Abstract
The increasing integration of distributed photovoltaics (PVs) has intensified voltage violations in active distribution networks (ADNs). Traditional centralized voltage regulation approaches face substantial challenges in terms of communication and computation. Distributed control methods can help mitigate these issues through distributed algorithms but struggle to track real-time fluctuations in PV generation. Local control offers fast voltage adjustments but lacks coordination among different PV units. This paper presents a hierarchical distributed and local voltage control strategy for PV clusters. First, the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) algorithm is adopted to coordinate the reactive power outputs of PV inverters across clusters, providing reference values for local control. Then, in the local control phase, a Q-P control strategy is utilized to address real-time PV fluctuations. The flexibility of the local control strategy is enhanced using the lifted linear decision rule, enabling a rapid response to PV power fluctuations. Finally, the proposed strategy is tested on both the modified IEEE 33-node distribution system and a practical 53-node distribution system to evaluate its performance. The results demonstrate that the proposed method effectively mitigates voltage issues, reducing the average voltage deviation by 53.93% while improving flexibility and adaptability to real-time changes in PV output.
1. Introduction
The high penetration of distributed generators (DGs) presents significant challenges to the control and operation of distribution networks [1]. Due to inherent uncertainties [2], the large-scale integration of photovoltaics (PVs) can cause substantial voltage deviations in active distribution networks (ADNs) [3].
Traditional voltage regulation devices, such as capacitor banks (CBs) and on-load tap changers (OLTCs) [4], face limitations due to delayed responses and discrete voltage adjustments, which make them less effective in addressing frequent voltage fluctuations [5]. In contrast, PV inverters can provide real-time reactive power and voltage support in ADNs [6]. With advantages such as economic efficiency and flexible regulation capabilities, managing reactive power through PV inverters offers a promising solution for achieving rapid voltage responses in ADNs [7].
The voltage and reactive power control methods are typically categorized into centralized, distributed, and local approaches [8]. Centralized control methods can provide superior performance by coordinating all controllable resources. However, they rely on optimal power flow, which requires comprehensive system measurement data. With the increasing integration of PVs and various flexible controllable resources in ADNs, the number of control variables and the complexity of optimization problems rise significantly. This growth also leads to massive data exchange, placing heavy burdens on communication systems. As a result, centralized control suffers from substantial computational and communication burdens [9].
Distributed control methods typically divide the distribution network into zones, where each zone exchanges limited information with its neighboring zones to meet control objectives. This approach reduces data communication and computational load, thereby alleviating pressure on ADN control systems and improving the management of distributed resources. The alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) is a widely used distributed algorithm for solving optimization control problems [10]. It solves optimization problems within each area, coordinates across areas using boundary information, and iteratively performs alternating solutions to achieve global optimization. Reference [11] proposed a dual time scale voltage regulation method for unbalanced ADNs by integrating model predictive control with ADMM. Reference [12] presented a distributed power optimization technique for wind farms using ADMM, ensuring turbine control constraints while achieving optimal power output. For multi-agent system control, reference [13] introduced a real-time ADMM algorithm in the continuous domain to address distributed control challenges. Reference [14] proposed a frequency synchronization optimization control method based on ADMM, which solves consensus states for distributed resources within finite horizons.
Due to the inherent need for iteration and communication between different clusters, distributed control methods must be optimized within a specified period. However, significant fluctuations in PV power may occur during these control intervals, which can render the control strategies optimized by distributed methods ineffective and even lead to voltage deviations. As a result, distributed control methods fail to meet real-time control objectives since they cannot track rapid changes in PV power.
Local control methods adjust PV outputs based on local measurements [15], enabling fast responses to frequent PV fluctuations while reducing communication and computational burdens. Existing standards and grid codes define two local control modes for PV inverters: Q-P (reactive power-active power) and Q-V (reactive power-voltage) modes. The Q-V mode determines reactive power based on nodal voltages, while the Q-P strategy adjusts reactive power according to active power changes. In Q-V mode, PV inverters regulate reactive power in response to voltage variations using a piecewise linear control curve. Reference [16] proposed a cloud-edge collaboration framework to tune the Q-V local control curve while considering privacy preservation. Reference [17] designed a robust optimization method for the Q-V control curve. Reference [18] developed an effective optimization model for inverter-based local voltage control, avoiding logic functions and systematically coordinating different Q-V droop functions under uncertainties. However, there is an issue that needs to be considered, which is that the Q-V mode may encounter stability problems [19]. This issue arises because reactive power output depends on voltage, which turns it into a voltage feedback control problem.
In the Q-P control strategy, the reactive power strategy is directly dependent on the active power generation, which in turn influences the voltage. Therefore, the design and implementation of the Q-P mode is simpler than Q-V mode. Various Q-P control strategies have been applied to voltage regulation in distribution networks [20]. Reference [21] proposed a voltage control framework to derive Q-P control strategy, incorporating active power curtailment during severe PV fluctuations to ensure voltage security constraints. Reference [22] introduced an equitable Q-P envelope calculation and optimization method to maximize allowable power injection ranges under security constraints. Reference [23] developed a distributed optimization method to determine the Q-P control strategy. The aforementioned Q-P control strategies typically employ single-segment linear functions, which limit the flexibility of PV power regulation. To address this limitation, reference [24] introduced a spatial dimension-raising segmentation method to partition the control curve into multiple segments, with simulation results validating its effectiveness. Unlike distributed and centralized control approaches, local control methods depend only on local measurements, enabling a rapid response to PV power fluctuations. However, local control methods can hardly achieve a system-wide optimum since only local information is used.
Combining the advantages of different control modes can help mitigate voltage issues in ADNs resulting from high PV integration [25]. Reference [26] proposed a combined central-local voltage control strategy in which the local control curve for PVs is established based on the reactive power determined in the central strategy. Reference [27] introduced a cooperative optimization method for medium and low-voltage distribution networks considering flexible interconnected distribution substation areas. Reference [28] presented a continuous-time voltage control method based on hierarchical coordination between central dispatch and local control. Reference [29] proposed a coordinated central-local control strategy where each PV inverter adjusts reactive power using control curves refined by the central controller to manage rapid PV fluctuations. Reference [30] presented a hierarchical voltage control framework that effectively coordinates various controllable devices with different response times in ADNs. However, in most of the existing work, the control strategy is usually defined based on a deterministic optimization model. Moreover, the Q-P control strategy typically uses a single-segment linear function, which makes it difficult to cope with the diverse fluctuations in PV generation.
As presented in Table 1, distributed control can achieve decentralized coordination among different PV clusters but struggles to respond quickly to PV fluctuations. While local control strategies enable real-time adjustments, they lack system-wide coordination of PV units. References [21,23] integrated centralized and distributed methods with local control strategies to achieve collaboration between PV clusters, but local control strategies utilize single-segment linear functions, which limit the flexibility of PV power regulation.

Table 1.
A comparison between the proposed method and the existing literature.
To cope with the issues discussed above, this paper proposes a hierarchical distributed and local voltage control strategy for PV clusters. The main contributions of this study are summarized as follows:
- (1)
- A hierarchical distributed and local voltage regulation architecture for PV clusters is proposed. The distributed optimization method is employed to coordinate reactive power across different PV clusters, serving as the reference for local control. The local control layer utilizes the Q-P affine control strategy as the complement to address real-time PV fluctuations.
- (2)
- A lifted linear affine control method is proposed for the local control of PV inverters, which segments the Q-P affine control curve to accommodate various PV fluctuation scenarios. The proposed method eliminates the integer variables introduced by traditional piecewise linearization while enhancing the flexibility of the local control strategy. Considering the uncertainty of PV, a robust optimization model is developed, and a dual transformation is performed to facilitate the solution of the proposed local control strategy.
The following sections of this paper are organized as follows. Section 2 presents the proposed hierarchical distributed and local voltage control architecture. Section 3 introduces the decentralized coordination control model based on ADMM. In Section 4, a lifted linear affine control method is introduced for local control of the PV inverters. Case studies and analysis with the modified IEEE 33-node distribution system and a practical 53-node distribution system are given in Section 5. Finally, Section 6 presents the conclusions.
2. Hierarchical Distributed and Local Voltage Control Architecture
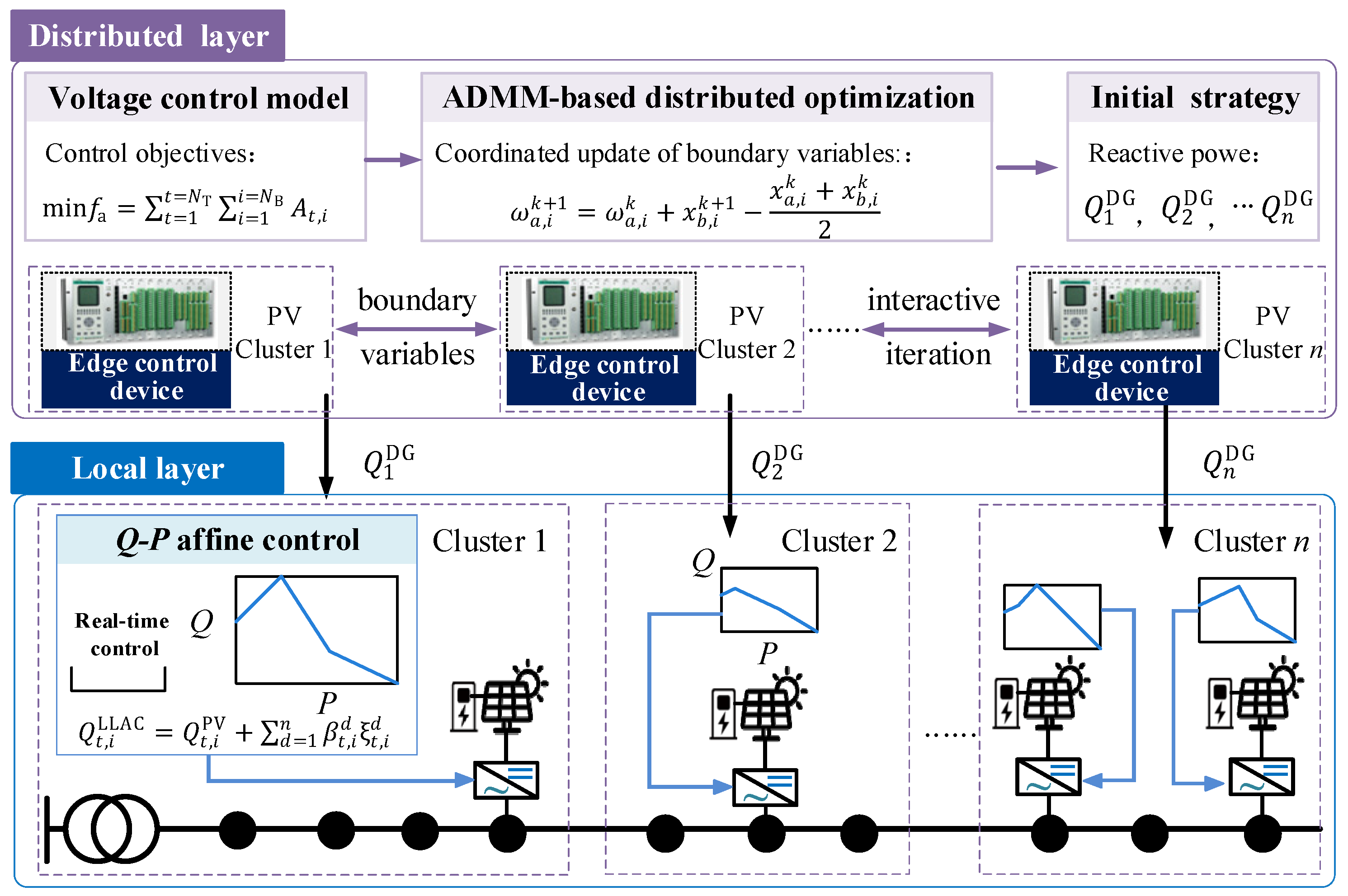
Coordinated optimization among different PV clusters is crucial for improving the overall voltage profile of ADNs. Due to the high sensitivity of distributed PVs to environmental variations, they inherently exhibit significant uncertainty in power generation. Consequently, the reactive power generated by PV inverters must be adjusted in response to real-time active power fluctuations. Therefore, this paper introduces a hierarchical distributed and local control architecture for voltage regulation, enabling both coordination control and dynamic reactive power adjustment. The proposed method effectively mitigates voltage violations resulting from high PV penetration and improves the voltage quality within ADNs. Figure 1 illustrates the voltage control architecture, which comprises two phases: distributed coordination and local control.
