted with distilled water to achieve an absorbance of 0.70 ± 0.02 at 734 nm, measured using a UV-Visible spectrophotometer (Cary 50 Bio UV-Visible, Varian, Mulgrave, Australia). For the determination, 50 µL of the sample were combined with 950 µL of the ABTS+ solution and homogenized using a vortex mixer (IKA Lab Dancer S000, Staufen, Germany), then the mixtures were incubated in darkness for 7 min before absorbance was recorded at 734 nm. The ABTS+ RSA (%) was calculated using the following Equation (3):
where Acontrol is the absorbance of the ABTS+ solution without the sample, and Asample is the absorbance with the sample. Calibration curves were constructed by plotting RSA (%) against the concentration of the samples (mg/mL).
2.10. Photostability Evaluation of the Entrapped Extract
To evaluate the photostability of the HVBCs stabilized in the emulsion, three samples of the optimal emulsion containing R. monantha extract were prepared at a final volume of 10 mL. Each formulation included 3% (w/v) C. uvifera seed protein, 20% (v/v) olive oil, 7.4 mL of distilled water, and 3% (v/v) of R. monantha extract, corresponding to its minimum inhibitory concentration (21 mg/mL). For comparison, three control samples containing only the R. monantha extract in 10 mL of distilled water were prepared.
Photodecomposition was induced using an Osram Ultra-Vitalux lamp (300 W) (Osram, Munich, Germany), designed to simulate sunlight. The lamp operates with a tungsten filament and quartz tube, generating UV radiation at 13.6 W. Samples were exposed to UV light at 37 °C, and aliquots (1 mL) were collected at determined intervals of 0, 6, 12, 24, and 48 h. To recover the extract from the emulsion, the pH of each sample was adjusted to the isoelectric point of the protein using 1N HCl. The resulting mixture was centrifuged at 10,000× g for 1 min to isolate the aqueous phase, which contained the released extract. Photostability was assessed by measuring the antioxidant activity of the extract through its ABTS+ radical scavenging capacity, using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Cary 50 Bio, Varian, Mulgrave, Australia). All experiments were conducted in triplicate.
2.11. Evaluation of Emulsion Stability Under Industrial Conditions
The stability of the optimal emulsion, prepared separately as described in Section 2.6, was evaluated under different environmental stress conditions typically faced during industrial processing, including storage, pH variation, ionic strength, and thermal treatment. These procedures were carried out following the methodology described by Vilchis-Gómez et al. [11]. Emulsion stability was evaluated by monitoring changes in particle size distribution after each treatment.
2.11.1. Storage Stability
The emulsion prepared with the optimal process conditions was transferred into glass vials and stored under two different conditions: refrigeration (4 °C) and room temperature (25 ± 2 °C). Particle size distribution and particle size of the emulsion were measured on days 0, 1, 15, and 30.
2.11.2. pH Stability
The freshly prepared emulsions (6 mL) were adjusted to different pH levels (2.0, 4.0, 6.0, 8.0, and 10.0) using 1N HCl or NaOH. After pH adjustment, the samples were left to stand in glass vials at room temperature for 24 h prior to analysis.
2.11.3. Ionic Strength Stability
The effects of ionic strength were tested by adding 1 M NaCl solution to 6 mL emulsion samples to reach final salt concentrations of 100, 200, 300, and 400 mM. After salt addition, the samples were kept at 25 °C for 24 h prior to evaluating particle size distribution.
2.11.4. Temperature Stability
To evaluate thermal resistance, emulsion samples were placed in a convection oven (Novatech, HS60-AID, Tlaquepaque, Jalisco, Mexico) and heated at 30, 50, 70, and 90 °C for 30 min. Following heat treatment, samples were cooled to room temperature and then stored for 24 h before analysis.
2.12. Thermal Stability of the Emulsion
To evaluate the thermal behavior of the emulsion obtained with the optimal UAEm conditions, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was performed using a TGA 550 instrument (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA). A sample of 5–10 mg was heated from 25 °C to 800 °C at a constant rate of 10 °C/min under an inert nitrogen atmosphere. Additionally, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was conducted using a DSC 250 Calorimeter (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA). Samples (1−2 mg) were sealed in hermetic aluminum pans and heated from 25 °C to 400 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min under a continuous nitrogen flow. An empty pan was used as a reference. All thermal profiles were analyzed using TRIOS software version 5.0.0.44616.
2.13. Statistical Analysis
The results were presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three replicates. Emulsion optimization was performed using the response surface methodology (RSM) and the desirability function. Statistical analysis of the emulsion characterization and stability results was performed using Statistica software version 12.0 (StatSoft, Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA). Data were subjected to one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), and a post hoc analysis was performed using the Least Significant Difference (LSD) method to compare means, with a significance level of p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Modeling and Optimization of UAEm Parameters
The determination coefficients (R2) for the predicted versus experimental responses were 0.8972 for PDI (y1), 0.9458 for D[3,2] (y2, µm), and 0.8852 for D[4,3] (y3, µm) (Table 2). These values indicate that the models adequately described the relationship between the independent variables and were able to explain over 88% of the observed variation, confirming their reliability. Additionally, the adjusted R2 values for y1, y2, and y3 were 0.8189, 0.9026, and 0.7934, respectively, following a similar trend to the unadjusted R2. These results demonstrate strong agreement between the experimental data and model predictions, further supporting the robustness and predictive capacity of the fitted quadratic models.

Table 2.
Fitted regression coefficients and quadratic models for PDI (y1), D[3,2] (y2), and D[4,3] (y3).
3.1.1. Influence of Variables on Polydispersity Index
The fitted quadratic models suggested that protein concentration, oil content, and UAEm process time had a statistically significant influence on the PDI of the emulsions (p < 0.05). PDI reflects the width of the particle size distribution and serves as an indicator of the uniformity of droplet sizes within the system. Protein molecules may adsorb on the oil/water interface, forming a cohesive interfacial layer that contributes to emulsion stability, limits droplet aggregation, and promotes a narrower size distribution. It has been reported that CUSP contains a high proportion of hydrophobic amino acids (81.08%), which likely enhances its interfacial activity and affinity for the oil phase. This hydrophobic character may facilitate the formation of a stable interfacial film around the droplets, contributing to improved emulsification. When sufficient protein is available to stabilize the increased interfacial area produced during emulsification, the system may exhibit less variability in droplet size. This reduction in heterogeneity could be associated with weaker interfacial restoring forces, lowering the probability of coalescence during droplet collisions [9,13].