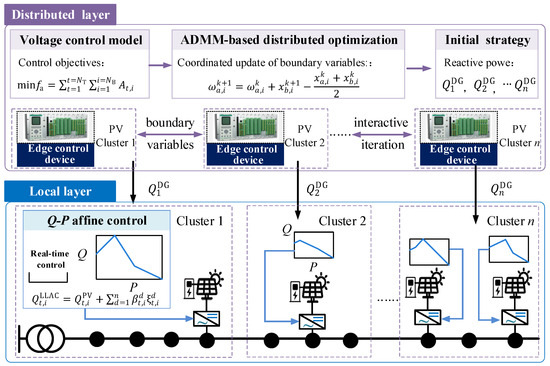
Figure 1.
Hierarchical distributed and local voltage control architecture.
In the distributed coordination phase, each cluster minimizes its voltage deviations by optimizing the reactive power output from the PV inverters within the cluster. The ADMM algorithm is employed to iteratively exchange boundary variables, enabling cooperative reactive power control strategies across different PV clusters. The reactive power generated by the PV inverters, optimized during the distributed coordination phase, serves as the reference for developing the local control strategy.
In the local control phase, a lifted linear affine control strategy is employed to achieve rapid voltage responses. The reactive power strategies obtained during the distributed coordination phase may become invalid due to significant fluctuations in PV generation. PVs in each cluster use the results from the distributed coordination phase as the base value to formulate the Q-P affine control strategy. This local control strategy allows for real-time reactive power adjustments according to PV active power fluctuations. The local control curve is segmented using the lifted linear decision rule, enhancing the flexibility of the control strategy to accommodate various PV fluctuation scenarios.
In practical operation, PV clusters require the installation of edge control devices to perform data calculation, storage, and decision. These devices have great advantages in compatibility and can replace the traditional terminal infrastructure in distribution networks, such as feeder terminal units. The development of communication speed can solve communication problems between different clusters. The implementation of edge control devices can realize the distributed operation between clusters and reduce reliance on the computational resources of the upper master. At the same time, the edge control device is arranged in the cluster to enable local control of the PV. With the development of ADNs, the proposed hierarchical distributed and local voltage control strategy will have promising prospects in practical application.
Communication is required in the proposed method, which mainly impacts the decentralized coordination among different PV clusters. However, the delay of communication generally does not exceed 1 s [31], while the distributed coordination and local Q-P control strategies of PVs in the proposed method are updated every 15 min. Thus, the impact of communication delay is relatively limited in the practical application of the proposed method. In the face of extreme communication delays and data loss, PV clusters can adopt previous local control strategies, operating independently without distributed coordination between different clusters.
3. Decentralized Coordination Based on ADMM
3.1. Voltage Control Model for PV Clusters
Each cluster is designed to minimize the total voltage deviation, thereby optimizing the reactive power output of distributed PV inverters. For cluster , the reactive power voltage control model is formulated as follows:
- (1)
- Objective function:where is the total voltage deviation in cluster ; represents the remaining time intervals in the optimization horizon; denotes the total nodes in cluster ; represents the proxy variable introduced by cone relaxation; denotes the voltage at node ; and and represent the permissible lower and upper bounds for voltage.
- (2)
- System power flow constraints:where and represent the sets of branches and nodes in cluster , respectively; and denote the reactive and active power flowing from node to ; and indicate the reactance and resistance of branch ; and refer to the net reactive and active power at node ; and represent the reactive power and active power of load at node ; and and represent the reactive power and active power generated by distributed PV at node .
We use convex relaxation to transform the constraint (5) into the second-order cone form, as shown in Equation (8).
- (3)
- System operation security constraints:where and represent the maximum and minimum allowable voltage levels for safe operation; represents the maximum current that can be tolerated by the branch; is the variable introduced through the cone transformation; and represents the current magnitude between nodes and .
- (4)
- PV operation constraints:where denotes the maximum reactive power output of the PV inverter at node , and is its installed capacity.
3.2. ADMM-Based Distributed Interactive Solution
The ADMM algorithm is employed at each time interval to coordinate the reactive power voltage control models among different PV clusters. The reactive power optimization problem defined by Equations (1)–(12) can be reformulated in a simplified form, as shown in Equation (13).
where is defined as the operational strategy vector of distributed PVs; represents the vector of power flow; and represents the objective function defined in Equation (1) for cluster . Inequality and equality represent system security and PV operation constraints given in Equations (2)–(12). For simplicity, the subscript is omitted. represents the global variable. and denote the sets of nodes in the overlapping area and area , respectively.
We define as the global state vector associated with boundary node . Coordination among different clusters is achieved via the exchange of boundary node injections and power flows along connecting lines.
Auxiliary variables are introduced to eliminate the global variable and accelerate convergence, enabling completely decentralized computation. The decentralized coordination model based on ADMM can be expressed as follows [15]:
where and denote the feasible regions for cluster . represents the set of areas that contain node . denotes the number of iterations of the ADMM algorithm.
As shown in Equation (15), the convergence criterion is computed using the dual residual and the primal residual .
where and are column vectors formed by aggregating and from all clusters, respectively. Parameter , representing the predefined residual tolerance in the ADMM algorithm, is set to 10−3.
Collaborative optimization of multiple PV clusters using distributed algorithms can improve the overall voltage profile of the ADN. Due to the requirements for iteration and communication between different clusters, distributed algorithms need to be optimized within a certain period of time. However, significant fluctuations in PV power may occur during these intervals. Consequently, the control strategies optimized in the distributed coordination phase may be ineffective. Therefore, a local control method is added to adjust the reactive power in response to real-time active power fluctuations. The reactive power optimized in the distributed coordination phase is used as the reference for the development of the local control strategy to achieve system-wide coordination. Meanwhile, the local control strategy is a complement to distributed coordination to address real-time PV fluctuations.
4. Local Affine Control Strategy Based on Lifted Linear Decision Rule
4.1. Lifted Linear Affine Q-P Control
In the local voltage control of distribution networks, linear affine control (LAC) has been implemented to formulate the Q-P control strategy for distributed PV. This method enables the dynamic adjustment of reactive power in response to real-time variations in active power generation, as shown in Equation (16).
where represents the fluctuation in PV active power generation; denotes the initial reactive power obtained from the distributed coordination stage; denotes the affine parameter of LAC used to tune reactive power in response to active power variations; and denotes the real-time adjustment of inverter reactive power.
While LAC is effective for voltage control in ADNs, the linear correlation between reactive and active power limits the flexibility of the control curve. Therefore, lifted linear decision rule (LLDR) is introduced to partition the Q-P curve into multiple segments, enabling distinct affine control strategies with variable slopes as detailed below.
First, the interval of is partitioned into sections based on the breakpoints defined in Equation (17):
where and denote the maximum and minimum values of ; , , …, represent the breakpoints; and .
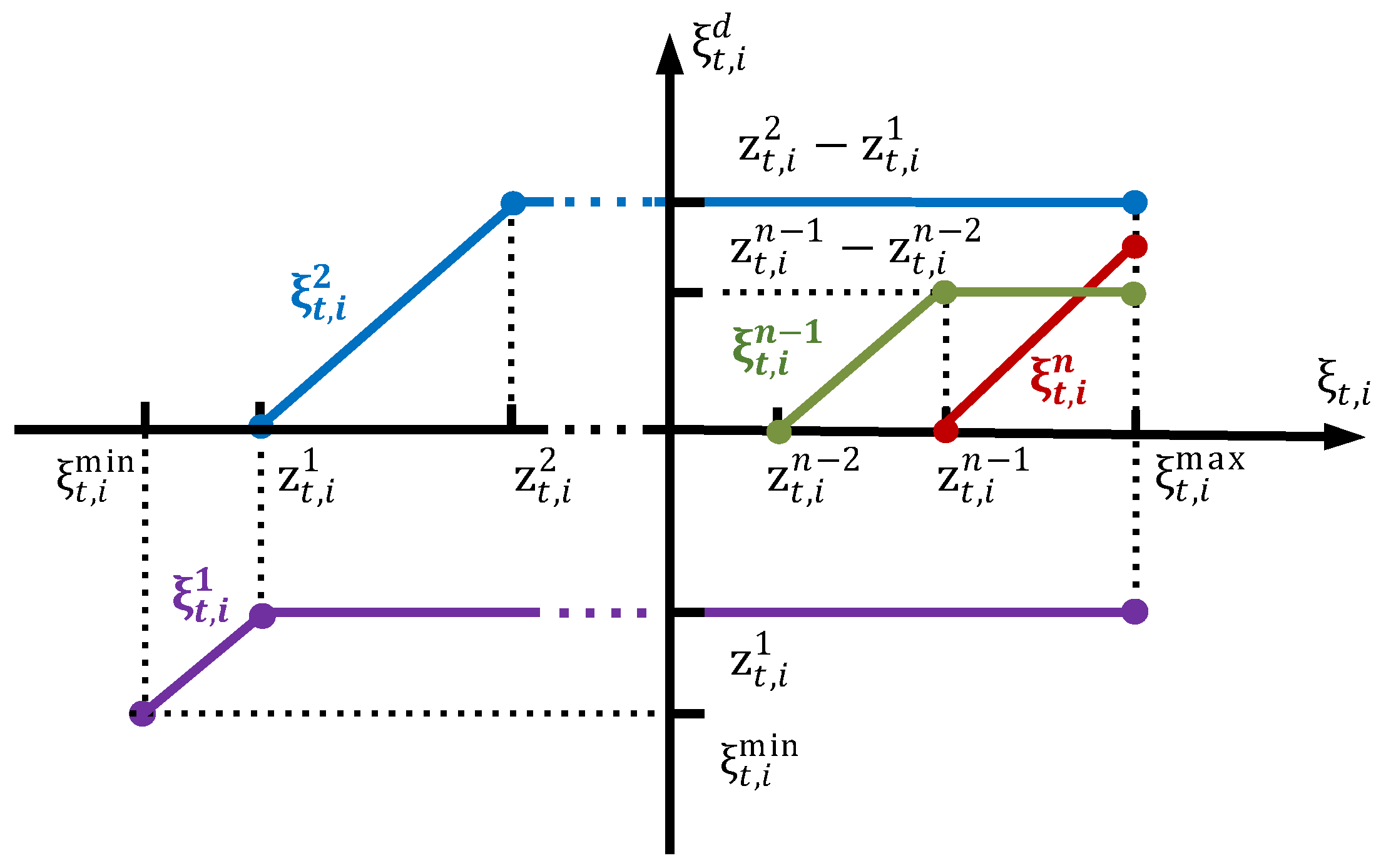
As shown in Figure 2, the dimension-lifted variables are introduced to represent the specific location of the current power variation within the segmented intervals, as described in [32]:
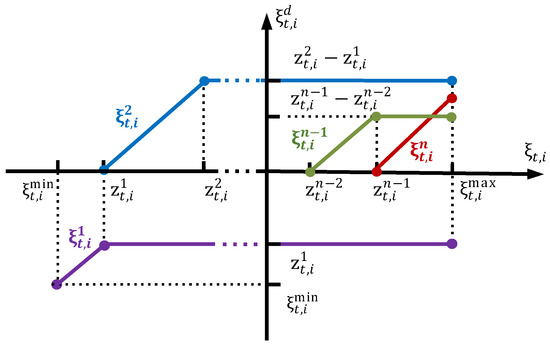
Figure 2.