At early stages of sonication, an increase in PDI may occur due to insufficient emulsifier to stabilize the newly formed oil/water interface, leading to a more heterogeneous size distribution. As sonication progresses and the interfacial area continues to expand, higher emulsifier loads may be required to maintain stability. If this demand is not met, droplet aggregation may occur, and the emulsifier may undergo structural modification due to ultrasonic stress, further contributing to broad size distributions [14]. Oil content may also play a role by influencing emulsion viscosity. A higher oil fraction increases viscosity, which restricts droplet movement and reduces the frequency of collisions, consequently lowering the flocculation, potentially helping to maintain a more consistent size distribution and thus a lower PDI [15].
Furthermore, cavitation effects generated during UAEm may contribute to the breakdown of larger droplets, promoting a more uniform dispersion and stabilizing the PDI [16]. However, prolonged sonication could lead to an over-processing effect, where the intense energy input and localized heating promote droplet reaggregation. This may decrease size homogeneity and destabilize the system, as previously associated with reductions in interfacial integrity [17].
3.1.2. Influence of Variables on Particle Size
The fitted quadratic models suggested that oil content and UAEm process time had a statistically significant influence on the mean particle diameter (D[3,2] and D[4,3]) of the emulsions (p < 0.05). The model indicates that increasing the proportion of the oil phase was associated with a tendency toward larger droplet sizes. This effect may be attributed to the elevated volume fraction of dispersed oil, which imposes a higher demand for interfacial stabilizers (emulsifiers). When the protein content is insufficient to fully cover the enlarged oil/water interface, coalescence and droplet aggregation are more likely to occur, leading to an increase in average particle size [18,19]. This observation suggests that under higher oil content conditions, a proportional increase in protein concentration is necessary to ensure complete interfacial coverage and avoid destabilization. Adequate surface coverage by the protein helps prevent droplet–droplet interactions and coalescence, thereby maintaining smaller particle sizes and improving emulsion stability.
Conversely, an unbalanced formulation, characterized by an excess of oil relative to protein, can lead to partial surface coverage, resulting in the formation of larger droplets and broader particle size distributions [20,21]. These results align with findings by Kasprzak et al. [22], who found that increasing the oil concentration leads to the formation of a larger interfacial area, requiring a greater proportion of available protein molecules to adsorb at the interface for stabilization. Consequently, fewer protein molecules remain unbound in the continuous phase, decreasing the size of the droplets in rapeseed stabilized emulsions.
Moreover, the model suggested that longer UAEm times contributed to the formation of emulsions with smaller droplet diameters. This effect is likely driven by the mechanical forces generated during ultrasonication, such as cavitation-induced shear, turbulence, and micro-jetting, which promote the fragmentation of larger oil droplets into finer ones. These forces increase with sonication time, enhancing energy transfer to the system and improving droplet breakup efficiency [23,24]. This observation aligns with the findings reported by Figueiredo-Furtado et al. [25], who demonstrated that extending ultrasound treatment time led to a reduction in droplet size in emulsions.
3.1.3. Response Surface Methodology
The interactions among the independent variables and their influence on the desirability of the responses are illustrated in the response surface methodology (RSM) plots (Figure 1). According to the model, increasing protein concentration is necessary when the oil content was raised, in order to maintain a balanced protein-to-oil ratio. This balance is essential to ensure adequate interfacial coverage of the oil droplets and reduction in interfacial tension, which in turn promotes the formation of smaller particles, increasing the repulsive forces and resulting in more stable immiscible phases [26,27]. However, excessive protein concentrations may result in a portion of unadsorbed proteins remaining in the continuous phase, which can induce flocculation and droplet aggregation through attractive forces. This process increases the possibility of coalescence and can ultimately compromise the stability of the emulsion [28,29].
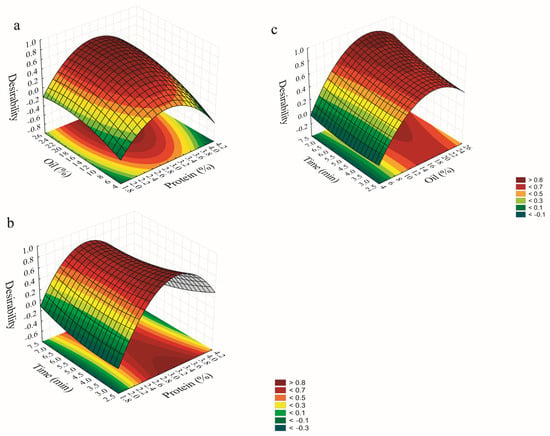
Figure 1.
Desirability surface plots showing the interaction effects of oil–protein (a), time−protein (b), and time−oil (c).
Regarding the interaction between protein concentration and UAEm time, the model suggests that intermediate protein levels are most favorable. Protein concentration emerged as the most influential variable on the overall desirability. Sufficient protein levels are required to enable adsorption at the oil/water interface, promoting effective droplet formation. At low protein concentrations, insufficient surface coverage may impair droplet formation and stability, leading to coalescence and increased particle sizes [30]. Conversely, excessively high protein concentrations may promote protein–protein interactions during sonication, leading to the formation of aggregates, flocculation, and emulsion destabilization [31].
For the interaction between UAEm time and oil content, the model indicates that maximizing the oil phase can improve desirability when sonication time increases. A well-balanced combination of higher oil content and sufficient ultrasound promotes droplet disruption through cavitation and turbulent flow, leading to finer particles. This enhanced droplet breakup contributes to greater emulsion stability by limiting particle–particle interactions and reducing the risk of flocculation or coalescence [32].
3.1.4. Validation of the Predicted Optimal UAEm Conditions
To achieve the desired optimization criteria, the model proposed conditions of 3% of protein concentration, 20% of oil content, and 7 min of UAEm time. Under these parameters, the emulsion exhibited the lowest values of PDI, D[3,2], and D[4,3] (Table 1). The experimental validation of the optimal formulation showed no significant differences (p > 0.05) compared to the predicted values, indicating strong agreement between the model and observed results (Table 3). These findings support the reliability of the model and confirm that UAEm is a practical approach for producing emulsions with small and uniformly distributed droplets, which are key indicators of emulsion stability. Although the optimization focused on the combined effect of the independent variables on the responses, likely, the observed improvements result not from a single factor, but from a potential synergistic interaction among the protein, the oil phase, and the ultrasound treatment, which could collectively influence droplet formation and the stability of the emulsion.

Table 3.
Experimental and predicted values of PDI, D[3,2], and D[4,3] using the optimal values of UAEm.
3.2. Photoprotective Effect of the Optimal Emulsion Under Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation
The ability of plant proteins to protect photosensitive bioactive compounds is crucial for maintaining their stability and biological activity. Both the free extract and the emulsion containing the extract exhibited a gradual decrease in RSA upon exposure to ultraviolet radiation. The reduction in RSA was particularly pronounced in the free extract, which demonstrated a 22% decrease after 48 h of exposure (Figure 2). In contrast, the emulsion experienced a 17% reduction in RSA over the same time frame. The retention of RSA in the emulsion suggests that the protein adsorbed at the oil/water interface may have formed a UV-protective barrier, potentially providing photoprotection to the extract.
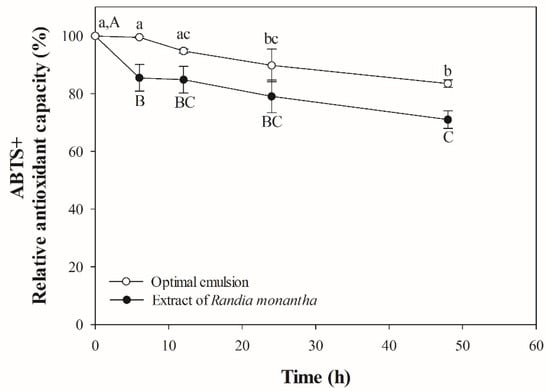
Figure 2.
Photooxidative stability of optimal emulsion and extract of Randia monantha. Lowercase letters indicate statistical differences within the same treatment group over time. Capital letters indicate statistical differences between treatment groups at the same time point.
Chromophore regions, composed of aromatic amino acids such as tyrosine and phenylalanine, along with sulfur-containing amino acids like cysteine, play a critical role in photoprotection [33]. Recent reports have indicated that CUSP contains high levels of phenylalanine [9], which exhibits the ability to absorb ultraviolet light. When proteins were subjected to UV radiation, phenylalanine acts as a chromophore, capturing UV energy and thereby providing a protective mechanism for other regions of the protein or other molecules, which aids in mitigating potential damage [33,34]. The photoprotective effects of plant proteins have been observed in multiple studies. For instance, Jiang et al. [35] reported that a nanoemulsion formulated with pea protein protects cholecalciferol from UV degradation. Additionally, Vilchis-Gómez et al. [13] found that a double emulsion (W/O/W) based on jackfruit leaf protein provides photoprotection for the hydroethanolic extract of Randia monantha. Therefore, the results indicate that CUSP also has potential as a photoprotective agent for photosensitive bioactives.
3.3. Optimal Emulsion Stability
3.3.1. Storage Stability of the Optimal Emulsion
Droplet size distribution plays a critical role in defining the physicochemical characteristics of emulsions, including their rheology, physical stability, and the performance of stabilizing agents [36]. During storage at room temperature, a significant increase in droplet size was observed (p < 0.05) (Figure 3a), likely due to physical and molecular interactions occurring over time. As emulsions are inherently non-equilibrium systems, they tend to minimize interfacial energy through various destabilization mechanisms such as coalescence, creaming, flocculation, and Ostwald ripening [37].
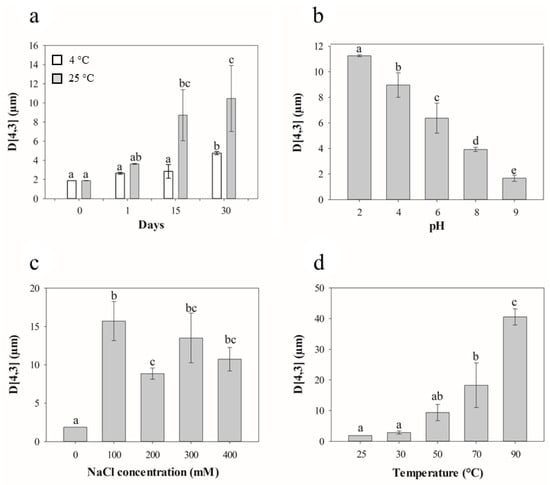
Figure 3.
Effect of storage (a), pH (b), NaCl concentration (c), and temperature (d) on the surface mean particle size of the optimal emulsion. Treatments with different letters differ significantly (p < 0.05).
The dispersed droplets remain in constant motion, and as their mobility increases, so does the frequency of collisions. These collisions promote coalescence, particularly when the interfacial layer becomes compromised. Proteins at the droplet interface may initially provide stabilization; however, over time, non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic forces can lead to the formation of protein–protein interactions at the interface [38]. These intermolecular associations may render the interfacial film more rigid or brittle, making it more susceptible to rupture under mechanical stress or droplet deformation, ultimately compromising emulsion stability. This phenomenon is accelerated at higher temperatures, where increased kinetic energy enhances droplet collisions and promotes aggregation, as supported by Yang et al. [39], who observed droplet size growth in emulsions stored under ambient conditions. Similar findings were reported by Sobhaninia et al. [40], who studied emulsions stabilized with whey protein and found that continuous droplet collision under storage led to droplet fusion and growth, especially in the absence of sufficient interfacial protection. In contrast, no significant changes (p < 0.05) in mean droplet size were observed in emulsions stored under refrigeration (4 °C) throughout the 30-day period, with only a slight increase detected at the end of storage. This stability may be attributed to the increased viscosity of the emulsion at lower temperatures, which can restrict the mobility of oil droplets and, consequently, reduce the probability of collision and aggregation. As reported by Ronningsen et al. [41], emulsion viscosity tends to decrease with rising temperature, which facilitates droplet movement. Therefore, the higher viscosity at 4 °C may act as a physical barrier, slowing down droplet dynamics and preserving the structural integrity of the emulsion. Additionally, the thicker oil/water interface could contribute to enhanced resistance against destabilizing effects, such as coalescence or structural breakdown during storage [42]. Similar behavior was observed by Laosinwattana et al. [43], who reported that ultrasound-assisted nanoemulsions remained stable with minimal changes in droplet size for at least five weeks when stored at 4 °C, supporting the protective role of low temperature storage in maintaining emulsion stability.