Relationship between original variable and dimension-lifted variables .
Thus, can be expressed as the sum of in Equation (19):
Then, by introducing the dimension-lifted variables to replace the original variable , the lifted linear affine control (LLAC) of PV inverters based on LLDR can be formulated as shown in Equation (20).
where represents the affine coefficient of LLAC; is the constant part of LLAC; and is defined as the adjustable part of LLAC. Compared to Equation (16), LLAC preserves the advantages of the linear model while providing greater control flexibility.
Then, the feasible region of the variables is analyzed. Let denote the vector of . Its feasible domain , as defined by Equation (18), is non-convex. To enable linear optimization, this domain is relaxed to its convex hull. The extreme points of are given by Equation (21).
Thus, the convex hull , defined by the vertices {}, represents the set containing all points within its domain, as shown in Equation (22).
Equation (22) can be reformulated as follows:
Therefore, the convex hull of can be presented as follows:
where
For simplicity, Equation (24) is expressed as a linear transformation using matrix and vector throughout the remainder of the paper.
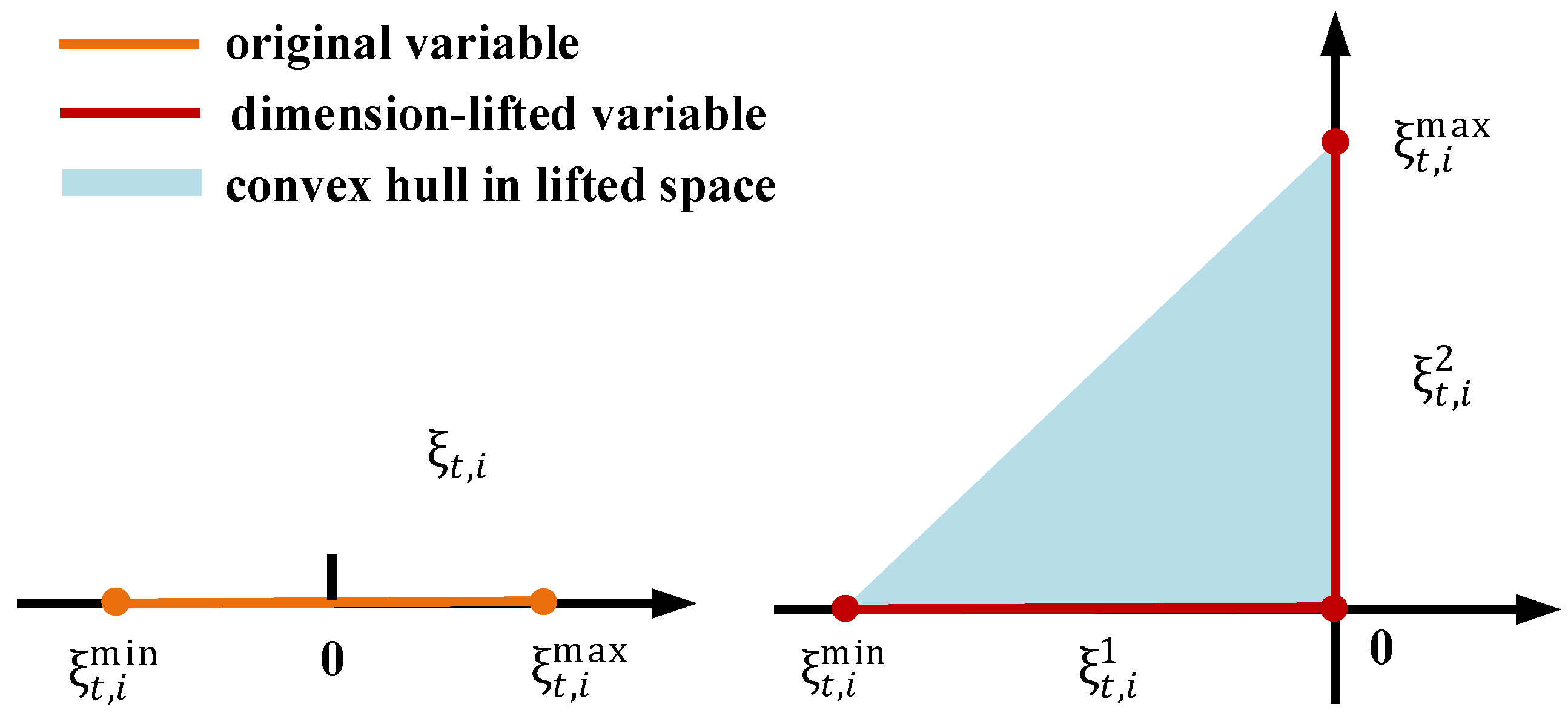
Given the significant differences in the feasible operating regions of the inverter during increases and decreases in PV active power, the Q-P control curve is divided into two segments, each implementing affine control strategies with distinct slopes. As shown in Figure 3, with the breakpoint defined as , the variable is lifted from a one-dimensional space to a two-dimensional space as follows:
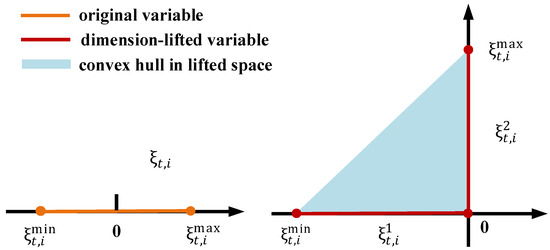
Figure 3.
Domains of original variables and lifted variables ().
The relationship between the dimension-lifted variables and the original variable is defined as follows:
Then, the reactive power control of PV via LLAC can be expressed as follows:
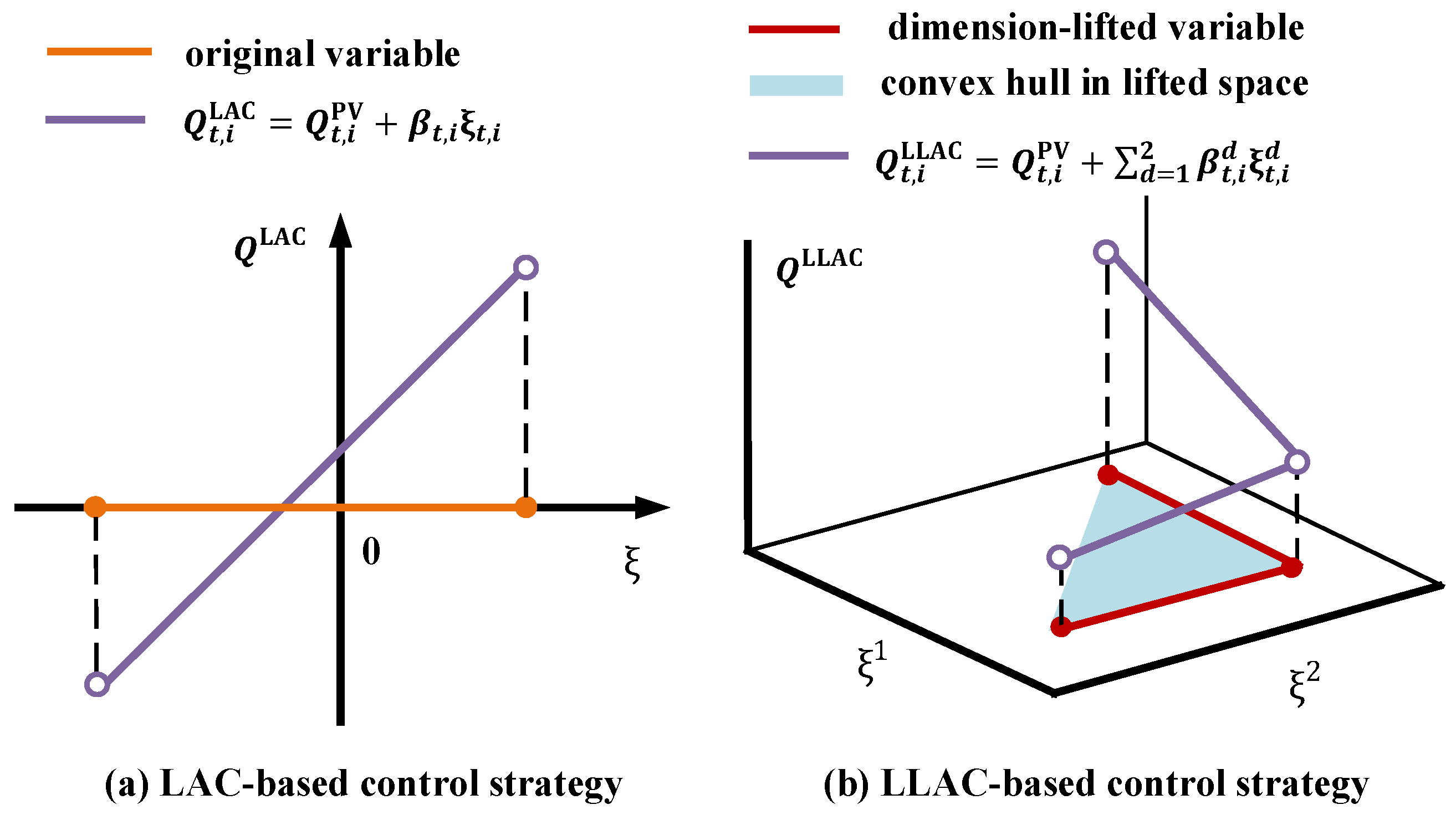
Figure 3 and Figure 4 present schematic diagrams of variable dimensional lifting and the corresponding piecewise linear functions in the lifted space. The feasible domain of the variable, as defined by Equation (27), is shown as the red polyline in both Figure 3 and Figure 4, which is non-convex. To facilitate optimization, the original domain is extended to its convex hull. The geometric representation of the convex hull is depicted as the triangular region in Figure 3 and Figure 4, mathematically expressed as
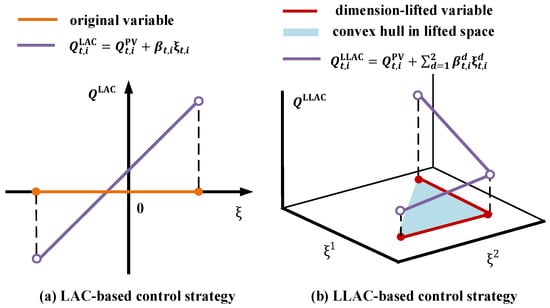
Figure 4.
Intuitive examples of LAC-based and LLAC-based PV power control strategies ().
Equation (30) can be reformulated as
In linear programming, the optimization objective value over the original domain is equivalent to that over its convex hull. Therefore, the convex hull can serve as a replacement for the original domain. By utilizing LLAC, the integer variables and associated constraints commonly introduced by traditional piecewise linear methods can be avoided. This approach achieves piecewise linear control strategies with reduced computational cost while effectively handling robust constraints.
4.2. Robust Control Model
During the operation of ADNs, real-time fluctuations in PV active power may lead to nodal voltage deviations from those determined during the distributed coordination phase. Therefore, taking into account the real-time fluctuation in PV active power, each cluster employs the aforementioned LLAC to adjust the reactive power of inverters in real time, further reducing system voltage deviations.