3.3.2. pH Stability Evaluation
A significant increase in particle size was observed as the pH of the emulsions decreased (p < 0.05), indicating a strong influence of pH on emulsion stability. This behavior is consistent with the sensitivity of protein-stabilized emulsions to pH, particularly near their isoelectric point (pI) (Figure 3b). At pH values close to the pI, electrostatic repulsion between protein-coated droplets is significantly reduced, which facilitates flocculation and droplet coalescence, ultimately leading to larger particle sizes and decreased stability. Conversely, at alkaline pH levels, emulsions exhibited enhanced stability, characterized by reduced droplet size and minimal phase separation. This improved performance may be attributed to the increased electrostatic repulsion between protein molecules, which inhibits droplet–droplet interactions and prevents interaction [44,45].
These findings align with the observations of Östbring et al. [46], who reported that emulsions stabilized with rapeseed protein exhibited smaller droplet sizes when formulated near neutral pH, likely due to a more favorable balance of repulsive and attractive forces under these conditions. Overall, maintaining the emulsion system at a pH sufficiently distant from the isoelectric point of the protein appears to be crucial for promoting electrostatic stabilization and achieving uniform droplet distribution.
3.3.3. Ionic Strength Stability Study
A significant increase in droplet size was observed as NaCl concentration increased (p < 0.05), highlighting the destabilizing effect of ionic strength on emulsions (Figure 3c). This destabilization can be primarily attributed to electrostatic screening, in which Na+ and Cl− ions reduce the surface charge of protein-coated droplets. By neutralizing these repulsive electrostatic forces, the ionic strength allows droplets to approach more closely, favoring flocculation and coalescence [15,47]. At high ionic strength, even though protein adsorption may increase, the interfacial layer becomes less cohesive, and the attractive forces can dominate, leading to the formation of larger oil droplets [48]. Moreover, high salt concentrations can lower the viscosity of the continuous phase, facilitating droplet mobility and increasing the probability of collisions, promoting coalescence [49].
These results are consistent with findings by French et al., who reported a continuous increase in droplet size as NaCl concentration was added from 0 to 1500 mM, likely due to reduced particle adsorption at the oil/water interface and decreased trapping energy caused by salt-induced charge screening. Interestingly, they observed that droplet size was minimized at 10 mM NaCl. This improvement may be explained by impeding the particle bridging at very low ionic strengths, where insufficient screening allows strong attraction between bridging proteins and multiple droplets. These findings suggest that low NaCl concentrations may favor more stable emulsions by minimizing aggregation without compromising electrostatic repulsion.
3.3.4. Temperature Stability Determination
The temperature range of 70 to 90 °C significantly influenced the size of emulsion droplets (Figure 3d). This phenomenon can be attributed to increased droplet aggregation and the formation of larger droplets resulting from the denaturation of proteins at the oil/water interface, which reduces the electrostatic repulsion [50]. Protein aggregation is generally associated with conformational changes and loss of structural integrity that result in the exposure of specific nonpolar residues [51]. Additionally, elevated temperatures reduce both interfacial tension and viscosity, particularly due to thermal thinning and partial oil phase separation. These effects compromise the structural integrity of the emulsifying layer and accelerate destabilization phenomena such as coalescence [52].
Thermal treatment may also promote lipid oxidation during storage, especially in emulsions, with higher temperatures promoting oxidative decomposition. Oxidation alters the composition of the interfacial layer, potentially inducing rearrangement or desorption of emulsifying agents, which in turn weakens the protective interface and destabilizes the emulsions [43]. In line with these observations, Chen et al. [53] reported that emulsions stabilized with whey protein isolate showed marked increases in droplet size after heat treatment. This could be attributed to the inability of these proteins to form a dense and ordered interfacial layer at the oil/water interface after thermal denaturation.
The findings suggest that lower temperatures, specifically between 25 and 50 °C, are more effective for preserving the integrity of the oil/water interface in emulsion droplets. In this sense, this emulsion may have potential applications in the food and cosmetics industries, particularly in processes that do not exceed temperatures of 50 °C.
3.4. Thermal Stability of the Optimal Emulsion
3.4.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis
The TGA and DTG curves of the extract and CUSP showed an initial thermal event associated with water content below 200 °C (Figure 4). The extract exhibited a second phase of mass loss between 174.22 and 237.4 °C, accounting for 57.2% of the total mass (Figure 4a). This mass loss could be attributed to the decomposition of acidic phenolic compounds present in the extract, such as ferulic acid, gallic acid, caffeic acid, vanillic acid, and chlorogenic acid [10]. Phenolic acids can undergo bond cleavage at elevated temperatures, resulting in the formation of smaller molecular structures [54,55]. A third mass loss of 7.8% was observed in the range of 399.1−467.3 °C. This mass loss was attributed to the decomposition of products derived from phenolic acids generated in earlier stages, as well as larger molecular structural compounds [56].
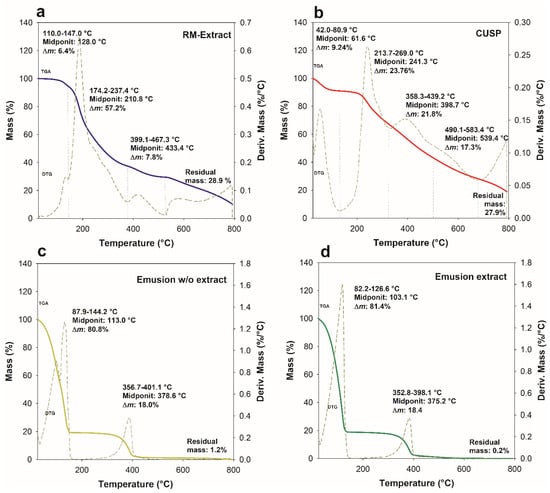
Figure 4.