First, the voltage sensitivity corresponding to variations in PV power can be derived from the operating conditions of the distribution system determined during the distributed coordination phase, as shown below:
where the variation in active power can be replaced by the variables , and the adjustment of reactive power is determined by LLAC functions:
By substituting Equations (33) and (34) into Equation (32), the relationship between PV power and voltage deviations is expressed as follows:
Then, a robust optimization problem is formulated to mitigate voltage deviations in the cluster under fluctuating PV generation:
where the objective function (36) calculates the total absolute voltage deviations. Constraints (37) and (38) define the absolute voltage deviations in the worst-case conditions in . Constraint (39) is the inverter capacity constraint. Constraints (40) and (41) give the feasible set for the dimension-lifted variables . Since constraint (39) is a circle based on the reactive and active power coordinates, it is expressed in a linear form as
where , and ; is an integer, which is chosen as 8 in this paper.
Equation (42) can be compactly expressed as
Due to the presence of stochastic variables and , the optimization problem cannot be solved directly and requires robust reformulation. Constraint (37) can be reformulated as follows:
Maximizing a linear function over a set is equivalent to maximizing it over its convex hull. Therefore, the right-hand side of Equation (44) simplifies to
The linear problem (45) has the following dual formulation:
where is the dual variable; is a vector of ones with matching dimensions; and . The nonlinear part of the optimization problem, , is eliminated by solving the original problem in duals.
According to the strong duality theory, the objective function values of the primal and dual problems are equal. Hence, Equation (46) can be substituted into the right-hand side of Equation (37).
Constraints (38) and (43) can be transformed into Equations (48) and (49) through a similar approach.
where and are the dual variables of constraints (38) and (43), respectively.
In conclusion, the local optimization problem is formulated as follows:
subject to the system’s operational constraints, as described in Equations (47)–(49).
5. Case Studies and Analysis
The effectiveness of the proposed hierarchical distributed and local voltage regulation strategy is validated in this section using the modified IEEE 33-node distribution system and a practical 53-node distribution system. The proposed voltage control method was implemented in MATLAB R2022a. The numerical experiments were conducted on a computer equipped with an Intel(R) Core (TM) i7-9750H CPU running at 2.60 GHz and 16 GB of RAM.
5.1. The Modified IEEE 33-Node Distribution System
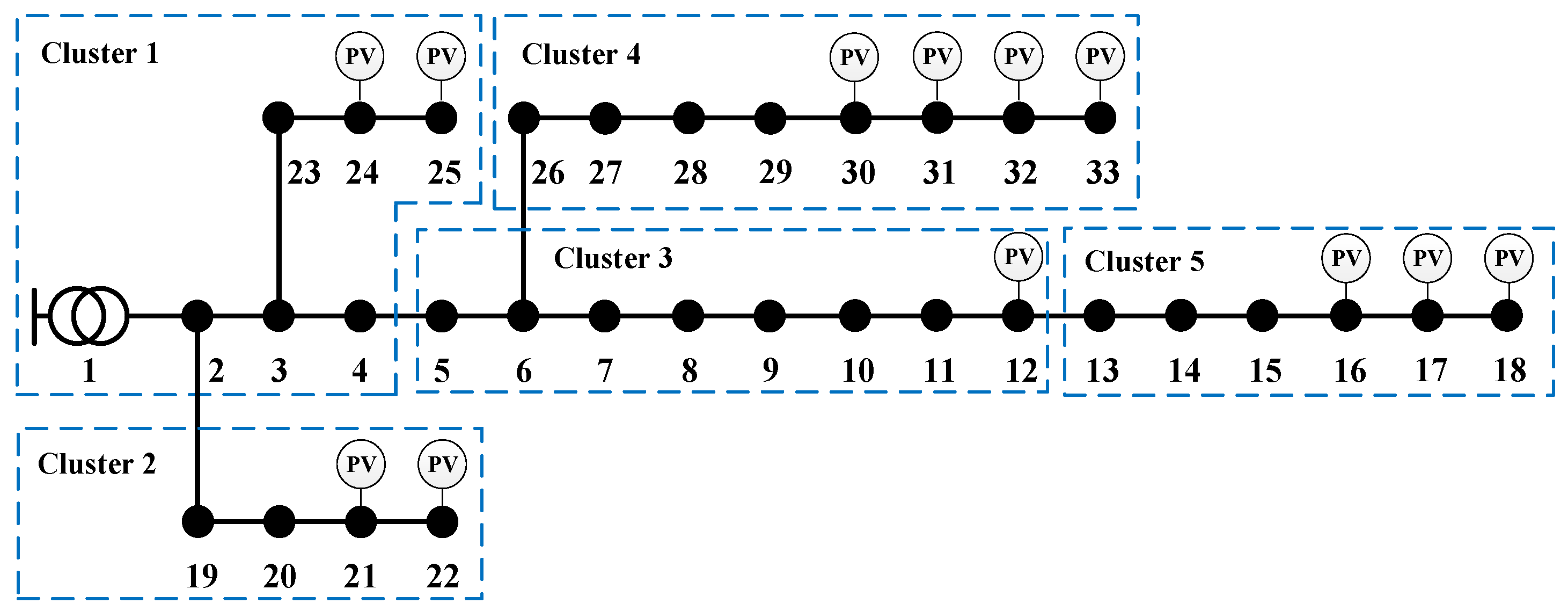
The modified IEEE 33-node distribution system consists of a substation and 32 branches, with a rated voltage of 12.66 kV. As shown in Figure 5, the system is divided into five clusters based on geographical proximity.
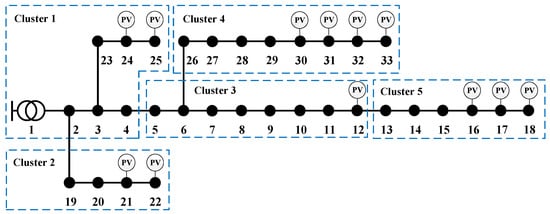
Figure 5.
Topology of modified IEEE 33-node distribution system.
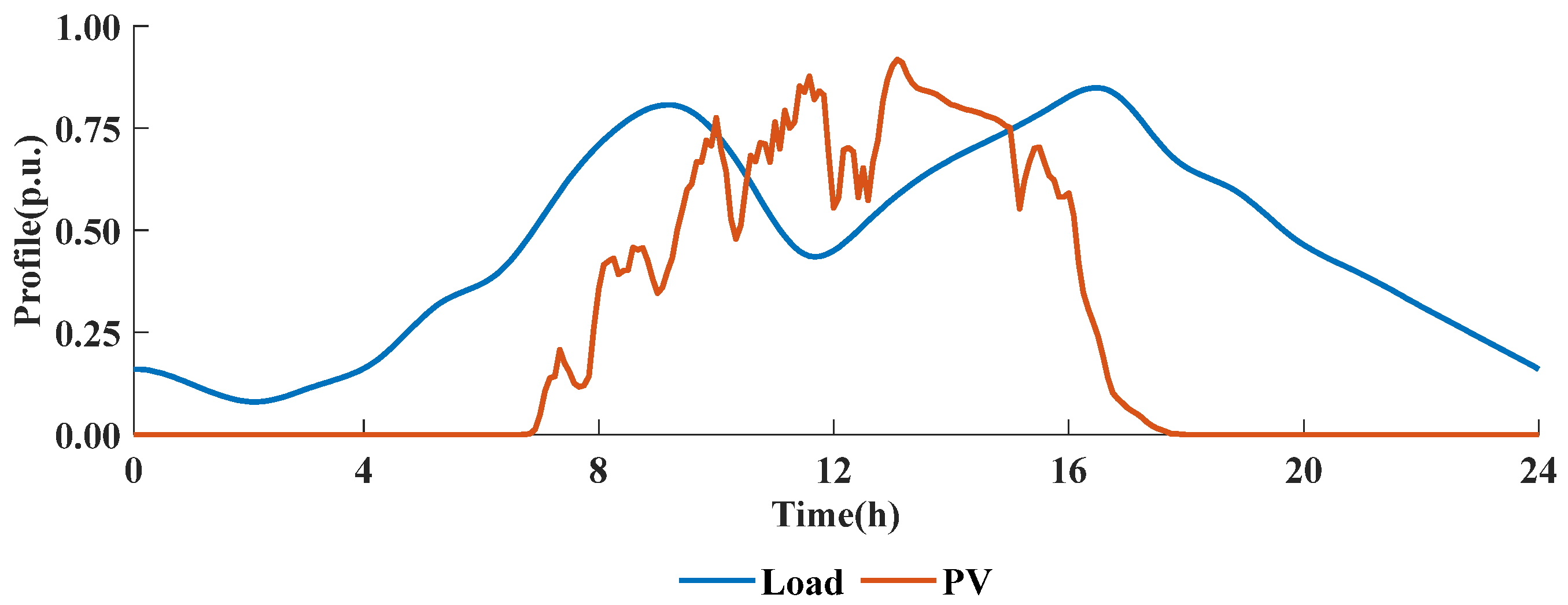
To fully reflect the severe voltage issues resulting from the large-scale integration of PV in ADNs, 12 PV units are installed as detailed in Table 2. The fluctuation curves of PV generation and load are shown in Figure 6. The legal voltage limits are 0.90 p.u. and 1.10 p.u., with the preferred range being between 0.98 p.u. and 1.02 p.u. The operational period is defined as 24 h, and the distributed coordination period is 15 min.

Table 2.
Allocations of distributed PVs in modified IEEE 33-node distribution system.
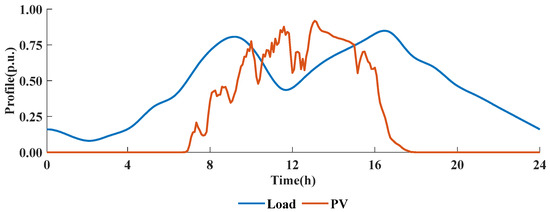
Figure 6.
The fluctuation curves of PVs and load.
The proposed hierarchical voltage regulation method for PVs is evaluated through five different scenarios to demonstrate its performance and advancement:
Scenario I: The initial operational condition of the ADN is obtained with no control strategy applied to the distributed PVs.
Scenario II: The ADMM algorithm is implemented to enable the collaborative optimization of PVs across different clusters.
Scenario III: The Q-P local control strategy is used without decentralized coordination.
Scenario IV: The proposed hierarchical voltage regulation method.
Scenario V: The centralized model-based approach is applied in real time to optimize the control strategy, delivering a theoretically optimal voltage control effect.
- (1)
- Evaluation of voltage regulation effectiveness
The average voltage deviation (AVD) index is used to show voltage control results across different scenarios, as described by Equation (51).
The optimization results for the five scenarios are presented in Table 3. It is evident that the uncontrolled integration of distributed PVs in Scenario I leads to significant voltage fluctuations and violations. This issue can be effectively mitigated by controlling the reactive power of PV inverters in Scenarios II to Scenario V to keep the voltage within the safe range. Compared to Scenario I, the proposed method in Scenario IV results in a 53.93% reduction in AVD. Additionally, the proposed method further improves the voltage level compared to Scenarios II and III due to the complementary effects of distributed and local control. Specifically, it achieves reductions of 19.84% and 8.17% in AVD compared to distributed control and local control, respectively.

Table 3.
Voltage control results in modified IEEE 33-node distribution system.
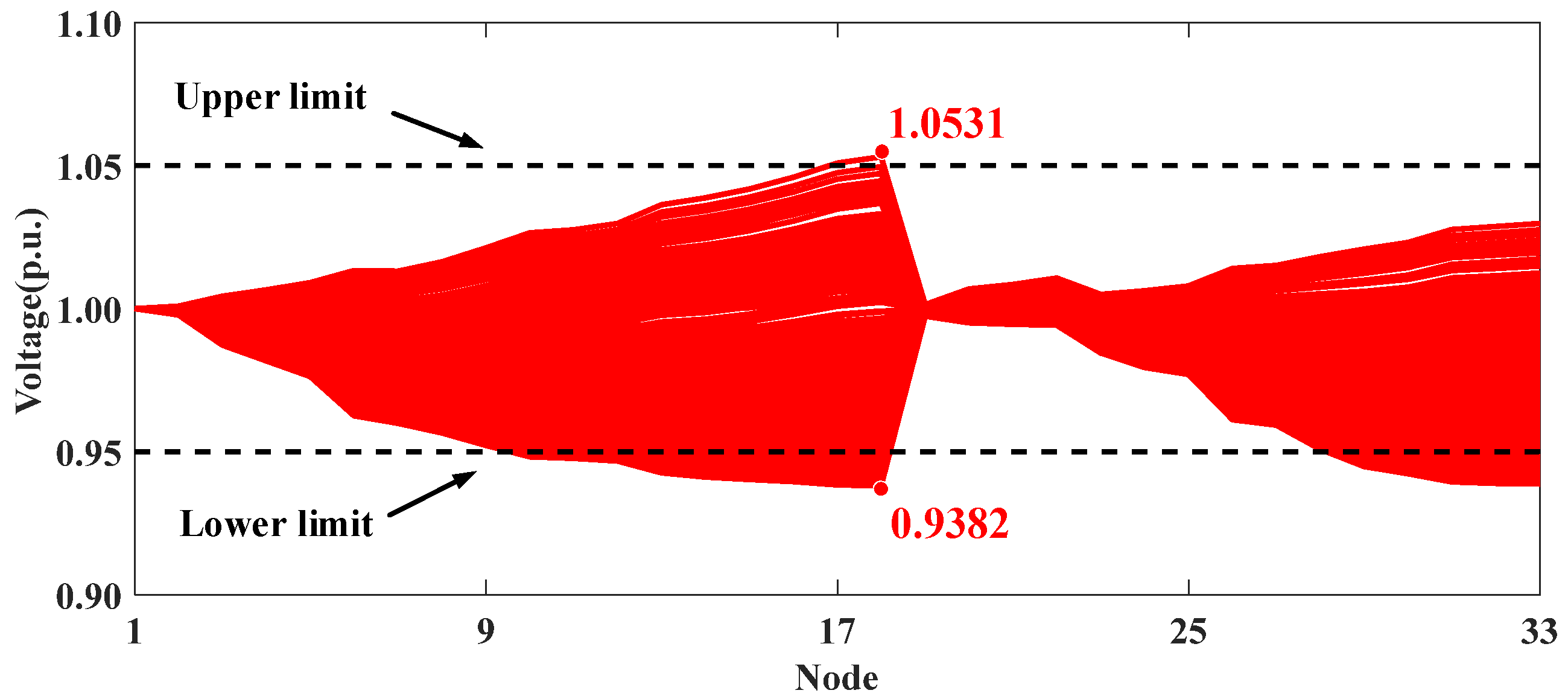
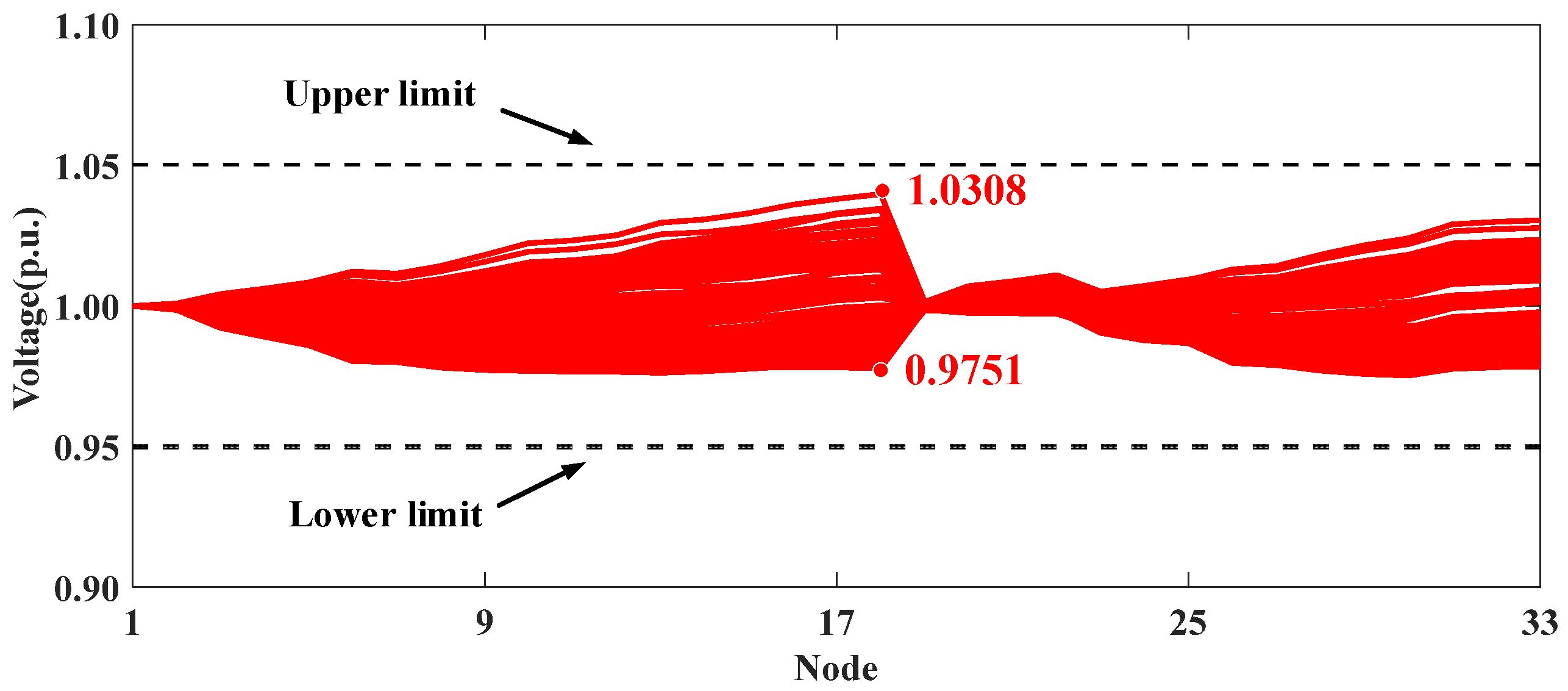
Figure 7 and Figure 8 present the voltage profiles for Scenarios I and II, respectively. The comparison of these two scenarios highlights the effectiveness of ADMM-based collaborative optimization methods. Specifically, high PV integration in Scenario I leads to voltage violations at node 18. However, in Scenario II, the use of distributed algorithms to coordinate the reactive power strategies of PV inverters across different clusters helps maintain the system voltage within secure operational limits.
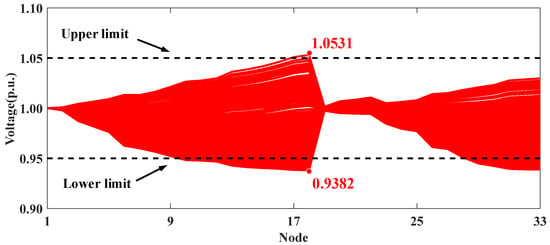
Figure 7.
Voltage profiles of modified IEEE 33-node distribution system in Scenario I.
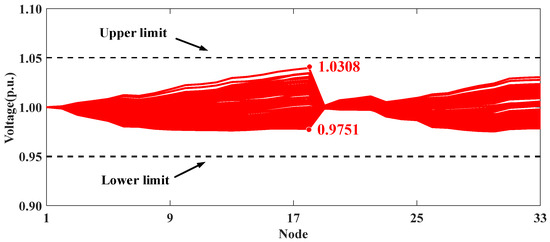
Figure 8.
Voltage profiles of modified IEEE 33-node distribution system in Scenario II.
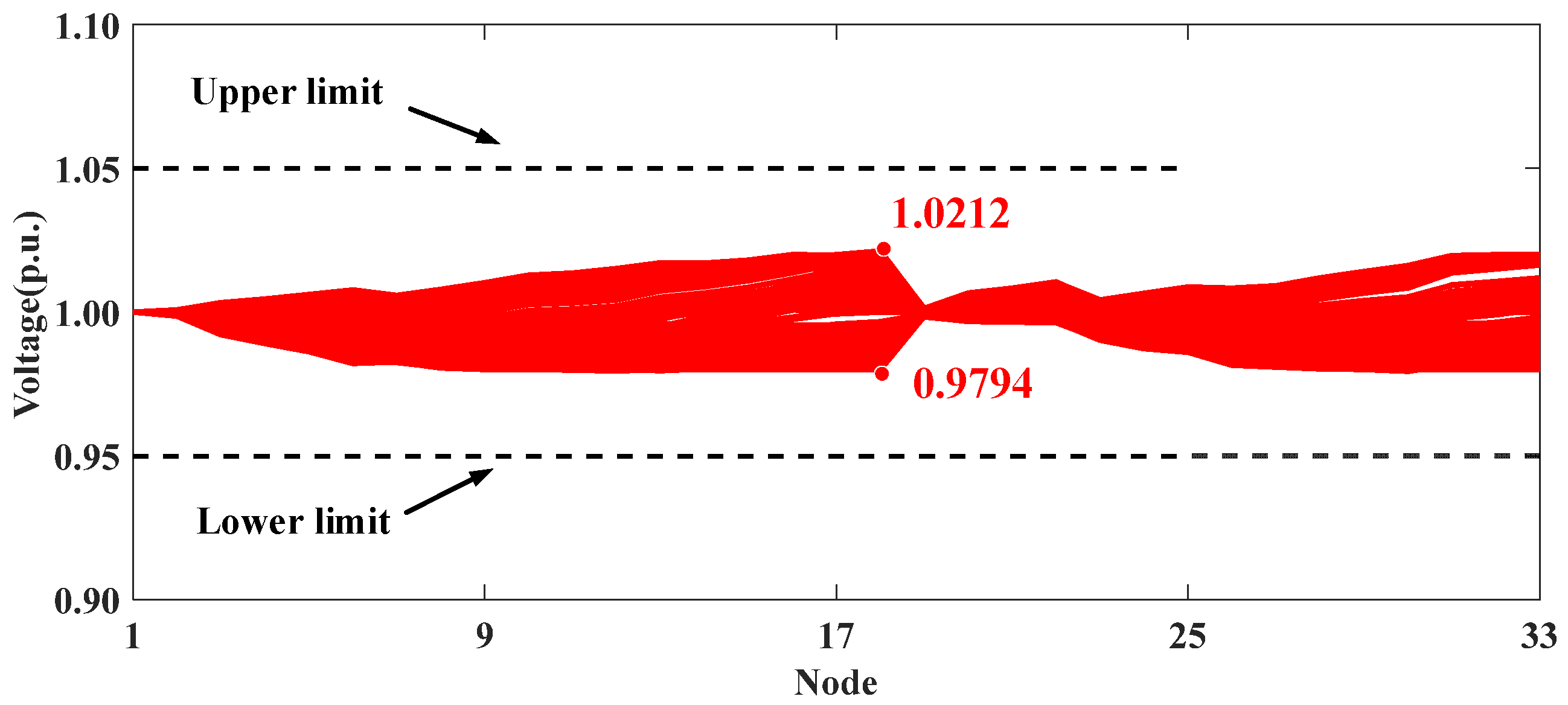
The comparison between Scenarios II and IV further demonstrates the effectiveness of the local affine control strategy based on LLAC. Due to the inherent real-time fluctuations in PV generation, it is crucial to adjust the reactive power of PVs. Scenario IV employs affine control to adjust reactive power based on the distributed coordination of different clusters. As shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9, the real-time reactive power adjustments in Scenario IV result in a narrower voltage fluctuation range compared to Scenario II. Moreover, as detailed in Table 3, Scenario IV reduces the AVD index from 0.5683 to 0.4555, thus confirming its superior voltage control performance.