TGA and DTG curves of Randia monantha extract (a), CUSP (b), emulsion w/o extract (c) and emulsion extract (d).
Regarding CUSP, the second (23.7%) and third (21.8%) mass losses were observed at 213.7−269.0 °C and 358.3−439.2 °C, respectively (Figure 4b). The second mass variation was associated with the release of protein fragments resulting from the onset of thermal decomposition. The third mass loss may be attributed to the decomposition of protein fragments with varying thermal stability, which were produced in the previous stage as a result of the increased heating temperature [57]. When proteins are exposed to heat, they undergo a decomposition process characterized by the disruption of intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, and electrostatic interactions. This event leads to the release of numerous small molecules and volatile fragments, which vary in their thermal stability [58]. The CUSP demonstrated a fourth mass loss of 17.3% occurring within the temperature range of 490.1 to 583 °C. This phenomenon may be associated with the decomposition of larger molecular structures, potentially including residual byproducts resulting from CUSP extraction, as well as the initiation of ash formation [59].
On the other hand, the emulsion with and without extract showed two distinct mass losses (Figure 4c,d). The first mass loss was due to the water content in the emulsion (80.8−81.4%). The second mass loss of the emulsion without and with extract occurred around 356.7−401.1 °C (18.0%) and 352.8−398.1 °C (18.4%), respectively. The observed mass loss has been associated with the decomposition of various components within the emulsion, specifically CUSP, extract, and oil. The results demonstrate that both emulsions exhibited closely comparable decomposition temperatures, which surpassed the initial decomposition temperature of the extract, recorded at 174.2 °C. The TGA curves of the emulsions did not show an overlapping of thermal events characteristic of either the extract or CUSP, as corroborated by the DTG curves. These curves demonstrated a singular thermal decomposition event, indicating a significant interaction among the components involved [60]. This trend was also observed in emulsions stabilized with jackfruit leaf protein [11,57]. Finally, at temperatures exceeding 600 °C, all the samples exhibited a residual mass resulting from the non-oxidative atmosphere used during thermal analysis, which was related to the carbonization of the material [61].
3.4.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Analysis
In DSC, the extract displayed two endothermic events: the first occurred at 167 °C, indicating the melting of the extract, while the second occurred at 196.5 °C, indicating its thermal degradation (Figure 5a) [62]. This observation was based on the fact that the specified temperature closely aligns with the second DSC event in the DTG curve, which indicates that the initial decomposition peak occurs at 210 °C.
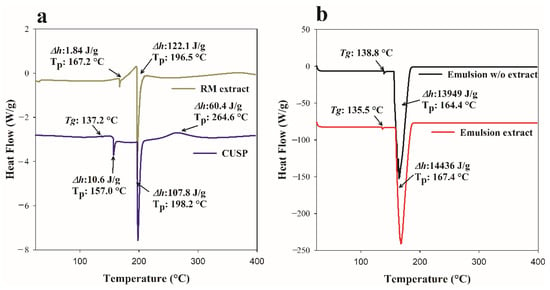
Figure 5.
DSC curves of Randia monantha extract, CUSP (a), and of emulsions w/o and with extract (b). Tp: Peak temperature; Tg: Glass transition temperature; Δh: Enthalpy.
The DSC curve of CUSP showed a glass transition temperature of 137.2 °C, along with two endothermic events at 157.0 °C and 198.2 °C that correspond to the denaturation (melting) and the beginning of oxidative decomposition and degradation processes [63], respectively. This second endothermic event corresponds to the onset temperature of decomposition (213.7 °C) of CUSP, as observed in the DTG curve (Figure 4a). Furthermore, the CUSP exhibited an exothermic event at a temperature of 264.6 °C, which was attributed to the disruption of hydrophobic interactions that led to particle aggregation upon heating [64,65,66]. Alsaleem et al. [67] observed this behavior in quinoa proteins. They suggested that the proteins may experience increased levels of denaturation or unfolding. In this study, the exothermic thermal event correlates with the final decomposition temperature of CUSP, recorded at 269.0 °C in the DTG curve. This observation could indicate that CUSP undergoes rapid decomposition at this temperature, accompanied by the release of heat during the decomposition process.
The emulsion, whether containing the extract or not, displayed a Tg very close to that of the protein, indicating an effect of CUSP on the formulation (Figure 5b). Both emulsions exhibited a single endothermic event. This event occurred at a higher temperature and with greater enthalpy in the emulsion that contained the extract, indicating better thermal stability. The DSC curve for the emulsion containing the extract did not show the typical endothermic peak associated with the extract itself (Figure 5a). This observation suggests that the extract has been effectively encapsulated within the emulsion droplets. Such findings may indicate a robust interaction between the CUSP and the core material, further corroborated by the high entrapment efficiency (Section 3.4). Consequently, the interactions among the various components contributed to the emergence of new endothermic peaks in the thermal profile (Figure 5b). Indeed, the interactions or formations of complexes may be discerned through the analysis of both the intensity (enthalpy) and the expansion of the endothermic peak relative to the other components present in the formulation [68]. The research findings suggest that CUSP functions as an emulsifier, imparting thermal stability to compounds with significant biological value. Consequently, it serves as an effective alternative to plant-based protein for preserving heat-sensitive compounds.
3.5. Efficiency of Extract Entrapment by Emulsification (EEE)
The DTG curve of the emulsion containing the extract indicated a direct correlation between the mass fraction of the extract and the amount of extract incorporated into the formulation. The added mass fractions of the components in the optimal emulsion, including water (76.5%), protein (3.0%), oil (20.0%), and R. monantha extract (0.5%), corresponded with the second mass loss event observed in the DTG curve (Figure 4). Therefore, the CUSP-stabilized oil-in-water emulsion, achieving an impressive encapsulation efficiency of 100%, represents a significant advancement that underscores the effectiveness of CUSP as an encapsulating polymer. This finding opens up exciting possibilities for applications that involve nano- and microencapsulation of bioactive compounds. However, the implications of using CUSP within the food industry are so significant that they demand further exploration. As a result, CUSP is likely to become an important focus for future research efforts.
4. Conclusions
This study highlights the effectiveness of Coccoloba uvifera seed protein, an often-overlooked food byproduct, in stabilizing oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions through comprehensive optimization processes. This emulsion has the potential to act as a delivery system for HVBCs with significant biological value. It demonstrates high entrapment efficiency, good photostability, and a droplet size of less than 2 µm, which meets the requirements for emulsions stabilized by plant proteins. These characteristics are particularly relevant for spray-drying processing, broadening the scope of its applications. Furthermore, the stability of the emulsion under various conditions (such as storage, pH, and ionic strength) can reveal its potential applications in dressings and similar products. The findings indicate that C. uvifera seed protein is a promising plant-based alternative for entrapment and photoprotection the of HVBCs. It is essential to recognize that this biopolymer is relatively new. Hence, optimizing processing parameters is crucial to achieve maximum performance in micro- and nanoencapsulation processes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.N.d.l.C., D.E.J.-S., C.C.-C., D.S.V.-G., J.A.R.-S. and M.C.-S.; Methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, data curation, visualization, and investigation, M.N.d.l.C., D.S.V.-G., C.C.-C. and J.A.R.-S.; Resources, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition, J.A.R.-S. and M.C.-S.; Writing—original draft preparation, D.S.V.-G., C.C.-C. and J.A.R.-S.; Writing—review and editing, D.E.J.-S., D.S.V.-G., C.C.-C., M.C.-S. and J.A.R.-S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data utilized in this research is available for access upon submission of a formal request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Δh | Enthalpy |
| CUSP | Coccoloba uvifera seed protein |
| D[3,2] | Surface-weighted mean diameter |
| D[4,3] | Volume-weighted mean diameter |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| DTG | Derivative Thermogravimetry |
| EEE | Entrapment efficiency of the emulsion |
| HIU | High-Intensity Ultrasound |
| HVBC | High-value biological compound |
| PDI | Polydispersity index |
| RSM | Response surface methodology |
| Tg | Glass transition temperature |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| UAEm | Ultrasound-assisted emulsification |
References
- Son, C.-G.; Hong, G.-P.; Jo, Y.-J. Fabrication and Stability of Oil-in-Water Emulsions with Mung Bean Protein Aggregates and Soy Lecithin. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 705, 135661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhou, J.; He, C.; He, L.; Li, X.; Sui, H. The Formation, Stabilization and Separation of Oil–Water Emulsions: A Review. Processes 2022, 10, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, M.; Kowalska, M.K.; Ludwiński, P. Emulsions, Their Quality and Importance in Food, Cosmetic, and Pharmaceutical Industries. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2024, 80, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun Capar, T.; Iscimen, E.M.; McClements, D.J.; Yalcin, H.; Hayta, M. Preparation of Oil-in-water Emulsions Stabilized by Faba Bean Protein—Grape Leaf Polyphenol Conjugates: pH-, Salt-, Heat-, and Freeze—Thaw-stability. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 6483–6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhi, L.; Jiao, B.; Hu, H.; Ma, X.; Agyei, D.; Shi, A. Plant Protein-Based Emulsifiers: Mechanisms, Techniques for Emulsification Enhancement and Applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 109008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hakim, F.; Gad, H.; Radwan, R.; Ayoub, N.; El-Shazly, M. Biological and Phytochemical Review on the Genus Coccoloba (Polygonaceae). Arch. Pharm. Sci. Ain Shams Univ. 2019, 3, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Campos, M.R.; Ruiz-Ruiz, J.; Chel-Guerrero, L.; Betancur-Ancona, D. Coccoloba uvifera (L.) (Polygonaceae) Fruit: Phytochemical Screening and Potential Antioxidant Activity. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 534954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.S.; Ruiz, J.R.; Guerrero, L.C.; Ancona, D.B. Coccoloba uvifera as a Source of Components with Antioxidant Activity. In Biotechnology of Bioactive Compounds: Sources and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2015; pp. 151–161. ISBN 9781118733103. [Google Scholar]
- Ragazzo-Calderón, F.Z.; Calderón-Chiu, C.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; Hernández-Molina, D.S.; Martinez-Ramos, K.E.; Ragazzo-Sanchez, J.A. Application of High-Intensity Ultrasound to Coccoloba uvifera Seed Proteins and Its Effect on the Amino Acid Profile, Techno-Functional Properties and Antioxidant Capacity. Rev. Bio Cienc. 2025, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Santoyo, M.; Calderón-Chiu, C.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A. Characterisation of Hydrophilic Bioactive Extracts of Fruits from Mexico: Phenolic Content, Thermal and Kinetic and Thermodynamic Analysis. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2025, 80, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchis-Gómez, D.S.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A. Double Emulsion (W/O/W) Added with Hydro-Ethanolic Extract of Randia Monantha Stabilized with Jackfruit Leaf Protein Fraction: Optimization, Characterization, and Antifungal Activity. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Montañez, G.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; Chevalier-Lucia, D.; Picart-Palmade, L.; Jimenez-Sánchez, D.E.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A. Ultrasound-Assisted Microencapsulation of Jackfruit Extract in Eco-Friendly Powder Particles: Characterization and Antiproliferative Activity. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 40, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.S.; Zhang, S.B.; Zhang, S.Y.; Peng, Y.X. Comparative Study of High-intensity Ultrasound and High-pressure Homogenization on Physicochemical Properties of Peanut Protein-stabilized Emulsions and Emulsion Gels. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramisetty, K.A.; Pandit, A.B.; Gogate, P.R. Ultrasound Assisted Preparation of Emulsion of Coconut Oil in Water: Understanding the Effect of Operating Parameters and Comparison of Reactor Designs. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2015, 88, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Protein-Stabilized Emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 9, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepišnik Perdih, T.; Zupanc, M.; Dular, M. Revision of the Mechanisms behind Oil-Water (O/W) Emulsion Preparation by Ultrasound and Cavitation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 51, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; He, M.; Xu, J.; Chen, F.