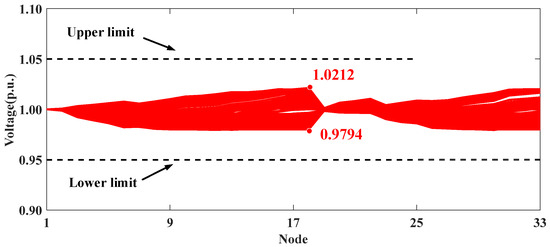
Figure 9.
Voltage profiles of modified IEEE 33-node distribution system in Scenario IV.
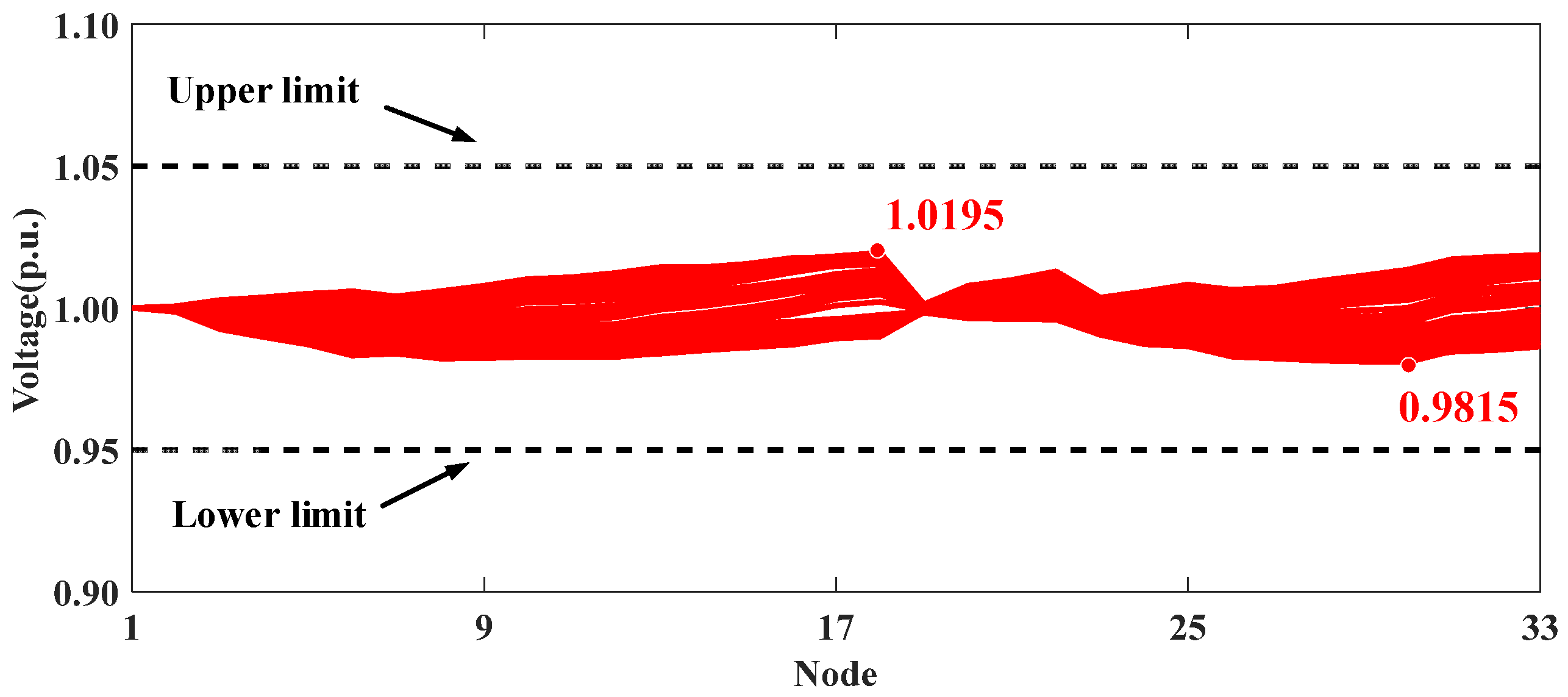
The voltage profiles for Scenario V are presented in Figure 10. The comparison between Scenarios IV and V emphasizes the effectiveness of the proposed hierarchical distributed and local voltage control method. Scenario V demonstrates that the real-time centralized model-based approach delivers the optimal reactive power solution for PV inverters, resulting in superior voltage control performance. It is observed that, by employing the ADMM-based collaborative optimization and local control method, a comparable level of overall optimization performance can be achieved in Scenario IV.
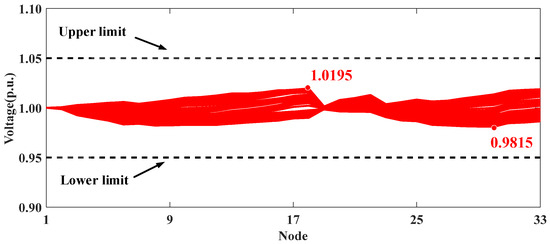
Figure 10.
Voltage profiles of modified IEEE 33-node distribution system in Scenario V.
- (2)
- Performance analysis of distributed algorithms
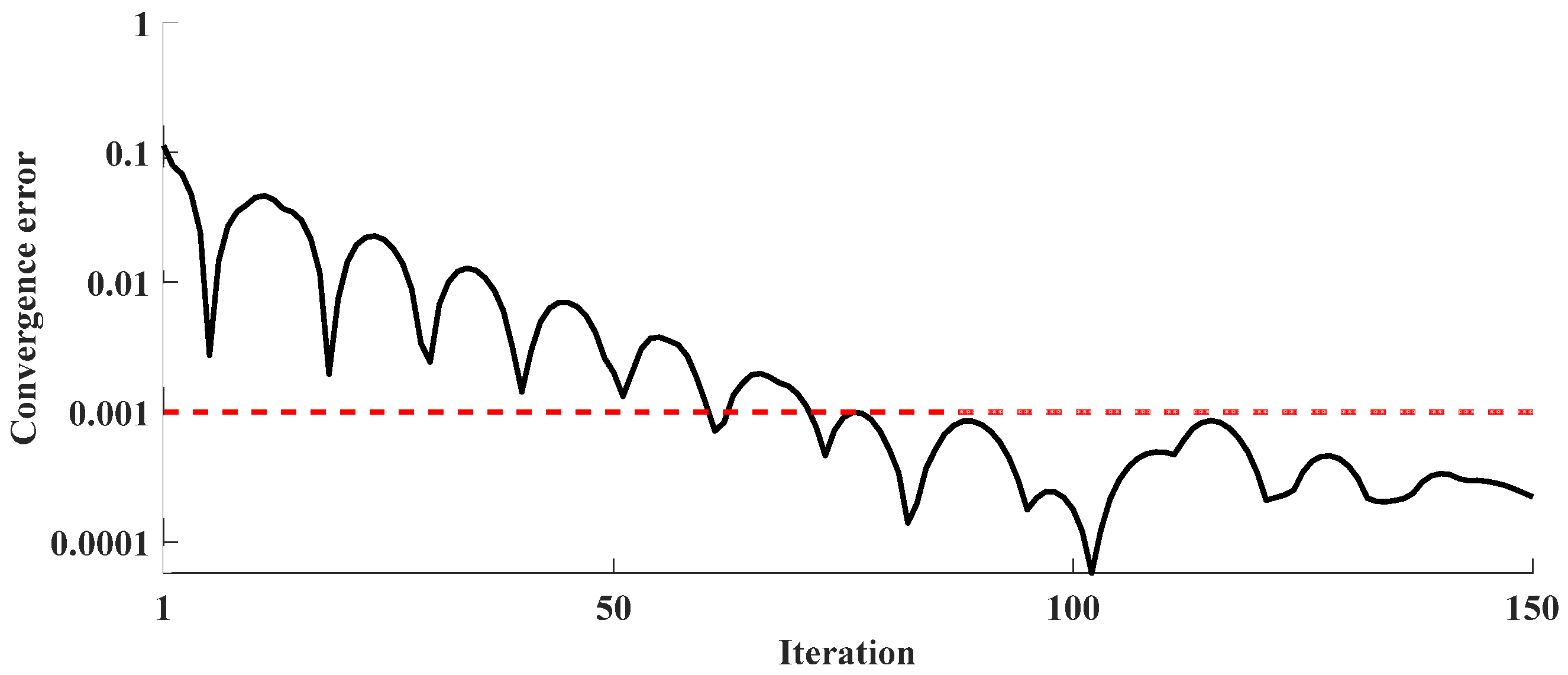
Regarding the convergence speed of the distributed optimization method, Figure 11 illustrates the error of the proposed approach during the time interval from 14:30 to 14:45. The convergence accuracy is set to 1 × 10−3. It is observed that the desired accuracy is achieved after approximately 70 iterations within this period, with the average number of iterations per day being less than 100.
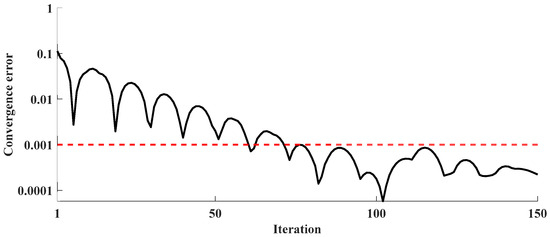
Figure 11.
Convergence error.
Table 4 summarizes the computational performance of solving voltage control problems in different clusters, with maximum and average iteration times of 1.9239 s and 0.7735 s, respectively. Additionally, the average time across different periods is 1.65 min, demonstrating that the proposed method meets the practical timing requirements for voltage regulation.

Table 4.
Time required for computation.
5.2. Practical Application
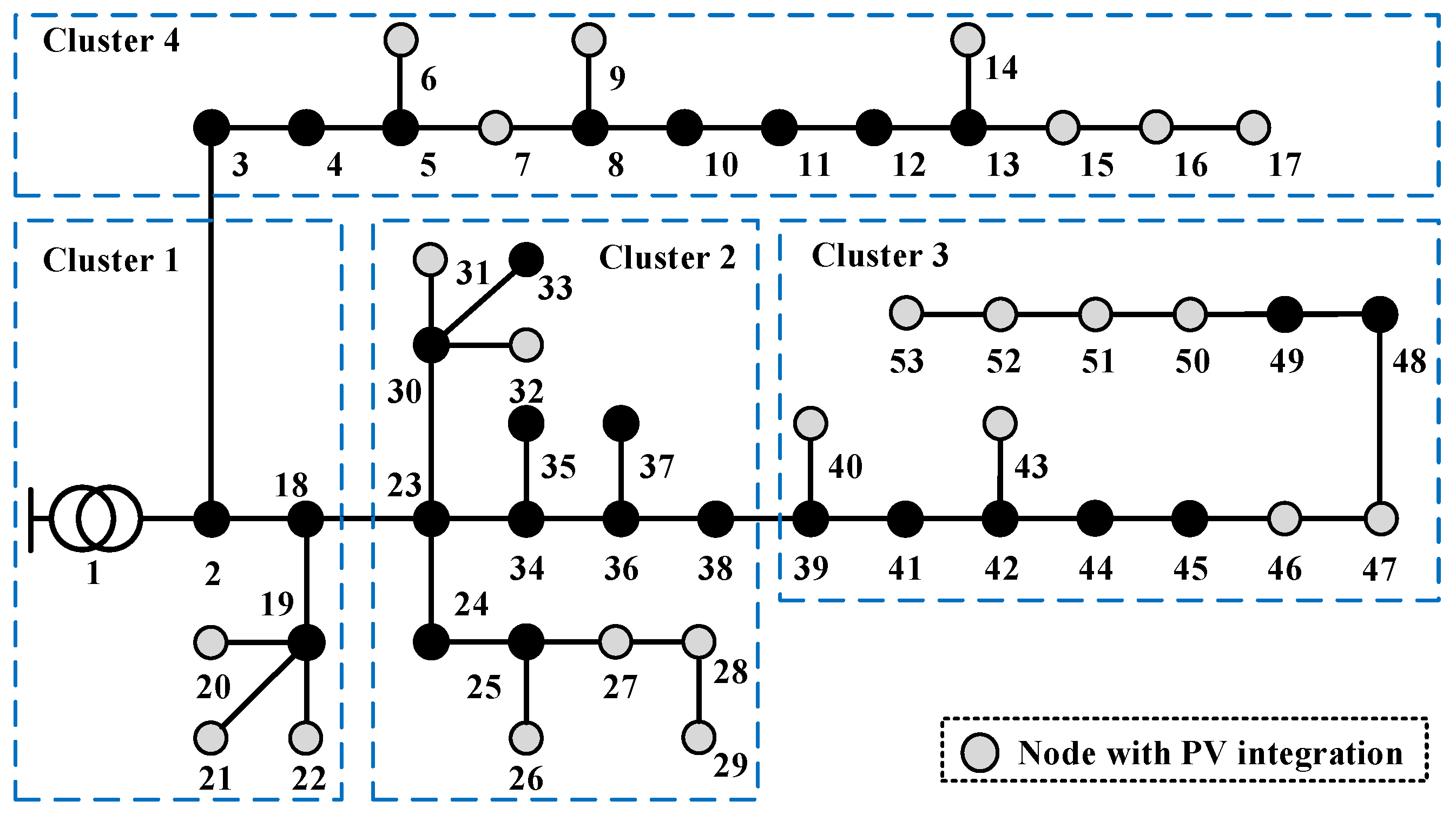
To further demonstrate the adaptability of the proposed method in the practical distribution network, a case study based on a real system in Guangzhou, China, is further adopted. The structure of the system is shown in Figure 12. As shown in Figure 12, the system is assumed to be divided into four clusters based on geographical proximity.
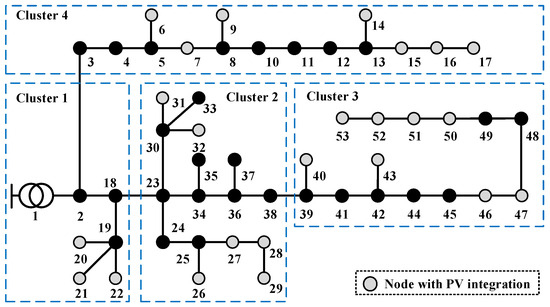
Figure 12.
Topology of HXF23 53-node practical distribution system.
The system consists of 52 branches, with a rated voltage of 10 kV, and the total active power and reactive power demands are 8790 kW and 1786 kvar, respectively. To simulate the impact on ADN caused by high penetration of PVs, 24 PV units are integrated into the test system. The locations and capacities of PVs are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Allocation of distributed PVs in HXF23 53-node practical distribution system.
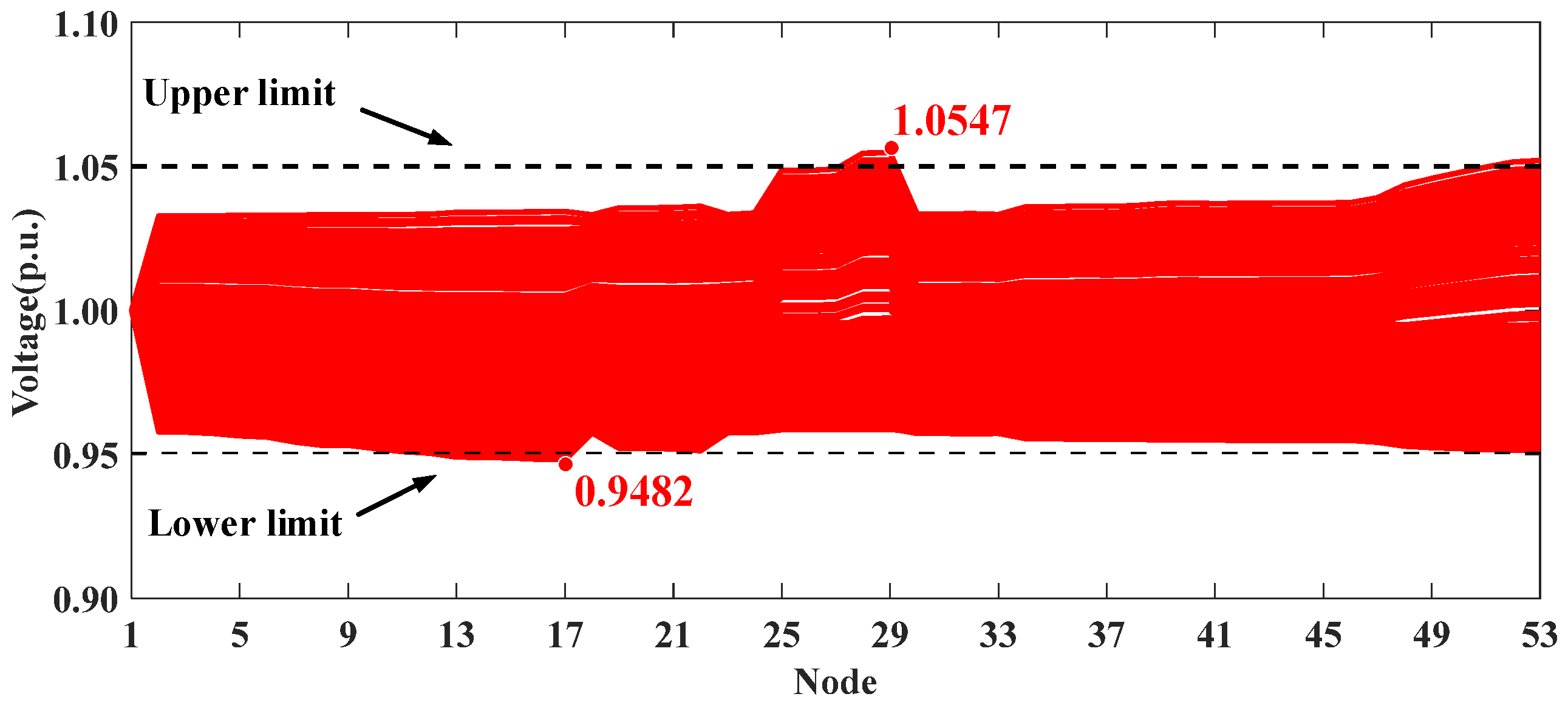
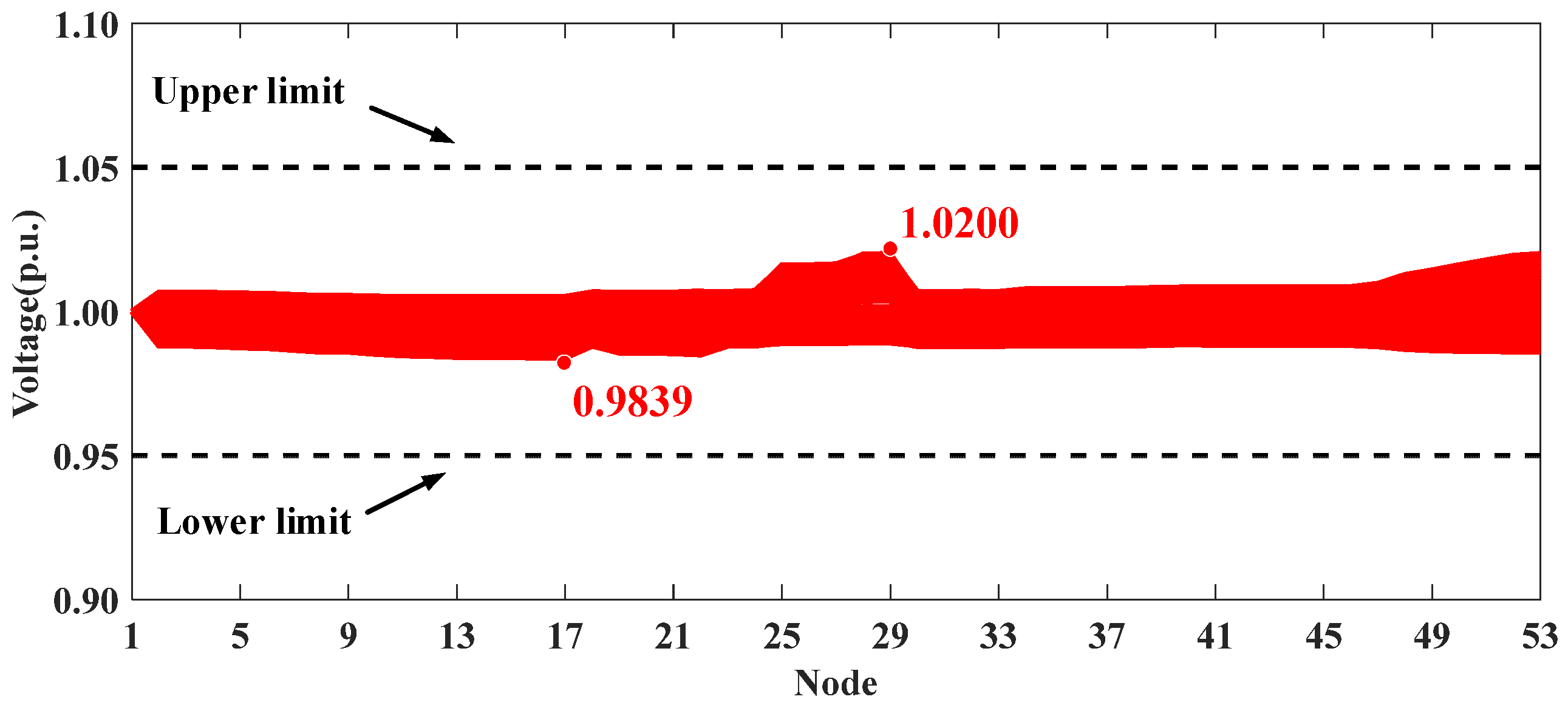
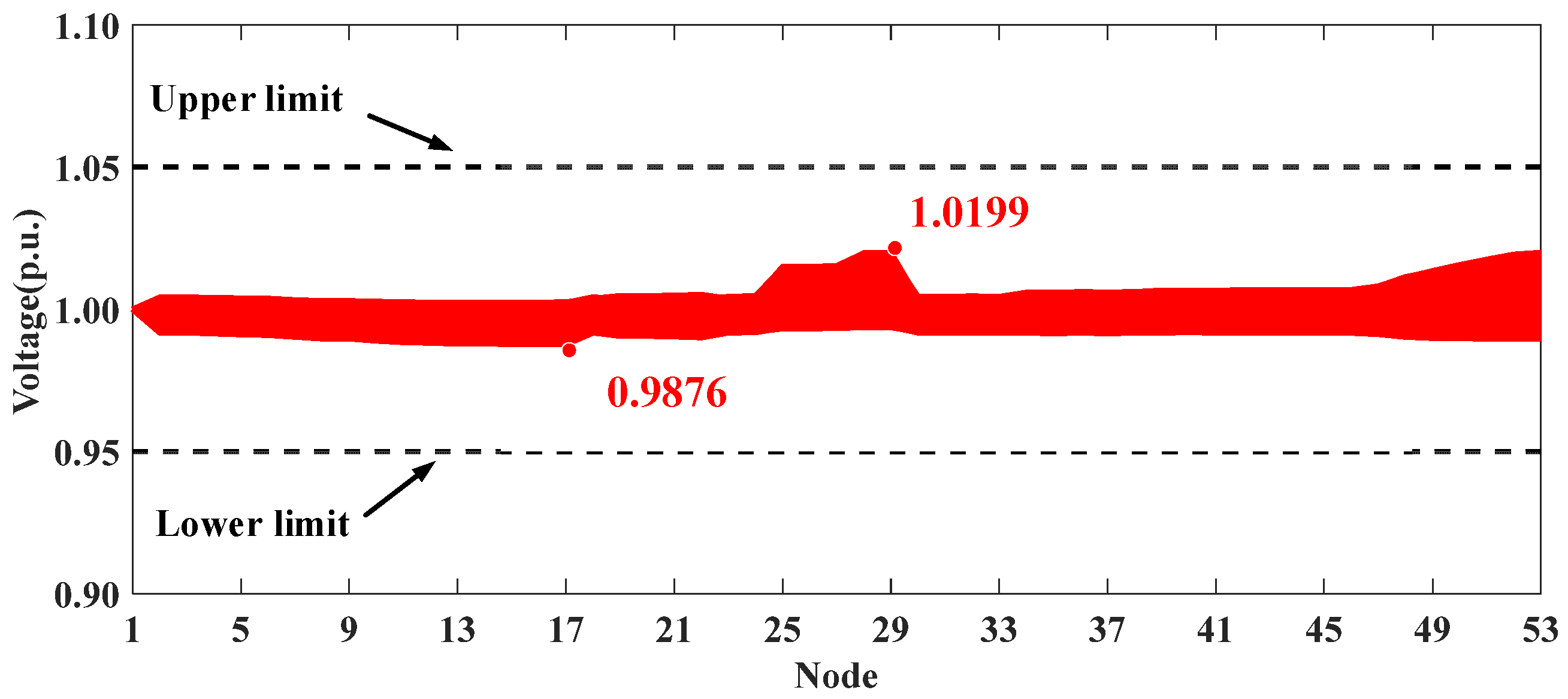
The optimization results for the five scenarios are presented in Table 6. Similarly to the conclusions in Section 5.1, the proposed voltage control strategy can effectively mitigate voltage violations. The voltage profiles of the whole system in Scenarios I, IV, and V are shown in Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15. It can be seen that the uncontrolled integration of distributed PVs in Scenario I causes significant voltage fluctuations and violations. The proposed method in Scenario IV can effectively address this issue, improving the voltage profile and achieving performance comparable to the centralized approach in Scenario V.