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Effect of Ultrasonication on the Stability and Storage of a Soy Protein Isolate-Phosphatidylcholine Nanoemulsions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Yi, J.; Cui, L.; Liu, N.; Cao, Y.; Decker, E.A. Ultrasound Improving the Physical Stability of Oil-in-Water Emulsions Stabilized by Almond Proteins. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4323–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions Principles, Practices, and Techniques; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J.; Lu, J.; Grossmann, L. Proposed Methods for Testing and Comparing the Emulsifying Properties of Proteins from Animal, Plant, and Alternative Sources. Colloids Interfaces 2022, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sakkaf, M.K.; Onaizi, S.A. Effects of Emulsification Factors on the Characteristics of Crude Oil Emulsions Stabilized by Chemical and Biosurfactants: A Review. Fuel 2024, 361, 130604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, M.M.; Jarzębski, M.; Smułek, W.; Berski, W.; Zając, M.; Östbring, K.; Ahlström, C.; Ptasznik, S.; Domagała, J. Effects of Concentration and Type of Lipids on the Droplet Size, Encapsulation, Colour and Viscosity in the Oil-in-Water Emulsions Stabilised by Rapeseed Protein. Foods 2023, 12, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.J.; Holkar, C.R.; Karekar, S.E.; Pinjari, D.V.; Pandit, A.B. Ultrasound Assisted Manufacturing of Paraffin Wax Nanoemulsions: Process Optimization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 23, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Leong, T.S.H.; Ashokkumar, M.; Martin, G.J.O. A Study of the Effectiveness and Energy Efficiency of Ultrasonic Emulsification. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Figueiredo Furtado, G.; Mantovani, R.A.; Consoli, L.; Hubinger, M.D.; da Cunha, R.L. Structural and Emulsifying Properties of Sodium Caseinate and Lactoferrin Influenced by Ultrasound Process. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, X. Thoroughly Review the Recent Progresses in Improving O/W Interfacial Properties of Proteins through Various Strategies. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1043809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.D.; Sidzhakova, D.; Ivanov, I.B.; Campbell, B. Interrelation between Drop Size and Protein Adsorption at Various Emulsification Conditions. Langmuir 2003, 19, 5640–5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Luo, Y. Plant Protein-Based High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsions: Functional Properties and Potential Food Applications. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 12, 100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Li, X.; Zhai, J.; Su, Y.; Gu, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Stability of Protein Particle Based Pickering Emulsions in Various Environments: Review on Strategies to Inhibit Coalescence and Oxidation. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahaije, R.J.B.M.; Hilgers, R.J.; Wierenga, P.A.; Gruppen, H. Relative Contributions of Charge and Surface Coverage on PH-Induced Flocculation of Protein-Stabilized Emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 521, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.J.; Kim, H.D.; Ye, Y.J.; Kong, M.; Lim, W.S.; Lee, M.H. Effects of Ultrasound-Induced Structural Modifications on the Emulsifying Properties of Tenebrio Molitor Proteins. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2025, 117, 107354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amal Sudaraka Samarasinghe, H.G.; Dharmaprema, S.; Manodya, U.; Kariyawasam, K.P.; Samaranayake, U.C. Exploring Impact of the Ultrasound and Combined Treatments on Food Quality: A Comprehensive Review. Turk. J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 12, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Srivastava, A.; Vashistha, V.K. The Effect of Ultraviolet Light Exposure on Proximate Composition, Amino Acid, Fatty Acid, and Micronutrients of Cold Water Fish, “Barilius Vagra”. Orient. J. Chem. 2019, 35, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, F.L.; Castro-Varela, P.; Vega, J.; Losantos, R.; Peñín, B.; López-Cóndor, L.; Pacheco, M.J.; Redoli, S.L.; Marí-Beffa, M.; Abdala-Díaz, R.; et al. Novel Synthetic UV Screen Compounds Inspired in Mycosporine-like Amino Acids (MAAs): Antioxidant Capacity, Photoprotective Properties and Toxicity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2024, 261, 113050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Yildiz, G.; Ding, J.; Andrade, J.; Rababahb, T.M.; Almajwalc, A.; Abulmeatyc, M.M.; Feng, H. Pea Protein Nanoemulsion and Nanocomplex as Carriers for Protection of Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3). Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollakhalili Meybodi, N.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Abdolmaleki, K.H. Effect of Dispersed Phase Volume Fraction on Physical Stability of Oil-in-Water Emulsion in the Presence of Gum Tragacanth. J. Food Qual. Hazards Control 2014, 1, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.H.; Chiang, B.H. Process Optimization and Stability of D-Limonene-in-Water Nanoemulsions Prepared by Ultrasonic Emulsification Using Response Surface Methodology. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, R.S.H.; Nickerson, M.T. Food Proteins: A Review on Their Emulsifying Properties Using a Structure–Function Approach. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Fan, C.; Gao, Q.; Xie, Q.; Jiang, C.; Wang, S.; Jiang, S.; Li, B. Physicochemical Characterization, Sensory Quality Analysis, and Shelf-Life Prediction during the Storage of a Total Nutrient Formula Emulsion. LWT 2024, 204, 116427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhaninia, M.; Nasirpour, A.; Shahedi, M.; Golkar, A. Oil-in-Water Emulsions Stabilized by Whey Protein Aggregates: Effect of Aggregate Size, PH of Aggregation and Emulsion PH. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronningsen, H. Correlations for Predicting Viscosity of W/O-Emulsions Based on North Sea Crude Oils. In Proceedings of the SPE International Symposium on Oilfield Chemistry, San Antonio, TX, USA, 14 February 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Jin, H.; Xu, J. Improvement of Protein Emulsion Stability through Glycosylated Black Bean Protein Covalent Interaction with (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 2546–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laosinwattana, C.; Somala, N.; Dimak, J.; Teerarak, M.; Chotsaeng, N. Ultrasonic Emulsification of Cananga Odorata Nanoemulsion Formulation for Enhancement of Herbicidal Potential. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, B.; Xie, F.; Hu, M.; Sun, Y.; Han, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Emulsion Stability and Dilatational Rheological Properties of Soy/Whey Protein Isolate Complexes at the Oil-Water Interface: Influence of PH. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Vardhanabhuti, B. The Influence of PH on the Emulsification Properties of Heated Whey Protein–Pectin Complexes. Foods 2024, 13, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Östbring, K.; Matos, M.; Marefati, A.; Ahlström, C.; Gutiérrez, G. The Effect of Ph and Storage Temperature on the Stability of Emulsions Stabilized by Rapeseed Proteins. Foods 2021, 10, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Li, X.; Yin, Y.; Kong, B.; Sun, F.; Liu, Q. Effects of Sodium Chloride on the Physical and Oxidative Stability of Filled Hydrogel Particles Fabricated with Phase Separation Behavior. Foods 2021, 10, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Deng, X.; Liu, T.; Yang, B.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, Q. Influence of NaCl on the Oil/Water Interfacial and Emulsifying Properties of Walnut Protein-Xanthan Gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 72, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narukulla, R.; Ojha, U.; Sharma, T. Effect of NaCl Concentration on Stability of a Polymer–Ag Nanocomposite Based Pickering Emulsion: Validation via Rheological Analysis with Varying Temperature. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 21545–21560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Chen, Q.; Li, G.; Zhu, Z.; Yi, J.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Properties and Stability of Perilla Seed Protein-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Influence of Protein Concentration, PH, NaCl Concentration and Thermal Treatment. Molecules 2018, 23, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabra, V.; Arreguin, R.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R.; Farres, A. Effect of Temperature and PH on the Secondary Structure and Processes of Oligomerization of 19 KDa Alpha-Zein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Proteins Proteom. 2006, 1764, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenci, D.F.; Kilian, J.; Janeczko, M.U.; Manzoli, A.; Rigo, E.; Soares, M.B.A. Effect of Meat and Water Temperature and Emulsion Speed on the Industrial Process for Chicken Mortadella. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Tang, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Physical Stability, Interfacial Composition and Protein-Lipid Co-Oxidation of Whey Protein Isolate-Stabilised O/W Emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoja-Castro, M.A.; González-Rodríguez, H. Study by Infrared Spectroscopy and Thermogravimetric Analysis of Tannins and Tannic Acid. Rev. Latinoam. Química 2011, 39, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhao, C.; Xue, F.; Zhao, Y. Decomposition of Five Phenolic Compounds in High Temperature Water. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2014, 25, 2102–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.F.C.; Rocha, W.R.V.; de Santana, C.P.; Alves, H.d.S. Use of Thermoanalytical Analysis for the Evaluation of a New Raw Material from Cnidoscolus Quercifolius Pohl. (Euphorbiaceae). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 134, 2409–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Chiu, C.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; Damasceno-Gomes, S.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A. Use of Jackfruit Leaf (Artocarpus heterophyllus L.) Protein Hydrolysates as a Stabilizer of the Nanoemulsions Loaded with Extract-Rich in Pentacyclic Triterpenes Obtained from Coccoloba uvifera L. Leaf. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Zou, P.-R.; Zhang, F.; Thakur, K.; Khan, M.R.; Busquets, R.; Zhang, J.-G.; Wei, Z.-J. Wheat Gluten Proteins Phosphorylated with Sodium Tripolyphosphate: Changes in Structure to Improve Functional Properties for Expanding Applications. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Gonzalez, C.N.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Aguirre-Loredo, R.Y.; Soriano-Melgar, L.d.A.A. Transformation of Agricultural Wastes into Functional Oligosaccharides Using Enzymes and Emerging Technologies. Phytochem. Anal. 2024, 35, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veras, K.S.; Fachel, F.N.S.; Pittol, V.; Garcia, K.R.; Bassani, V.L.; dos Santos, V.; Henriques, A.T.; Teixeira, H.F.; Koester, L.S. Compatibility Study of Rosmarinic Acid with Excipients Used in Pharmaceutical Solid Dosage Forms Using Thermal and Non-Thermal Techniques. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malucelli, L.C.; Massulo, T.; Magalhães, W.L.E.; Stofella, N.C.F.; Vasconcelos, E.C.; Filho, M.A.S.C.; Murakami, F.S. Thermal and Chemical Characterization of Dicksonia Sellowiana Extract by Means of Thermal Analysis. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2018, 28, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaro, L.; Balcão, V.; Rocha, L.; Silva, E.; Oliveira, J., Jr.; Vila, M.; Tubino, M. Physicochemical Characterization of a Crude Anthocyanin Extract from the Fruits of Jussara (Euterpe edulis Martius): Potential for Food and Pharmaceutical Applications. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2018, 29, 2072–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Porras, C.; Cruz-Alcantar, P.; Espinosa-Solís, V.; Martínez-Guerra, E.; Piñón-Balderrama, C.I.; Compean Martínez, I.; Saavedra-Leos, M.Z. Application of Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Modulated Differential Scanning Calorimetry (MDSC) in Food and Drug Industries. Polymers 2020, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schön, A.; Clarkson, B.R.; Jaime, M.; Freire, E. Temperature Stability of Proteins: Analysis of Irreversible Denaturation Using Isothermal Calorimetry. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2017, 85, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzsimons, S.M.; Mulvihill, D.M.; Morris, E.R. Denaturation and Aggregation Processes in Thermal Gelation of Whey Proteins Resolved by Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Matteo, P.; Luziatelli, F.; Bortolami, M.; Mele, M.L.; Ruzzi, M.; Russo, P. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) as a Tool for Studying Thermal Properties of a Crude Cellulase Cocktail. Chem. Pap. 2023, 77, 2689–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaleem, K.A.; Moftah, R.F.; El-Geddawy, M.M.A. New Insights into Red and White Quinoa Protein Isolates: Nutritional, Functional, Thermal Properties. Processes 2024, 12, 2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.C.P.; Deyse Gurak, P.; Damasceno Ferreira Marczak, L. Maltodextrin, Pectin and Soy Protein Isolate as Carrier Agents in the Encapsulation of Anthocyanins-Rich Extract from Jaboticaba Pomace. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 102, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).