Table 6.
Voltage control results in HXF23 53-node practical distribution system.
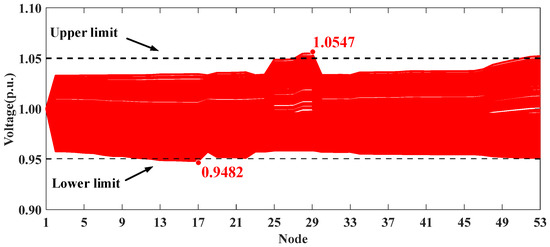
Figure 13.
Voltage profiles of HXF23 53-node practical distribution system in Scenario I.
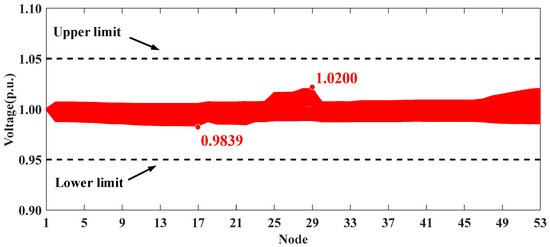
Figure 14.
Voltage profiles of HXF23 53-node practical distribution system in Scenario IV.
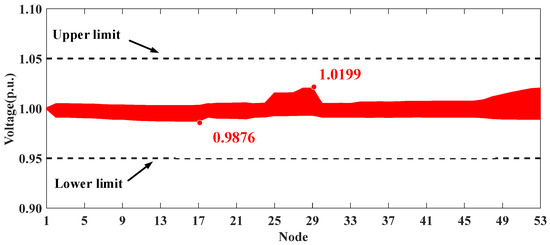
Figure 15.
Voltage profiles of HXF23 53-node practical distribution system in Scenario V.
In summary, the proposed hierarchical distributed and local voltage control strategy for PV clusters enables efficient reactive power management of distributed PVs. By coordinating different PV clusters through ADMM and employing real-time local affine control, the proposed method effectively mitigates voltage violations in ADNs with high levels of distributed PV penetration.
6. Conclusions
This paper presents a hierarchical distributed and local voltage control strategy for PV clusters in ADNs to address voltage violations. First, the ADMM is employed to coordinate the reactive power of PVs across different clusters, providing reference values for local control. Then, in the local control stage, the Q-P affine control strategy is introduced to manage real-time PV power fluctuations. Additionally, the flexibility of the local control strategy is enhanced by the implementation of LLAC. The effectiveness of the proposed hierarchical distributed and local voltage control strategy is evaluated through simulations on both the modified IEEE 33-node and a practical 53-node distribution systems. Compared to traditional distributed control methods, the proposed approach exhibits superior performance, effectively mitigating real-time PV fluctuations and achieving results comparable to centralized control methods. This strategy effectively mitigates voltage violations in ADNs with high PV penetration by regulating PV reactive power, resulting in a 53.93% reduction in AVD.
Several notable issues are worth further research. The active power curtailment can be further integrated to cope with the occurrence of severe overvoltage in future work. In addition, different PV clusters are divided based on geographical proximity in this study, and the cluster division method can be further investigated in future work to achieve load balancing across different clusters and enable more efficient multi-cluster control. Furthermore, it is crucial to consider practical constraints, such as communication delays and data loss, in future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z.; methodology, Z.W.; validation, Y.C.; formal analysis, Q.R.; investigation, S.Q.; resources, Y.Z. and H.Z.; writing, Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Laboratory Specialized Scientific Research Projects of Beijing Smart-chip Microelectronics Technology Co., Ltd. (SGSCDT00XPQT2400763).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Z.W., Y.C., Q.R., S.Q., Y.Z. and H.Z. were employed by the Beijing Smartchip Microelectronics Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Jian, J.; Zhao, J.; Ji, H.; Bai, L.; Xu, J.; Li, P.; Wu, J.; Wang, C. Supply Restoration of Data Centers in Flexible Distribution Networks with Spatial-Temporal Regulation. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 15, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zou, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Sun, Y.; Li, G. Microgrid Energy Management Strategy Considering Source-Load Forecast Error. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2025, 164, 110372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamana, M.; Chowdhury, B. Optimal Voltage Regulation of Distribution Networks with Cascaded Voltage Regulators in the Presence of High PV Penetration. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 9, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, T.; Mohapatra, A.; Anand, S. Coordinated Control of OLTC and Energy Storage for Voltage Regulation in Distribution Network with High PV Penetration. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 12, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Xie, Q.; Hui, H.; Ding, Y.; Cui, J.; Shao, L. Use of Inverter-based Air Conditioners to Provide Voltage Regulation Services in Unbalanced Distribution Networks. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2022, 38, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Ji, H.; Yu, H.; Zhao, J.; Xi, W.; Wu, J. Adaptive Voltage Control of Inverter-based DG in Active Distribution Networks with Measurement-strategy Mapping Matrix. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2025, 16, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zu, G.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X. Total Quadrant Security Region for Active Distribution Network with High Penetration of Distributed Generation. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2020, 9, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou-Plytaria, K.; Kouveliotis-Lysikatos, I.; Georgilakis, P.; Hatziargyriou, N. Distributed and Decentralized Voltage Control of Smart Distribution Networks: Models, Methods, and Future Research. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 2999–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, D.; Liu, C.; Gu, Y.; Duan, Y.; Li, Y. Collaborative Control of Reactive Power and Voltage in A Coupled System Considering the Available Reactive Power Margin. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Niu, Z. Distributed Optimization for Active Distribution Network Considering the Balance of Multi-stakeholder. Processes 2020, 8, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Huang, S.; Shen, F. Double-time-scale Distributed Voltage Control for Unbalanced Distribution Networks Based on MPC and ADMM. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 145, 108665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chu, B.; Geng, H.; Nian, X. Distributed Power Optimization of Large Wind Farms Using ADMM for Real-time Control. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2022, 37, 4832–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Xu, Y.; Qu, Z. Continuous-domain Real-time Distributed ADMM Algorithm for Aggregator Scheduling and Voltage Stability in Distribution Network. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 19, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Chu, C. Optimal Distributed ADMM-based Control for Frequency Synchronization in Isolated AC Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 2458–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ji, J.; Ji, H.; Jian, J.; Ding, F.; Wu, J.; Wang, C. MPC-based Local Voltage Control Strategy of DGs in Active Distribution Networks. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 11, 2911–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Ji, H.; Li, P.; Xi, W.; Yan, J.; Wang, C. Cloud-edge Collaboration-based Local Voltage Control for DGs with Privacy Preservation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, S.; Attarha, A.; Scott, P.; Thiebaux, S. Affinely Adjustable Robust Volt/Var Control for Distribution Systems with High PV Penetration. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2021, 36, 3238–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, R.; Yang, L. Optimization of Local Voltage Control with Coordinating Droop Functions Under High PV Penetration. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 6776–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Yan, Z.; Shahidehpour, M.; Wang, H.; Ping, J. Robust Parametric Programming for Adaptive Piecewise Linear Control of Photovoltaic Inverters to Regulate Voltages in Power Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 3685–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabr, R.A. Linear Decision Rules for Control of Reactive Power by Distributed Photovoltaic Generators. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 33, 2165–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, Z.; Ma, H.; Shahidehpour, M. Hierarchical Central-local Inverter-based Voltage Control in Distribution Networks Considering Stochastic PV Power Admissible Range. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 14, 1868–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Yan, Z.; Shahidehpour, M. Equitable Active-Reactive Power Envelopes for Distributed Energy Resources in Power Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2025, 16, 1480–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, F.U.; Pal, B.C.; Jabr, R.A. Affinely Adjustable Robust Volt/Var Control without Centralized Computations. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2022, 38, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, Z.; Shahidehpour, M.; Tan, Z. Distributionally Robust Optimization of Photovoltaic Power with Lifted Linear Decision Rule for Distribution System Voltage Regulation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2024, 15, 758–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, P.; Almeida, A.; Souza, A.; Marujo, D.; Souza, J. Unified Centralized/Decentralized Voltage and Frequency Control Structure for Microgrids. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2024, 38, 101366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Ji, H.; Zhao, J.; Xi, W.; Wang, C. Combined Central-local Voltage Control of Inverter-based DG in Active Distribution Networks. Appl. Energy 2024, 372, 123813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Jie, G.; Ren, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H. A Cooperative Operation Optimization Method for Medium-and Low-Voltage Distribution Networks Considering Flexible Interconnected Distribution Substation Areas. Processes 2025, 13, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, D.; Liao, W.; Fan, Q. A Continuous-time Voltage Control Method Based on Hierarchical Coordination for High PV-penetrated Distribution Networks. Appl. Energy 2023, 347, 121274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Huang, Y.; Qian, T.; Wei, C.; Wu, J. Coordinated Central-local Control Strategy for Voltage Management in PV-integrated Distribution Networks Considering Energy Storage Degradation. Appl. Energy 2025, 389, 125684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Dai, N.; Huang, Y. Voltage Regulation Enhanced Hierarchical Coordinated Volt/var and Volt/watt Control for Active Distribution Networks with Soft Open Points. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2024, 15, 2021–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, S.; Khambadkone, A.; Peng, J. Robust Constrained Model Predictive Voltage Control in Active Distribution Networks. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 12, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georghiou, A.; Kuhn, D.; Wiesemann, W. The decision rule approach to optimization under uncertainty: Methodology and applications. Comput. Manag. Sci. 2019, 16, 545–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).